23 Med Chem Antibiotics, Antifungals, Antiparasitics, Antimicrobials
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
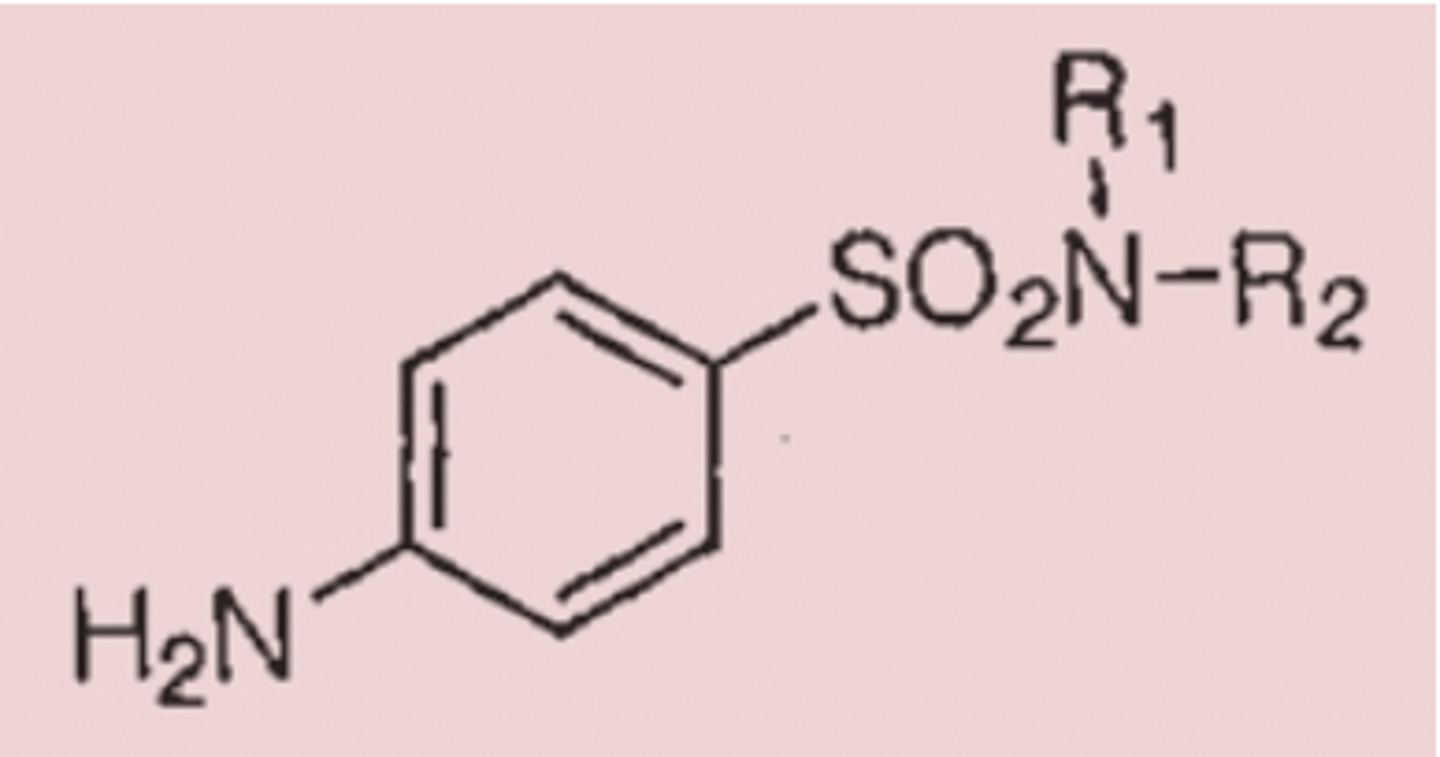
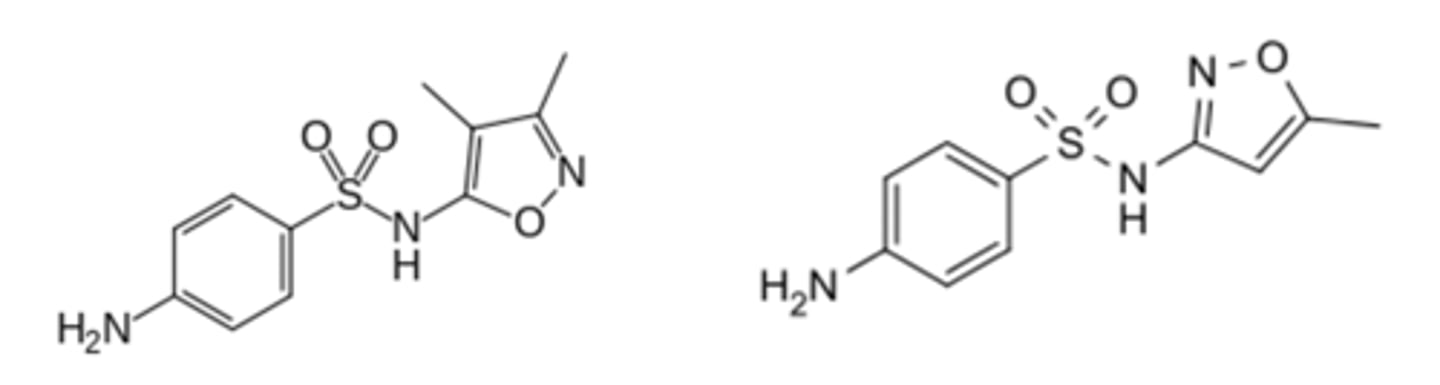
Sulfonamide
Identify the pharmacophore
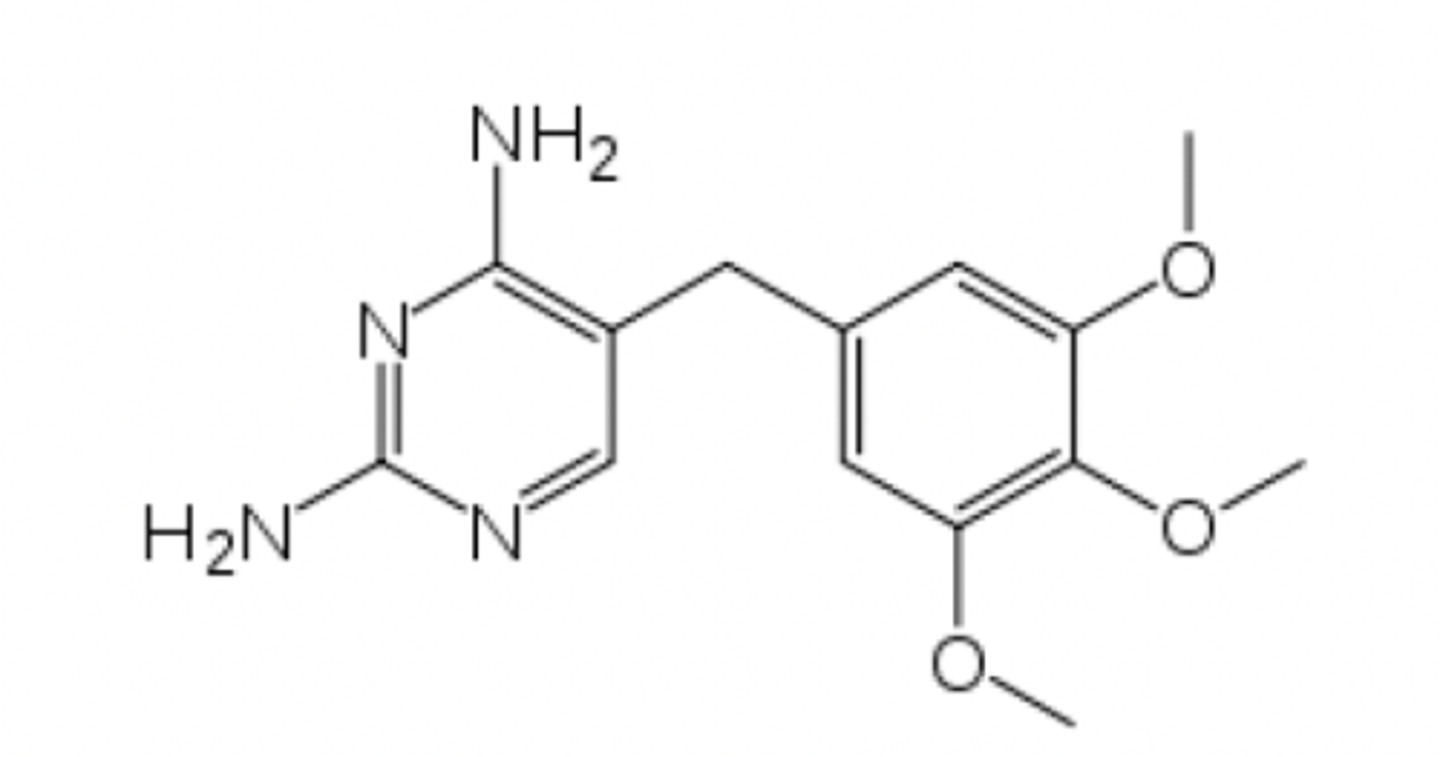
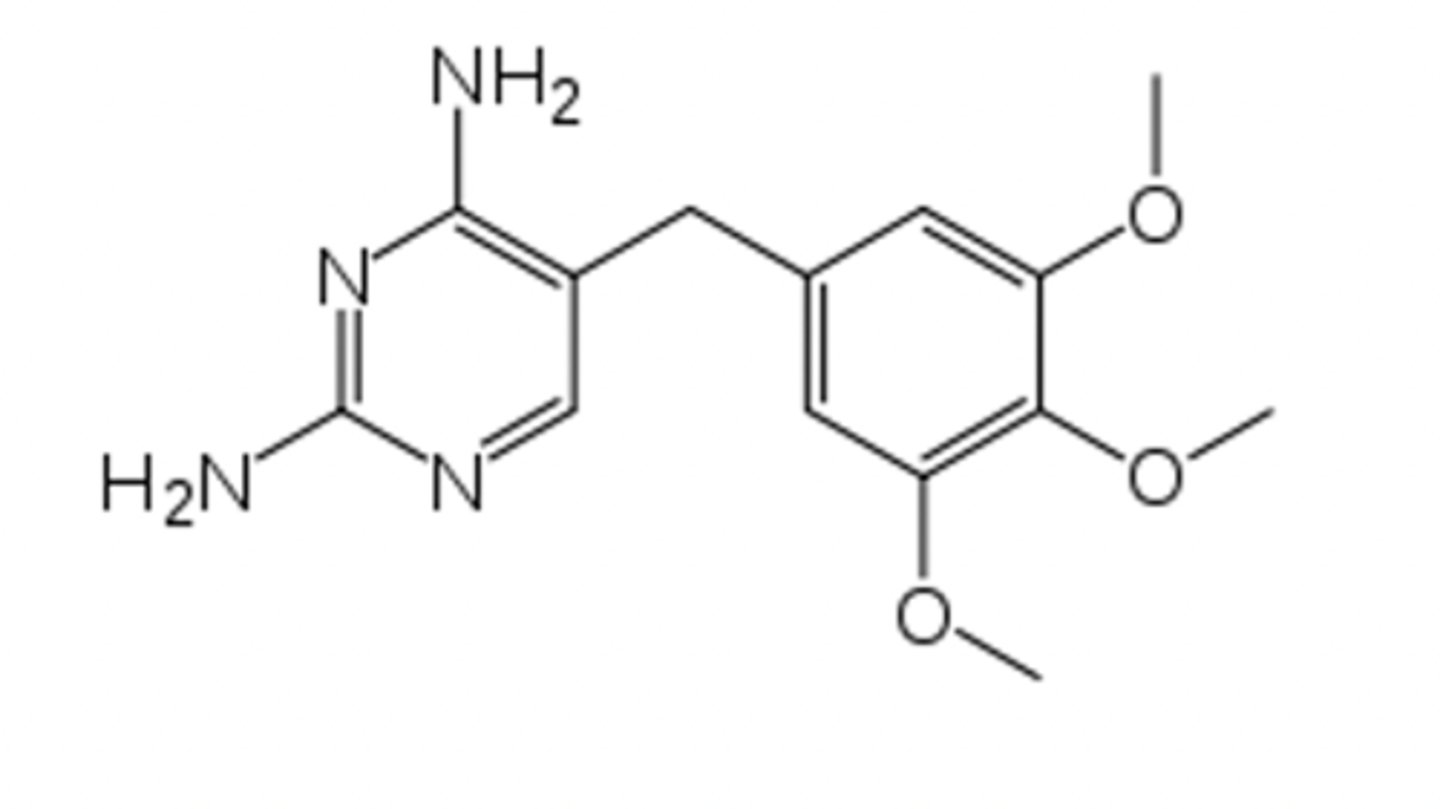
trimethoprim
Identify the structure
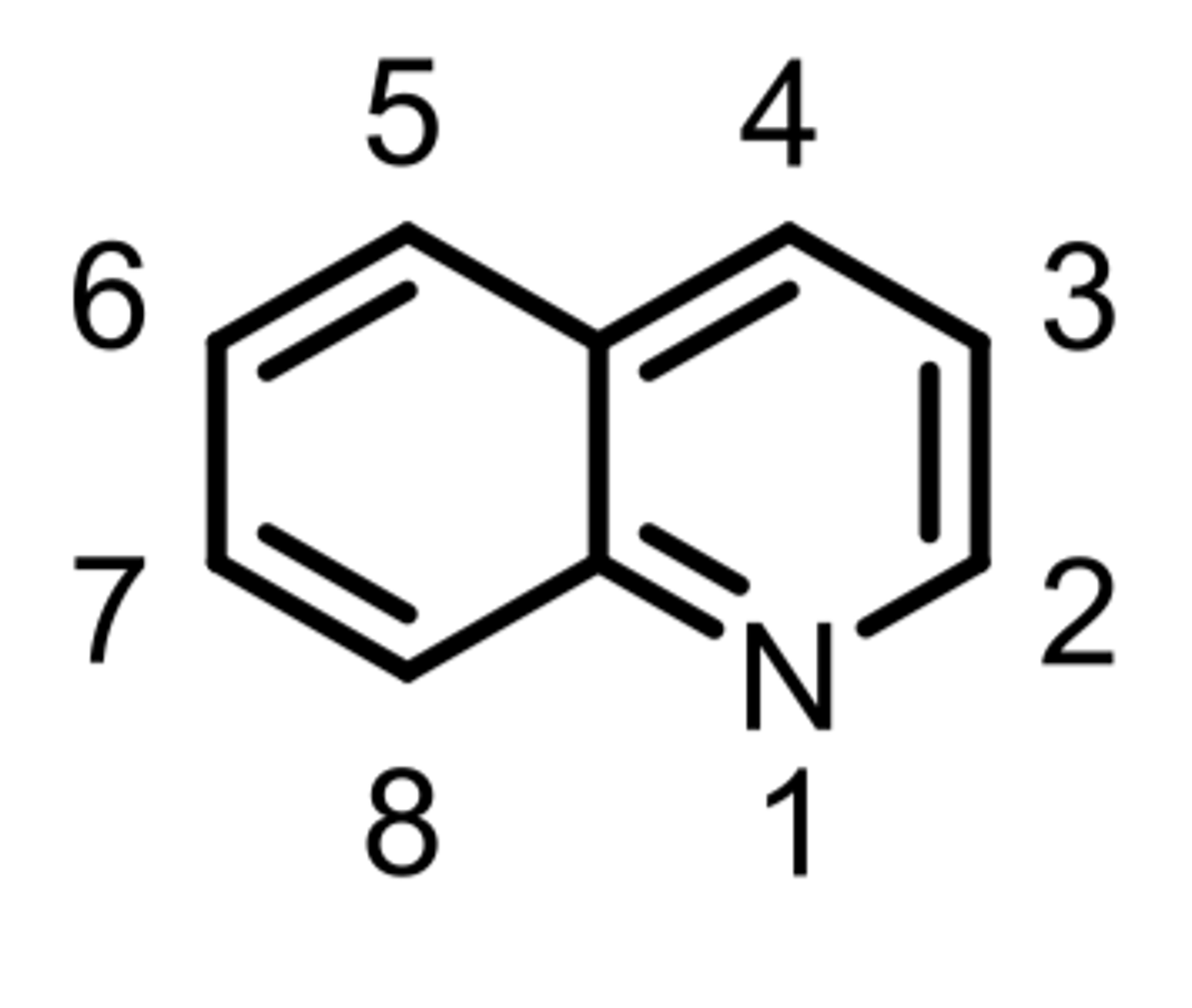
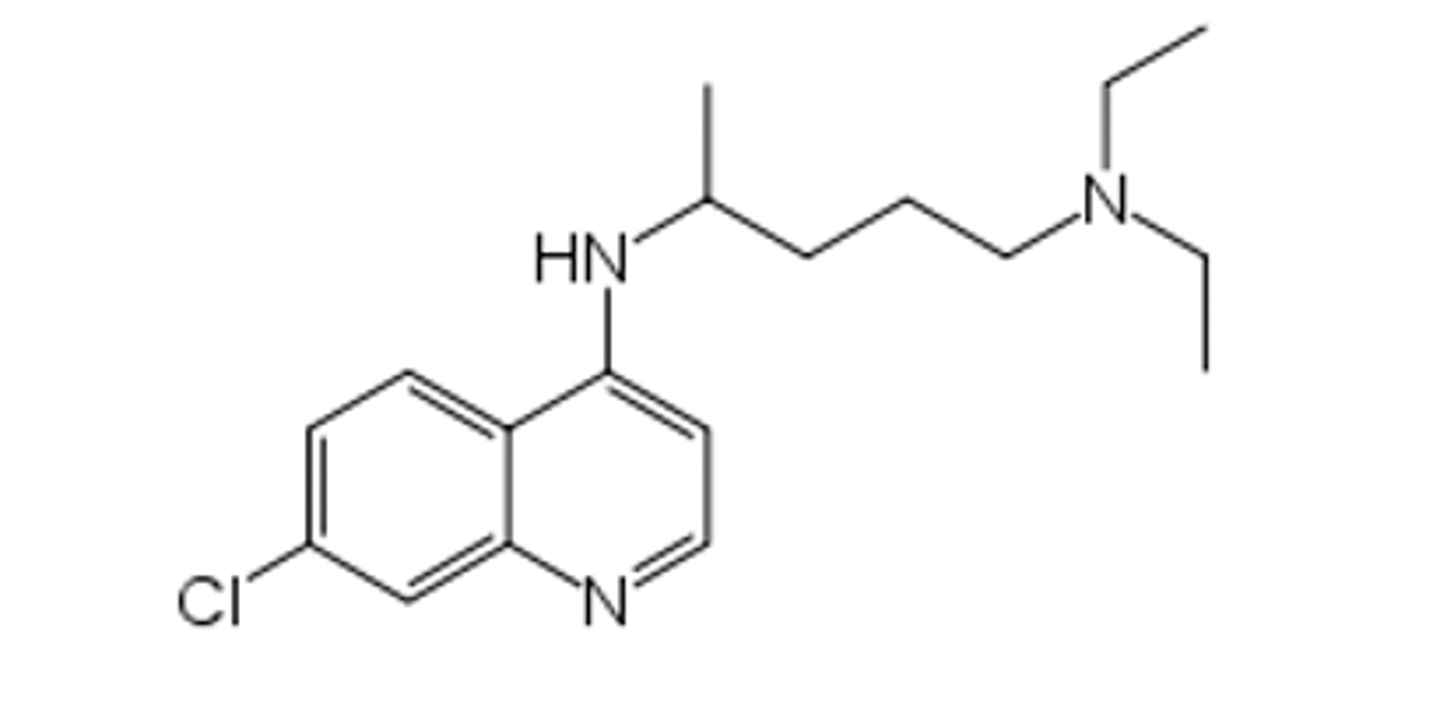
quinoline
Don't mix-up with anti-malarial quinolones (the -F and carboxyl-group help to distinguish)
identify the pharmacophore
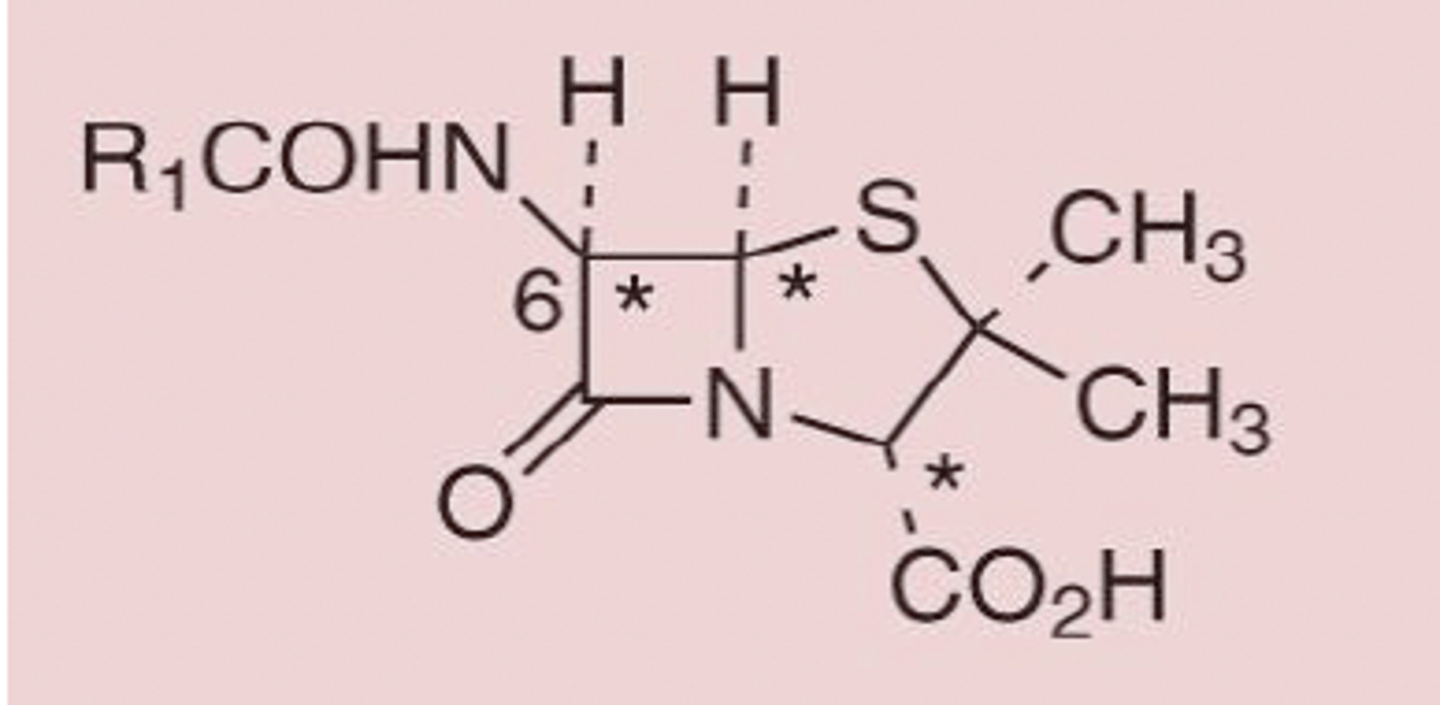
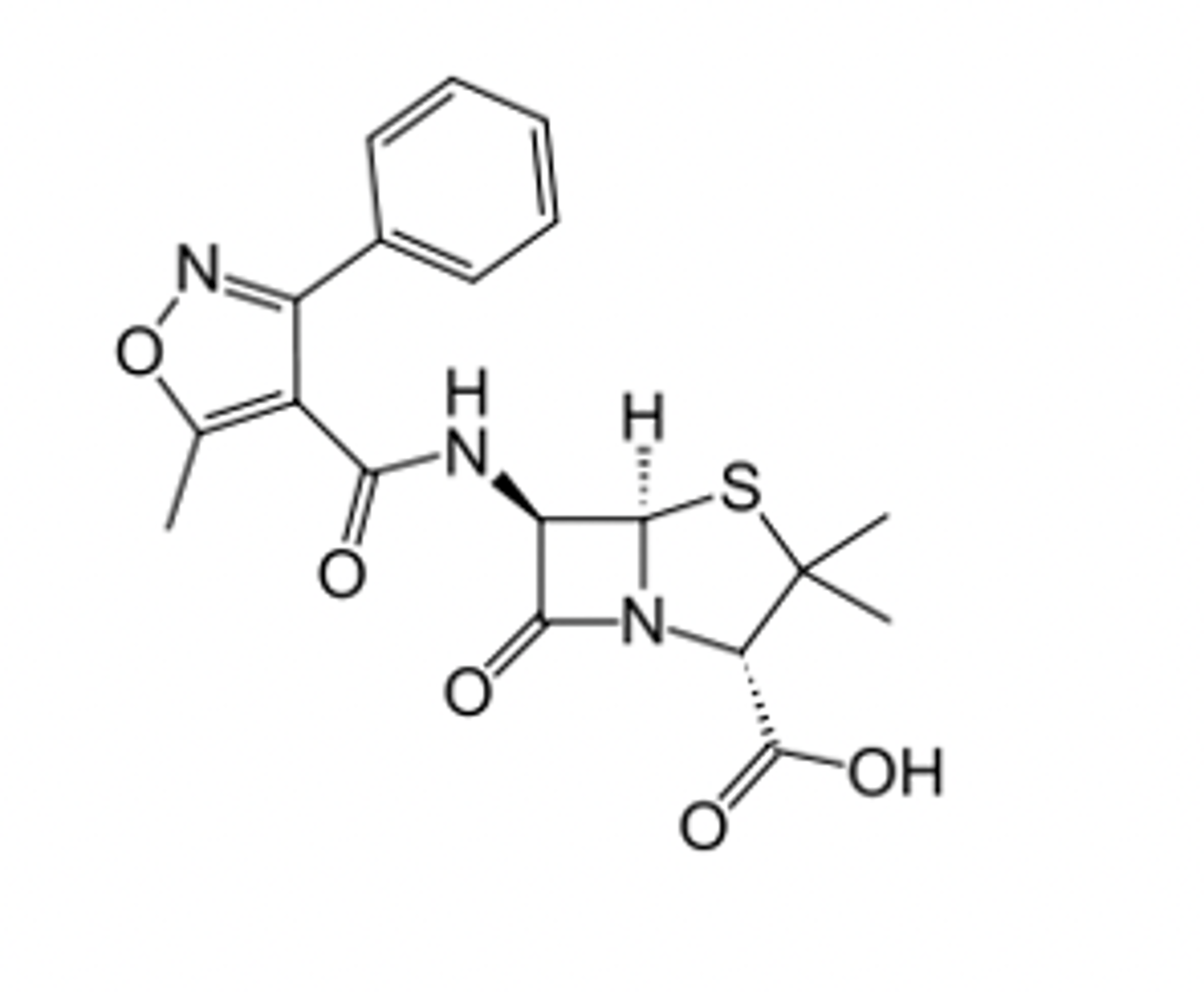
Penicillin pharmacophore with beta lactam azetidinone
identify the pharmacophore
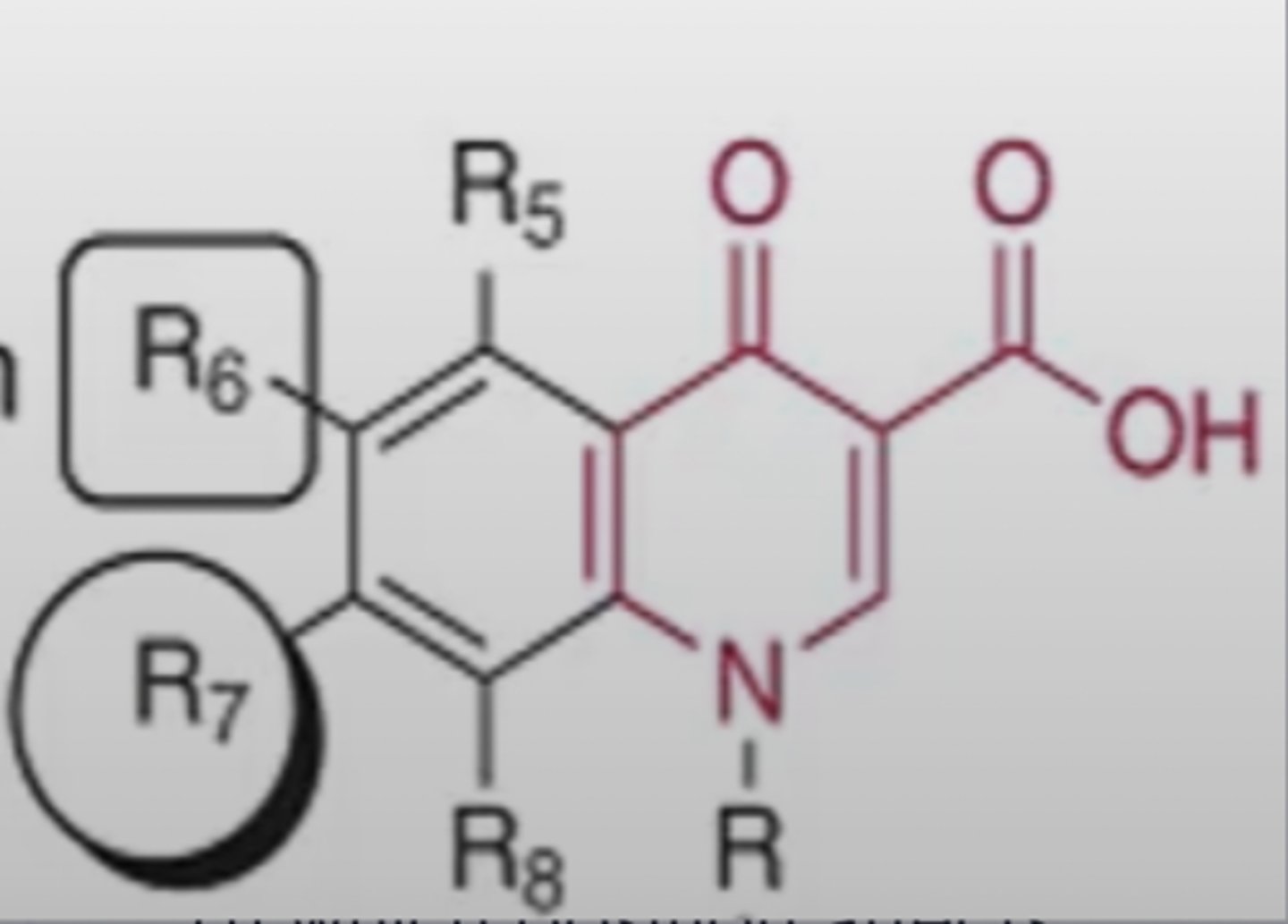
a) 6-fluoroquinolone pharmacophore
b) R6 for penetration (Fluorine)
c) R7 for spectrum
d) R for potency (often cyclopropyl moiety)
DO NOT confuse these with the antimalarial quinolines (Fluorquinolones have ketone)
a) what pharmacophore is this?
b) which moiety is required for penetration?
c) which moiety affects spectrum of activity?
d) which position affects potency, and what is commonly used to increase potency?
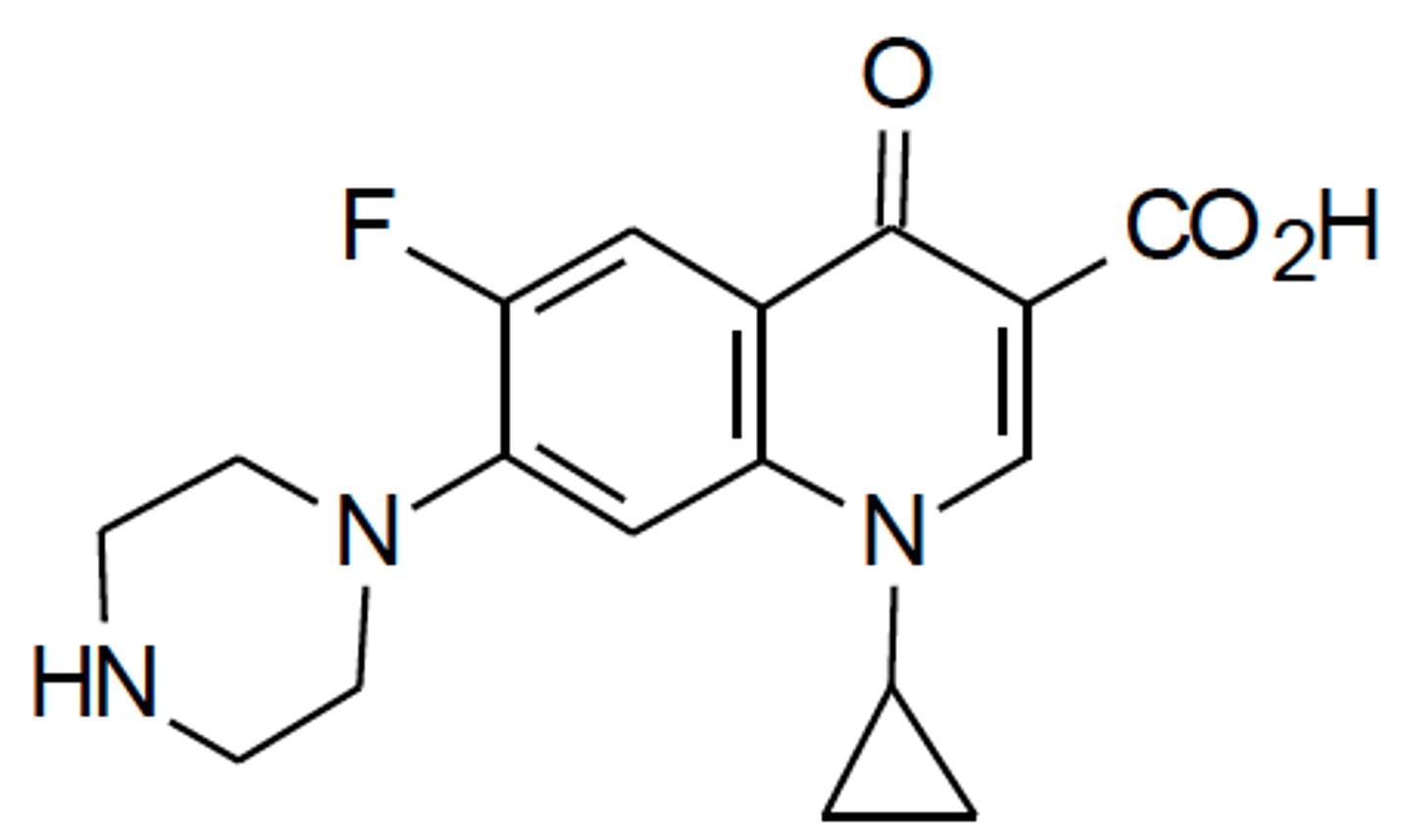
ciprofloxacin
Note the R-6 fluorine essential for penetration of bacterial cell wall
Note the R-7 moiety increases spectrum
Note the cyclopropyl increases potency
a) what pharmacophore is this?
b) which moiety is required for penetration?
c) which moiety affects spectrum of activity?
d) which position affects potency, and what is commonly used to increase potency?
