RAD111: Unit 1
1/193
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
194 Terms
Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen
Who discovered X-Ray?
Friday, November 8, 1895
When were X-Rays discovered?
Manmade ionizing radiation
What are X-Rays?
Ionization
Any process by which a neutral atom gains of loses an electron, thus acquiring a net charge
Radiation
Energy transmitted by waves through a space or medium
Diagnostic Radiography
Specializes in the use of X-rays to create images (Radiograph) of the body. Uses ionizing radiation
Computerized Tomography (CT)
Highly specialized equipment is used to view multi-planar images of the body using X-rays and computer generated images. Uses ionizing radiation
Sonography/ Ultrasound
Visualize structures through high frequency sound waves. Uses NONionizing radiation
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Highly specialized equipment uses strong magnetic field and radio waves to generate sectional computer images. Uses NONionizing radiation
Mammography
Radiographic imaging of the breast. Uses ionizing radiation
Interventional Technology
Assists the doctor during angiography, cardiac catheterizations, and angioplasty. Uses ionizing radiation
Nuclear Medicine
Injects radiopharmaceuticals into patient for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Usually involves imaging the patients organ function. Uses ionizing radiation
Radiation Therapy
Deliver planned treatments of high energy ionizing radiation to treat primarily malignant (cancerous) tumors
Radiologist Assistant (RA)
Advanced-level radiographer who extends the capacity of the radiologist in the diagnostic imaging environment
Board of Directors
The hospital is governed by the
______ of __________
VPs
Directors of various department report to the ____
Board
The VPs report to the _____
CEO- President
Responsible for managing the daily operations of the hospital and its entities; works directly with the board of directors to institute strategic planning for the hospital facility
Regulating Agencies (External)
Accredit hospitals and other health care institutions in the U.S.
-The Joint Commission (TJC)
-DNV
What are the two accrediting agencies?
The joint Commission (TJC)
What regulating agency regulates the quality & safety of care provided to patients?
DNV
What regulating agency has guidelines that assign responsibilities within the hospital?
" To care for others as we would care for those we love- to enhance their well-being and improve their health"
What is Riverside's mission statement?
Accreditation
Process through which an agency grants recognition to an institution for a program of study that meets specified criteria
ABHES (Accrediting Bureau of Health Education Schools)
Riverside College of Health Sciences is accredited by _______
JRCERT (Joint Review Committee on Education in Radiologic Technology)
RCHS School of Radiology Technology is accredited by _______
1. Promotes Excellence
2.Curricula & Guidelines
3. Elevate Quality & Safety of Patient Care
4. Reviews & Site Visits
The (4) purposes of JRECT includes.....
Certification
Process for development procedures to which certain private and all out-of-state post secondary institutions must adhere in order to receive approval to confer degrees, certification or diplomas in Virginia
SCHEV (State Council of Higher Education in Virginia)
Riverside College of Health Sciences is certified by _______. Which ensures quality and allows students to apply for federal financial aid
ARRT (American Registry of Radiologic Technologists)
Who certifies individuals in Radiography?
Licensure
The process by which a governmental agency (usually a state) grants permission to individuals to practice their profession
ASRT (American Society of Radiologic Technologists)
Membership provides a pathway to continued successful professional development,networking, keeps you up to date on changing technology, development of leadership skills, helps share your profession through legislation
VSRT (Virginia Society of Radiologic Technologists)
Virginia state level professional organization
Profession
A calling that requires specialized knowledge and intensive academic preparation, has a professional organization and ethical code of conduct, and serves a specific social need
Patient Bill of Rights
A document that states a patient has certain rights
ASRT Practice Standards (also known as Scope of Practice)
The standards provide role definition and identify Clinical, Quality, and Professional Standards of practice
Assault
Any willful attempt or threat to inflict injury on the person of another
Battery
any unlawful touching of another that is without justification or excuse
False Imprisonment
Conscious restraint of freedom of a person without proper authorization, privilege, or consent
Defamation
Holding up a person to ridicule, scorn, or contempt in a respectable and considerable part of the community by either Slander (spoken word) or Libel (written, published comments, pictures)
Autonomy
Theory that patients have the right to decide what will or will not be done to them
Respondeat Superior
"Let the master answer"
The "master" can be held liable for wrongful acts of the "servant," or employee, then causing injury during employed activities
Re ipsa loquitur
"The thing speaks for itself"
It becomes the radiographer's burden to disprove negligence is the patient is injured as a result from misperformance of a duty in the routine scope of practice
Invasion of Privacy
Discloses confidential information to unauthorized individuals
Informed consent
The patient is given enough information to make an educational decision about his or her health care. They are informed of the
-benefits of the procedure
-the alternatives to the procedure
-how the procedure will be performed
Implied consent
An emergency room patient is alone and unconscious, what consent is assumed?
