Trauma/Stress Disorders, Sleep Disorders, Dissociative Disorders
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
trauma
response to an incident or series of events that are emotionally disturbing or life-threatening with lasting adverse effects on the individual
examples of traumatic events
war, interpersonal trauma, sexual/physical/emotional abuse, neglect, abandonment, sudden traumatic loss
Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs)
preventable traumatic events occurring during childhood.

what does posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) look like in preschool children
reduction in play, repetitive play that includes aspects of traumatic event, social withdrawal, and negative emotions such as fear, guilt, anger, horror, sadness, shame or confusion
reactive attachment disorder (RAD)
a disorder describing children who have a consistent pattern of inhibited, emotionally withdrawn behavior and who rarely direct attachment behaviors toward any adult caregivers

disinhibited social engagement disorder (DSED)
a condition in which children demonstrate no normal fear of strangers, seem unfazed in response to separation from a primary caregiver, and are usually willing to go off with people who are unknown to them

RAD and DSED are a result of
insufficient care in early development
assessment for trauma-related disorders in children
- play activities for younger children
- observance of caregiver interactions
- post traumatic symptoms: nightmares, night terrors, flashbacks, traumatic play, bedwetting
- somatic symptoms: headache, stomachache, pain
child dissociative checklist
a tool that compiles observations by an adult observer regarding a child's behaviors on a 20-item list
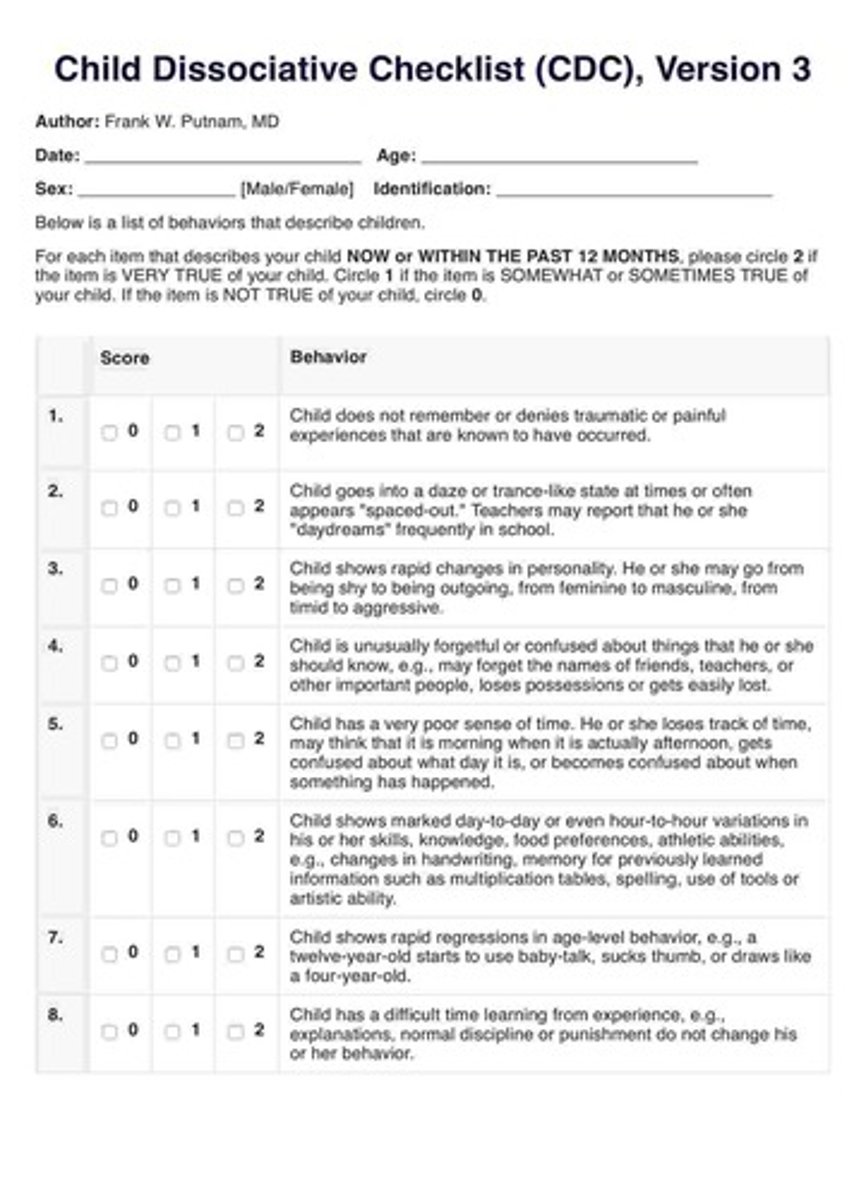
trauma symptoms checklist for children
measures posttraumatic stress and related psychological symptomatology in children ages 8-16 years who have experienced traumatic events
child sexual behavior inventory
a psychological assessment tool used to evaluate a child's sexual behavior, primarily designed to identify potential signs of sexual abuse by assessing a wide range of sexual behaviors reported by a parent or primary caregiver, usually the mother, in children aged 2 to 12 years old
denver II developmental screening test
assess a child's development in four key areas: personal-social, fine motor-adaptive, language, and gross motor skills

staged model of treatment for trauma
overall treatment plan for trauma includes psychobiological, psychological, and family goals within a staged treatment protocol
providing safety and stabilization through creating a safe, predictable environment; stopping self-destructive behaviors; providing education about trauma and its effects.
