Alberta Social 20-1 Final (not mine)
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Nation
-An ideology focusing on a feeling of connection one has to their nation
-Feelings, “imagined community”, shared characteristics
-This idea can shift with time and events
Country
A state with boarders, government, institutions, taxes, and military
Collective Consciousness
-A feeling towards a nation
-This connection can form a large part of someone’s individual and/or collective identity - how they see themselves
Patriotism
-Civic nations can try to generate a sense of collective consciousness through the promotion of patriotism (love of country)
-This can bring up divisive issues of “us” vs. “them”
Ethnic Nation
-Membership in the nation is based on similarities in race, culture, language, religion, or a combination of these and other factors
-In ethnic nationalism, the nation creates the state
-Romantic idea, not always rational
-Started with the 19th C. German and Italian unification
-Mazzini/Garibaldi romantic, republicanism, German writers (Grimm, Goethe, etc.)
-Since the 19th C., ethnic nationalism has continued to be a major factor in many places around the world, including Canada
This brings up the question: Is Canada really a nation?
Civic Nation
-Not necessarily based on common language, ethnicity, etc.
-In civic nationalism the state is created first, then a nation can be built out of the people who live there
-The members of a civic nation makes a choice:
Join together and live according to shared principles, values, ideals that they create and modify to fit their needs
-Often outlined in laws and policies that form the basis of the nation, and that all members of the nation agree to respect and obey
Canada’s Charter of Rights and Freedoms, the US Constitution, DROMAC, etc.
Today, civic nationalism allows multicultural, multiethnic states (like Canada, the US, Britain, etc.) to function effectively as nations
National Symbols
National Symbols: people, places, or things that come to represent the characteristics of a nation it would like to promote
-Ex. Eagles, US
-The sharing of common myths and revering of common symbols promote unity, patriotism, and collective consciousness
National Myths
National Myths: Stories that become part of a nation's sense of identity
-”creation myths” often describe how a nation came to be
-Ex. Storming of the Bastille, France
Challenges to the Myths of Early Canada
-Many of the stories (myths) told about early CDN history have begun to be re-evaluated
Issues with Western Expansion
-Asian immigrants (Chinese/Japanese) were exploited as navvies to ensure construction stayed on-time/budget
-Needed to dispossess Metis and FN
Manitobia and Red River Resistance
CPR led to land distribution and the placement of First Nations onto reserves
Contending Loyalty
-People can feel a strong sense of loyalty, or connection, to different things in their lives
-Sometimes these loyalties can coexist easily, but they can often contend or conflict with one another
-These conflicts can be:
Internal (within the conflicted person)
External (between the conflicted person and others)
Nationalist Loyalties
-Loyalty to a particular nation/state
-Individuals or groups living in a state can feel loyalty to multiple nations simultaneously
Ex. international sports events
-Most obvious in pluralistic nations -
Nations that have a lot of immigration, diversity, and multiculturalism
Canada, US, Britain, etc.
-They experience contending nationalist loyalties more strongly than nations that encourage a single national identity-
Non-Nationalist Loyalties
-Loyalty to something other than a nation
-People can also feel conflicted between their national loyalty and their loyalty to other elements of their life:
Class, religion, ideology, region, culture, race, etc.
Reconciling Loyalties
-At some point, there is a need to reconcile (deal with) the contending loyalties
-A conflicted person may choose to either:
Live with and accept the contending loyalties
Choose one loyalty and discard another
Attempt to bring about change in their environment to remove the conflict
Reasonable Accommodation
An adjustment made to include an individual
ex. Hutterite Drivers license
Sovereignty
-Legitimate, recognized political authority to control one’s affairs
-AKA independence
-In the early 20th C. the desire for self-determination became very important
Woodrow Wilson (14pts) claimed self-determination was a natural right of people and one of the keys to keeping world peace
Nations were granted sovereignty/self-determination immediately after WWI (Hungarians, Czechoslovakia, Polish, etc.)
-However, in the Middle East, self-determination for the Arab people was ignored
Federalists
A person who advocates or supports a system of government where several states unite under a central authority.
Reconciliation
Reconciliation is the process of restoring social cohesion in societies damaged by conflict and investing in local and national capacities to heal past wrongs.
Alienation
Regional Alienation: The feelings in a region that they are being “left out” from, or ignored by, the country
-Regional alienation has been a particularly serious issue in Western Canada, but it has also been felt in the Atlantic Provinces
What Drives Western Alienation?