-The patient must be of legal age
-The patient must be of sound mind
-The patient must give consent freely
-The patient must be adequately informed of the procedure about to take place
For informed consent to be valid, the (4) conditions are....
YES
But we are not able to let them see it, refer them to their physician
Can a patient view his/or her chart?
YES or NO?
And are we able to let them see?
Patient date of birth
Patient name
The most commonly preferred method to identify a patient for a radiography exam
-Name and MRN
-Patient DOB
-Date of Exam
-Rt or Lt maker
For medicolegal reasons, images are required to include (4 things)
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
Passed to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the health care system in processing health care information to provide privacy, security, and electronic transmission of certain patient health information
FERPA (Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act)
A federal law that protects the privacy of student education records
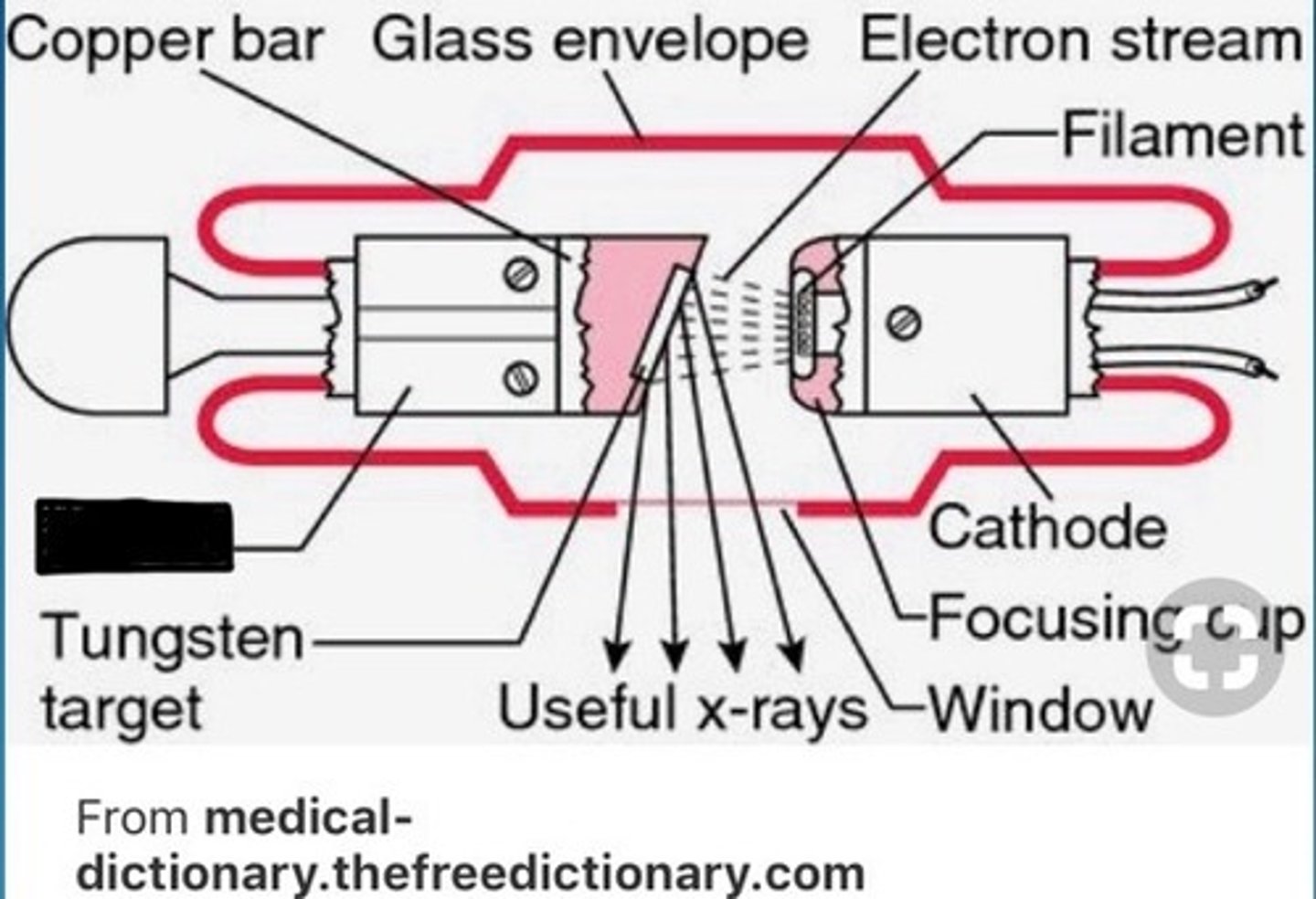
Anode
Positive end (no free electrons); contains the target to stop electrons
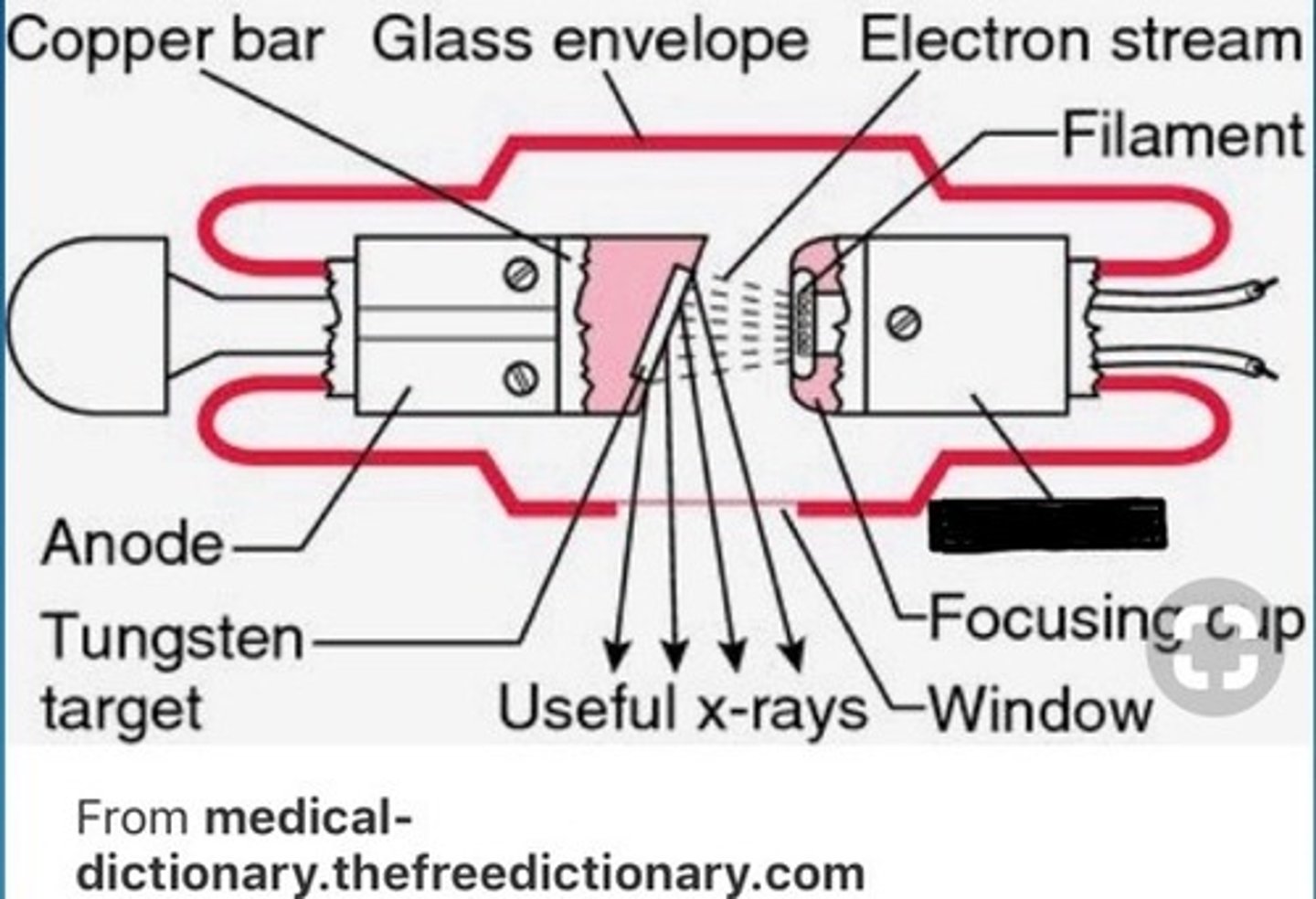
Cathode
Negative end (electrons negative); contains the filament
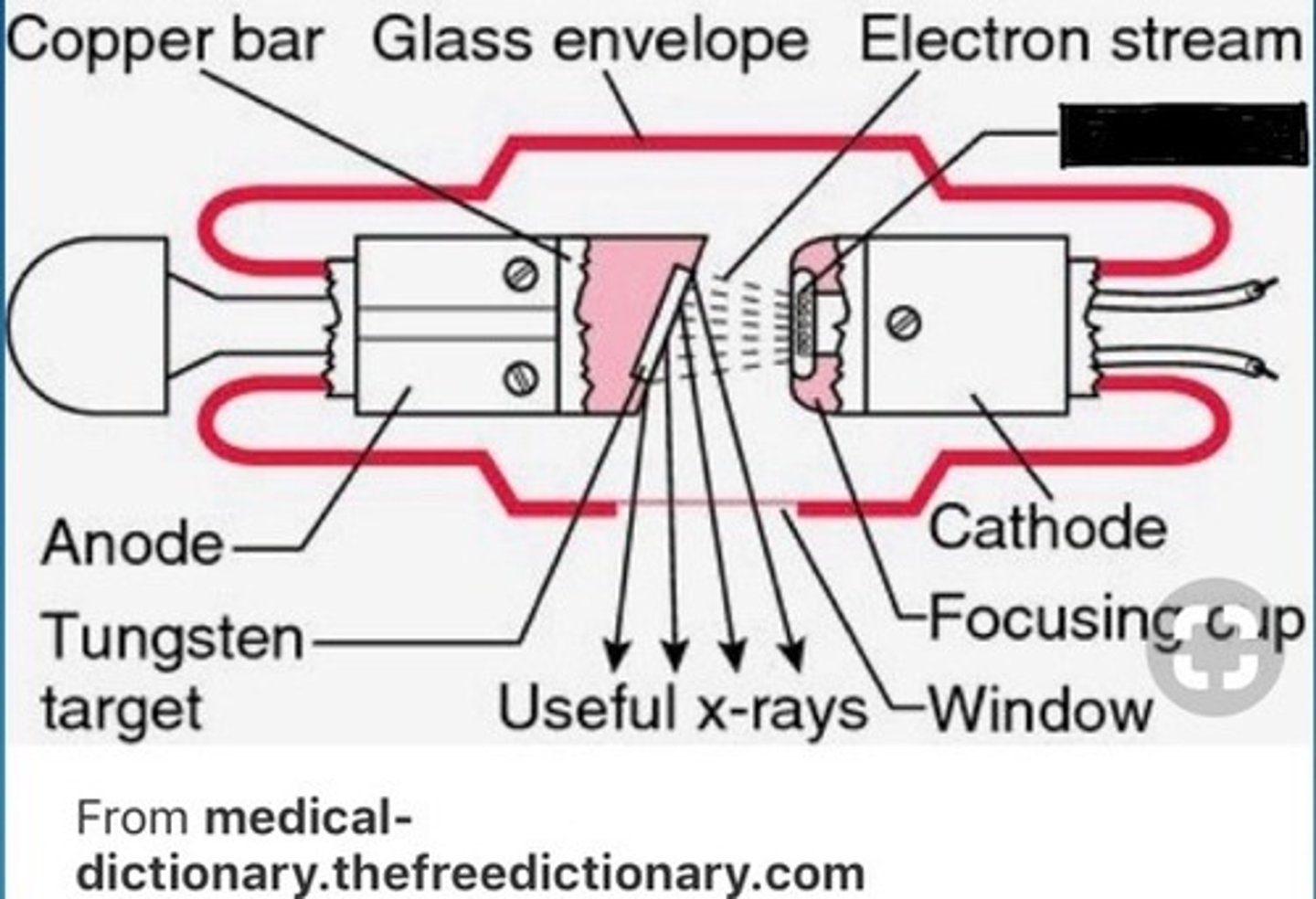
Filament
Source of electrons
Attenuation
Process by which primary radiation is changed (partially absorbed or scattered)
Collimation
Limiting the beam- Result in reduced patient dose, less scatter, and better deal
Contrast
The visible difference (variation) between adjacent densities
Density
The overall darkness (blackness) of the image or the amount of light that can shine through
