Lecture 24: Endocrine System I
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/153
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
154 Terms
1
New cards
what are the only retinal cells that produce action potentials?
ganglion cells
2
New cards
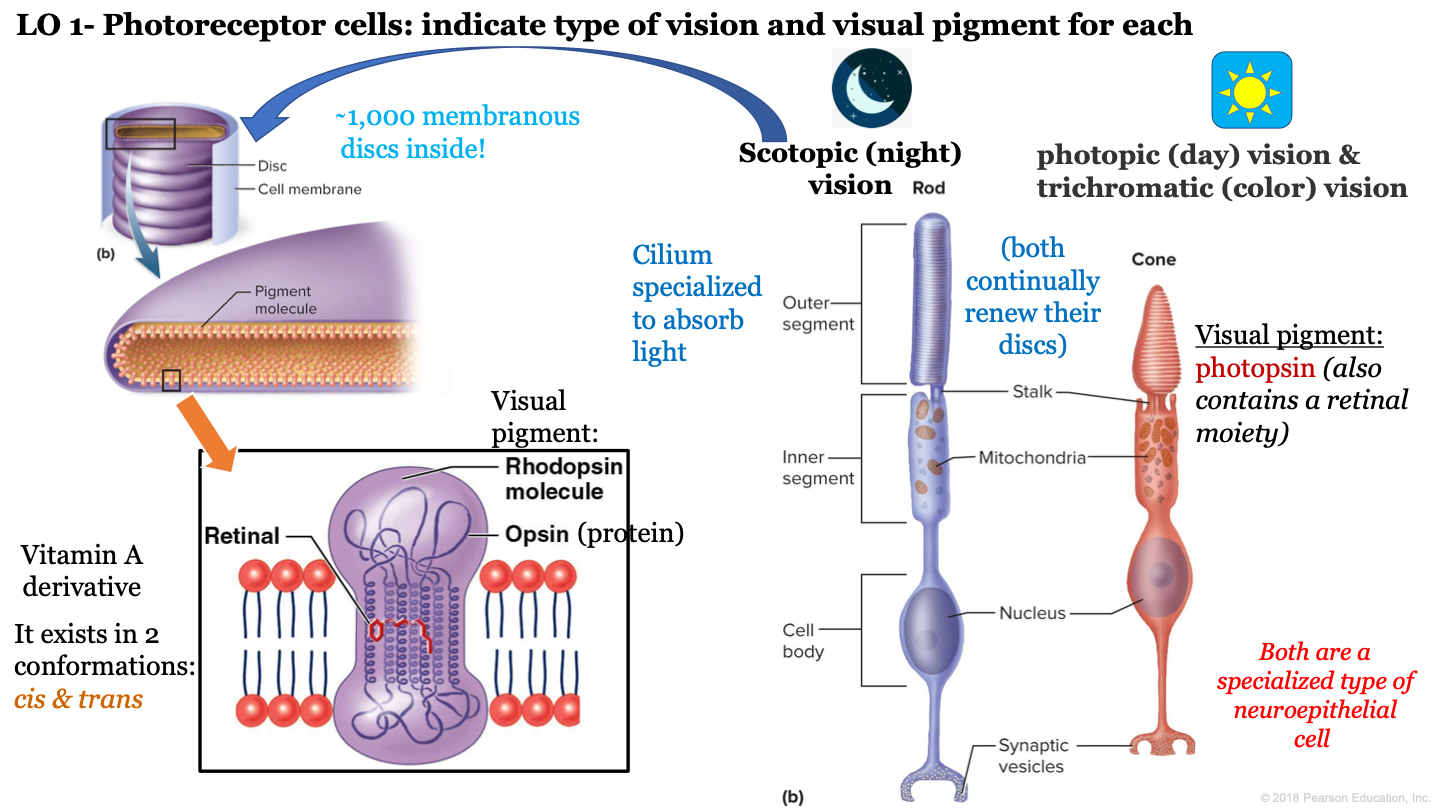
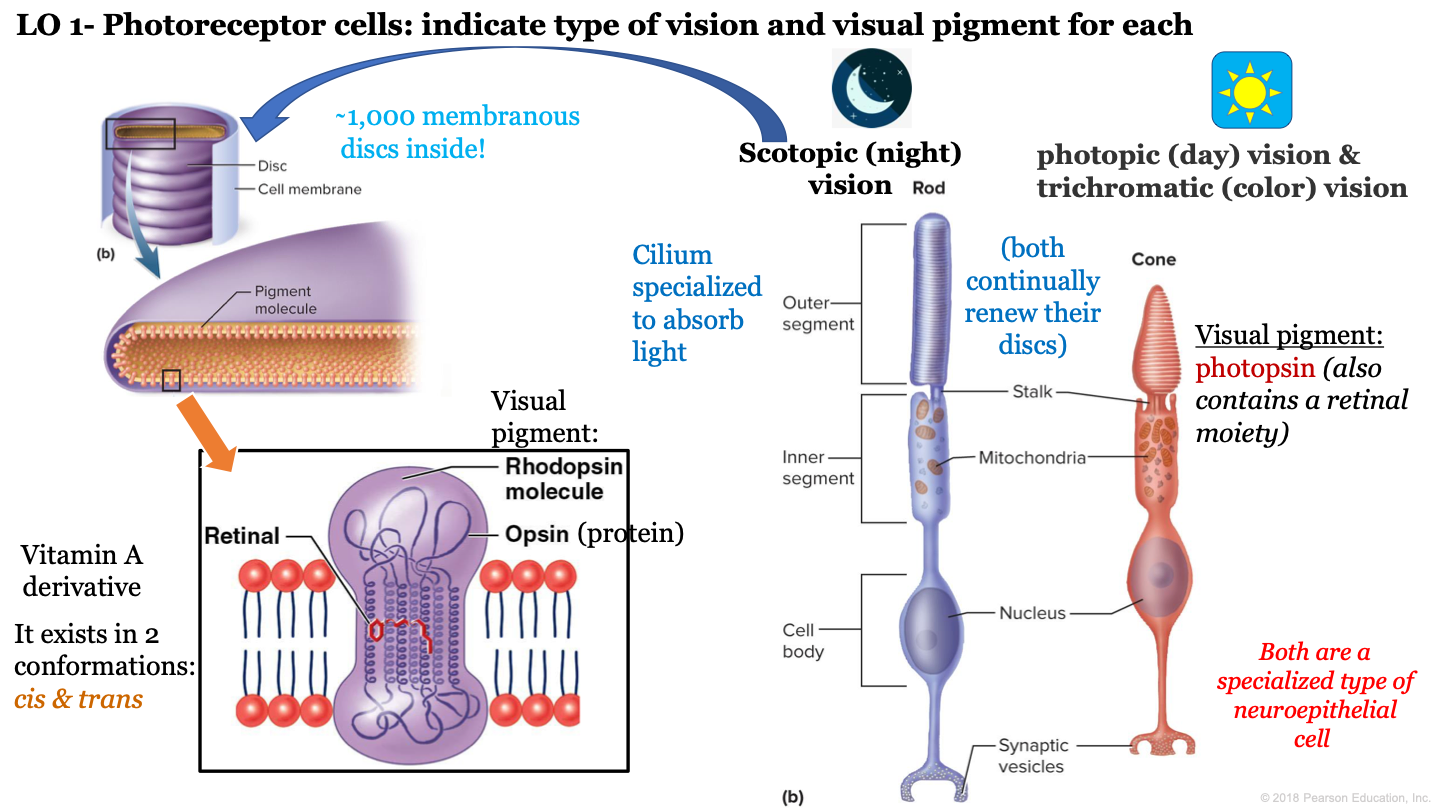
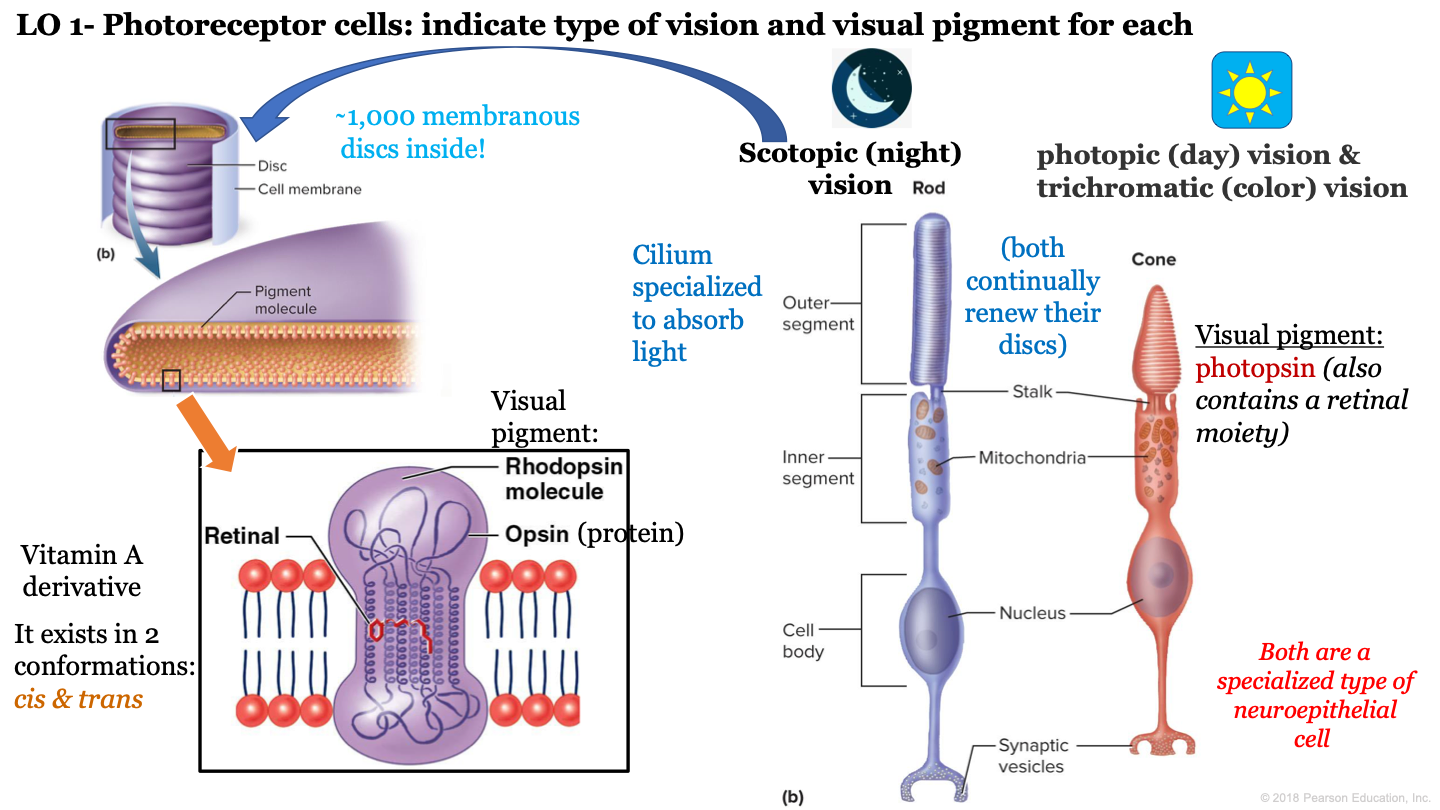
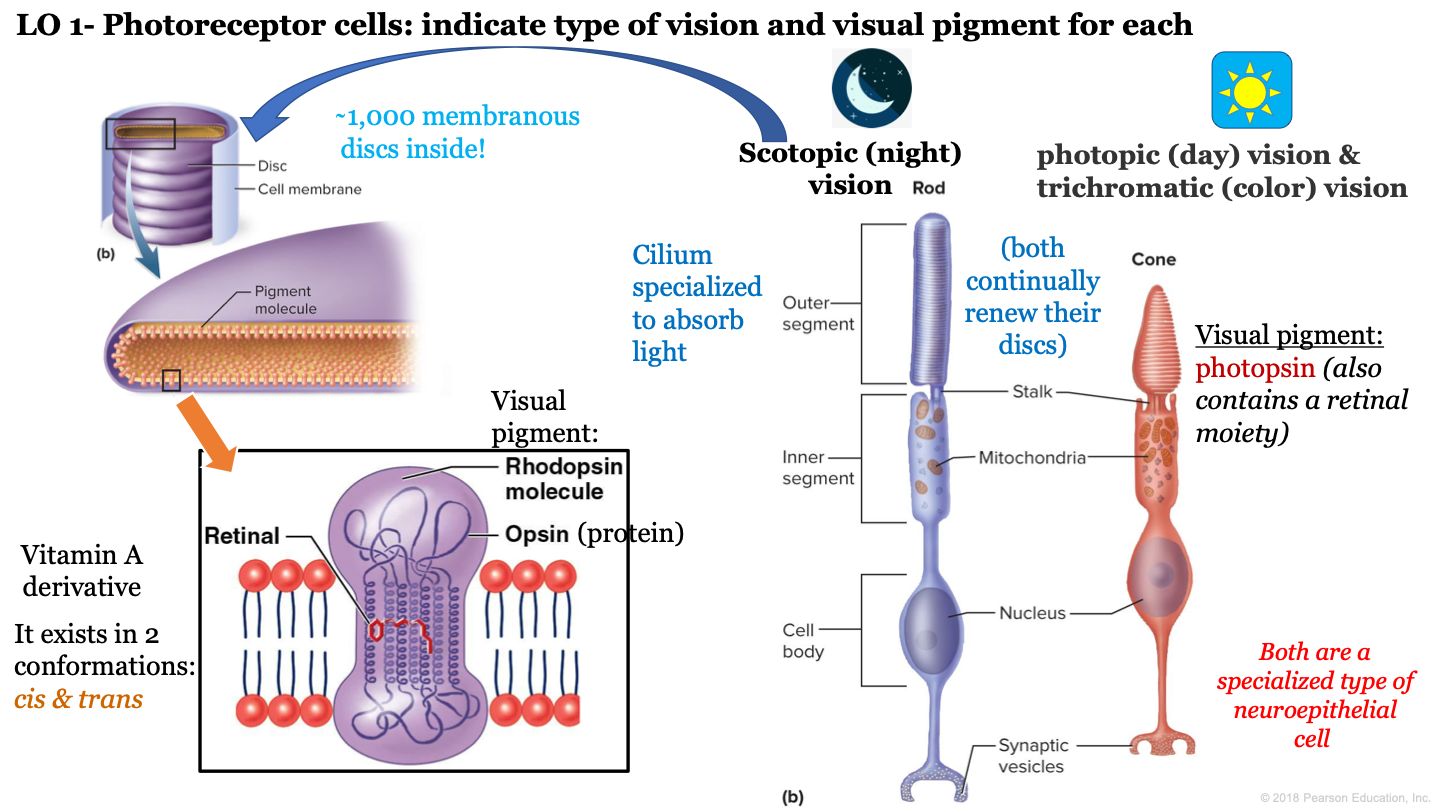
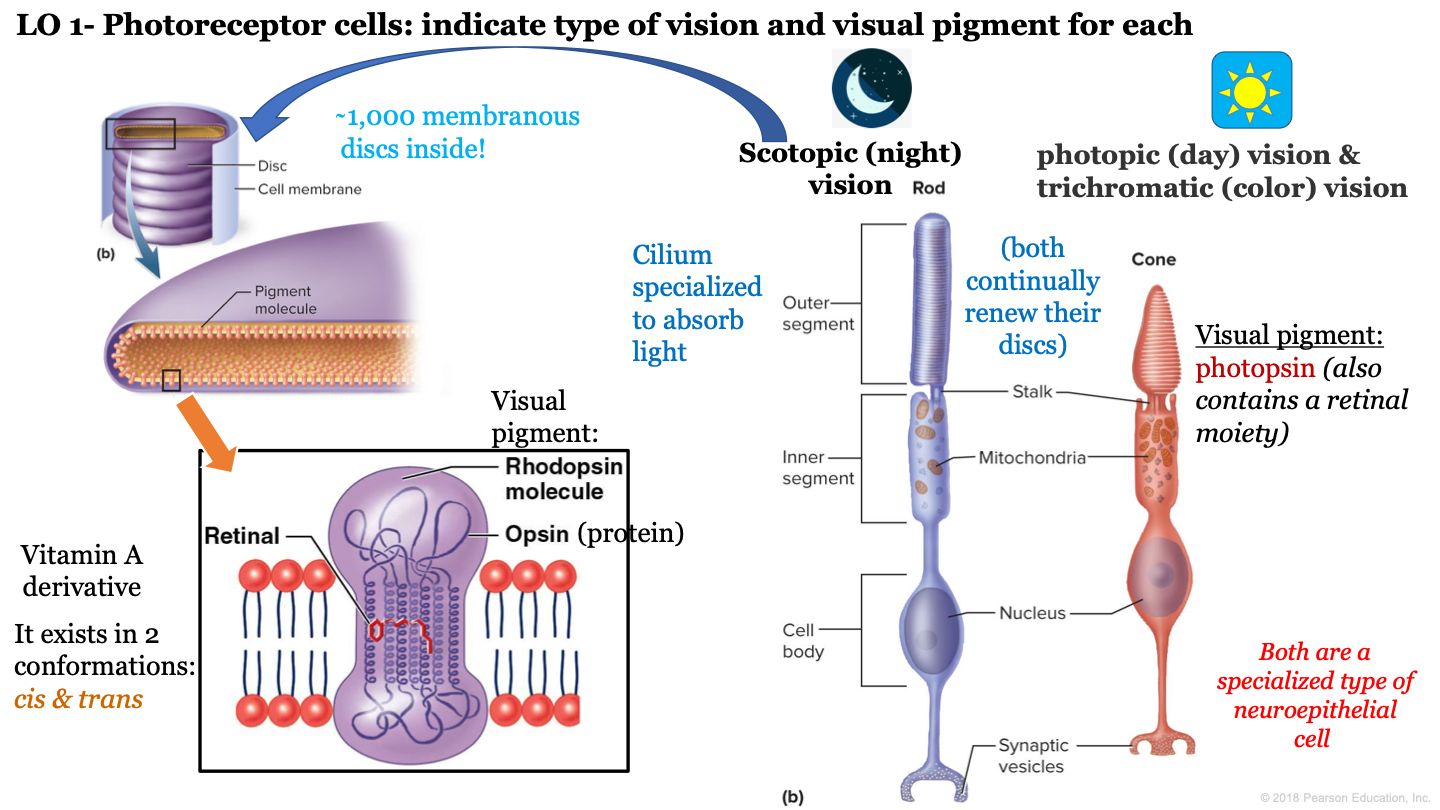
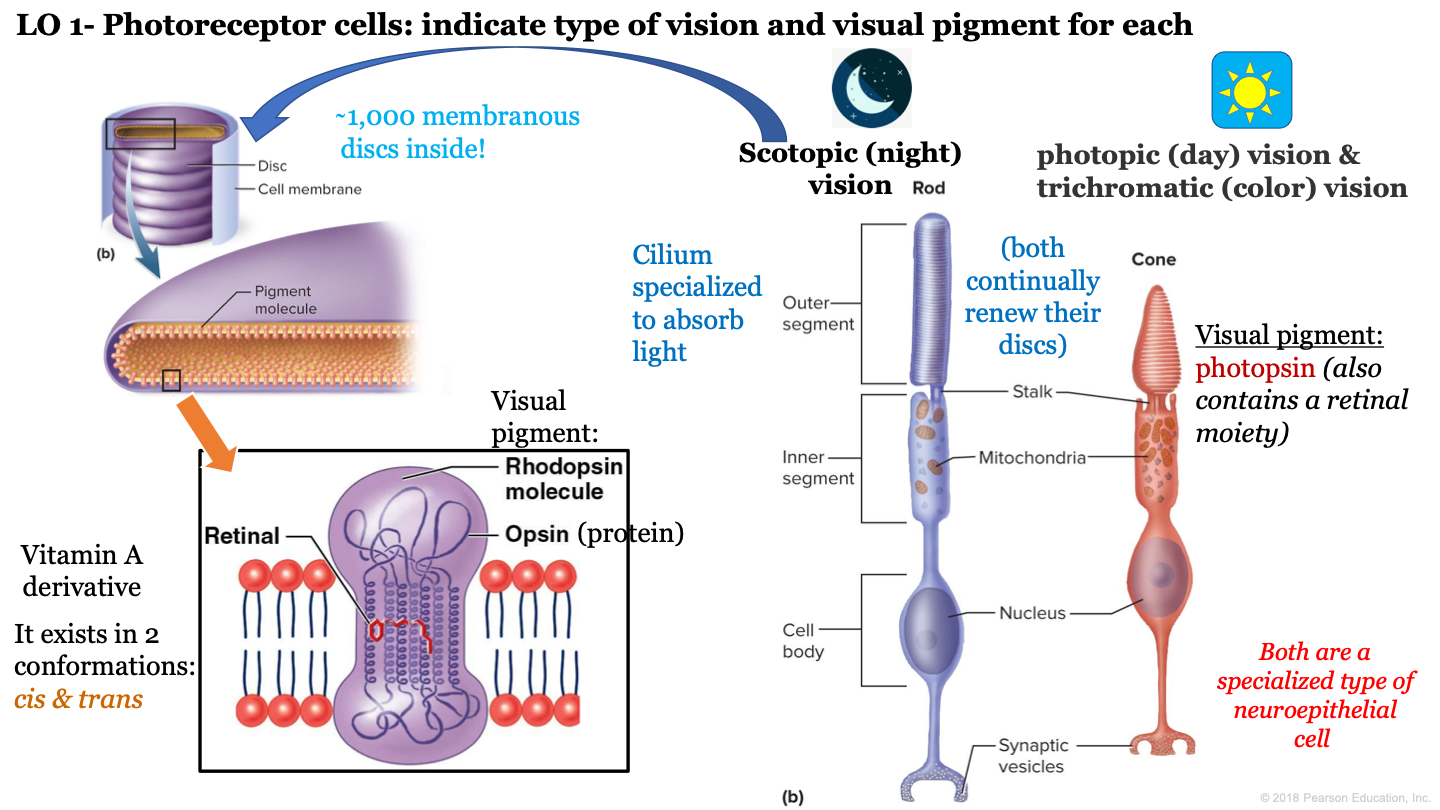
photoreceptor cells
convert light into electrical signals
3
New cards
what is night vision called?
scotopic vision
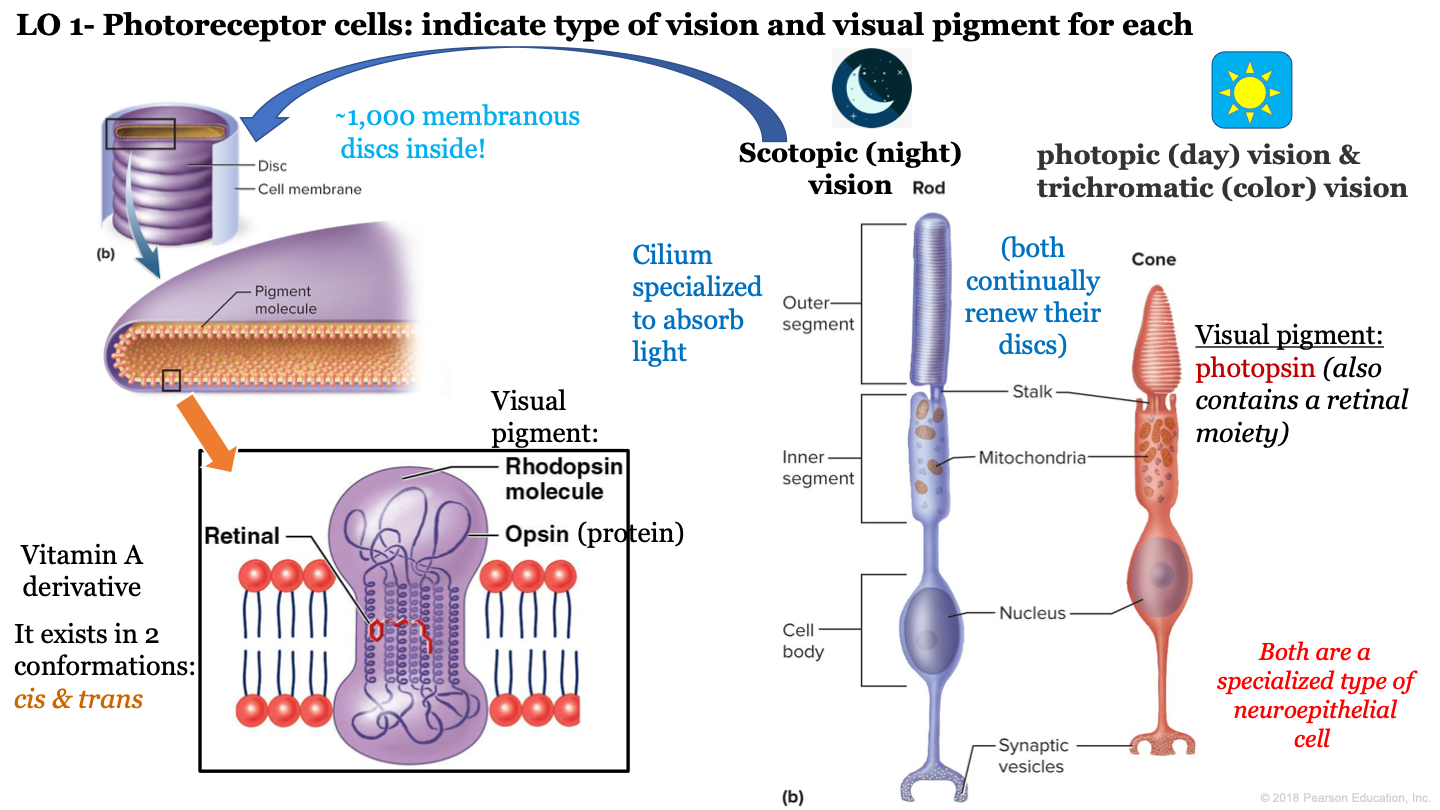
4
New cards
which neuroepithelial cell is responsible for night/scotopic vision?
rod cells
5
New cards
which neuroepithelial cell is responsible for photopic (day) vision and color vision?
