Economics IB 3
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/219
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
220 Terms
1
New cards
What is economic growth?
It refers to the increase in the quantity of output produced over a period of time, usually a year.
2
New cards
How can economic growth be expressed?
A percentage change in real GDP/GNI or a percentage change in real GDP/GNI per capita.
3
New cards
How to calculate economic growth?
* With GDP: ((GDP f - GDP i)/ GDP i) x 100
* With GNI: ((GNI f - GNI i)/ GNI i) x 100
* With GNI: ((GNI f - GNI i)/ GNI i) x 100
4
New cards
What is an increase, decrease and negative GDP growth?
* Increasing GDP is when the % keeps growing.
* Decreasing GDP is when the % is reducing but it’s still positive.
* Negative GDP is when the % is negative.
* Decreasing GDP is when the % is reducing but it’s still positive.
* Negative GDP is when the % is negative.
5
New cards
What is the difference between a decrese in GDP and GDP growth?
A decrease in GDP is when the GDP is less than in the last year and GDP growth decrease in the percentage. You can increasing GDP but decreasing GDP growth.
6
New cards
What is a business cycle?
The fluctuations in the growth of real output, consisting of alternating periods of expansion and contraction. They usually last several years. It can also be called short-term economic fluctuations.
7
New cards
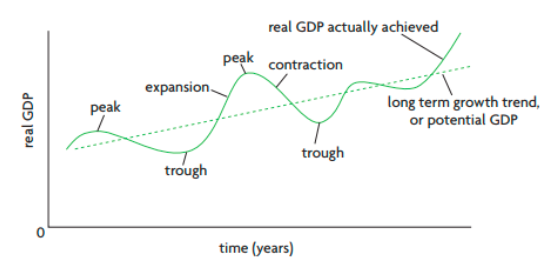
What are the 4 phases of the business cycle?
Expansion, peak, contraction, trough.
8
New cards
What is an expansion in the business cycle?
It’s when there is positve growth in real GDP, they are the parts of the curve that slope upwards. Expansions usually last longer than contractions.
9
New cards
What happens in the expansion phase of the business cycle?
Umployment of resources decreases and the general pricel level of the economy begins to rise more rapidly, meaning they experience inflation.
10
New cards
What is a peak in the business cycle?
It represents the max real GDP of the cycle and marks the end of an expansion.
11
New cards
What happens in the peak of the business cycle?
Unemployment of resources falls substantially and the economy may be experiencing inflation.
12
New cards
What is a contraction in the business cycle?
After a peak the economy experiences a falling GDP (negative growth) shown by the downwards slopes of the curve. If it lasts two quarters it’s called a recession.
13
New cards
What happens in the contraction phase of the business cycle?
Unemployment increases and the increase in price level may slow down a lot and it’s possible that prices in some sectors begin to fall.
14
New cards
What is a trough in the business cycle?
It’s when the GDP is at its minimum, it marks the end of a contraction.
15
New cards
What happens in a trough of the business cycle?
There may be widespread unemployment. The preiod of expansion adtr a trough is called recovery and marks the beginning of a new cycle.
16
New cards
What happens when real GDP increases?
Unemployment ↑ → Inflation ↓
17
New cards
What happens when real GDP decreases?
Unemployment ↓ → Inflation ↑
18
New cards
What is full employment?
When unemployment is equal to the natural rate of employment.
19
New cards
What is the natural rate of unemployment?
When even at full employment not all people are employed because they are:
* in between jobs
* moving geographical areas
* people are training or retraining to get a better job
* people are temporarly out of work
* in between jobs
* moving geographical areas
* people are training or retraining to get a better job
* people are temporarly out of work
20
New cards
What is the full employment level of output or real GDP?
It is the level of real GDP at which the economy experiences full employment. In the curve is when the growth is equal to the trend line.
21
New cards
At what points the unemployment is different or equal to the natural rate of employment?
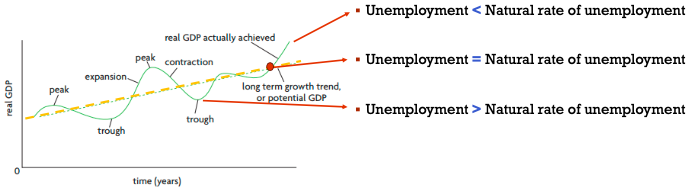
22
New cards
What does the trend line mean in the business cycle graph?
The trend curve (straight line) is the long term growth tren or potential GDP.
23
New cards
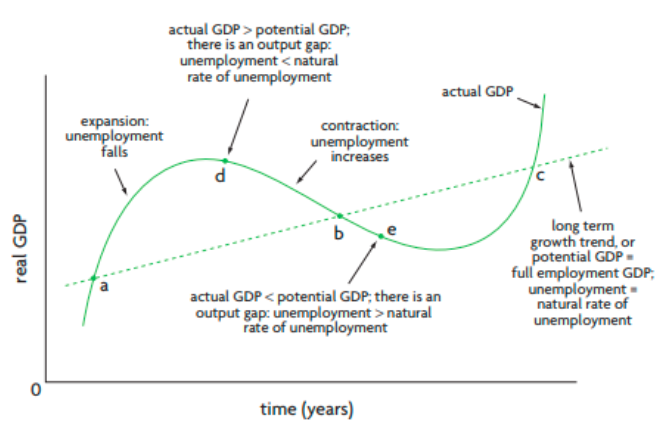
What is an output gap?
The difference between the real GDP and potential GDP, it can be positive or negative.