Detail
Distinct representation of an objects true borders
Distortion
Misrepresentation of objects size or shape
Image Receptor (IR)
Intercepts the X-ray photons that exit the patient (captures the image)
Inverse Square Law
Mathematic formula that describes the relationship between radiation intensity and distance from the source of the radiation
Grid
Device consisting of thin led strips designed to permit primary radiation to pass while reducing scatter radiation by absorption
Kilovolt Peak (KvP)
Energy or x-ray beam. Measure of electrical pressure forcing current through tube. Controls penetrable ability
Millampere-seconds (mAs)
Amount of x-radiation produced in tube (Quantity)
Photon
Particle of radiant energy
Primary Radiation
Prior to reaching the patient
Radiolucent
Allows x-rays to pass through easily
Examples: Air in lungs, Skin, and very thin body parts
Radiopaque
Not easy for x-rays to penetrate and pass through
Remnant Radiation
The part of the beam that passes through the patient
Scatter Radiation
Interacts with the patient and changes direction
Source-to-image Distance (SID)
Distance between point of x-ray exiting tube and image receptor (IR)
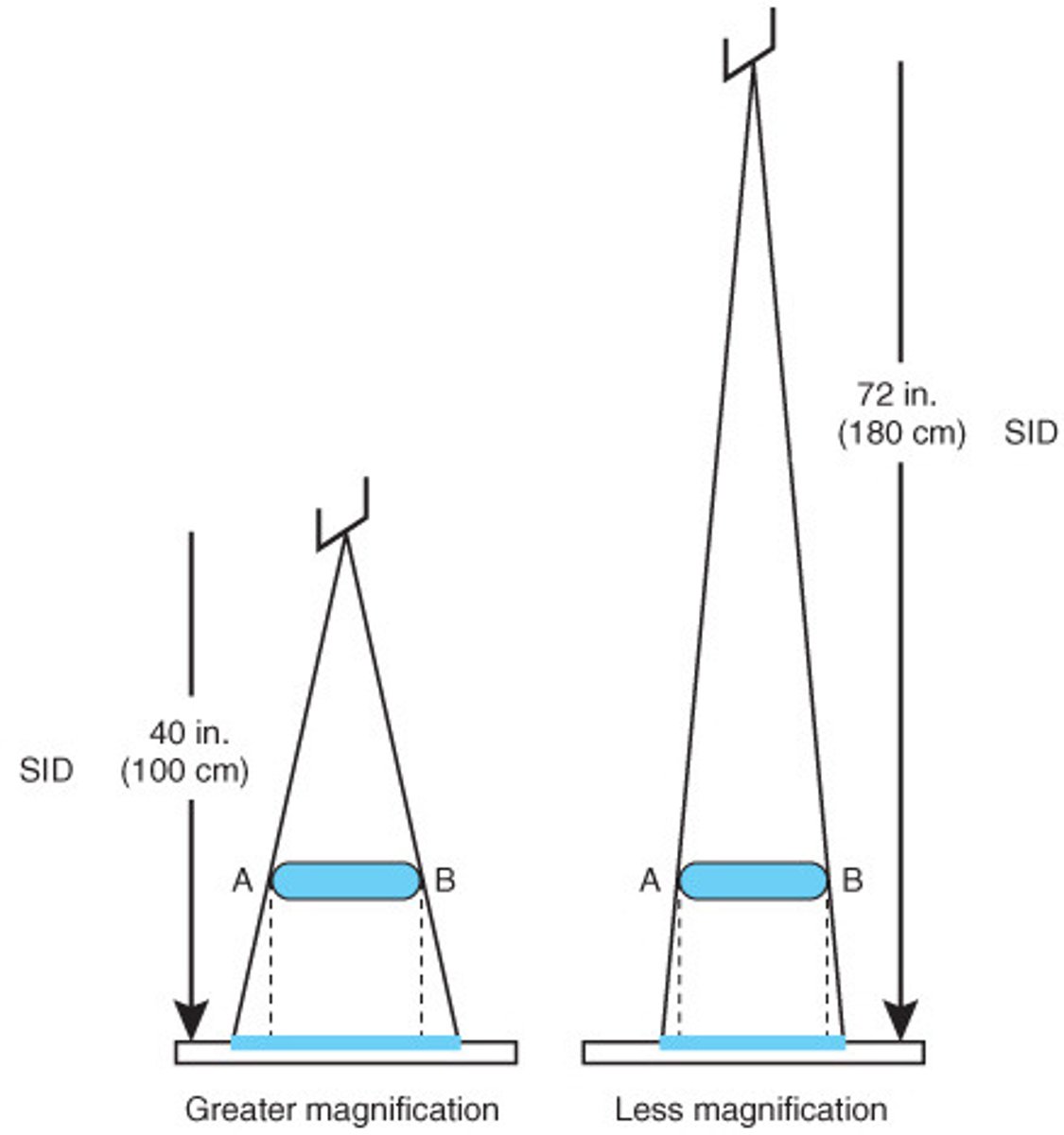
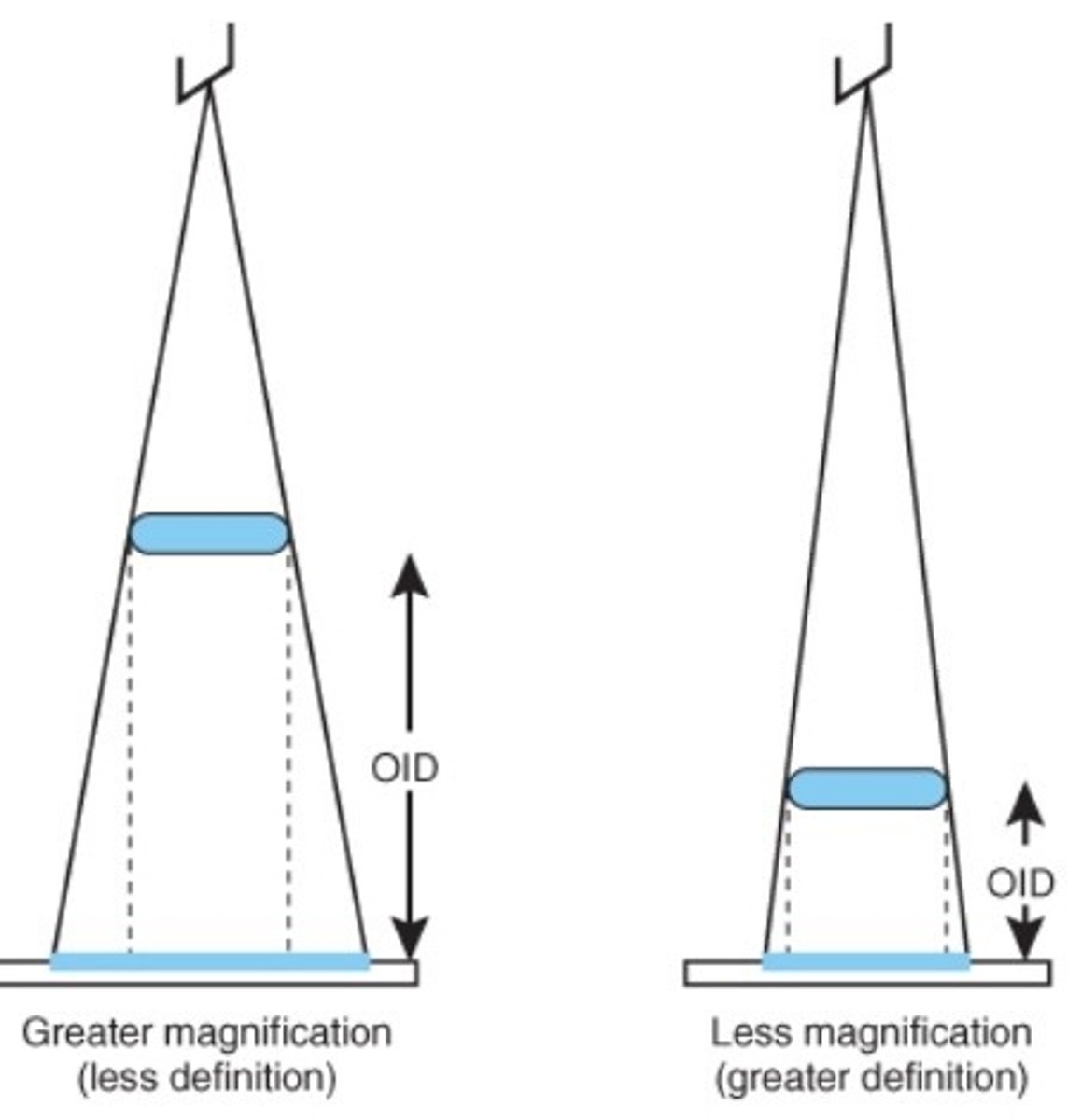
Object-to-image Distance (OID)
Distance between patient and image receptor (IR)
X-ray Tube
Where are x-rays produced
Roentgen (R)/ Coulombs per kilogram)
The amount of radiation exposure in air
Rad (rad) / Gray (Gy)
Radiation absorbed dose
Sievert (Sv)/Rem (rem)
Radiation dose equivalent
Curie (Ci) / Becquerel (Bq)
Radiation activity
As Low As Reasonably Achievable
What does ALARA stand for?
Time, Distance, Shielding