C7
C3
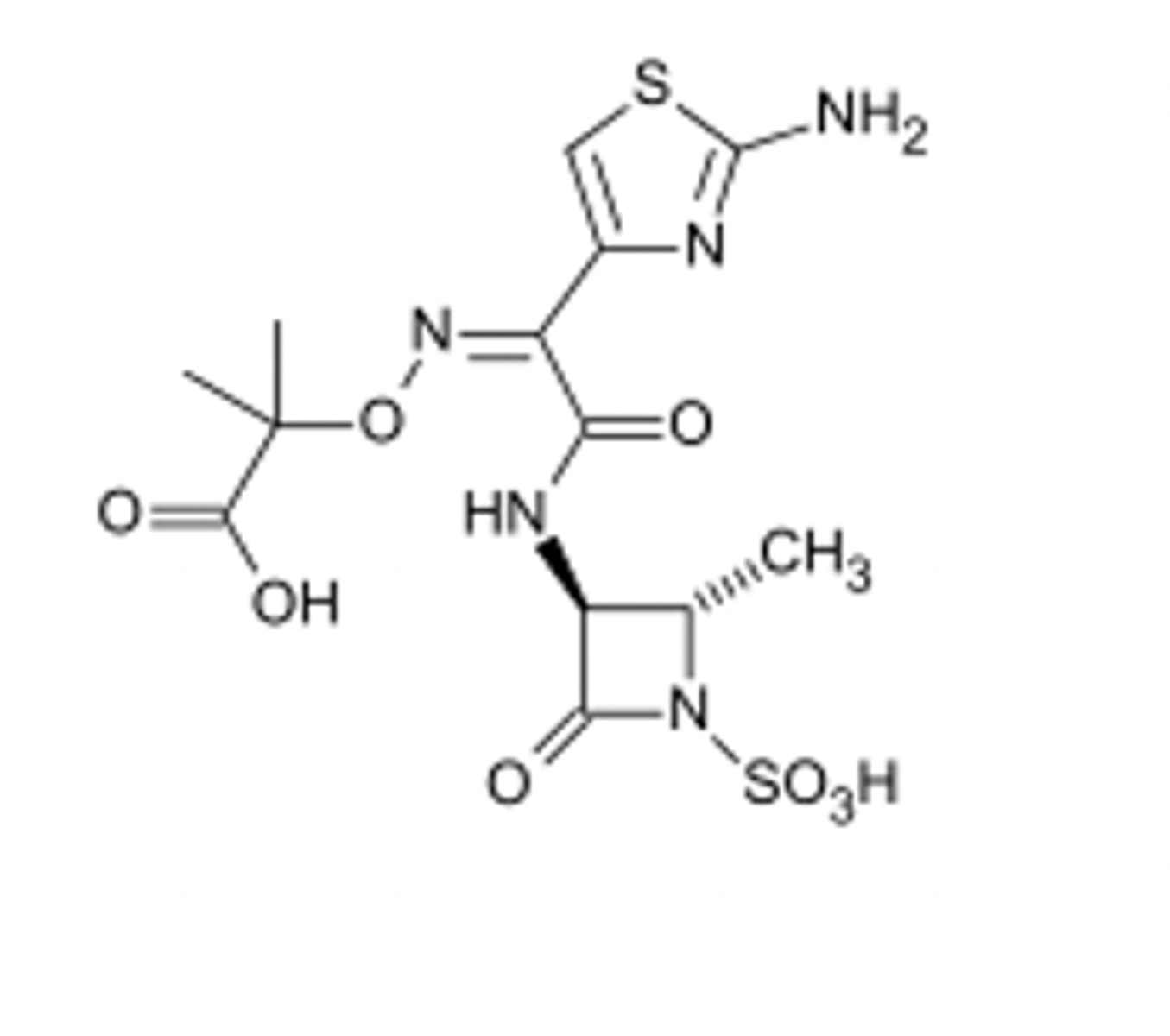
where do cephalosporins differ?
sulfur
which moiety enhances the activity of cephalosprins?
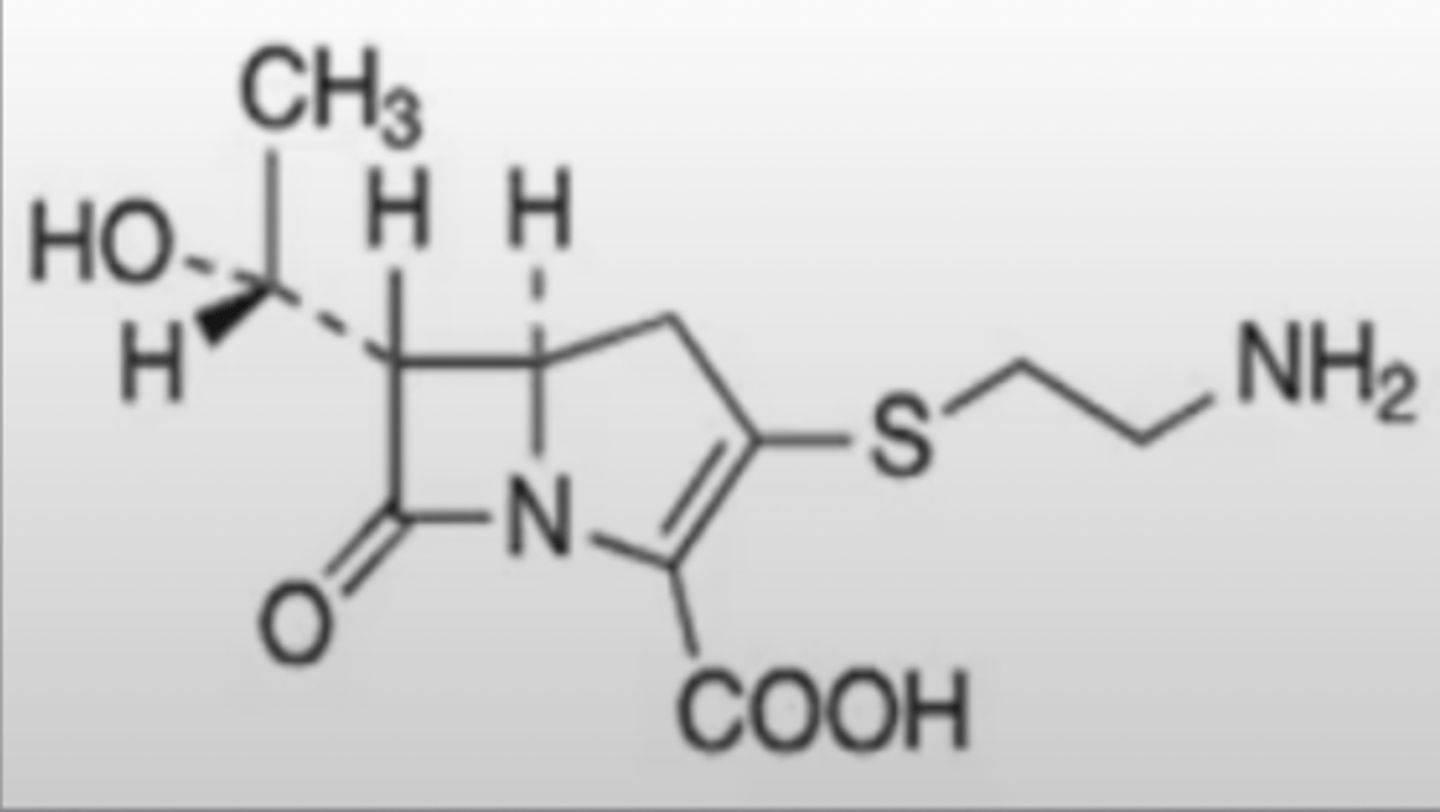
carbapenem pharmacophore (thienamycin shown here)
Note the LACK of sulfur in the thaizolidine ring that differentiates this from the penems/penams -- this makes the ring more strained and reactive. BUT also note that there is STILL a sulfure, it is just outside of the ring
Note the methylene group
Note the azetidinone (beta lactam)
Identify the pharmacophore
monobactam (ONLY has the beta lactam ring) -- aztereonam shown here
Identify the pharmacophore
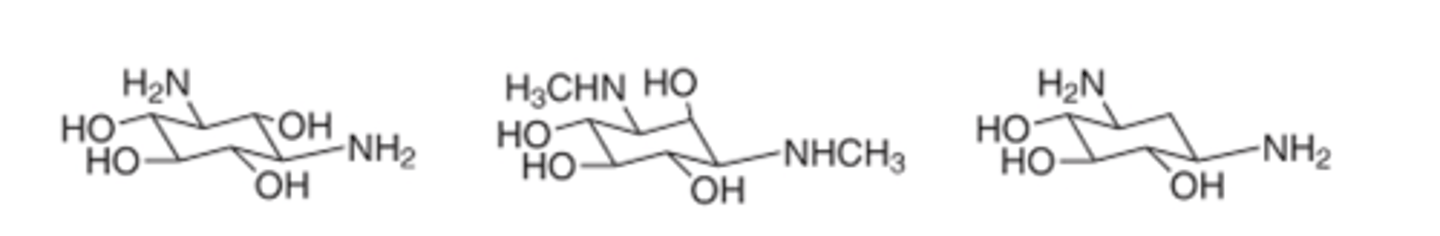
1,3-diaminoinositol pharmacophore of the AGS
what pharmacophore is this and what drug class are they representative of?
12-membered ring, lactone cyclic ester with sugars attached as esters
every 2nd carbon has a methyl group
Macrolides
what pharmacophore is this and what drug class does it represent?
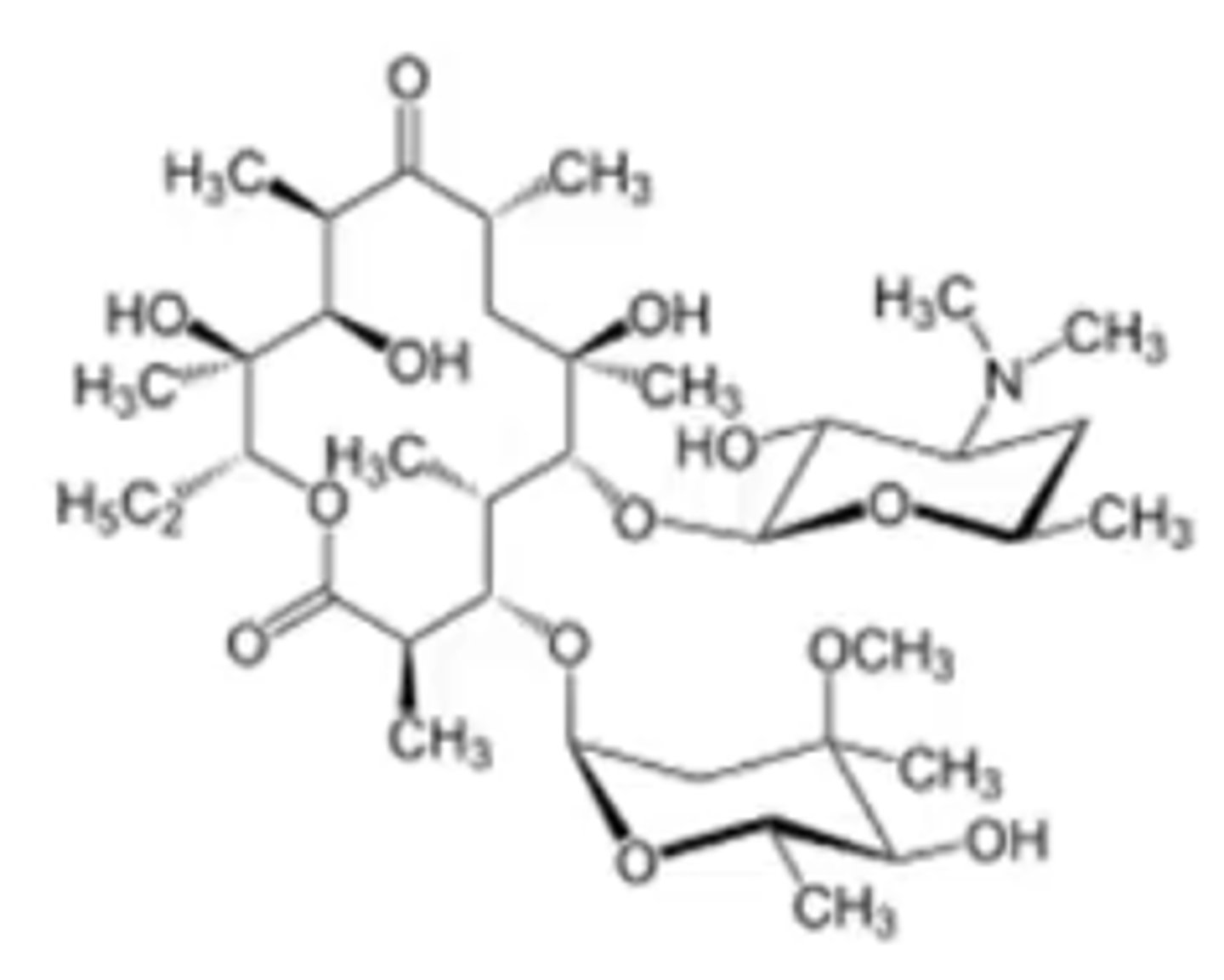
propionic acid residues
what acid residues are macrolides made of?
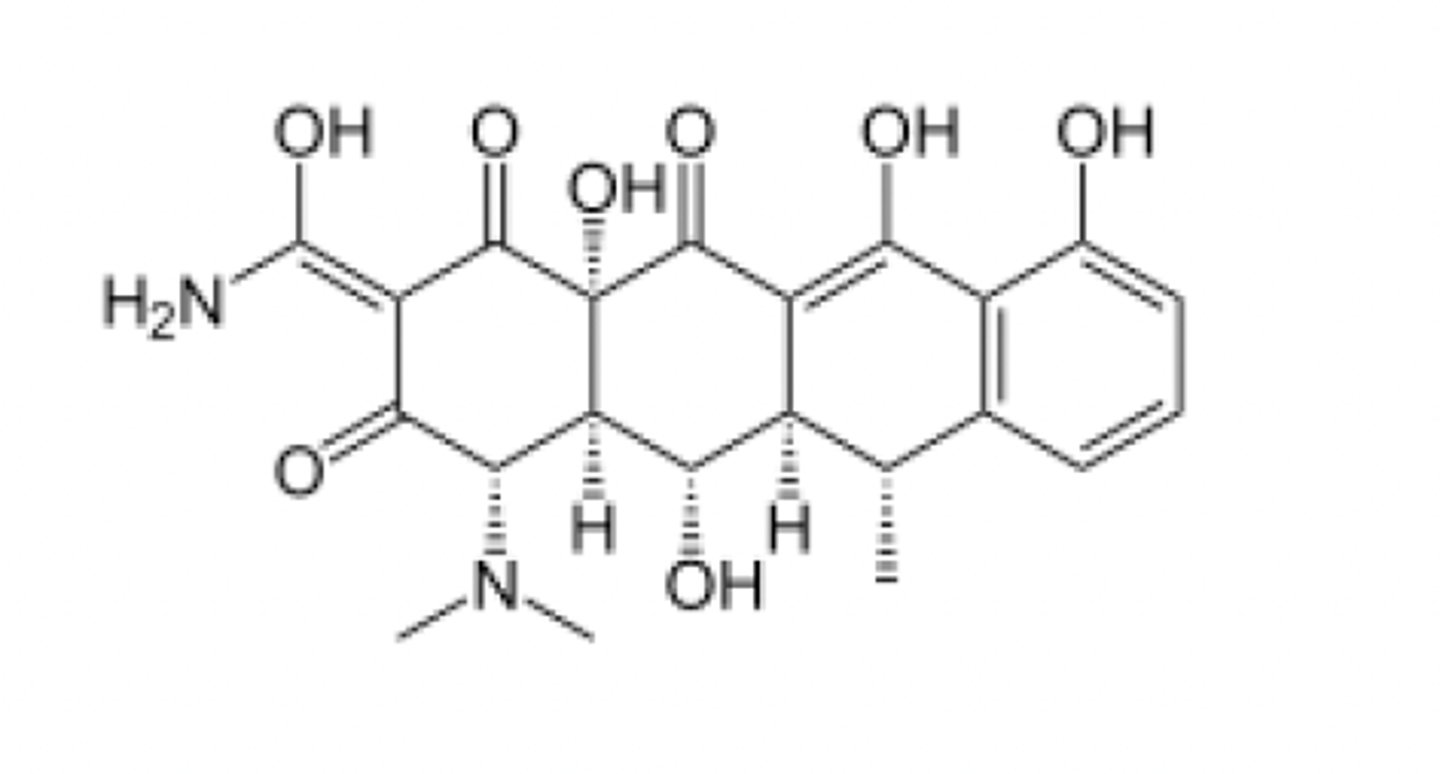
tetracyclines (4 rings) -- doxycycline shown here
Tri-carbonyl species that are highly keto-enol resonance stabilized (this is why they chelate divalent ions = discolor teeth, bind antacids, etc.)
what drug class is this?
what drug class is this?
nitroaryl pharmacophore antiparasitics
-metronidazole
-tinidazole
-nitazoxanide
etc.
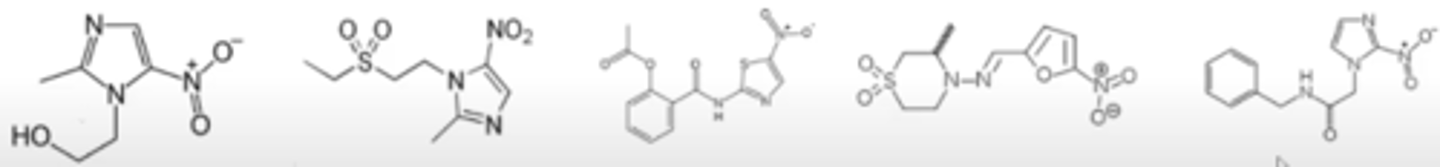
Note they are Nitro groups connected to azole rings (structure 1) or something similar (thio-azole in structure 3), furan in structure 4
Used for Trichomonas, amebiasis, giardia, C. diff, Chagas disease
what pharmacophore are these and what are the important parts of the pharmacophore?
primaquine (8-aminoquinoline) of the quinoline antimalarials
Pharmacophore?
Drug class?
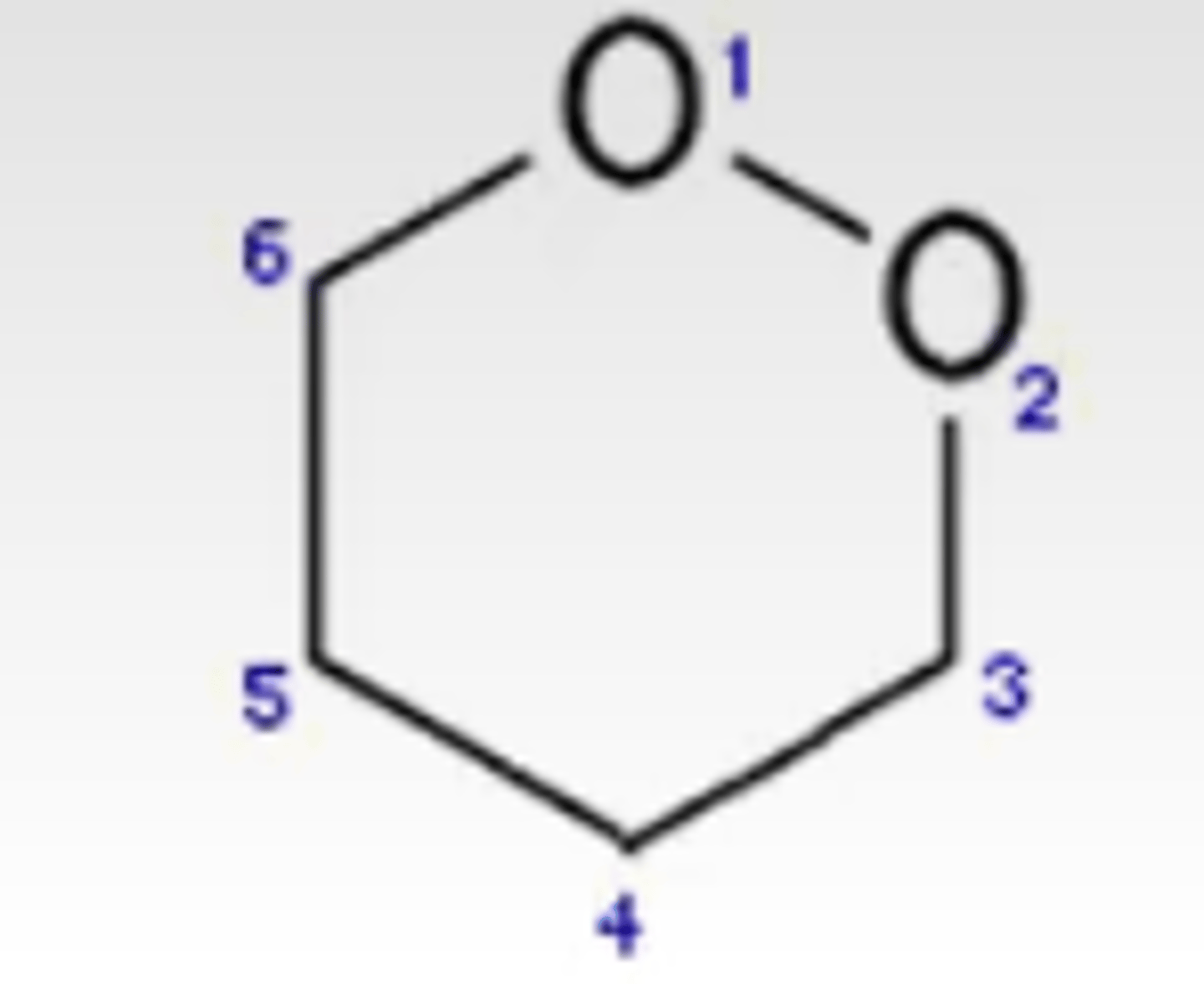
1,2 dioxane
found in artemisinins (antimalarials)
Forms endoperoxides (R-O-O-R) that bind Fe in hemozioin that kills parasite
Pharmacophore?
Drugs this is found in?
MOA?
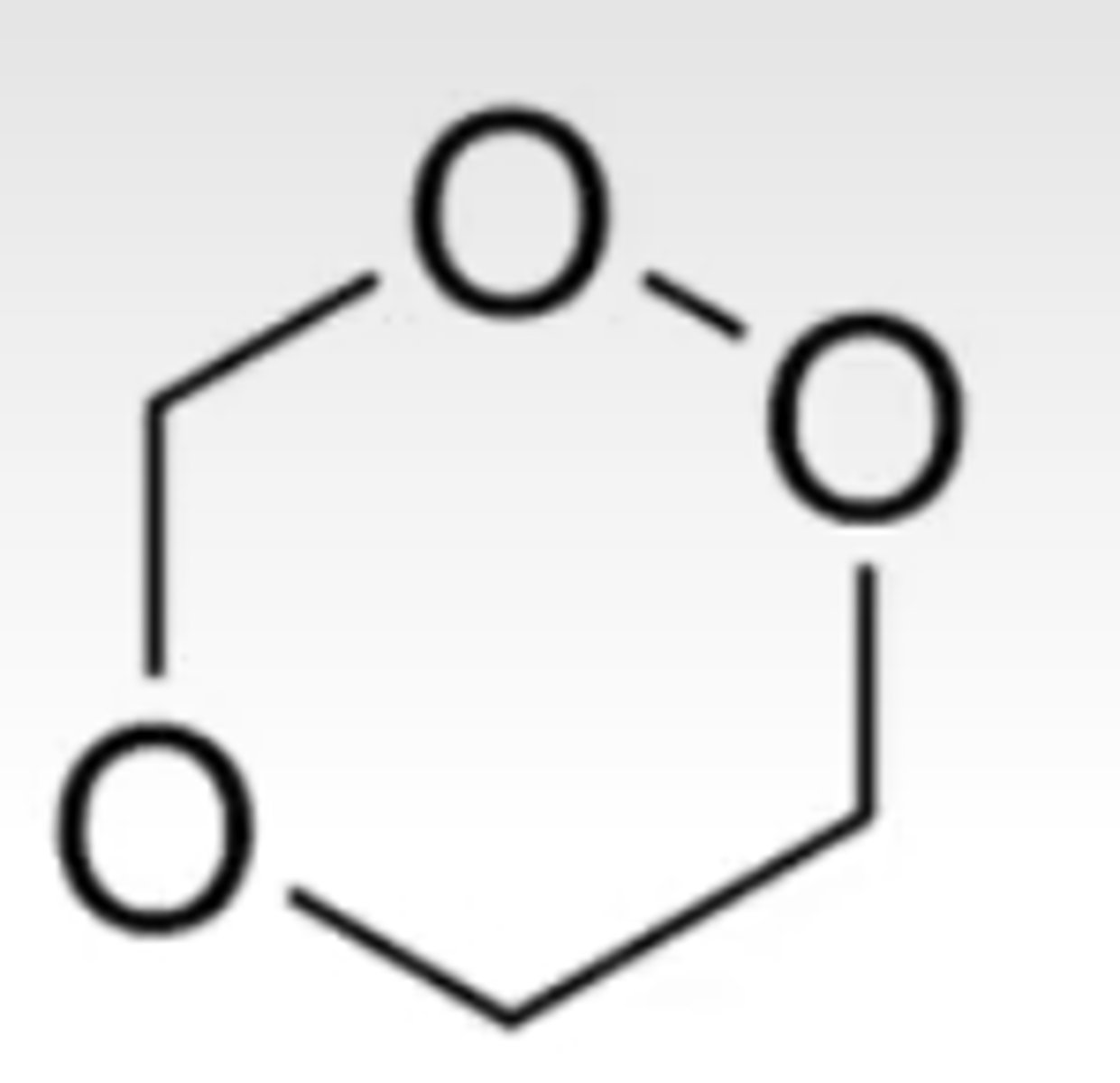
1,2,4-trioxane
found in artemisinin antimalarials (just like 1,2-dioxanes)
Pharmacophore?
Drugs that exhibit this species?
1,2,4-trioxane
artesunate shown here (artemisinin antimalarial)
Pharmacophore?
Drug class?
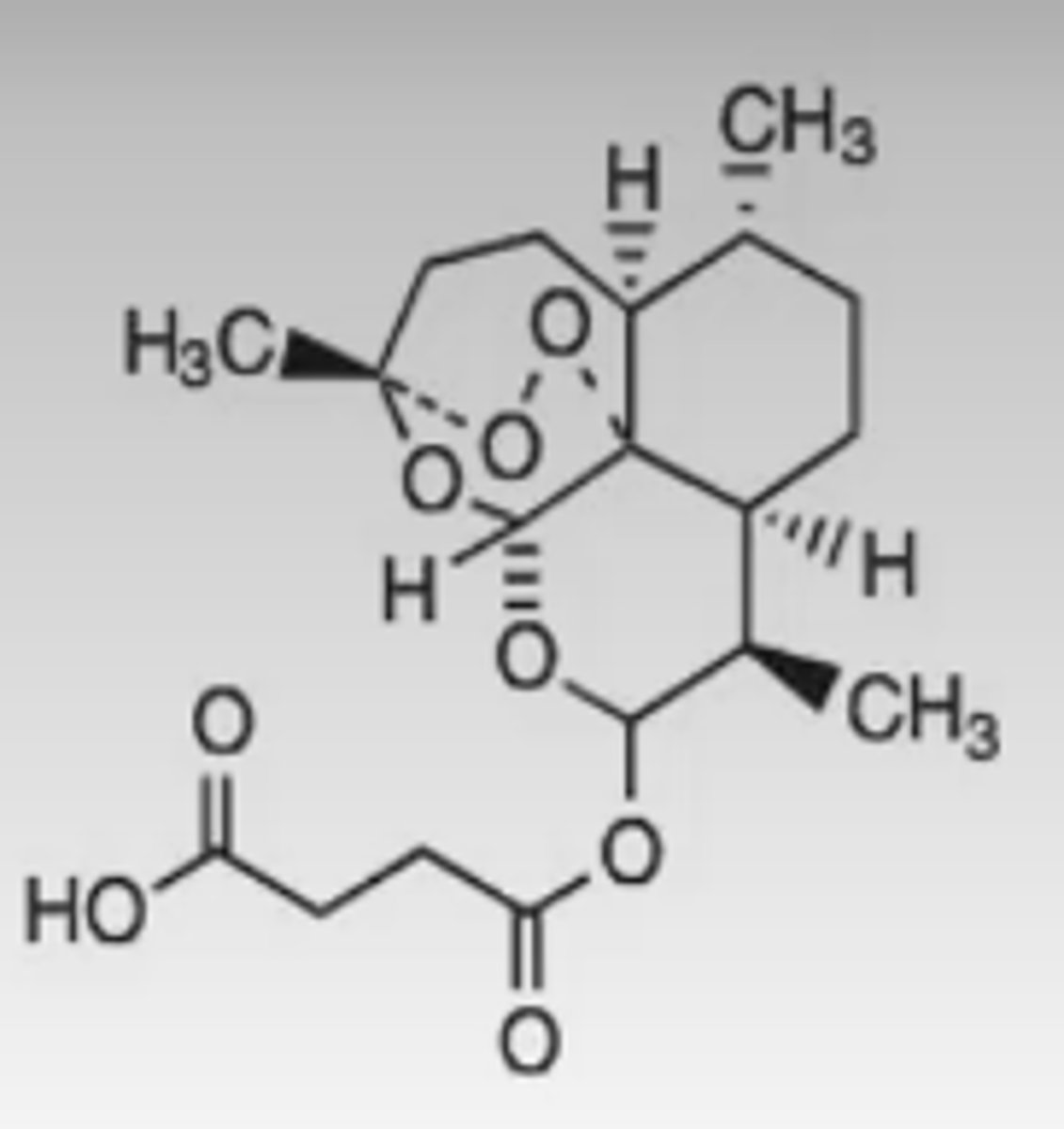
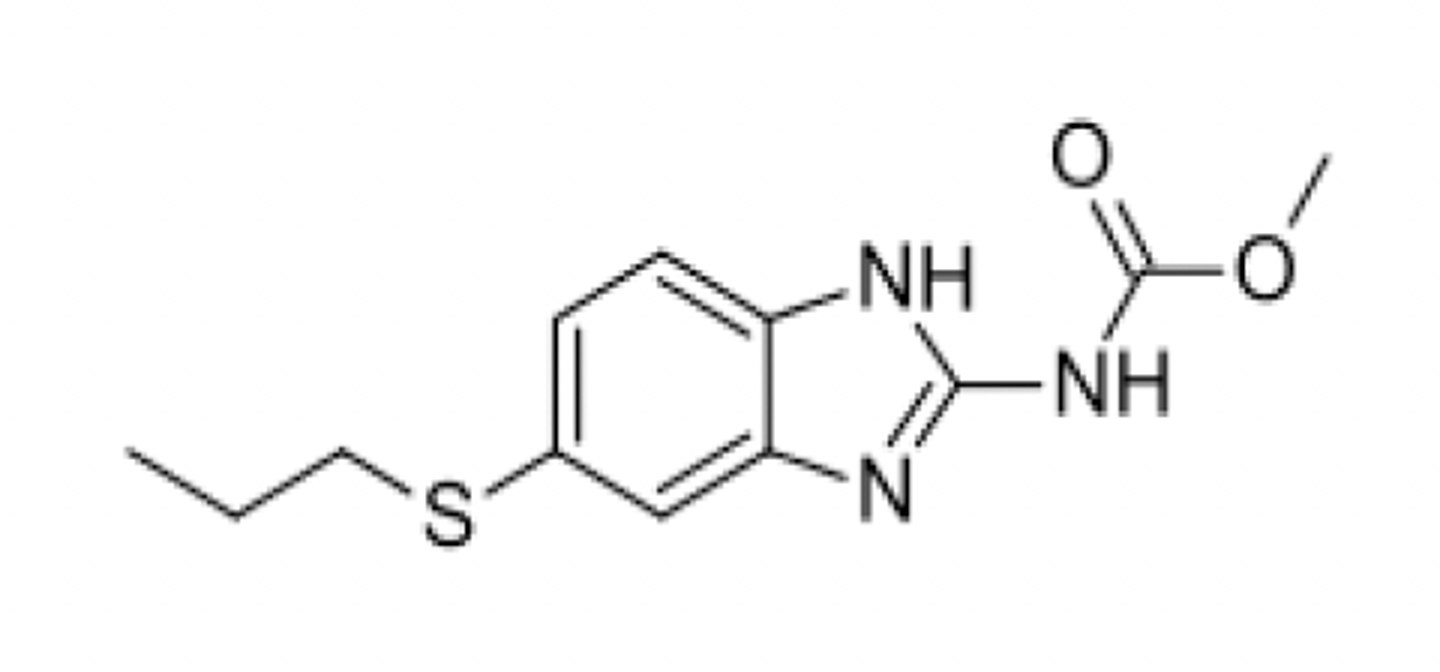
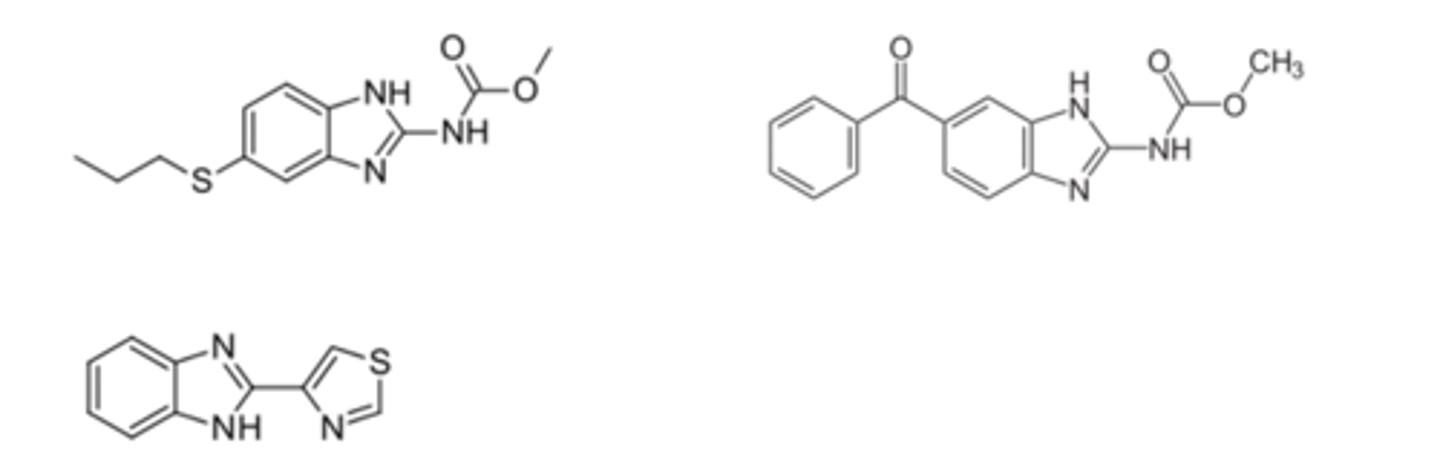
benzimidazole
Identify the pharmacophore
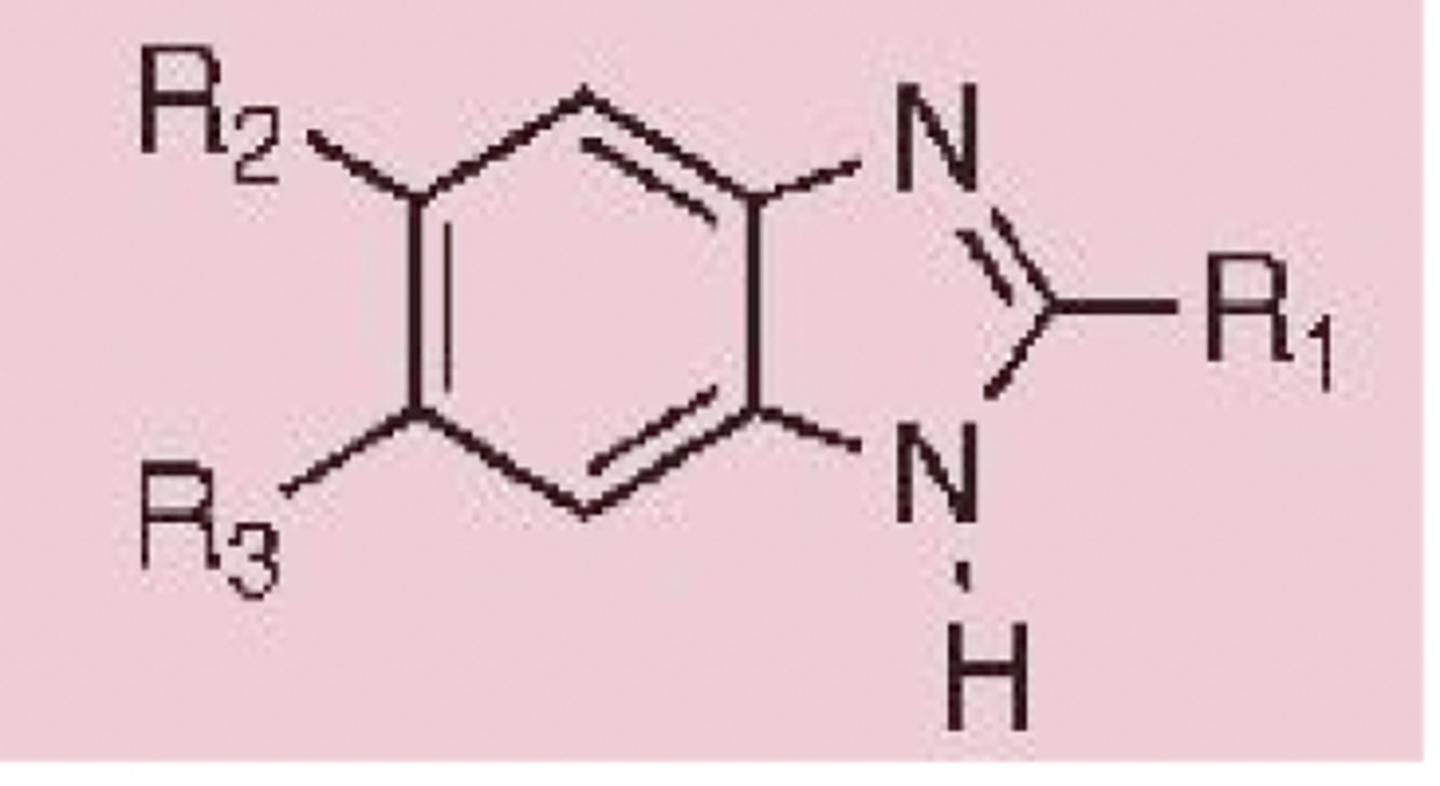
benzimidazole pharmacophore
antihelmintic
Pharmacophore?
