AEECO U2 test 4
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
income distribution & gov in the economy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
earned income
private income earned from work
unearned income
private income received from the ‘sale’ of household resources, e.g. rent, interest, dividends
minimum wage is set by…
fair pay australia
government transfers
pension, unemployment benefits, etc.
gross income
private income + transfers
disposable income
gross income - tax
social wage
goods and services provided for little to no cost by the government like public education, healthcare, use of roads, libraries, etc.
GST
a 10% tax on most goods and services
excise tax
a tax on products that are bad for society (alcohol, cigarettes, etc.) that the government wants to discourage
wealth formula
household assets - household liabilities
lorenz curve
displays the percentage of income earned (y axis) by the percentage of the population (x axis).
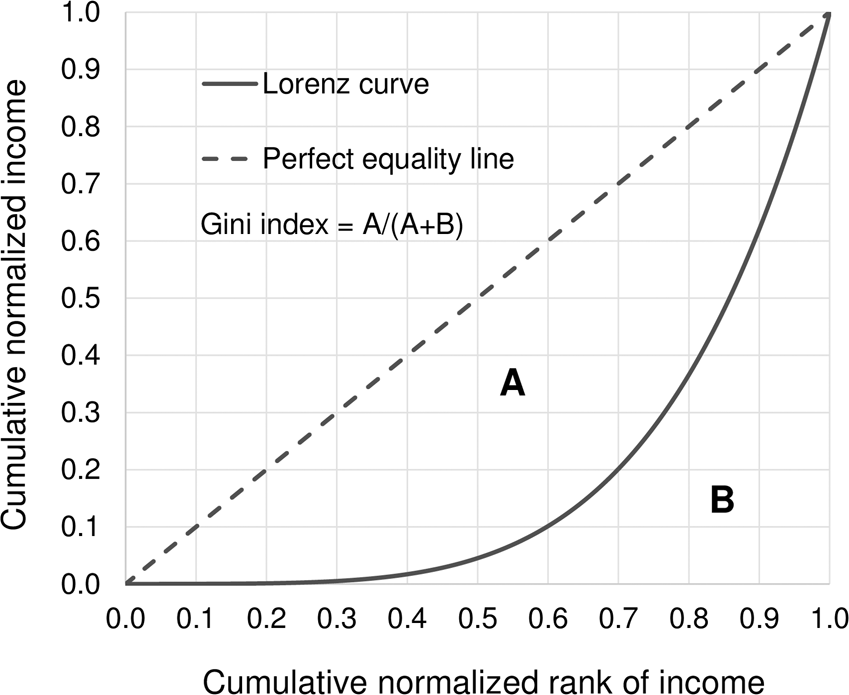
gini coefficient
area between lorenz curve and perfect equality divided by entire area under perfect equality. 1 = perfect inequality, 0 = perfect inequality
government policy objectives
sustainable economic growth, price stability, full employment, equitable income distribution, efficient resource allocation
sustainable economic growth target
3-4% GDP growth
price stability target
2-3% CPI growth
full employment target
4.5% unemployment
tax impact
where the tax is levied/collected
tax incidence
where the burden of the tax falls
direct tax
collected on taxpayer’s income. same impact and incidence
indirect tax
levied when people spend money or undertake certain activities. impact and incidence fall on different people
progressive tax
increasing proportion of tax as income increases
regressive tax
decreasing proportion of tax as income increases
proportional tax
constant proportion of income
specific tax
charged on the volume of sales regardless of price
ad valorem (value added tax)
levied as a percentage of price
types of taxes
income, goods & services, property & wealth
taxes on income
personal income, company, fringe benefits
personal income tax
direct and progressive, levied on all wage and salary income
company tax
proportional, impact is company, incidence is consumers
fringe benefits tax
levied on the value of non-cash benefits given to employees in addition to their salary or wage, e.g. company cars, schools fees for children
taxes on property and wealth
capital gains tax
capital gains tax
progressive tax, levied on profits from the sale of assets held for over 12 months, inflation adjusted. applies to shares, investment properties and some personal items if they were purchased with the intention of resale (e.g. jewellery)
taxes on goods and services
GST, excise duty, customs duty
customs duty
indirect, levied on imported goods
taxes on resources
resource rent tax, carbon tax, emissions trading scheme
resource rent tax
progressive, equitable, tax revenue share increases as the resource rent increases so the tax is based on ability to pay. as natural resources belong to the public, some profits should be returned to the public.
carbon tax
charged on the carbon content of fuels. higher prices discourage consumption of carbon.
emissions trading scheme
firms must purchase permits to allow them to use materials that pollute. they pay a charge for polluting.
income
flow of funds
wealth
stock of assets
the four largest types of gov expenditure are…
social security and welfare, health, education, defence
the four largest types of gov revenue are…
personal income tax, company tax, GST, excise and customs duty