population
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ccc 2nd year geography
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
what is birth rate
the number of live births per thousand of the population in one year
if birth is higher then date rat5e there is a natural increase
what is death rate
the number of deaths per thousand of the population in one year
when the death rate is higher then the birth rate a natural decrease will occur
the population cycle
demographic transition model
stage 1 of demographic transition model
high fluctuating
birth and death rates high
not economically developed
population grows very slowly
e.g. none at the moment

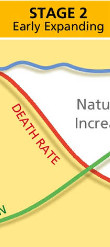
stage 2 of demographic transition model
early expanding
birth rates high
death rates fall
economy starting to grow
population grows quickly
e.g. nigeria
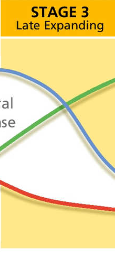
stage 3 of demographic transition model
late expanding
birth rate falls
death and birth rate gap becomes smaller
economy growing
population grows quickly
e.g. India
stage 4 of demographic transition model
low fluctuating
both birth and death rates low
economy is developed
population increases slowly
e.g. Ireland

stage 5 of the demographic transition model
natural decrease
low death and birth rates
population is in decline
economy is very well developed
e.g. germany

factors influencing population change
war
health
food
place of women in society
war
lots of people die
familys are split leading to less people being born
when a war is over and soliders return home birth rates increase
health
vaccines and antibiotics have helped many people survive once fatal illnesses
more access to doctors has helped people who are sick
death rates decline → population increases
food
machinery and farming methods → farmers can produce more food
fertilisers improved crop production
increases in food supply → fewer famines → higher population
place of women in society
equality between men and women → making decisions about own life
women have careers and are having less kids
women are have no job and are married off young have more kids
types of population structures
expansive
stationary
constrictive
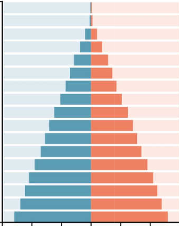
expansive
young and growing
looks like triangle
slowly developing countries
e.g. Nigeria
stationary
not growing
high life expectancy and low birth rate
narrow at top
developed countries
e.g. Ireland
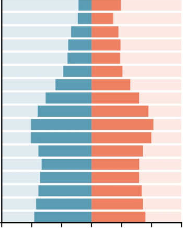
constrictive
becoming old and shrinking pop.
low birth rate
beehive look
developed countries
e.g. Germany
ireland population history
1841 republic of ireland pop. is 6.5 million
the famine ment 1 million died and 1 million emigrated
ireland pop. after famine
people left ireland for US, britian and canada
mainly young females left
had an impact on marriage and birth rates
irelands current population
developed country
pop. is growing slowly
stationary shaped pyramid
2022 = 5.1 million
future for irelands population
5.1 million in 2030
largest increase in dublin an mid east
nigeria pop. history
located in west africa
colony of british empire till 1960
up to laate 1700s active slave trade operating from there
nigeria modern era
less then 40 million
rapid and large po. increase in last 60 years
factors influencing pop. change in Nigeria
RELIGION
islam promotes large families and encourages early marriages and encourage ploygamy where a man take smore then 1 wife
MALE CHILD PREFERENCE
in many cultures in Nigeria male children are more highly valued then females
HIGH INFANT MORTALITY
ther is a need to have many babies in the hope that some will survive to work on the farm, support parents in old age and provide an income for the family