What does this agent act against?
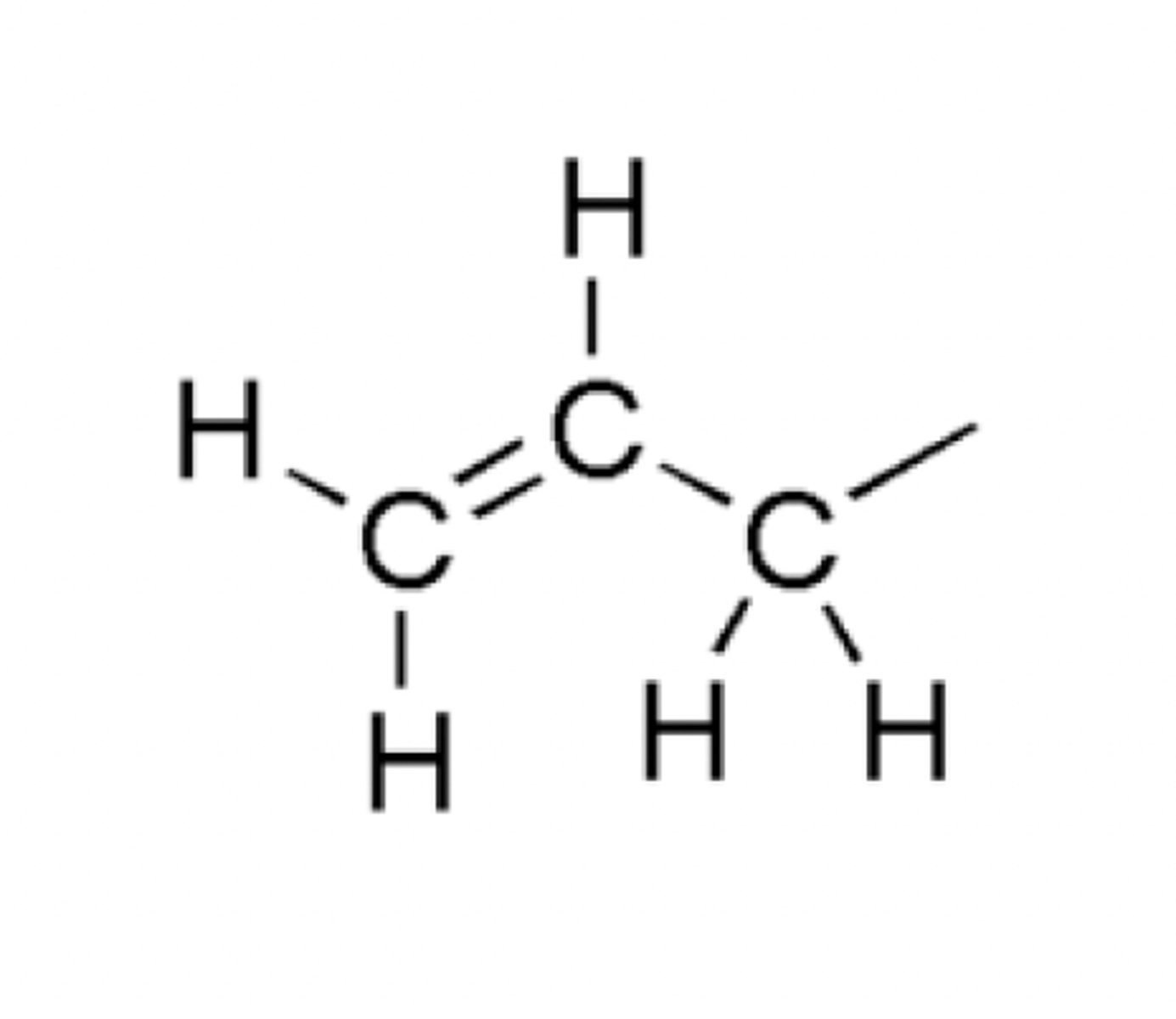
Pyrethroid
Contain a dimethylcyclopropanewith allylic component
Identify the pharmacophore
macrocyclic lactones (antifungals)
-hydrophilic portions (alcohols, carboxylate, sugar)
-lipophilic portions (chromophore of 4-7 conjugated double bonds)
Identify the pharmacophore
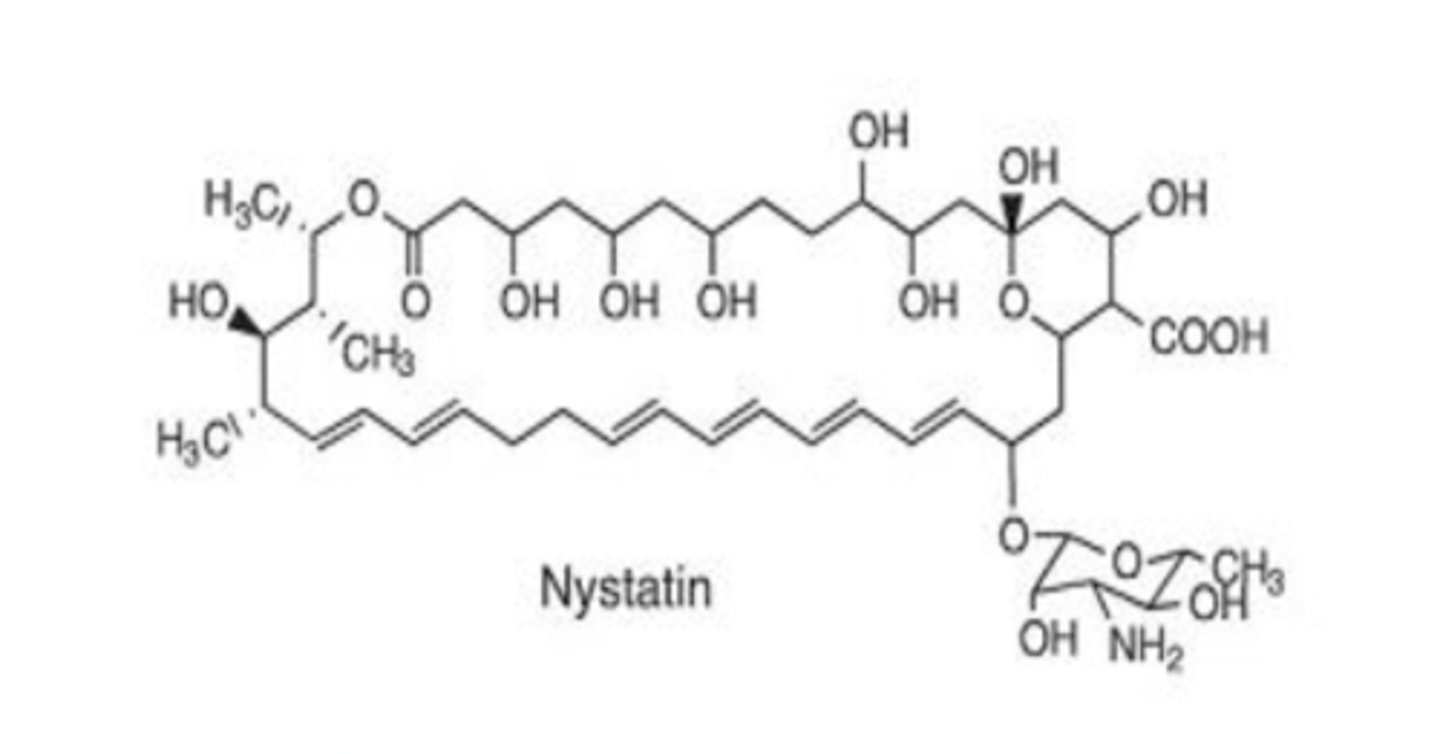
azole
Identify the pharmacophore
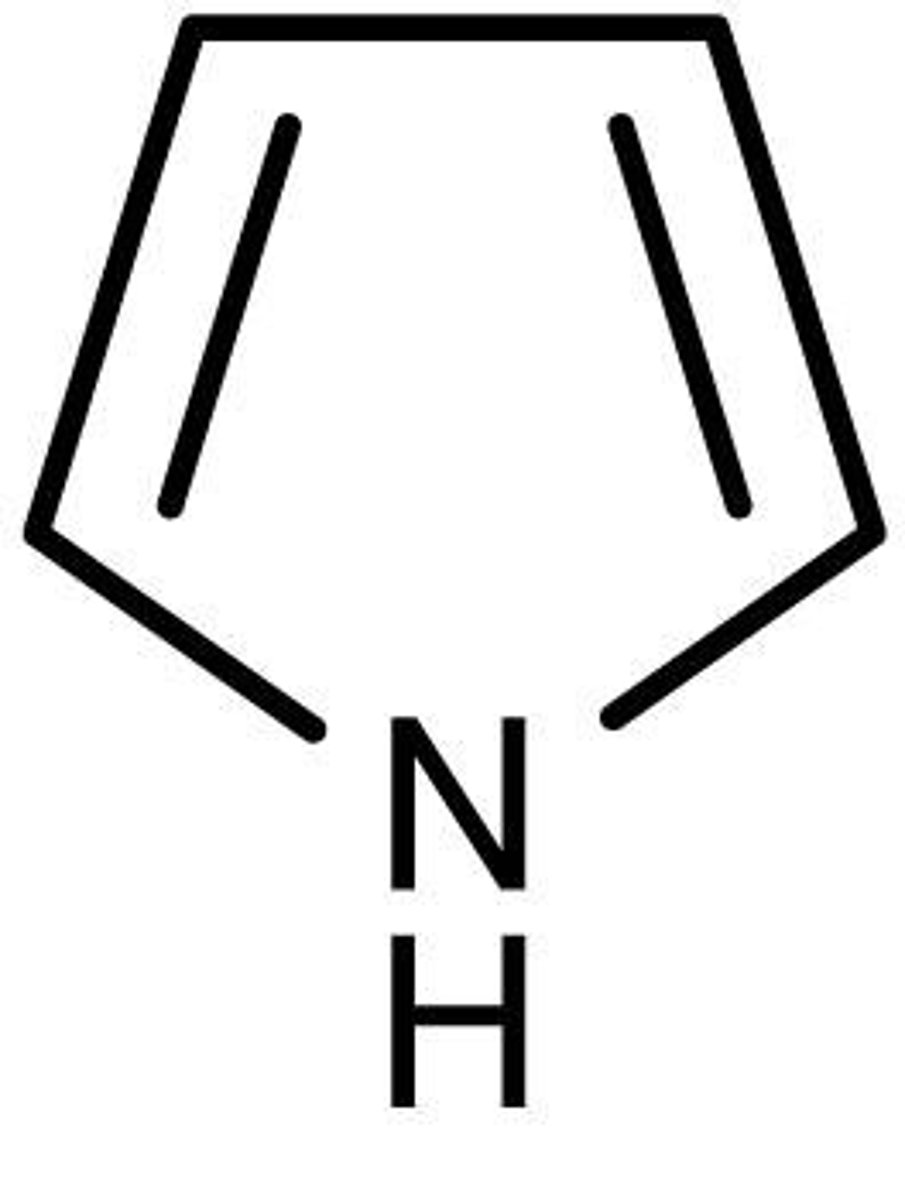
triazole
Identify the pharmacophore
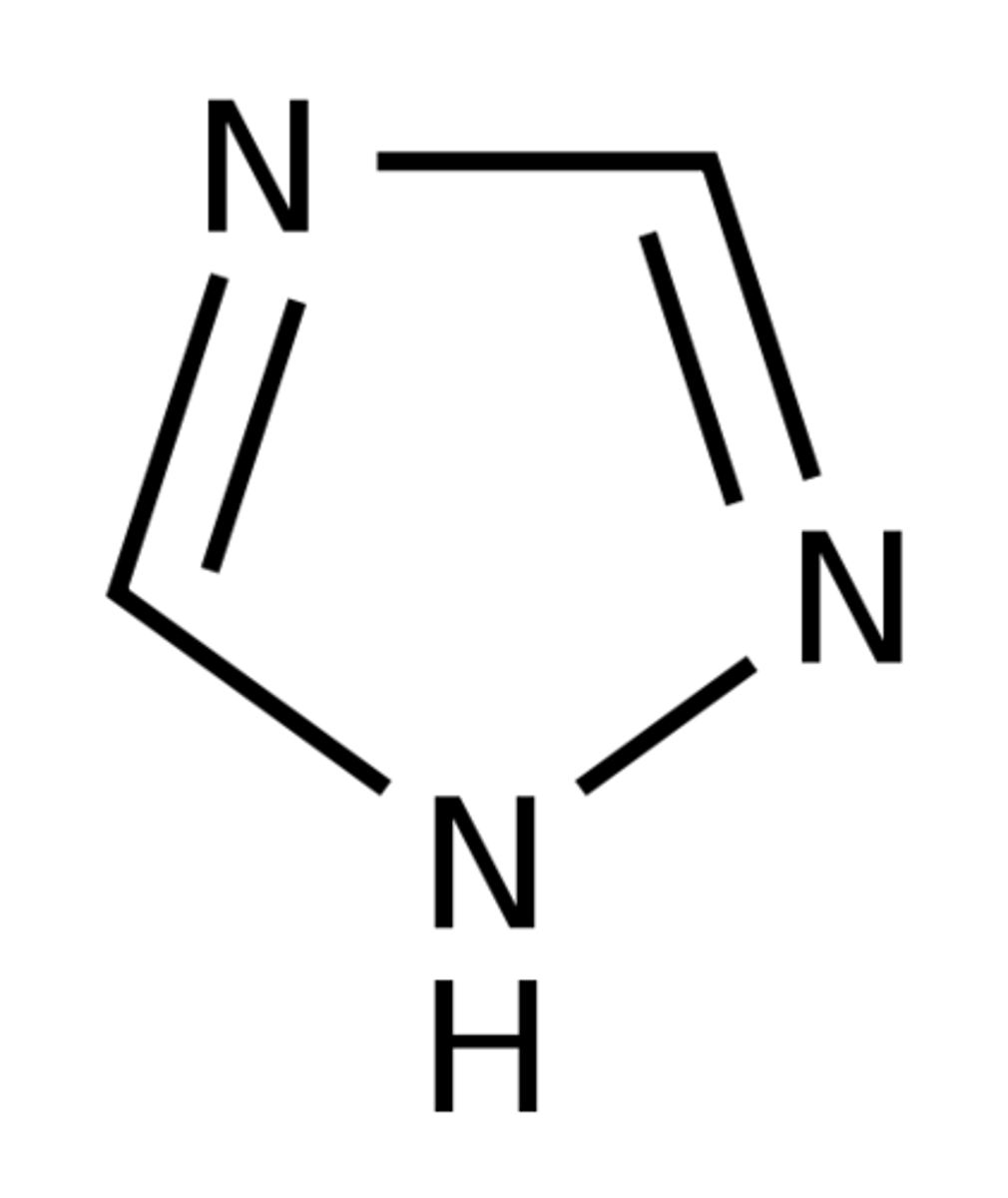
Squalene epoxidase inhibitors
Identify the pharmacophore
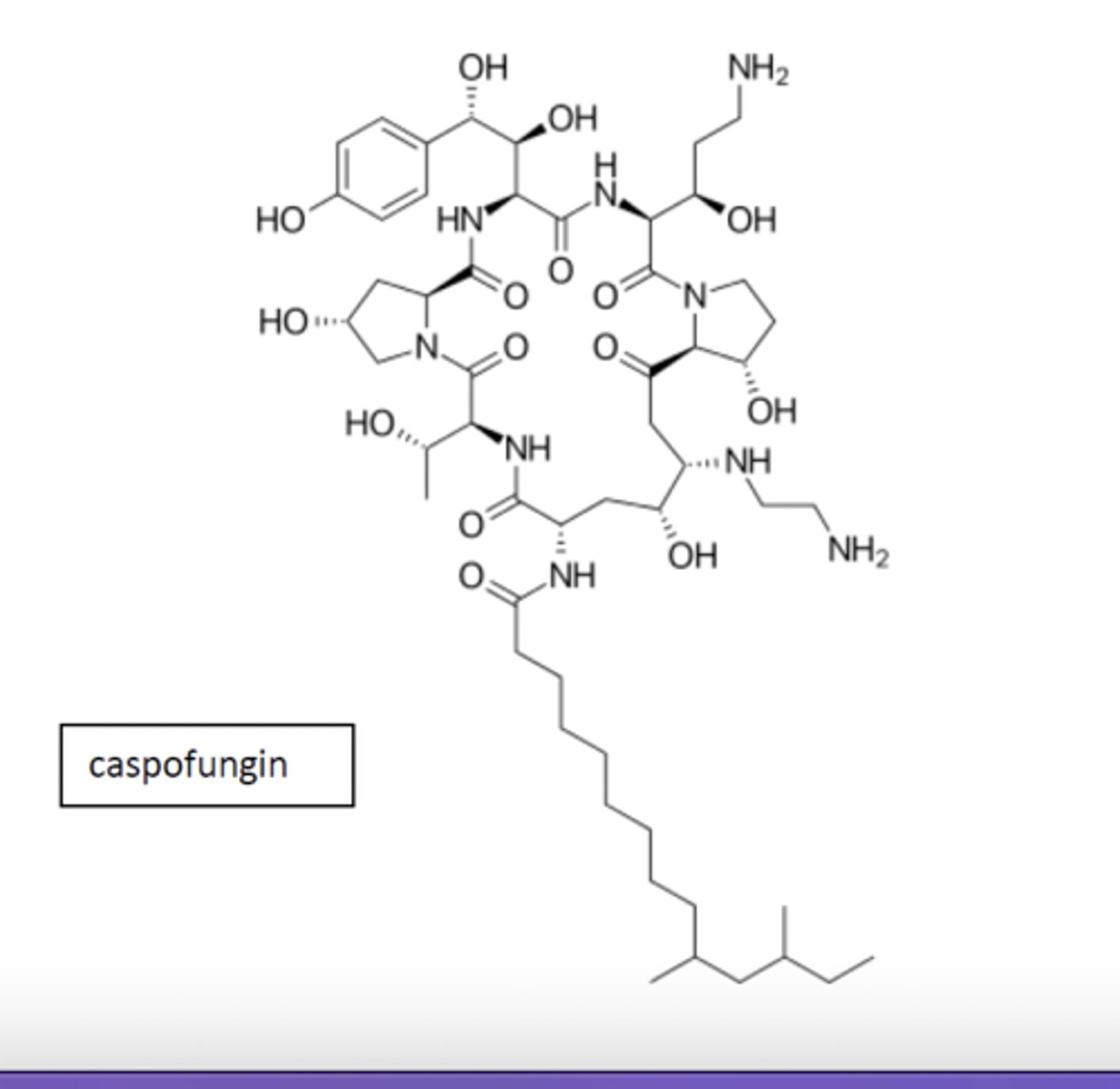
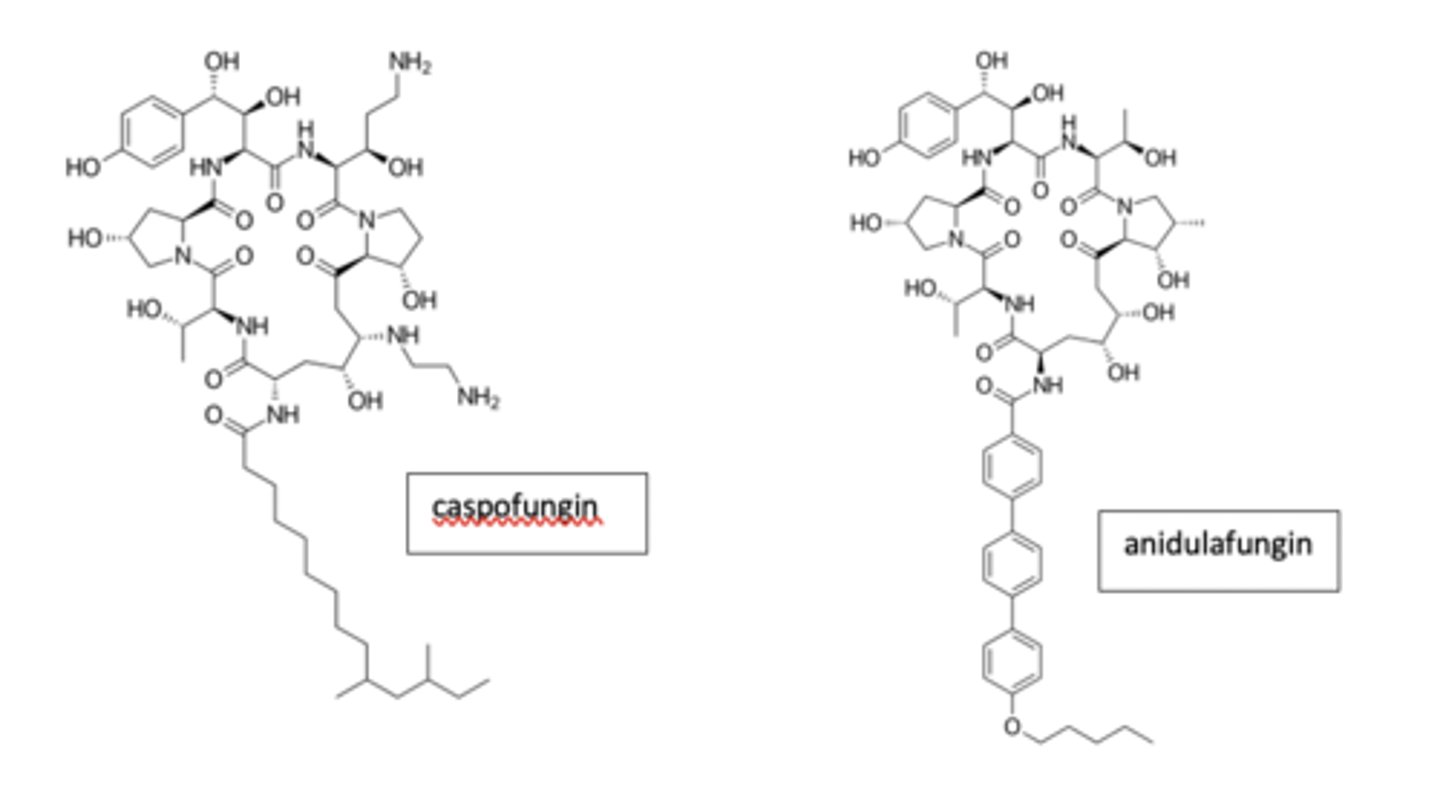
lipopeptide of the echinocandins
Recognize the lipophilic portion at the bottom and peptide bonds at the top
pharmacophore AND what is the important portion to recognize?
Drug class?
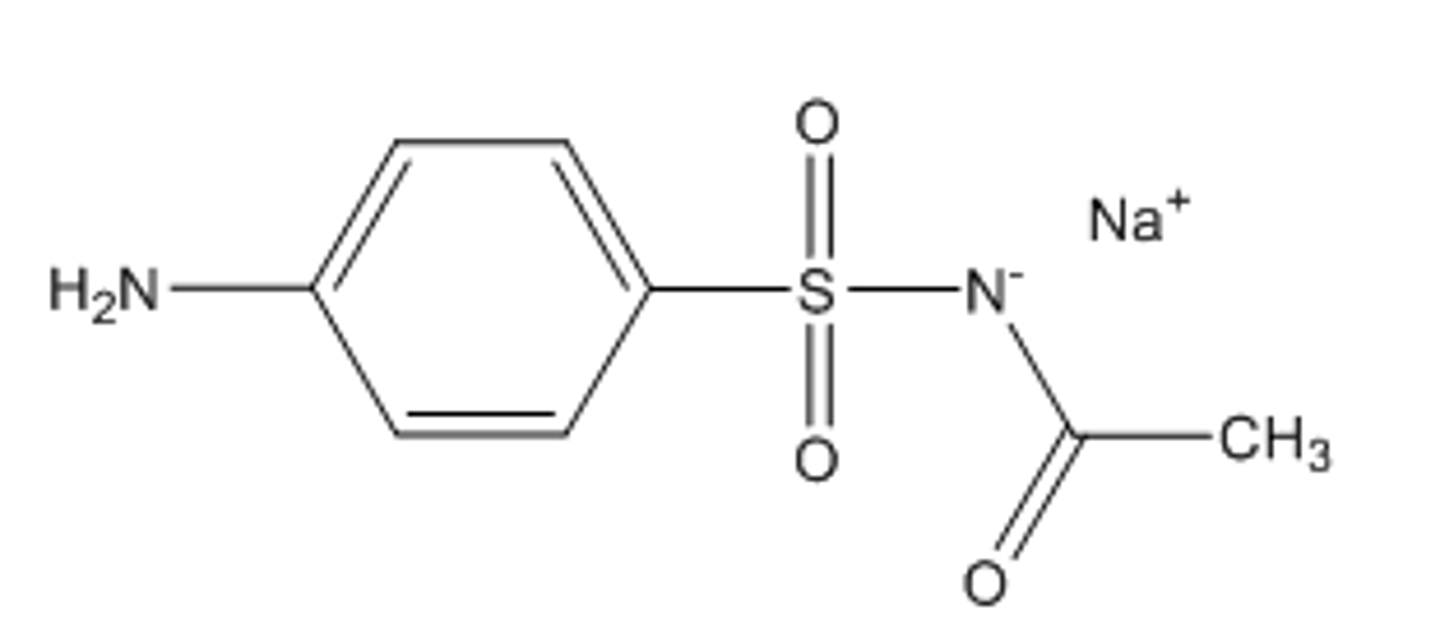
PABA (para-aminobenzoic acid)
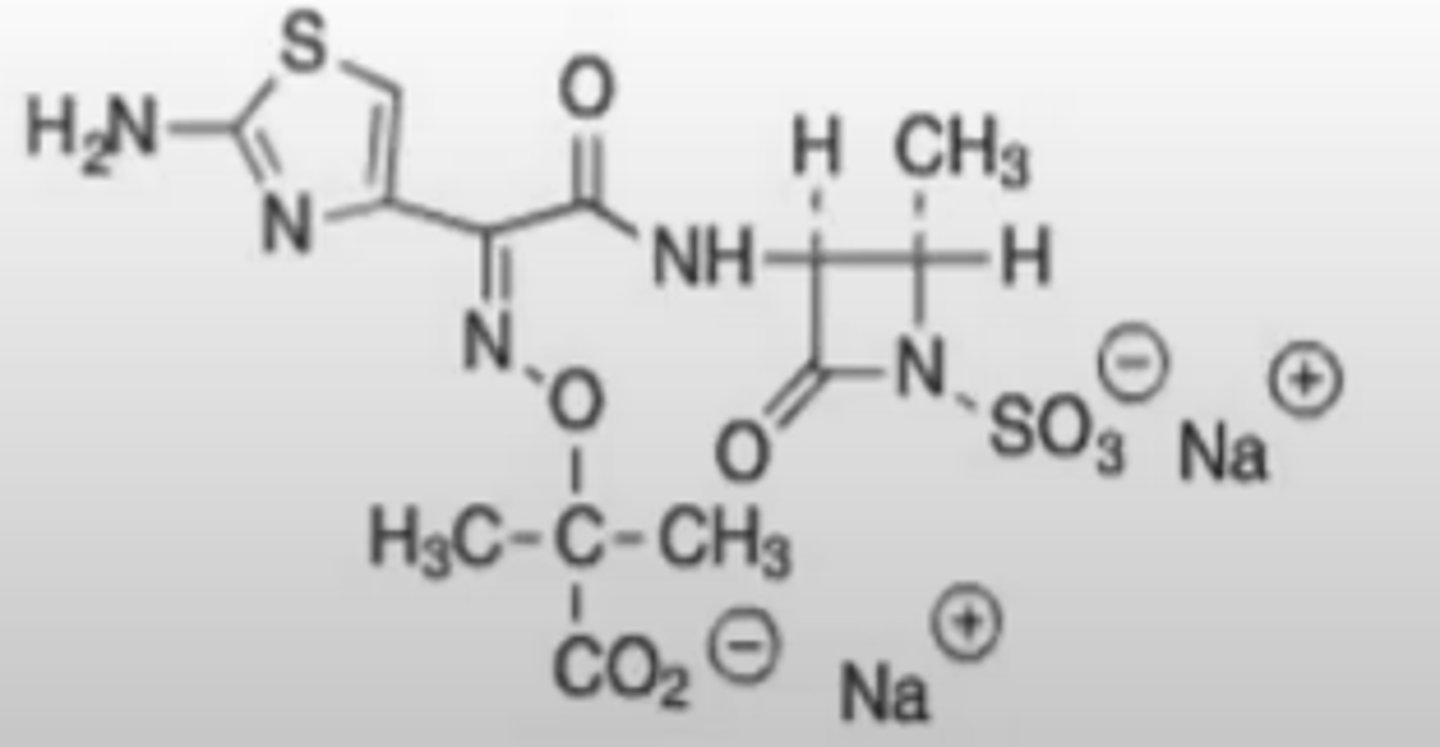
What intermediate in thymidine synthesis is mimicked by sulfisoxazole and sulfamethoxazole?
inhibits 2 different steps in the formation of dihydrofolic acid, a key cofactor in thymidine synthesis
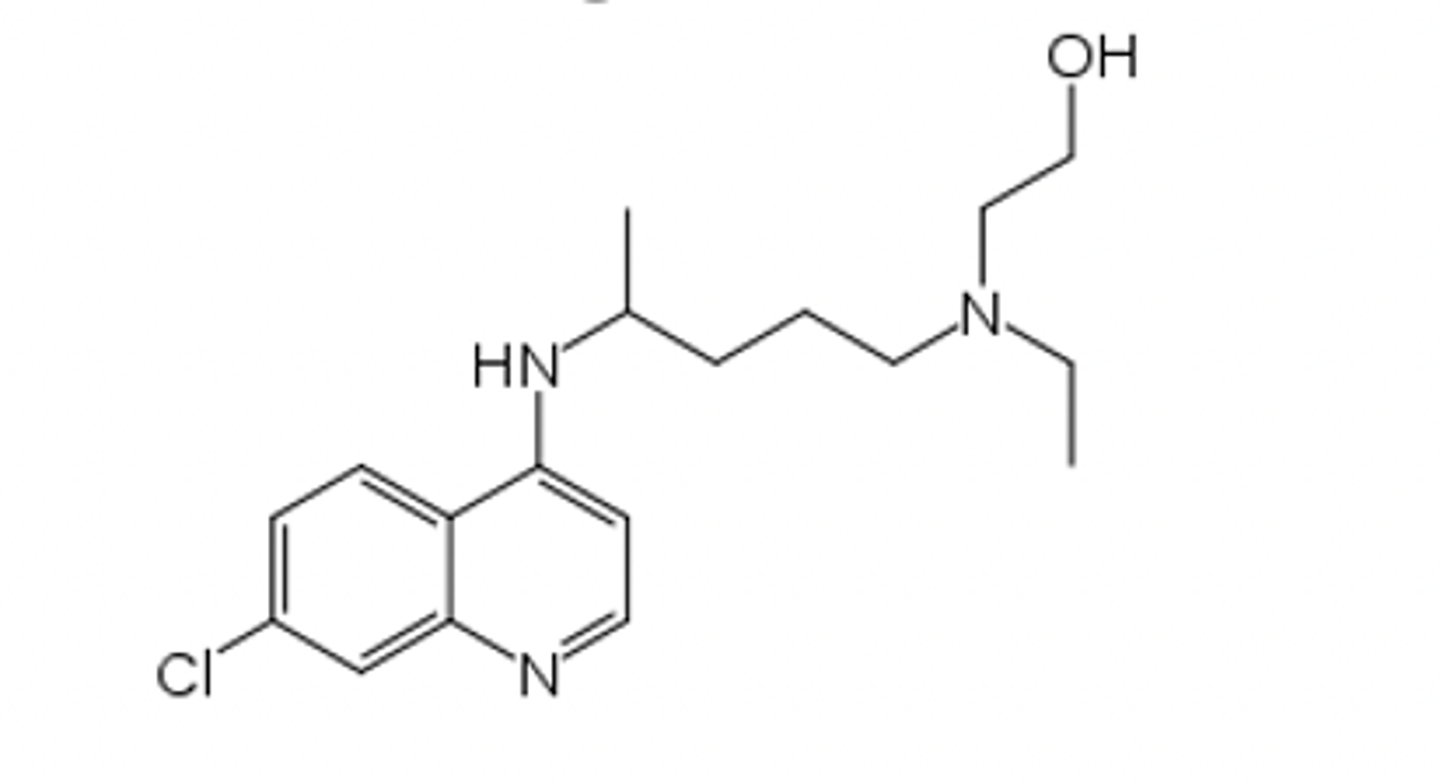
Why is giving trimethoprim (below) with a sulfonamide (above; Bactrim) a very effective antibiotic intervention?
