Coastal Processes & Landforms
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This set of flashcards covers essential vocabulary and concepts related to coastal processes, landforms, and their characteristics.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Coastal Processes
The natural processes that shape coastlines, involving both marine and terrestrial actions.
Wave Action
The movement of sea waves that erodes, transports, and deposits materials along the coastline.
Erosion
The process by which material is worn away from the coastline by the action of waves, currents, and weathering.
Dependent Factors of Wave Height
Three main factors that affect wave height: fetch (distance wind travels), duration (time wind blows), and wind strength.
Swash
The movement of water up the beach following the breaking of a wave.
Backwash
The return flow of water down the beach after the swash.
Destructive Waves and its features
Waves that erode the beach, that have a weak sawash. strong backwash, short wavelength, and high frequency.
Constructive Waves
Waves that build up the beach, they have a strong swash, weak backwash, long wavelength, and low frequency.
Types of Erosion
hydraulic action, attrition, corrosion, and abrasion.
Hydraulic Action
Hydraulic action is the sheer force of the waves hitting the coast
Attrition
Attrition occurs when material carried in the waves bumps against each other and becomes smaller and smoother, forming sand and shingle
Corrosion
Erosion that occurs when seawater dissolves some coastal rocks, such as limestone.
Abrasion
Erosion that happens when waves pick up and throw materials against the coastline.
Describe and explain the process of longshore drift
Longshore drift is the process where the waves transport material (1), such as sand along the beach in the direction of the prevailing wind(1). The swash moves material up the beach at an angle (1), as the waves approach in a similar direction to the wind. The material then moves back down the beach at 90° due to gravity(1), this is the backwash. This movement continues along the beach in a zig-zag motion(1) in the direction of the prevailing wind
Rates of erosion are affected by what three factors?
Energy(more energy →More Erosion), Materials(greater amount of materials→more abrasion) Geometry(created by a steep seabed, these lead to more erosion)
4 ways material is moved by?
Traction, Saltation, Suspension and Solution
Traction
Traction is when large heavy material is dragged along the sea floor
Saltation
Saltation occurs when smaller material bounces along the sea floor
Suspension
Suspension is the fine material held in the water
Solution
Solution is dissolved material carried in the water
Three types of sub-aerial weathering
Mechinical, Chemical & Biological
Explain mechinical weathering/Free-thaw weathering?
Water gets into cracks and joints in the rock
When the water freezes it expands and the cracks open a little wider
Over time, pieces of rock split off the rock face, whilst big boulders are broken into smaller rocks and gravel
Chemical mechinical?
Water in cracks evaporates leaving salt crystals
The salt crystals expand and the cracks become larger
Over time, pieces of rock split off the rock face, whilst big boulders are broken into smaller rocks and gravel
What is biological weathering?
Animals like rabbits can burrow in cracks making them bigger, breaking the rocks overtime
Tree roots can do a similar thing
What is mass movement?
The downhill mass-movement of material under the influence of gravity
What are the three types of mass-movement?
Slumping
Landslides
Rockfall
What is slumping?
When a large area of land on a cliff becomes saturated and heavy “slumps” down the cliff in one peice with the assistance of gravity, leaving a curved surface
What are landslides?
When a section of material slides down a slope
The section of material will stay together until it hits the bottom of the slope
What is rockfall?
When fragments of debris break away from a cliff and fall quickly down a cliff- face and land at the bottom of the cliff
What is a headland?
An area of land formed of resistant rock which protrudes out to sea
Outline two ways that sub-aerial processes can affect the shape of a cliff (4 Marks)
1) One sub-aerial process is freeze-thaw weathering (1), where temperatures need to go above and below freezing 0° C. Any water trapped in cracks of a rock, freezes and expands, exerting pressure on the crack. When temperatures rise, water melts, pressure is released and the crack contracts. Repeated cycles eventually break the rock apart. Therefore,there will be more freeze-thaw occurring in winter than in summer, resulting in more weathering of the cliff face (1). This means that the cliff is weakened and can then be eroded more easily by the waves (1) .
2) Chemical weathering (1) is another sub-aerial process and the rock type will decide on how quickly the rock will dissolve. Rainwater and seawater are both slightly acidic. Less resistant rock, such as limestone, will react with the acid in the water faster than granite. Therefore, a cli made of softer, less resistant rock will weather faster than a cli made of harder, more resistant rock (1)
What is a bay?