Generally - a feeling of Western interests being “ignored: in favour of Eastern Canada…
Historically
-Red River Resistance (Riel)
-John A. MacDonald’s “National Policy”
High tariffs on US imports
Meant to protect/build Canada’s industry
But hurt Western farmers
-National Energy Program (NEP), 1980
Oil price spikes/Inflation
PM Pierre Trudeau lowered oil prices to E> Canada, introduced new regulations
Cost Alberta millions of $
Current Alienation Issues
-Political inequality
Representation by population means more seats in ONT/QUE
Governments tailor policies to benefit more voters
-Resources Issues
Seen as an attack on Western economies to benefit Eastern voters
West often resents environmental legislation
-Carbon taxes, pipeline restrictions, etc.
-Alienation has led to the rise of historical and current Western “movements” and political parties:
Western Canada Concept Party
Reform Party
Segregation
Act of separating groups of people
National Interests
-Nations always act according to what they see to be their “national interests”.
-Examples of important national interests include:
Ensuring economic prosperity
Promoting security, safety, or sovereignty
Promoting beliefs and values (environment, social justice, etc.)
-There are often disagreements about what the “national” interests actually are…
Especially in nations with diverse political, economic, cultural viewpoints
Peacekeeping
-Designed to preserve an existing peace
-Only enter after a peace agreement is signed
-Act as negotiators, mediators, deterrents
-All sides have to agree, cannot take sides
-Armed, but cannot use force except to defend the lives of peacekeepers (not civilians…)
Peacemaking
-Designed to force an end to an ongoing conflict
-Usually more heavily armed
-More flexibility to use force when needed against aggressive sides, protect civilians, etc.
Domestic and foreign policy
-Pursuit of national interests leads nations to make certain policy choices.
Foreign policies: decisions made affecting relations with other countries
Methods of Foreign Policy:
Diplomacy: negotiating with other countries, signing treaties and alliances
Economic Actions: signing trade deals, loans, aid, boycotts and sanctions
Military Actions: Spying, propaganda, war
Propaganda
Information presenting a biased or misleading view, such as a poster, used to promote a political view.
Appeasement
Giving aggressive foreign powers what they want to avoid conflict.
Ex. National interest of Britain in WWII to avoid aggression of Germany.
Conscription
Enrollment of people for military service. Used during WWI, created some conflict within Canada, like in Quebec
Crimes against humanity
Specific crimes used in large-scale attacks used against civilians
-Ultranationalism often leads to crimes against humanity
Genocide
The deliberate elimination of a group of people based on their race, ethnicity, religion, or other factors
Ex. Rwanda, Holocaust
War Crimes
Actions during war that violate international rules of war
ex. murder, extermination, deportation, enslavement
Ethnic Cleansing
Mass killing of an ethnic group
ex. Yugoslavia
Decolonization
-A state withdrawing from a colony
-Can arise from self-determination
-It can also lead to conflict such as Rwanda decolonization from Belgium
Successor States
a new smaller country formed after a larger country has been divided up
Russia, Georgia and Ukraine are three of the successor states to the Soviet Union
Refugees
Individuals fleeing their country to escape, war, persecution, or disaster
Isolationism
A country cuts themselves off from other countries ex. Japan, North Korea
Unilateralism
A country acts on their own to pursue national interest ex. US invasion of Iraq
Bilateralism
Bilateralism - Two countries making an agreement together ex. Canada and US make an agreement
Multilateralism
Multilateral - Many countries involved making decisions together
Supranationalism
give up nationalism for the sake of internationalism ex.EU
Internationalism
The act of becoming involved in the world’s political and economic affairs
-Internationalists argue that members of the global community share responsibility for the issues that affect the entire world
-Therefore, every nation can (and should) contribute to the solution for these issues
-Driving question: To what extent should nationalism be sacrificed for internationalism?
Collective Security
Joining organization for sake of safety and security such as UN or NATO
Tied Aid
Aid is often “tied” to targets - purchasing donors, goods, etc.
Voluntary Balkanization
the process where individuals within a larger society choose to segregate themselves into smaller, isolated groups based on shared characteristics such as ethnicity, culture, religion, or political beliefs. This self-segregation often leads to a lack of interaction and understanding between different groups, which can contribute to social fragmentation and division.
