auto sympathomimetics part 4- indirect and mixed acting agonists
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
which of the following sympathomimetic categories would be expected to have diminished or abolished effects following reserpine pretreatment?
a. direct acting
b. indirect acting
c. mixed acting
d. 2 of the above
e. all of the above
d. 2 of the above
indirect and mixed
amphetamine
a. levo isomer has greater potency at DAT than dextro
b. can cause the phosphorylation of the DAT transporter and inhibit function
c. causes release of dopamine from vesicles into the cytoplasm
d. can reverse DAT function and cause efflux of dopamine into the synaptic space
e. 2 of the above
f. 3 of the above
g. all of the above
f (b, c, and d are correct)
a should be dextro
all of the following statements about sympathomimetics are true except
a. amphetamine and ephedrine may inhibit micturitation
b. both tyramine and amphetamine can displace catecholamines from neuronal storage vesicles
c. cocaine binds to DAT and NET, but not to SERT
d. methylphenidate has a more pronounced effect on mental rather than motor activity
e. selegiline is less likely than pargyline to cause hypertension after ingesting a large meal of tyramine rich food
c
(cocaine binds to all 3)
the principal targets of amphetamine include
a. TAAR1
b. DAT
c. VMAT2
d. voltage dependant sodium channels
e. 2 of the above
f. 3 of the above
g. all of the above
f. 3 of the above (D is not true; does not affect sodium)
all of the following statements about neurotransmission at the neuromusc junction are true except
a. 2 ACh molecules need to bind to single Nm receptor in order for cation channel to open
b. an AP associated w muscle fibril will cause the L type calcium channels to open
c. the ionic flux through single Nm receptor channels has been successfully measured and D-tubocurarine was found to decrease the frequency of channel opening evenets, but not amplitude or duration
d. the membrane potential of the muscle fibril must move in a positive direction after Nm receptors are activated in order for receptors to be activable again
e. when NM receptors are activated there is an increase int he conductance for both Na and K
d
the membrane potential must move in a negative direction to become activable again
(when membrane is depolarized/positive for long time its inactivated until returns to resting potential)
succinylcholine
a. stimulates N-M receptors
b. causes long lasting depolarization
c. is resistant to ACHE
d. actions would be enhanced co-administration of D-tubocurarine
e. 2
f. 3
f. 3 (a, b, c)
succinylcholine
a. is metabolized by butyrylcholinesterase
b. causes paralysis by depolarizing the myofibril
c. action can be prolonged during the phase 1 response by neostigmine
d. causes flaccid paralysis during phase 2 response
e. 2
f. 3
g. all
g. all of the above
(remember neostigmine= ache-I)
d-tubocurarine
a. duration can be decreased by administering neostigmine
b. at a dose on a poison arrow that can kill an animal would not be expected to hurt human that eats it
c. is depolarizing agent
d. at paralytic doses, does not prevent the activation of a muscle by electrical stimulation
e. 2
f. 3
g. all
f. 3 of the above
-a is true: neostigmine would increase ACh and compete w d-tubocurarine
-b is true: quaternary amine, not rlly absorbed in GI
- c is FALSE: its competitive
- d is true: ion channel is still working (w depolarizing agents that doesnt work)
all of the following are true except
a. ganglionic blockade caused by competitive neuromusc blocking agents can be reversed by pyridostigmine
b. succinylcholine can elicit cardiovasc effects by stimulating autonomic ganglia
c. hypotension and bronchospasm may result from systemic D-tubocurarine and is caused by histamine release from mast cells
d. an advantage of using neuromusc blockers is the prolonging of general anesthetic action
d is incorrect
- not always selective, may affect neuronal type
- pyridostigmine will reverse this by increasing ACH and competing
- succinylcholine may effect cardiovasc effects (not completely selective)
which is true?