An inland area made of less resistant rock which is usually found between headlands on a discordant coastline
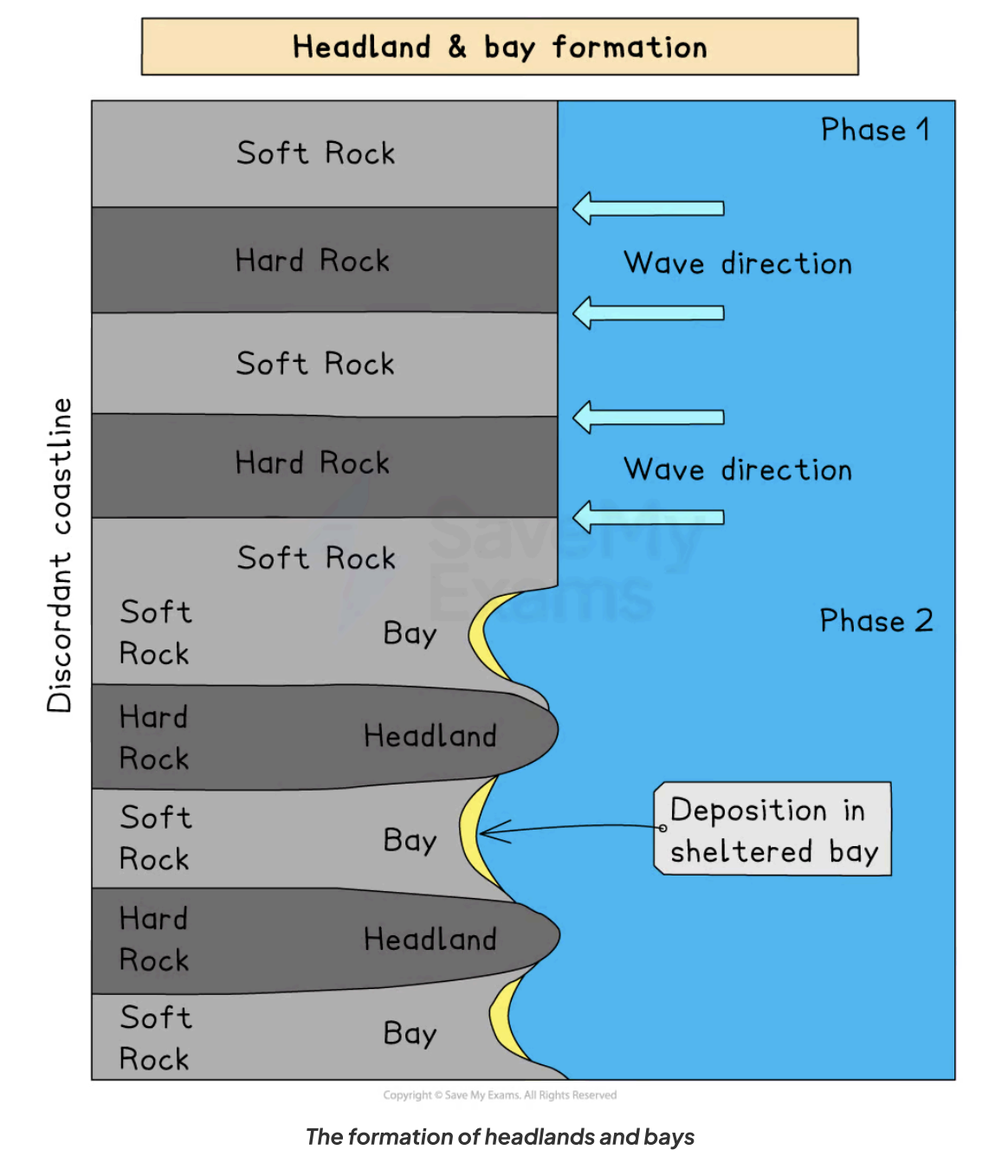
How is a headland formed?
