Sports psych - 4.5 arousal, stress & anxiety - stress & the influence of arousal on sporting performance
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
What is stress?
-A state of physiological or psychological tension produced by internal or external forces
What are sources of stress (stressors)
-External stressors —> usually are physiological & measurable, such as extremes in temperature, illness, injury & hard physical training
-Internal stressors —> usually psychological, such as changing a coach, failing a test, an unhappy relationship or losing a competition
What is arousal?
-The amount of readiness or activation a person experiences when faced with a task
-Arousal = the heightened sense of physical & mental alertness or activation. and is an organism’s overall state of readiness for action
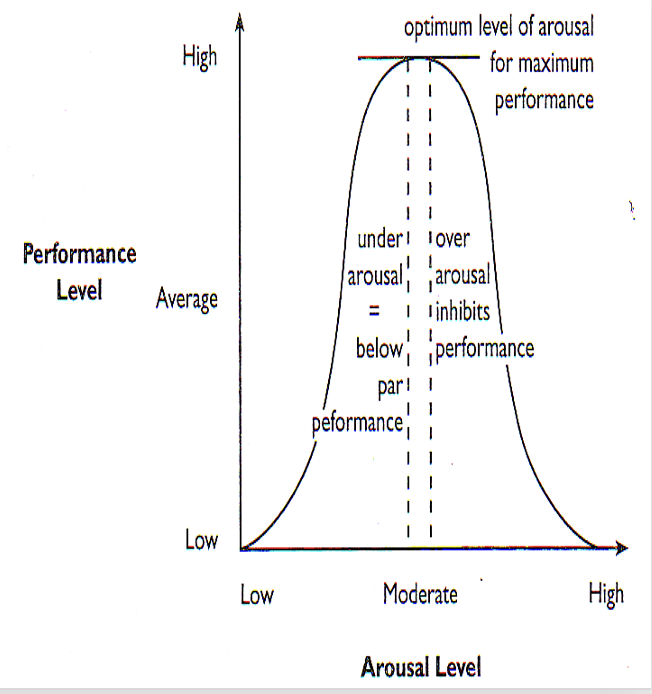
Yerkes and Dodson’s inverted U hypothesis:
-This theory states that as arousal increases, so too will the quality of performance until arousal passes beyond an optimal level; beyond this optimal range of arousal, performance will diminish
What is the primary role of a coach?
-To place each of their athletes in their optimum range of arousal just as they enter competition —> difficult as an athlete’s arousal levels can change by the minute
What can affect an athlete’s optimum level of arousal?
-Level of experience of the athlete
-The person’s perception of the competition
-The degree of distraction or disruption in the pre-competition phase
-Their personality
How can the relationship between performance and arousal be affected?
It can be affected by:
-The type of skill or sport —> in this concept, the level of arousal must still be optimal for that athlete in that sport
-The relationship between arousal and performance differs greatly between sports
-For instance, a golfer requires far less arousal for optimal performance than a hockey goalie
-Fine motor skills tend to require low arousal compared to gross motor skills
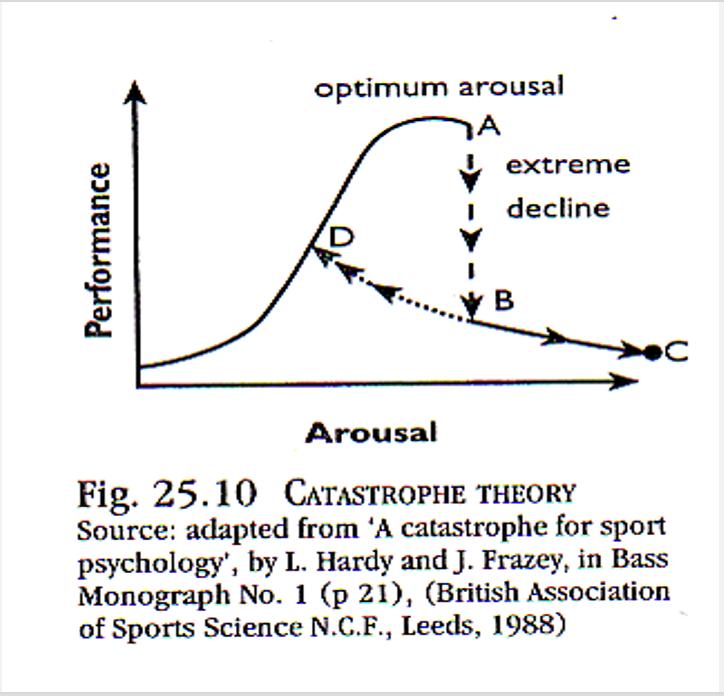
What is the catastrophe theory?
-The theory is three-dimensional as it includes physiological arousal and performance, as in the Inverted U theory, and also cognitive anxiety (trait and state anxiety acting together)
-Increased arousal will benefit performance as long as cognitive anxiety is relatively low