Odious debt
Responsible government
government representing peoples wishes
Historically:
-1840 - Upper and Lower Canada merged
-French was banned in the legislature (assimilation)
-Together, representatives Robert Baldwin and Louis La Fontaine pushed for:
•Shown primarily through electing/increasing the power of local Canadian officials
-Reintroduction of French in politics
-Political partnership between French and English in Canada
Confederation
-In the 1860’s - colonies began to meet (Charlottetown) to discuss forming a new nation:
Kept British traditions
Improve the economy
Strengthen Canada in face of US threats
-1867 - London Conference
Provinces (Ontario, Quebec, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia) created
BNA Act created “Dominion of Canada”
-John A. McDonald
Expanding the Nation
-Opportunities in the “empty” West
-A country stretching “from sea to sea”
-So, pushed for the building of a national railway
Open the interior to settlement
Union with BC colony
Increase Canada’s Western sovereignty (vs. US)
The CPR (Canadian Pacific Railway) wa completed in 1885
-In the early 1900’s, PM Sir Wilfred Laurier began to push Western settlement
-Interior Minister Clifford Sifton attracted new immigrants through advertising campaigns promoting Canada as a “land of plenty”
-At first, Sifton only recruited Englishman and Americans, but spread to other European nations
Ukrainians, Germans, Norwegians, Icelanders, etc.
-Attracted by promises of free land and easy homesteading