24
New cards
What are the 3 possible outcomes of real GDP fluctuations around full employment GDP?
* Real GDP = to potential GDP → full employment and unemployment = natural rate (Curve and straight intersect)
* Real GDP > potential GDP → output gap and unemployment < natural rate (curve is above straight)
* Real GDP < potential GDP → output gap nad unemployment > natural rate (curve is under straight)
* Real GDP > potential GDP → output gap and unemployment < natural rate (curve is above straight)
* Real GDP < potential GDP → output gap nad unemployment > natural rate (curve is under straight)
25
New cards
What are some of the macroeconomic objectuves?
Economic growth, full employment and price stability.
26
New cards
What are some difficulties for macoeconomic’s objectives?
* If real GDP increases eventhough unemployment decreases inflation increases and that is a undesirable consequence.
* If real GDP decreases unemployment increases and that is an undesirable consequence.
* If real GDP decreases unemployment increases and that is an undesirable consequence.
27
New cards
What are some ways macroeconomic objectives avoid negative consequences?
* Reducing the intensity the intensity of expansions and cotractions (making output gaps as small as possible)
* Achieving more rapid economic growth (making poyential GDP or the straight steeper)
* Achieving more rapid economic growth (making poyential GDP or the straight steeper)

28
New cards
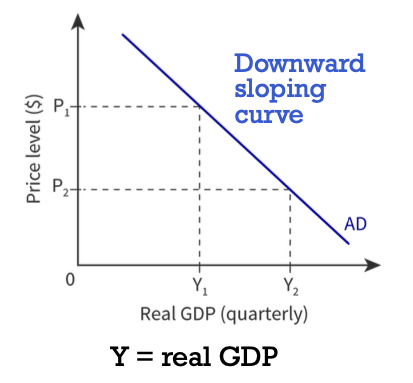
What is aggregate demand AD?
It is the total demand for goods and services produced in an economy and consist of consumption and government expenditure and investment and net exports spending. (GDP = C+I+G+(X-M).
29
New cards
Why is the AD curve downward sloping?
Beacuse of the wealth effect, the interest rate effect and the net balance effect.
30
New cards
What is the wealth effect?
Greater purchasing power.
31
New cards
What is the interest rate effect?
Lower prices lead to lower interest rates meaning people have more disposable income to demand higher volume of output and there is low incentives to save.
32
New cards
What is the net balance effect?
Lower prices lead to higher net exports because goods and services are cheaper for other countries and the for imports from abroad falls.
33
New cards
What is the difference between the demand curve in micro and an aggeragate demand curve in macro?
\
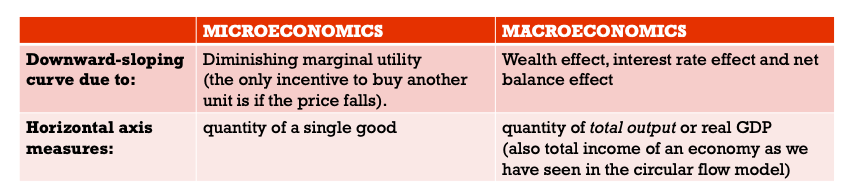
34
New cards
What happens when the components of AD increase?
If the change causes an increase, then at any price level, say P, aggregate demand will increase from AD to AD’, and real demanded output from Y1 to Y2.
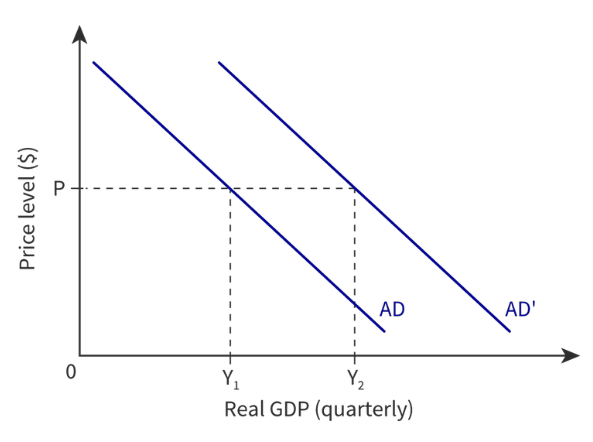
35
New cards
What happens if the components of AD decrease?
If the change causes a decrease, then at any price level, say P, aggregate demand will decrease from AD1 to AD2, and real demanded output from Y1 to Y2.
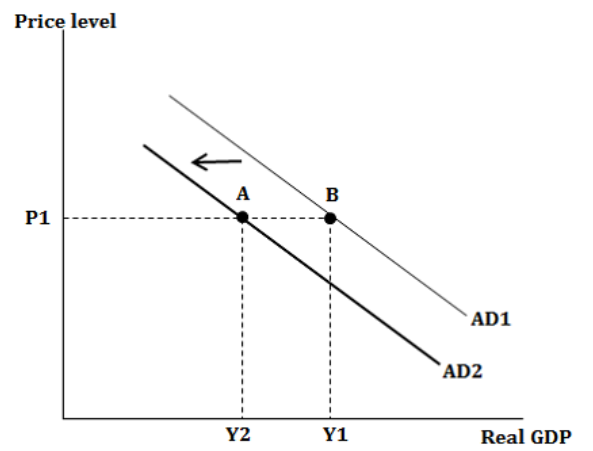
36
New cards
What are the seven determinants that cause consusmption to change?
Confidence, unemployment, real interest rates, wealth, personal taxes level of household debt and expectations of future price level.
37
New cards
What is and how does confidence affect consumption?
Confidence refers to the confidence about their future income and employment.