Shown are several synthetic fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Highlight the pharmacophore of the quinolone backbone?
beta lactam
cyclic amide
2-azetidinone
Shown is the key pharmacophore of many of the naturally occurring antibiotics. What are two common names for this structure?
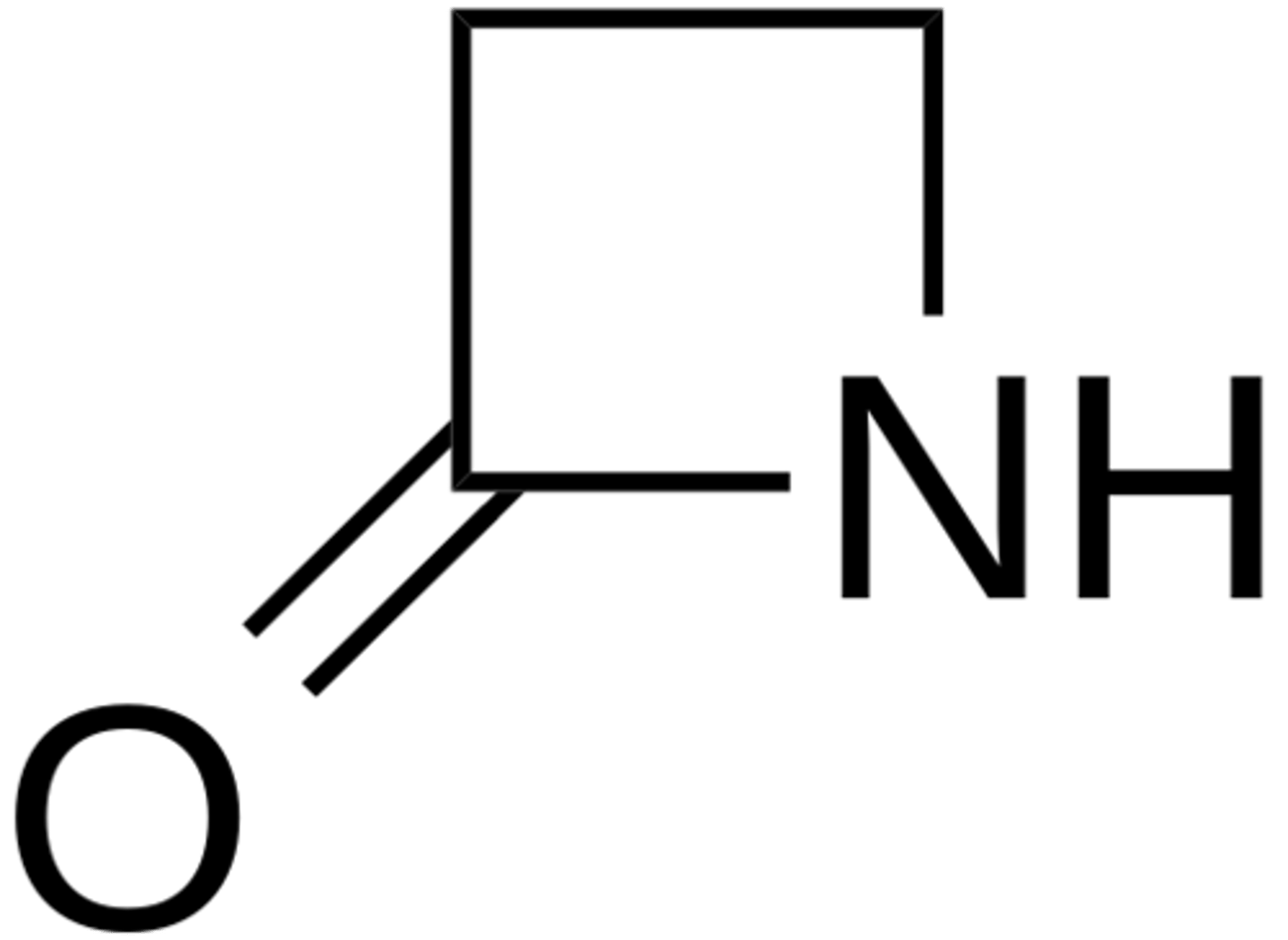
penicillin type thiazolidine
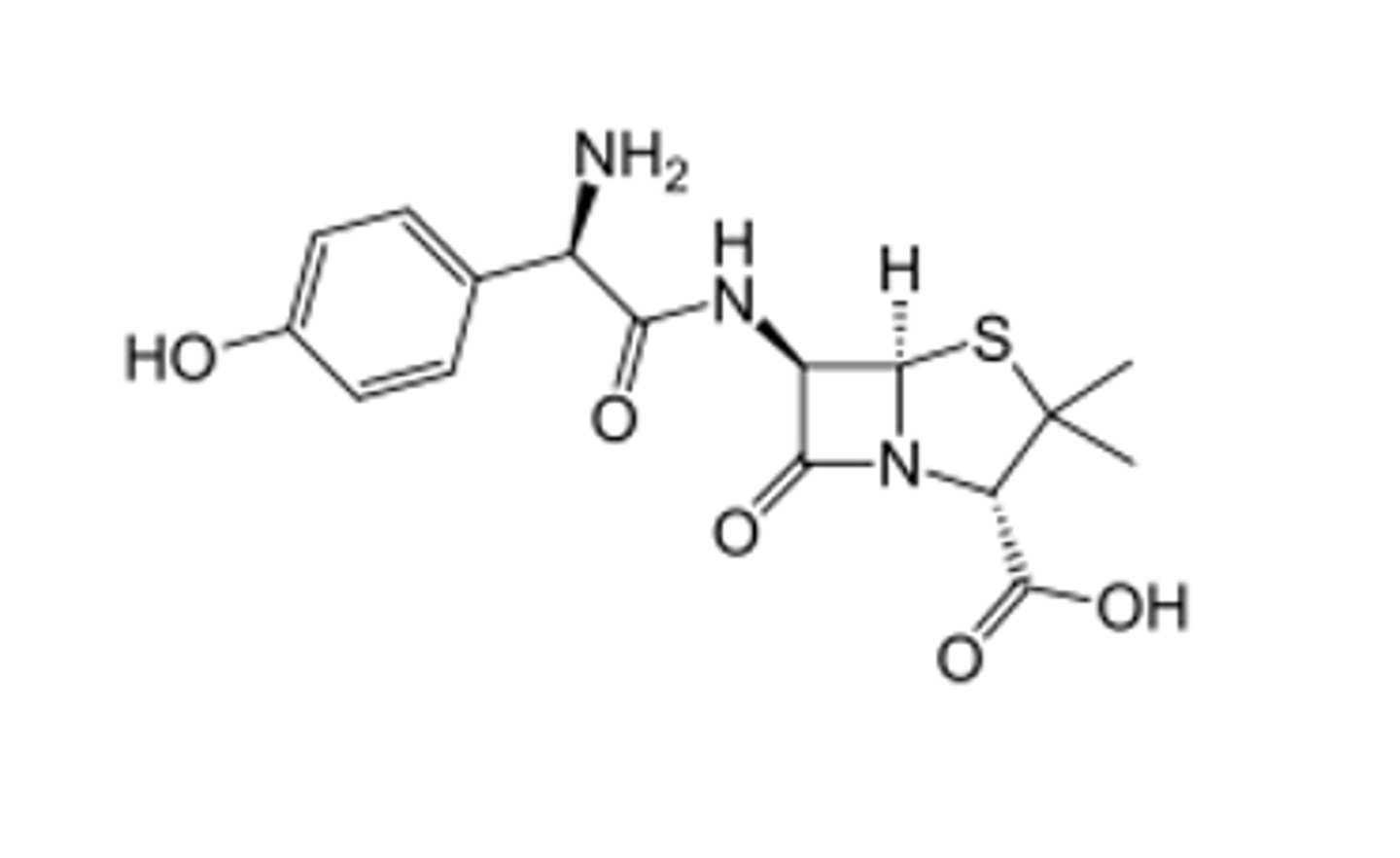
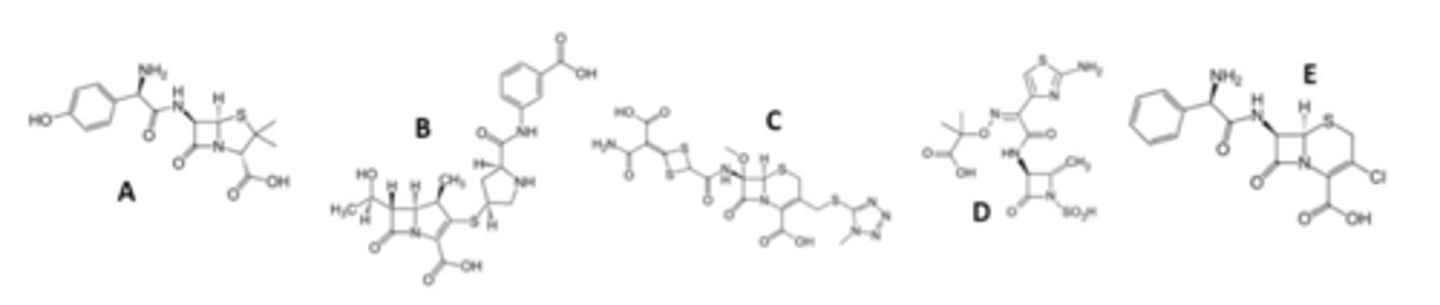
Classify as a penicillin, cephalosporin, carbapenem, or monobactam agents. Further, where applicable highlight the thiazolidine or dihydrothiazine backbone of these agents.
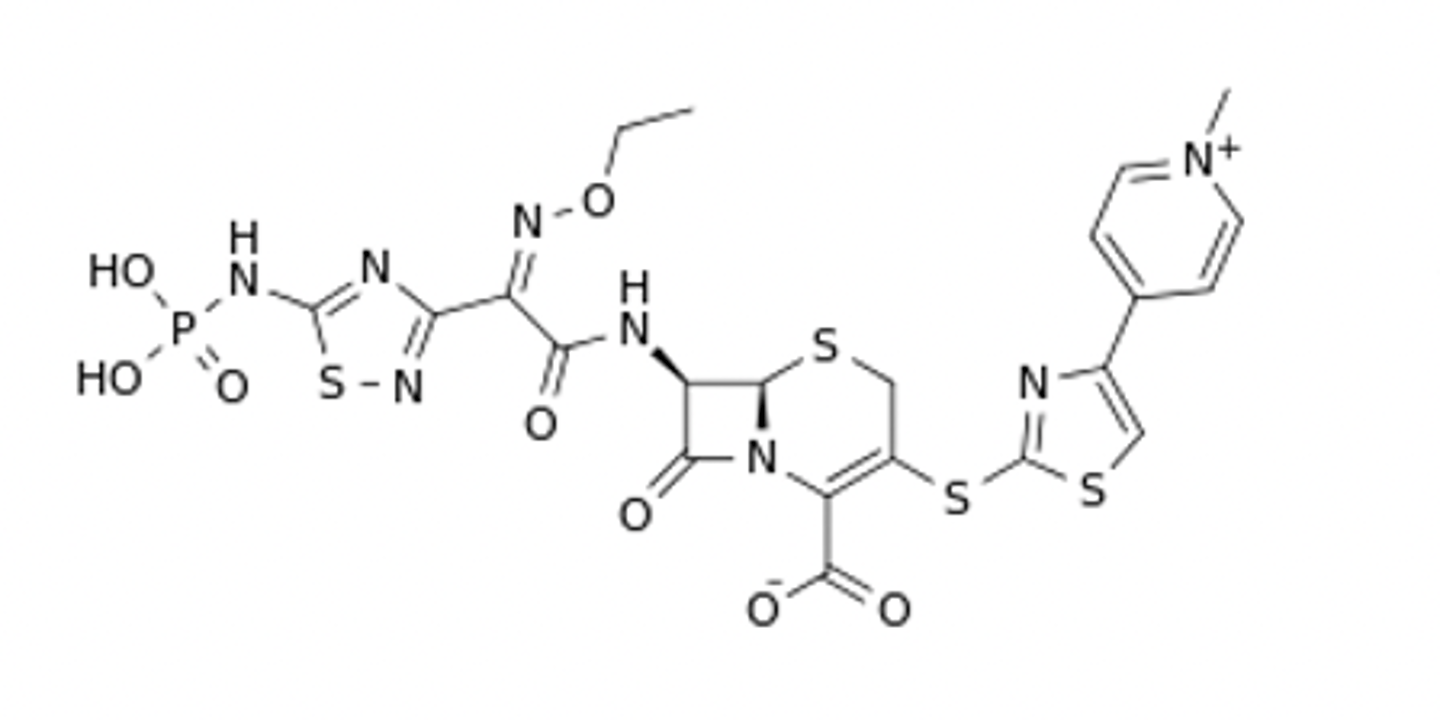
carbapenem
Classify as a penicillin, cephalosporin, carbapenem, or monobactam agents. Further, where applicable highlight the thiazolidine or dihydrothiazine backbone of these agents.

cephalosporin type dihydrothiazine
Classify as a penicillin, cephalosporin, carbapenem, or monobactam agents. Further, where applicable highlight the thiazolidine or dihydrothiazine backbone of these agents.
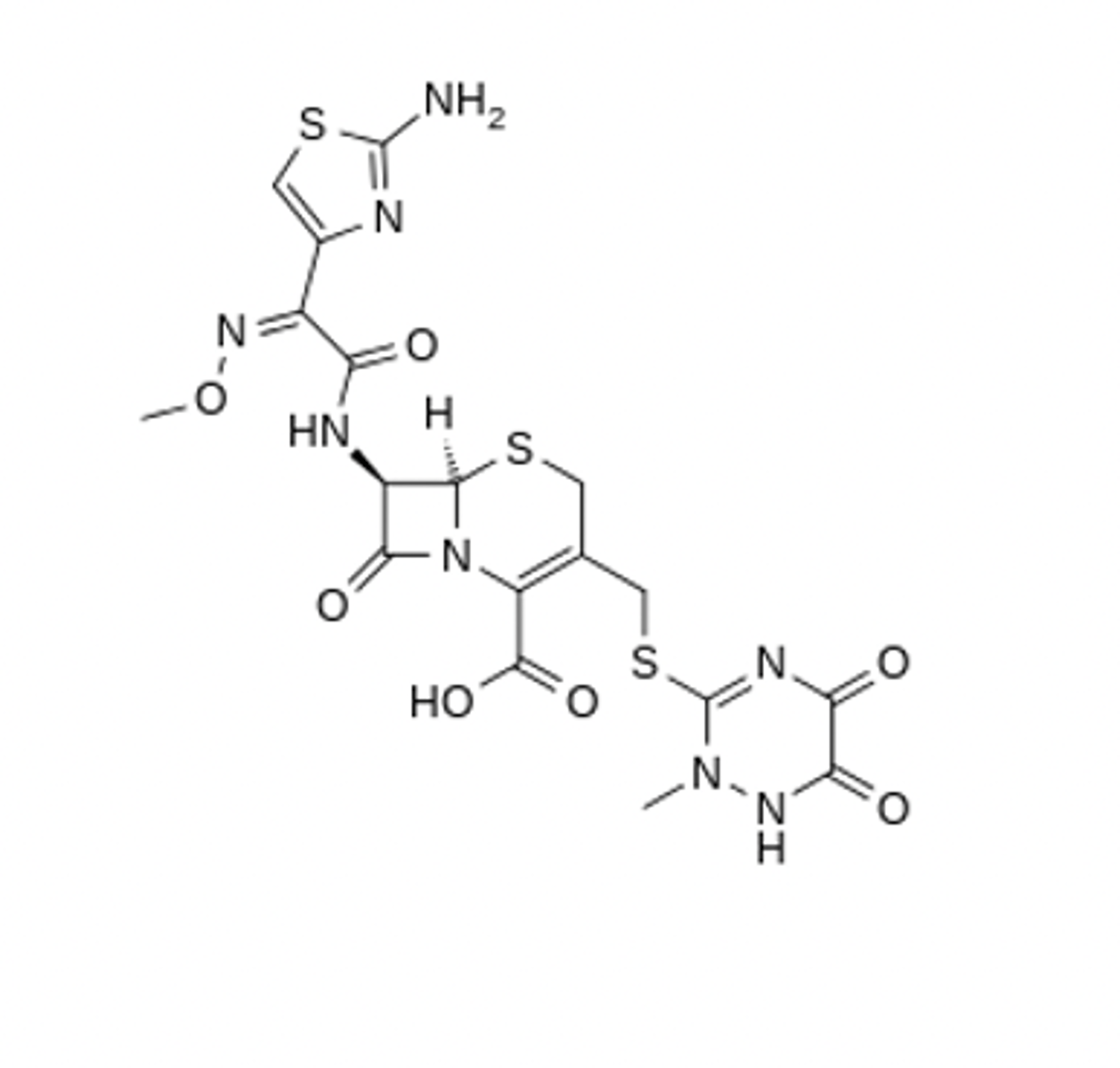
cephalosporin type dihydrothiazine
Classify as a penicillin, cephalosporin, carbapenem, or monobactam agents. Further, where applicable highlight the thiazolidine or dihydrothiazine backbone of these agents.
penicillin type thiazolidine
Classify as a penicillin, cephalosporin, carbapenem, or monobactam agents. Further, where applicable highlight the thiazolidine or dihydrothiazine backbone of these agents.
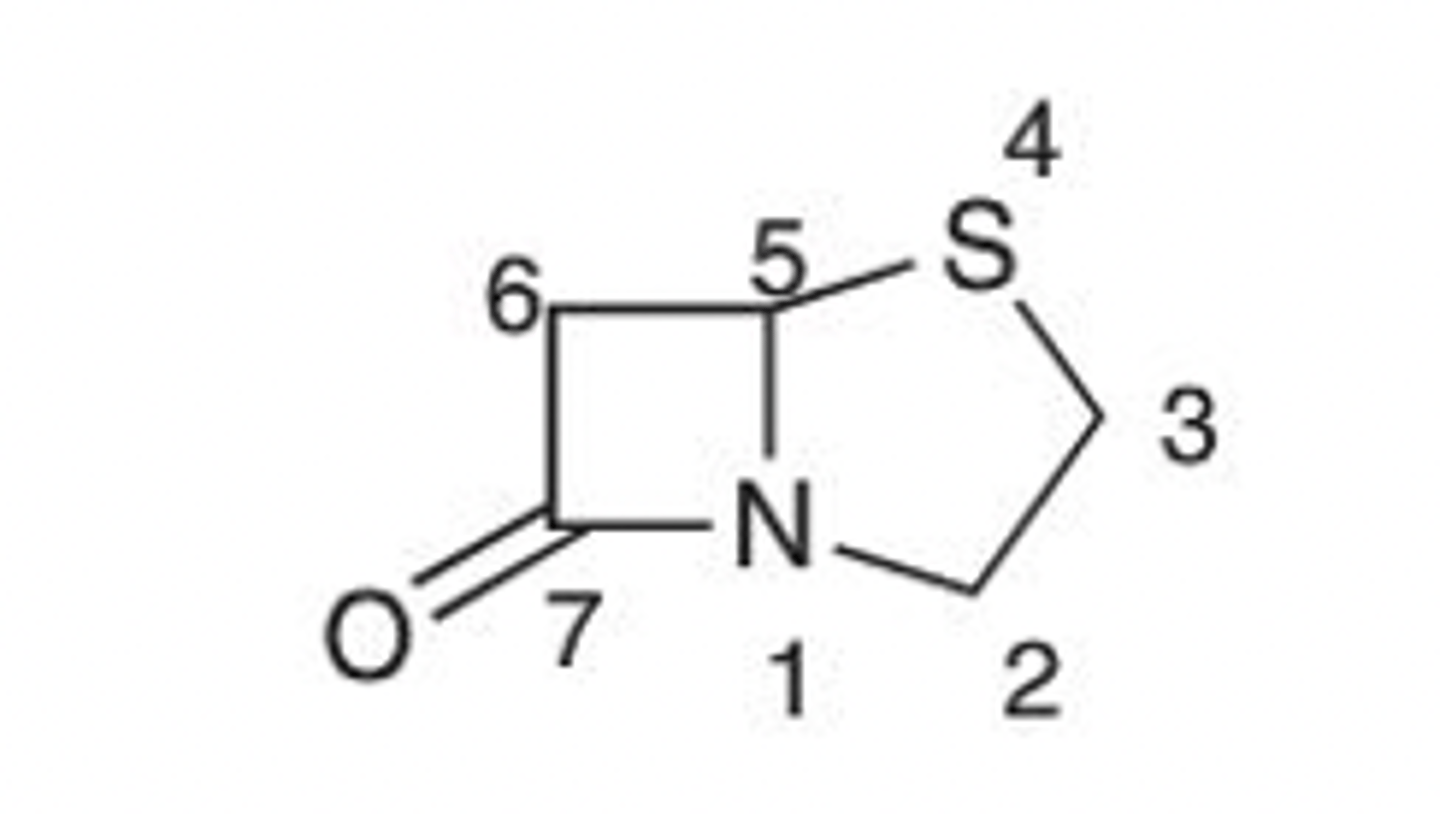
monobactam
Classify as a penicillin, cephalosporin, carbapenem, or monobactam agents. Further, where applicable highlight the thiazolidine or dihydrothiazine backbone of these agents.
Penam
(4-Thia-1-azabicyclo-[3.2.0]heptane)-7-one
Be 100% sure you can differentiate between a penam, penem, carbapenem, cefem and monobactam! Identify
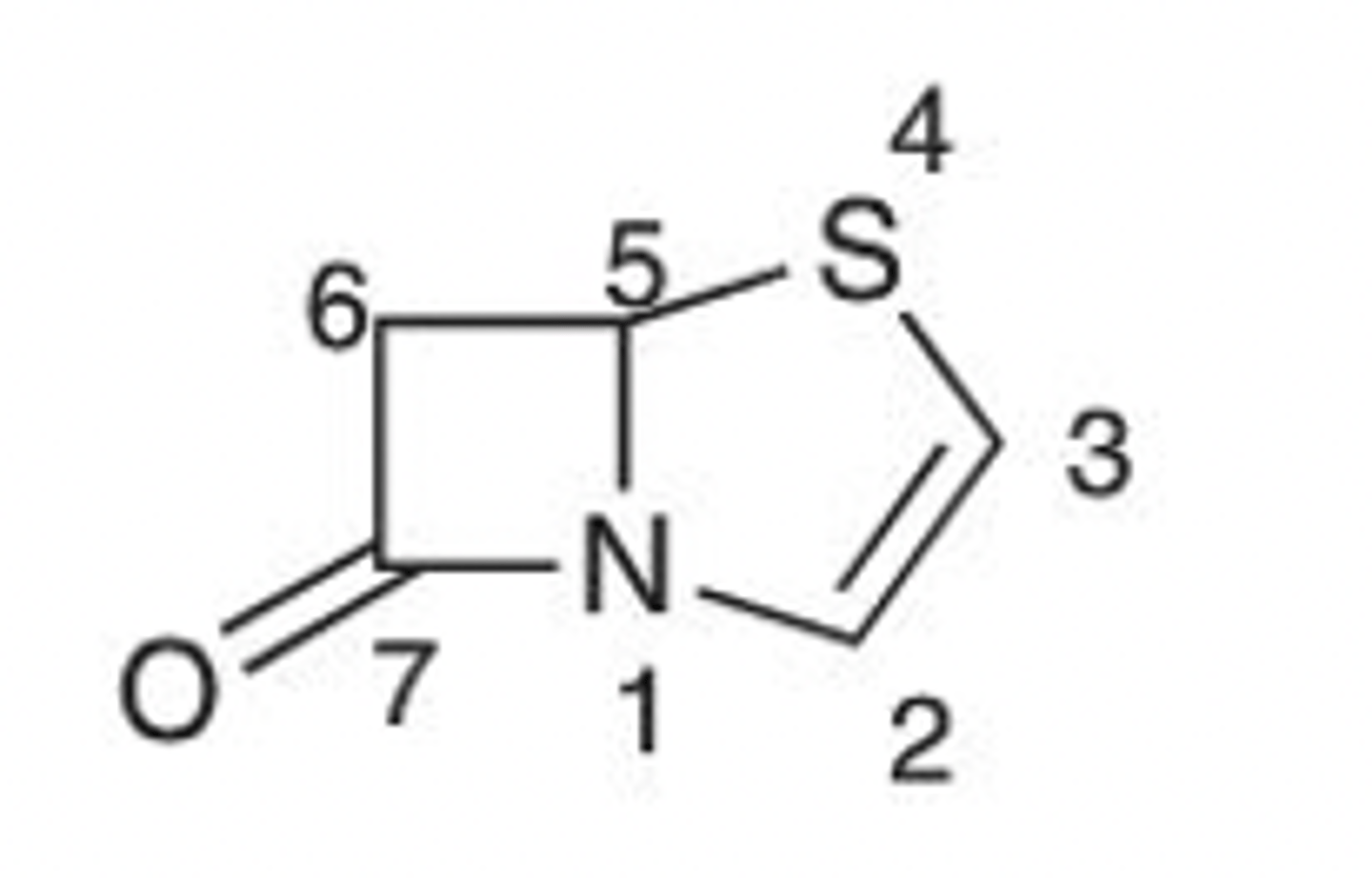
Penem
(4-Thia-1-azabicyclo-[3.2.0]hept-2-ene)-7-one
Be 100% sure you can differentiate between a penam, penem, carbapenem, cefem and monobactam! Identify
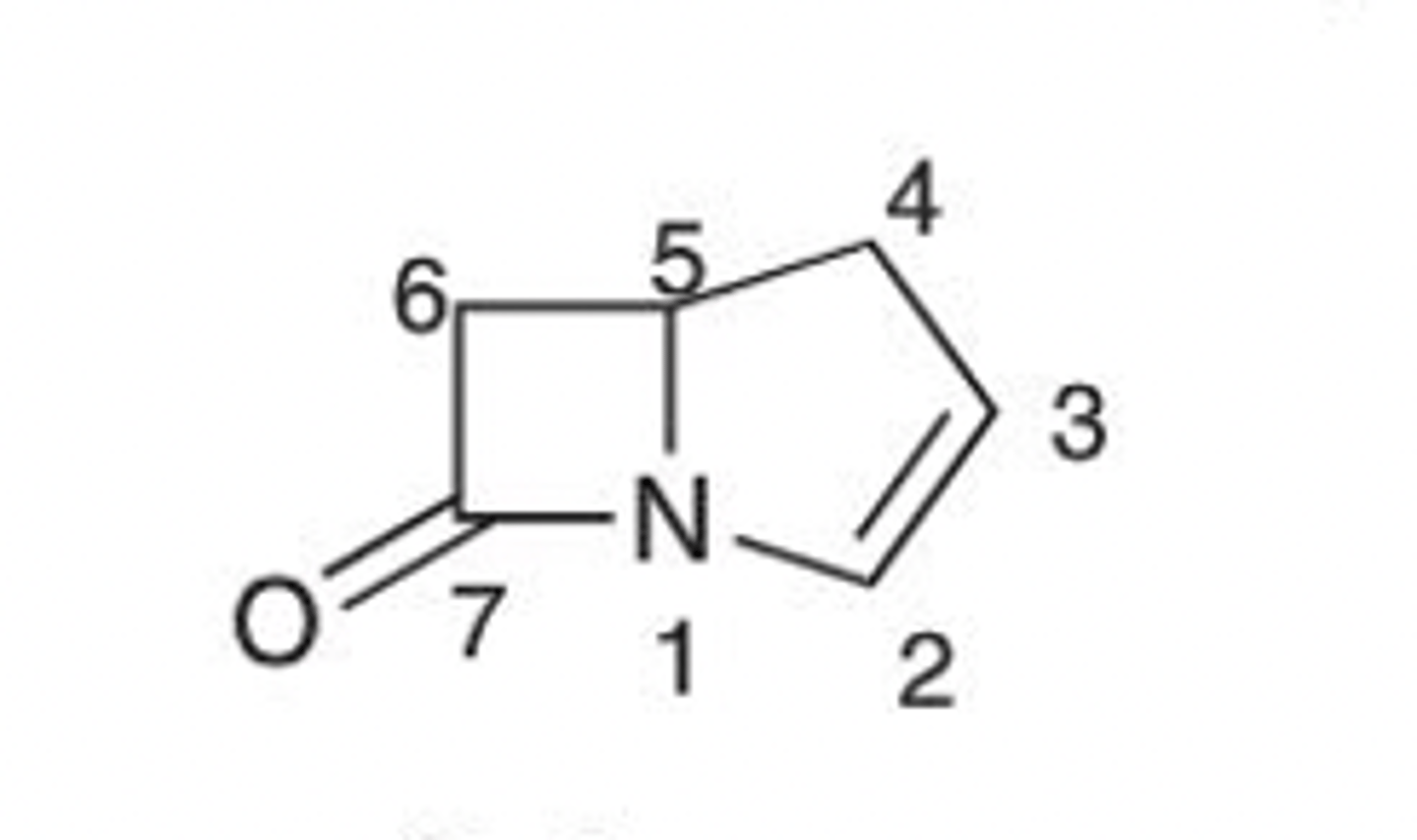
Carbapenem
(1-Azabicyclo[3.2.0]-hept-2-ene)-7-one
Be 100% sure you can differentiate between a penam, penem, carbapenem, cefem and monobactam! Identify
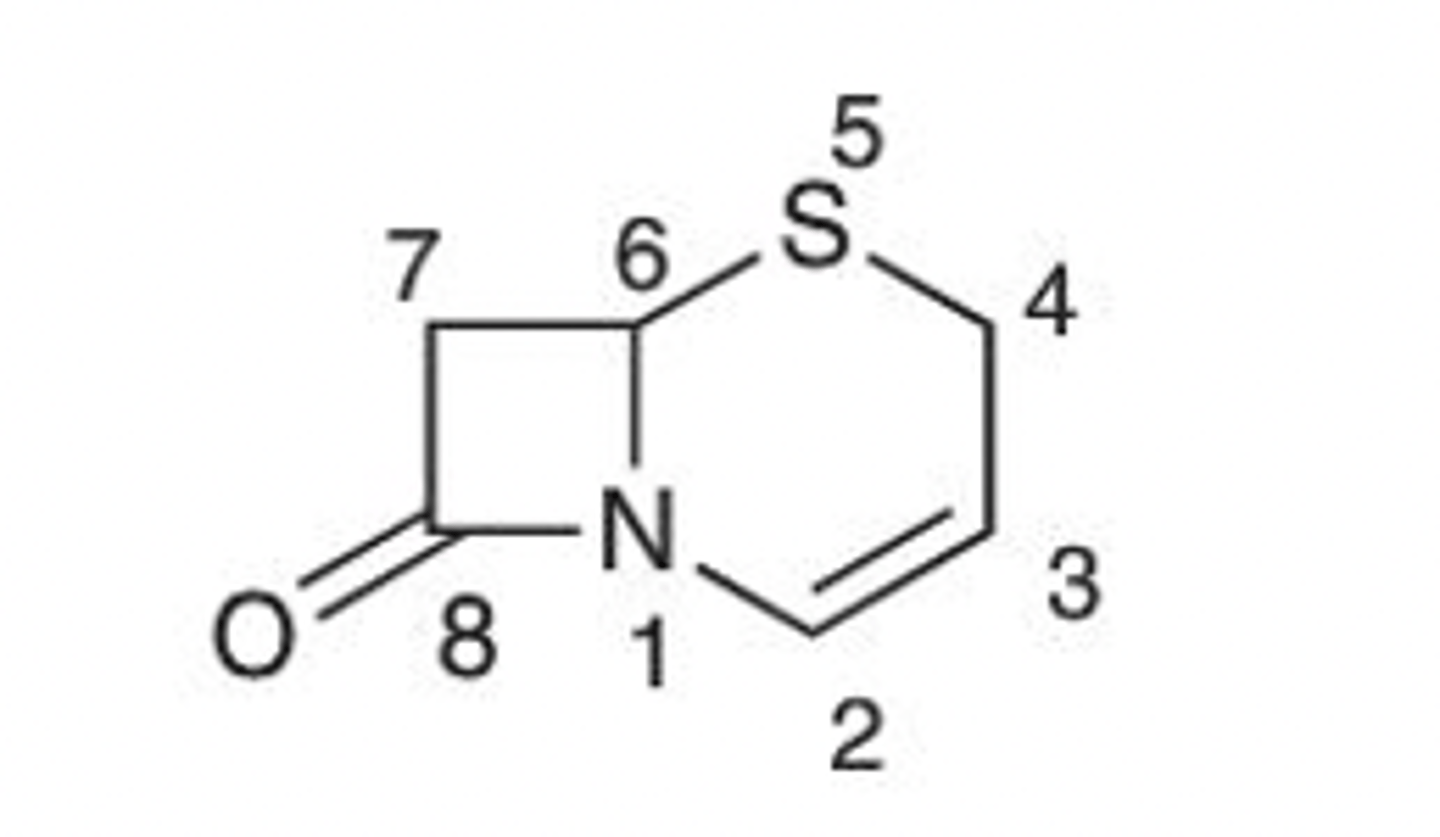
Cefem
(5-Thia-1-azabicyclo-[4.2.0]oct-2-ene)-8-one
Be 100% sure you can differentiate between a penam, penem, carbapenem, cefem and monobactam! Identify
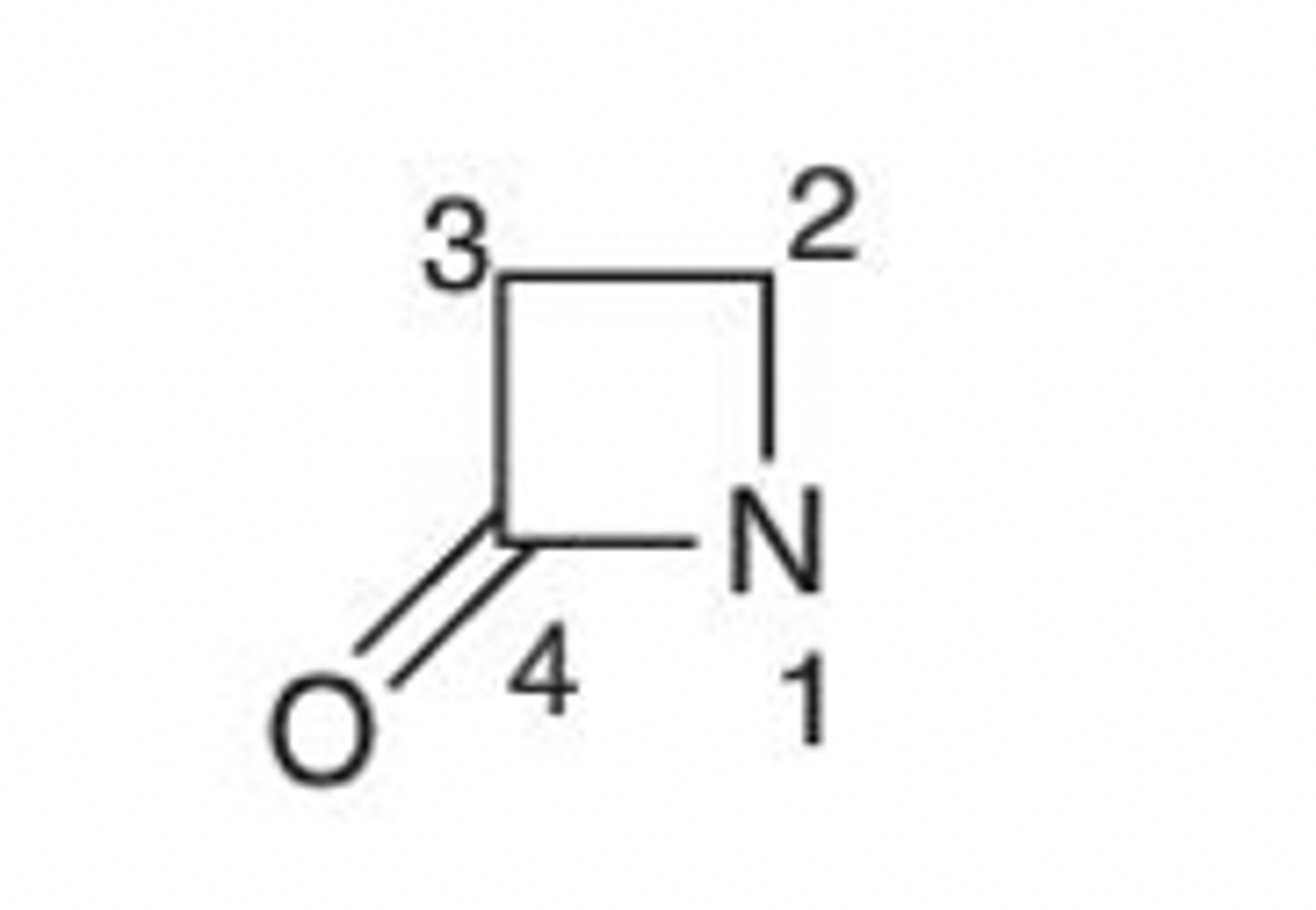
Monobactam
(1-Azacyclobutan-4-one)
Be 100% sure you can differentiate between a penam, penem, carbapenem, cefem and monobactam! Identify
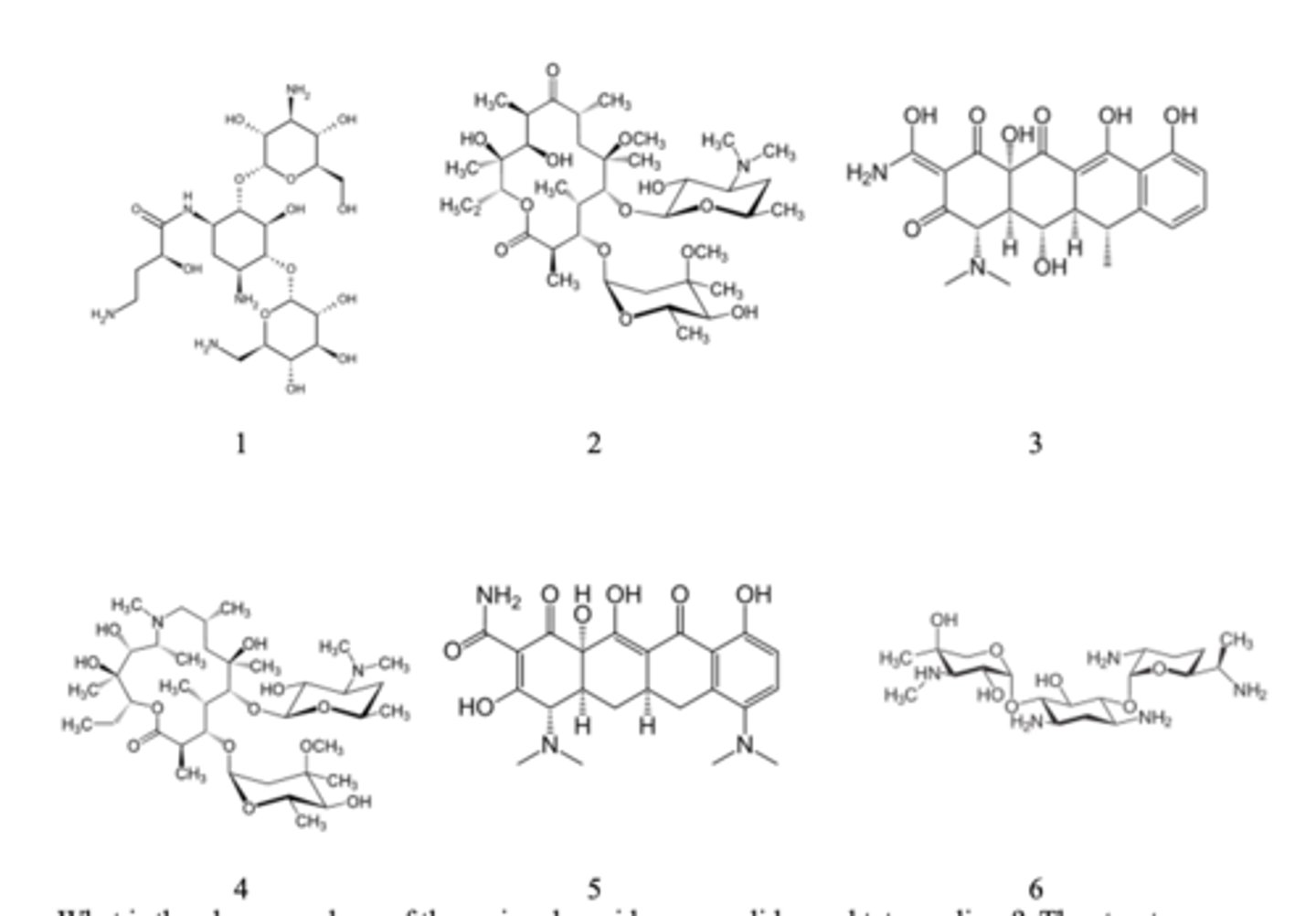
1 = aminoglycoside
2 = macrolide
3 = tetracycline
4 = macrolide
5 = tetracycline
6 = aminoglycoside
Shown below are several antibiotics. Classify them as either aminoglycoside, macrolide or tetracycline?