cone cells
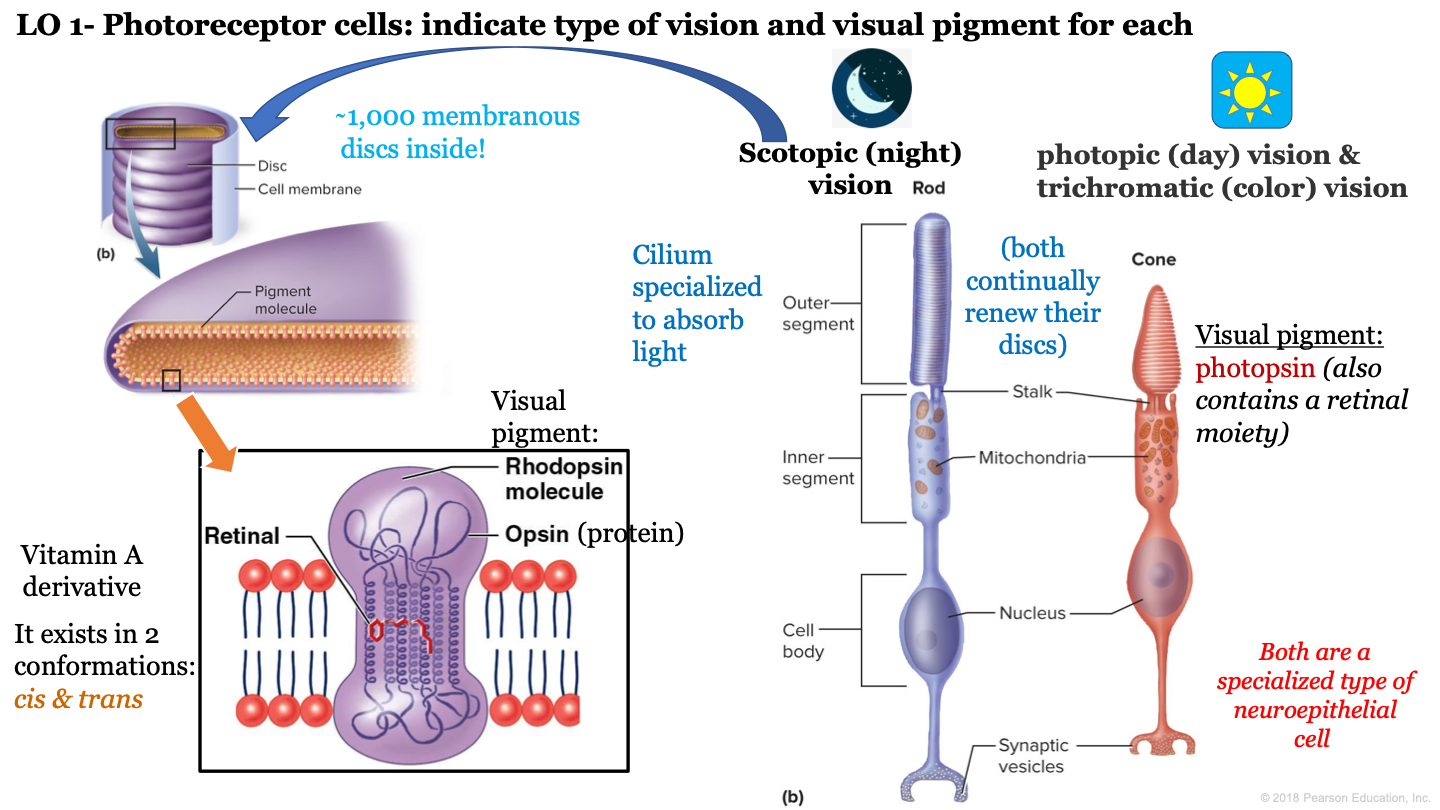
6
New cards
T or F: cone and rod cells are both a specialized type of neuroepithelial cell
true
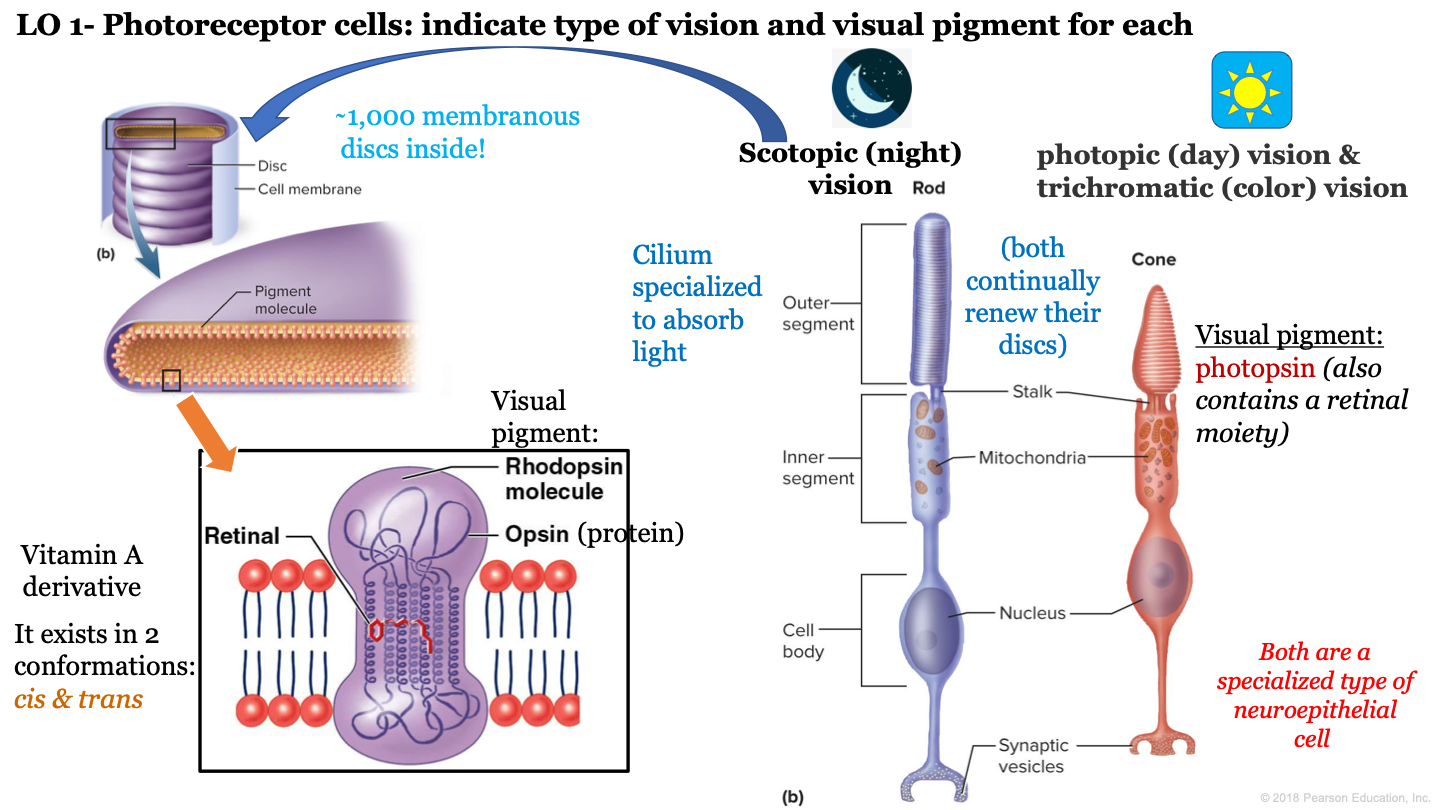
7
New cards
T or F: cone and rod cells do not continually renew their discs
F: these cells continually renew their discs
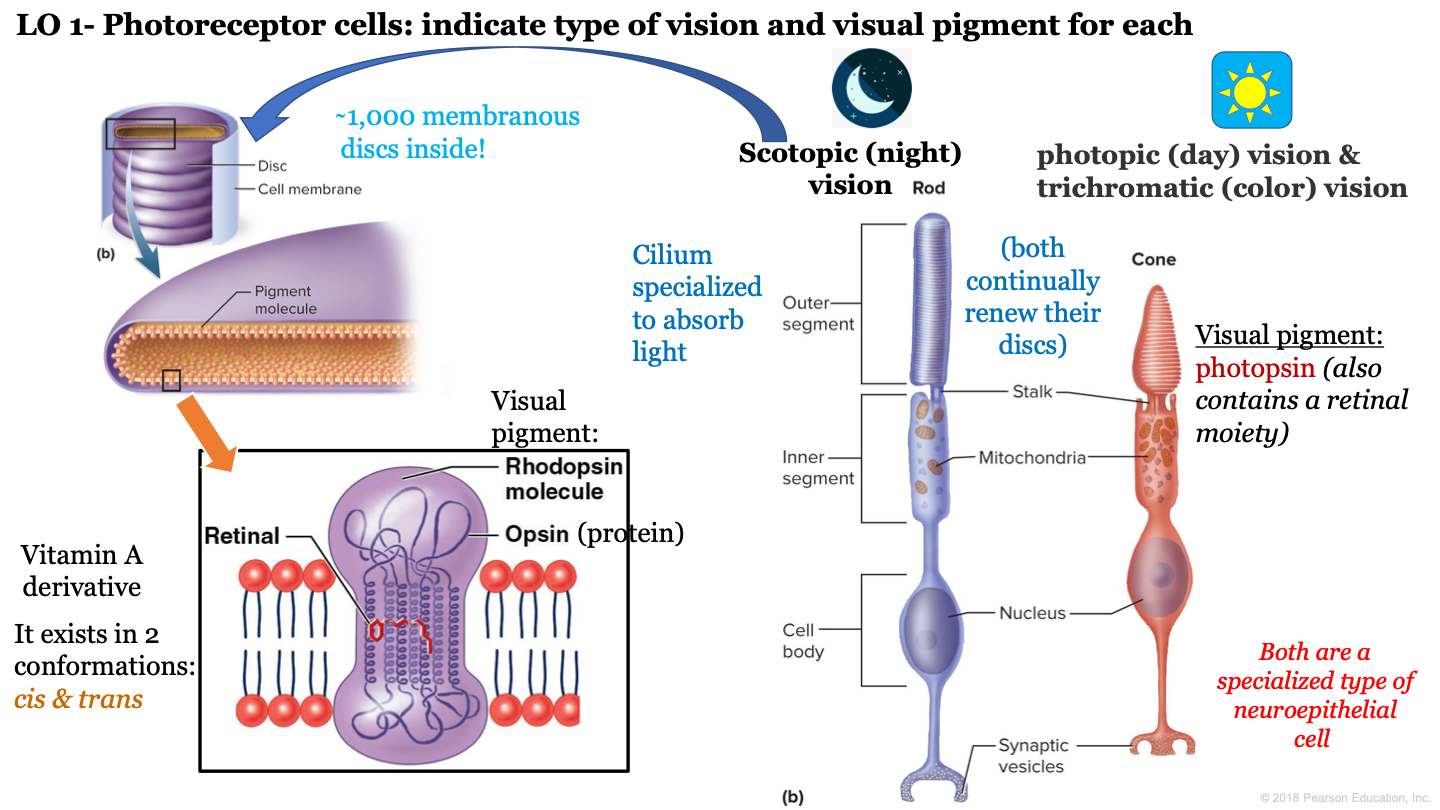
8
New cards
how many discs are inside the outer segment of rod cells?
approx 1,000
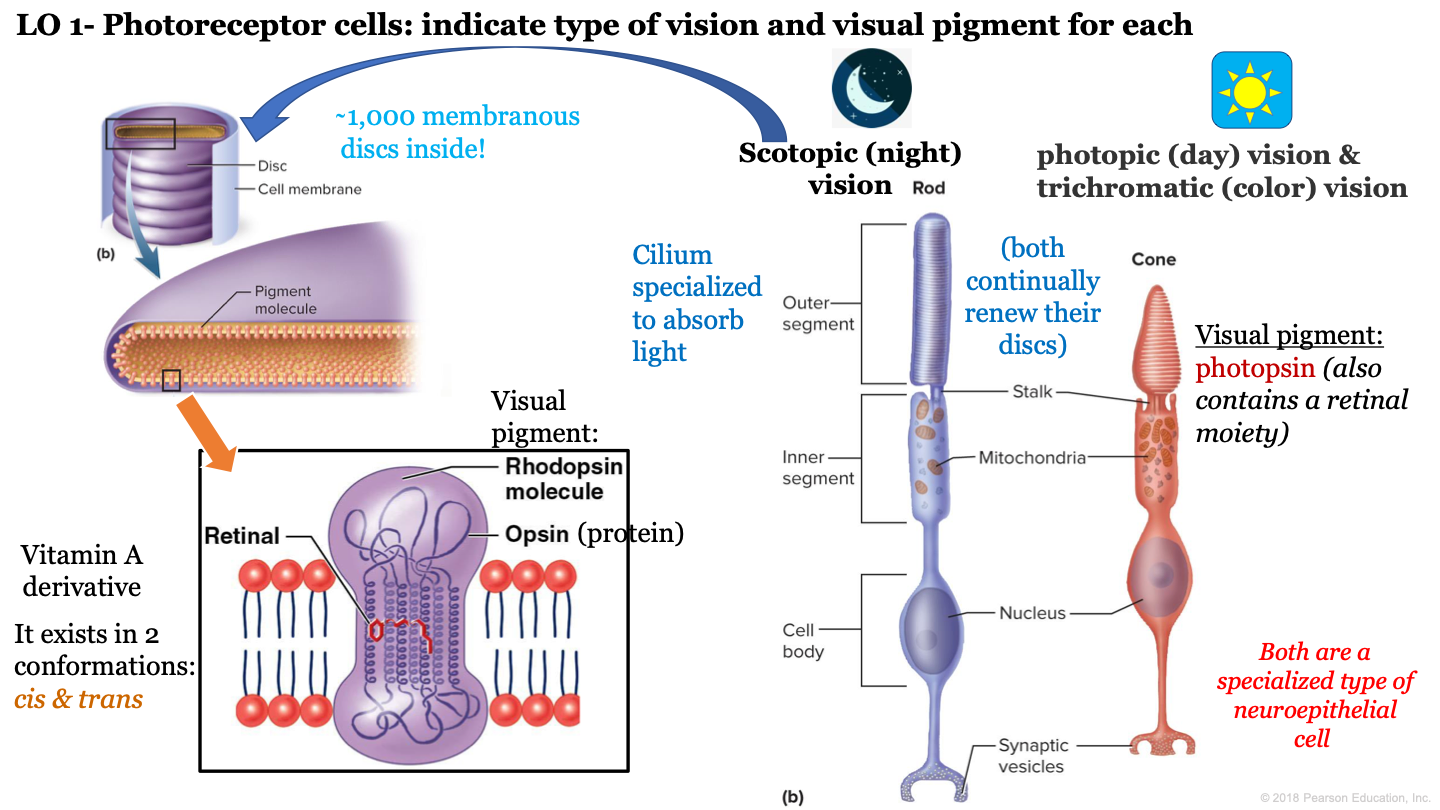
9
New cards
which visual pigment molecule is found inside a a rod's discs?
rhodopsin molecules
10
New cards
what structure of neuroepithelial cells is specialized to absorb light?
cilium
11
New cards
what are the 3 segments of rod cells?
-outer segment
-inner segment
-cell body
-inner segment
-cell body
12
New cards
what is the visual pigment of cones?
photopsin (also contains a retinal moiety)
13
New cards
what makes up a rhodopsin molecule?
-opsin (protein)
-retinal (vitamin a derivative)
-retinal (vitamin a derivative)
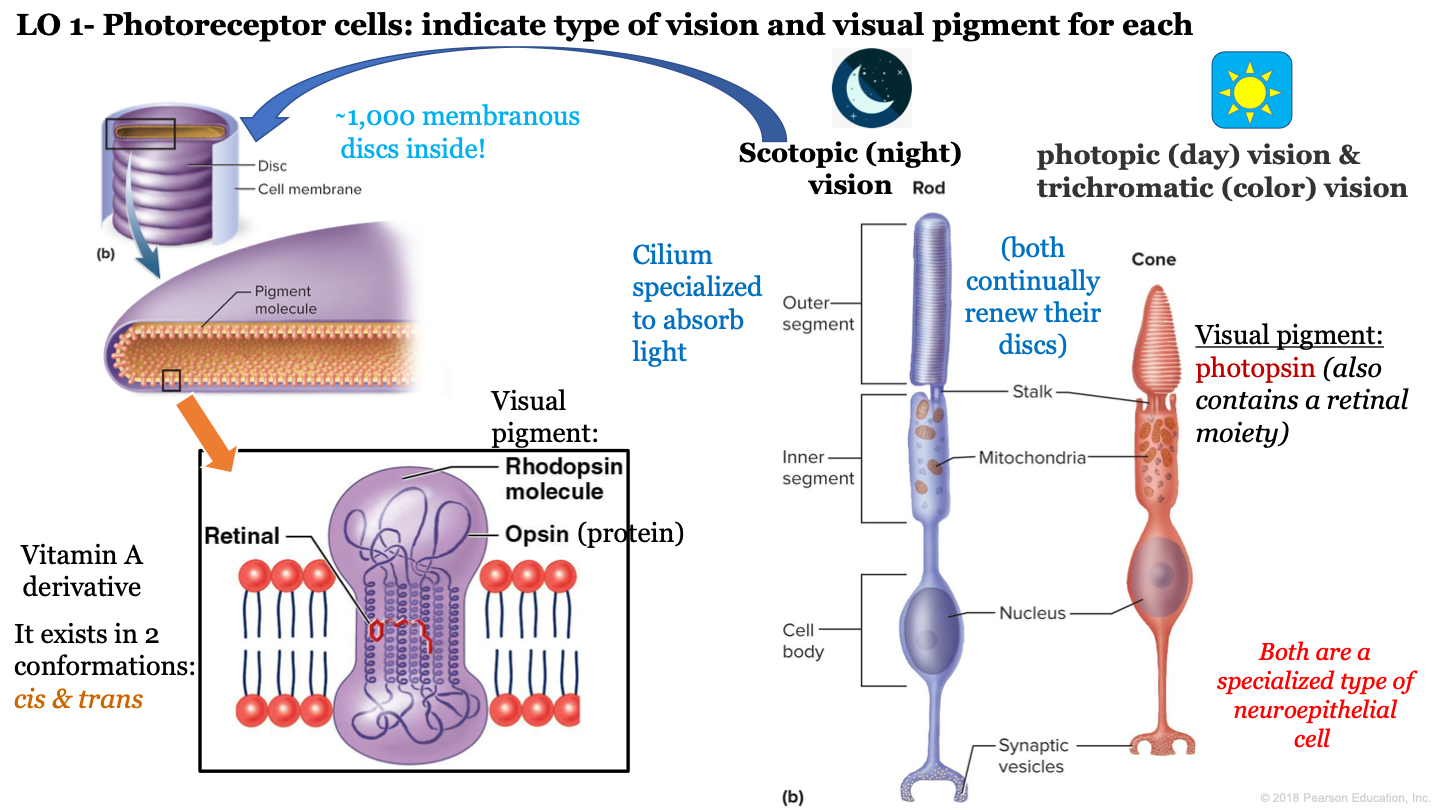
14
New cards
what are the two conformations of retinal?
cis and trans
15
New cards
structures inside cones and rods
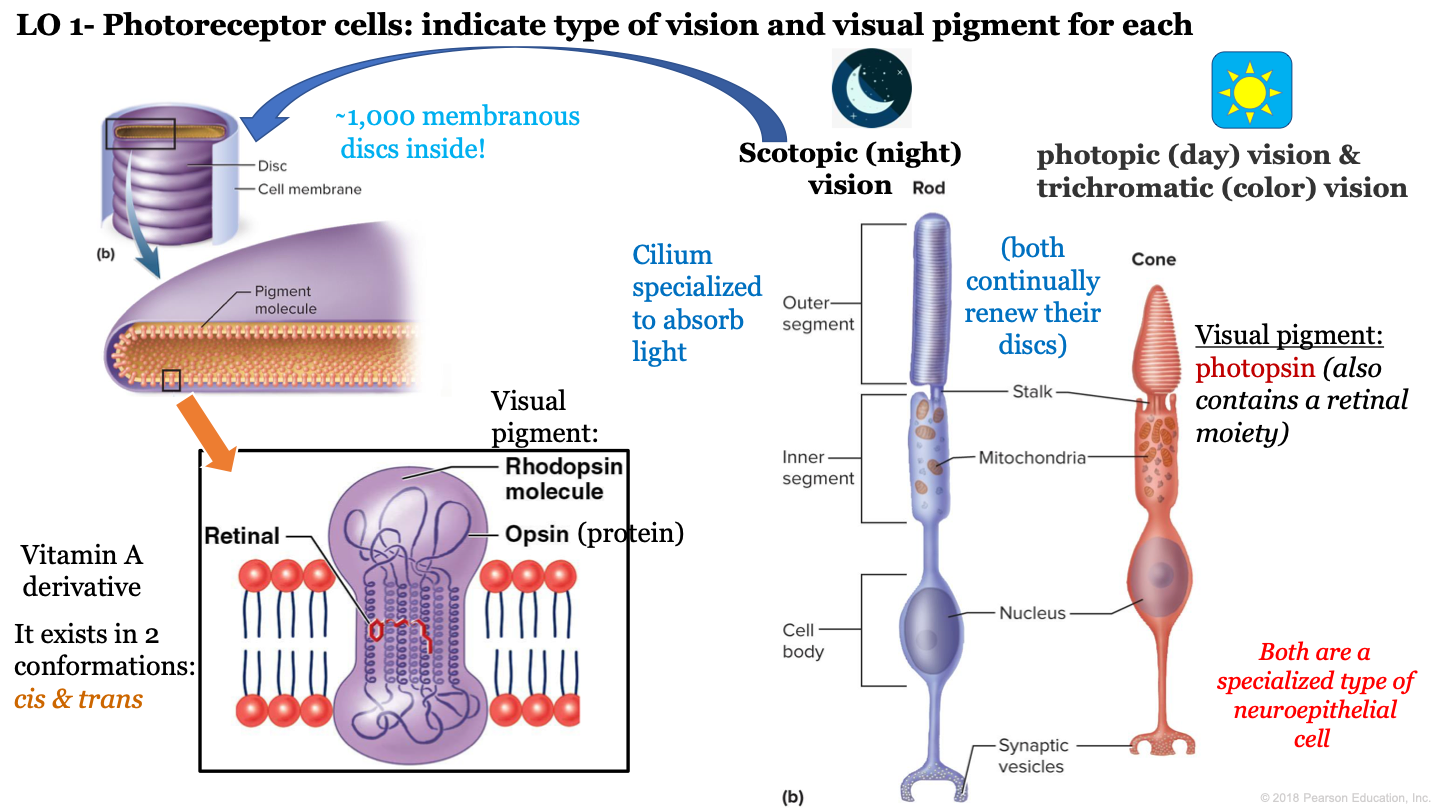
16
New cards
how many types of cones do we have? what are the types?
3; S cones (blue), M cones (green), L cones (red)
17
New cards
what is our perception of color based on?
a mixture of nerve signals representing cones with different absorption peaks
18
New cards
what is normal color vision called?
trichromatic vision (we can see all three colors)
19
New cards
wavelengths of the different cones
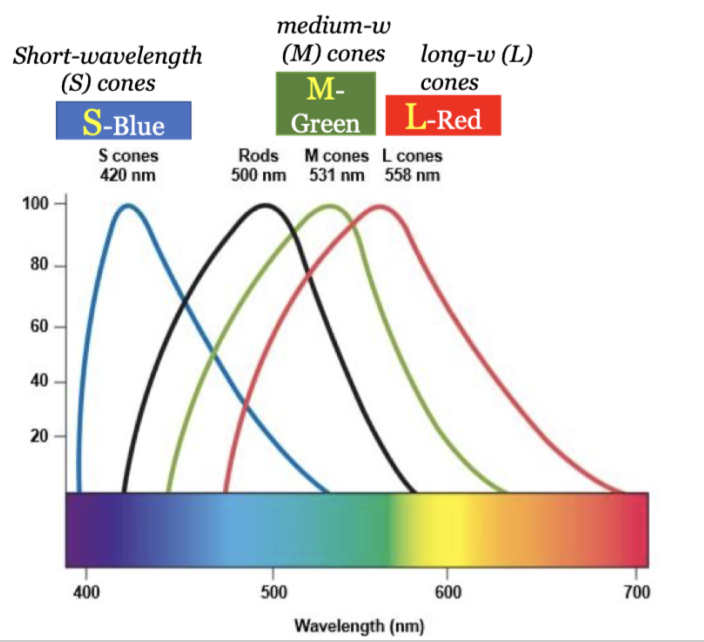
20
New cards
the rods contain ______________ which is a visual pigment specialized in ___________ vision.
rhodopsin; scotopic
21
New cards
the cones contain ______________ which is a visual pigment specialized in ___________ vision.
photopsin; photopic/trichromatic
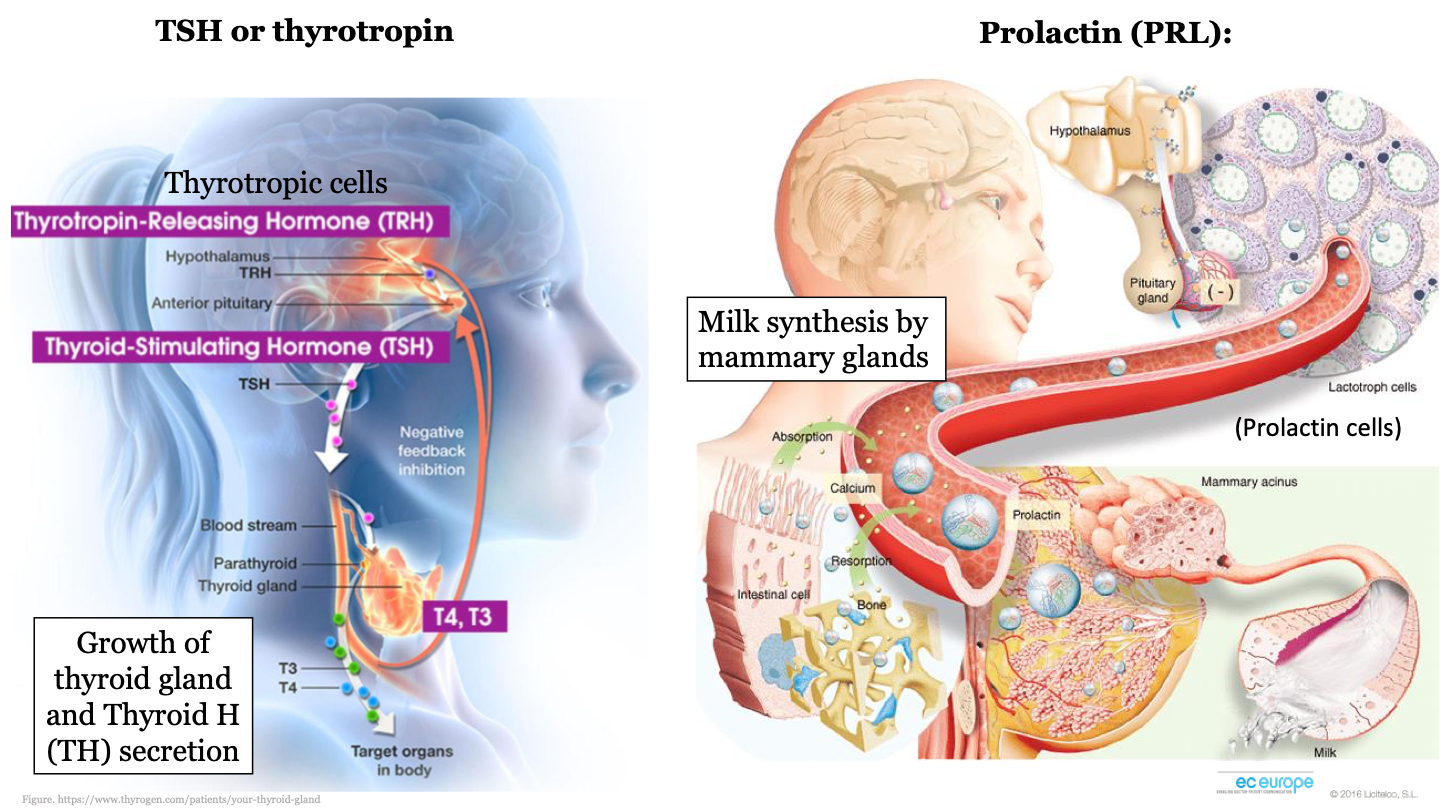
22
New cards
In the dark, photoreceptors are depolarized/hyperpolarized and decrease/increase their release of glutamate neurotransmitter
depolarized; increase
23
New cards
Light causes these photoreceptors to depolarize/hyperpolarize and decrease/increase their release of glutamate neurotransmitter