stage 1
3 multiple choice options
reducing arousal and regulating emotion through symptom reduction and memory work; finding comfort from others; tolerating affect; integrating disavowed emotions and accepting ambivalence; overcoming avoidance; improving attention and decreasing dissociation; working with memories; and transforming memories.
stage 2
3 multiple choice options
developmental skills catch-up by enhancing problem-solving skills; nurturing self-awareness; social skills training; and developing a value system. Interventions in this phase should focus on teaching coping skills to deal with trauma, supporting efforts to achieve socially appropriate goals, and facilitating the development of and integration into healthy social support systems.
stage 3
3 multiple choice options
interventions for children with PTSD
- establish trust and safety
- convey empathy and acknowledging the child's feelings
- use developmentally appropriate language
- explain and reinforce reality (this is not your fault)
- teach relaxation techniques
- calm manner and low, comforting voice
- use art and play to promote expression of feelings
- stay with the child until anxiety decreases
- involve caretakers in 1:1s, unless they are the cause of trauma
- educate child and caretakers about grief process
- assist caretakers in resolving personal distress
- coordinate with social work for protections as needed
treatment for child with PTSD
cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR)
uses psychoeducation, behavior modification, cognitive therapy, and stress management to help child manage behavior and change maladaptive thoughts and beliefs.
cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
first line treatment for traumatized children that processes traumatic memories though a specific eight-phase protocol that allows the person to think about the traumatic event while attending to other stimulation, such as eye movements, audio tones, or tapping
eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR)
posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in adults
persistent re-experiencing of a highly traumatic event; involves actual or threatened death or serious injury to self or others
characteristics of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in adults
- re-experiencing the traumatic event (Flashbacks)
- sustained high level of anxiety or arousal
- general numbing of responsiveness
- intrusive recollections or nightmares
- amnesia to certain aspects of the trauma
- depression, survivor's guilt
- substance use
- anger and aggression
- relationship problems
assessment of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in adults
- screening tools (Primary Care PTSD Screen, PTSD Checklist, Severity of Posttraumatic Stress Symptoms, National Stressful Events Survey PTSD Short Scale [NSESSS])
- daily functioning (sleep, nutrition, withdraw from friends/family)
- depression and suicide screening
outcomes identification for posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in adults
1. The patient is able to manage anxiety as demonstrated by the use of relaxation techniques, adequate sleep, and the ability to maintain a role or work requirements.
2. The patient experiences enhanced self-esteem, as demonstrated by maintenance of grooming/hygiene, maintenance of eye contact, positive statements about self, and acceptance of self-limitations.
3. The patient exhibits an enhanced ability to cope as demonstrated by a decrease in physical symptoms, an ability to ask for help, and seeking information about treatment.
nursing interventions for posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in adults
- explain physical symptoms as related to the psychological state
- listen and validate feelings
- teach anxiety reduction strategies (breathing exercises, muscle relaxation)
- ongoing, routine screening for signs and symptoms of PTSD
treatment for posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in adults
- cognitive (behavioral) therapy
- dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT)
- prolonged exposure therapy
- group/family therapy
- eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR)
- psychopharmacology
SSRIs for PSTD
paxil and zoloft
3 multiple choice options
SNRI(s) for PTSD
effexor
3 multiple choice options
TCA(s) for PTSD
remeron
3 multiple choice options
hyperarousal/panic/intrusive symptoms meds for PTSD
clonidine, minipress, propranolol
2 multiple choice options
Nightmares
Disturbing dreams related to traumatic events.