* Confidence ↑ → consumption ↑ → AD curve ↑
* Confidence ↓ → consumption ↓ → AD curve ↓
* Confidence ↑ → consumption ↑ → AD curve ↑
* Confidence ↓ → consumption ↓ → AD curve ↓
38
New cards
How does unemployment affect consumption?
\
* Unemployment ↑ → consumption ↓ → AD curve ↓
* Unemployment ↓ → consumption ↑ → AD curve ↑
* Unemployment ↑ → consumption ↓ → AD curve ↓
* Unemployment ↓ → consumption ↑ → AD curve ↑
39
New cards
What is and how do real interest rates affect consumption?
Real interest rates are the price of the money and is widely used in loans for big purchases.
* Interest rate ↑ → consumption ↓ & savings ↑ → AD curve ↓
* Interest rate ↓ → consumption ↑ & savings ↓ → AD curve ↑
* Interest rate ↑ → consumption ↓ & savings ↑ → AD curve ↓
* Interest rate ↓ → consumption ↑ & savings ↓ → AD curve ↑
40
New cards
What is and how does wealth affect consumption?
Wealth refers to assets including ownership of property, bonds, shares of a company, etc.
* Feeling wealth ↑ → consumption ↑ → AD curve ↑
* Feeling wealth ↓ → consumption ↓ → AD curve ↓
* Feeling wealth ↑ → consumption ↑ → AD curve ↑
* Feeling wealth ↓ → consumption ↓ → AD curve ↓
41
New cards
What and how do income taxes affect consumption?
Personal taxes refer to income taxes, indirect taxes, import duties, etc.
* Personal taxes ↑ → consumption ↓ → AD curve ↓
* Personal taxes ↓ → consumption ↑ → AD curve ↑
* Personal taxes ↑ → consumption ↓ → AD curve ↓
* Personal taxes ↓ → consumption ↑ → AD curve ↑
42
New cards
What is and how does the level of household debt?
Level of household debt can include university education, cars, home renovations, etc. It could exceed annual national output several times over.
* Debt ↑ → consumption ↑ → AD curve ↑
* In the LR (long run), AD curve might ↓ as debt is repaid.
* Debt ↓ → consumption ↓ → AD curve ↓
* In the LR (long run), AD curve might ↑ as people may have more disposable income in the future.
43
New cards
How do expectations of future price level affect consumption?
* Expectations of inflation ↑ → consumption ↑ → AD curve ↑
* Expectations of deflation ↓ → consumption ↓ → AD curve ↓
* Expectations of deflation ↓ → consumption ↓ → AD curve ↓
44
New cards
What is investment (component of AD)?
It is not financial investment like in the stock market or bond market bit an investment of businesses to add to their capital stock so in machinery, buildings replacing olf equpment, etc.
45
New cards
What are the five determinants that cause investment to change?
Interest rates, business confidence, technology, business taxes, level of corporate debt.
46
New cards
How do interest rates affect investmet?
\
As businesses also borrow money for large-scale investments how high interest rates affect how much they invest.
* Interest rates ↑ → investment ↓ → AD curve ↓
* Interest rates ↓ → investment ↑ → AD curve ↑
As businesses also borrow money for large-scale investments how high interest rates affect how much they invest.
* Interest rates ↑ → investment ↓ → AD curve ↓
* Interest rates ↓ → investment ↑ → AD curve ↑
47
New cards
What is and how does business confidence affect investment?
Business confidence refers to like from the consumer point of view the confidence in their income and employment.
* Confidence ↑ → investment ↑ → AD curve ↑
* Confidence ↓ → investment ↓ → AD curve ↓
* Confidence ↑ → investment ↑ → AD curve ↑
* Confidence ↓ → investment ↓ → AD curve ↓
48
New cards
How does technology affect investment?
Technology can reduce costs and save time allowing for countries to best use their resources but it takes time and money to develop.
* Innovation of tech ↑ → production costs ↓ → AD curve ↓
* Innovation of tech ↓ → production costs ↑ → AD curve ↑
* Innovation of tech ↑ → production costs ↓ → AD curve ↓
* Innovation of tech ↓ → production costs ↑ → AD curve ↑
49
New cards
How do business taxes affect investment?
* Taxes ↑ → investment ↓ → AD curve ↓
* Taxes ↓ → investment ↑ → AD curve ↑
* Taxes ↓ → investment ↑ → AD curve ↑
50
New cards
How does level of corporate debt affect investment?
* Debt ↑ → investment ↑ → AD curve ↑
* In the LR (long run), AD curve might ↓ as debt is repaid.
* Debt ↓ → investment ↓ → AD curve ↓
* In the LR (long run), AD curve might ↑ as firms may have more disposable income to invest in the future.
* In the LR (long run), AD curve might ↓ as debt is repaid.
* Debt ↓ → investment ↓ → AD curve ↓
* In the LR (long run), AD curve might ↑ as firms may have more disposable income to invest in the future.
51
New cards
What is government expenditure (component AD)?
It refers to the money governments spend on infrastructure like roads, hospital public sector employees etc.
52
New cards
What are the three determinants that cause government expenditure to change?
Tax collection level, health of the economy and political priorities of the governing parties.
53
New cards
How does tax collection level affect government expenditure?
* Tax collection ↑ → government expenditure ↑ → AD curve ↑
* Tax collection ↓ → government expenditure ↓ → AD curve ↓
* Tax collection ↓ → government expenditure ↓ → AD curve ↓
54
New cards
How does health of the economy affect government expenditure?