-AFFECT - British and French began losing their role as the dominant European cultural groups in Canada (esp. In the West)
-Issues with early immigration/settlement
Black immigrants from US often rejected as unsuitable, faced segregation and discrimination
-New immigrant farmers (Ukrainians, esp.) found conditions harsh and limited assistance form often resentful Anglophones
Chinese Head Tax - $50/$10/$500
Repatriation/Patriated
To return something to its own country.
Equalization
the process of making laws or treatment the same for all people or companies in a group or place
Federal System
Combines general and regional governments into one political system
Official Multiculturalism
Canadian’s rights (including multiculturalism) “entrenched” in the Charter of R and F.
-civic nationalism allows multicultural, multiethnic states (like Canada, the US, Britain, etc.) to function effectively as nations
--From the early 1900’s, special preference was given to American and European immigrants
-Changed in the late 1960’s (Trudeau):
All ethnic immigration rules (quotas) were removed
Focus on “culturally-neutral” immigrant categories:
-Family
-Refugees
-Independent (economic/point system
-Opened the doors to new immigrants from India, Africa, Asia, Middle East, etc.
-As a result, Canada has become a much more pluralistic (diverse) society
-Led to official multiculturalism policies
Cosmopolitan
Canadians have become more cosmopolitan -
Accepting, borrowing and adopting diverse customs and traditions