hyperpolarize; decrease
24
New cards
T or F: Biochemical reactions return the cell to its 'dark state' and the visual cycle converts all-trans retinal back to 11-cis retinal for rhodopsin regeneration
T
25
New cards
phototransduction
conversion of light energy into action potentials (in retina)
26
New cards
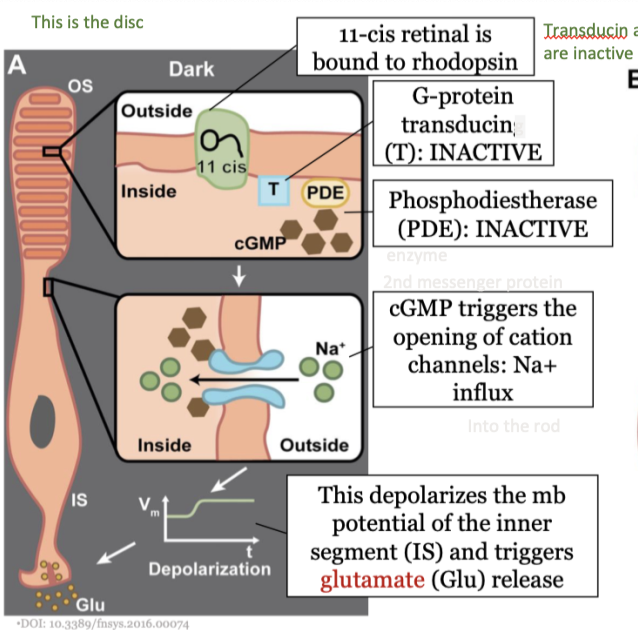
steps in phototransduction in the rods (dark) - step 1
11-cis retinal is bound to rhodopsin
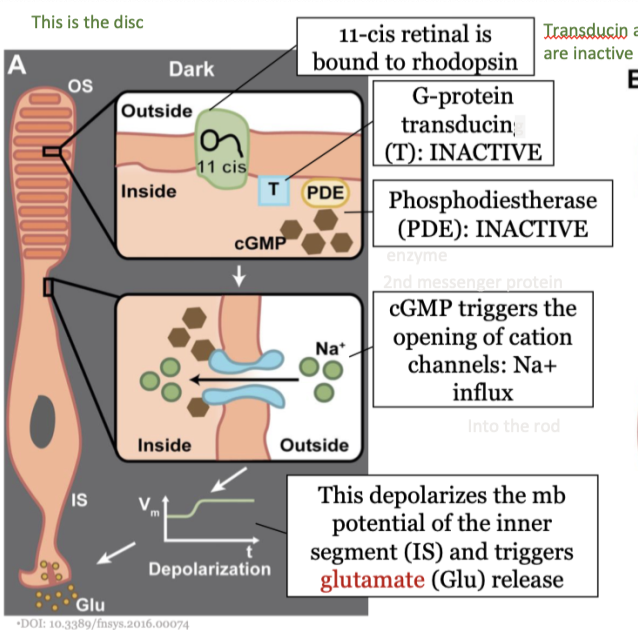
27
New cards
steps in phototransduction in the rods (dark) - step 2
The G-protein transducin (T) is inactive
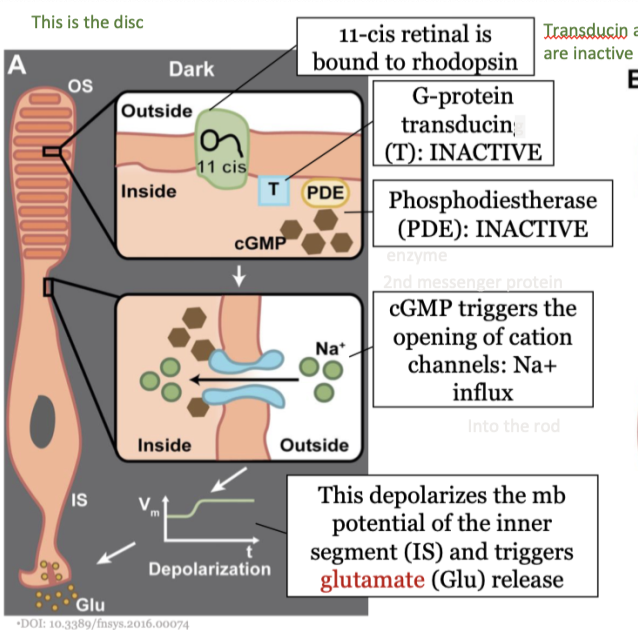
28
New cards
steps in phototransduction in the rods (dark) - step 3
phosphodiestherase (PDE) is inactive
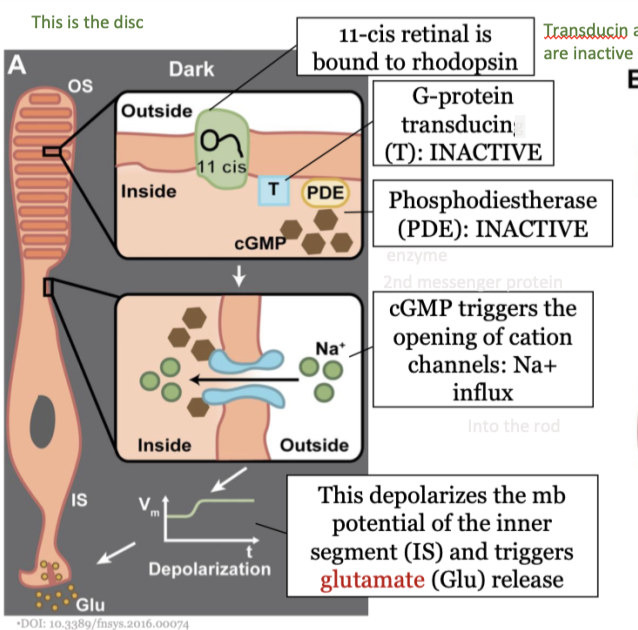
29
New cards
steps in phototransduction in the rods (dark) - step 4
cGMP triggers the opening of cation channels: NA+ influx
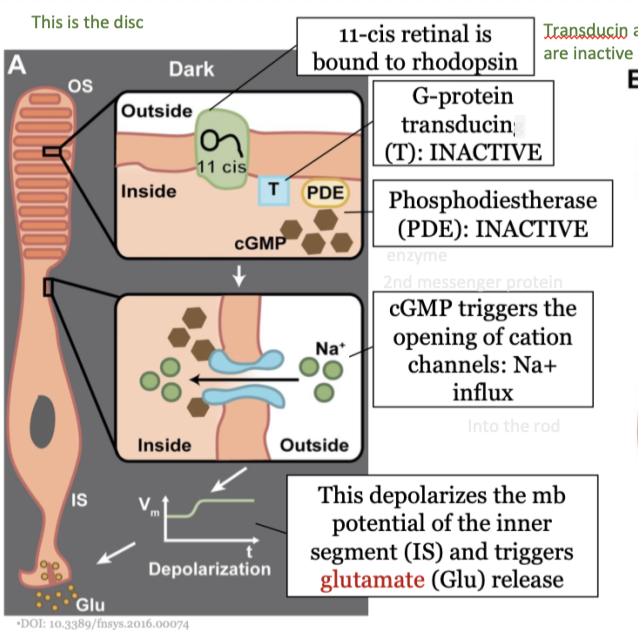
30
New cards
steps in phototransduction in the rods (dark) - step 5
This depolarizes the mb potential of the inner segment (IS) and triggers glutamate (Glu) release
31
New cards
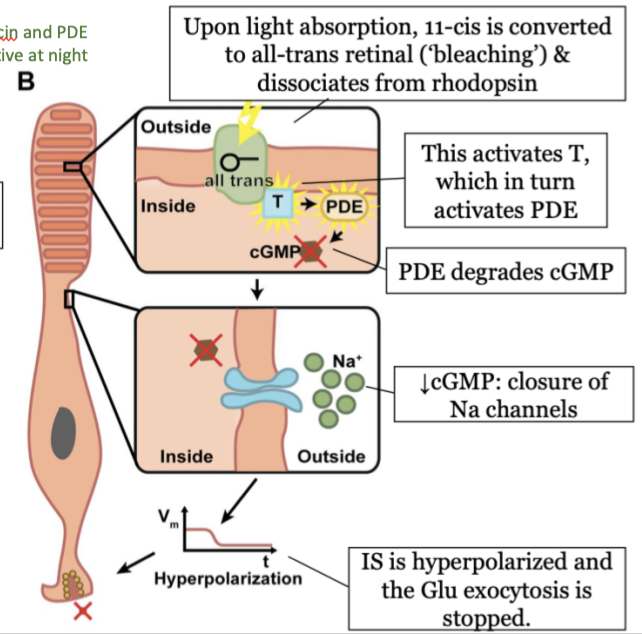
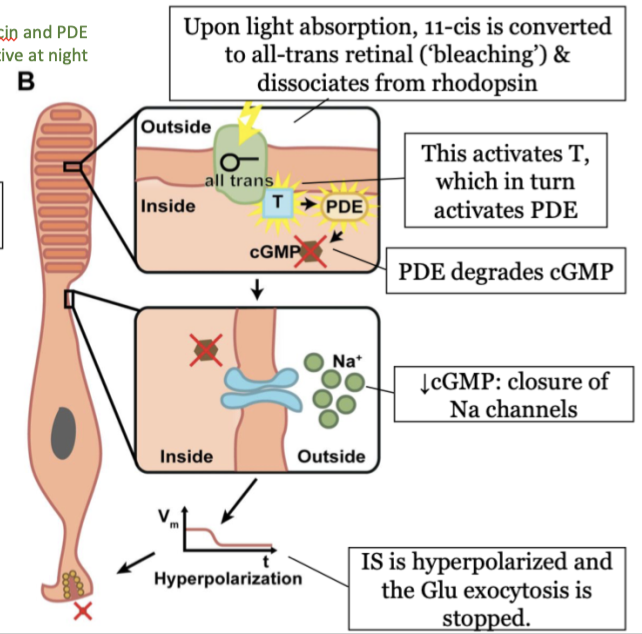
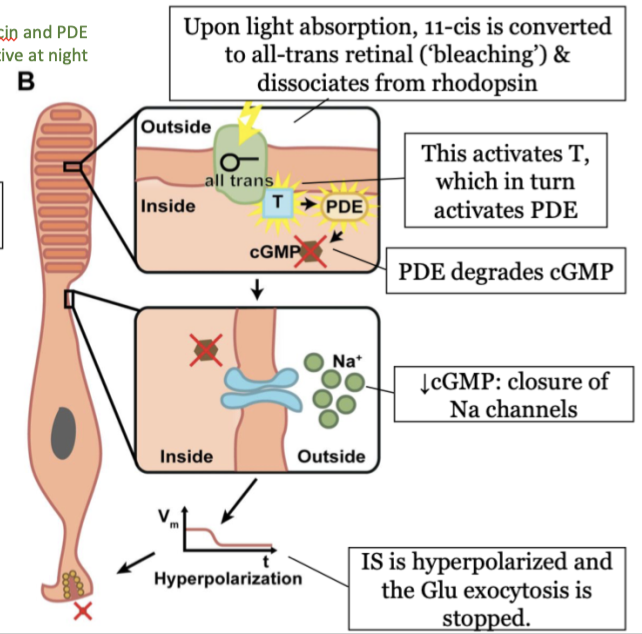
steps in phototransduction in the rods (light) - step 1
upon light absorption, 11-cis is converted to all-trans retinal (bleaching) and dissociates from rhodopsin
32
New cards
steps in phototransduction in the rods (light) - step 2
this activates T, which in turn activated PDE
33
New cards
steps in phototransduction in the rods (light) - step 3
PDE degrades cGMP
34
New cards
steps in phototransduction in the rods (light) - step 4
decrease in cGMP causes a closure of Na channels
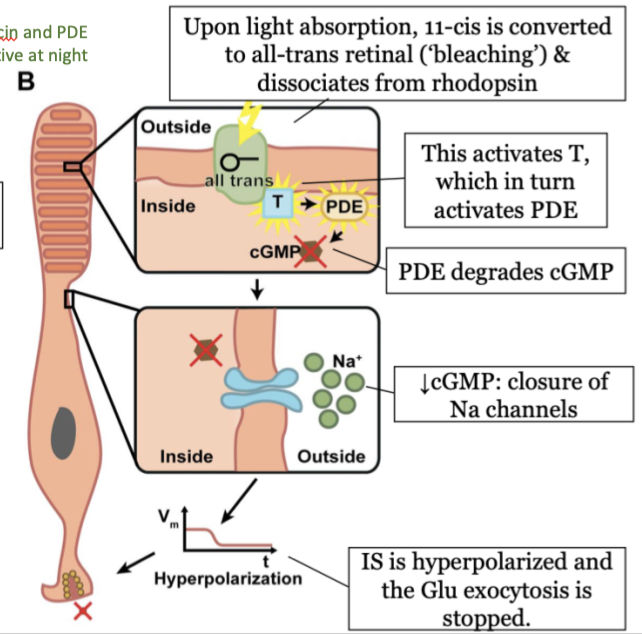
35
New cards
steps in phototransduction in the rods (light) - step 5
the inner segment (IS) is hyperpolarized and the Glu exocytosis is stopped
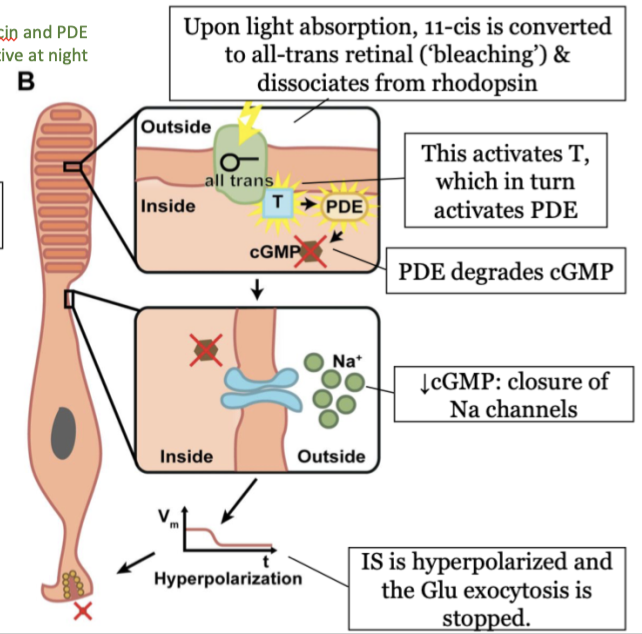
36
New cards
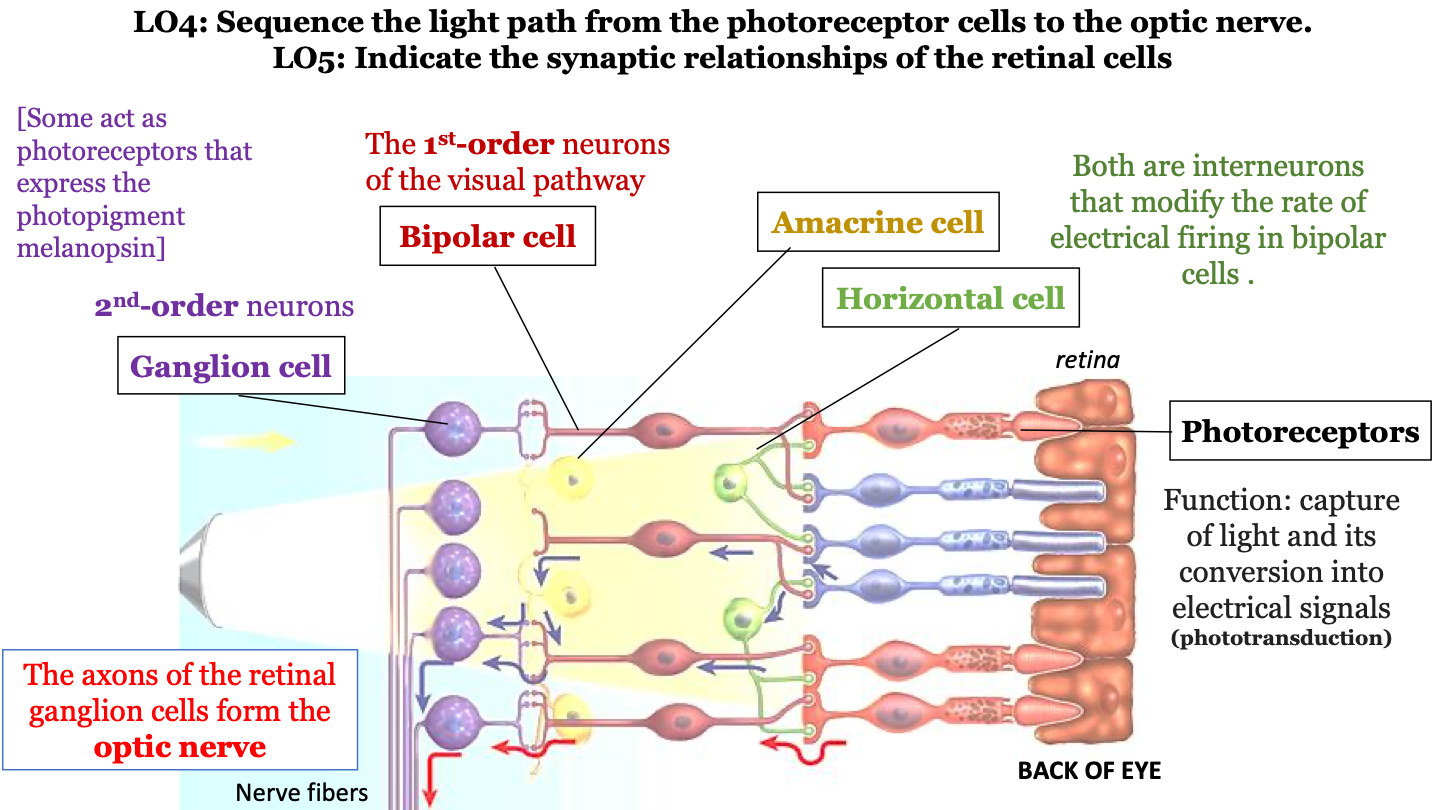
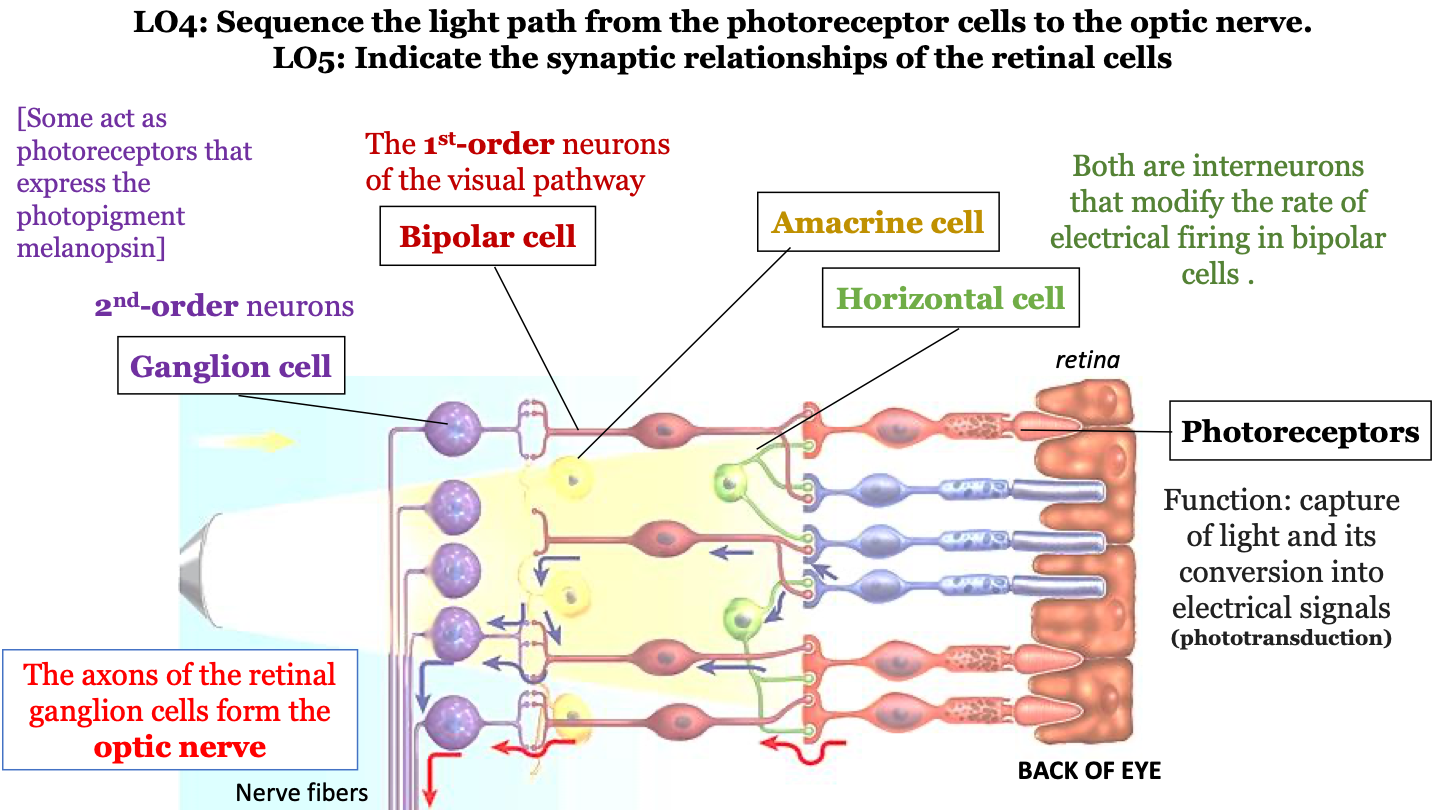
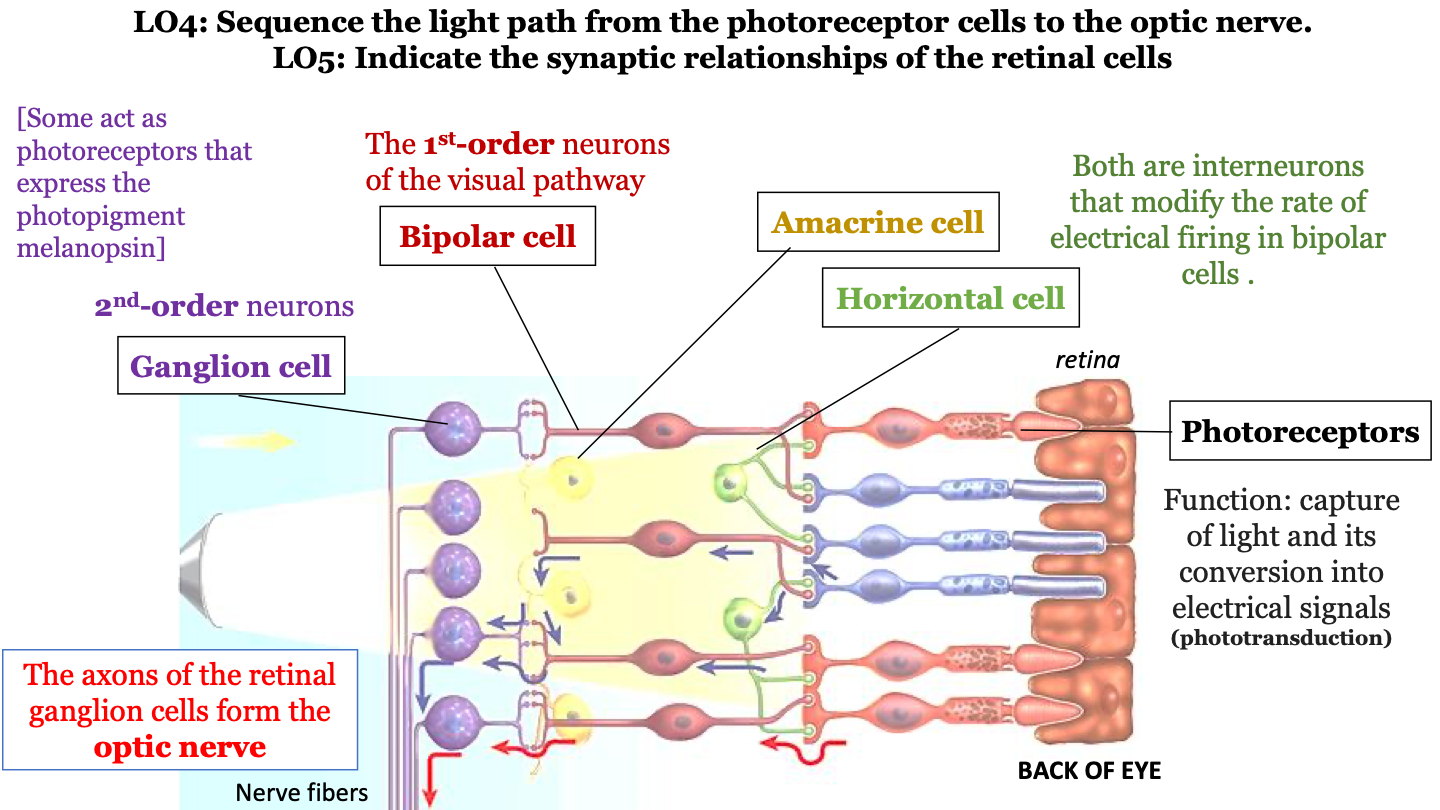
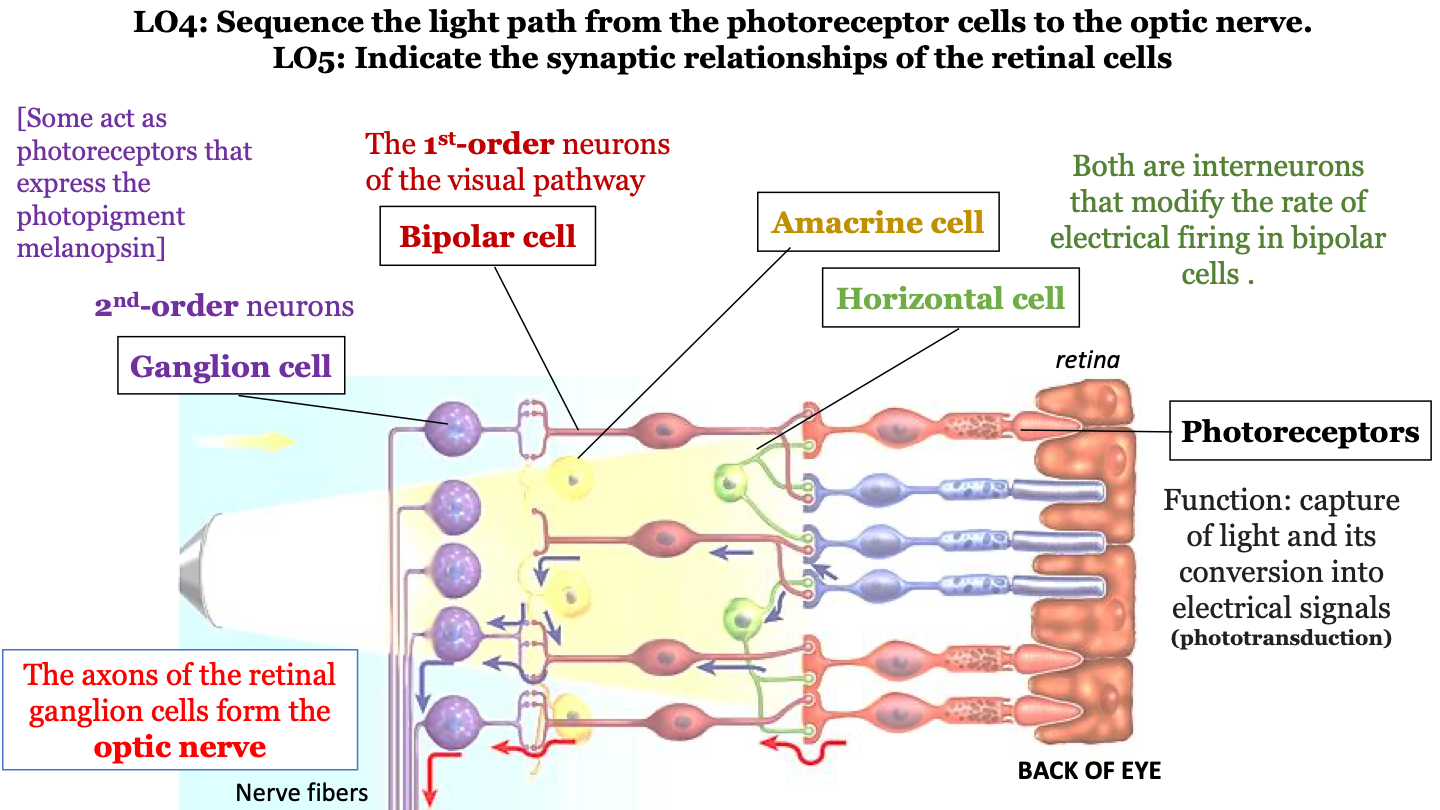
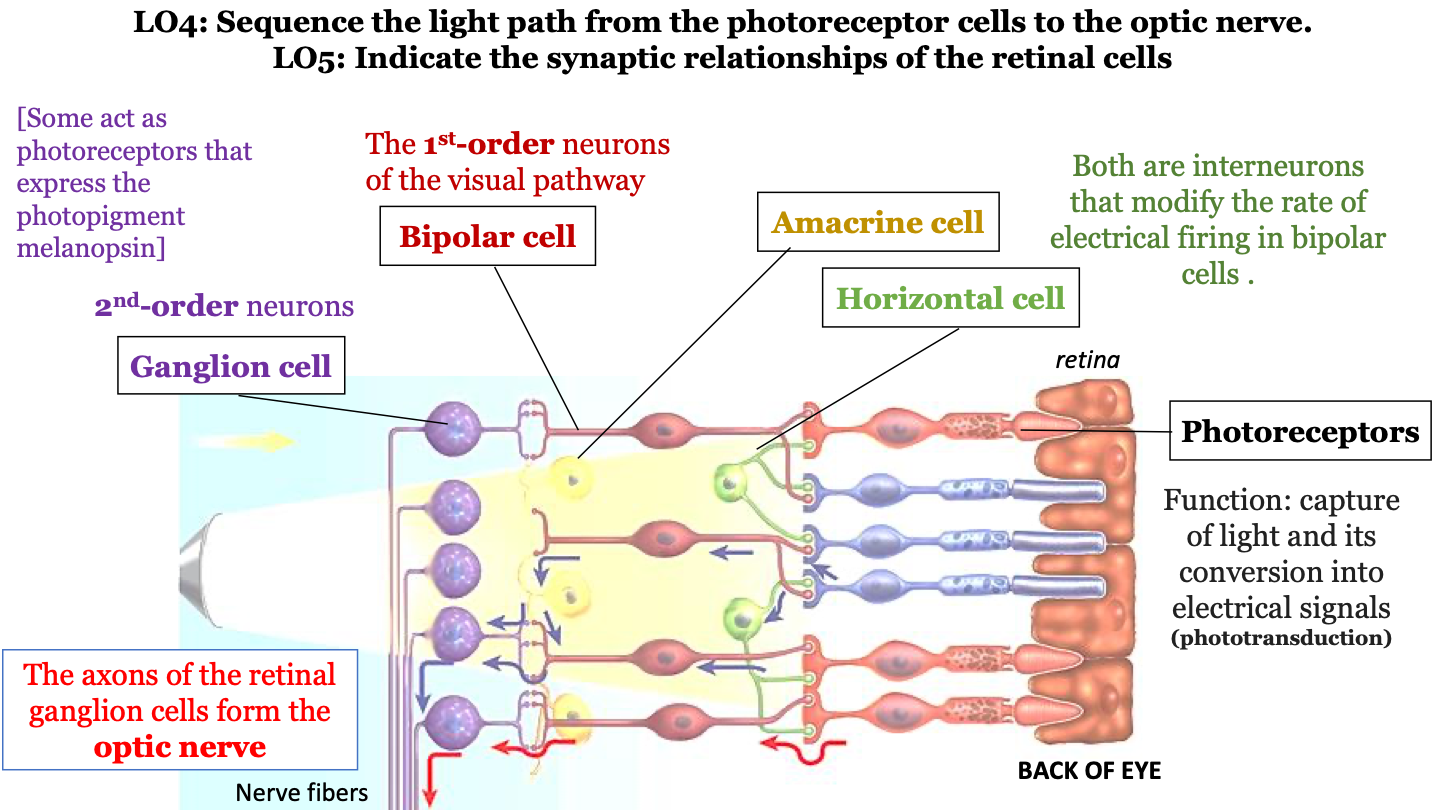
what is the sequence of the light path from the photoreceptor cells to the optic nerve?