acute stress disorder (ASD)
severe numbing, derealization, inability to remember stressful event, fear, helplessness, or horror that occurs within 1 month of exposure to extreme stress
diagnosis of acute stress disorder (ASD)
- alterations in concentration
- anger
- dissociative amnesia
- headache
- irritability
- nightmares
implementation of nursing care for acute stress disorder (ASD)
- establish therapeutic relationship
- assist to problem solve
- connect person to supports
- collaborate for coordination of care
- ensure and maintain safety
- refer to a licensed mental health provider
- monitor response and/or adherence to treatment
- advanced practice: cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
sleep
1 of 3 most important considerations in maintaining good mental/physical health
insomnia
chronic inability to sleep or to remain asleep throughout the night; wakefulness; sleeplessness.
diagnosis for insomnia is based on
interviews, subjective data
sleep diary
a self-report record of an individual's sleep and waking time activities
sleep studies
monitoring of a patient's sleep for 6 or more hours; expensive, but necessary to diagnose and treat sleep disorders
consequences of insomnia/poor sleep
- memory impairment
- automobile accidents
- poor job/school performance
- relationship between insomnia and depression, pain disorders, heart disease
- higher rate of hospitalizations
- increased risk for GAD (general anxiety disorder) and MD (major depression)
- four-fold increase in new-onset psychiatric episodes
sleep hygiene
conditions and practices that promote continuous and effective sleep (exercise [not before before], hot bath 2 hours before bed, hot non-caffeinated drink, avoiding heavy meals before bedtime, comfortable room to sleep in)
stimulus control
a strategy for self-modification that depends on manipulating the causes of behavior to increase goals or behaviors desired by a patient while decreasing those that are undesired.
imagery distraction
- think of an interesting, but at the same time, pleasant and relaxing image or activity such as: gardening, decorating, sitting on a beach
- when intrusive thoughts start to occur, say 'stop' to the thought
- then immediately substitute the intrusive thought with your relaxing image or activity
relaxation training
a treatment procedure that teaches clients to relax at will so they can calm themselves in stressful situations (meditation, yoga, Tai Chi, progressive muscle relaxation, biofeedback, hypnosis)
hypnotics
drugs used to induce sleep
zolpidem (Ambien), extended-release (Ambien-CR)
a controlled substance used to decrease time to sleep onset and increase amount of sleep
zaleplon (Sonata)
used to decrease time to sleep onset
eszopiclone (Lunesta)
used to decrease time to sleep onset and increase amount of sleep but takes up to an hour to start working
ramelteon (Rozerem)
non-habit forming hypnotic to decrease time to sleep onset
dissociation