\
This is not a rule but happens often:
* Health of the economy ↑ → government expenditure ↓ → AD curve ↓
* Health of the economy ↓ → government expenditure ↑ → AD curve ↑
This is not a rule but happens often:
* Health of the economy ↑ → government expenditure ↓ → AD curve ↓
* Health of the economy ↓ → government expenditure ↑ → AD curve ↑
55
New cards
How do political priorities of the governing parties affect government expenditures?
* Government expenditure ↑ → AD curve ↑
* Government expenditure ↓ → AD curve ↓
* Government expenditure ↓ → AD curve ↓
56
New cards
What are the three determinants that cause net exports to change?
Income of trading partners, exchange rates and changes in trade policies.
57
New cards
What is and how does income of trading partners affect net exports?
Income of trading partners is related to economic growth abroad whic is needed sustain demand for exports.
* Income ↑ → net exports ↑ → AD curve ↑
* Income ↓ → net exports ↓ → AD curve ↓
* Income ↑ → net exports ↑ → AD curve ↑
* Income ↓ → net exports ↓ → AD curve ↓
58
New cards
How do exchange rates affect net exports?
The values of currencies determine the relative prices of goods and services traded. The size of the trade balance and relative price elasticity of demand (PED) of imports and exports will determine to what extent changes in the exchange rates will affect the aggregate demand.
* Exchange rate appreciation ↑ → net exports ↑ → AD curve ↑
* Exchange rate depreciation ↓ → net exports ↓ → AD curve ↓
59
New cards
What are and how do changes in trade policies affect net exports?
Changes in trade policies include taxes on imports, restriction o volume of goods imported, subsidies, etc.
* Import restrictions ↑ → net exports ↑ → AD curve ↑
* Import restrictions ↓ → net exports ↓ → AD curve ↓
* Import restrictions ↑ → net exports ↑ → AD curve ↑
* Import restrictions ↓ → net exports ↓ → AD curve ↓
60
New cards
What other things can affect net exports that are not the main three causes?
Exchange rate manipulation, health and safety requirements and protectionism. The last one is set of policies designed to protect domestic firms from the competition of foreign firms in the domestic firms market.
* Protectionism ↑ → net exports ↑ → AD curve ↑
* Protectionism ↓ → net exports ↓ → AD curve ↓
* Protectionism ↑ → net exports ↑ → AD curve ↑
* Protectionism ↓ → net exports ↓ → AD curve ↓
61
New cards
What is aggregate supply AS?
It is the total quantity of good and services produced in an economy (real GDP) over a specific time period at differnet price levels.
62
New cards
What is considered short-run in macroeconomics?
It is the length of time during which resource prices and costs of production stay relatively constant, specially wages.
63
New cards
Why is the AS curve upward sloping in the short run?
Because as firms receive higher prices for the goods that they sell they will be more willing and able to produce output as long as costs of production stay constant in the short run.
64
New cards
What are the components that change short run aggregate supply SRAS?
Resources prices, government intervention, government subsidies and supply shocks.
65
New cards
What does an increase in SRAS mean?
SRAS ↑ → firms produce a larger quantity of real GDP at any price level (shift rightward / outward).
66
New cards
What does a decrease in SRAS mean?
SRAS ↓ → firms produce a smaller quantity of real GDP at any price level (shift leftward / inward).
67
New cards
What is and how do resource prices affect AS?
It refers to input price changes that will be so significant that they will have an impact on the majority of firms within a country.
* Resource prices ↑ → SRAS curve ↓
* Resource prices ↓ → SRAS curve ↑
68
New cards
How does government intervention affect SRAS?
* Regulations are supposed to keep workers safe, the environment clean and market movements fair but if they become outdated or repressive can slow economic growth.
* Changes in business taxes
* Business taxes ↓ → profit ↑ → efficiency or number of fators of production ↑ → SRAS curve ↑
* Business taxes ↑ → profit ↓ → efficiency or number of fators of production ↓ → SRAS curve ↓
* Changes in business taxes
* Business taxes ↓ → profit ↑ → efficiency or number of fators of production ↑ → SRAS curve ↑
* Business taxes ↑ → profit ↓ → efficiency or number of fators of production ↓ → SRAS curve ↓
69
New cards
Who can the government provide subsidies to and how does this affect SRAS?
An industry that holds a large share of the nation’s economic capacity or energy providers. For the first they need to be large enough so that it can have an in impact in the SRAS. And the second subsudies allow for lower prices that can result in cheaper production costs for many or all firms in an economy.
70
New cards
What is and how do supply shocks affect SRAS?
A supply shock is what happens to SRAS in a country when affected by an event. For example, a natural disaster or climate change.
71
New cards
What is considered long-run in macroeconomics?
When all factors of production (Fop) are variable and what determines how much firms can produce are quality and quantity of the Fop.
72
New cards
What are the two schools of thought to see LRAS?
The new classical or monetarist school and keynesian school.
73
New cards
What are the beliefs of the new classical school of the LRAS?