a. acetylcholinesterase inhibitors can worsen paralysis due to depolarizing neuromusc blocking agents
b. prolonged depolarization by depolarizing neuromusc blocking agents can cause life threatening hyperkalemia
c. dantrolene can be used to treat malignant hyperthermia caused by succinylcholine
d. low butyrylcholinesterase levels are associated w slow succinylcholine metabolism and can prolong metabolism
e. 2
f. all
f
ultra short duration non-depolarizing
a. d-tubocurarine
b. gantacurium
c. succinylcholine
b. gantacurium
a short acting beta-2 selective agonist developed as a uterine relaxant
midodrine
a selective alpha 2 agonist that can lower bp through central action when given orally and cause vasoconstriction when given IV
a. metaraminol
b. clonidine
c. phenylephrine
d. apraclonidine
b. clonidine
alpha methyldopa
a. crosses BBB
b. requires conversion to an active metabolite to elicit its action
c. mediates its action by stimulating central alpha 1 receptors
d. 2 of the above
e. all of the above
d (c is incorect)
amphetamine is a _________ agonist
indirect-acting adrenergic
what are the 2 enantiomers of amphetamine and what are the characteristics? which catecholamine are they similar to?
similar to dopamine in structure (lack OH groups to cross BBB)
Dextro: better at CNS stimulation (4x) and potency at DAT
Levo: better at cardiovasc/periphery effects
amphetamine ______ catecholamine and serotonin (at high doses) release
increases
what are the 3 principal targets of amphetamine
1. activates TAAR1: trace amine associated receptor
- activation causes increased cAMP
- non-competitively inhibits transporters via phosphorylation-> efflux
2. stops transporters: DAT and NET (+ SERT at high doses)
- amphetamine competitively inhibits transport of dopamine, NE, serotonin
3. inhibits VMAT2: vesicular monoamine transporter 2
