A*R*C*C B*U* REVIEWER PART 1 (Plumbing System)
1/106
Earn XP
Description and Tags
From recorded lecture video (2024)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
Plumbing system
The work or business of installing in buildings the pipes, fixtures, and other apparatus for bringing in the water supply and removing liquid and waterborne wastes.
Water supply piping
Plumbing system which provides and distributes water to the different parts of the building, for purposes of drinking, cleaning, washing, culinary, etc.
Sanitary piping system
Piping which conveys sewage and other liquid wastes away from the building to the point of disposal
1-2%
Slope for drainage pipes going to the means of disposal in a sanitary piping system
Septic tank
Widely used means of disposal
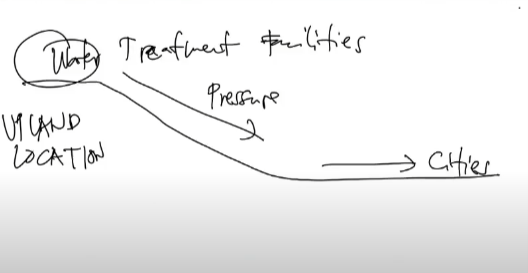
Upland location
Preferred location for public water treatment facilities in cities
20-30 psi
Local water pressure standard of public water systems in cities (international standard is 40-50 psi)
Riser
Water supply pipe that extends vertically one full storey or more to convey water
Downfeed pipes
Pipes with smaller diameter than risers that utilize gravity to convey water from overhead water supply
7 days
Maximum number of days where the capacity of a water tank can service a hospital
Gas, Electric, Solar Type Water Heaters
Storage or tank type water heater categories in hot water supply system
In-line type, point of use type (latter can be divided into multi-point or single-point types)
Instantaneous (tankless) categories in hot water supply system
Multi-point water heater
Type of electric water heater that can connect to multiple fixtures for instantaneous supply of hot water
In-line type water heater
Type of water heater used in multi-unit buildings such as condos and hotels to supply hot water through connecting to a main pipe supplying to multiple room units
Water pump
a mechanical device or plumbing equipment that utilizes energy, usually by converting electrical energy into mechanical (hydraulic) energy, to move, transfer, convey, lift, circulate or pressurize water in a system of pipes, devices or vessels (tanks).
Centrifugal pump
Water pump best used for moving large volumes of water at low-to-medium pressures (40-50 psi); good for steady flows, low-to-high discharge pressures, and dirty, abrasive, or partly solid liquids; used in large buildings
Positive displacement pump
Type of water pump that displaces a set volume of water with each turn of the pump; usually used as a construction pump
Rotary pump
Type of water pump that is best for moving viscous or high-pressure liquids; good for steady flows, medium discharge pressures, and small-to-medium capacities; not good for abrasive liquids
Reciprocating pump
Type of water pump that is good for high discharge pressures and small capacities, clean and clear liquids, and pulsing flows; therefore not good where pulsing flows are undesirable
Submersible pump
Type of water pump that consists of one or more pump stages driven by a closely coupled motor designed for submerged operation; useful in dewatering tunnels, foundation pits, trenches, and similar locations
Helical rotor pump
Type of water pump that consists of a spiral rotor that rotates in a sleeve, trapping water between the rotor and the sleeve, and forcing it to the outlet end of the sleeve
Jet pump
Type of water pump that combines centrifugal and ejector pumps; economical for low-volume facilities and commonly used in wells
Sump pump
A pump (as in a basement) to remove accumulations of liquid (such as rainwater) from a sump pit
Booster pump
A pump which is used where pressure is low and needs to be increased
Jockey pumps
Type of pump that is small and motor-driven, used in conjunction with main fire pumps to compensate for minor leaks in the fire protection system and automatically maintain stand-by pressure.