1. photoreceptors (cones, rods)
2. bipolar cells
3. ganglion cells
4. optic nerve
2. bipolar cells
3. ganglion cells
4. optic nerve
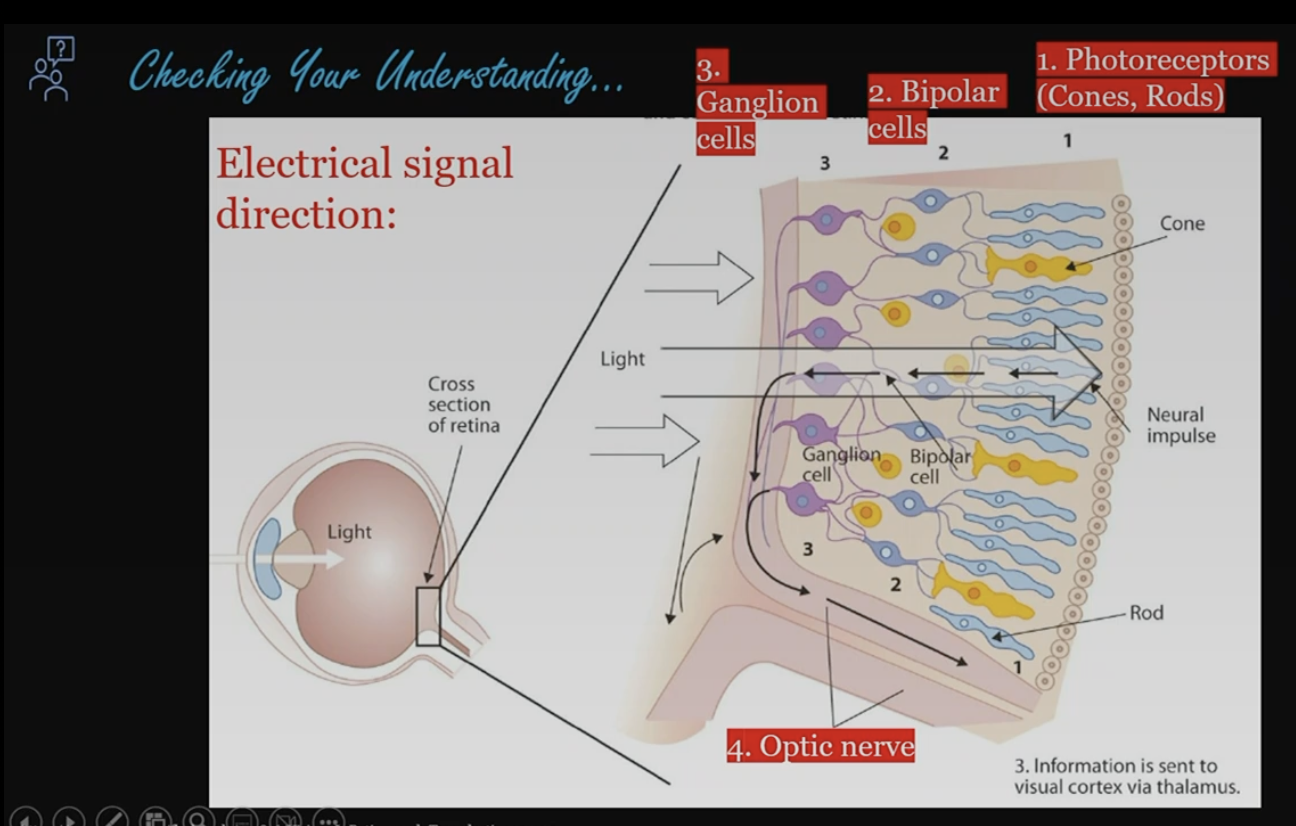
37
New cards
amacrine cell
interneuron that modifies the rate of electrical firing in bipolar cells
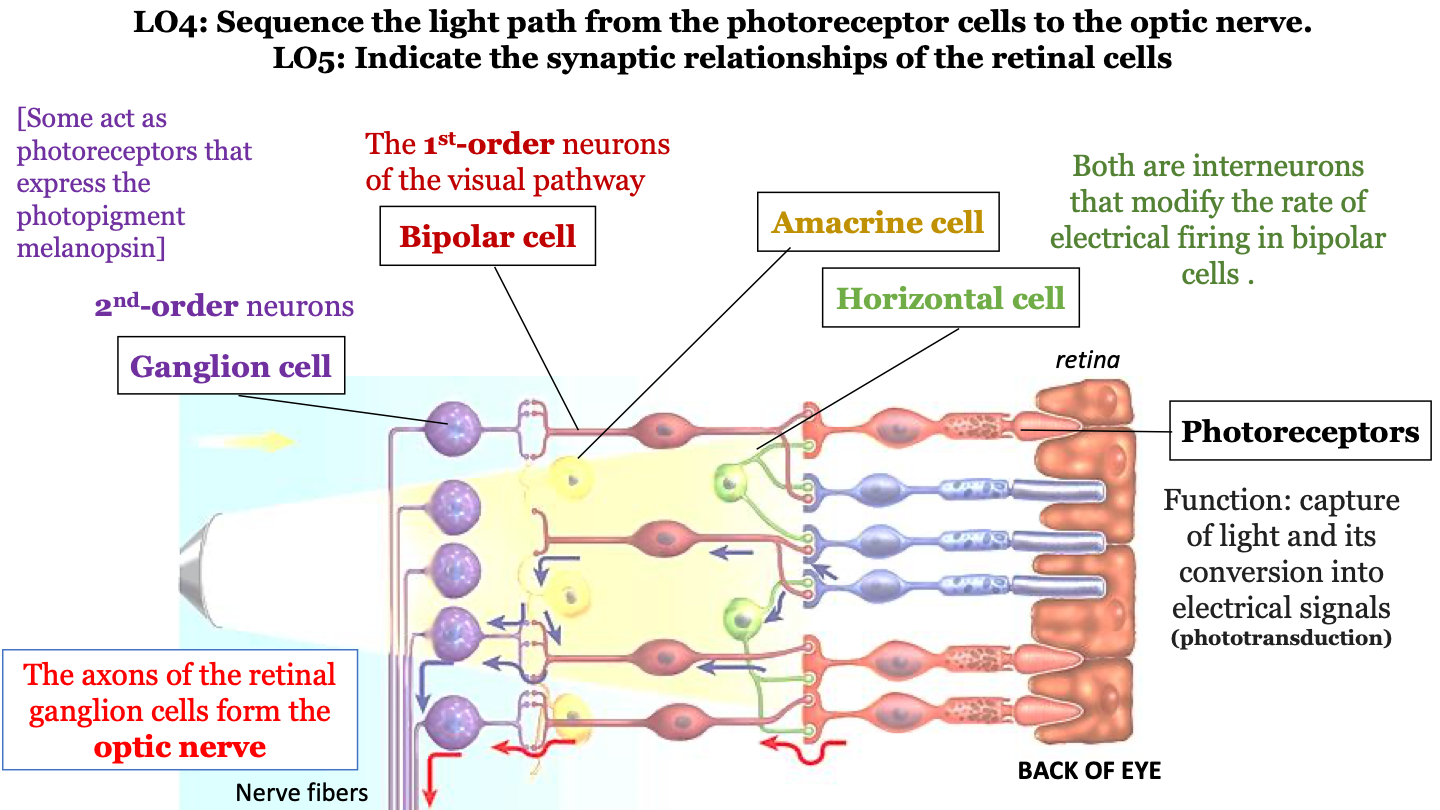
38
New cards
horizontal cell
interneuron that modifies the rate of electrical firing in bipolar cells
39
New cards
function of photoreceptors
captures light and converts it into electrical signals (phototransduction)
40
New cards
bipolar cells
1st-order neurons of the visual pathway
41
New cards
ganglion cell
2nd-order neurons (some act as photoreceptors that express the photopigment melanospin)
42
New cards
the axons of the retinal ganglion cells form the ___________ ___________.
optic nerve
43
New cards
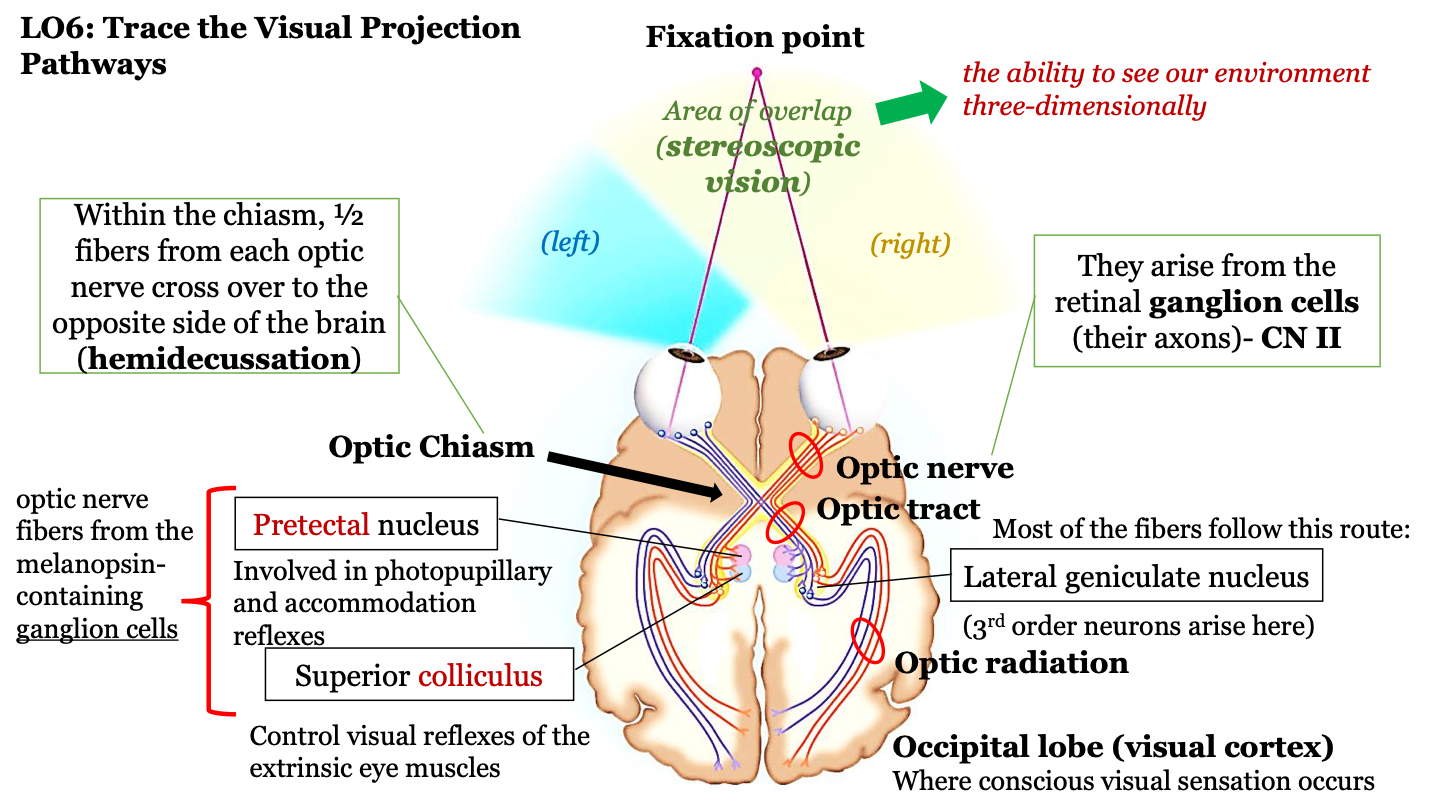
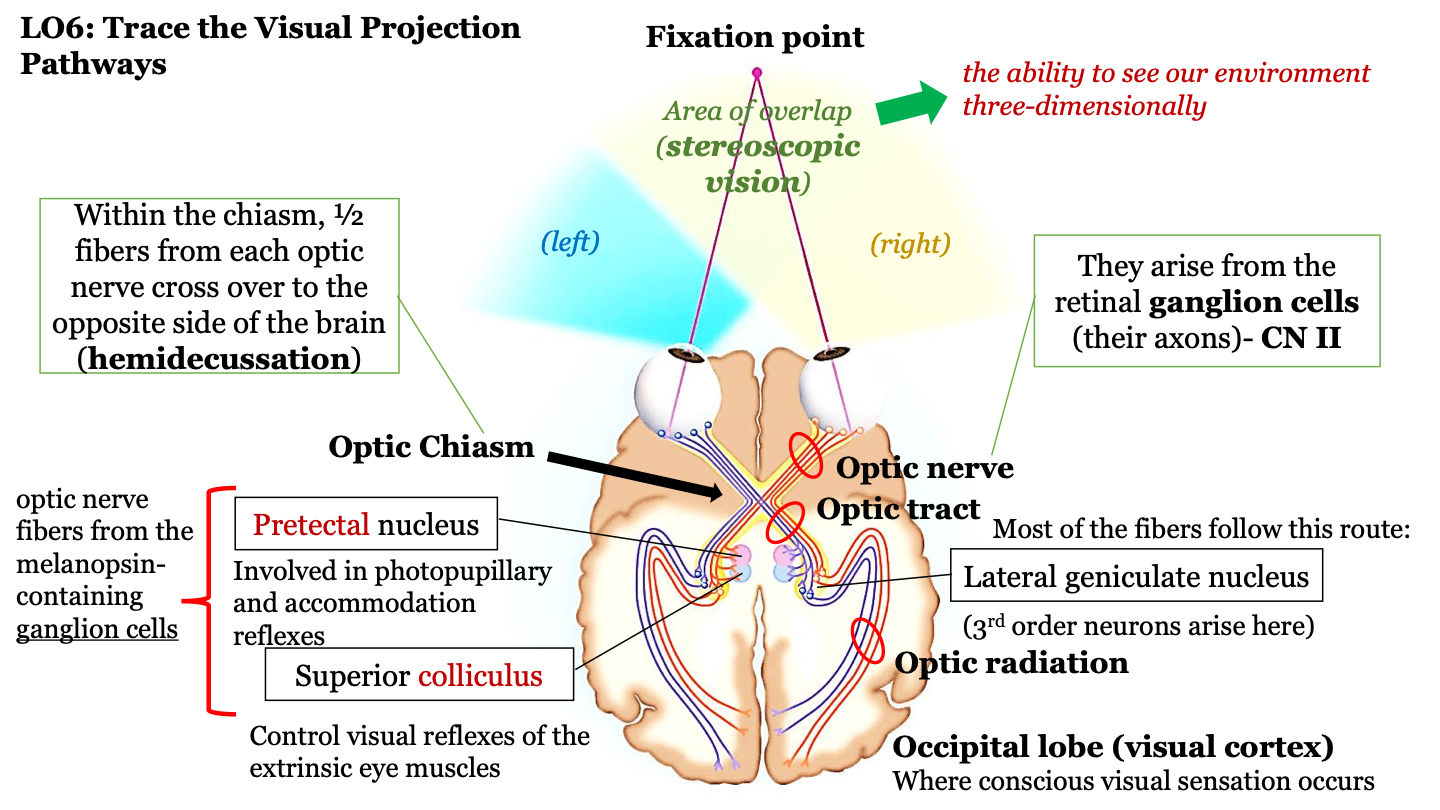
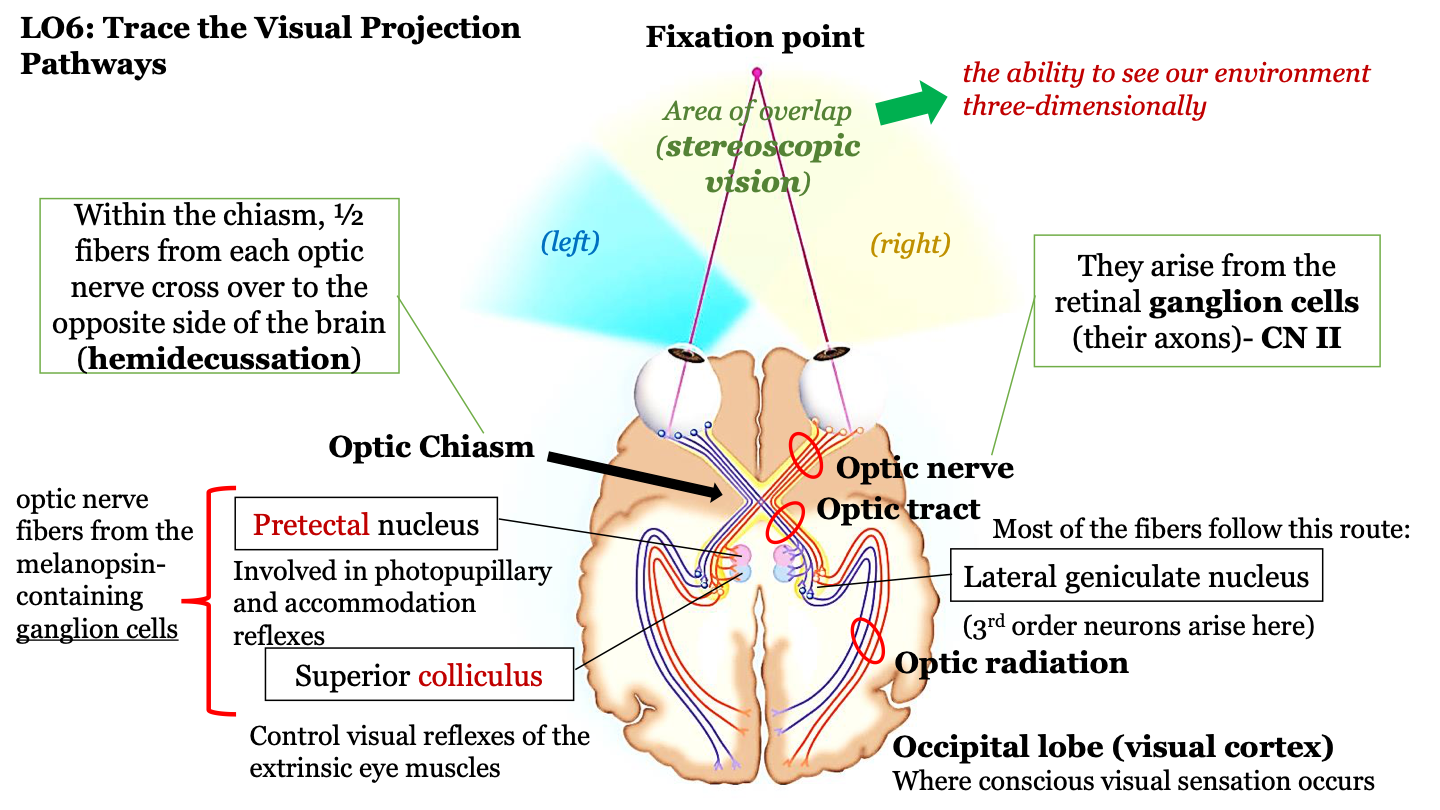
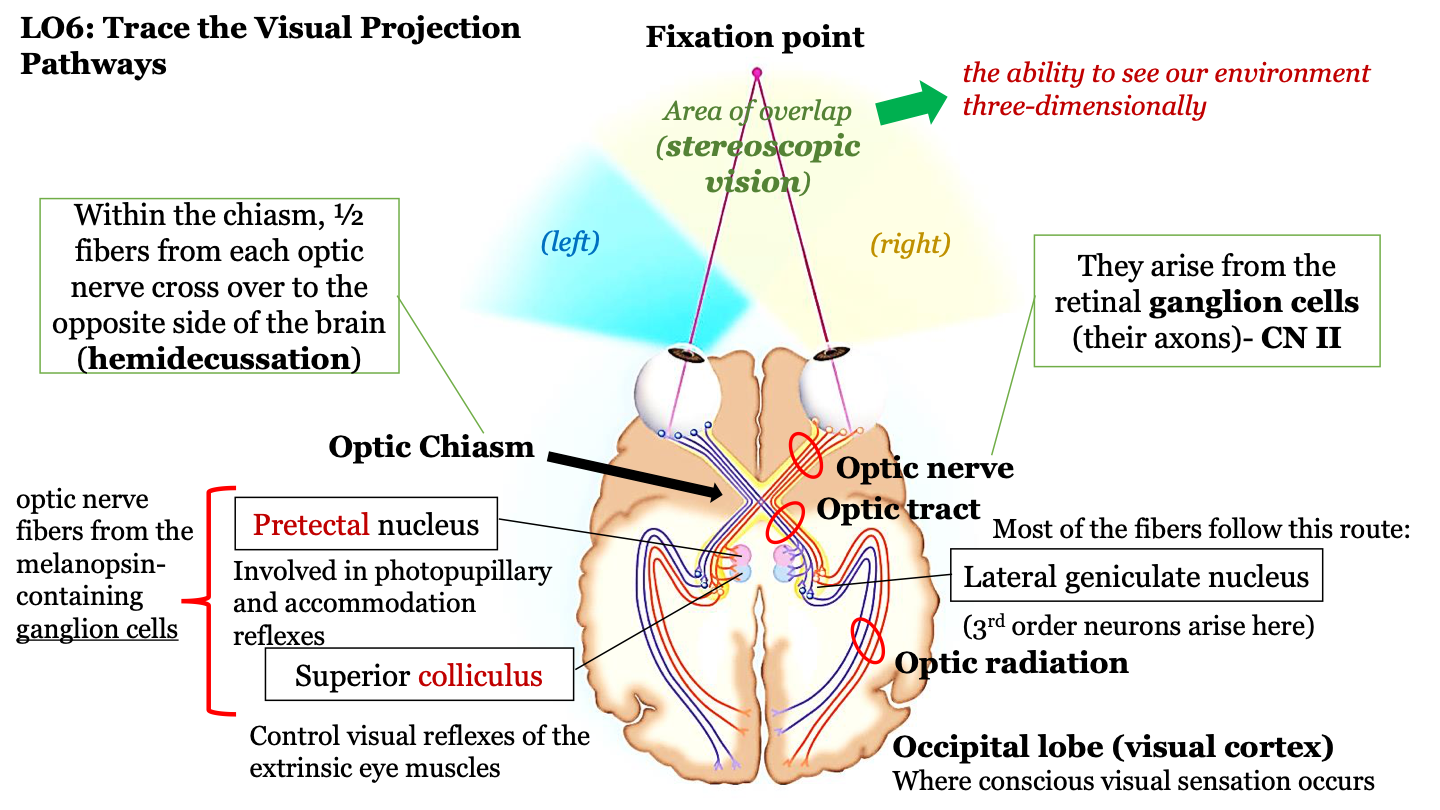
stereoscopic vision
the ability to see our environment in 3D
44
New cards
fixation point
area of overlap (stereoscopic vision) between the left and right visual fields
45
New cards
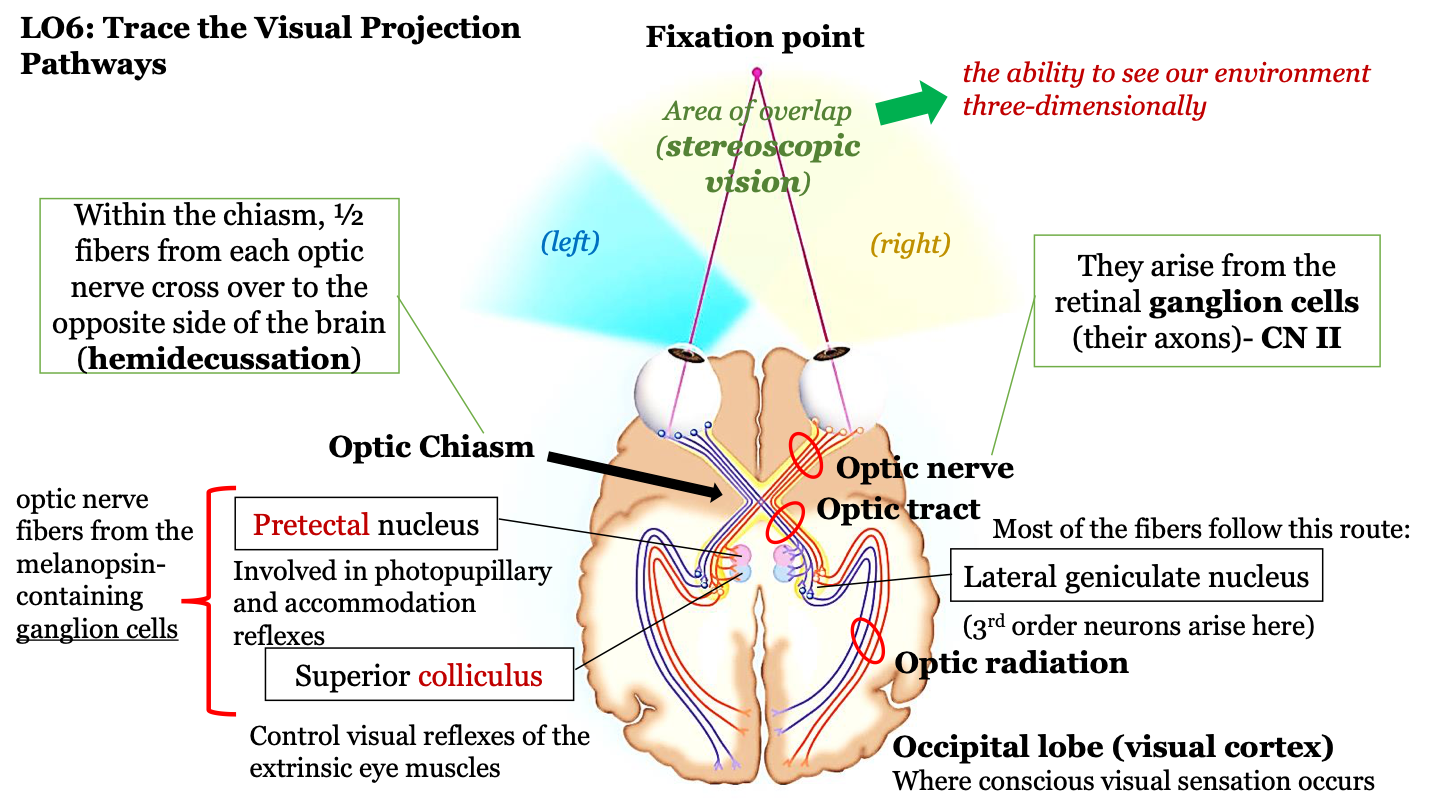
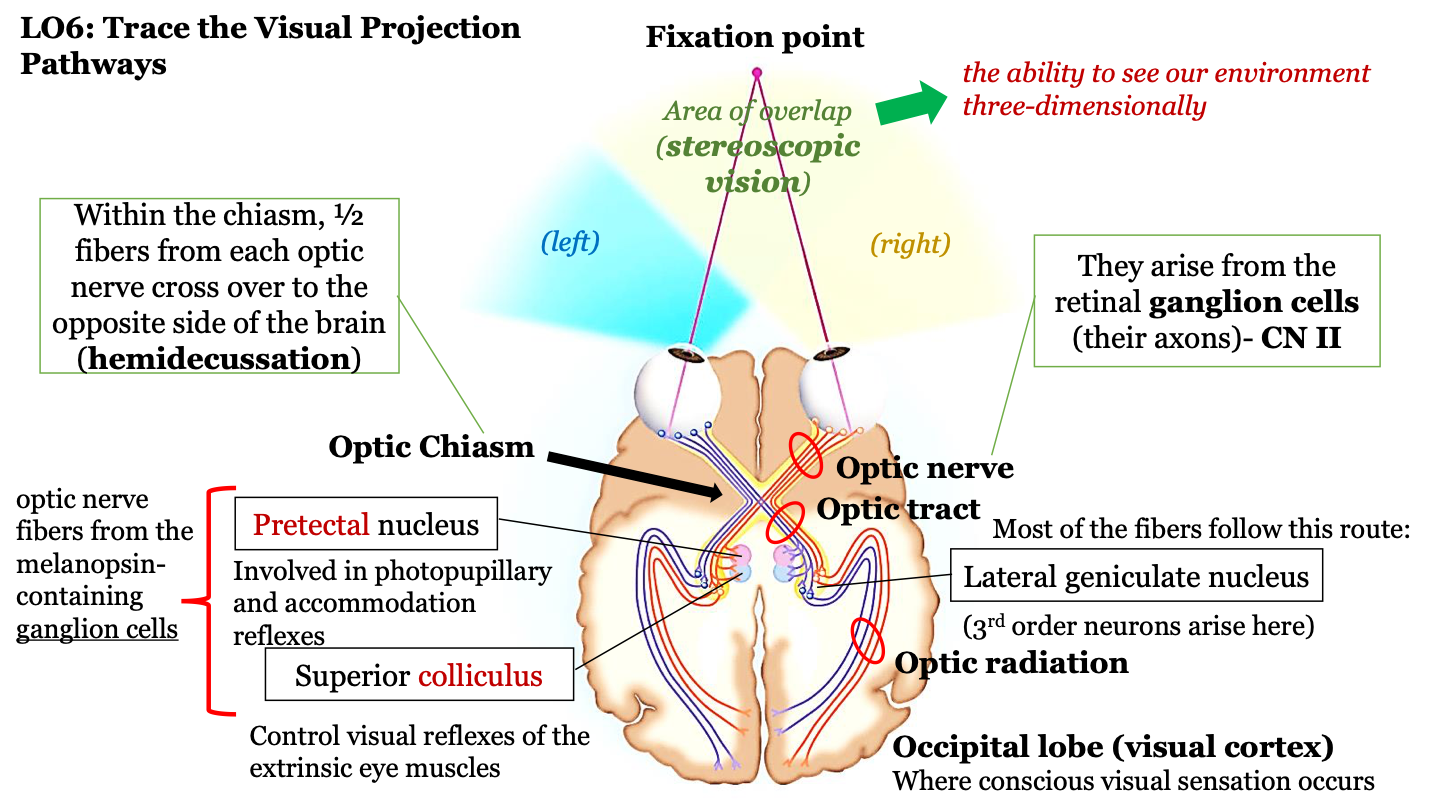
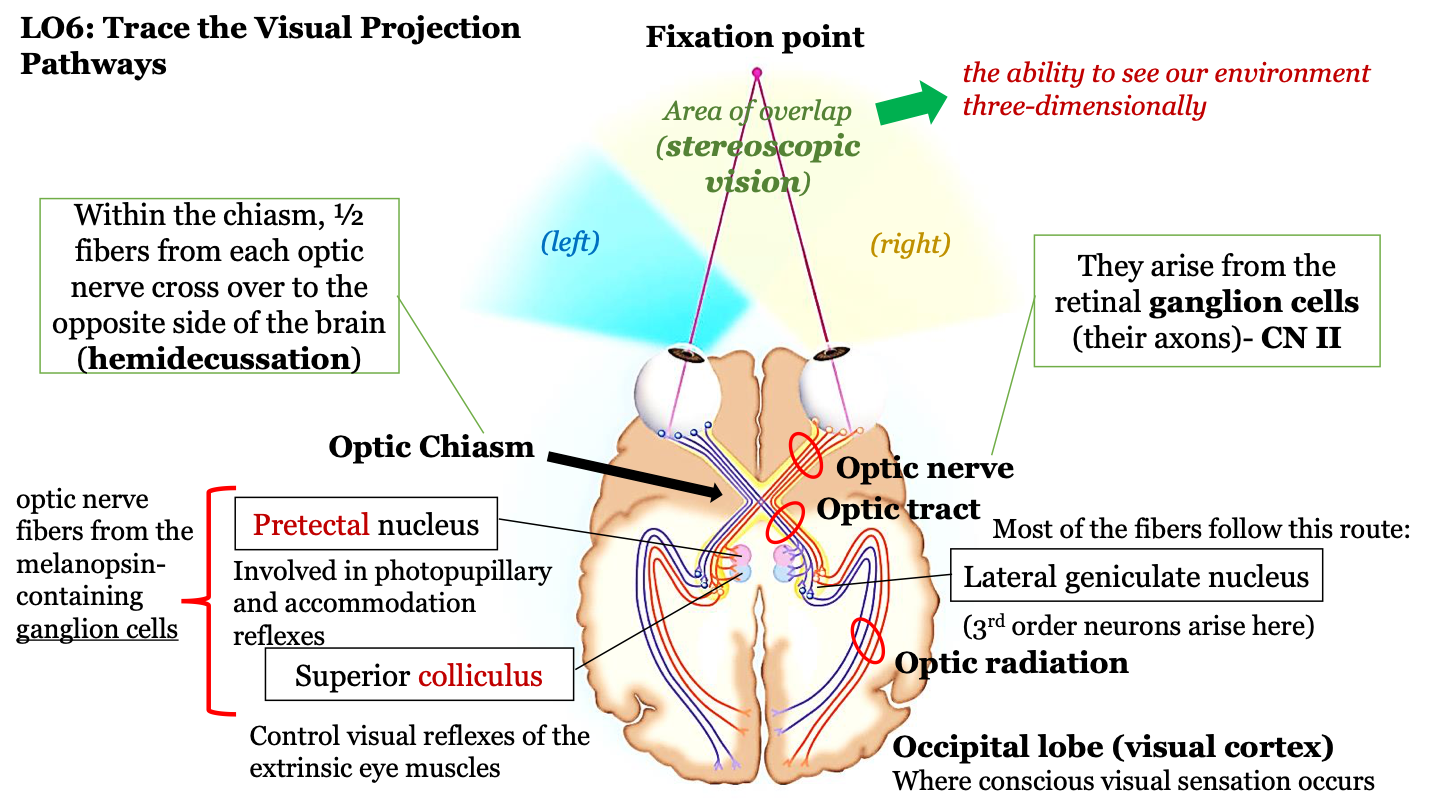
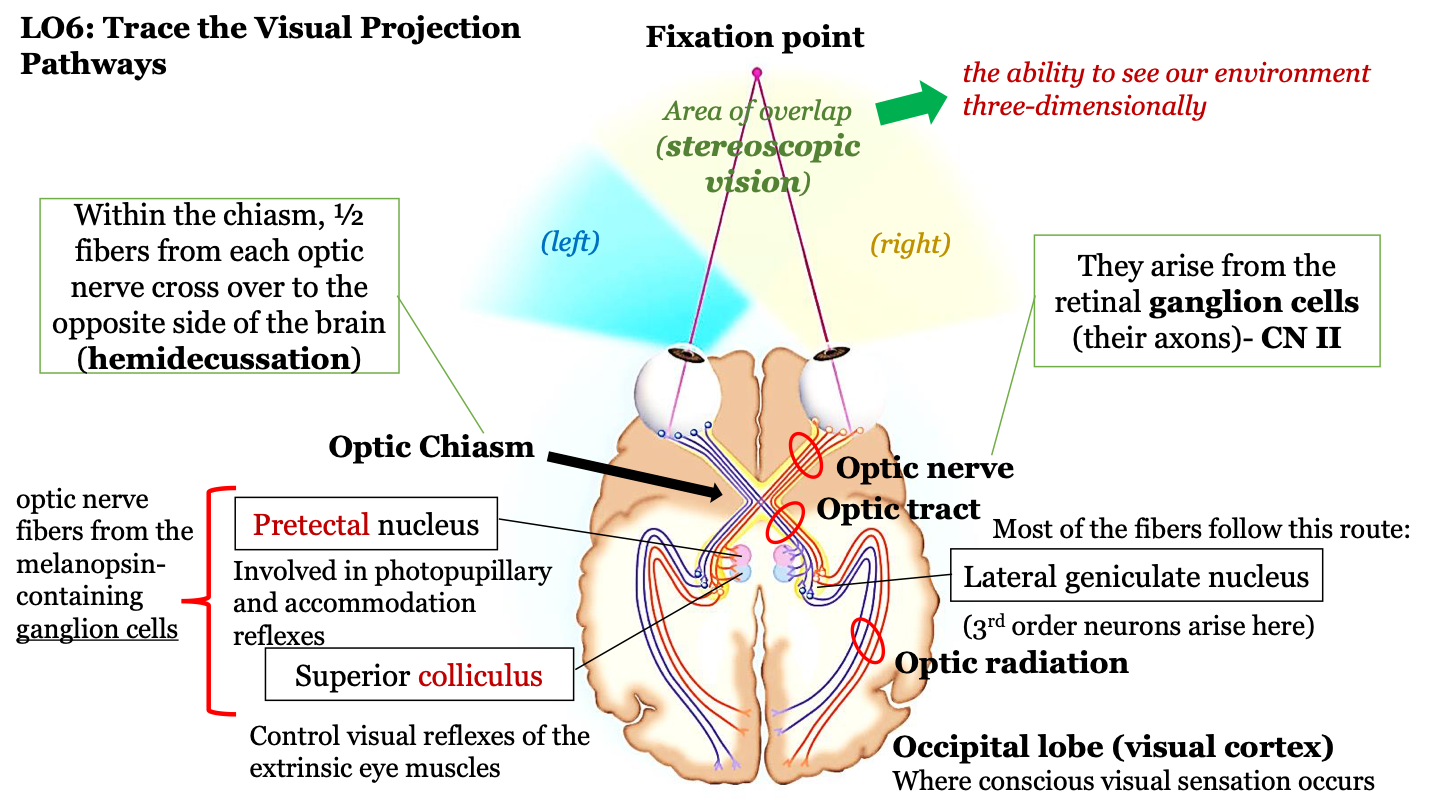
what happens in the optic chiasm?