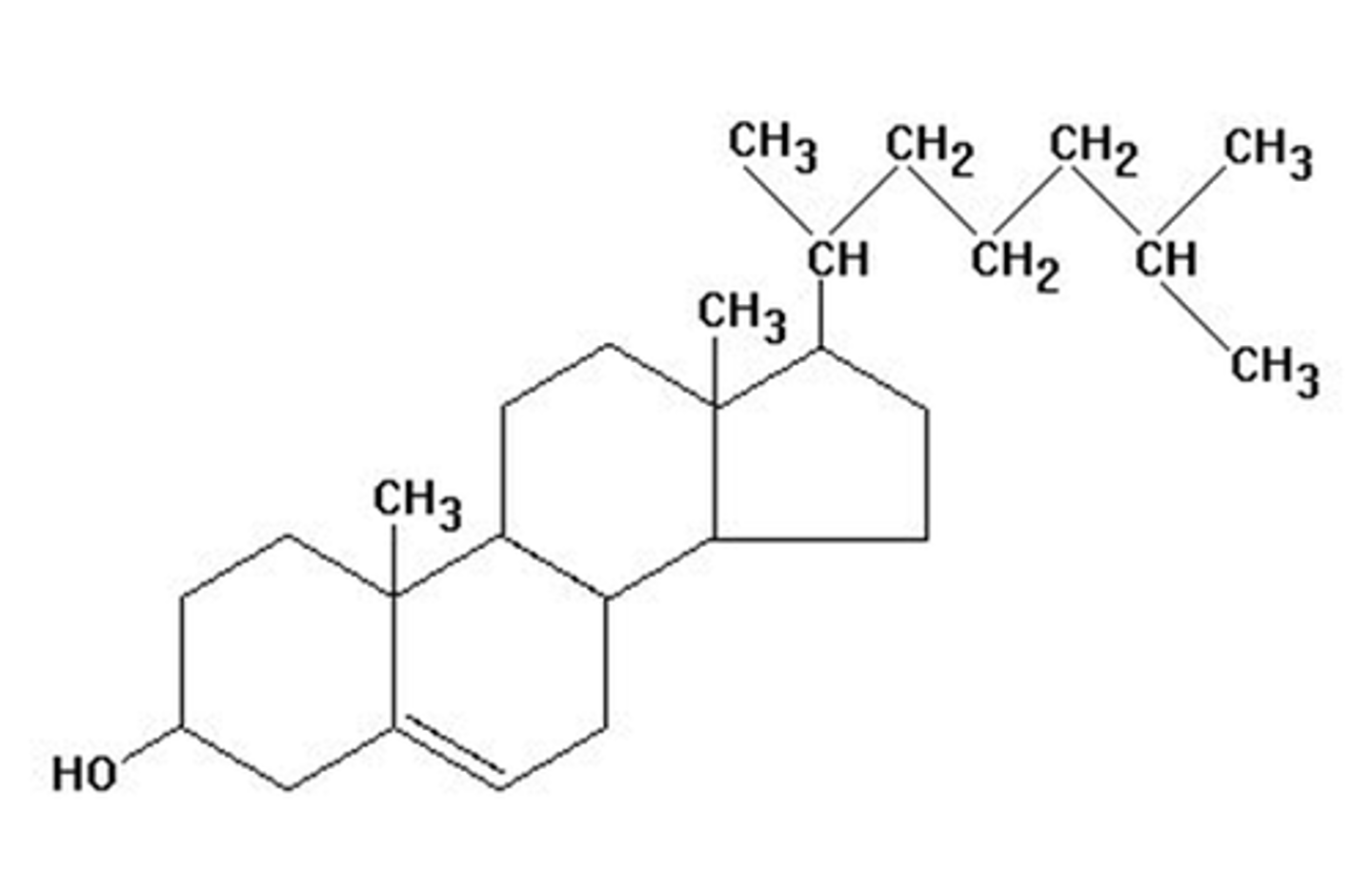
Cholesterol
Identify the structure
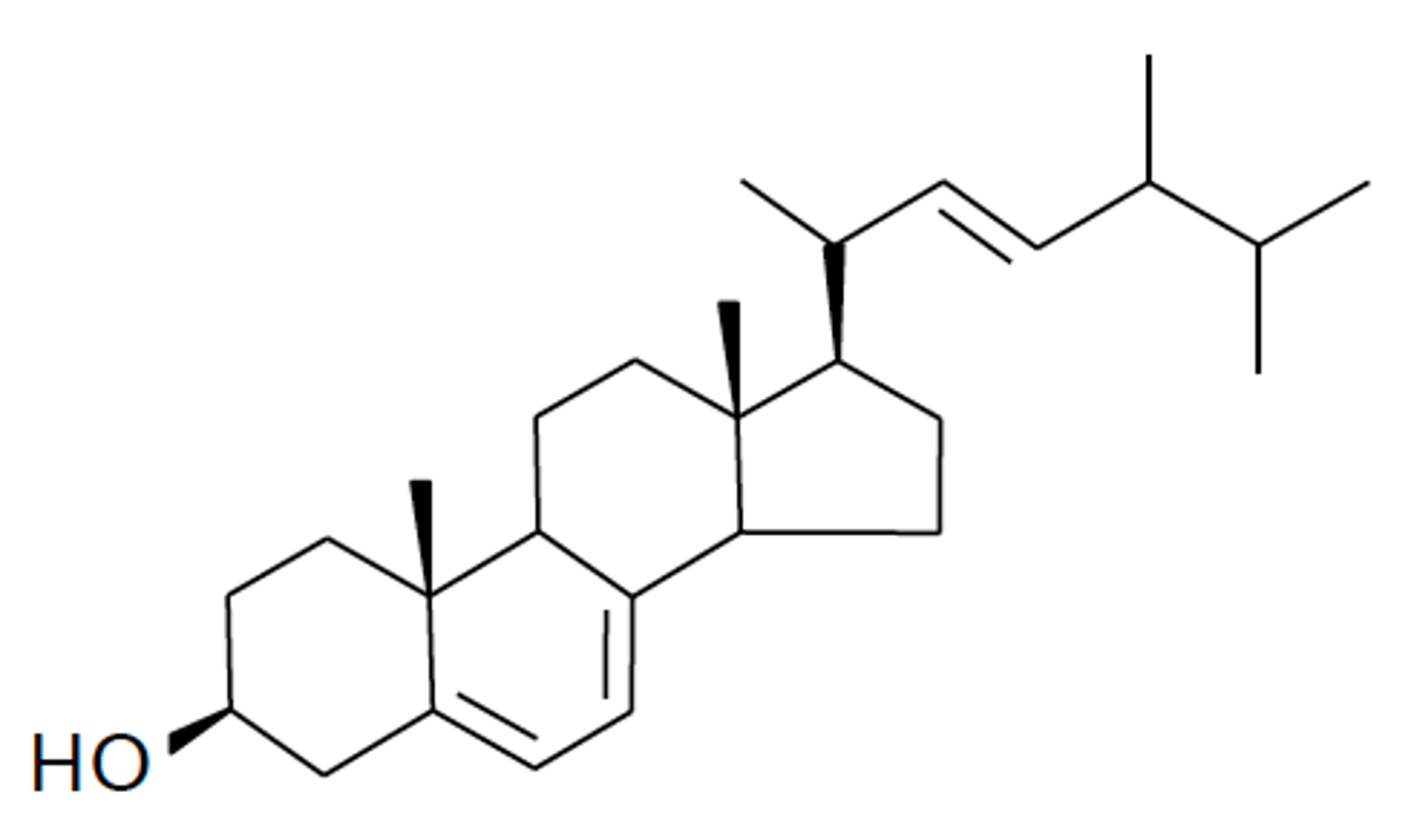
Ergosterol
Identify the structure
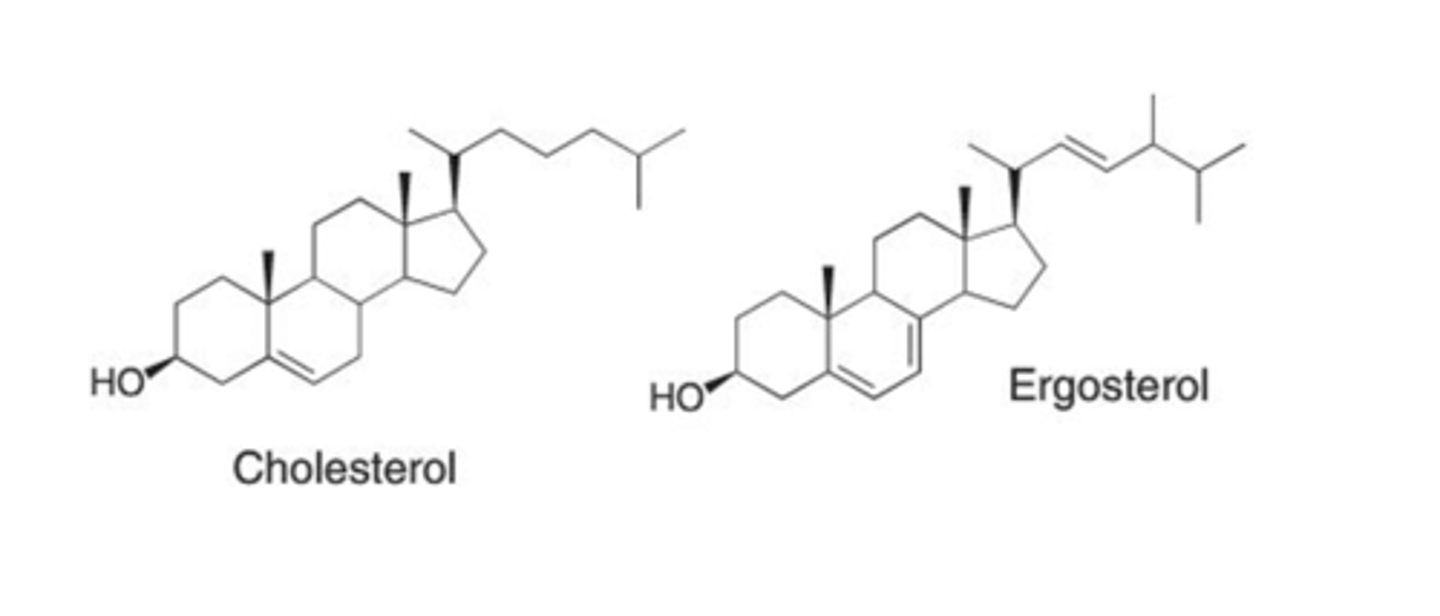
Know the difference in cell wall membrane sterols between mammals and fungi with regard to ergosterol. Recognize the subtle differences in these two sterols.
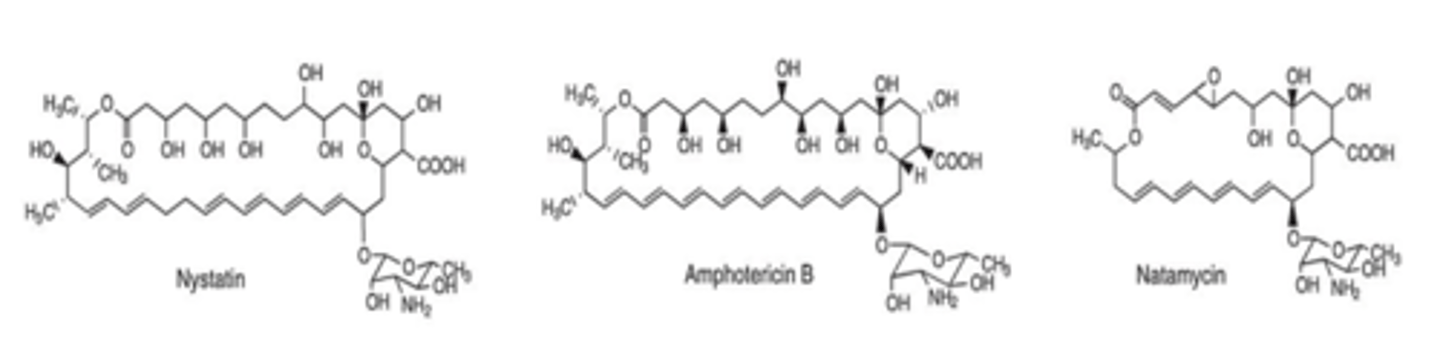
Recognize the general structure-activity relationships of the polyene membrane disruptors, in which the hydrophilic region contains several alcohols, a carboxylic acid, and often a sugar, while the lipophilic region contains a chromophore of four to seven conjugated double bonds.
CYP51 converts methyl- of C14 in lanosterol to a double bond. Azole blocks CYP51 oxygenation reaction by binding heme iron
Describe the key reactions in ergosterol biosynthesis that are the targets of inhibition by antifungal drugs, especially CYP51. How do the azole antifungals inactivate CYP51 and disrupt the formation of ergosterol?
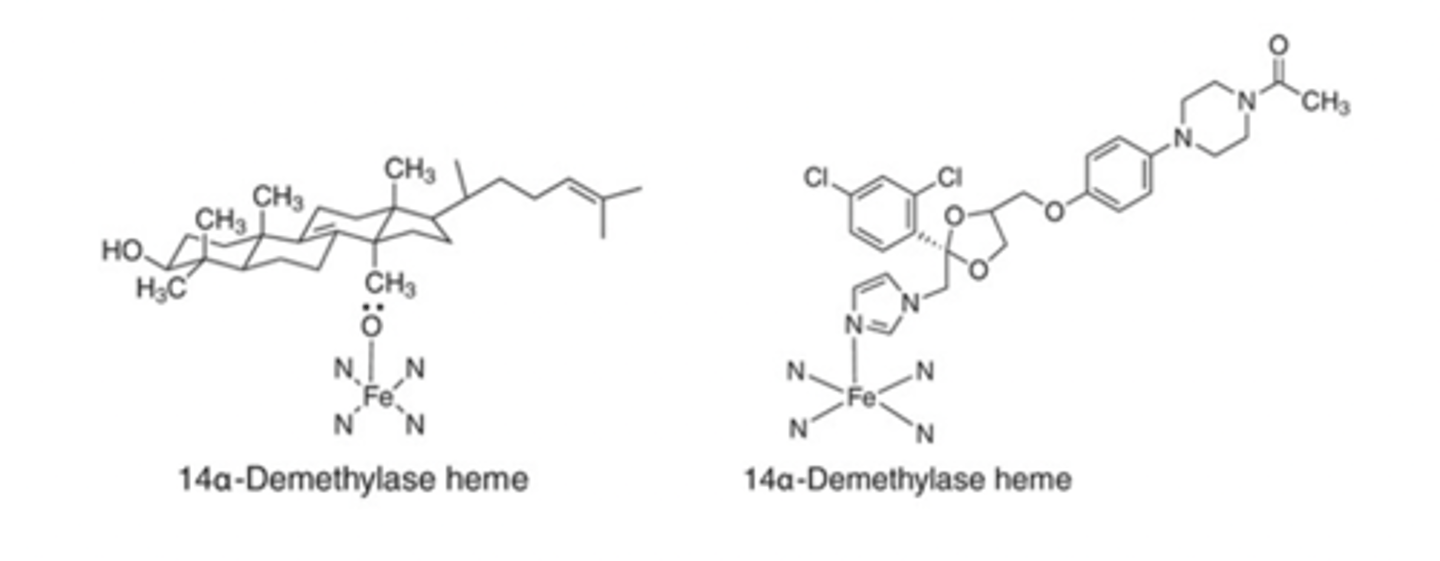
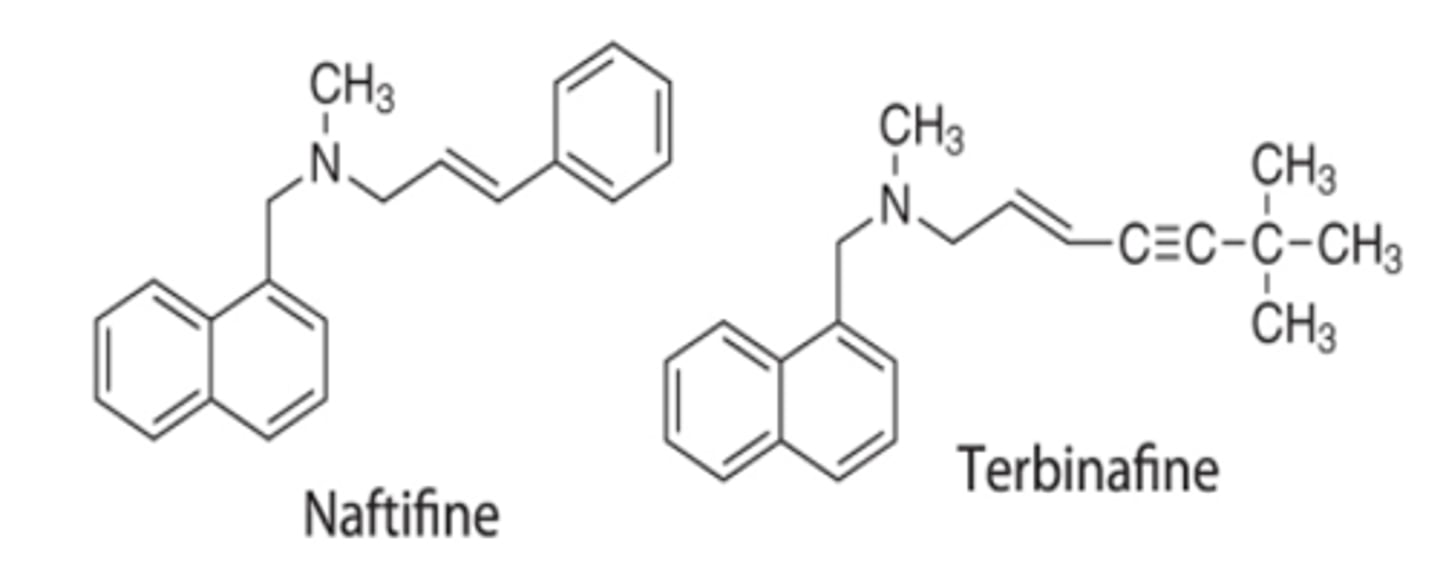
allylamine block squalene synthesis
Recognize the pharmacophore of the allylamine antifungals and their target in the ergosterol biosynthetic pathway. Highlight the pharmacophore of the two agents below.
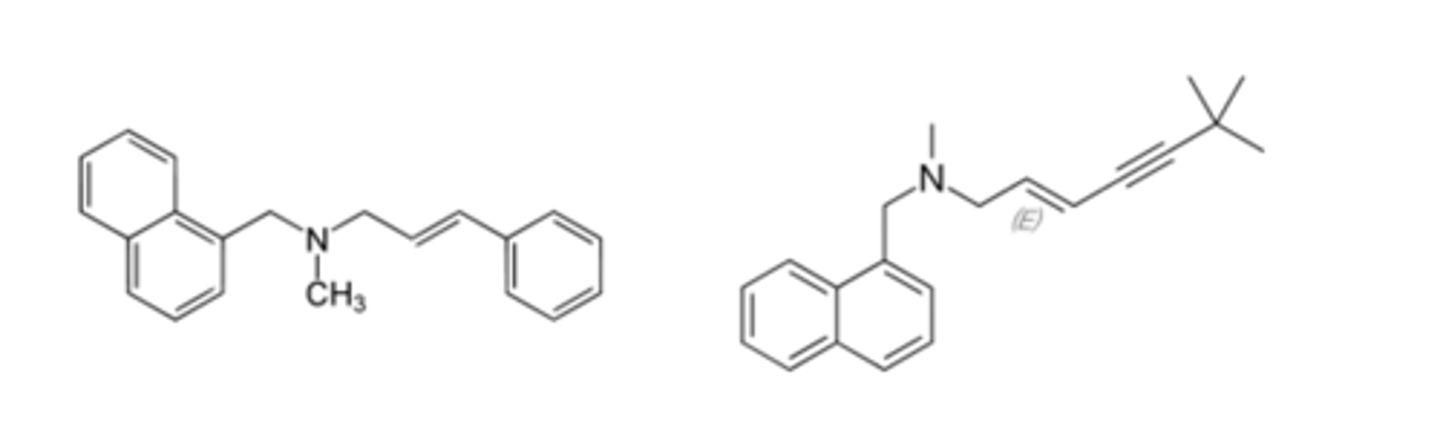
Inhibit glucan 1-3 synthase needed for cell wall synthesis
Be able to recognize the general structure and role of the echinocandins, which are lipopeptide macrocyclic antifungals. Briefly describe their role in disrupting cell wall formation in fungi.
nitroaryls
Shown below are five antiparasitic species used in the treatment of Trichomonas vaginalis, amebiasis, giardiasis, C. difficile, and Chagas disease. Highlight the important structural component of these agents that is toxic to the parasite.