They are formed on a discordant coastline
The areas with rocks of lower resistance are eroded by marine erosional processes at a faster rate than the areas of higher resistant rock
The areas of higher resistant rock, which were not eroded as much, protrude out - this is a headland
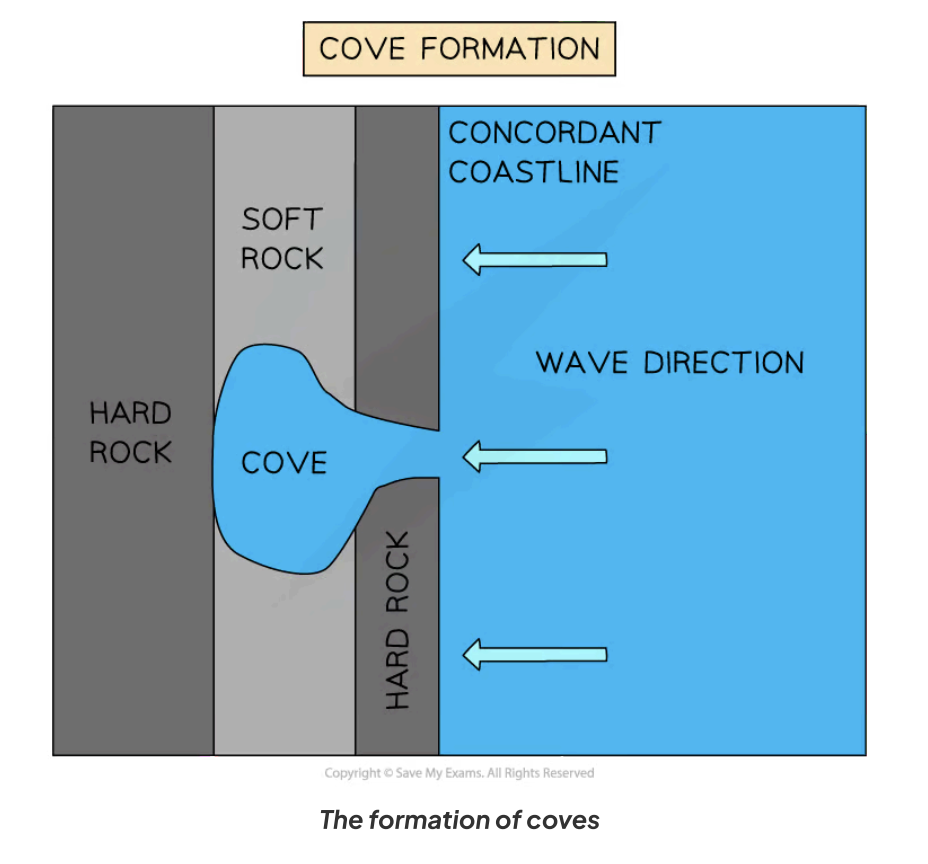
How is a cove formed?
A cove forms along a concordant coastline with:
Bands of resistant rock facing oncoming waves
Softer rock behind the resistant rock
Erosion processes involved:
Wave abrasion, corrosion, and hydraulic action exploit faults in the resistant rock
Erode through to the softer rock quickly
Result:
Circular cove with a narrow entrance to the sea
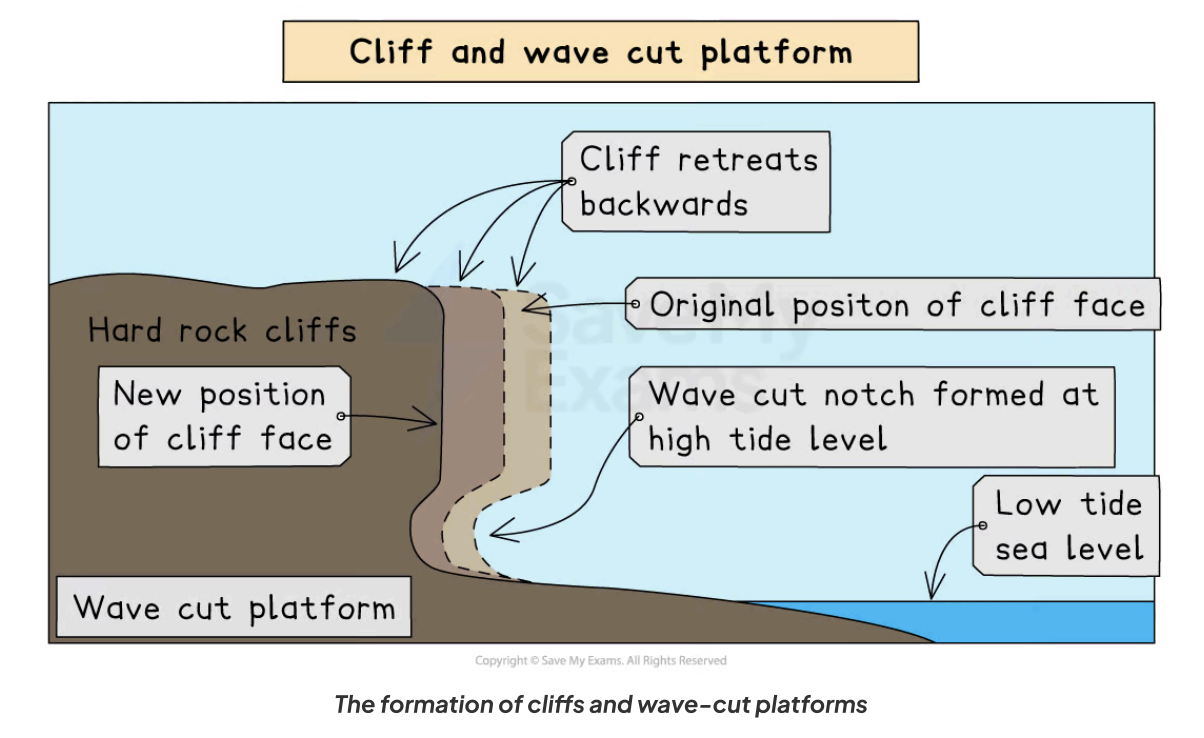
How is a wave cut platform formed?