half of the fibers from each optic nerve cross over to the opposite side of the brain (hemidecussation)
46
New cards
the visual projection pathway
1. eyes
2. optic nerve
3. optic chiasm
4. optic tract
5. optic radiation
6. occipital lobe
2. optic nerve
3. optic chiasm
4. optic tract
5. optic radiation
6. occipital lobe
47
New cards
where does the optic nerve arrive?
axons of the retinal ganglion cells (CN II)
48
New cards
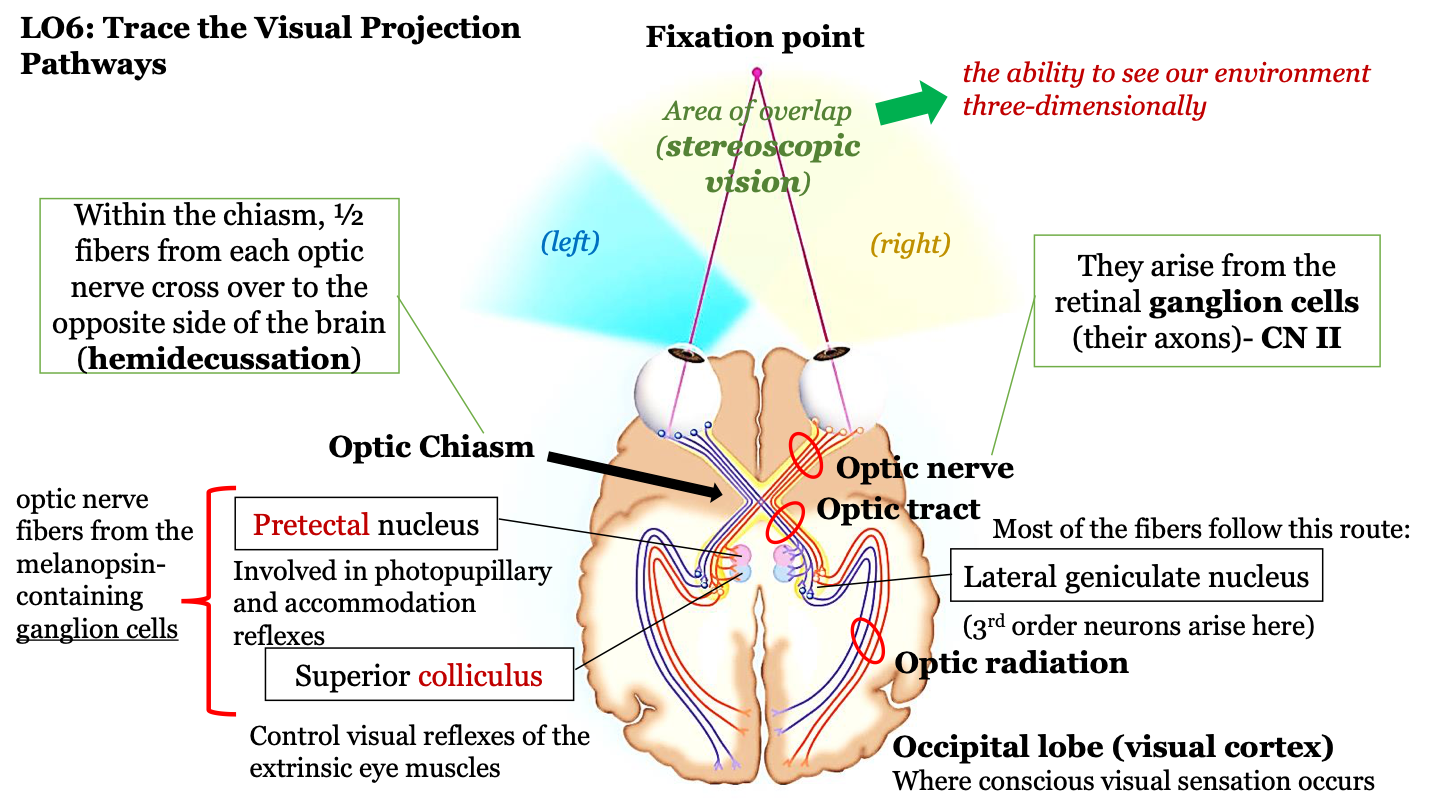
where route do most fibers in the optic tract follow?
the neurons in the optic tract go through the thalamus (where the lateral geniculate nucleus) is located and then to the cortex; 3rd order neurons arise in the LGN
49
New cards
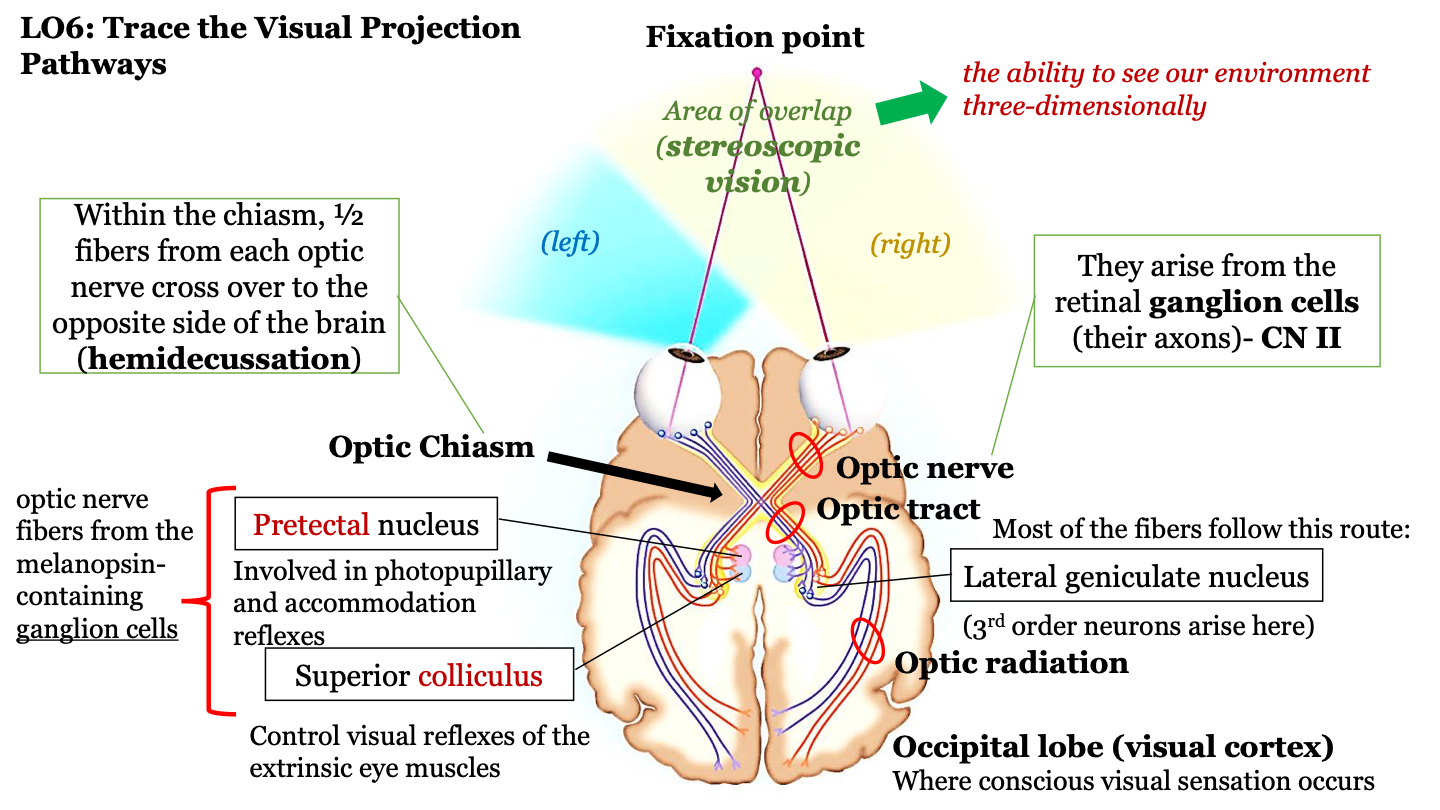
where does conscious visual sensation occur?
occipital lobe (visual cortex)
50
New cards
pretectal nucleus
involved in photopupillary and accommodation reflexes
51
New cards
superior colliculus
control visual reflexes of the extrinsic eye muscles
52
New cards
optic nerve fibers from the melanopsin-containing ganglion cells
pretectal nucleus and superior colliculus
53
New cards
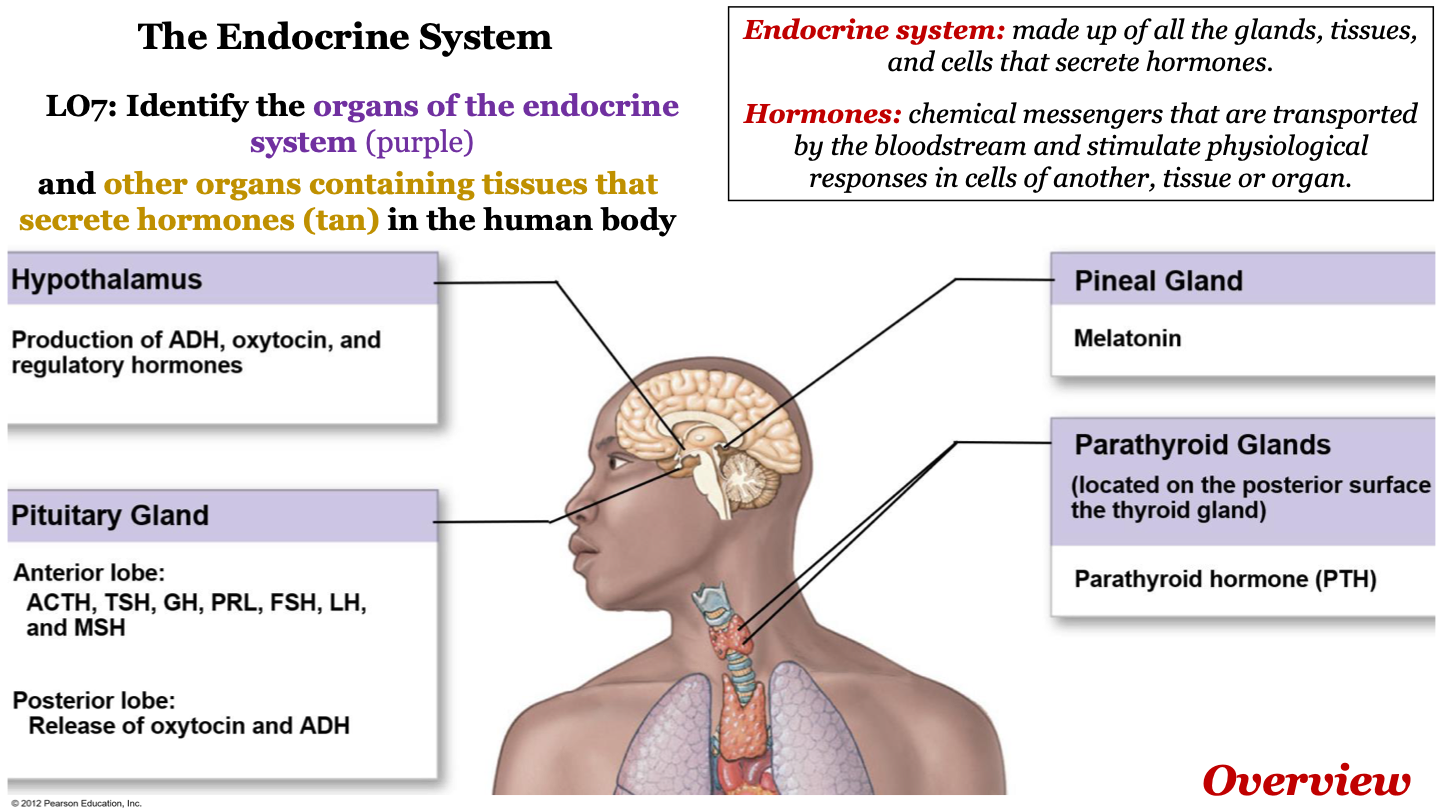
endocrine system
made up of all the glands, tissues, and cells that secrete hormones
54
New cards
hormones
chemical messengers that are transported by the bloodstream and stimulate physiological responses in cells of another, tissue or organ
55
New cards
organs of the endocrine system
-hypothalamus
-pineal gland
-parathyroid glands
-pituitary gland
-thyroid gland
-adrenal gland
-pancreas
-pineal gland
-parathyroid glands
-pituitary gland
-thyroid gland
-adrenal gland
-pancreas
56
New cards
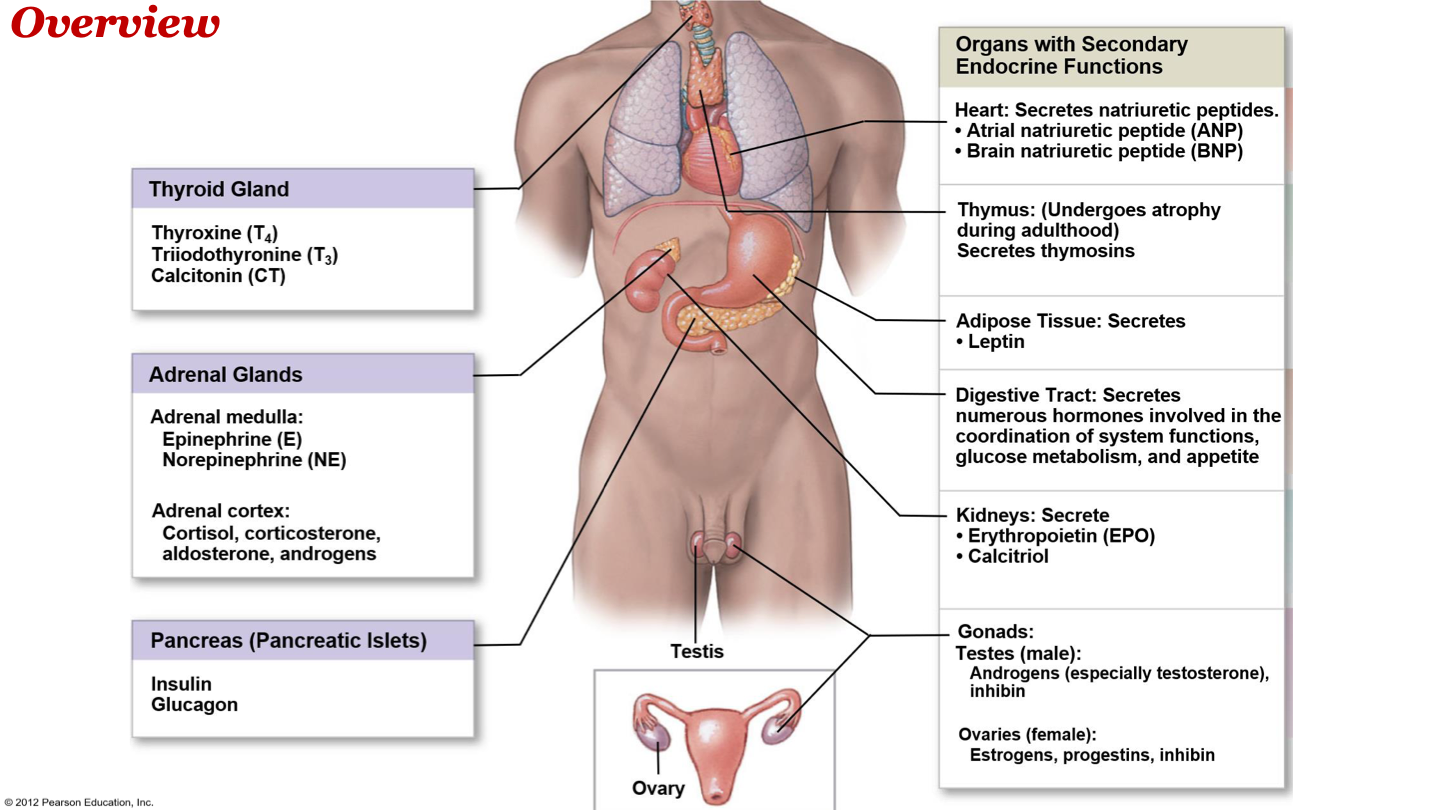
organs containing tissues that secrete hormones (organs that have secondary endocrine functions)
-heart
-thymus
-adipose tissue
-digestive tract
-kidneys
-gonads
-ovaries
-thymus
-adipose tissue
-digestive tract
-kidneys
-gonads
-ovaries
57
New cards
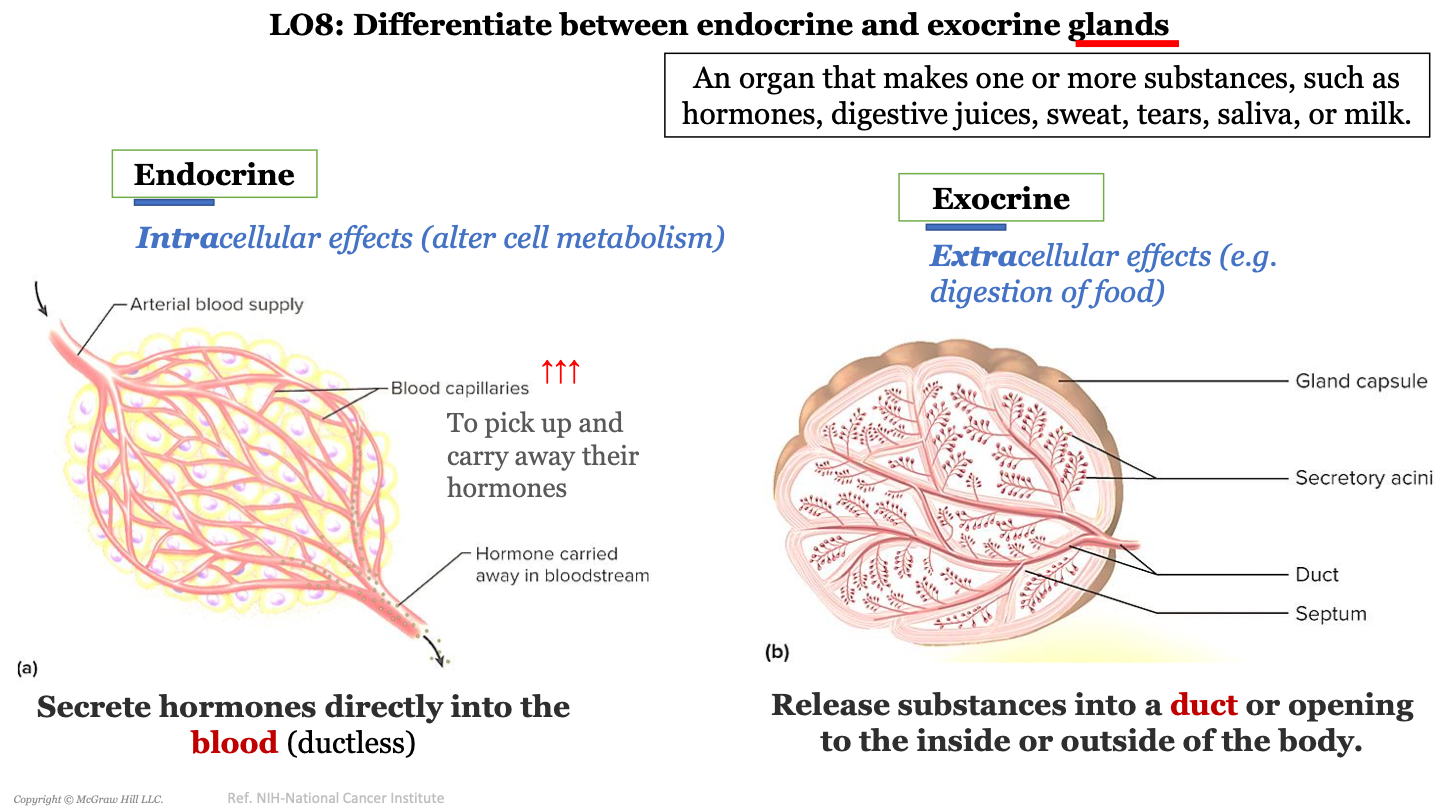
endocrine glands
have intracellular effects (alter cell metabolism); secrete hormones directly into the blood (ductless)
58
New cards
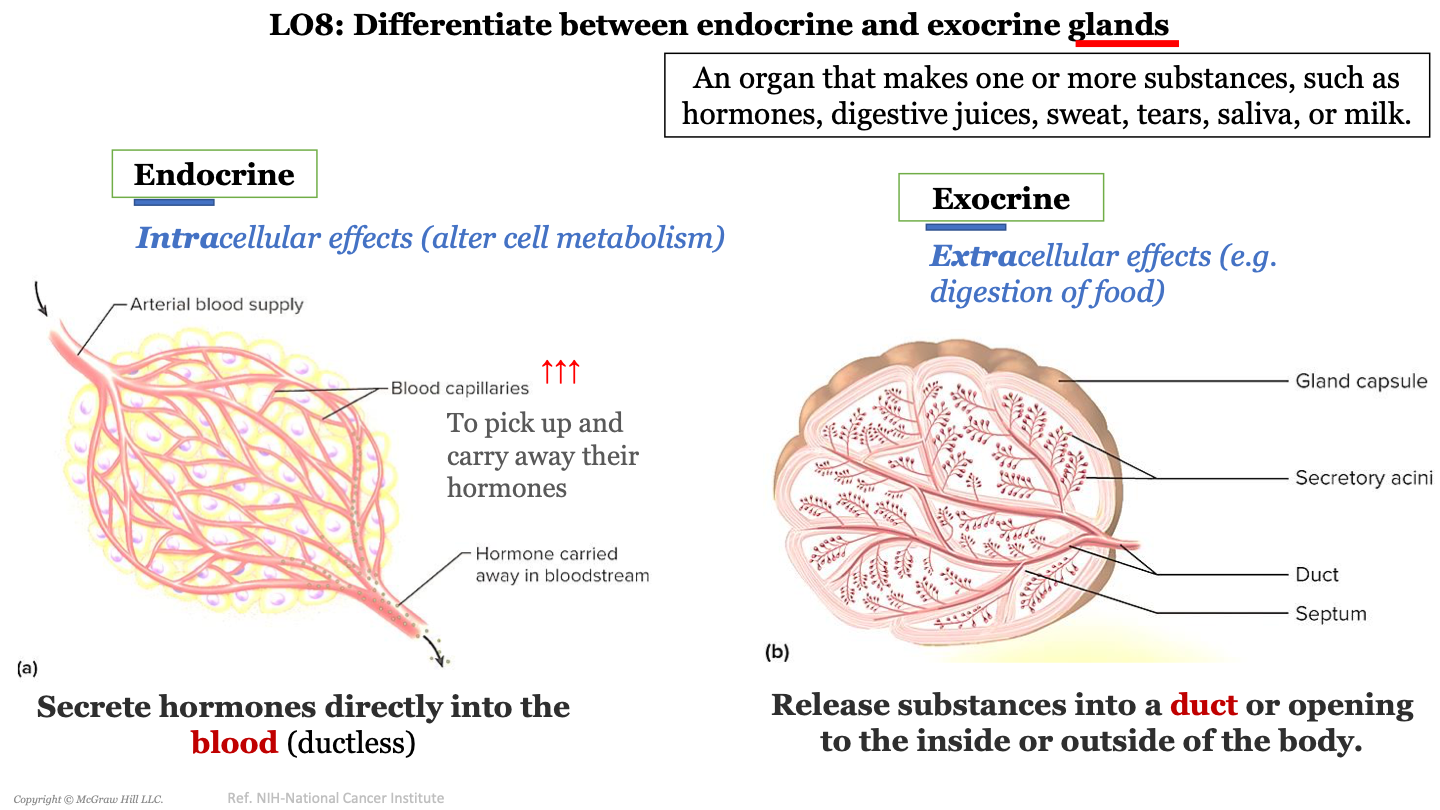
exocrine glands
extracellular effects (e.g. digestion of food); release substances into a duct or opening to the inside or outside of the body
59
New cards
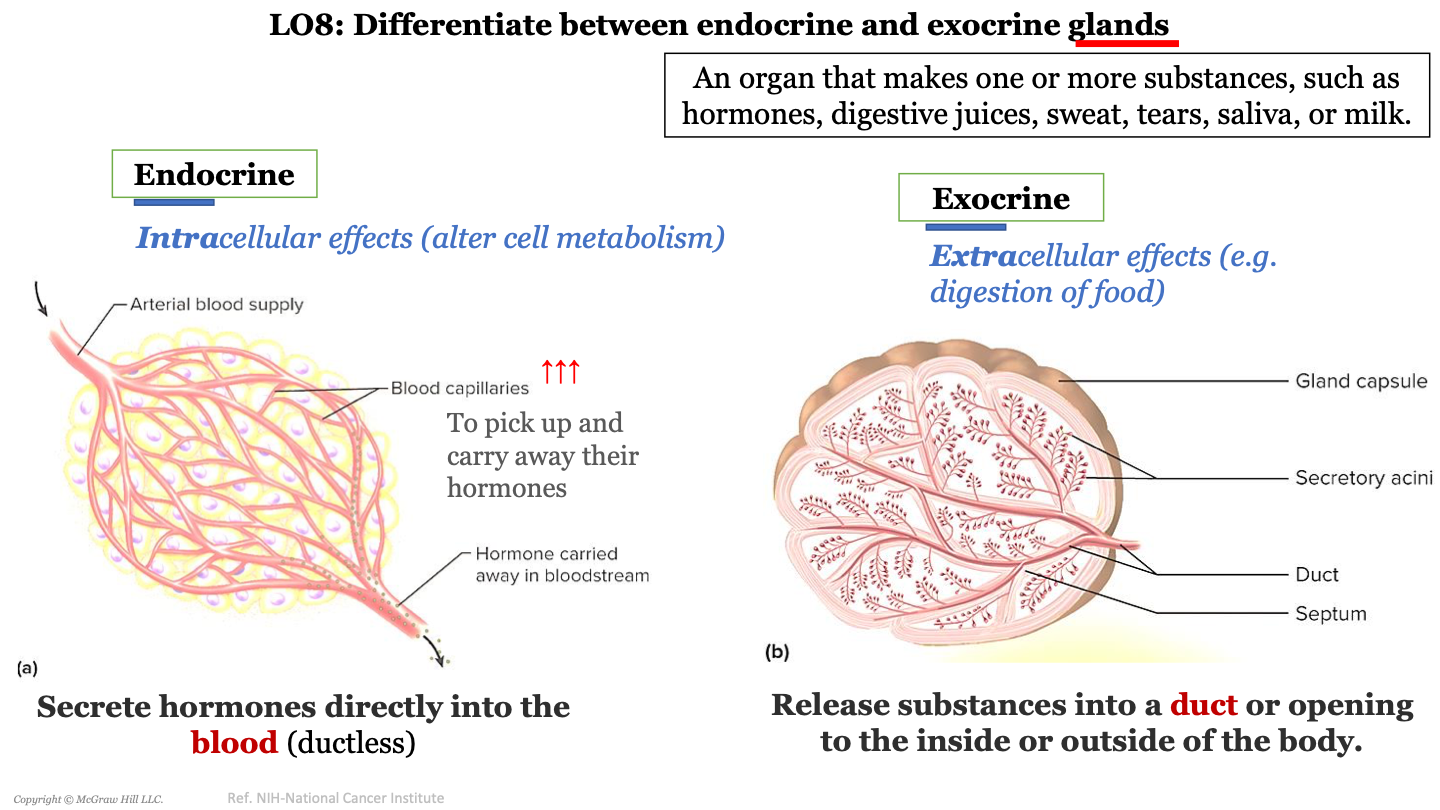
what is a gland?