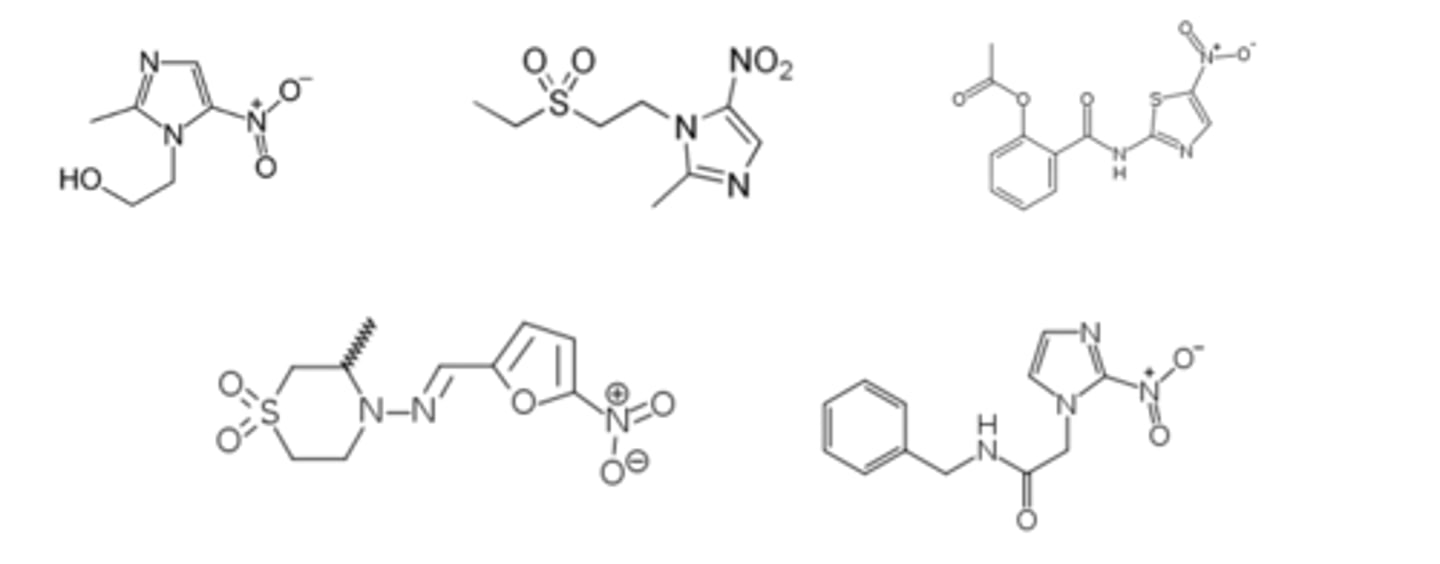
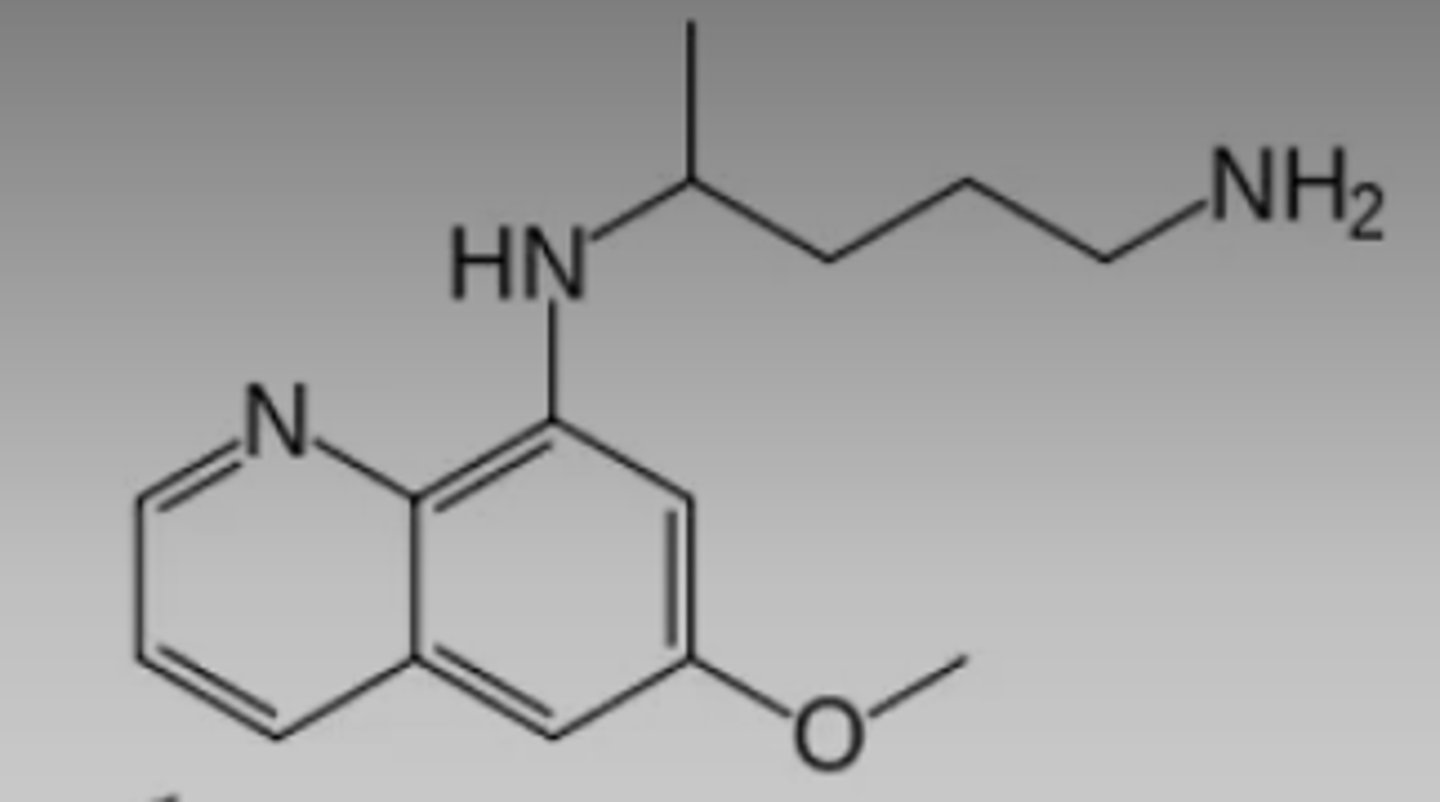
4-aminoquinoline
Identify the pharmacophore
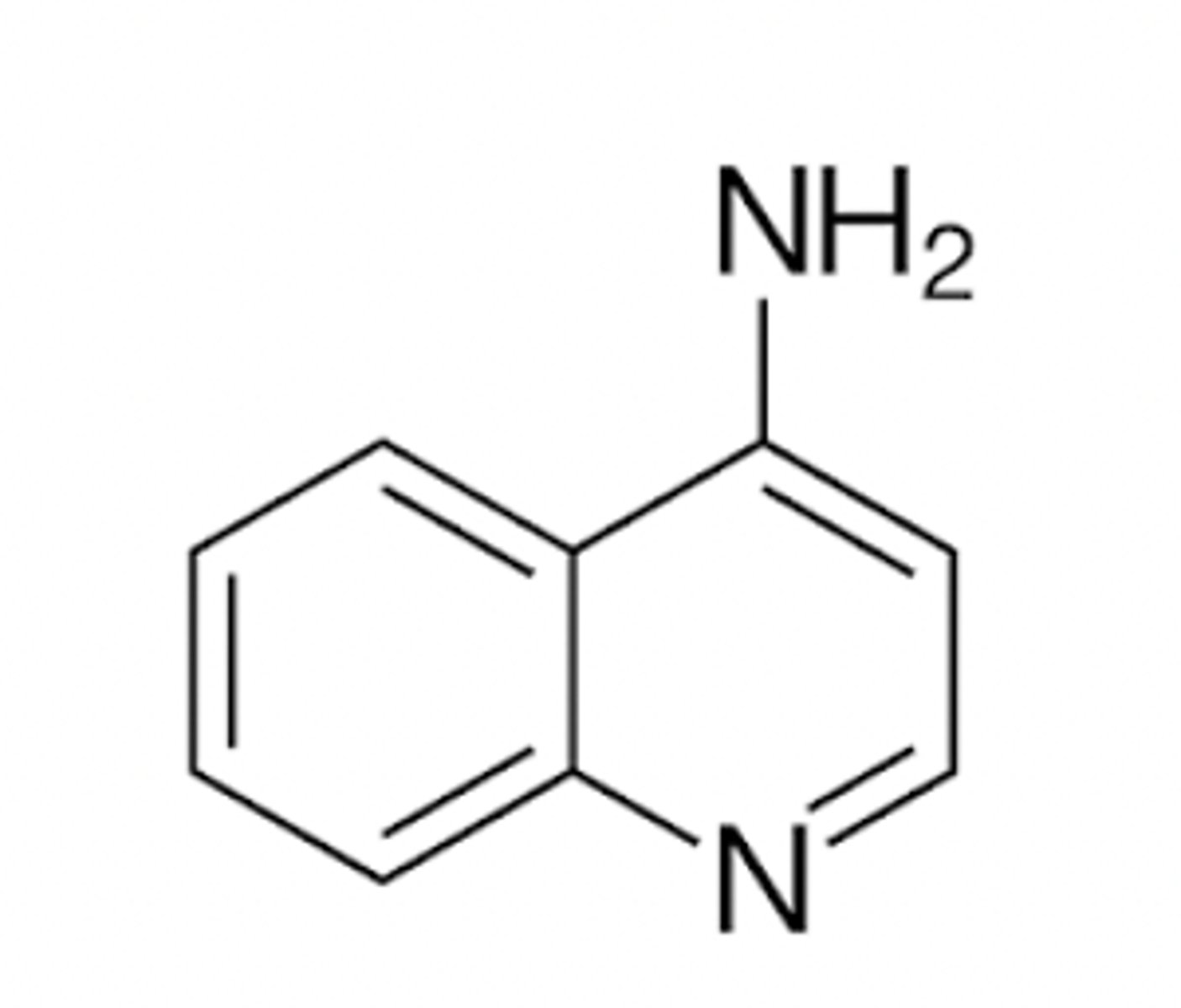
8-aminoquinoline
Identify the pharmacophore
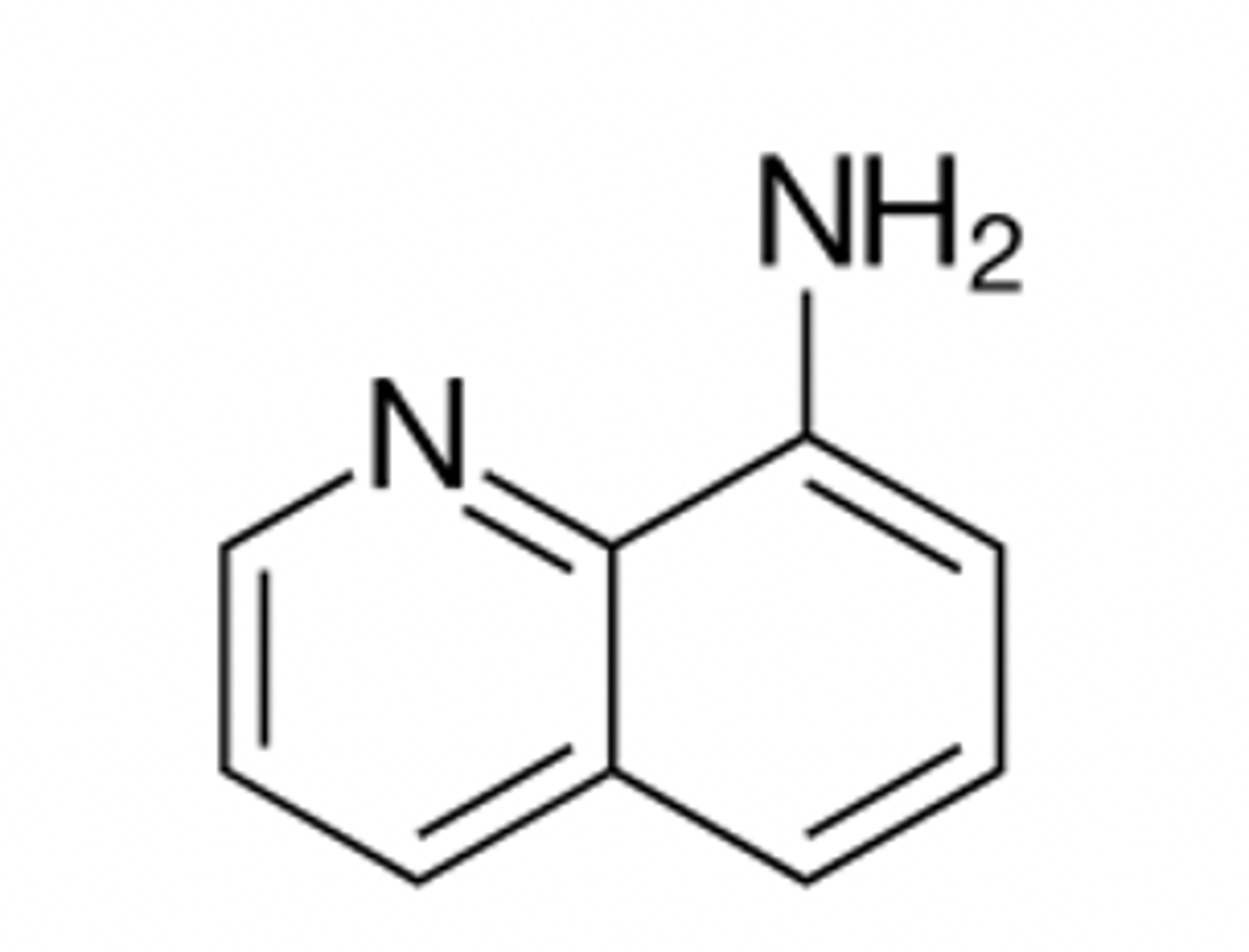
8-aminoquinoline
Identify the pharmacophore
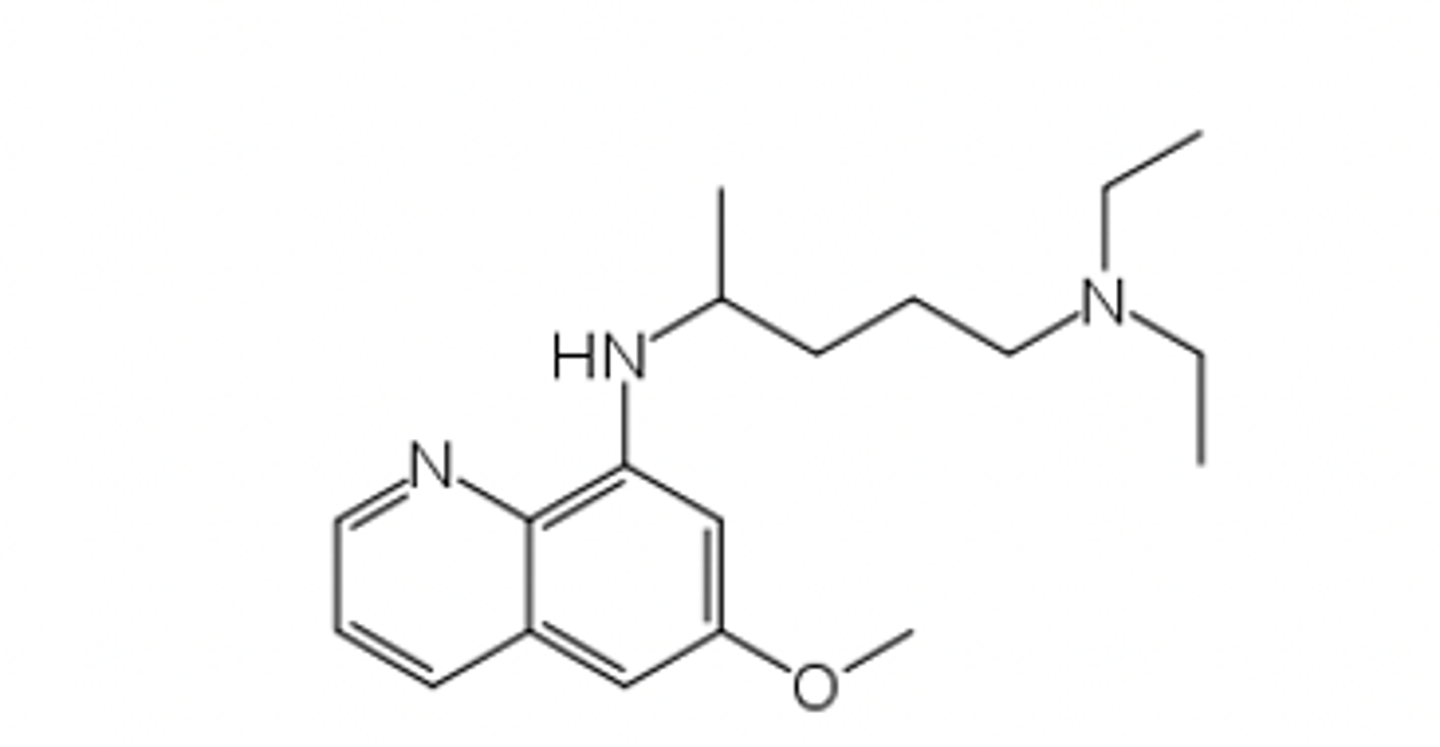
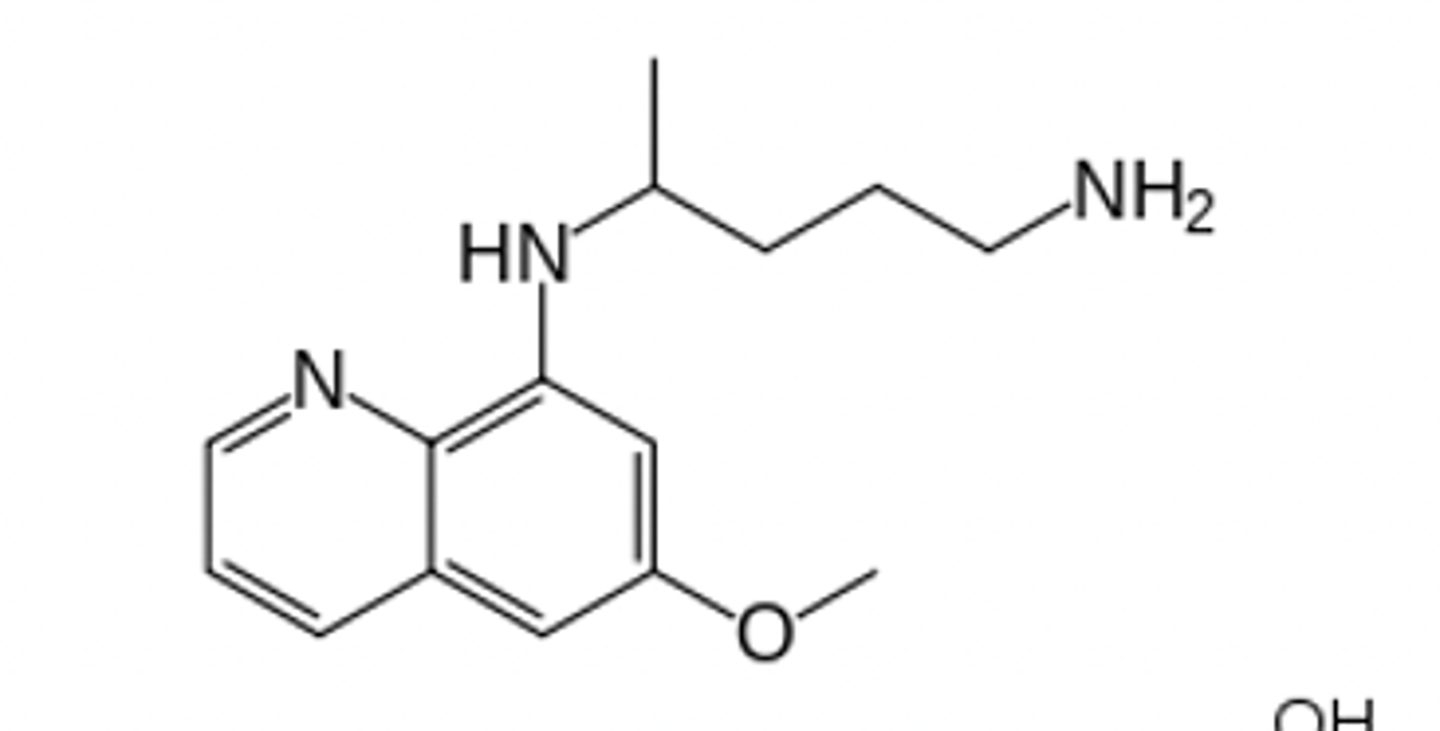
8-aminoquinoline
Identify the pharmacophore
4-aminoquinoline
Identify the pharmacophore
4-aminoquinoline
Identify the pharmacophore
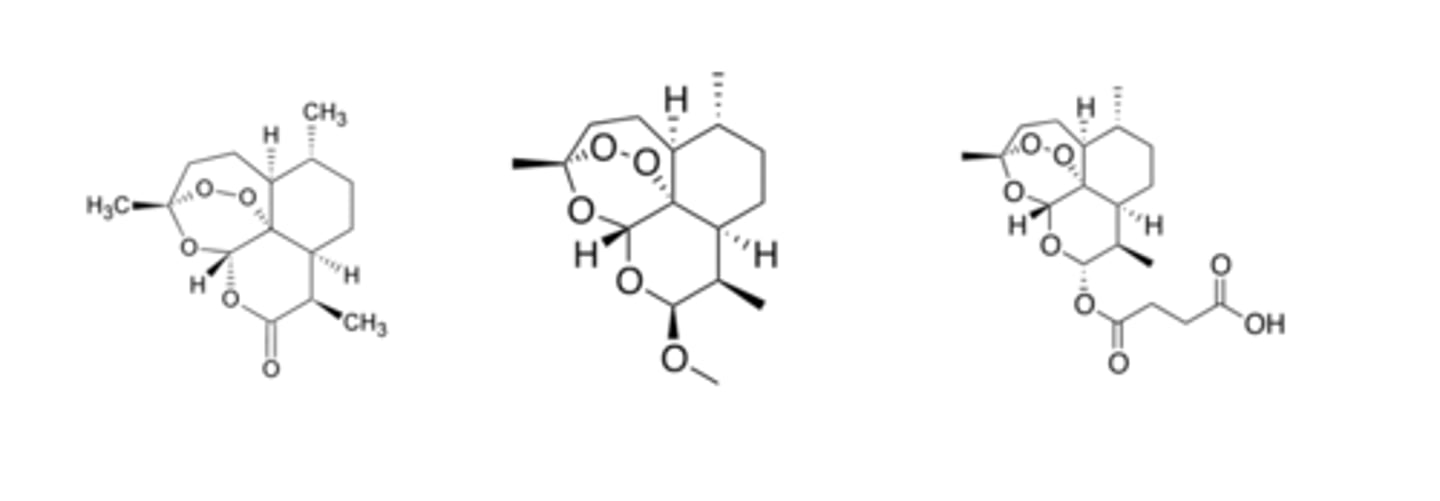
form endoperoxides
Shown below are antiparasitic artemisinins. Highlight the pharmacophore (dioxane or trioxane) of these compounds. What active intermediates are formed from these?
benzimidazole
Identify the pharmacophore in the following antihelmintic agents.
fluoroquinolones
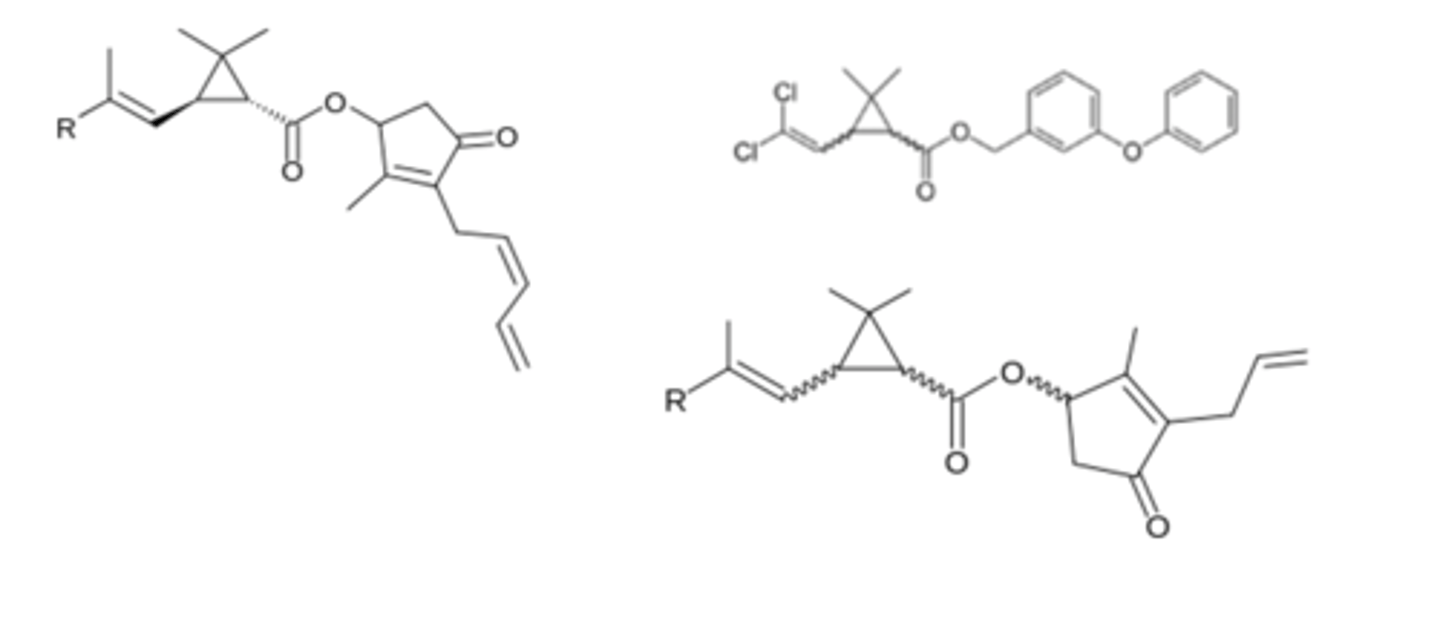
Recognize the following natural product pyrethroids that are nerve membrane sodium channel toxins. Be able to recognize allylic dimethylcyclopropane backbone in these agents. What antibiotic has a cyclopropyl- moiety that enhances antibiotic coverage?
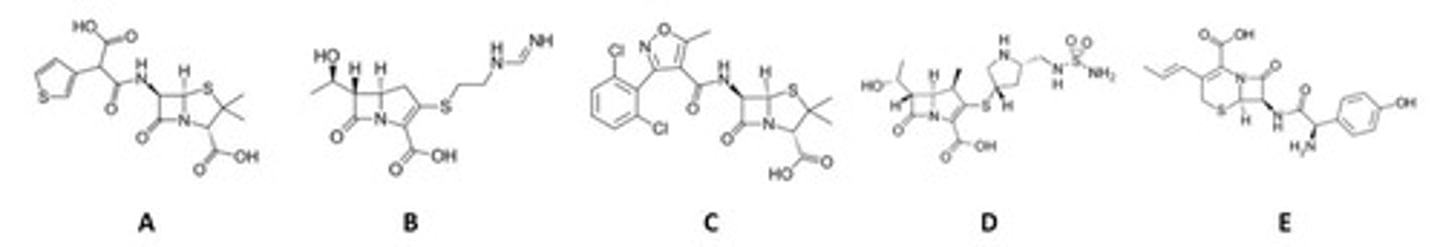
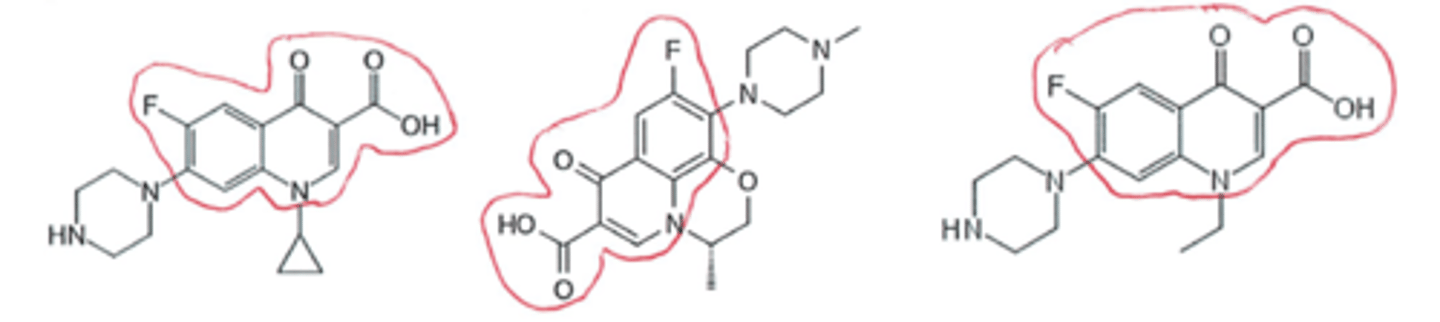
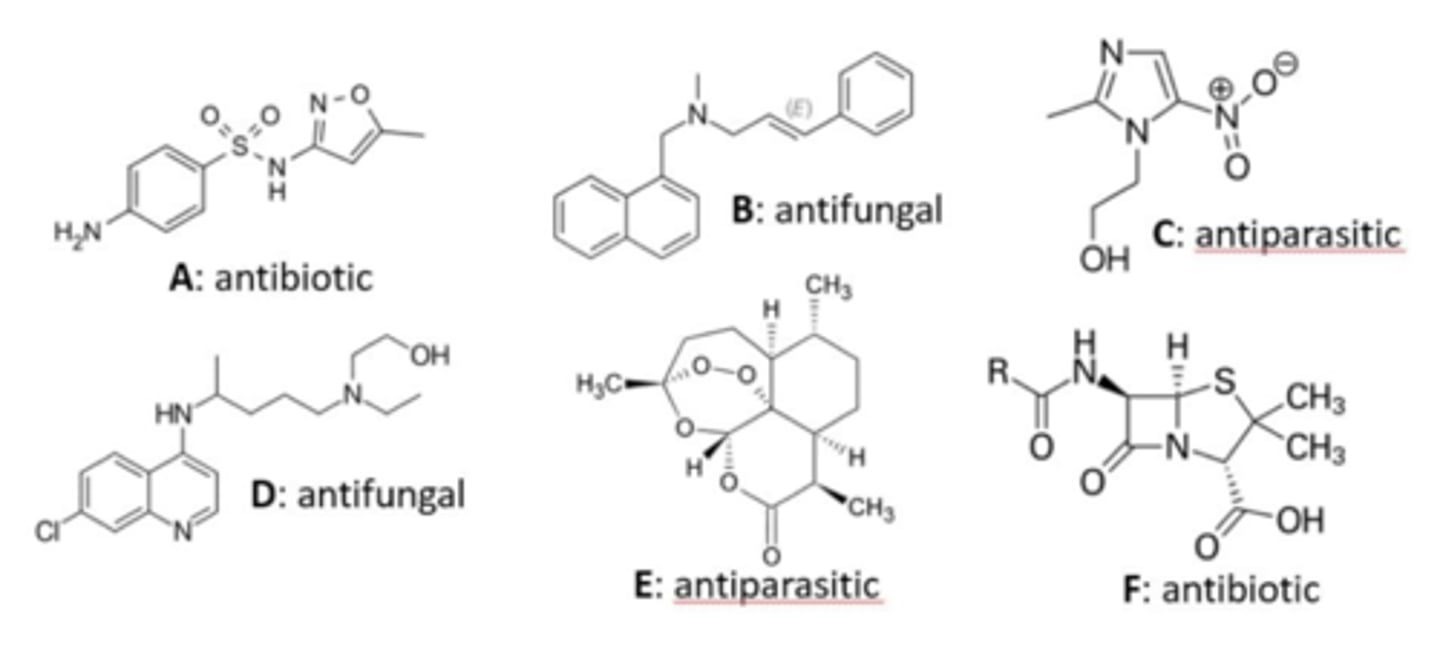
A,C,E
all have ketones attached to a piperidine-like ring, as well as a fluorine
look closely at C → it's a bit hard to make out b/c it's sideways
Based upon pharmacophore, identify the quinolone antibiotics in this group? (select all that apply)
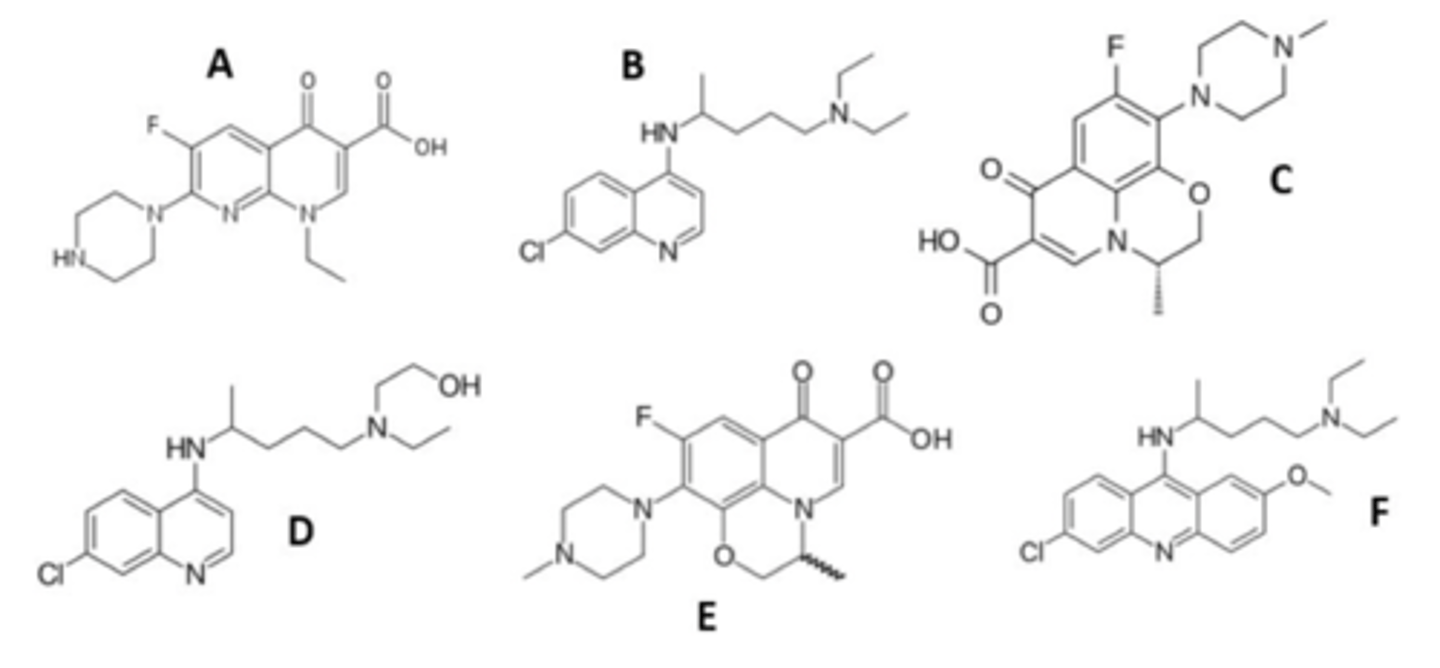
C, E
"dihydro" comes from the unsaturation
thiazine is sulfur + nitrogen in the ring
Which drugs represent dihydrothiazine antibiotics? (select all that apply)
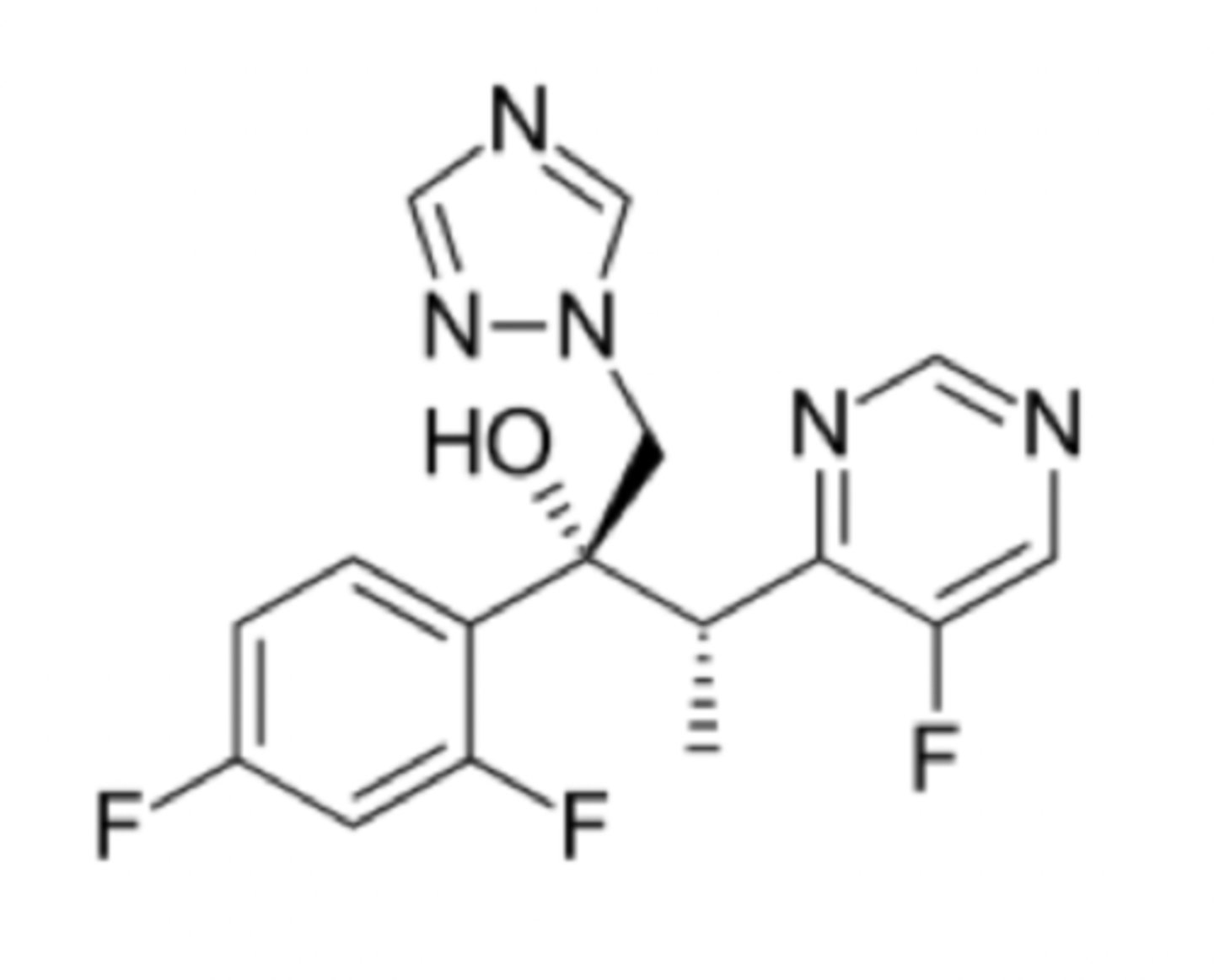
e. It is an antibiotic.
Which is the one false statement about voriconazole?
a. It is an antifungal agent.
b. It blocks ergosterol synthesis.
c. It binds iron in a fungal CYP 450.
d. It is a triazole drug.
e. It is an antibiotic.