Less resistant rock erodes quickly, leading to sloping cliff faces
Steeper cliffs form where there are harder rock faces facing the sea
A wave-cut platform is a wide, gently sloped surface found at the foot of a cliff
The sea attacks the base of a cliff between the high and low water marks, creating a wave-cut notch
Abrasion, corrosion, and hydraulic action expand the notch into the cliff
Undercutting the cliff leads to instability and collapses
Backwash from the waves carries away eroded material, resulting in a wave-cut platform
This cycle repeats, causing continued retreat of the cliff and coastal retreat.
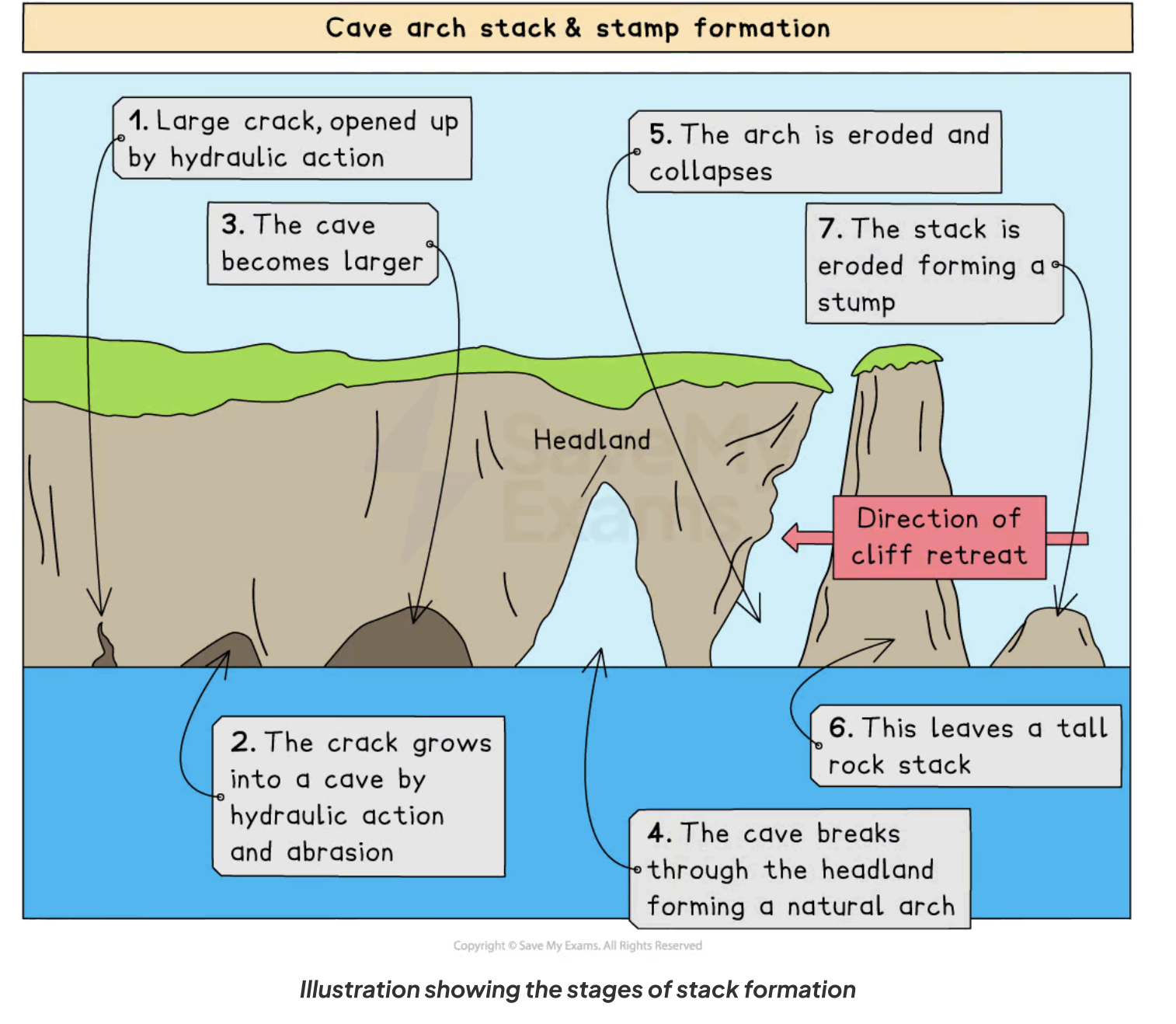
Cave stack and stump formation?
How are beaches formed?