-Canada has become more cosmopolitan as a result of:
Increasing levels of immigration from all parts of the world (pluralism)
The policy of official multiculturalism
The increased recognition of francophone and aboriginal rights
-This vision implies a continuous growth and expansion of these processes
-Denies the value of a single unifying identity
Asymmetrical Federalism
-Historically, Canada has always been multinational
First nations confederacies
Canadian Confederation in 1867
-Our government system still promotes the idea of a “multinational” Canada:
Federal and powerful provincial governments
-Under this vision, national groups like Francophones and Indigenous Peoples would be entitled to self-government and greater self-determination
-At the minimum, it could lead to more asymmetrical federalism (not all provinces being treated equally)
-At its extreme, it would permit the pursuit of sovereignty by groups with distinct national identities
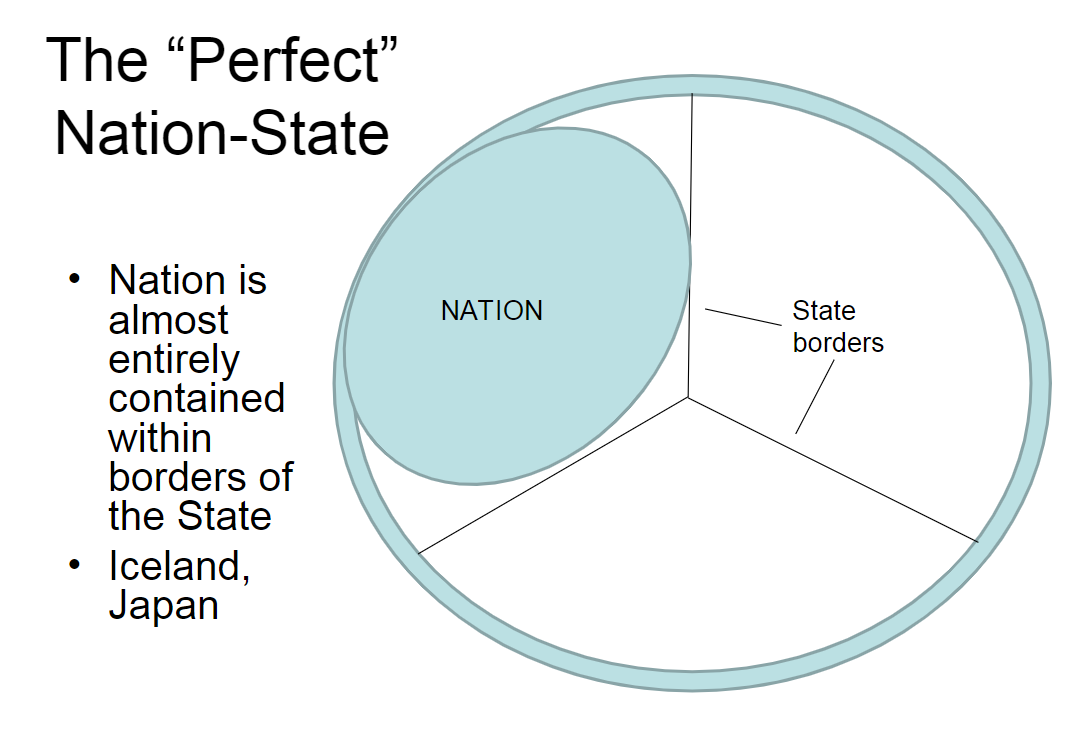
Nation-States
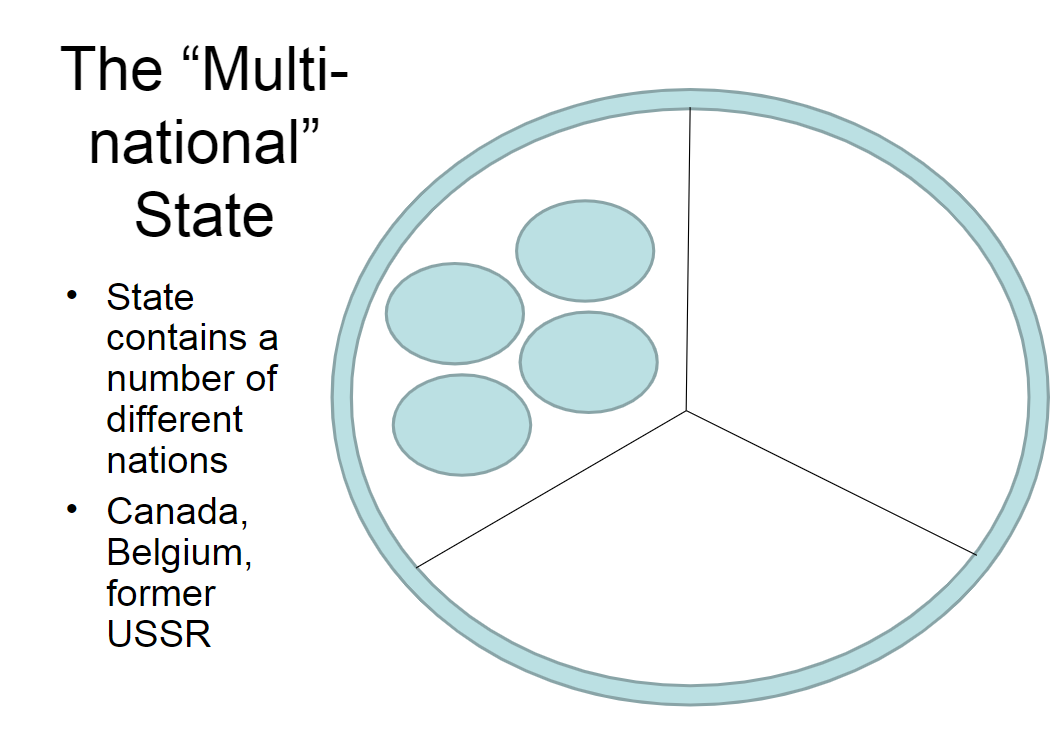
Multi-National States
Multi-State Nation

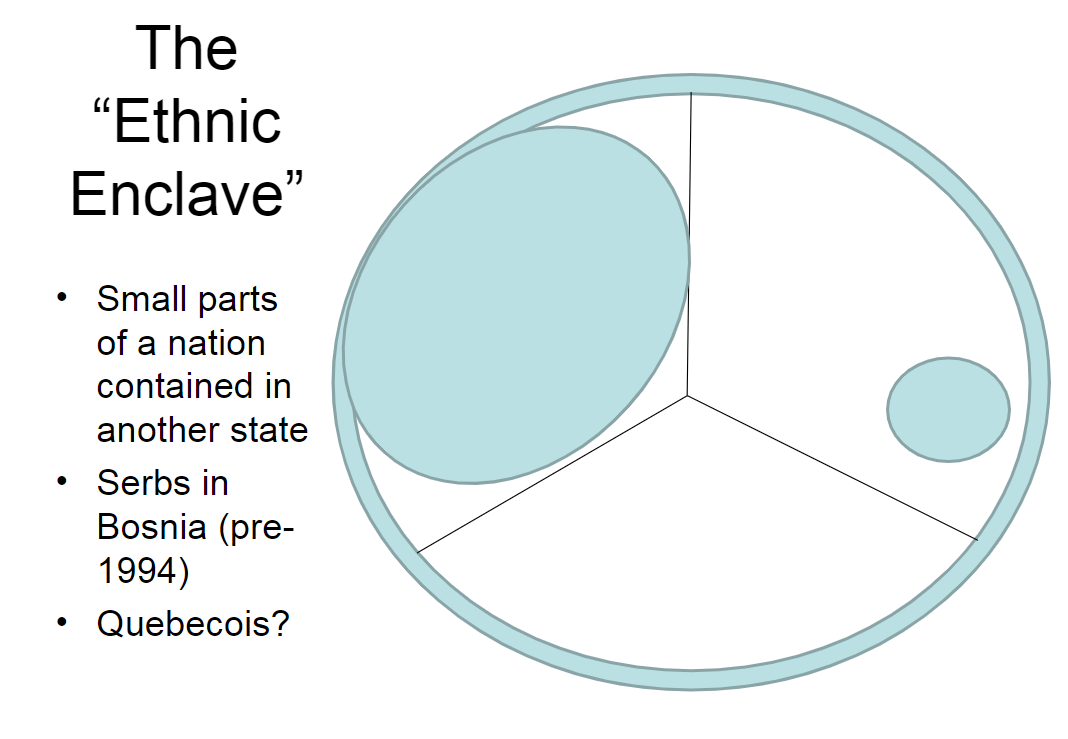
Ethnic Enclave
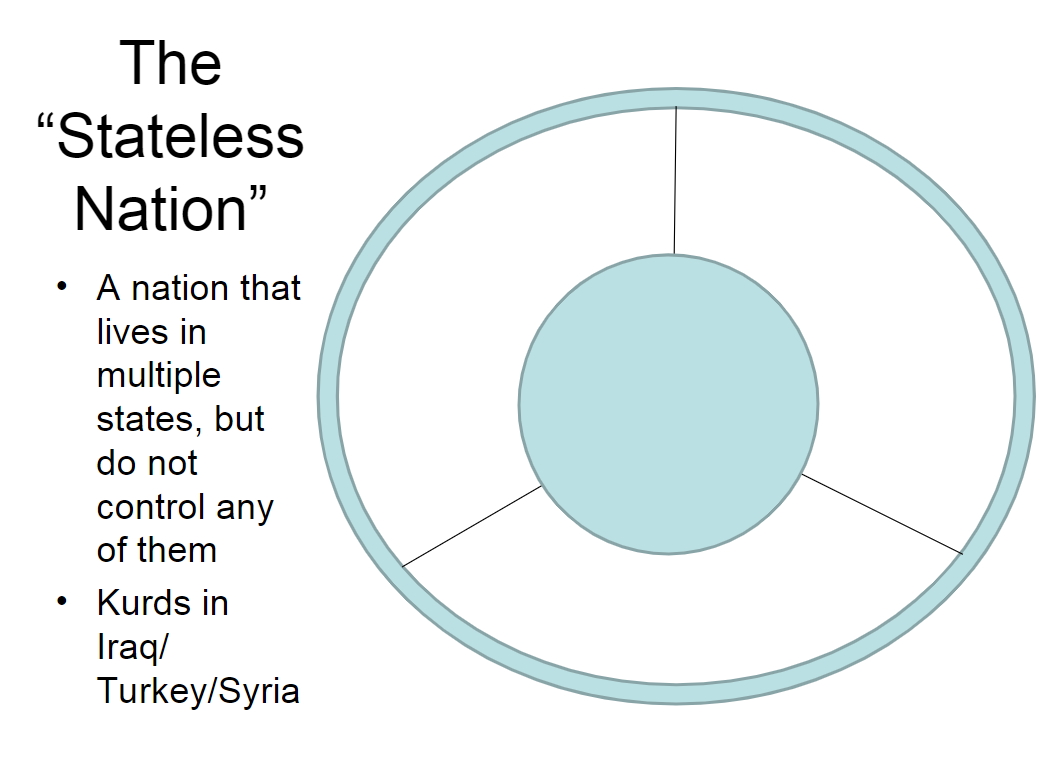
The Stateless Nation
Reconciling Loyalties
-At some point, there is a need to reconcile (deal with) the contending loyalties
-A conflicted person may choose to either:
Live with and accept the contending loyalties
Choose one loyalty and discard another
Attempt to bring about change in their environment to remove the conflict