AQA GCSE Psychology Unit 2 - Perception
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Sensation
the processing of information from our sense receptors to allow us to experience the world around us
Perception
The organisation and interpretation of sensory information
Size constancy
When an object looks small so our brain scales up the image so the object is percieved at a normal size
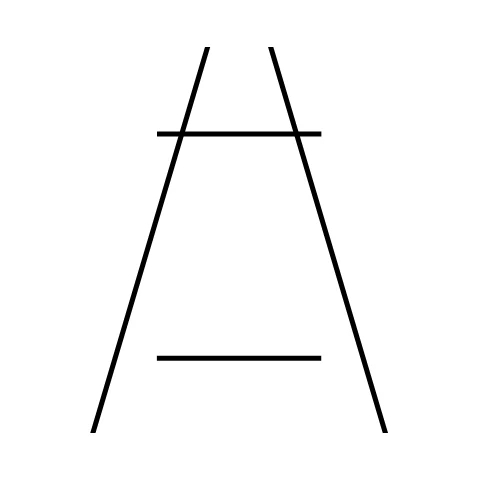
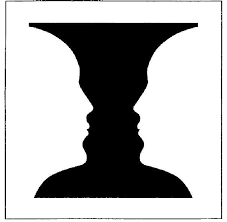
Ambiguity
when there are two possible interpretations of an image
e.g. in Rubin’s Vase
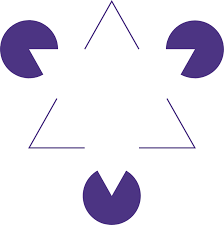
Fiction
when a figure is percieved even when it is not actually in the image
e.g.Kanizsa Triangle
Gibson’s Direct Theory of Perception
Sensation and perception are the same
our eyes evolved no notice precise changes
everything we can see gives us all the information we need
+ Gibson’s theory has been used to train pilots
+ supported by the baby cliff walk experiment
- struggles to explain illusions
Gregory’s Constructivist Theory of Perception
we use past experiences to interpret everything
the brain combines incoming information with what we already know to fill in the gaps
+ has good support by studies based on cross cultural research
- based on research with 2d images which are designed to fool us
- cannot show how perception appears in babies who cant have ‘learned’ it yet
Carpented world hypothesis
People from places where straight lines and right angles are orevalent features of buildings are more likely to fall for straight line illusions such as the muller-lyer or sanders parallelogram
Monocular depth cues
Linear perspective:when parallel lines appear to converge in the distance
Relative size: the further away an object is, the smaller it appears
Height in plane: objects higher up in the visual field appear to be further away
Occlusion: when one object is obscured by another object
Binocular depth cues
Retinal disparity: The eyes are separated by an interocular distance of 6cm which means each eye sees slightly different things
Convergence: less retinal disparity when seeing objects further due to the lines of sight for each eye converging
Perceptual set
a way of thinking set up by our context, culture, motivations and emotions
Factors affecting Perception: Culture
Perceptual set leads to a tendency to focus on particular aspects of the environment
This means that other aspects of the sensory environment might be noticed less
Hudson (1950)
ppts shown drawings of a man with a spear, an antelope and an elephant and asked what they see and what the man is doing, and whether the elephant or man was closer
White schooled were the best at percieving depth followed by black schooled who lead white unschooled with black unschooled in last
results suggest culture affects perception
Evaluation of Hudson
- Cross-Cultural research
task and instruction may have been incorrectly translated meaning some ppts didnt complete it correctly therefore decreasing the validity
- Problems with the method
ppts may have been more interested in the method of presentation than the actual procedure as some had never seen paper before
+ supports greogry’s theory
Factors affecting Perception: Expectation
expectation sets out an initial idea of what is going to be experienced, in a given situation which causes something specific to be percieved
Bruner and Minturn’s study
24 psychology students shown a series of letters, numbers or a mix which were flashed on a screen.
series ended with an ambigous 13/B figure which ppts were asked to draw
ppts who’d seen letters first more often reported it as a B
Expectation affects perception
Evaluation of Bruner and Minturn’s study
- used independent groups design
induvidual differences may have skewed results
-low mundane realism
study used an ambigous figure to test expectation which is not something we usually come across
+ real world application
study can explain errors where people act based on expectation such as when a us navy cruiser which knew there had been military activity in the area shot down a civilian plane
Factors affecting Perception: Motivation
Gilchrist and Nesberg (1952)
26 student volunteers
13 go hungry and 13 dont
ppts shown slides of a meal for 15 seconds and then shown the image again but dimmer and were asked to adjust the lighting back to normal levels
after six hours the hungry group adjusted the brightness 1 volt higher than the non hungry, and after 20 hours 2 volts higher
Evaluation of Gilchrist and Nesberg (1952)
- low populational validity
sample was 26 student volunteers which is not a representative sample and therefore decreases validity
- low mundane realism
participants were asked to judge pictures of food rather than real food and judging brightness isnt something we do in an everyday situation
+ support from similar studies
sanford (1936) found that a longer a person had been deprivedfrom food, the more likeley they were to percieve ambigous brown blobs as hamburgers
Factors affecting Perception: Emotion
Mcginnies (1949)
8 male and 8 female were shown a series of words flashed on a screen
ppts had to say the word out loud as they saw them and the time it took them was recorded
ppts required a longer time to say words that were ‘emotionally charged’
emotion is a factor in perception
Evaluation of Mcginnies (1949)
-low populational validity - 16 psychology students isnt a representative sample and so decreses the validity
- mundane realism - shouting words flashed on a screen isnt a usual task and so decreases the validity of the results
+ lab experiment with good control - tachiscoscope would flash the same amount of time