Constructive waves deposit material such as shingle or sand onto the shore with their swash
This sediment is eroded over time through marine process of erosion such as attrition, making it smaller and smoother (rocks become sand)
What is a spit how are they formed?
Spits are narrow projections of sand or shingle that are attached to the coastline at one end which extend across a part of the coastline where it changes direction
Sediment moving along the shore by longshore drift is deposited on an area of the coastline which is sheltered and shallowed where there is insufficient energy to carry the sediment further, and it builds up to form a spit with a salt marsh forming behind it
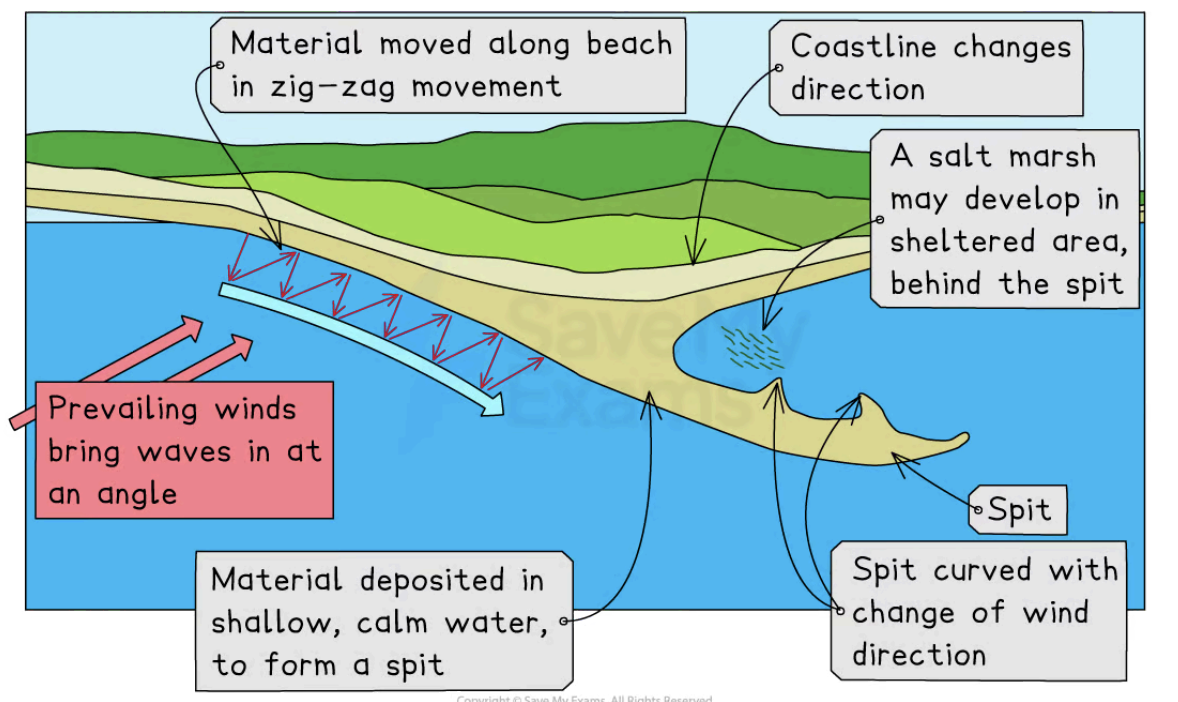
What are bars?