an organ that makes one or more substances such as hormones, digestive juices, sweat, tears, saliva, or milk
60
New cards
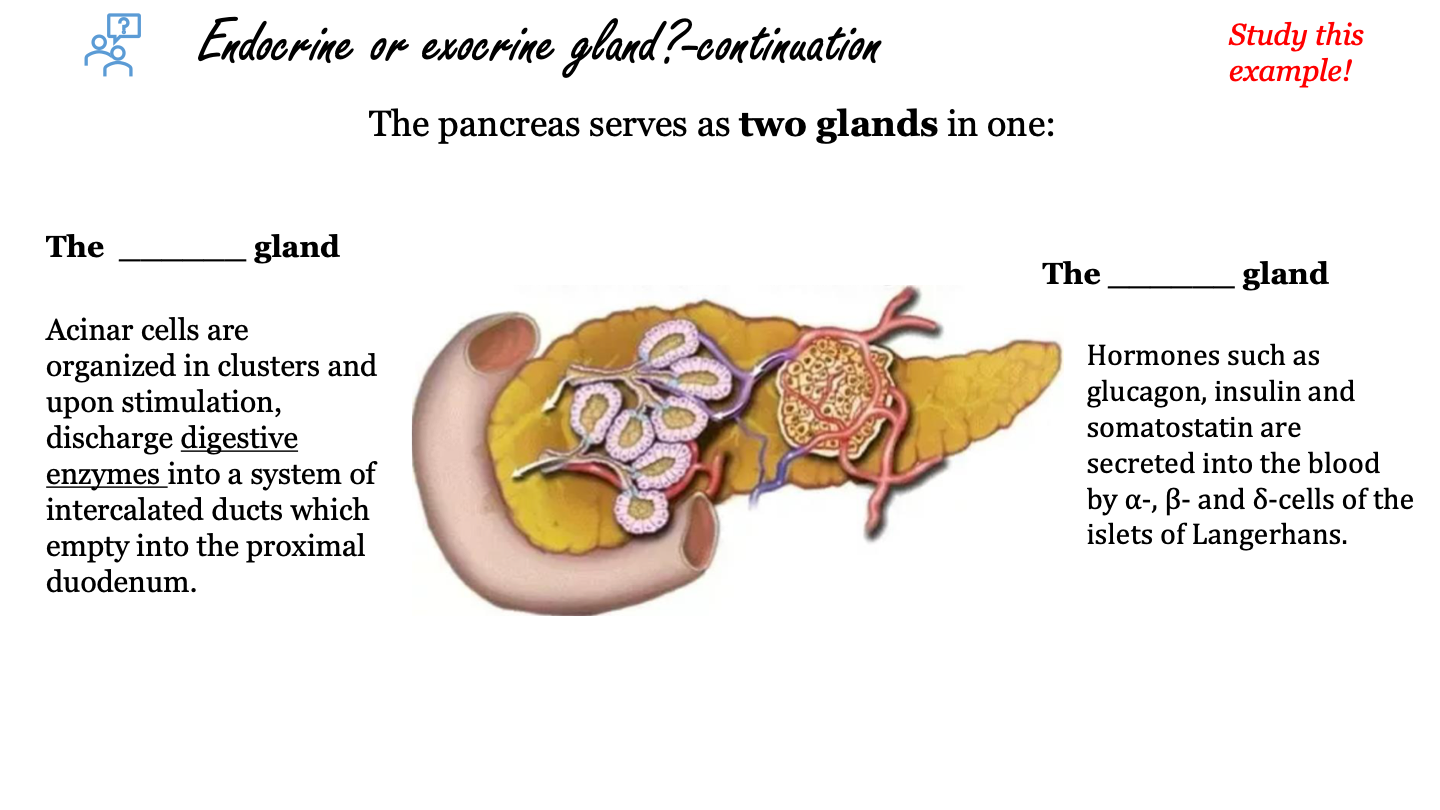
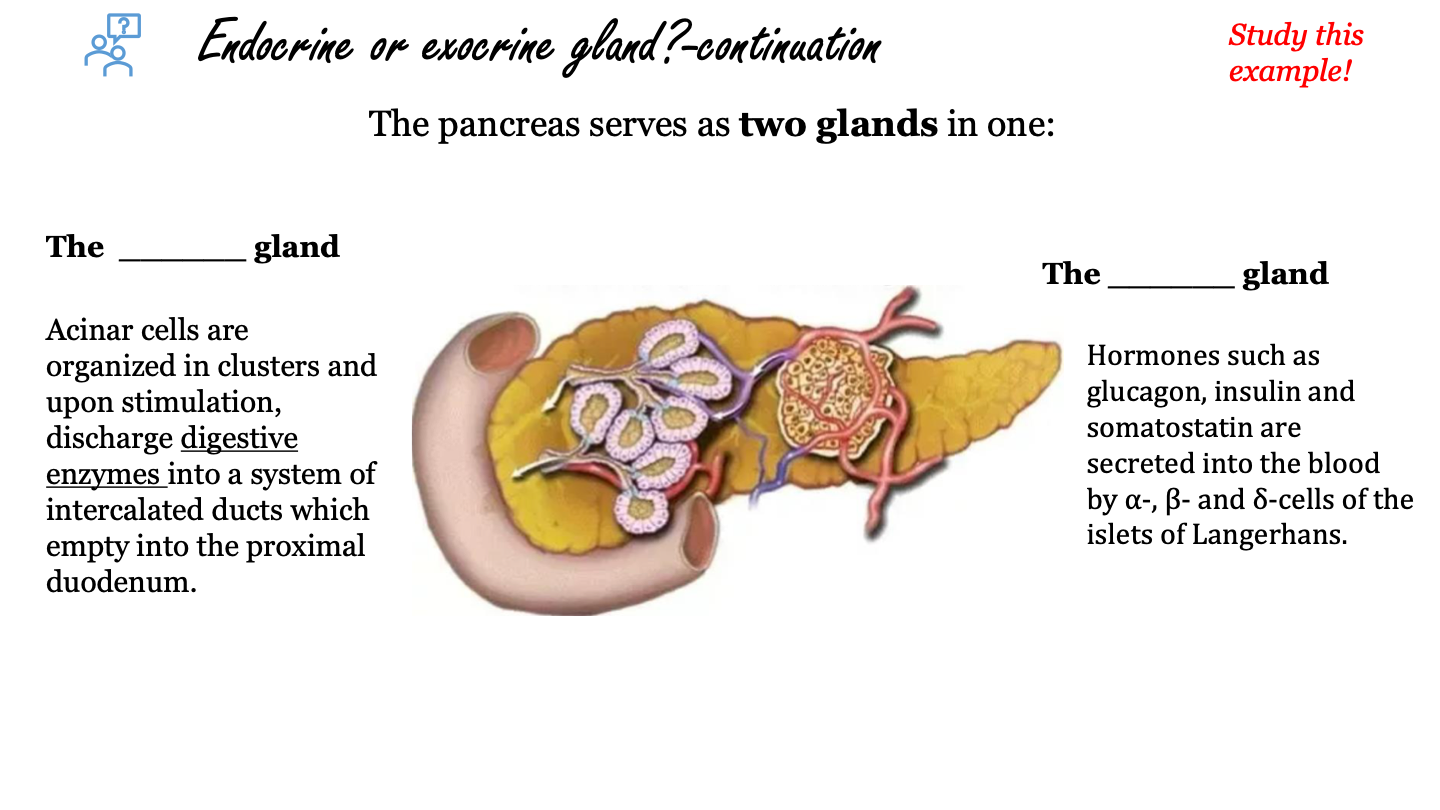
the pancreas as an exocrine gland
acinar cells are organized in clusters and upon stimulation, discharge digestive enzymes into a system of intercalated ducts which empty into the proximal duodenum
61
New cards
the pancreas as an endocrine gland
hormones such as glucagon, insulin and somatostatin are secreted into the blood by alpha, beta and delta cells of the islets of Langerhans
62
New cards
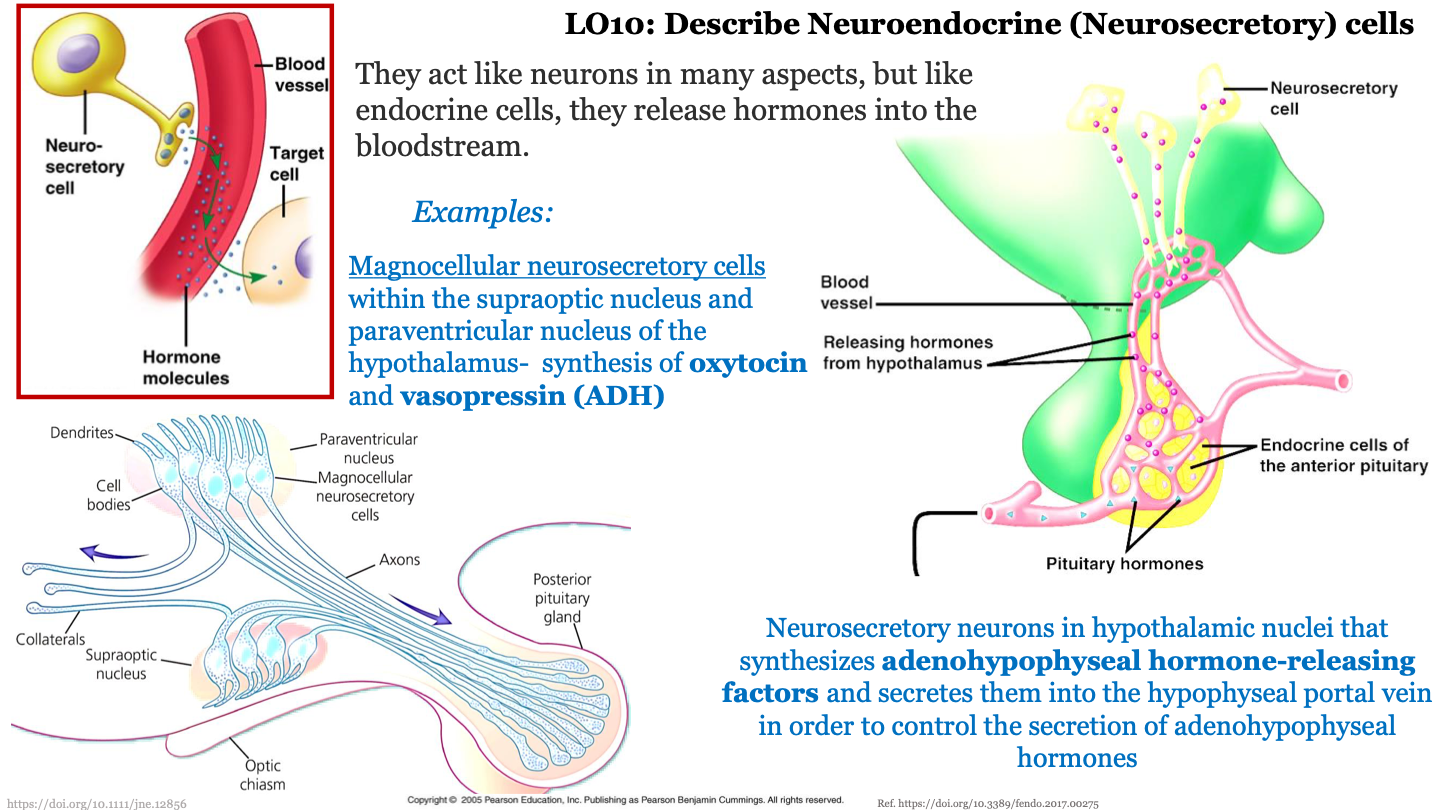
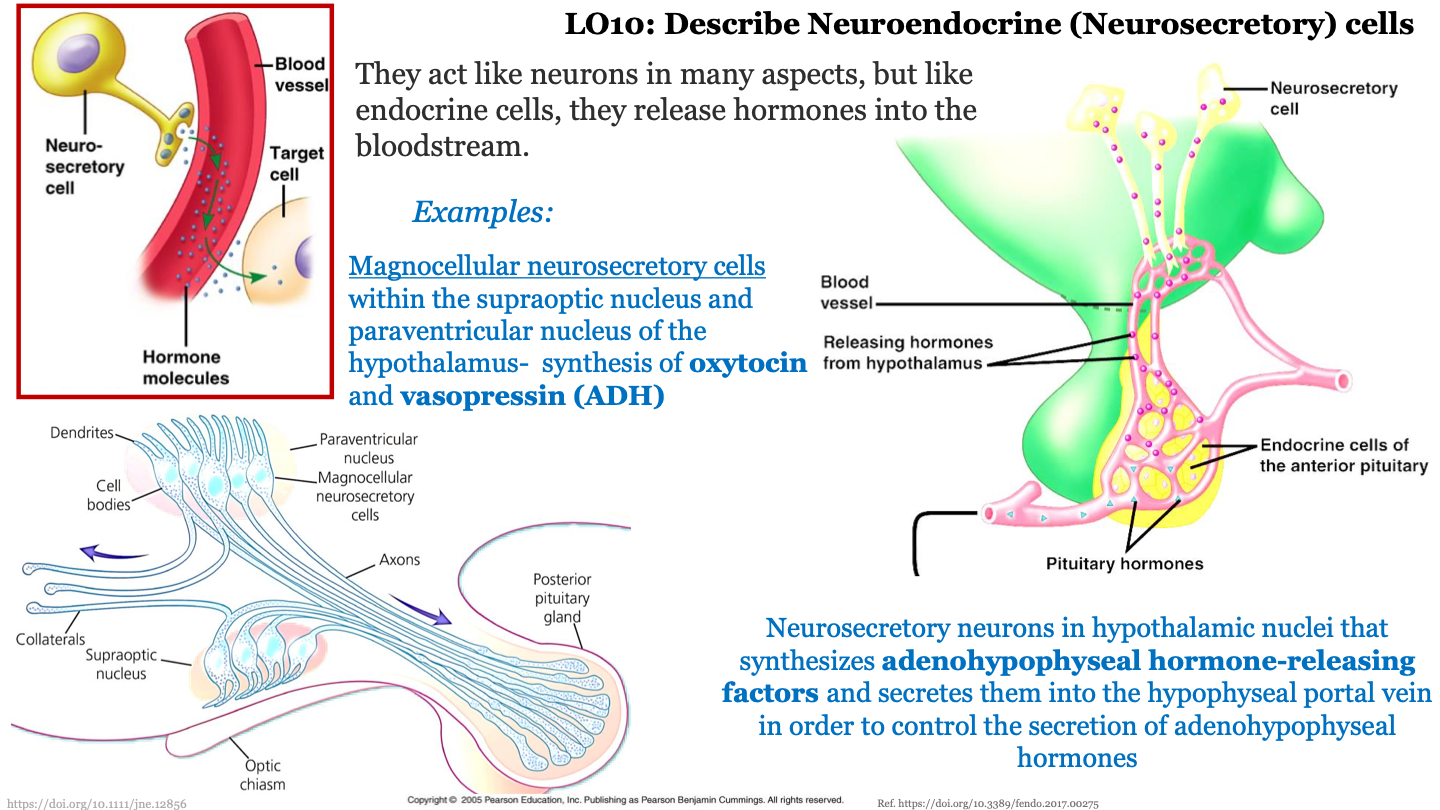
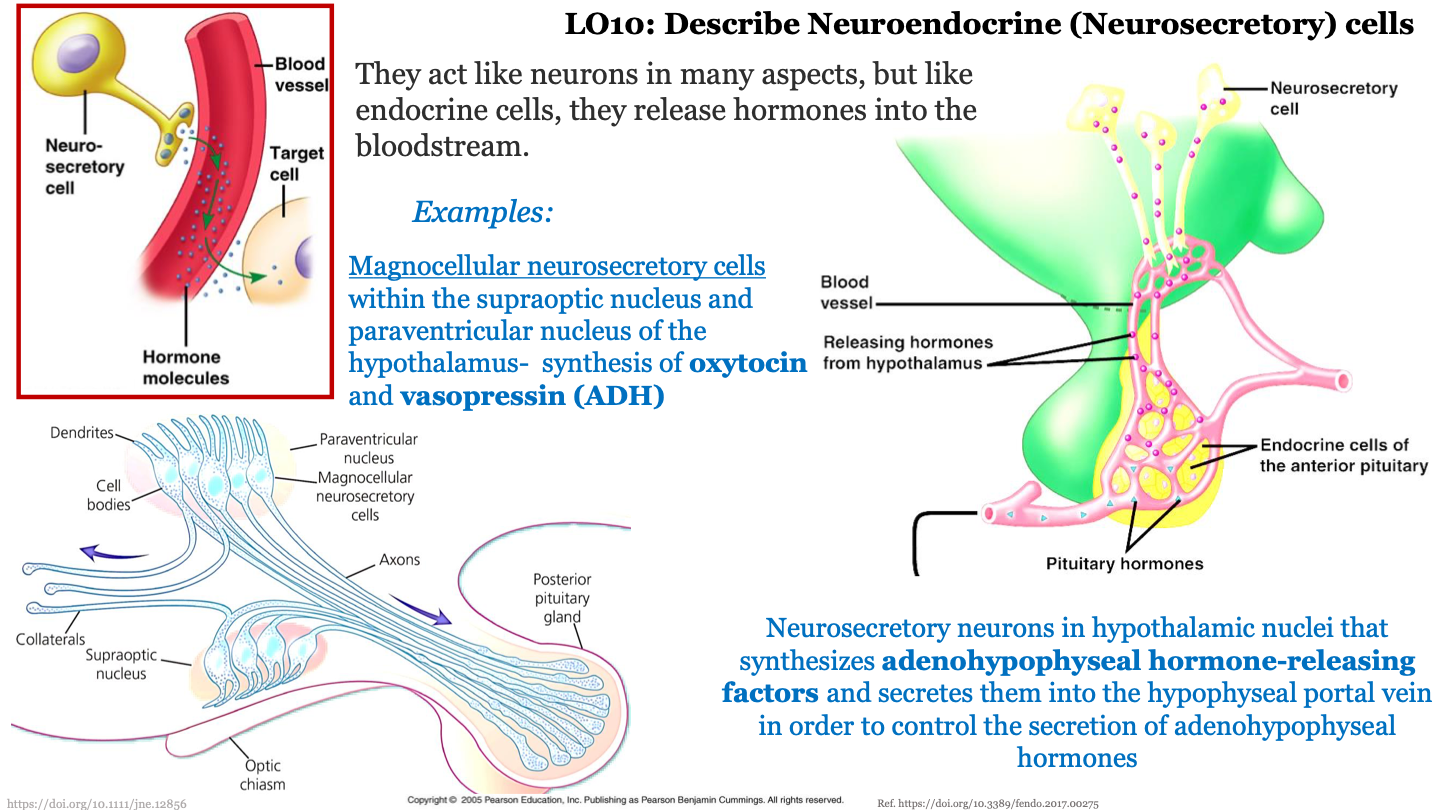
neuroendocrine (neurosecretory) cells
they act like neurons in many aspects, but like endocrine cells, they release hormones into the bloodstream
63
New cards
example of neuroendocrine (neurosecretory) cells - magnocellular neurosecretory cells
magnocellular neurosecretory cells within the supraoptic nucleus and paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus; synthesize oxytocin and vasopressin (ADH) and release them into bloodstream; these cells have neurons that have axons that travel towards the posterior pituitary gland
64
New cards
example of neuroendocrine (neurosecretory) cells - neurosecretory neurons in hypothalamic nuclei
neurosecretory neurons in hypothalamic nuclei synthesize adenohypophyseal hormone-releasing factors and secrete them into the hypophyseal portal vein in order to control the secretion of adenohypophyseal hormone from the anterior pituitary gland
65
New cards
similarities between the NS and endocrine systems - communication
-both serve for internal communication: they complement each other
-some neurons trigger H secretion, and some H stimulate or inhibit neurons
-some neurons trigger H secretion, and some H stimulate or inhibit neurons
66
New cards
similarities between the NS and endocrine systems - function
-several chemicals function as both NT and hormones: noepinephrine, dopamine, and antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
-ex: dopamine can be considered a hormone when secreted by an endocrine cell but a NT when secreted by a nerve cell
-ex: dopamine can be considered a hormone when secreted by an endocrine cell but a NT when secreted by a nerve cell
67
New cards
similarities between the NS and endocrine systems - effects
-some hormones and NT produce identical effects on the same organ
-ex: both NA and glucagon stimulate the liver to break down glycogen and release glucose
-ex: both NA and glucagon stimulate the liver to break down glycogen and release glucose
68
New cards
similarities between the NS and endocrine systems - target cells
-only certain target organs or target cells respond to NT or H (receptors)
-In the case of hormones, it can also occur that the circulating hormone is inactive and only the target cells have the enzyme needed to convert it to active form
-In the case of hormones, it can also occur that the circulating hormone is inactive and only the target cells have the enzyme needed to convert it to active form
69
New cards
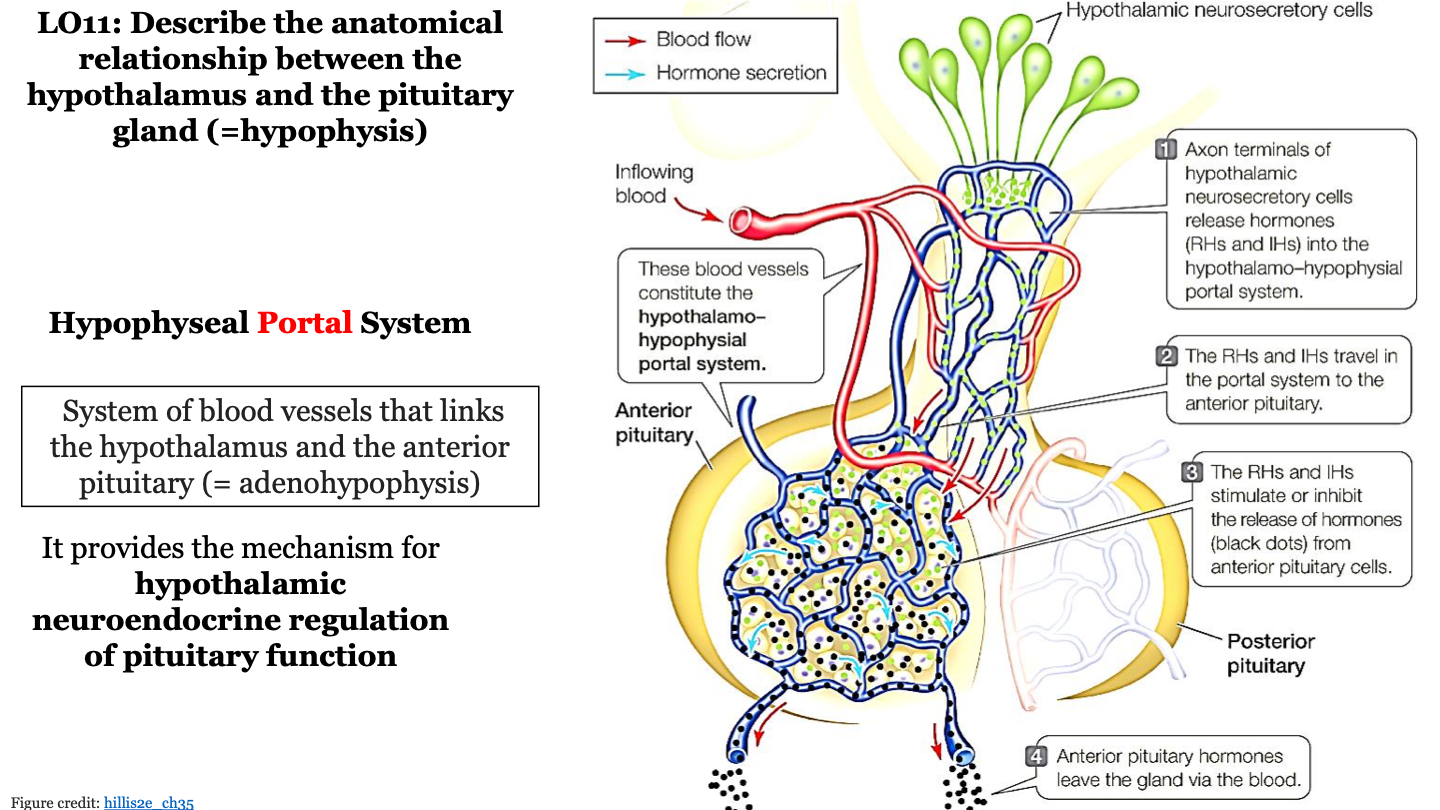
hypophyseal portal system
system of blood vessels that links the hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary
70
New cards
steps in hypophyseal portal system
71
New cards
what mechanism does the hypophyseal portal system provide?
it provides the mechanism for hypothalamic neuroendocrine regulation of pituitary function
72
New cards
anterior pituitary = ?
adenohypophysis
73
New cards
what is the hypophyseal portal system known as?
"blood connection"
74
New cards
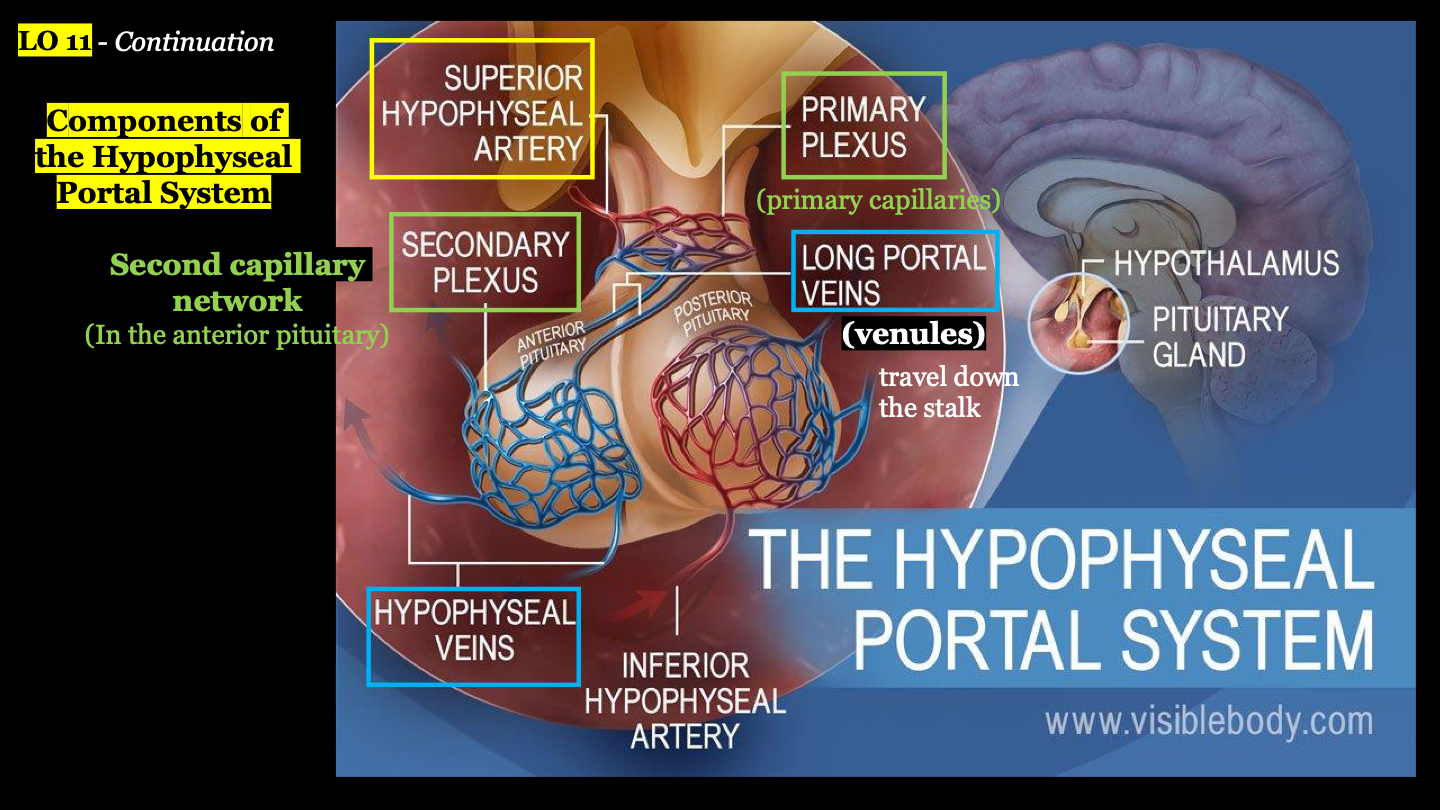
components of the hypophyseal portal system
1. superior hypophyseal artery
2. primary plexus (primary capillaries)
3. long portal veins
4. secondary plexus (second capillary network)
5. hypophyseal veins
2. primary plexus (primary capillaries)
3. long portal veins
4. secondary plexus (second capillary network)
5. hypophyseal veins
75
New cards
plexus
network of capillaries
76
New cards
where is the secondary plexus?
in the anterior pituitary
77
New cards
what are the primary and secondary plexus connected by?
long portal veins (AKA venules); these travel down the stalk
78
New cards
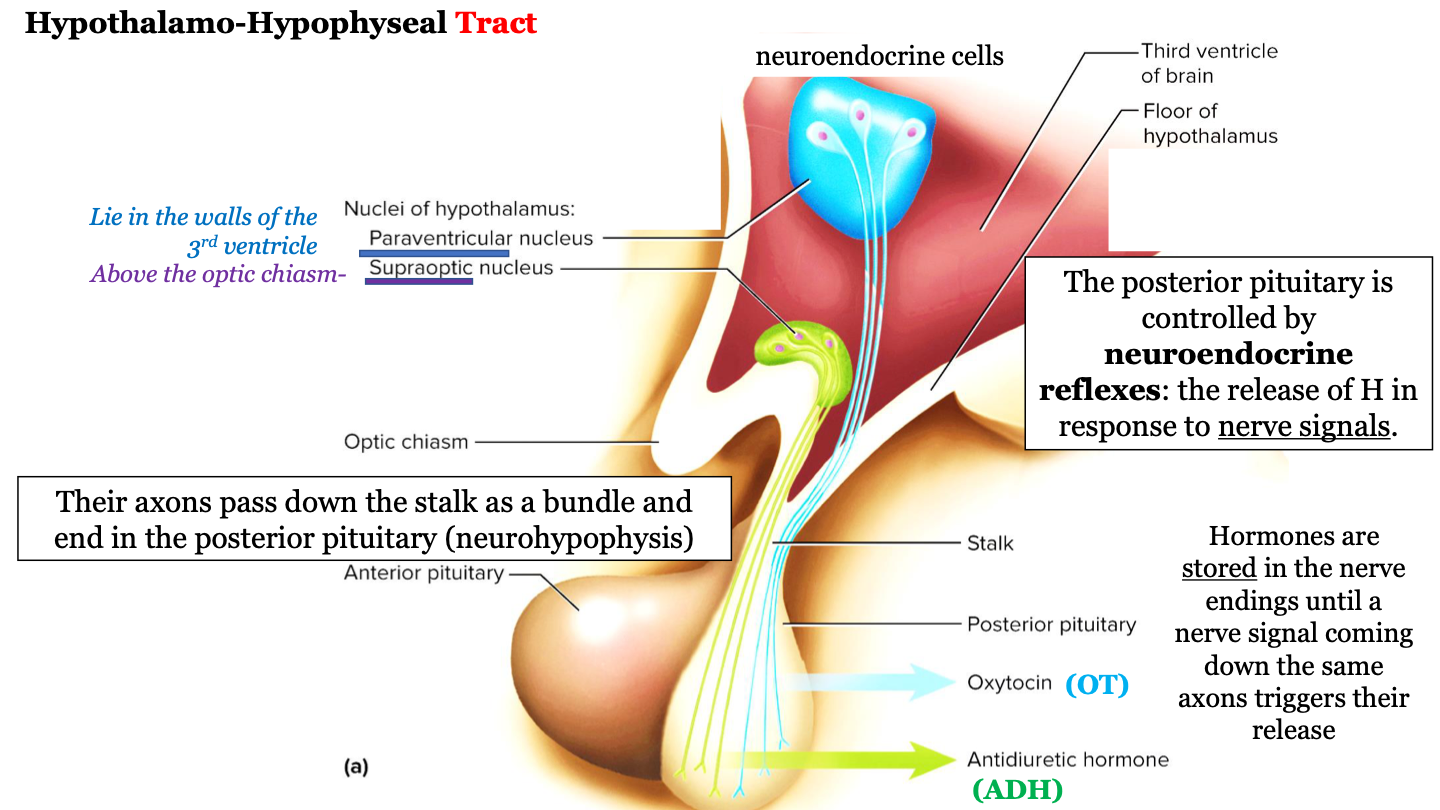
what is the posterior pituitary controlled by?