* Believes in the power of market
* Inelastic LRAS curve
* They believe the economy will always return to full employment level of output as price level has no effect on it
* They believe if prices increase but also costs in the same proportion and then firms aren’t incentivized to increase production
* Prices are fully flexible upwards or downwards
* Inelastic LRAS curve
* They believe the economy will always return to full employment level of output as price level has no effect on it
* They believe if prices increase but also costs in the same proportion and then firms aren’t incentivized to increase production
* Prices are fully flexible upwards or downwards
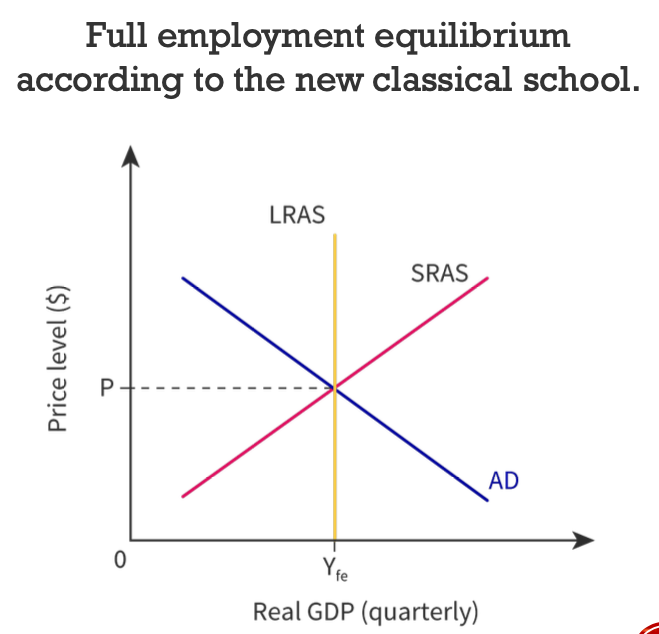
74
New cards
Why is the new classical school LRAS curve perfectly inelastic?
If resource prices are allowed to rise and fall according to market behaviour, then all resources can be fully employed in the long run, maximising the nation’s output. The economy will always return to the full employment level of output (or potential GDP) as the price level has no effect on it (potential GDP).
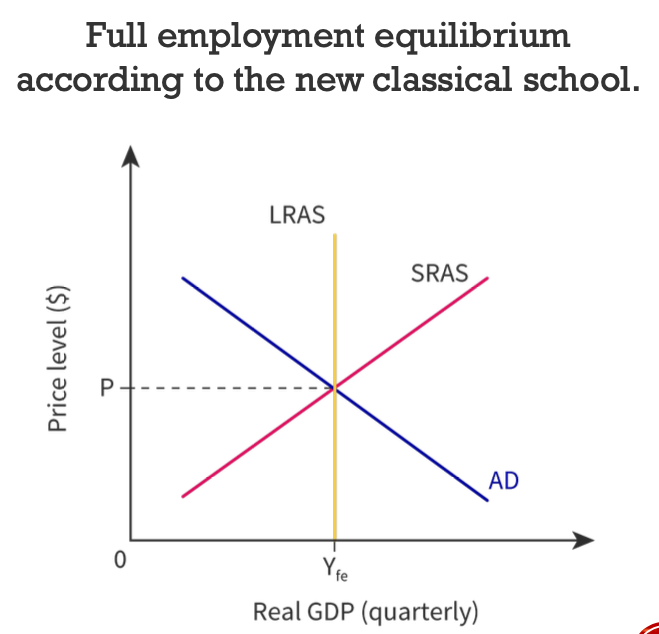
75
New cards
What are the beliefs of the keynesian school of the LRAS?
* Believes in the power of givernment action
* It explained why the economy wasn’t recovering in the way new classical school suggests.
* They believe resource prices exhibit downwards inflexibility (sticky downwards)
* If there is spare capacity in the economy keynes believed they can’t cut wages to cut costs because of labor contractas, unions and laws.
* During recession they may lay off workers and very rarely if it is a very long recession cut wages. They are also reluctant to reduce prices.
* The curve is divided in three sections horizontal, upward sloping and vertical.
* It explained why the economy wasn’t recovering in the way new classical school suggests.
* They believe resource prices exhibit downwards inflexibility (sticky downwards)
* If there is spare capacity in the economy keynes believed they can’t cut wages to cut costs because of labor contractas, unions and laws.
* During recession they may lay off workers and very rarely if it is a very long recession cut wages. They are also reluctant to reduce prices.
* The curve is divided in three sections horizontal, upward sloping and vertical.
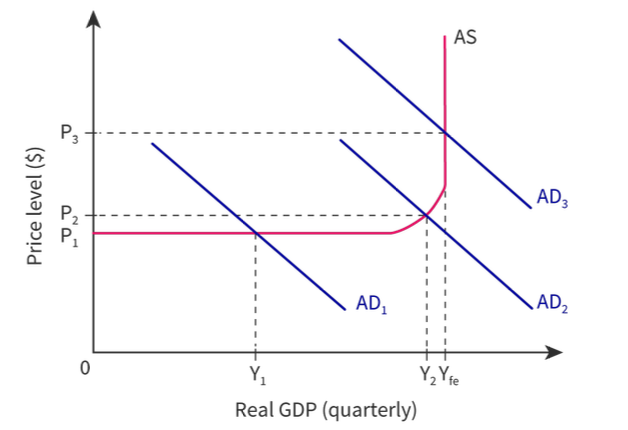
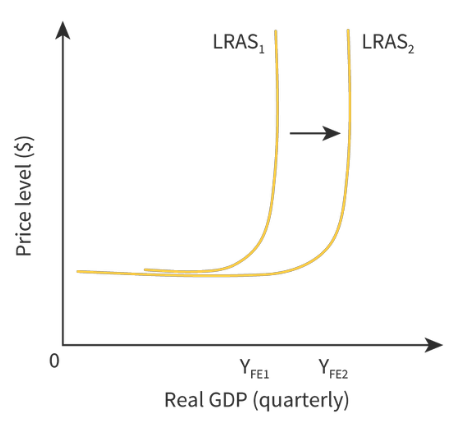
76
New cards
Why is the keynesian school LRAS curve in three sections?