Turbine pump (vertical)
A type of pump consisting of one or more centrifugal pump stages driven by a vertical shaft, connecting the pumping assemply to a motor mounted at the surface; used as a fire pump
175 psi
Required water pressure for sprinkler system with jockey pump
G.I. pipe
Pipe material usually used for sprinkler system with jockey pump
3/4” ⌀ (19 mm)
Minimum fixture feed pipe size for water heater
1/2” ⌀ (13 mm)
Minimum fixture feed pipe size for kitchen sink (main pipe), washing machine, shower, water closet (main pipe)
3/8” ⌀ (9.5 mm)
Minimum fixture feed pipe size for kitchen sink (flexible hose), water closet (flexible hose)
Piping system
System that consists of pipe, tubings, and fittings
Copper, plastic, steel piping
Usual pipe materials for potable water; Steel piping (cold water) and copper piping (hot water) during the 70s-80s, with plastic piping used in modern applications
Copper piping
Potable pipe material used for gas pipes for cooking equipment supplying fuel, and medical gas applications
Copper piping
Potable pipe material with strong resistance to corrosion, and referred to as tubing because of its thin walls
Plastic piping
Potable pipe material produced from synthetic resins derived from fossil fuels, such as coal and petroleum, which does not present corrosion problems
Polyvinyl Chloride
Type of rigid plastic pipe called as PVC, widely used for low-pressure (10-15 psi) cold water
Solvent
This is used to connect PVC pipes to PVC fittings
Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride
Type of rigid plastic pipe used for both hot and cold water applications
Heat-fusion machine
This is used to connect rigid-form plastic pipes through the use of heat
Unplasticized Polyvinyl Chloride
Type of rigid plastic pipe also known as uPVC and can be used for hot and cold applications
Polybutylene
Type of plastic pipe that is widely used in indoor cold water piping; can be in roll form (60 meters per roll) and in rigid form
Low Density Polyethylene
Type of roll-form plastic pipe known as LDPE that is widely used in cold water applications
High Density Polyethylene
Type of plastic pipe known as HDPE that is in rigid form that is widely used in cold water applications
Barbed tee
Pipe fitting that is used in roll-form plastic pipes
Polypropylene Random Copolymer Pipe
Type of rigid plastic piping used in multistory applications supplying hot and cold water
Steel piping
Pipe material that is available in galvanized or black types in standard, extra heavy, and double extra heavy weights; widely used in fire protection systems
Threaded
Term referring to grooves that are found in steel pipes and fitting ends for connection
Potable water
Grade of water that is usually treated and suitable for drinking, mainly supplied by public water services
Rainwater
Grade of water that pertains to stormwater from precipitation
Graywater
Grade of water that is considered as wastewater not from toilets or urinals, can be reused for watering plants
Blackwater
Grade of water that refers to water containing toilet or urinal waste
Dark graywater
Grade of water referring to water from washing machines with dirty diaper loads, kitchen sinks, and dishwashers; prohibited for reuse
Clearwater
Grade of water referring to backwash water from reverse osmosis water treatment; condensation from a cooling coil
Soil pipe
Any sanitary pipe which conveys the discharge of water closets or similar fixtures
Waste pipe
Any sanitary pipe that conveys only liquid waste free of fecal matter; smaller than a soil pipe
Vent pipe
Any sanitary pipe that provides flow of air to and from a drainage system, or to provide circulation of air to protect the trap seal from siphonage and backpressure
Stack
General term referring to any sanitary pipe (soil, waste, vent) in vertical orientation
Plastic piping
Most common sanitary pipe material used in high-rise buildings, providing that its use shall be in the discretion of the Designer/Master Plumber
Cast iron piping
Sanitary pipe material fabricated from a carbon and silicon alloy, used in mid-rise to high-rise applications for its low maintenance and durability (100-200 year longevity)
Hub
Term referring to an end of a cast iron pipe used to connect pipes and fittings, with an oakum filled to secure the connection
Abaca
Common material for oakum in securing hubs in cast iron piping
Hubless cast-iron pipe
Alternative to hubbed cast iron introduced in the United States that uses a rubber gasket to connect pipes and fittings
Galvanized wrought and steel piping
Types of sanitary pipe material that shall not be used underground
152 mm
Galvanized wrought and steel pipe shall be kept at least _____ above ground (NPCP, Sec 701).