the neuroendocrine reflexes (the release of hormone in response to nerve signals)
79
New cards
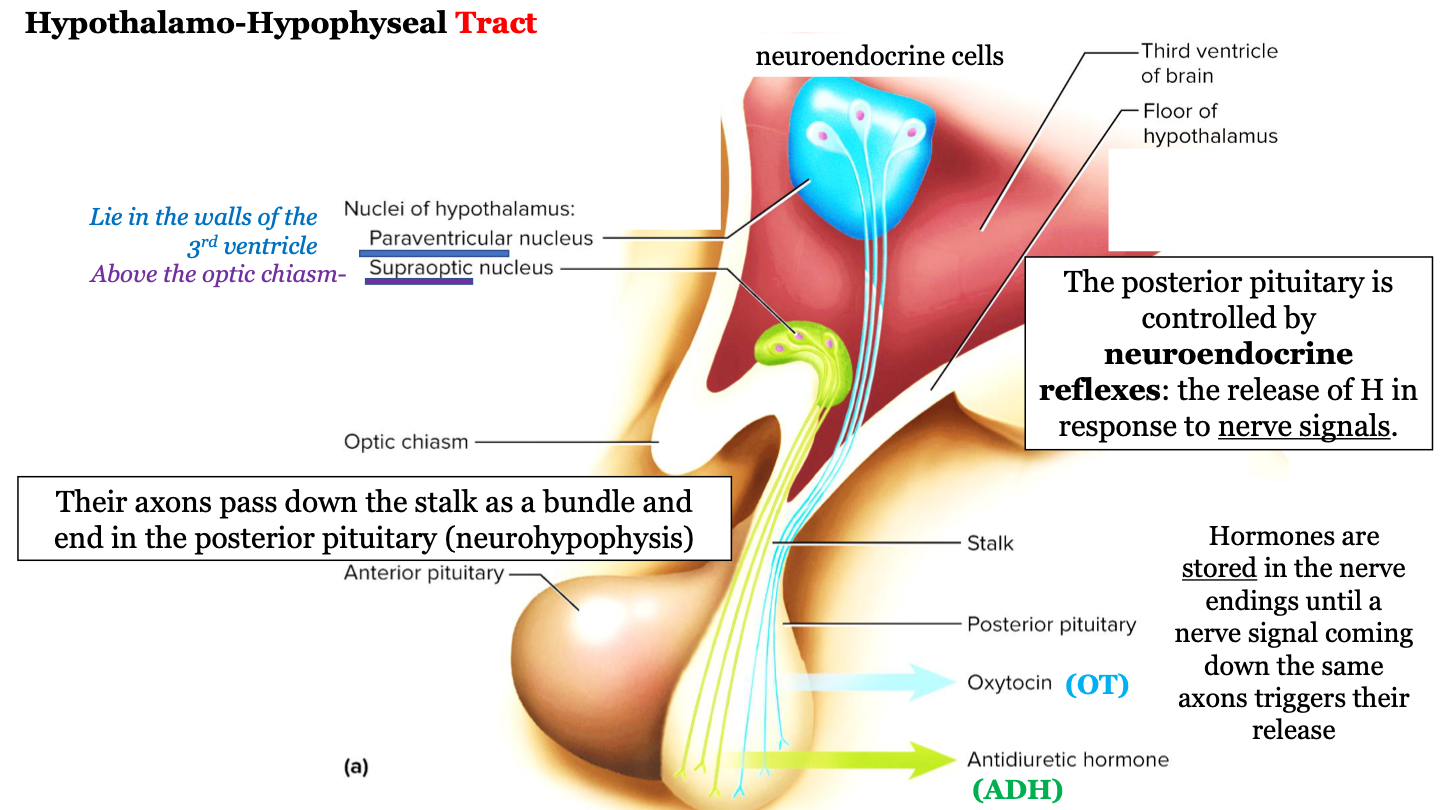
where are hormones stored?
hormones are stored in the nerve endings until a nerve signal coming down the same axons triggers their release
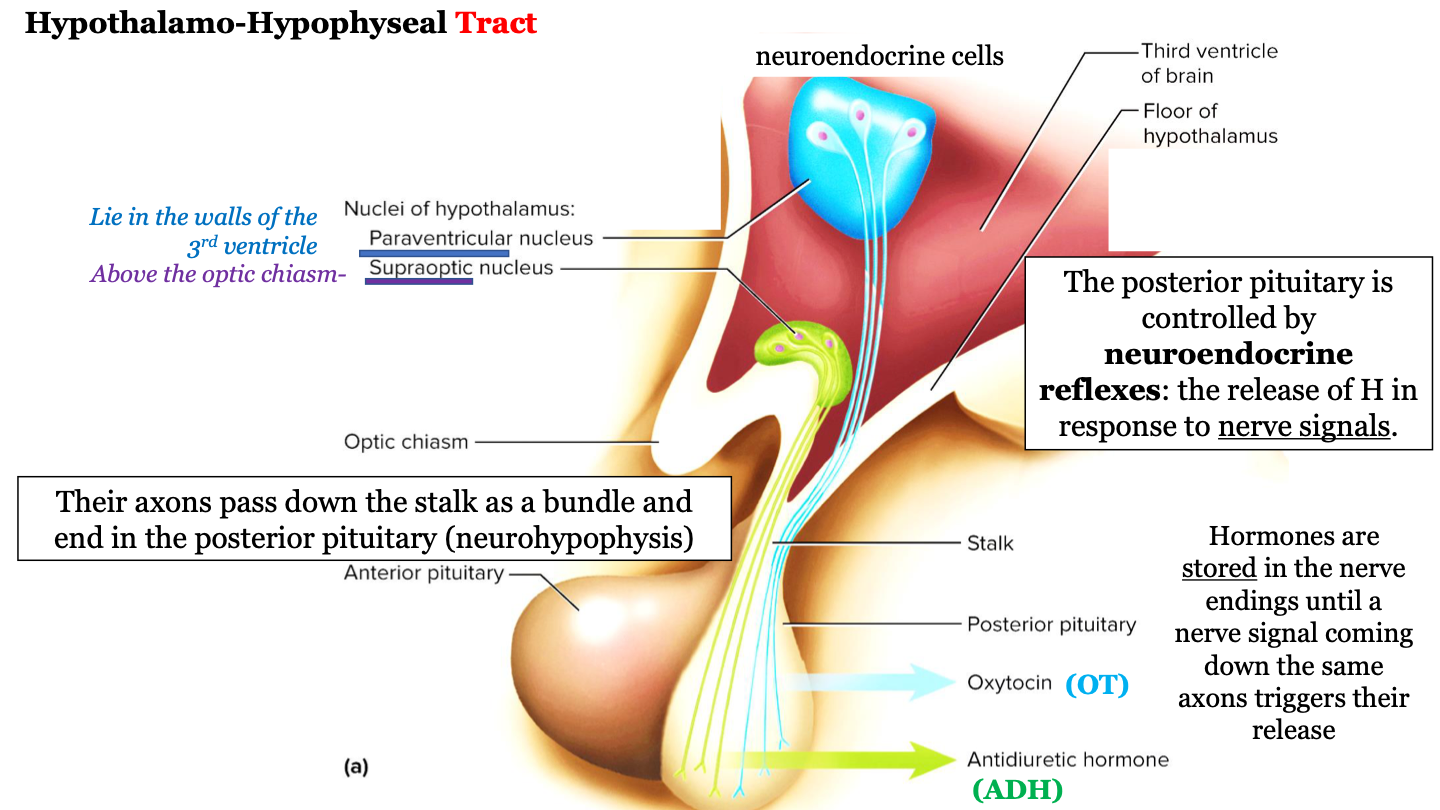
80
New cards
what is the hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract known as?
"nerve connection"
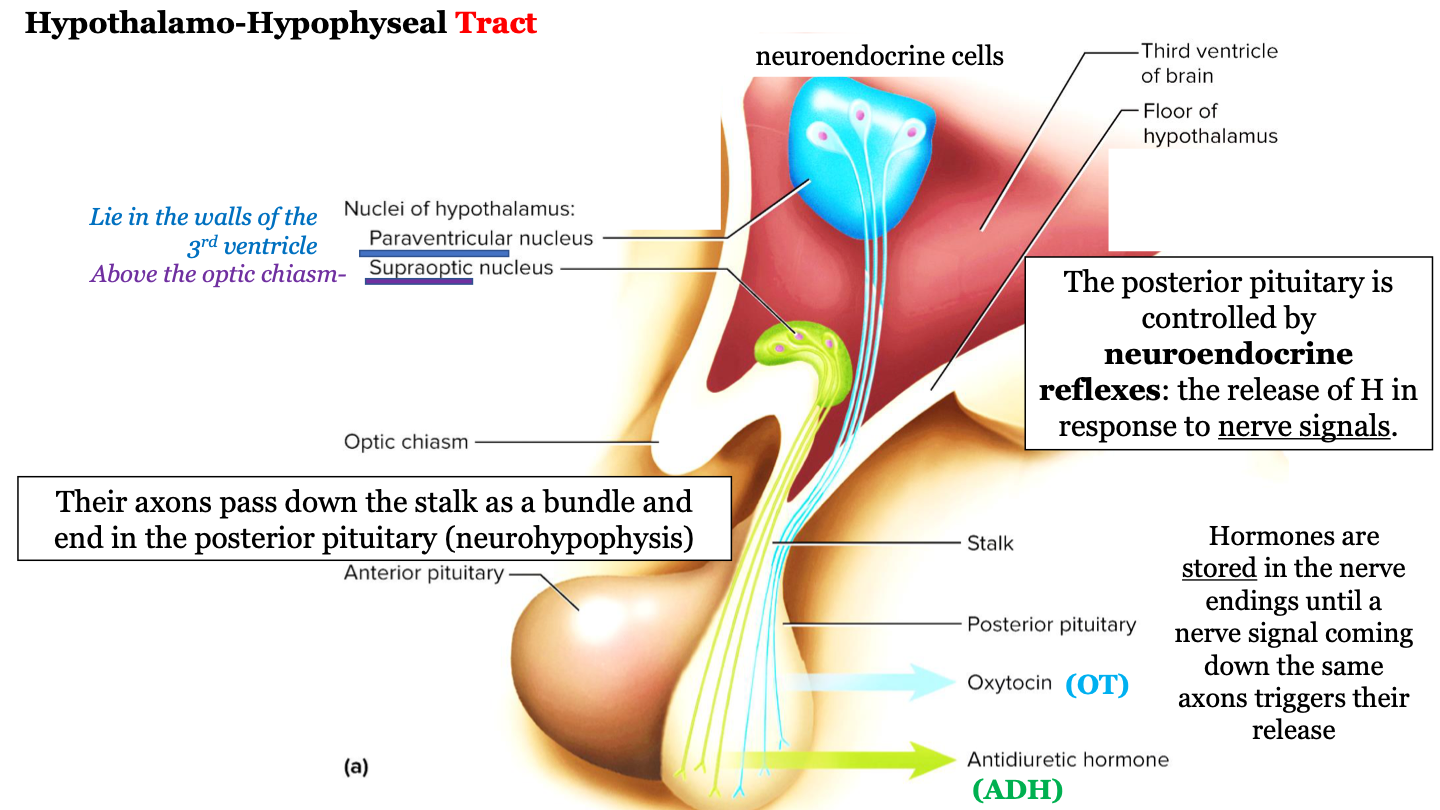
81
New cards
neurohypophysis = ?
posterior pituitary gland
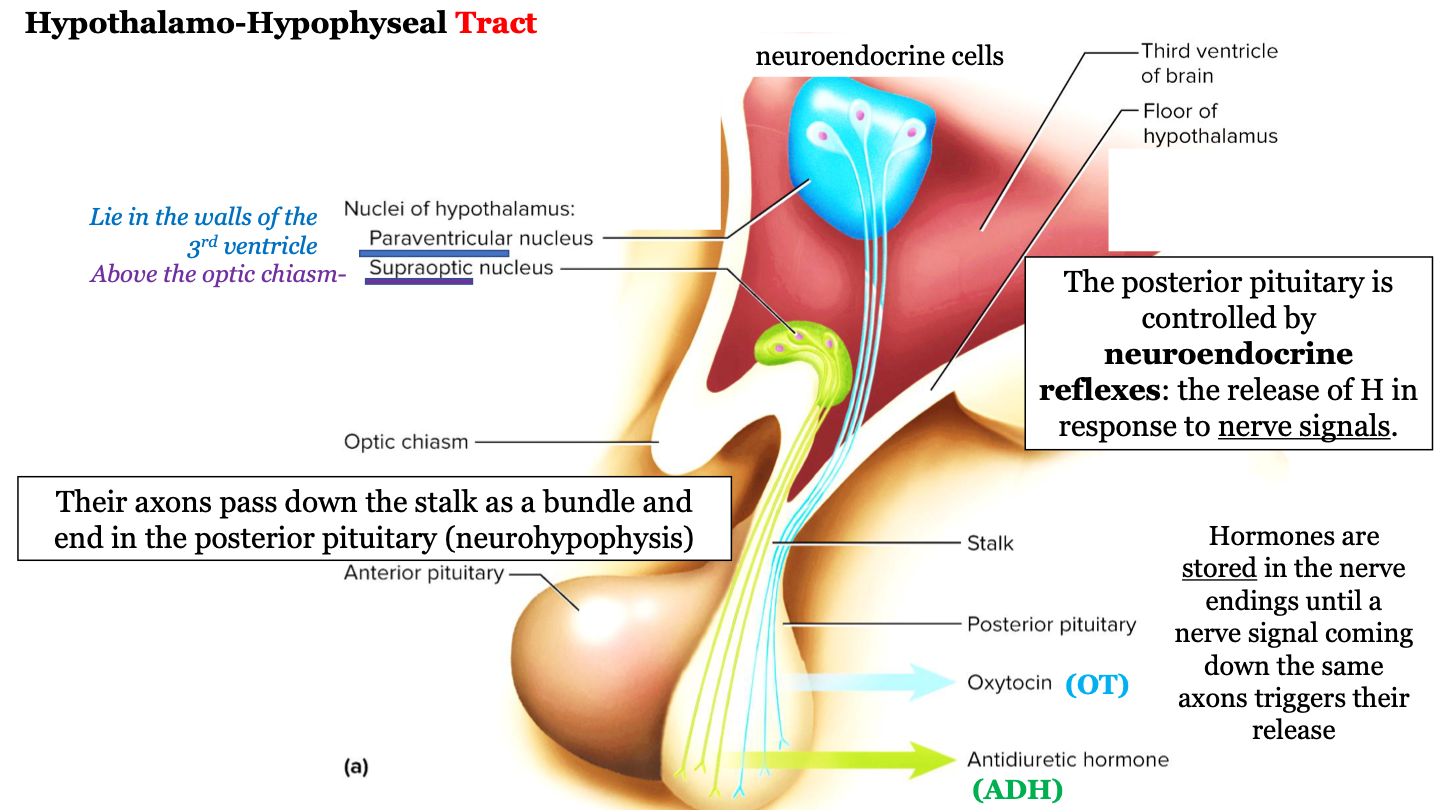
82
New cards
where does the hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract run?
The axons (nerves) run down the stalk as a bundle from the hypothalamic nuclei to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis)
83
New cards
which hypothalamic nuclei are involved in the hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract?
paraventricular nucleus and the supraoptic nucleus
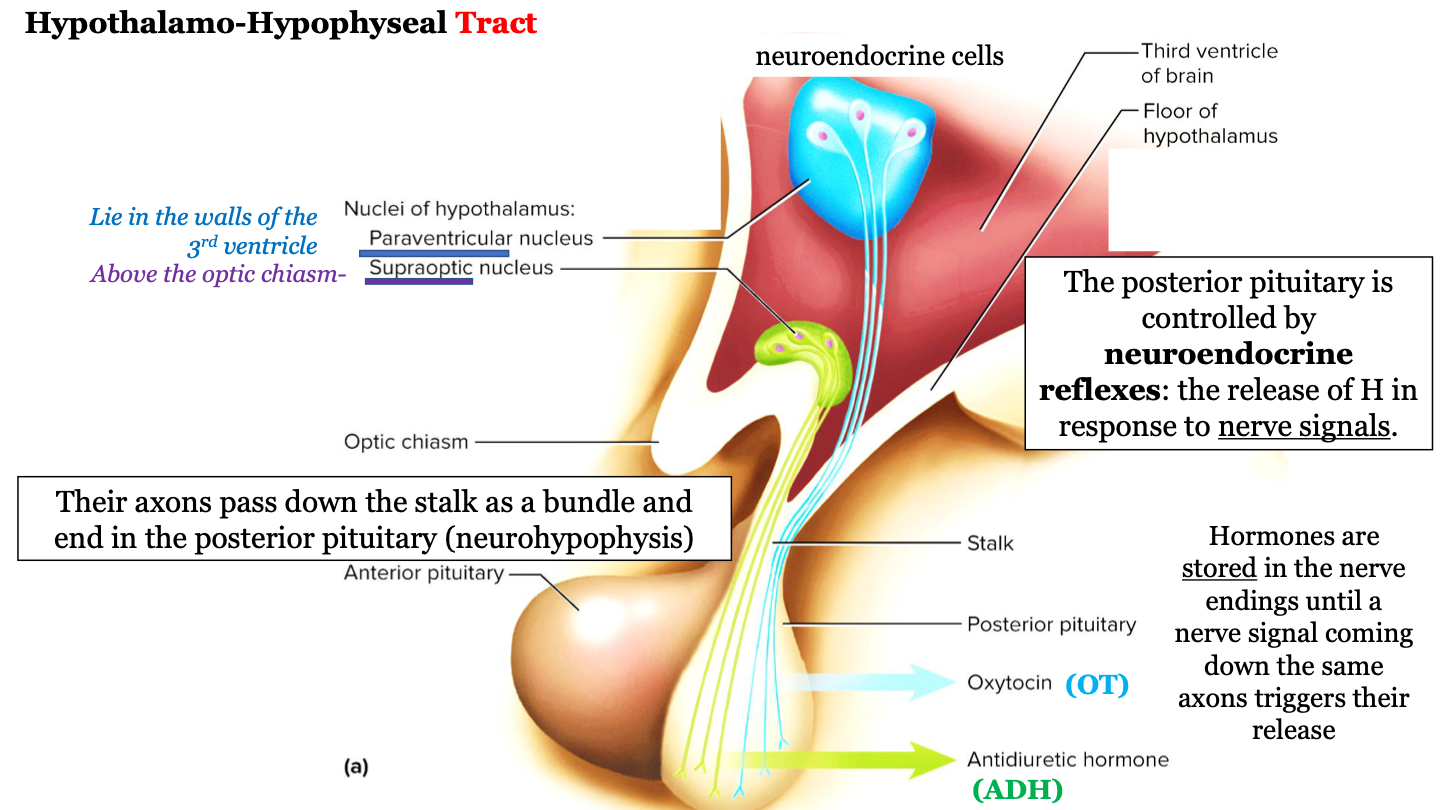
84
New cards
where is the supraoptic nucleus located?
above the optic chiasm
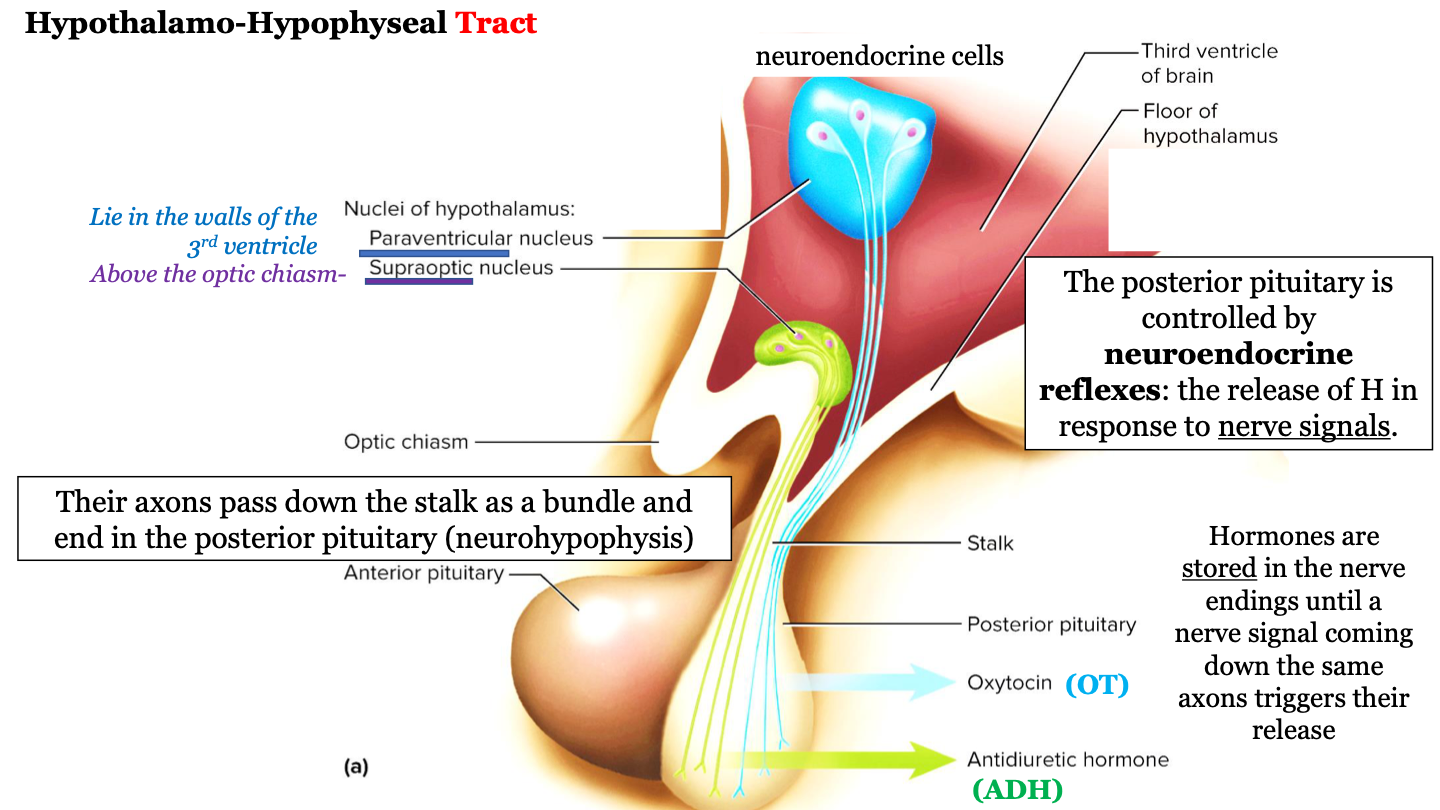
85
New cards
where is the paraventricular nucleus located?