* Horizontal- There is a good deal of spare capacity in the economy
* Upward sloping- There is some spare capacity in the economy but there is also some competition for scarce resources
* Vertical- Full employment level is reached
* Upward sloping- There is some spare capacity in the economy but there is also some competition for scarce resources
* Vertical- Full employment level is reached
77
New cards
What is the difference between shifts in SRAS and the LRAS?
* The SRAS curve shifts due to factors that change the costs of production,
* The LRAS represents the potential capacity of an economy's FoP.
* The LRAS represents the potential capacity of an economy's FoP.
78
New cards
Will what shifts the LRAS curve be different for the new classical school and keynesian school?
No they both shift according to the quality and quantity and quality of a country’s land labour and capital
79
New cards
What are the three components that change LRAS?
Land, labor and capital.
80
New cards
What is and how does land affect LRAS?
Land is the anatural resources and input the country has available.
* If they have a higher quantity of resource there will be more spare capacity and a shift to the right. Ex. Discovery of new oil deposits.
* If they have a higher quality there would be more efficiency and shift the curve to the right. Ex. New technology to use oil.
* If they have a higher quantity of resource there will be more spare capacity and a shift to the right. Ex. Discovery of new oil deposits.
* If they have a higher quality there would be more efficiency and shift the curve to the right. Ex. New technology to use oil.
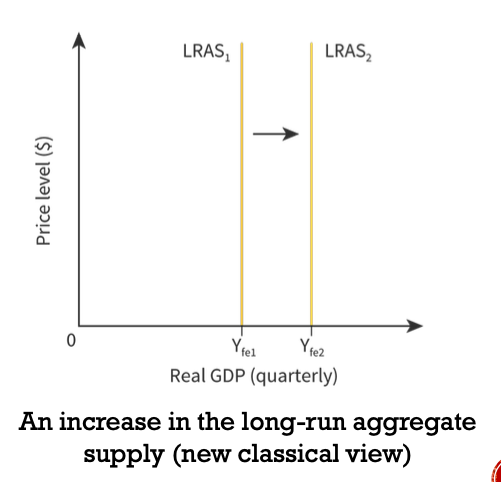
81
New cards
What is and how does labor affect LRAS
Labor is the people that make the workforce of a country.
* Higher quantity means more people to work so it shifts the curve to the right. Ex. Increase in domestic birth rates.
* Higher quality means a more skilled or educated workforce. Which also shifts the curve to the right.
* Higher quantity means more people to work so it shifts the curve to the right. Ex. Increase in domestic birth rates.
* Higher quality means a more skilled or educated workforce. Which also shifts the curve to the right.
82
New cards
What is and how does capital affect LRAS?
Capital is the tools and machinery that are used inn economic production.
* If there is higher quantity like more factories it shifts the curve to the right.
* If there is a higher quality like making the factories more energy efficient it shifts the curve to the right.
* If there is higher quantity like more factories it shifts the curve to the right.
* If there is a higher quality like making the factories more energy efficient it shifts the curve to the right.
83
New cards
What are some other things that can shift the LRAS?
* Improvements of technology
* Increases in efficiency
* Changes in institutions
* Degree of competition or private vs public ownership
* Quantity and quality of government regulations
* Bureaucracy or lack of it
* Increases in efficiency
* Changes in institutions
* Degree of competition or private vs public ownership
* Quantity and quality of government regulations
* Bureaucracy or lack of it
84
New cards
How is the equlibrium determined in the SR?
It is the intersection of AD and SRAS, the result is the real output at Y and an averge price level of P. There is no upward or downward pressures in prices and all output is bought.
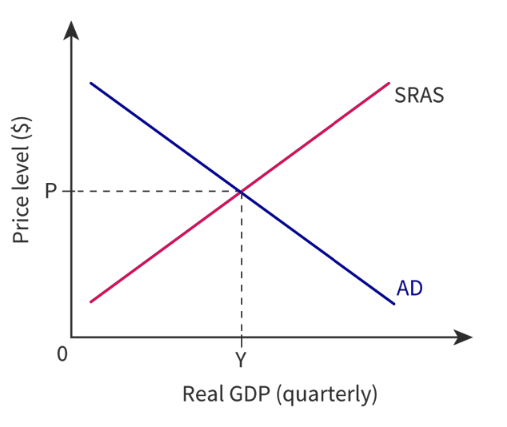
85
New cards
How will a decrease in AD impact the economy in the SR?
It causes the economy to produce under the full employment level which is called a recessionary or deflationary gap.
* Unemployment is above the natural rate of unemployment
* The real GDP is under the potential GDP
* Price level falls in order to convince consumer to keep spending.
* Unemployment is above the natural rate of unemployment
* The real GDP is under the potential GDP
* Price level falls in order to convince consumer to keep spending.
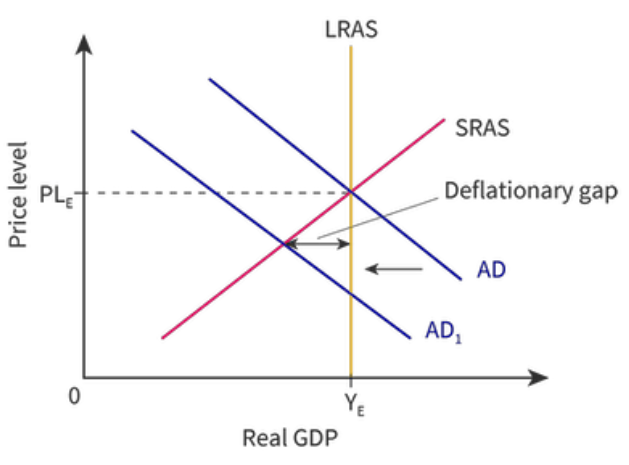
86
New cards
How will a increase in AD impact the economy in the SR?