Vitrified clay piping
Type of sanitary pipe material that is not used above ground or whenever a piping is pressurized
300 mm
Vitrified clay pipe shall be kept at least ____ below ground (NPCP, Sec 701).
Inlet pipe
Pipe in sanitary system that conveys potable water to fixtures
Trap
Refers to a fitting or device that provides a liquid seal to prevent the emission of sewer gasses without affecting the flow of sewage or wastewater through it
Trap arm
Refers to the horizontal pipe in between a sanitary trap and a a vent pipe
1 ½“⌀ (38 mm)
Trap arm and inlet pipe size for bathubs, bidets, sink (residential, commercial, industrial, school), urinal, wash basin (in sets),
2” ⌀ (51 mm)
Trap arm and inlet pipe size for floor drains, grease and oil interceptors, single-stall showers, urinals
3” ⌀ (76 mm)
Trap arm and inlet pipe size for sand and autowash interceptors, urinals, water closet (both public and private)
Pipe chase
Shaft space found in multistory buildings that contains soil and waste stacks, risers, horizontal branches, etc.; can also accommodate electrical and mechanical systems
Sewage disposal system
A system of collection, transportation, treatment, and disposal of sewage
Septic Tank
On-site sewage disposal watertight receptacle which receives the discharge of a plumbing system to partially remove and digest suspended solid matter through a period of detention
1.50 m
Minimum horizontal distance of septic tank from building/structure and on-site domestic water service line
15.20 m
Minimum horizontal distance of septic tank from water supply wells and streams
3.00 m
Minimum horizontal distance of septic tank from public water main
Aerobic Treatment Unit (ATU)
Sustainable sewage disposal alternative for septic tank that utilizes aerobic bacteria in a chamber to digest solid water
Sewage Treatment Plant (STP)
Refers to the apparatus, vessels, pumps, filters, pipeworks, etc. for treating raw sewage
Stormwater system piping
A system of pipes, fittings, devices, and appurtenances for removing storm water, rainwater, surface runoff, and underground seepage from precipitation
Downspout
Vertical portion of a stormwater system installed in the exterior or integrated within the walls or columns of a building
Catch basin
Box-like device installed at the base of a downspout that collects rainwater to convey it to storm drain pipes at ground level
Storm drain pipe
Pipe intended to collect rainwater or surface-runoff from a catch basin to convey to a place of disposal
Maintain conditions conducive to life safety, property protection, and minimized business interruption.
Fire Protection Objectives
(1) Detect a fire in a building or space
(2) Warn the occupants, and
(3) Supress the fires until the fire department arrives
Overall aim of fire protection system
Early detection and alarm system, means of egress, compartmentation, smoke control, emergency power, fire suppression system
Elements of fire protection
Fire extinguisher, standpipe, fire sprinkler
Elements of a fire supression system
Standpipe
Fire suppression vertical pipe system that delivers water supply for fire hose
Standpipe and fire hose system
Fire suppression system required for structures up to four storeys (can be retained when storeys exceed in some cases)
Sprinkler system
Fire suppression system required for structures exceeding four storeys
Steel Piping
Pipe material used for fire protection systems
Automatic wet system
Standpipe and fire hose system that has water supply within the pipes ready on demand, and therefore considered as the most effective and most reliable system
Automatic dry system
Standpipe and fire hose system that is normally filled with pressured air, with a hose valve required to admit water in the system; used in climate conditions where freezing may occur
Manual wet system
Standpipe and fire hose system that does not have water in the pipes, but is connected to a low-pressure water supply that must be pumped by the fire department for use
Manual dry system
Standpipe and fire hose system that does not have water in the pipes or in an attached supply, where the water is sourced externally from the fire department; commonly used in parking garages
Semi-automatic dry system
Standpipe and fire hose system that is similar to an automatic dry system, but a remote control at the hose connection is required to activate the valve to admit water into the system
Quartzoid
Type of sprinkler head that has a glass tube used to retain a water valve on its seating
Standard spray head
Type of sprinkler head that is most common and can be used in most occupancies and building uses