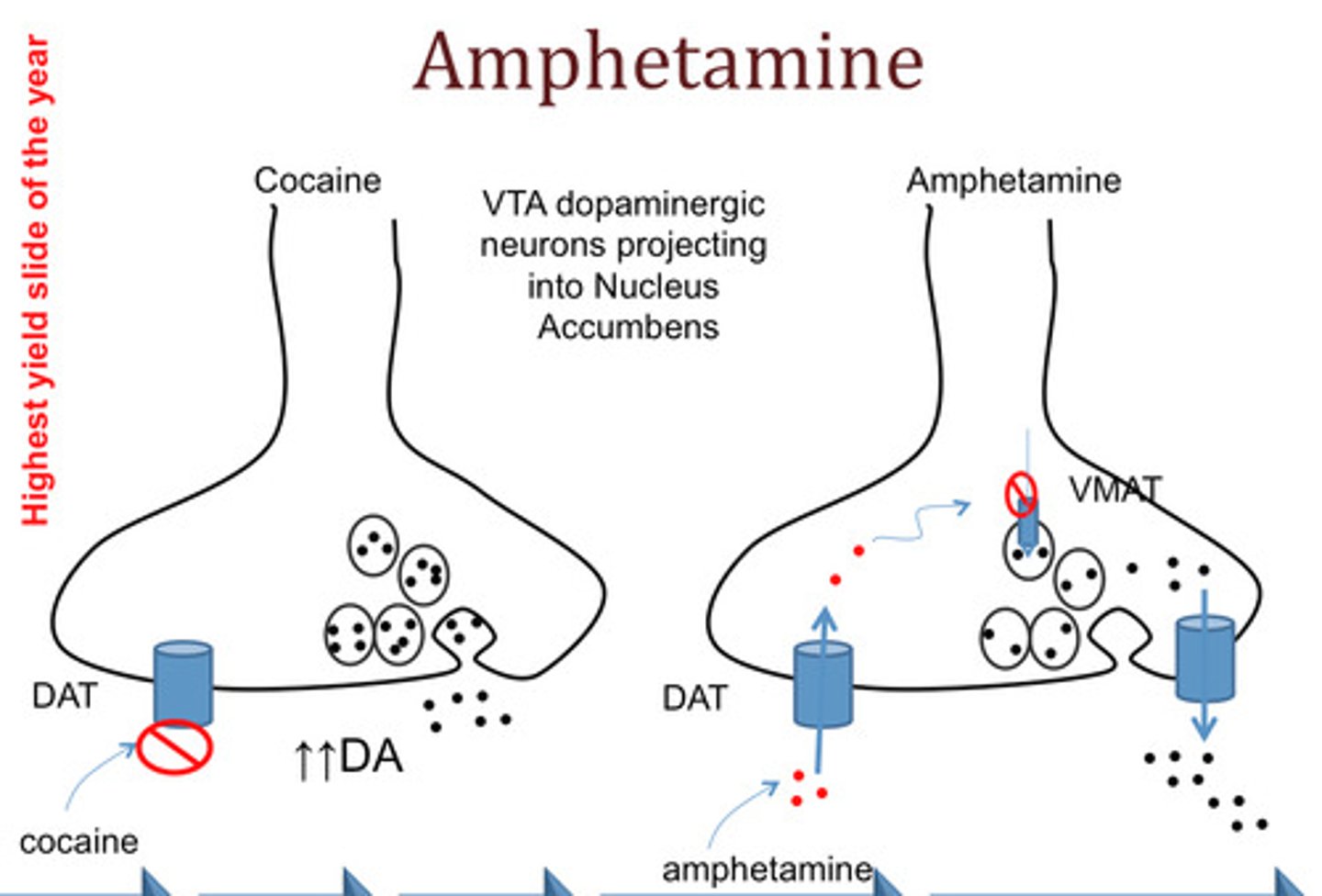
what can TAAR1 activation via amphetamine cause
- inhibits transporter DAT and NET fxn via phosphorylation; becomes internalized/ comes off of membrane (NON competitive)
- can also REVERSE transport fxn-> causes an efflux/ increase in NT in synaptic space
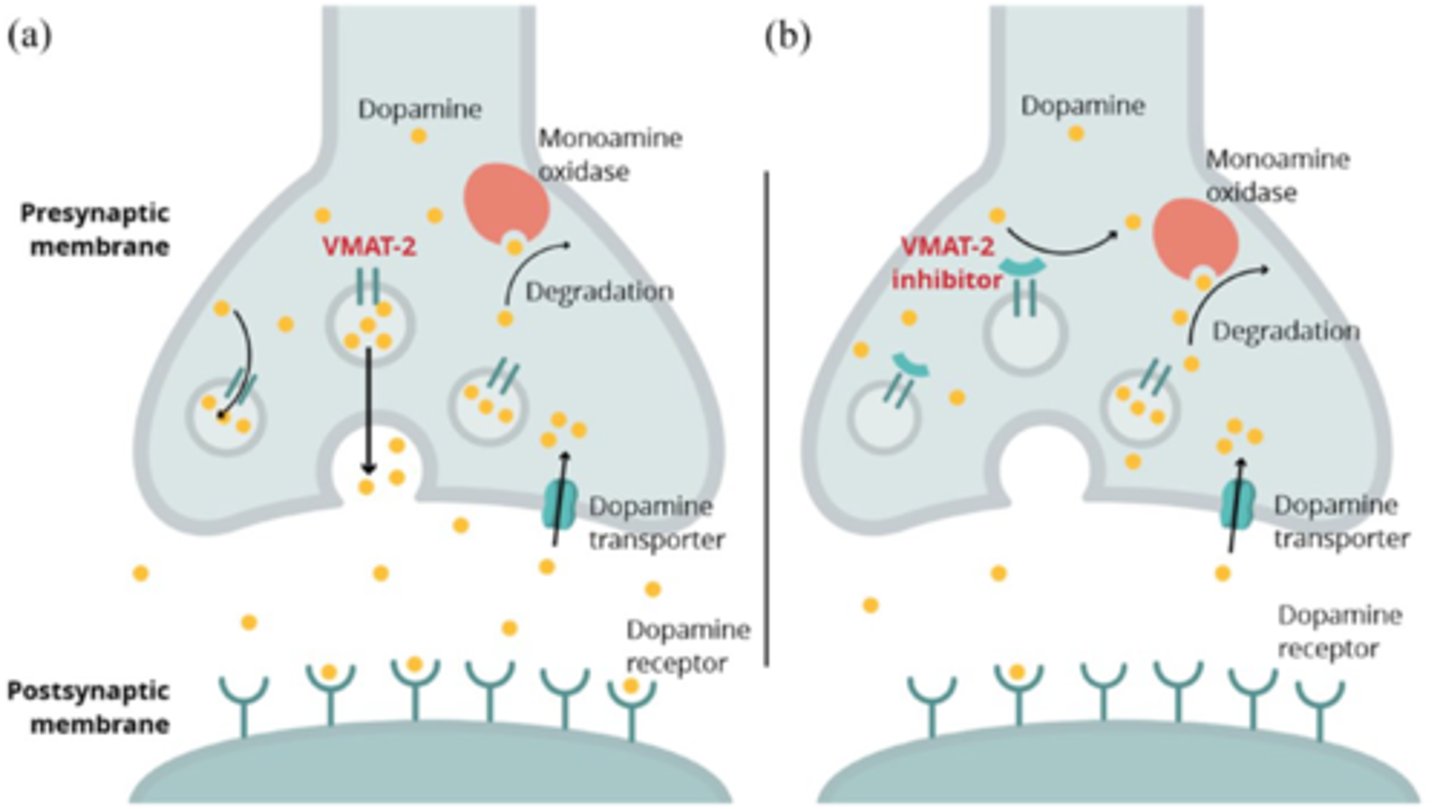
what effect does amphetamine have on VMAT2
inhibits VMAT2 (vesicular monoamine transporter-2)
- this displaces neurotransmitters (dopamine, NE)-> released into cytoplasm-> increased efflux from terminal
in which ways can amphetamine cause neurotransmitter efflux
- TAAR activation can reverse transport of DAT and NET (so instead of taking in, its pumping out into cleft)
- inhibits VMAT 2 which displaces dopamine out of vesicle and into cytoplasm
how does amphetamine interact with DAT, TAAR1, and VMAT2 to cause increased dopamine (and NE) in the cleft
DAT transporter
1. direct competition with dopamine causes more to stay in cleft
2. phosphorylation via TAAR1 causes
- internalization (removed from membrane)
- reverses pump to efflux more DA out
TAAR1
1. dopamine is taken in and activates TAAR1= phosphorylation of DAT-> internalization and efflux
VMAT2
1. amph enters vesicle and displaces DA out into cytoplasm

amphetamine exhibits ________ antagonism to other CNS depressants
functional
(not physical competition at receptor, but rather counters effect)
for amphetamine
the _____ isomer is more potent at CNS stimulation causing:
the ______ isomer is more potent at cardiovasc stimulation causing:
r-isomer: CNS
- stimulates medullary respiratory
- DA and NE
- stimulates RAS
L-isomer: cardiovasc
- alpha and beta peripheral effects (indirect)
- increase in systolic and diastolic
- HR depends on reflex, usually slowed bc of increased bp
what effect does amphetamine have on urinary smooth muscle