It causes the economy to produce above the full employment level which is called an inflationary gap or experiences inflationary pressures as the price level increases.
* Unemployment is below the natural rate of unemployment
* The real GDP is above the potential GDP
* Price level rises due to increased production costs of increased volume of output.
* Unemployment is below the natural rate of unemployment
* The real GDP is above the potential GDP
* Price level rises due to increased production costs of increased volume of output.
87
New cards
How will a decrease in SRAS impact the economy?
It can happen due to a supply shock or increased resource prices.
* The economy will produce less real GDP but the price level will increase.
* This is called stagflation and its undersirable as GDP falls while unemployment and price level rises.
* The economy will produce less real GDP but the price level will increase.
* This is called stagflation and its undersirable as GDP falls while unemployment and price level rises.
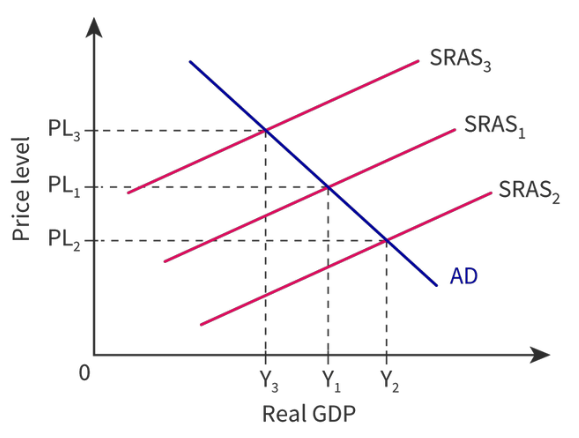
88
New cards
How will an increase in SRAS impact the economy?
It can shift rightwards due to the determinants of SRAS.
* There is an expansion of real GDP.
* There is a fall in price level.
* There is an expansion of real GDP.
* There is a fall in price level.
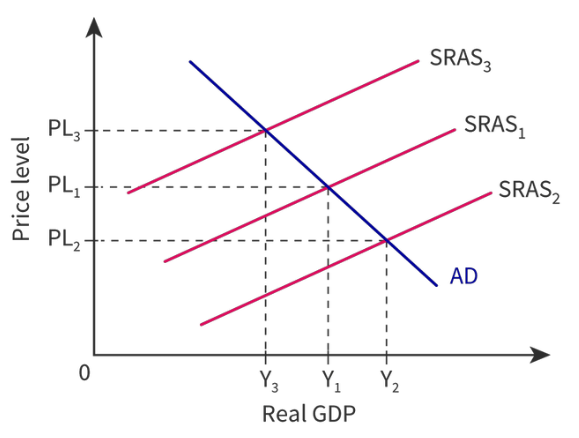
89
New cards
What happens in the LR equilibrium according to the new classical school?
They believe government should be conservative in its intervention. They want governments to invest in education and infrastructure to increase production potential and shift LRAS outwards.
Example: if there is an increase in AD there is
* Upwards pressure on wages to account for inflation.
* There are more jobs available and demand for labor will rise.
* Firms would compete for remaining workers giving them stronger bargaining power when negotiating wages.
* The economy will self correct at some point with the SRAS shifting back to full employment level.
Example: if there is an increase in AD there is
* Upwards pressure on wages to account for inflation.
* There are more jobs available and demand for labor will rise.
* Firms would compete for remaining workers giving them stronger bargaining power when negotiating wages.
* The economy will self correct at some point with the SRAS shifting back to full employment level.
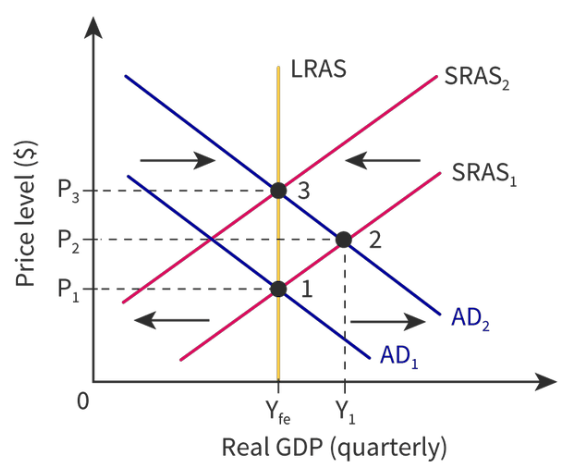
90
New cards
What happens in the LR equilibrium according to the keynesian school?
They believed prices didn’t always correct downwards and economies could get stuck in a SR position (specially a deflationary gap) so they advocated for increased government spending to correct the economy.
* This would correspond to AD being in the horizontal part of the curve.
* Only when aggregate demand increases to the upward sloping part of the curve that upward pressure starts to build on the price level.
* This would correspond to AD being in the horizontal part of the curve.
* Only when aggregate demand increases to the upward sloping part of the curve that upward pressure starts to build on the price level.
91
New cards
What is the governments role in the economy according to the new classical school?
* It is the government's role to reduce restrictions on markets and engage in what might be deemed a 'supply-side' policy (policies that might increase the aggregate supply):
* Expanding business investment, production and growth, and lowering unemployment.