unconscious defense mechanism by which an idea, thought, emotion, or other mental process is separated from the consciousness and thereby loses emotional significance
depersonalization/derealization disorder
characterized by a temporary change in awareness displaying depersonalization, derealization, or both, often in response to stress
depersonalization
a feeling of strangeness or unreality concerning oneself or the environment, often resulting from anxiety or fatigue
derealization
false perception by a person that his or her environment has changed
dissociative amnesia
the inability to recall important personal information, often the result of a trauma or severe stress; can be of events of a certain period of time or just certain details
dissociative fugue
characterized by sudden, unexpected travel away from the customary locale and an inability to recall one's identity and information about some or all of one's past; can last weeks to months and usually follows a traumatic event
dissociative identity disorder
characterized by the existence of two or more distinct, clearly differentiated personality structures within the same individual, any of which may dominate at a particular time
each personality is a complex unit with separate well-developed emotional and thought processes, behavior patterns, and social relationships

risk factors for dissociative disorders
- childhood physical/sexual/emotional abuse
- traumatic life effects
- dissociative symptoms
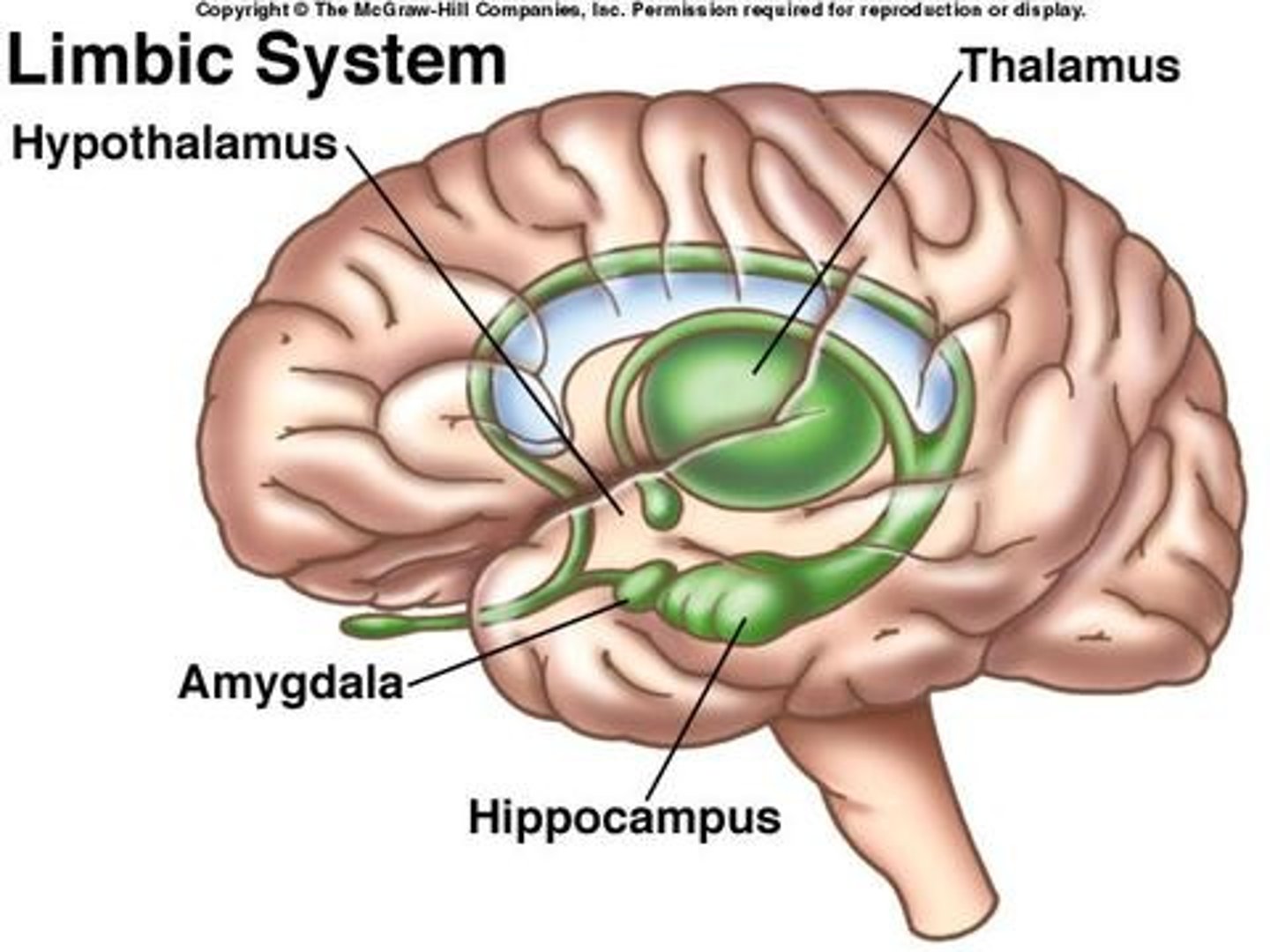
limbic system
involved in the development of dissociative disorders since it processes traumatic memories and stores them in hippocampus
assessment of dissociative disorders
- history
- memory
- impact on patient and family
- suicide risk
- self-assessment
phase-oriented treatment model for dissociative disorders
treatment for patient with dissociative disorders grouped in phases
establishing safety, stabilization, and symptom reduction
phase 1
3 multiple choice options
confronting, working through, and integrating traumatic memories
phase 2
3 multiple choice options
identity integration and rehabilitation
phase 3
3 multiple choice options
psychoeducational and pharmacological interventions for dissociative disorders
- provide education on illness
- educate on coping skills and stress management
- teach grounding techniques
- medications that target symptoms of depression, anxiety, and psychosis
basic interventions for dissociative disorders
- provide undemanding, simple routine
- safe environment with frequent observation
- confirm identity of patient and orientation to time and place
- encourage pt to do things for self and make decisions about routine tasks
- support pt during exploration of feelings
- do not flood pt with data regarding past events
- provide supportive, empathetic listening
advanced practice interventions for dissociative disorders
CBT, psychodynamic psychotherapy, exposure therapy, modified EMDR therapy, hypnotherapy, neurofeedback, ego state therapies, somatic therapies, and medication