increased tone of urinary bladder sphincter (alpha 1)
= inhibits micturition
amphetamine ADEs
- overstimulation of CNS
- headache, angina, palpitations, arrythmias, etc
therapeutic uses of amphetamine
narcolepsy, ADHD
methamphetamine (aka crystal meth) has pharmacodynamic effects similar to _________
amphetamine; also has 2 isomers
characteristic changes for individuals on methamphetamine
"meth mouth"= loss of teeth
due to xerostomia, poor oral hygiene, bruxism (teeth grinding)
compare methylphenidate (Ritalin) to amphetamine
pharmacodynamic properties similar to amphetamine but more mild CNS stimulant
- higher effect on mental vs motor activity
- used for ADHD
cocaine is a ____mimetic
indirect acting sympathomimetic
cocaine
____ BBB
inhibits ______________ reuptake
acts as local anesthetic via ________
metabolized by:
crosses BBB
TRIPLE REUPTAKE INHIBITOR:
inhibits reuptake of monoamine neurotransmitters (DAT, NET, SERT)= DA, NE, 5HT
local anesthetic via blocking Na channels and APs
metabolized by serum esterases (short acting)
cocaine is _____ acting because it is metabolized by
short acting; serum esterases
cocaine causes
_______ BP
toxicity:
increases BP
toxicity: HTN, arrhythmias, MI, cardiac arrest, stroke seizures
t/f: cocaine causes displacement of neurotransmitters such as DA and NE, similar to amphetamine
false. cocaine does not cause displacement. it is only a reuptake inhibitor of DA, NE, 5HT via inhibiting DAT, NET, SERT
phentermine MOA
indirect sympathomimetic (like amphetamine)
1. inhibits NE reuptake by binding to NET
2. TAAR1 agonist
3. may suppress appetite/ lower hunger
fen-phen
diet drug
approved in 1996 was recalled later because it caused serious heart valve problems
(fenfluramine + phentermine)
Qsymia
phentermine/topiramate (anti-seizure)
- for weight loss
CI: MAO inhibitors and pregnancy