* Increasing the quantity and quality of the FoP.
There have been many attempts by governments around the world to do this in the past decade and their success or failure is contested/opposing.
* Expanding business investment, production and growth, and lowering unemployment.
* Increasing the quantity and quality of the FoP.
There have been many attempts by governments around the world to do this in the past decade and their success or failure is contested/opposing.
92
New cards
What is the governments role in the economy according to the keynesian school?
* Governments need to focus on the present, more so than looking towards long-term growth, especially when economic activity is low, by implementing fiscal and monetary policy.
* Demand side policies
* Demand side policies
93
New cards
What is the assumption of people being rational according to the new classical school?
They believe that people are rational, and their decisions are based on rational choice.
94
New cards
What is the assumption of people being rational according to the keynesian school?
* They believe the economy could get 'stuck' in a recession, not only because of sticky prices, but also because of low feelings of people in the economy.
* The government would have to intervene to spend and invest, propelling the economy forward until spirits had recovered.
* Many politicians today implement these policies at the first sign of economic slowdown. Implementing expansionary policies would result in AD shifting rightward.
95
New cards
Government budgets and deficits according to the new classical school
* They believe government borrowing crowds out private investors
* As governments engage in deficit spending, that money may be raised by selling bonds to domestic investors. Therefore, those investors do not save their money in banks and other institutions, reducing the supply and raising the price of those funds.
* In this case, that price is expressed in terms of an interest rate. You can see this reduced supply driving up interest rates.
* As governments engage in deficit spending, that money may be raised by selling bonds to domestic investors. Therefore, those investors do not save their money in banks and other institutions, reducing the supply and raising the price of those funds.
* In this case, that price is expressed in terms of an interest rate. You can see this reduced supply driving up interest rates.
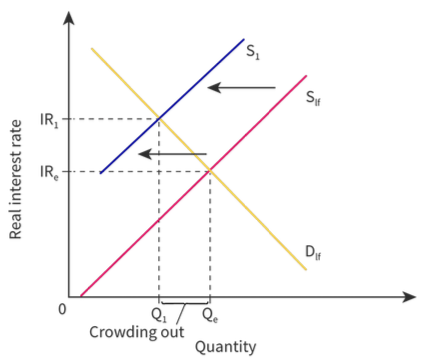
96
New cards
Government budgets and deficits according to the keynesian school
* They see recessions as times when governments should borrow and spend to boost the economy,
* Borrowing would be less likely to crowd out private investment.
* This is what Keynes called the paradox of thrift.
* Borrowing would be less likely to crowd out private investment.
* This is what Keynes called the paradox of thrift.
97
New cards
New classical vs. Keynesian
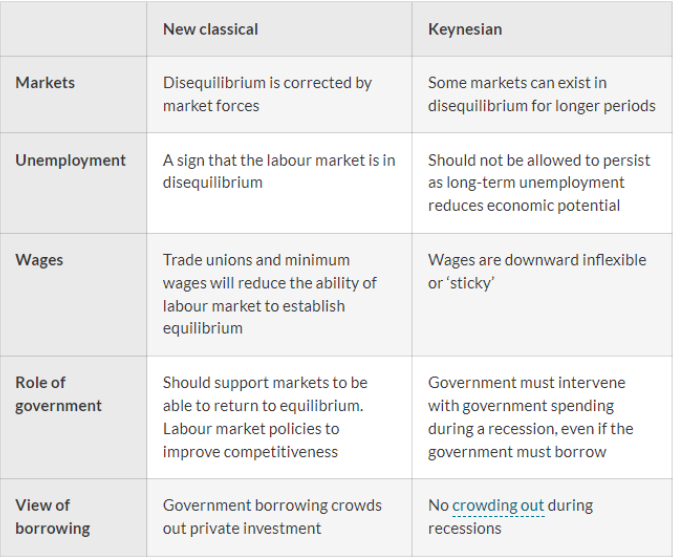
98
New cards
How can economic growth be illustrated?
Using the production possibility curve (PPC) and AD and AS diagram.
99
New cards
What are the two ways to depict economic growth using PPC?
* Increase in actual output (short term)
* Increase in potential output (long term)
* Increase in potential output (long term)
100
New cards
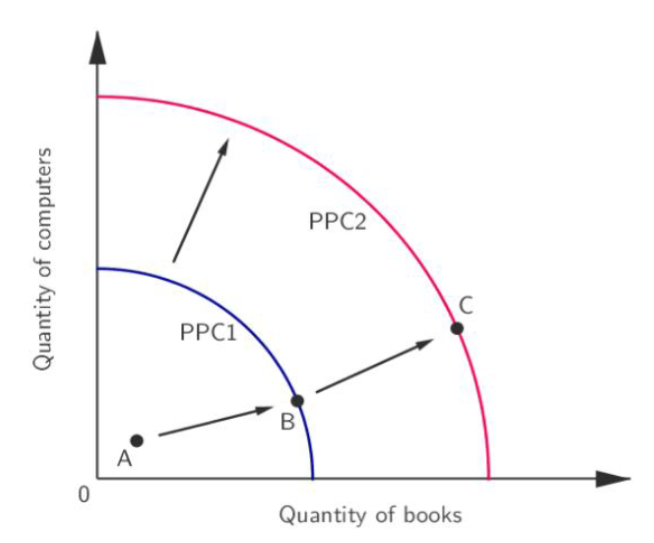
What happens in position A (PPC curve)?
* There is a recession
* Output falls below full employment level
* Output falls below full employment level