D
Which is the one false pharmacophore/drug class association?
c. It is an aminoglycoside
It is NOT an AGS (recall these are the 1,3 diaminositol sugar-like structures)
It IS a macrolide
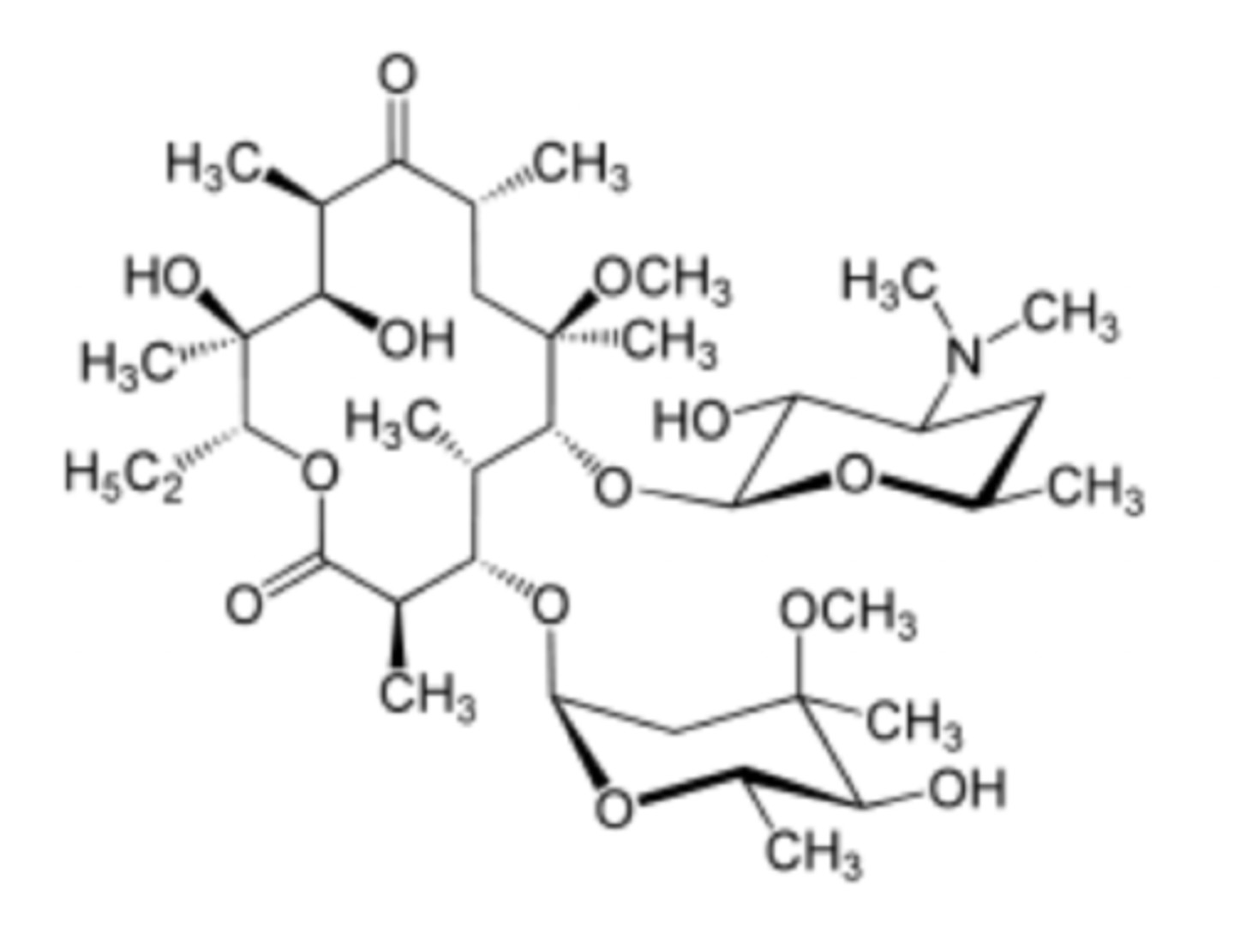
Which is the one false statement concerning clarithromycin?
a. It contains a cyclic lactone.
b. Its backbone ring contains 14 atoms.
c. It is an aminoglycoside
d. It is synthesized from propionate units.
e. It is a macrolide.
c. PABA (4-aminobenzoic acid)
What intermediate in thymidine synthesis does sulfacetamide mimic to act as an antimicrobial?
a. GABA (4-aminobutyric acid)
b. folic acid
c. PABA (4-aminobenzoic acid)
d. thymidine
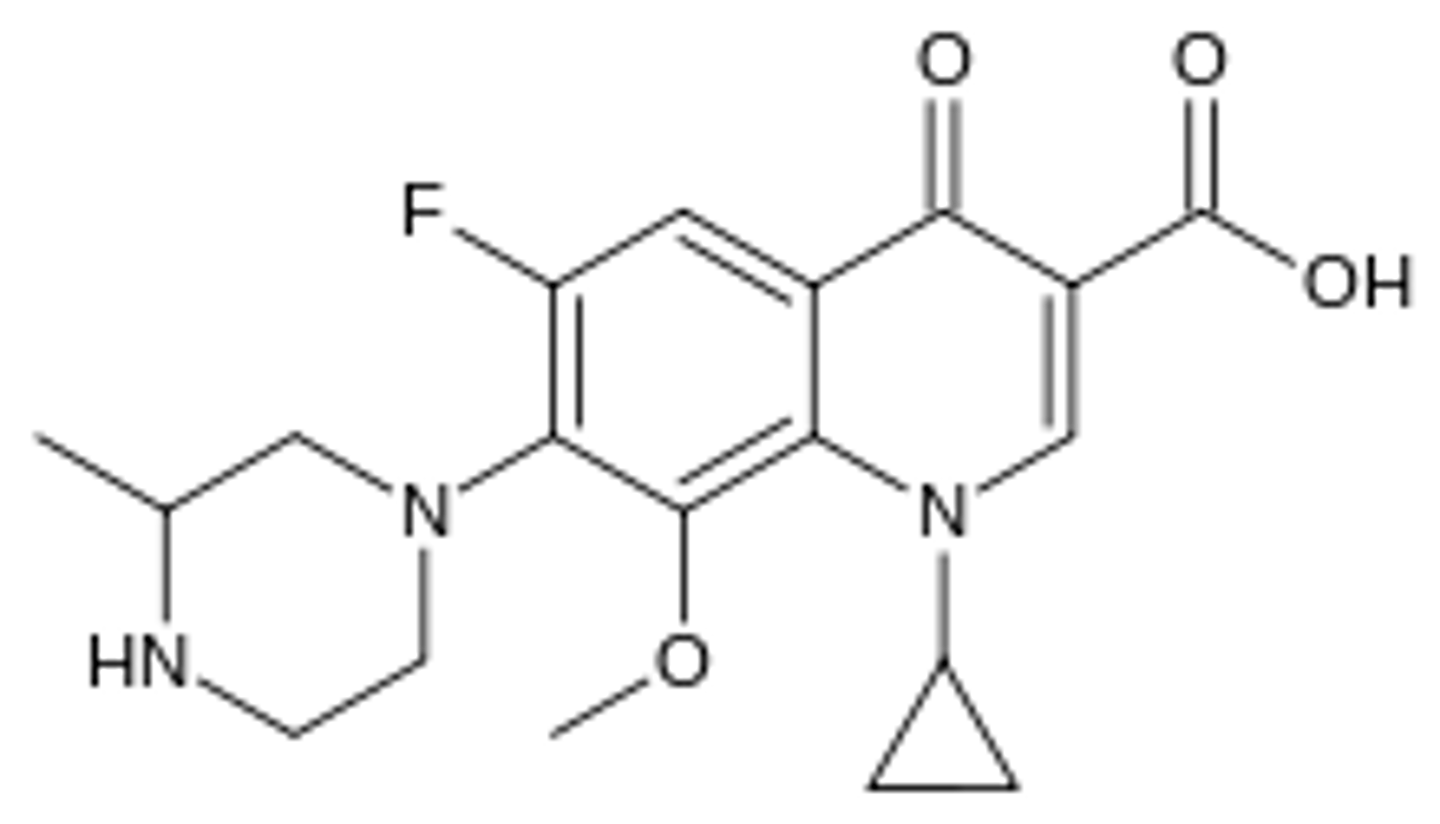
b. it is a quinoline antibiotic
Which is the one false statement about gatifloxacin?
a. it is a quinolone antibiotic
b. it is a quinoline antibiotic
c. fluorine is critical for bacterial cell wall penetration
d. the cyclopropyl- moiety broadens antibiotic capacity
b. beta lactam fused to a thiazolidine ring
Which pharmacophore correctly describes ampicillin?
a. beta lactam fused to a dihydrothiazine ring
b. beta lactam fused to a thiazolidine ring
c. monobactam
d. carbapenem
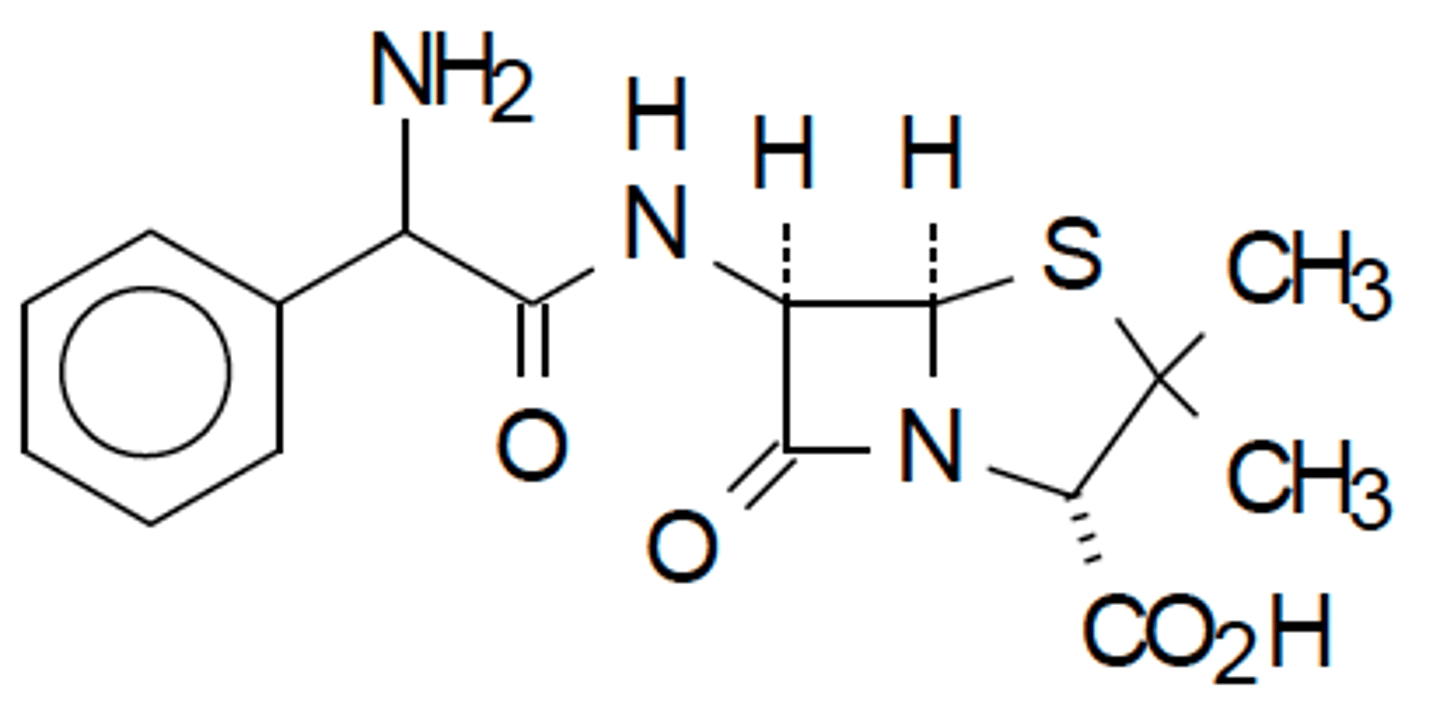
C
Which of these is a carbapenem antibiotic?
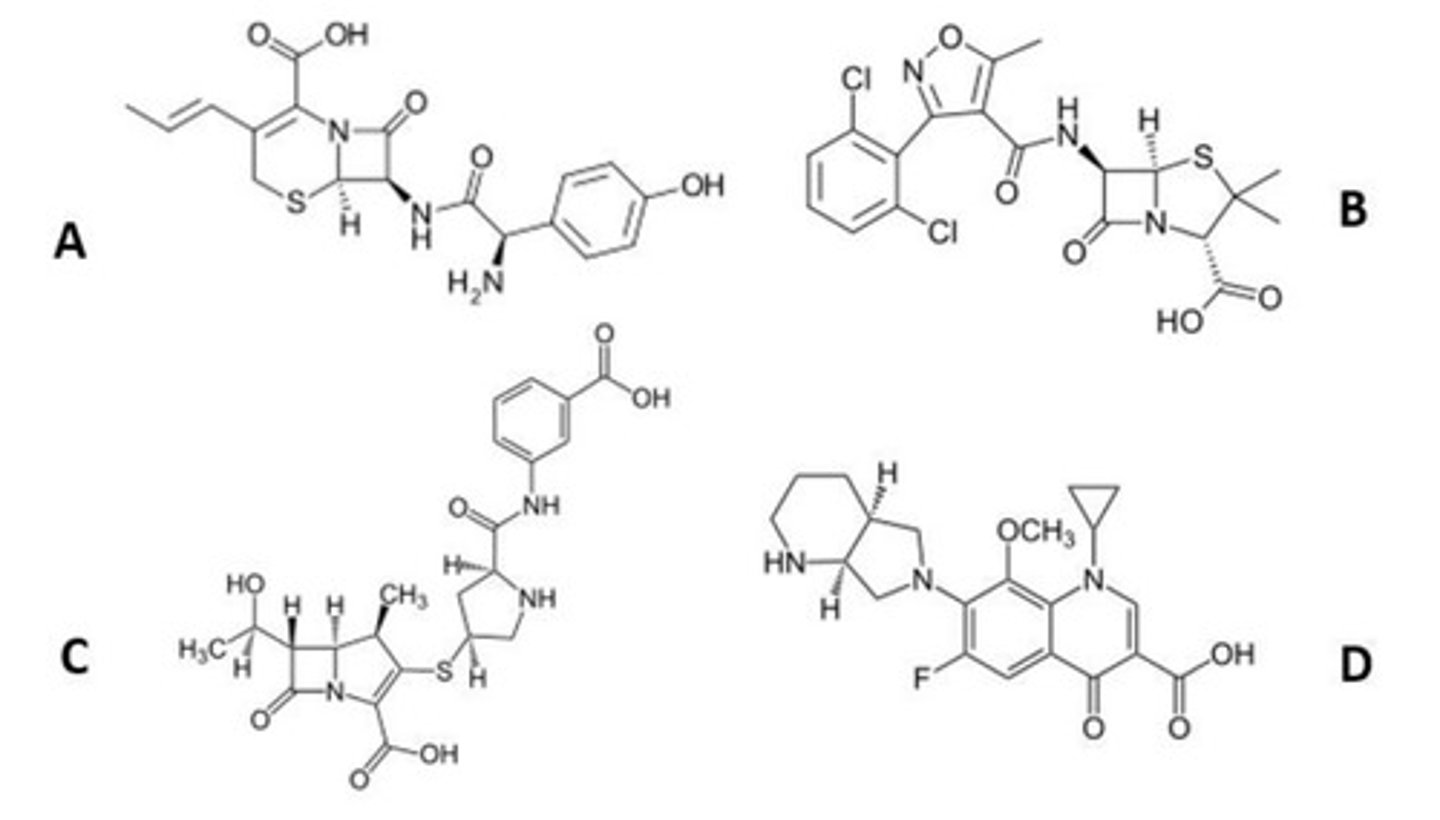
d. beta lactam fused to a dihydrothiazine ring
Which pharmacophore correctly describes ceftazidime?
a. monobactam
b. carbapenem
c. beta lactam fused to a thiazolidine ring
d. beta lactam fused to a dihydrothiazine ring
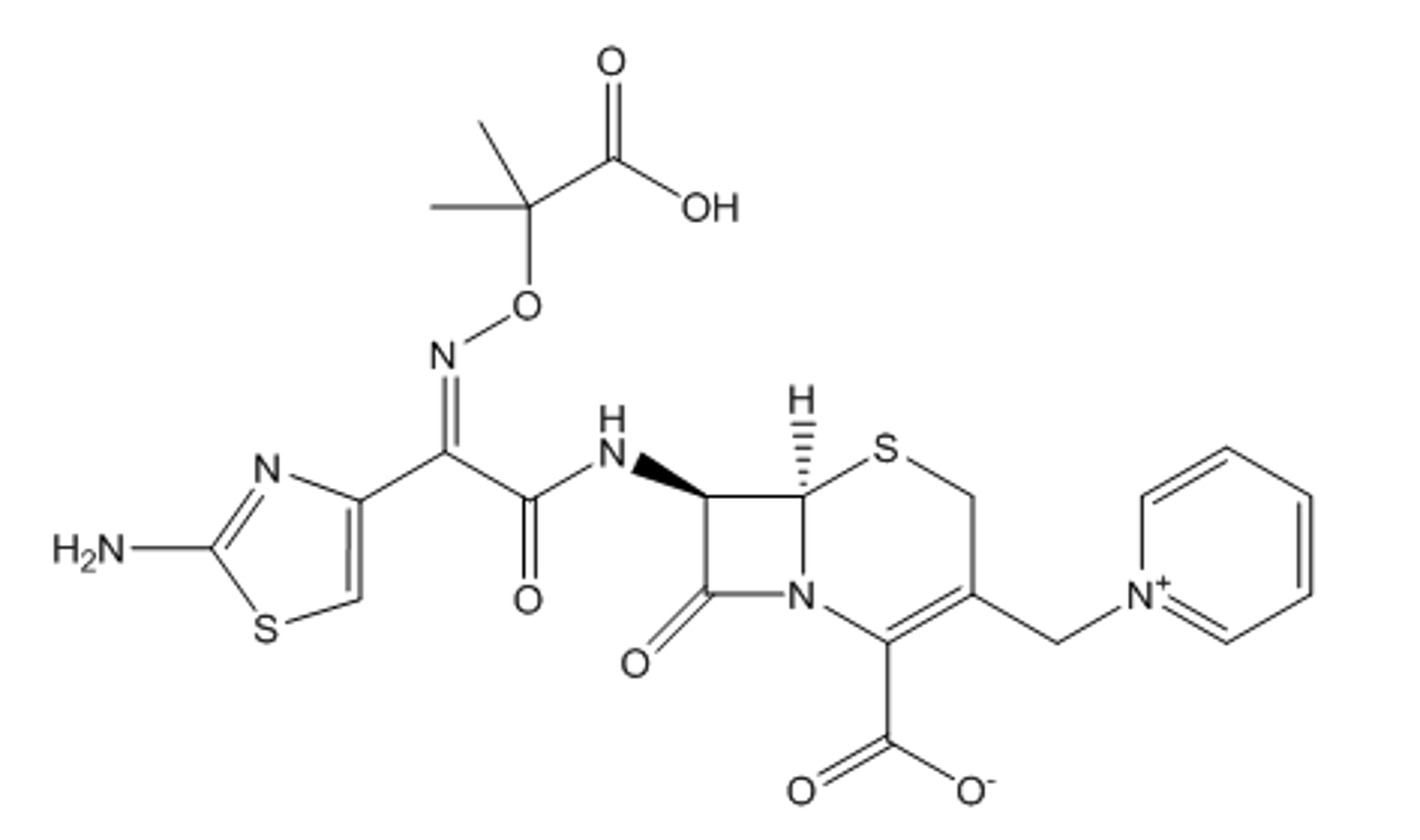
c. the sulfur is removed from the ring and functionalized to C3
Why is thienamycin a carbapenem antibiotic?
a. its azetidinone pharmacophore is unique
b. it contains a dihydrothiazine ring
c. the sulfur is removed from the ring and functionalized to C3
d. it contains a thiazolidine ring
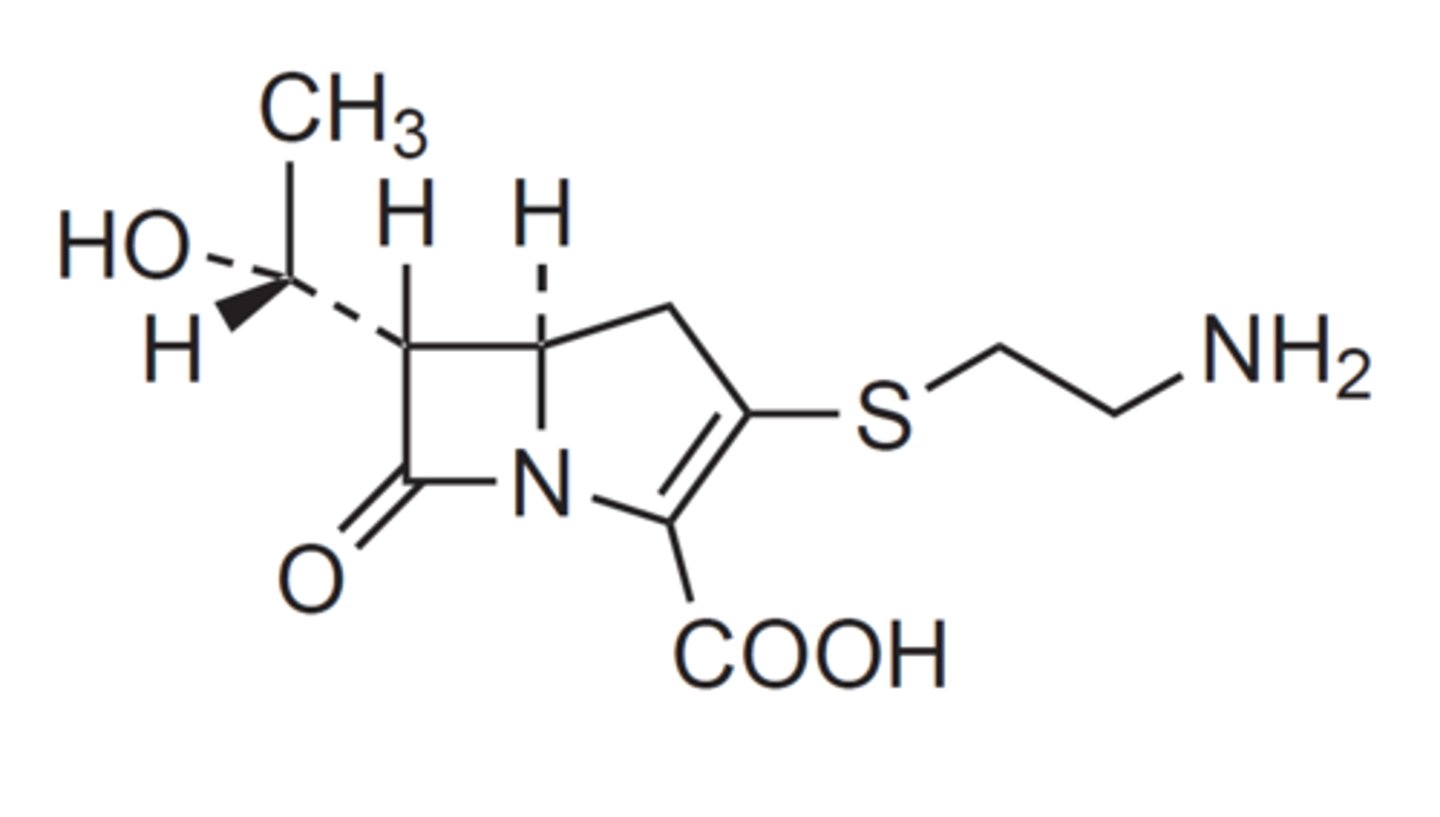
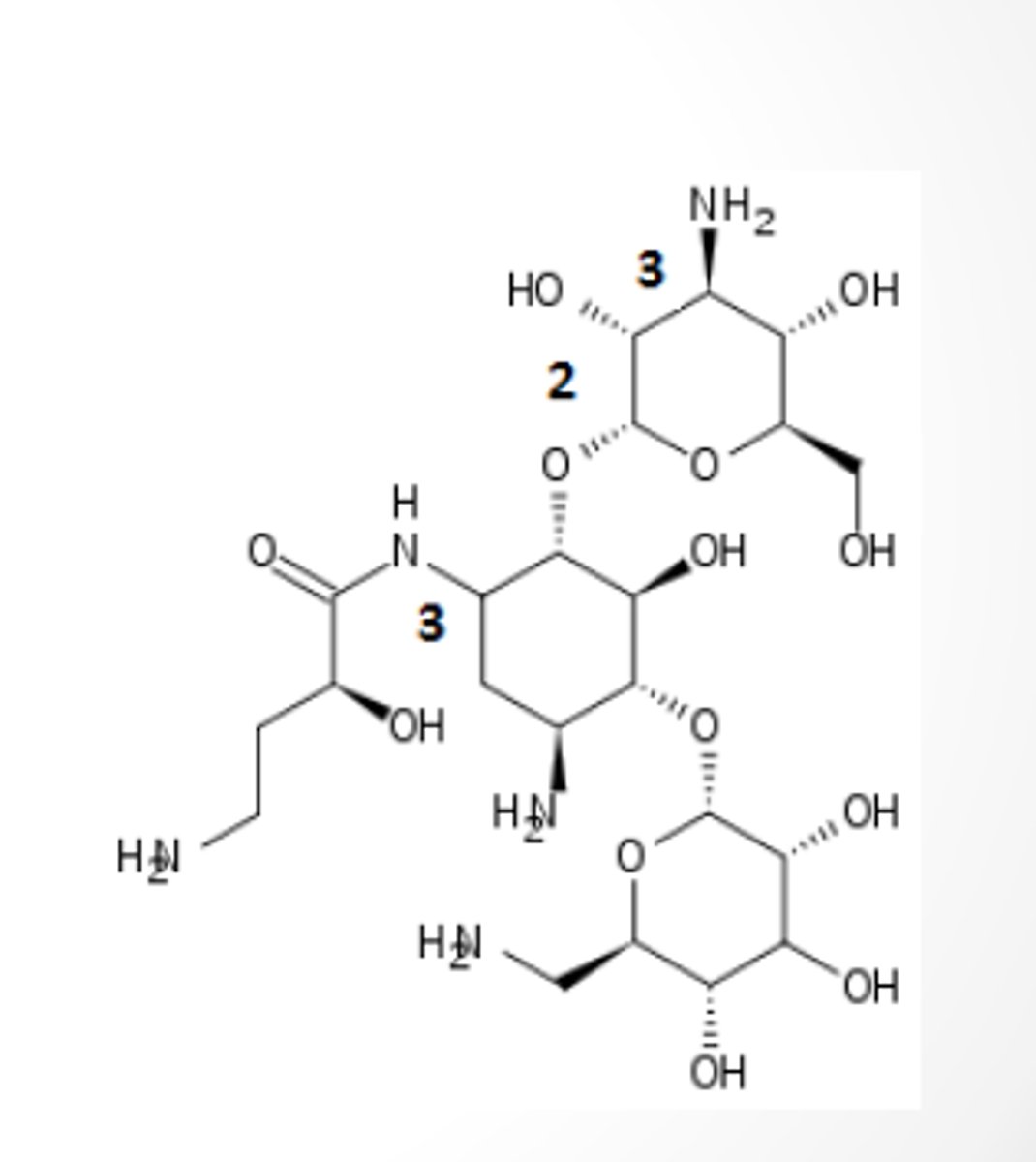
aminoglycoside
Class of drugs amikacin belongs in based on pharmacophore?
c. it contains an internal cyclic lactone ester
Which is the one true statement concerning azithromycin?
a. it is an aminoglycoside
b. it is a tetracyline
c. it contains an internal cyclic lactone ester
d. it is constructed from butyric acid ester

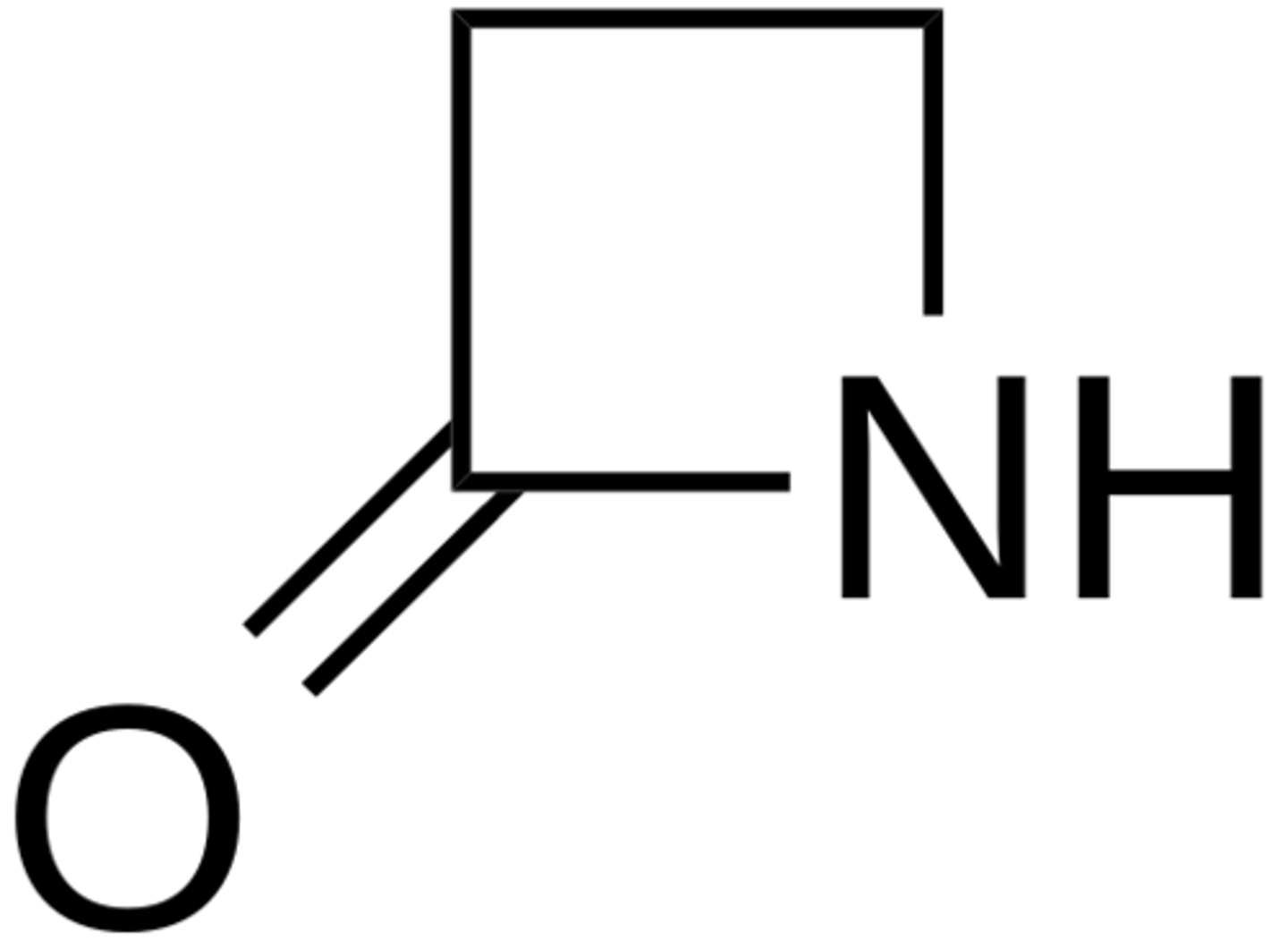
d. hemiacetal
Which is the one false statement regarding this structure?
a. beta lactam
b. cyclic amide
c. 2-azetidinone
d. hemiacetal
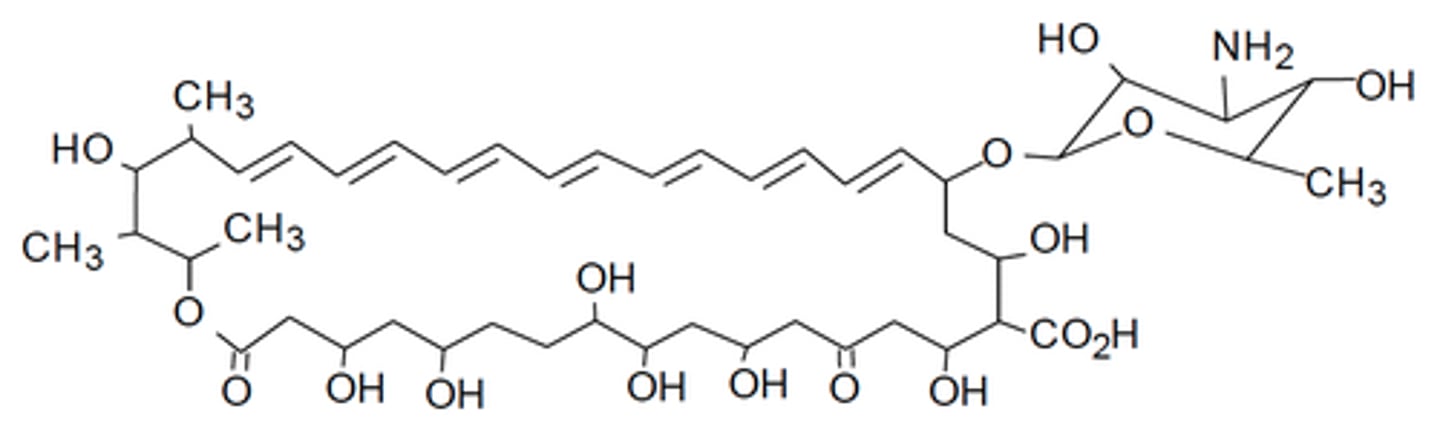
b. this drug prefers membranes containing cholesterol
Which is the one false statemetn regarding amphotericin B?
a. this is an antifungal agent
b. this drug prefers membranes containing cholesterol
c. amphotericin B has both hydrophilic and lipophilic regions
d. amphotericin B induces membrane pores
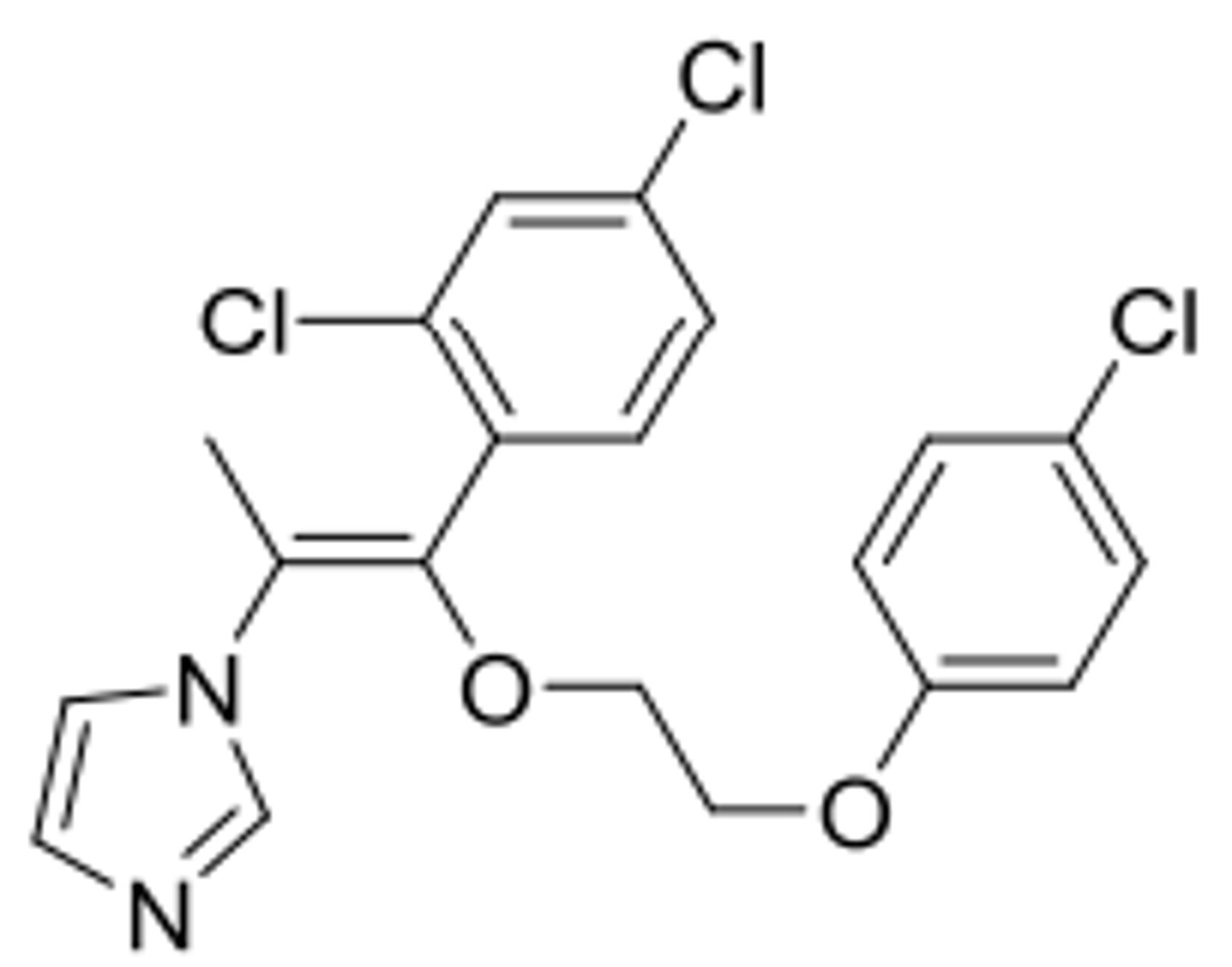
d. omoconazole inhibits UGT1AB
Which is the one false statement about the antifungal omoconazole?
a. this agent disrupts ergosterol synthesis
b. this is an antifungal agent
c. omoconazole bonds with CYP51 Fe
d. omoconazole inhibits UGT1AB
d. it is a squalene epoxidase inhibitor
Which is the one true statement regarding terbinafine?
a. it is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor
b. it is a disrupter of cholesterol synthesis
c. it is a beta adrenergic receptor antagonist
d. it is a squalene epoxidase inhibitor
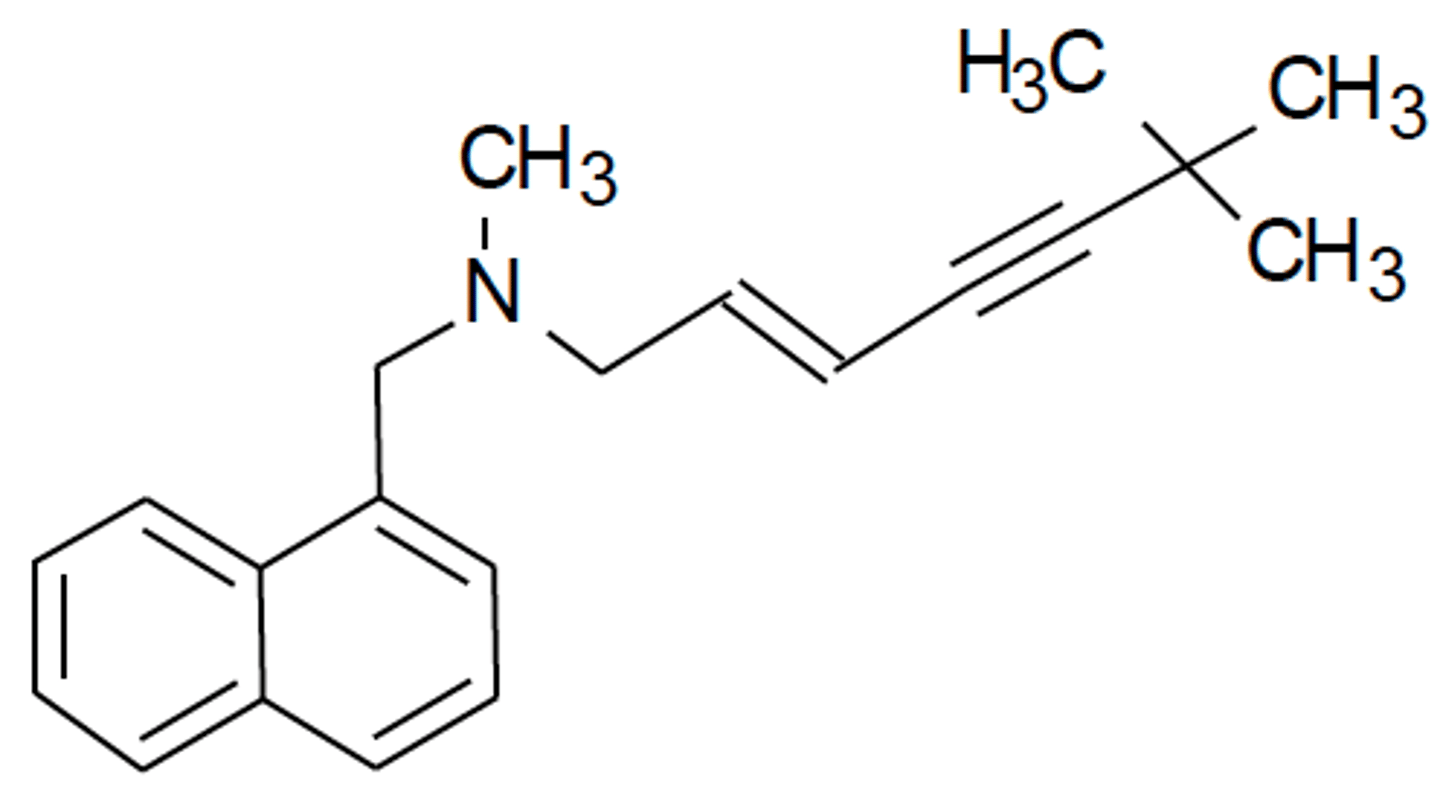
d. it is given orally with good F
Which is the one false statement about caspofungin?