tyramine MOA
broken down by?
BBB?
Indirectly acting sympathomimetic
- broken down by MAOa
- displaces NE and EPI from vesicles
- high affinity for TAAR1
- does NOT cross BBB
[so like amphetamine but wont cross BBB]
![<p>Indirectly acting sympathomimetic</p><p>- broken down by MAOa</p><p>- displaces NE and EPI from vesicles</p><p>- high affinity for TAAR1</p><p>- does NOT cross BBB</p><p>[so like amphetamine but wont cross BBB]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3267efe5-fa64-45d7-8704-27c4ca7631cb.jpg)
what happens when taking MAO inhibitor with tyramine
if taking MAO inhibitor, large amounts of tyramine will cause massive NE release and hypertensive crisis
tyramine rich foods
cheese, alcohol, chocolate, processed meat, veggies, dairy, nuts
what breaks down tyramine
MAO isozyme A
(therefore avoid MAO inhibitors with tyramine)
ephedrine MOA
mixed acting sympathomimetic
1. CNS stimulant
-increases NE release from post gang neurons (via NET)
2. weak alpha and beta agonist
-alpha can inhibit micturition and beta can relax bronchioles
cardiovasc: increases HR, CO, TPR, BP [note maybe decreased HR if reflex]
ephedrine therapeutic use
used to treat bronchospasm (replaced by beta 2 agonists)
used for narcolepsy (replaced)
ephedrine contraindication
MAO inhibitors
pseudoephedrine is an __________ of ephedrine with _________ CNS effects
SS; less CNS effects
pseudoephedrine MOA
mixed acting sympathomimetic
1. indirect= MORE IMPORTANT
- increased NE release via NET
2. direct
- alpha/beta agonist
== vasoconstriction, bronchiolar relaxation, increased HR
== used for nasal decongestion
pargyline MOA
where in the body does it work?
effect?
non-selective MAOa inhibitor
- liver, pulmonary vasc, GI
- inhibiting increases tyramine response= hypertensive crisis
t/f: while pargyline is selective, selegiline is not
false.