What are the Cardinal Rules of Protection?
Lead walls, Aprons, Glasses, Thyroid shields, Gloves
What are the 5 types of protective equipment used by radiographers?
DISTANCE
What is the best measure of radiation protection?
Annual 50 mSv
What is the annual dose limit for the Occupational population?
Annual 5 mSv
What is the annual dose limit for the General population ?
OSLD (Optically Stimulated Luminescent Dosimeter)
What is used to monitor radiation dose?
sensitive to as low as 1 mrem (10 micro SV)
Fluoroscopic Imaging
Uses x-ray to make a real time dynamic (action) image rather than a static image uses x-ray to make a real time dynamic (action) image rather than a static image
Digital Imaging: Cassette based (CR- computed radiography)
Where an image is captured and stored
Non-Cassette based (DR-direct digital (capture) or flat panel)
Where an image and captures with no Cassete & no reader, quickly viewed (less than 1 second)
Competency exams
Performed by students under supervision of any registered tech
Direct supervision
___________ supervision, when the technologists is in the room
Indirect supervision
_________supervision, when the technologist is close by ( out of view of student,) but is able to assist if necessary
Define a radiographic exam
An image of a patients anatomic part(s), as produced by the action of x-rays on an image receptor
What is a PA chest x-ray?
CR enters at a posterior surface and exits at the anterior surface
What is a true PA/AP?
- No rotation
- CR perpendicular to the coronal body plane and parallel to the sagittal plane

What is an AP chest x-ray?
CR enters at an anterior surface and exits at a posterior surface
What is an AP oblique projection?