Bars are when a spit full extends across the bay, leaving a lagoon behind it
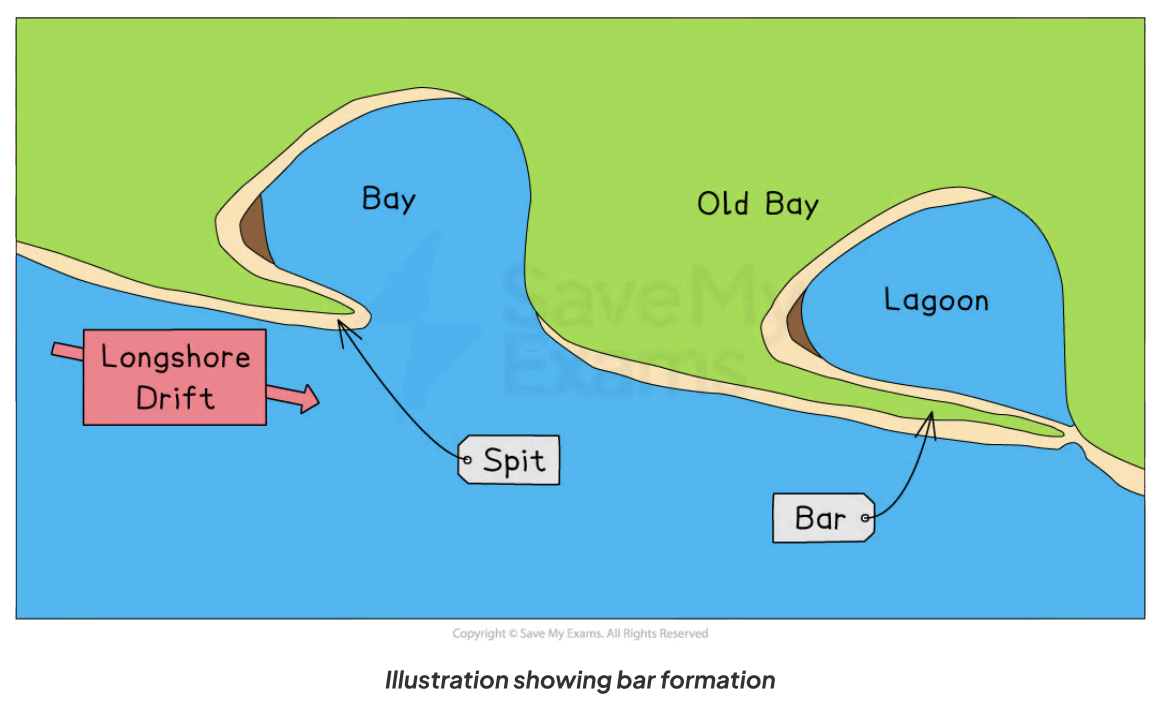
What is a lagoon?
- A lagoon is a small body of water that is cut off from the sea.
- Lagoons may form behind a bar or tombolo.
- They do not last forever and may fill with sediment, eventually forming new land.
What is a tombolo?
- A tombolo is created when a spit connects the mainland to an island.
- An example of a tombolo is Chesil Beach in Dorset, which joins the mainland to the Isle of Portland.
What are barrier islands?
Barrier islands form parallel to the coast.