pargyline= non selective MAOa
selegiline: selective for MAOb; less likely to potentiate tyramine response
selegiline MOA
effect
use
selective MAOb inhibitor
- platelets and brain
-LESS likely to potentiate tyramine response but selectivity lost at higher doses
- used in Parkinsons to increase DA
MAOa vs MAOb
MAOa
- pargyline inhibits
- liver, pulmonary vasc, GI
MAOb
- selegiline inhibits
- platelets, brain
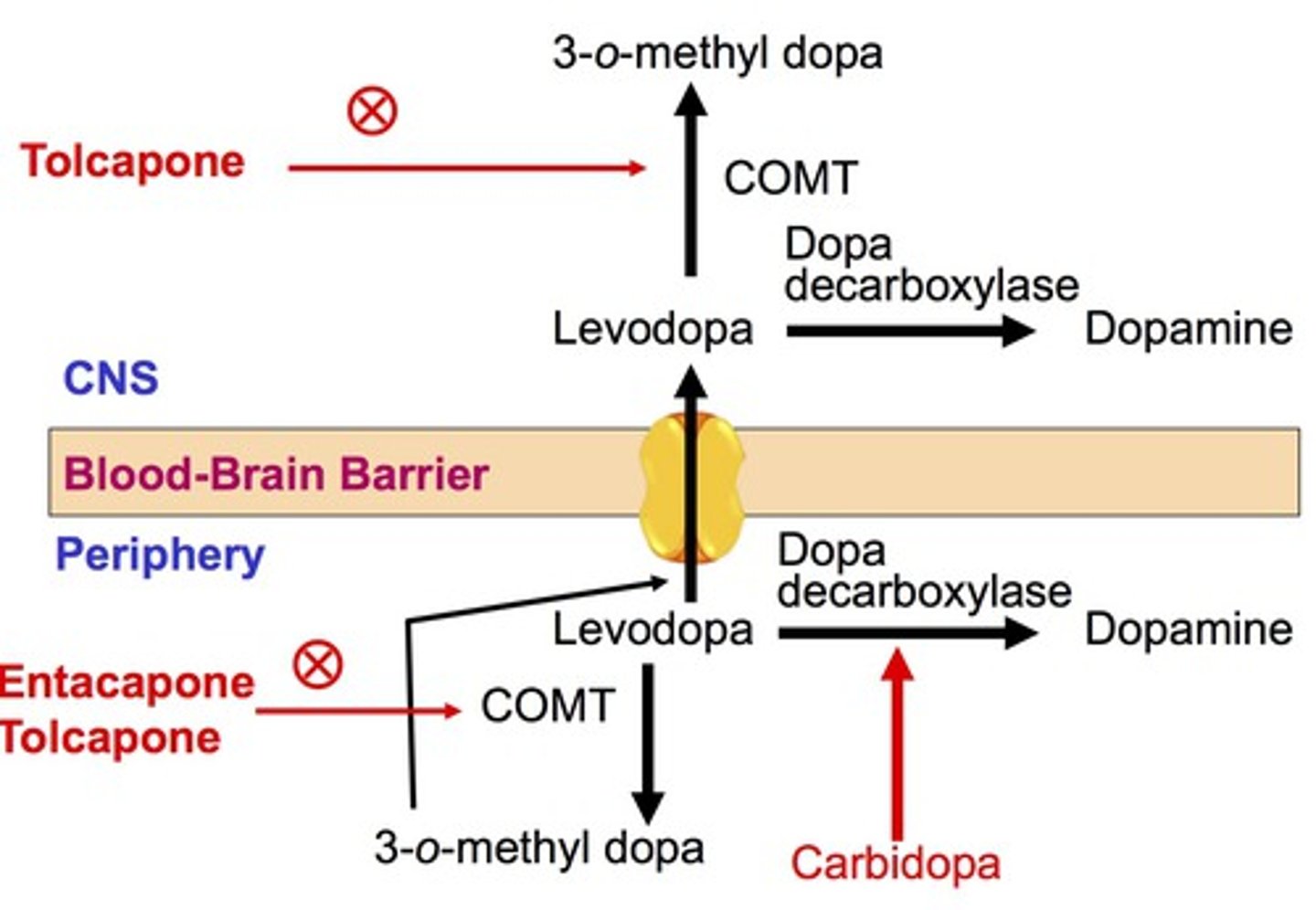
entacapone moa
COMT inhibitor
-prevents L-dopa degradation into 3-O- methyl DOPA
- more L DOPA delivered to brain in tx of Parkinsons