a. it inhibits Beta-1,3-glucan synthase
b. it is a lipopeptide antifungal
c. it is a fungal cell wall synthesis inhibitor
d. it is given orally with good F
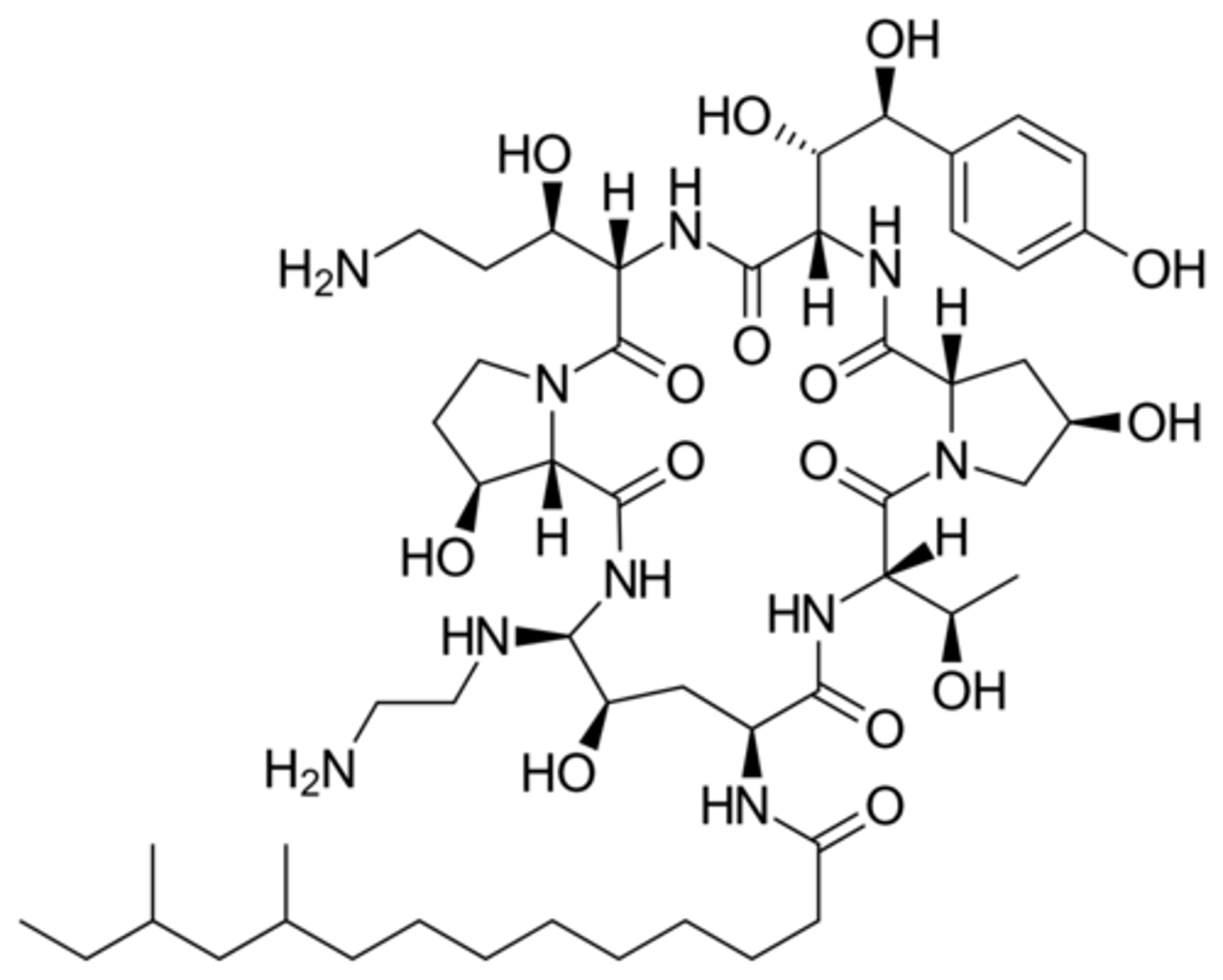
b. aspergillus
Which is the one non-protozoan infection?
a. leishmaniasis
b. aspergillus
c. trichomaniasis
d. chagas disease
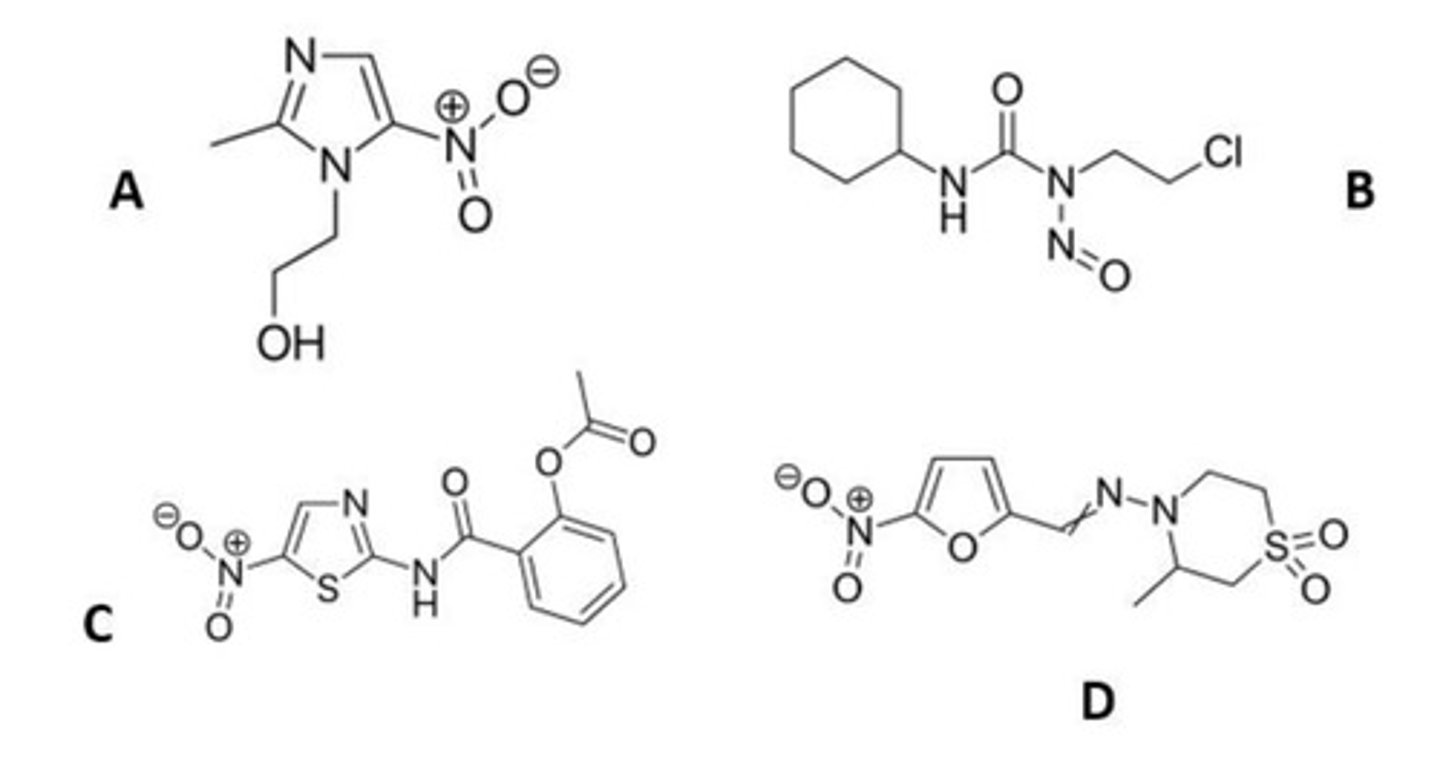
B
Which one of the following is not a nitroaryl antiparasitic?
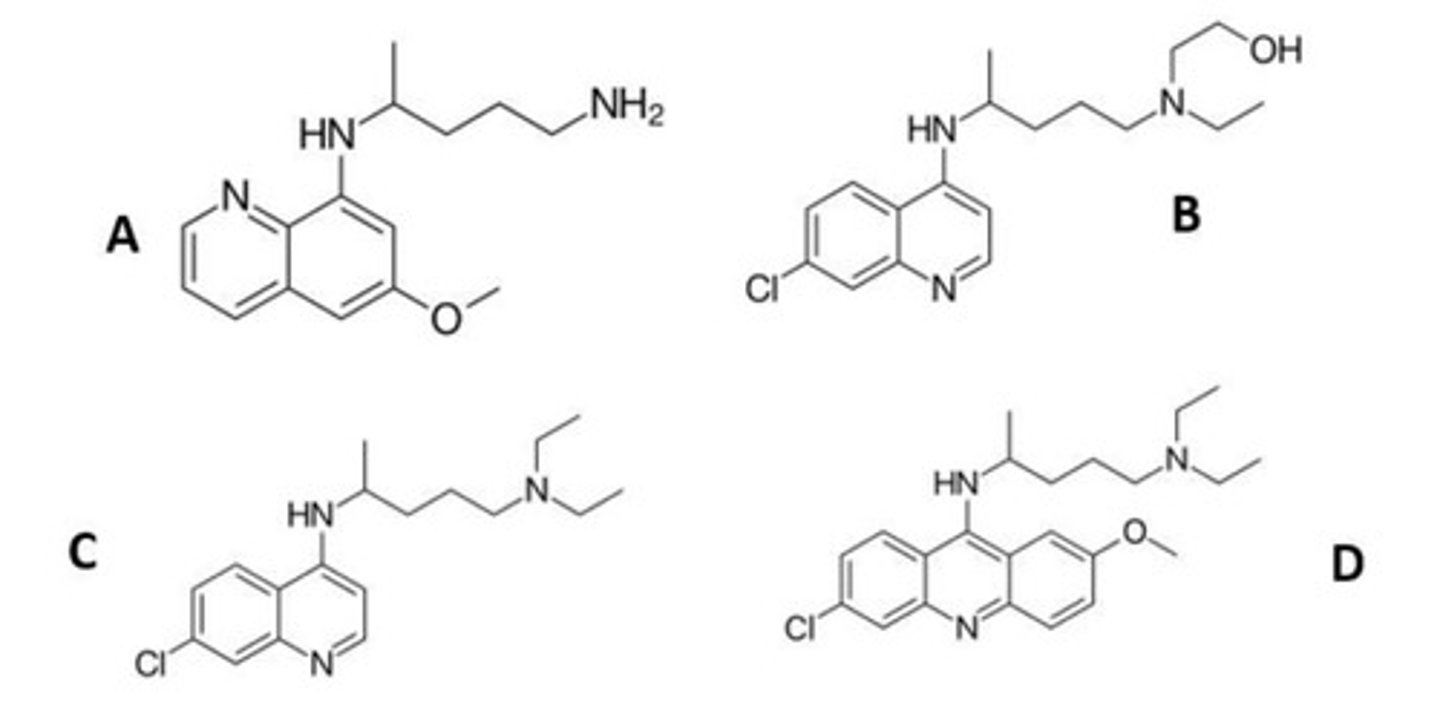
A
Which one of the following is not a 4-aminoquinoline antimalarials?
c. endoperoxides form adducts with Fe in hemozin
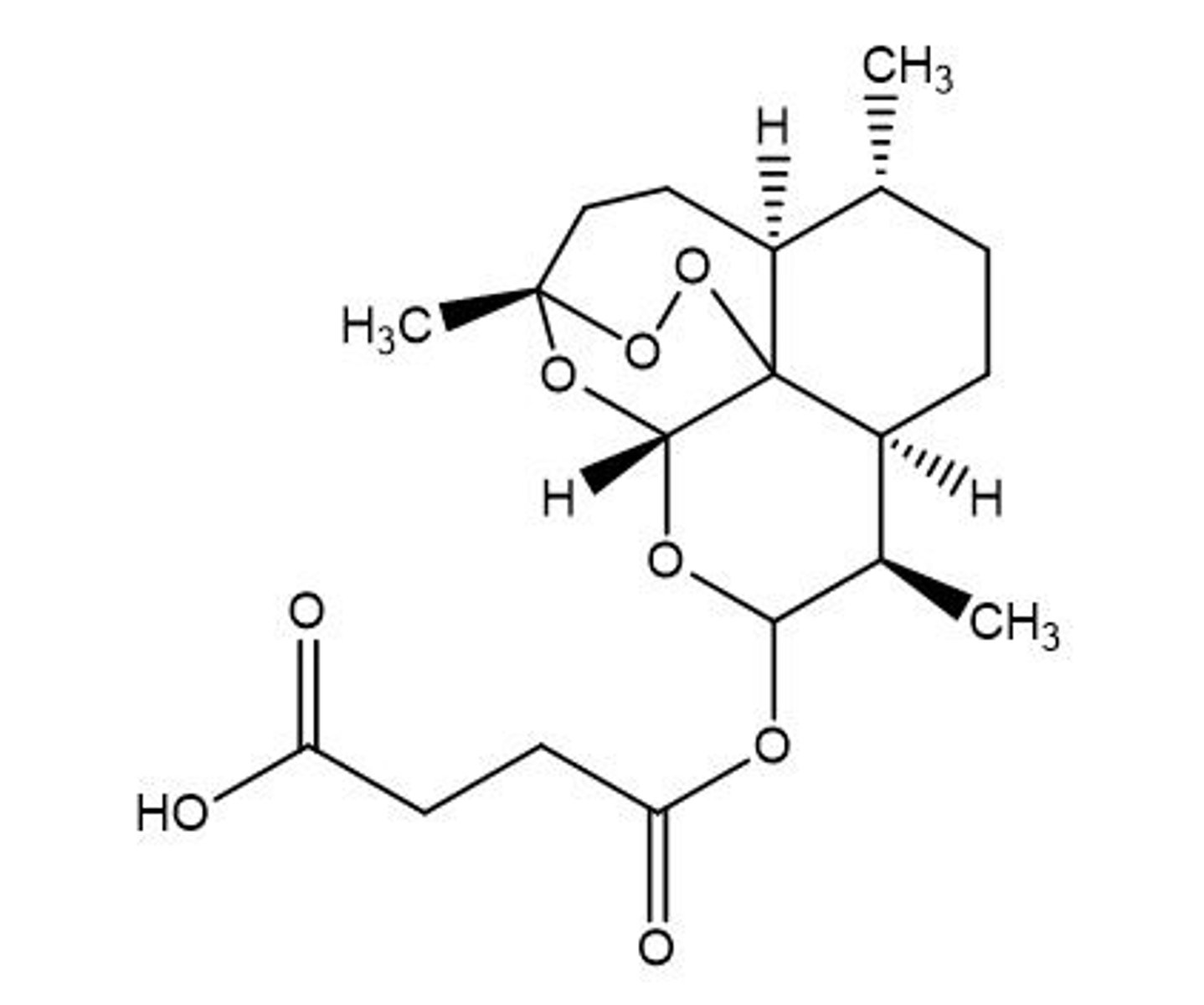
Which is the one true statement regarding artesunate?
a. it is seldom used to treat malaria
b. it forms hydrogen peroxide within the parasite
c. endoperoxides form adducts with Fe in hemozin
d. it is a synthetic agent
B
Which of these is not a benzimidazole antihelmintic?
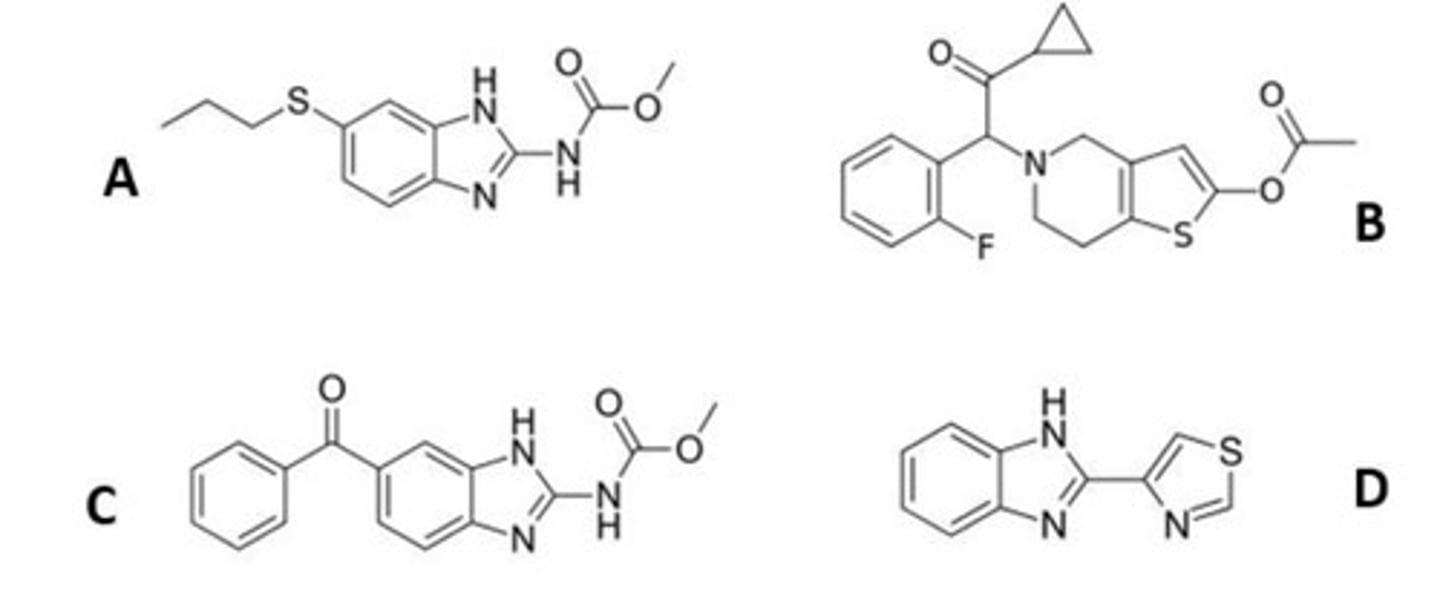
c. it blocks parasite calcium channels
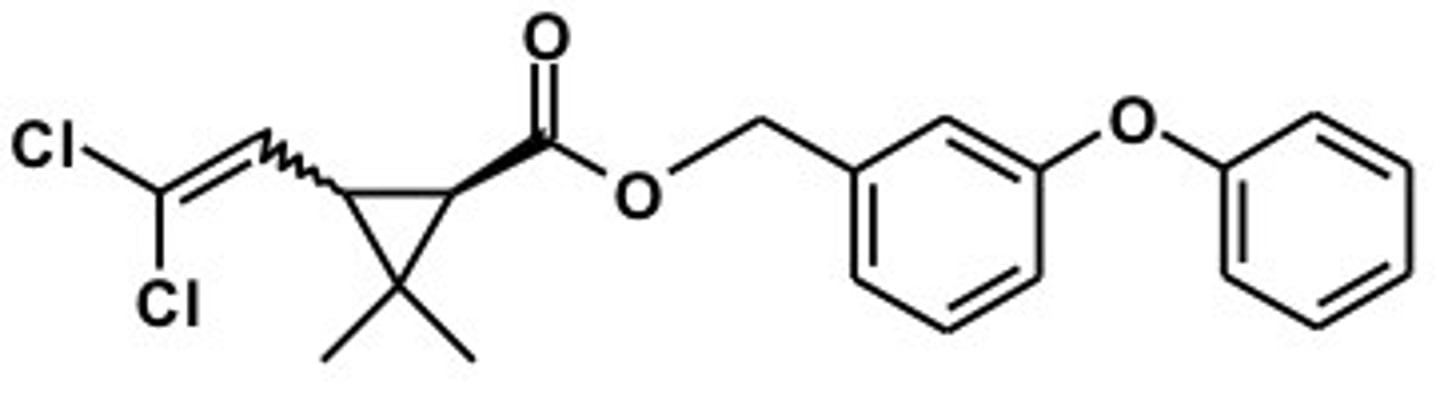
Which is the one false statement regarding permethrin?
a. it has a diphenyl ether backbone, like the thyroid hormones
b. it contains a dimethylcyclopropane
c. it blocks parasite calcium channels
d. it contains an allylic component
c. inhibits two different steps in folate synthesis
Logic behind the use of bactrim (1:5 trimethoprim: sulfamethoxazole) as an antibiotic?
a. inhibits identical step in folate synthesis
b. both bind to different sites on dihydrofolate reductase
c. inhibits two different steps in folate synthesis
d. both bind to different sites on dihydropteroate synthase
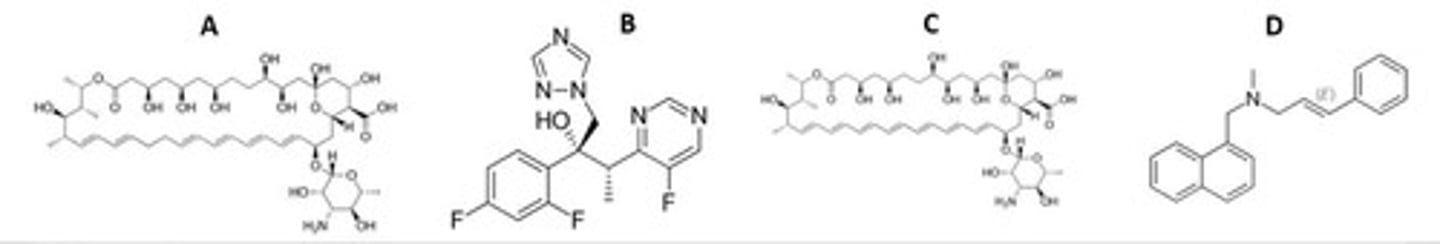
A and C
Which are predicted to intercalate fungal membranes?
B and F
Which are carbapenem antibiotics?
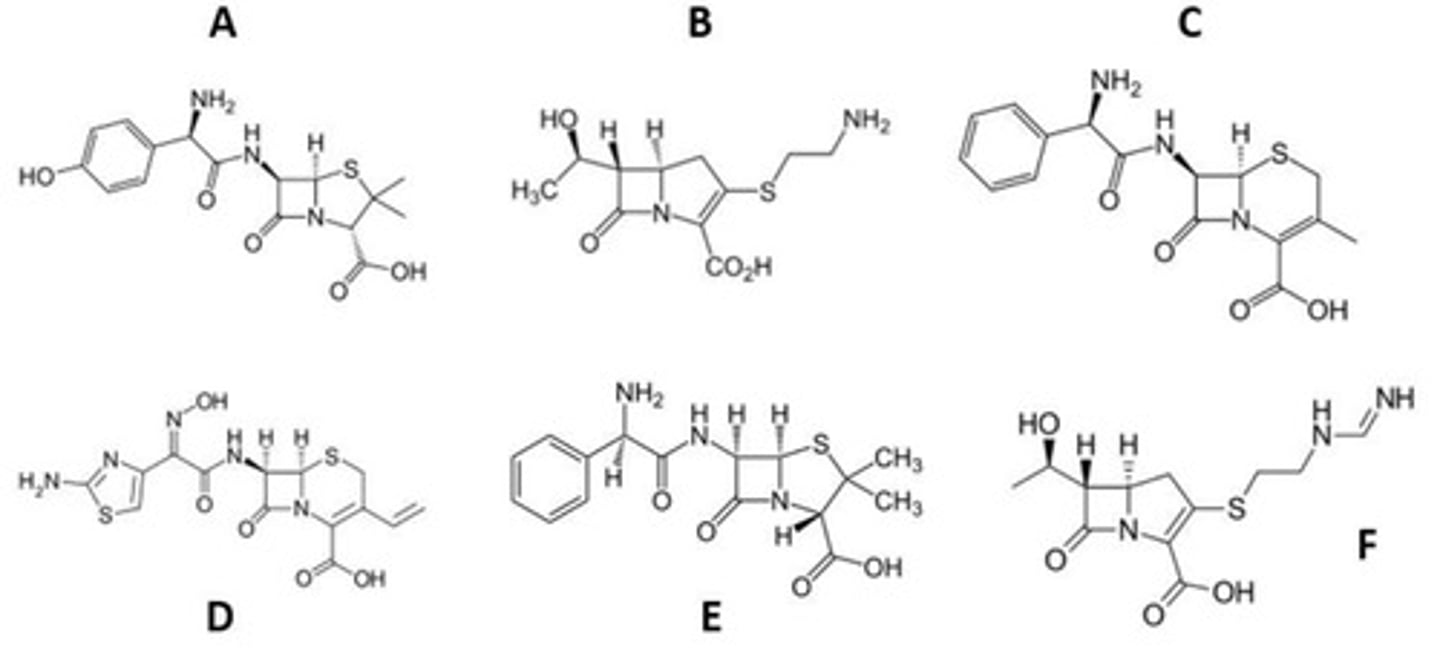
B and E
Which are thiazolidine antibiotics?
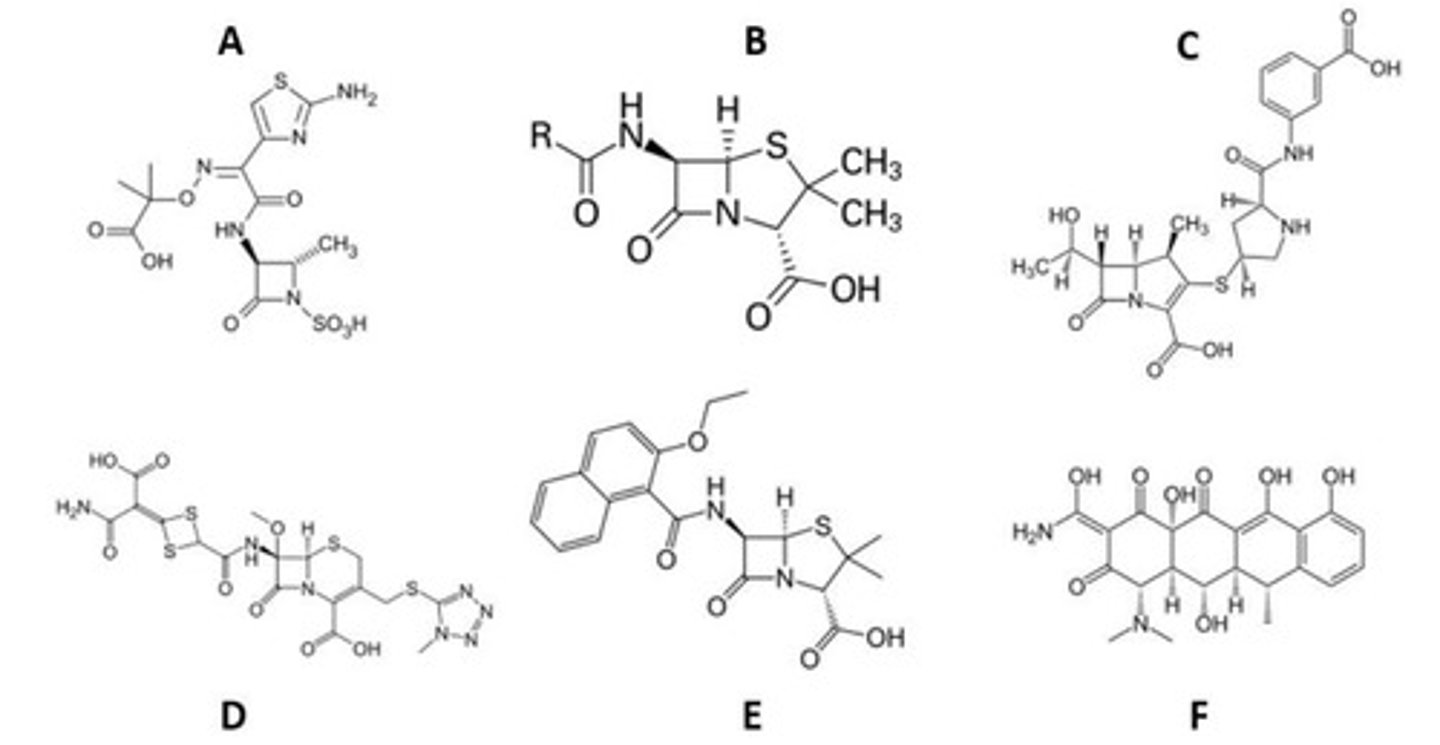
D
Which is the incorrect pharmacophore-drug class association?
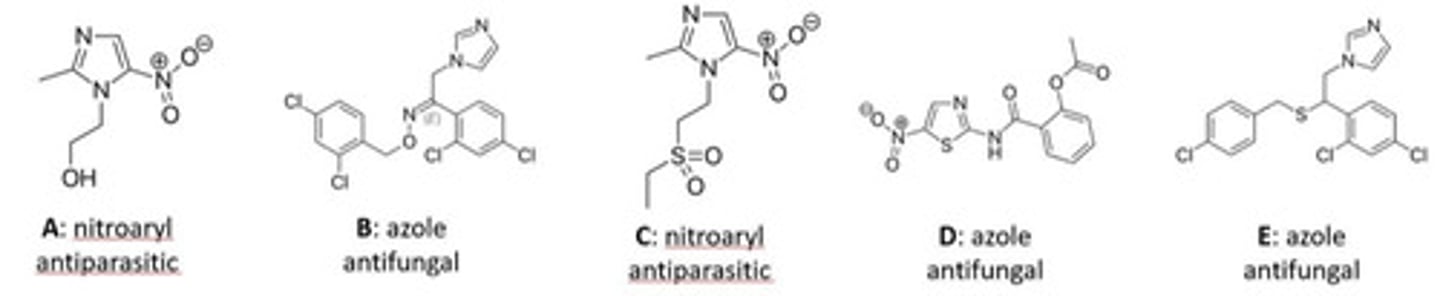
D
Which is the imidazole moiety of this benzimidazole antihelmintic?
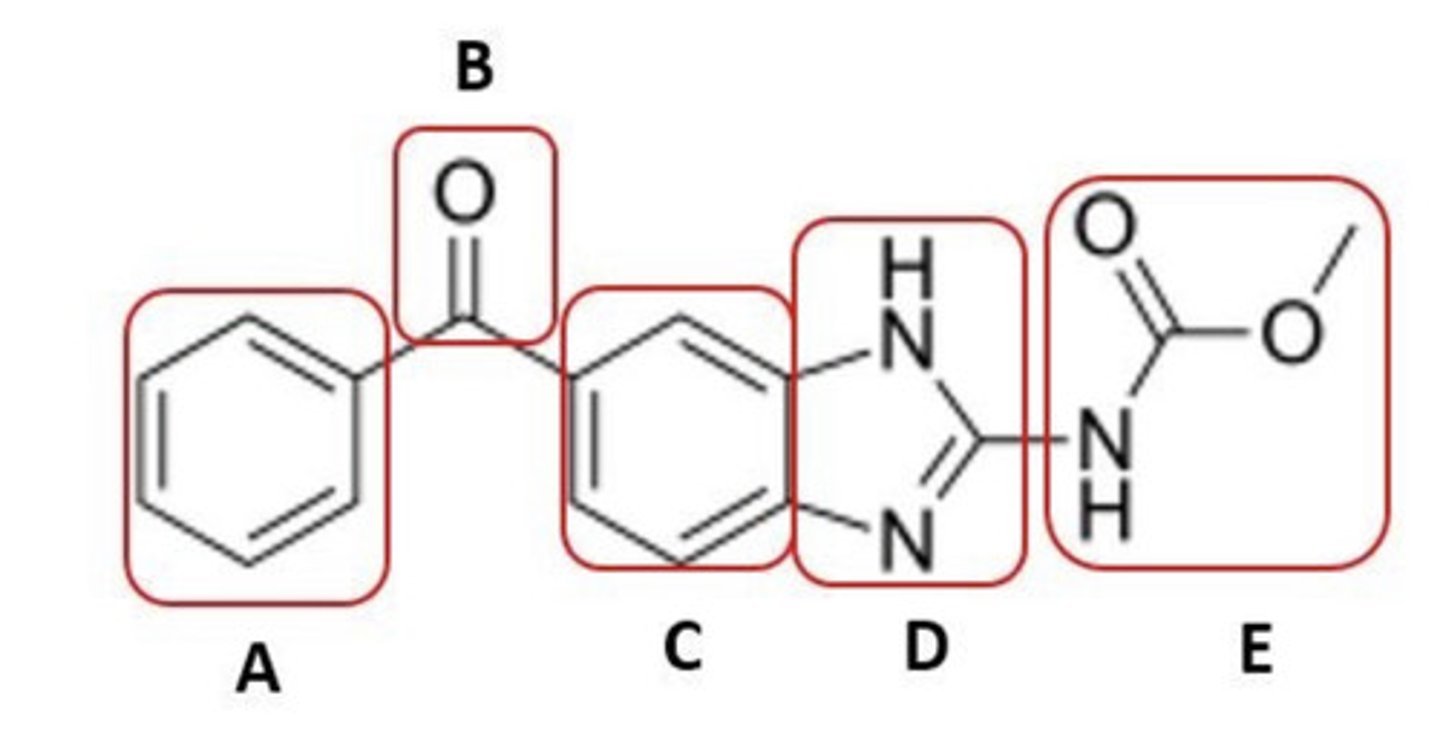
A and C
Which are the quinolones?
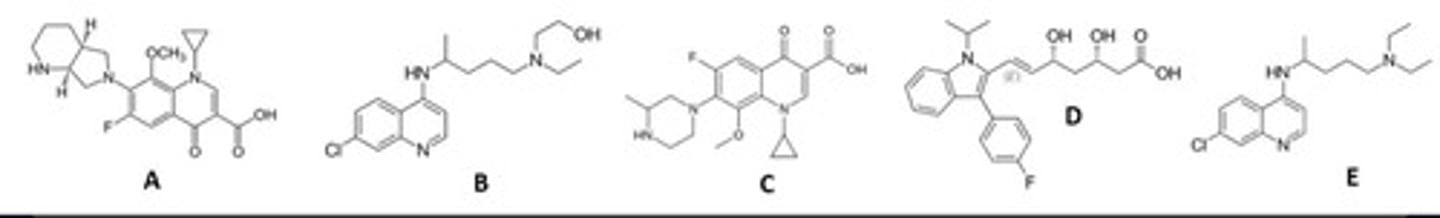
E
Which is the dihydrothiazine antibiotic?