The main difference between a bar and a barrier island is that a bar joins two headlands, whereas a barrier island is open at one or both ends
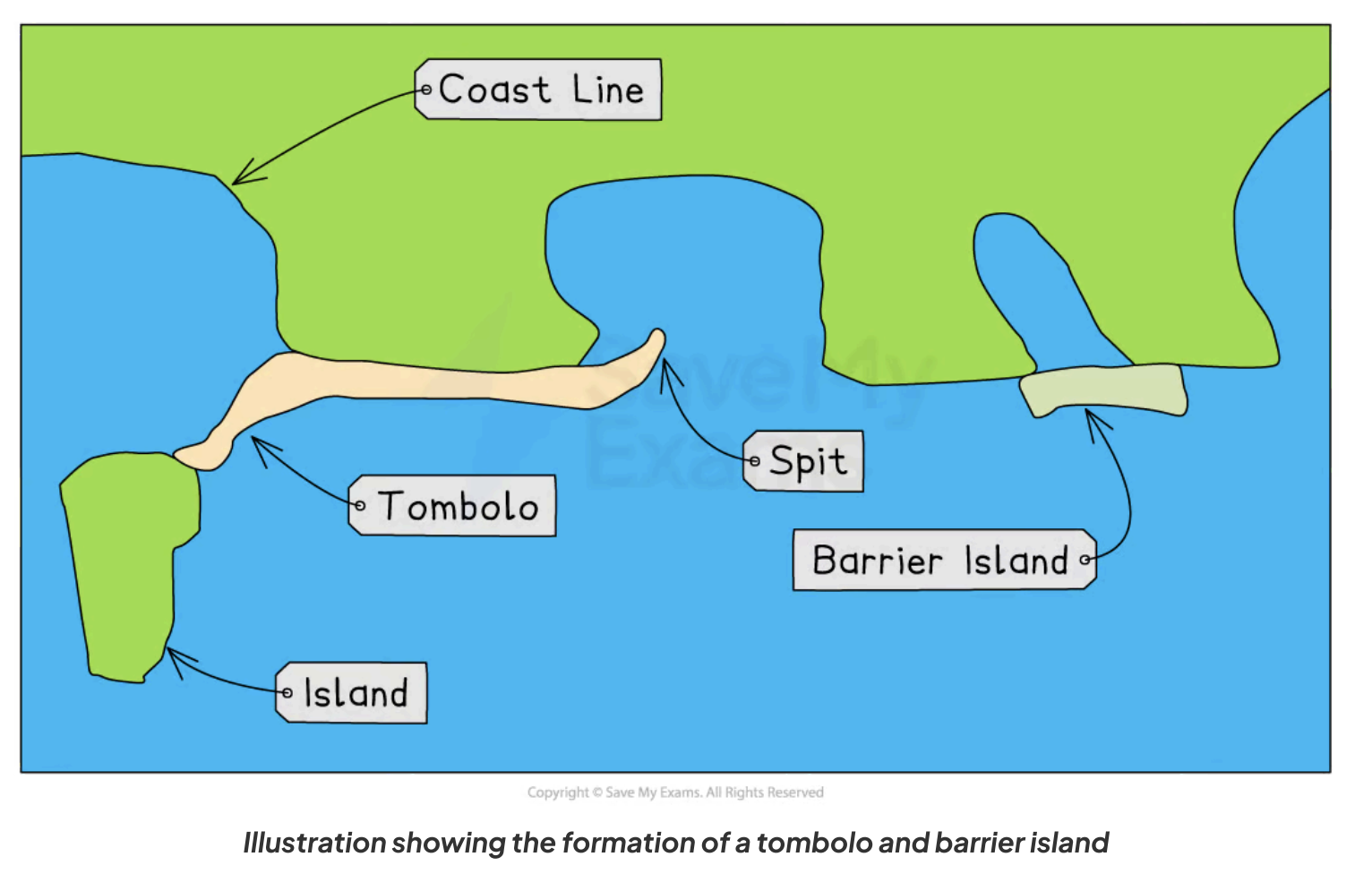
How does sea level change affect the coast?
Sea levels can change from eustatic change (change of water levels) or isostatic change (change of land levels)
Rising sea levels create submergent coastlines, with submergent features like rias and fjords forming
Falling sea levels create emergent coastlines, with emergent relic features like raised beaches, wave cut notches and arches
How does vegetation affect the coast?
The main role is the protection of landforms from erosion and wind, preserving them
They also stabilise landforms like sand dunes and provide habitats for wildlife
It is an indication of how long the cliff has been there, as well as its gradient and how resistant the rock is
How does geology affect the coast?
Soft rock like sand and clay will be eroded easy to form low flat beaches and bays
Hard rock will be eroded less easily and will form headlands and steep cliffs
Soft = Smooth, gently sloping cliffs with vegetation
Hard = Rugged, bare, steep cliffs.
What are 2 ways in which people affect the coast?
Deforestation: More sediment is washed into the sea which destroys habitats like coral reefs, less protection is provided to landforms, the likelihood of flooding is increased (from the removal of trees like mangroves)
Ports and trade: Pollution is created by boats which degrades the water quality and can kill marine life, dredging of harbours can be required which will significantly disrupt marine flora and fauna