CR enters the anterior surface and exits the posterior surface of the body or body part
What is a PA oblique projection?
CR enters posterior surface and exits the anterior surface of the body or body part
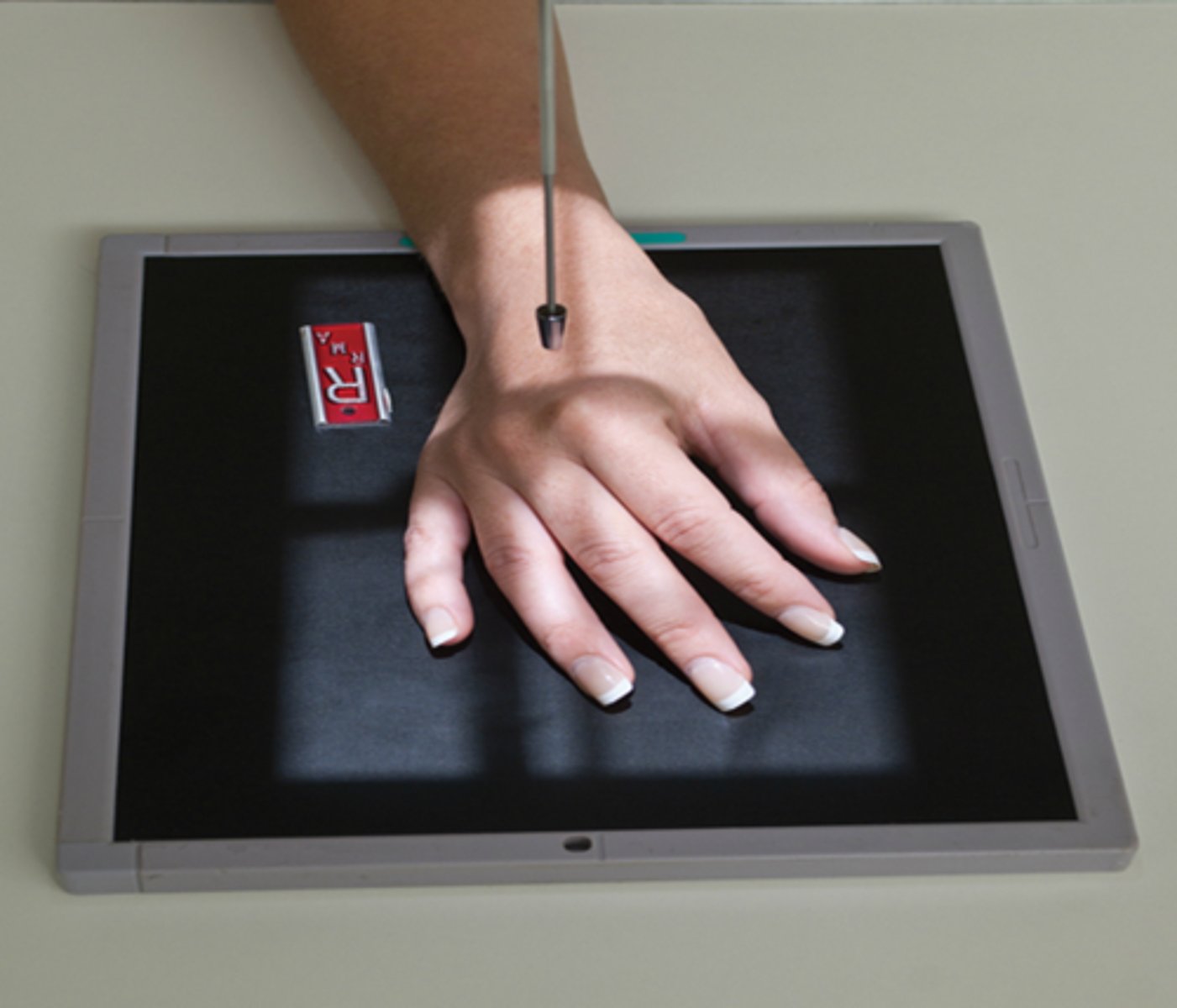

AP Chest
What x-ray is this?

PA Chest
What x-ray is this?