walls of the 3rd ventricle
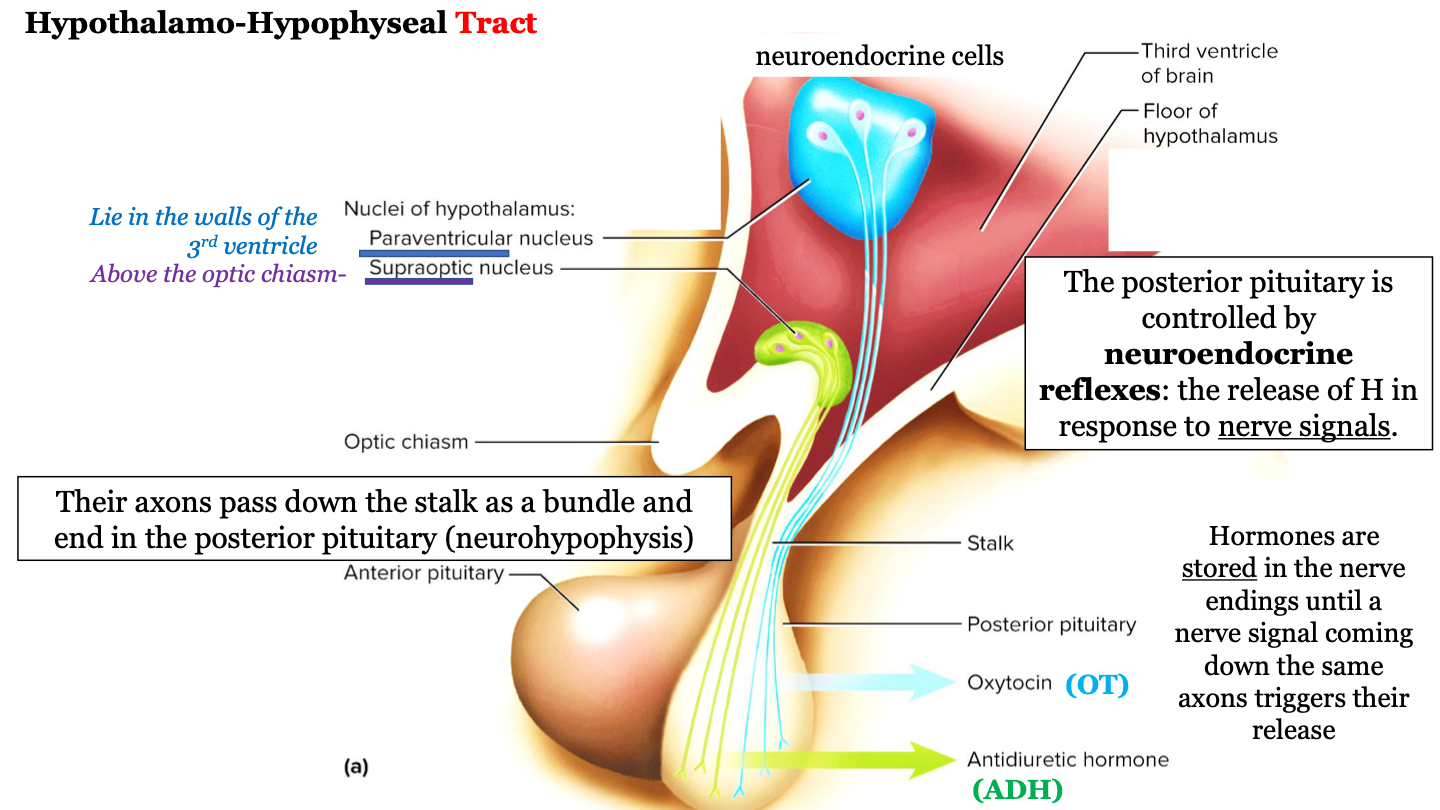
86
New cards
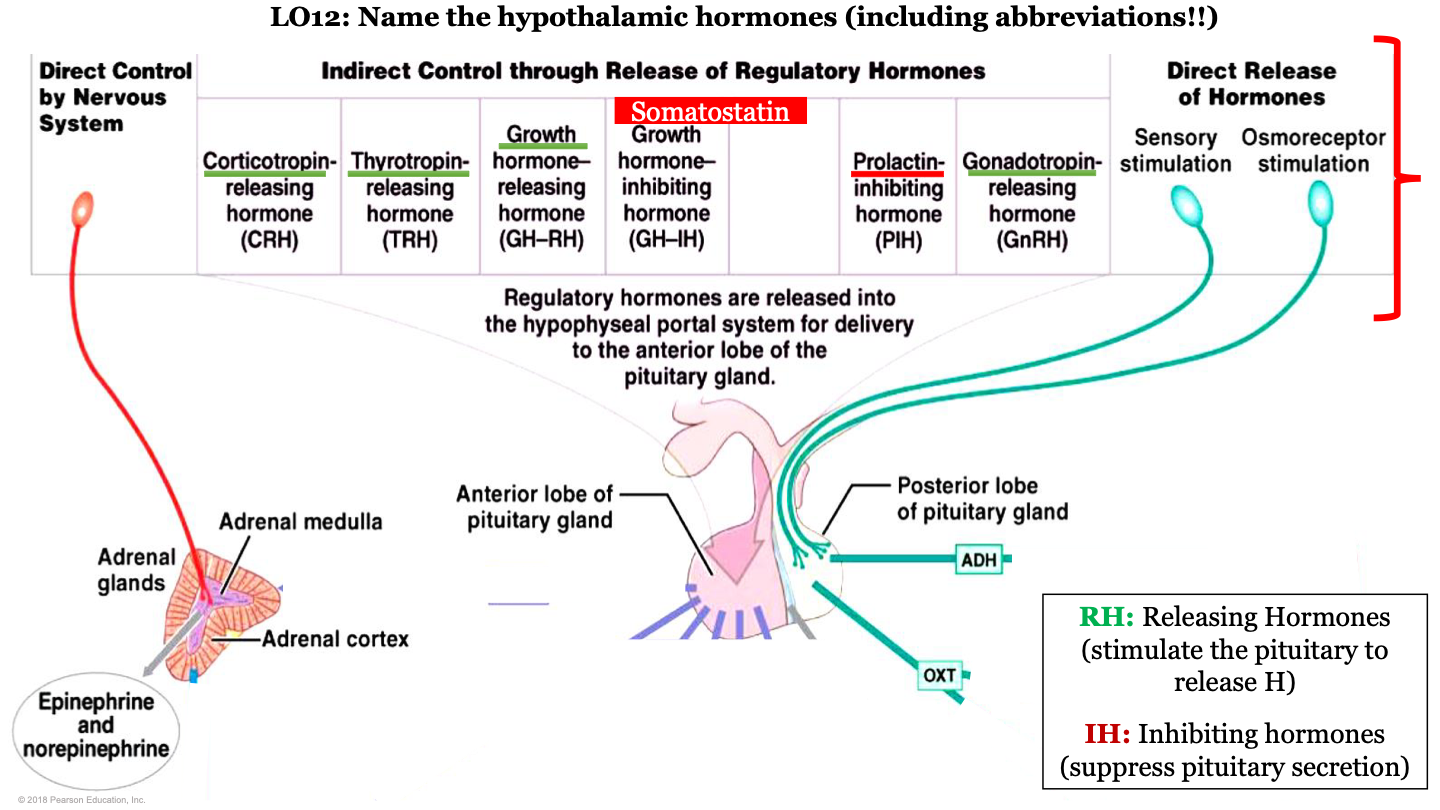
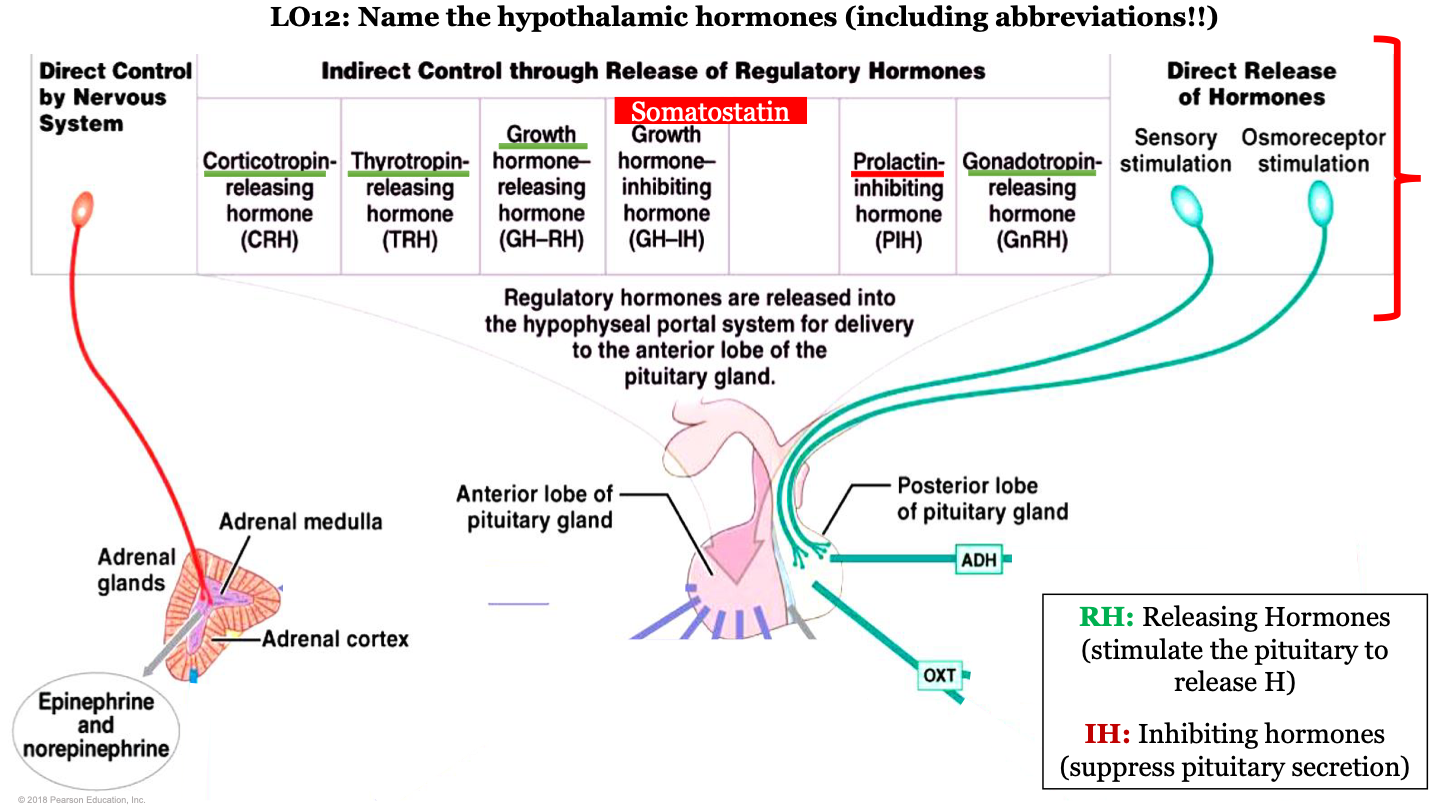
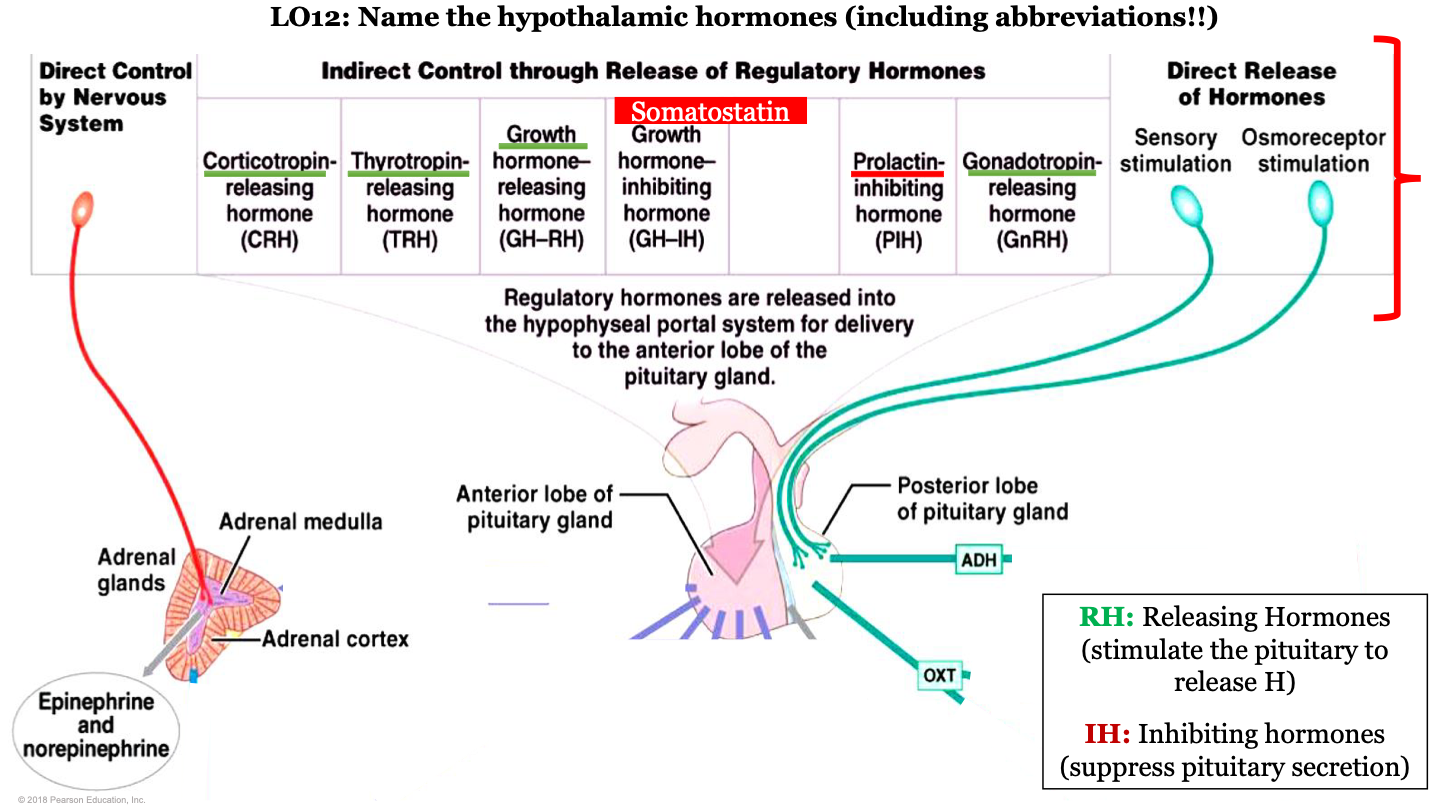
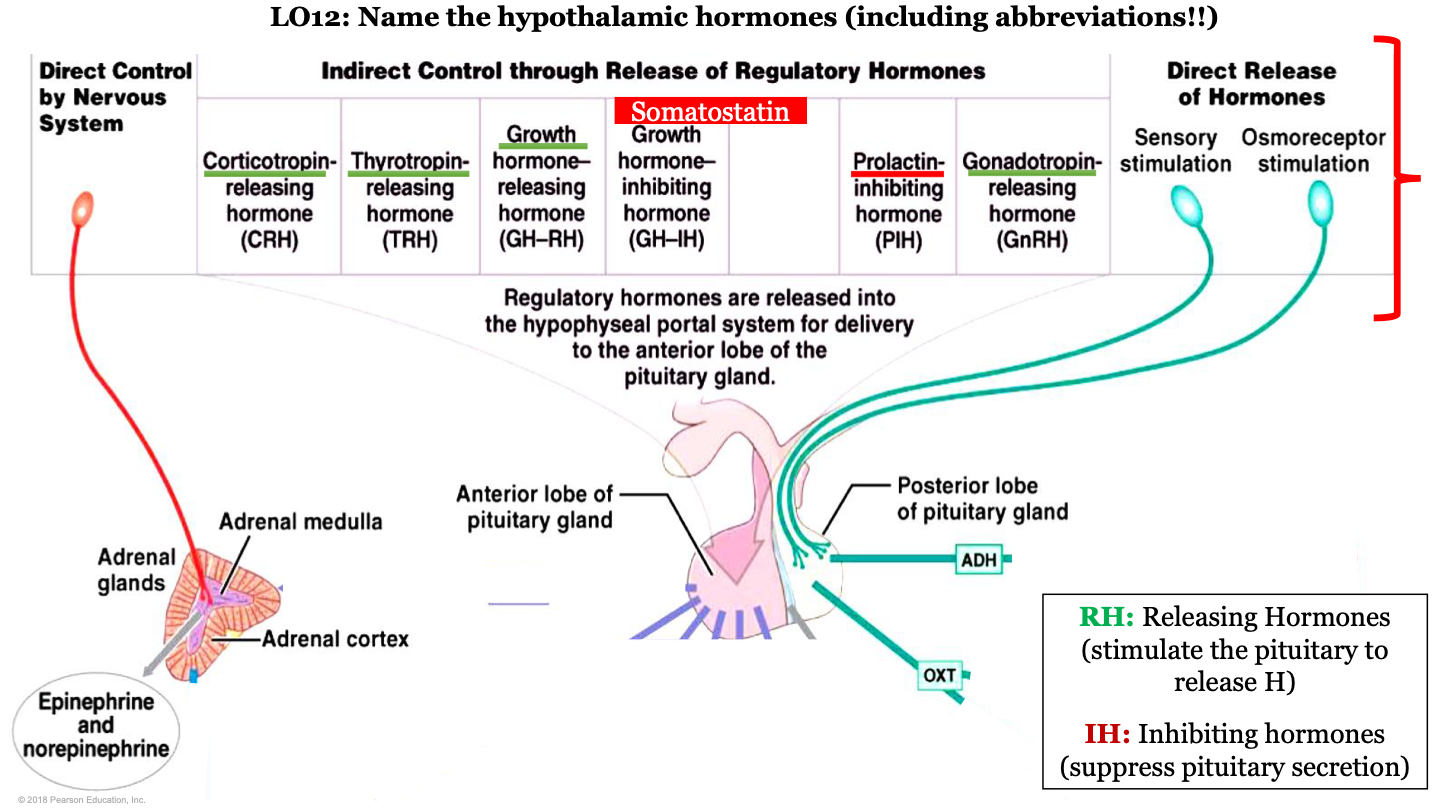
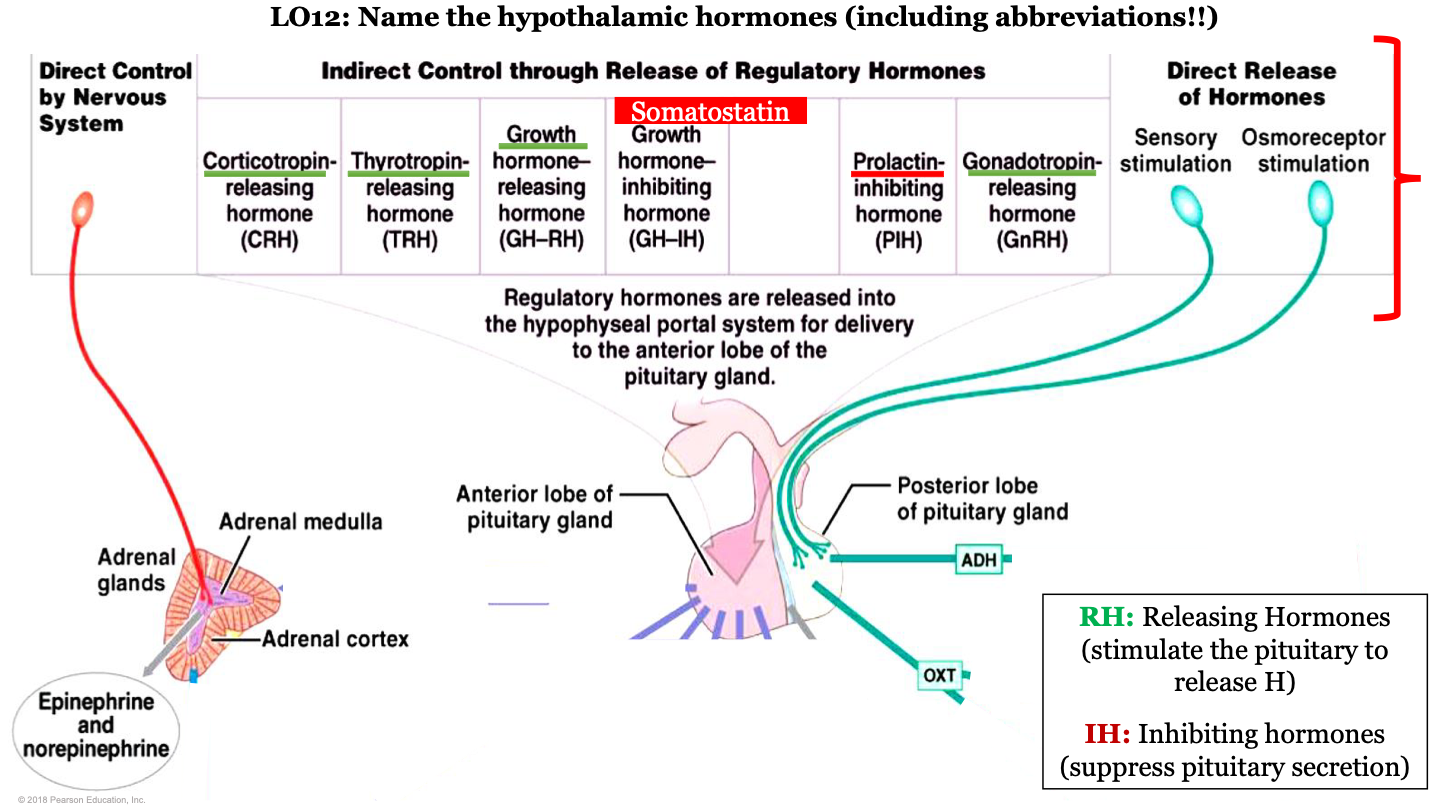
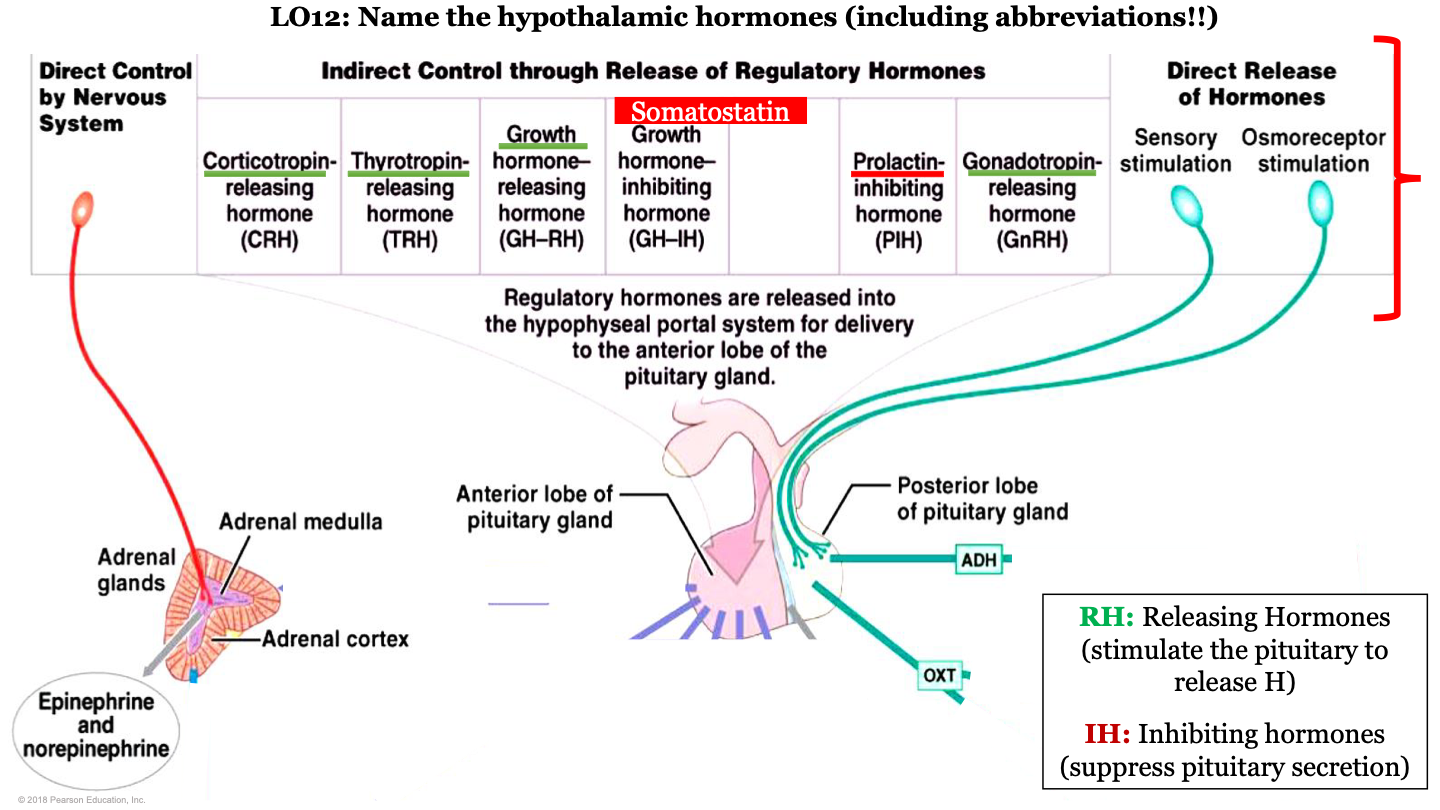
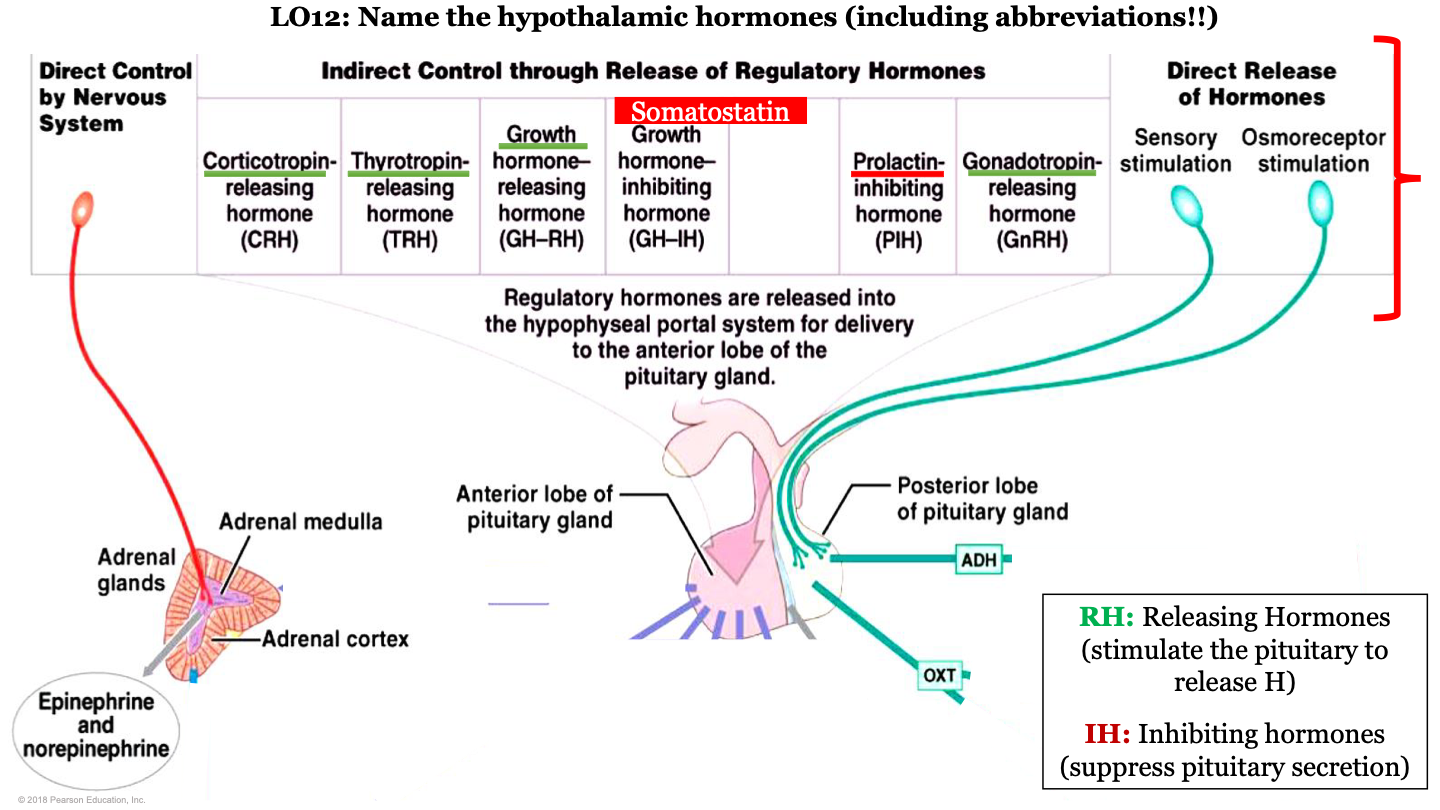
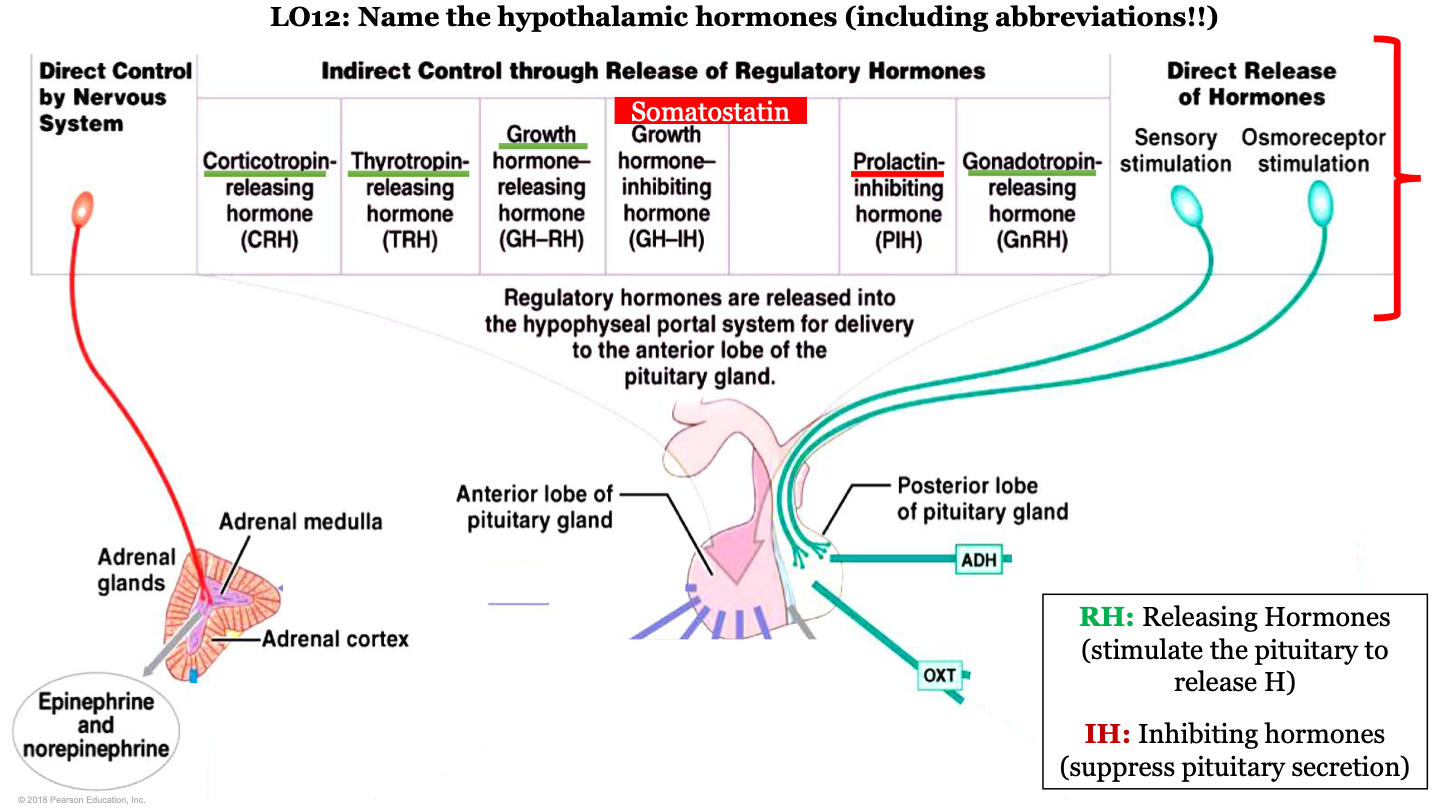
hypothalamic hormones - CRH
corticotropin-releasing hormone; this is a releasing regulatory hormone
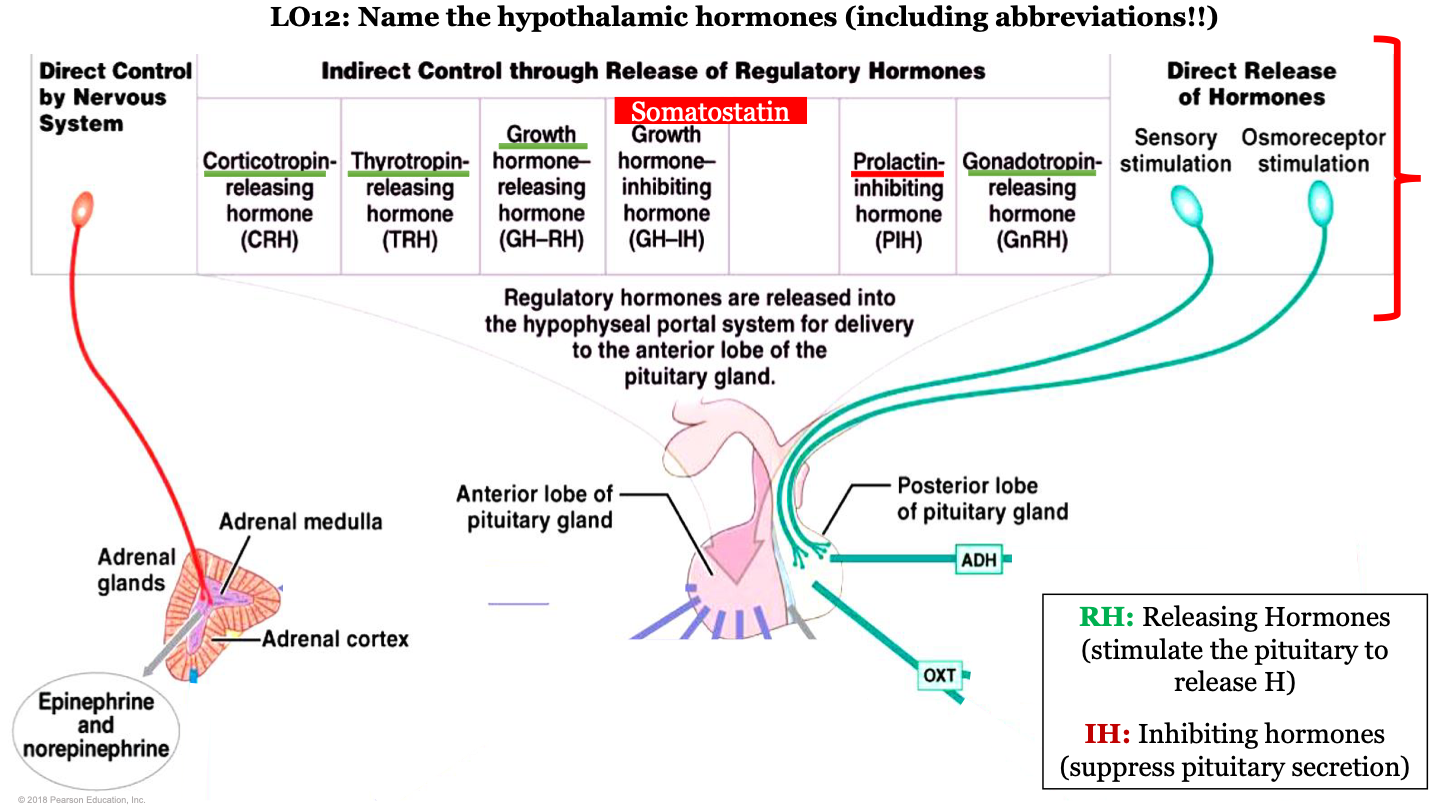
87
New cards
what are the hypothalamic hormones released by?
released by hypophyseal portal system for the delivery to the anterior pituitary gland
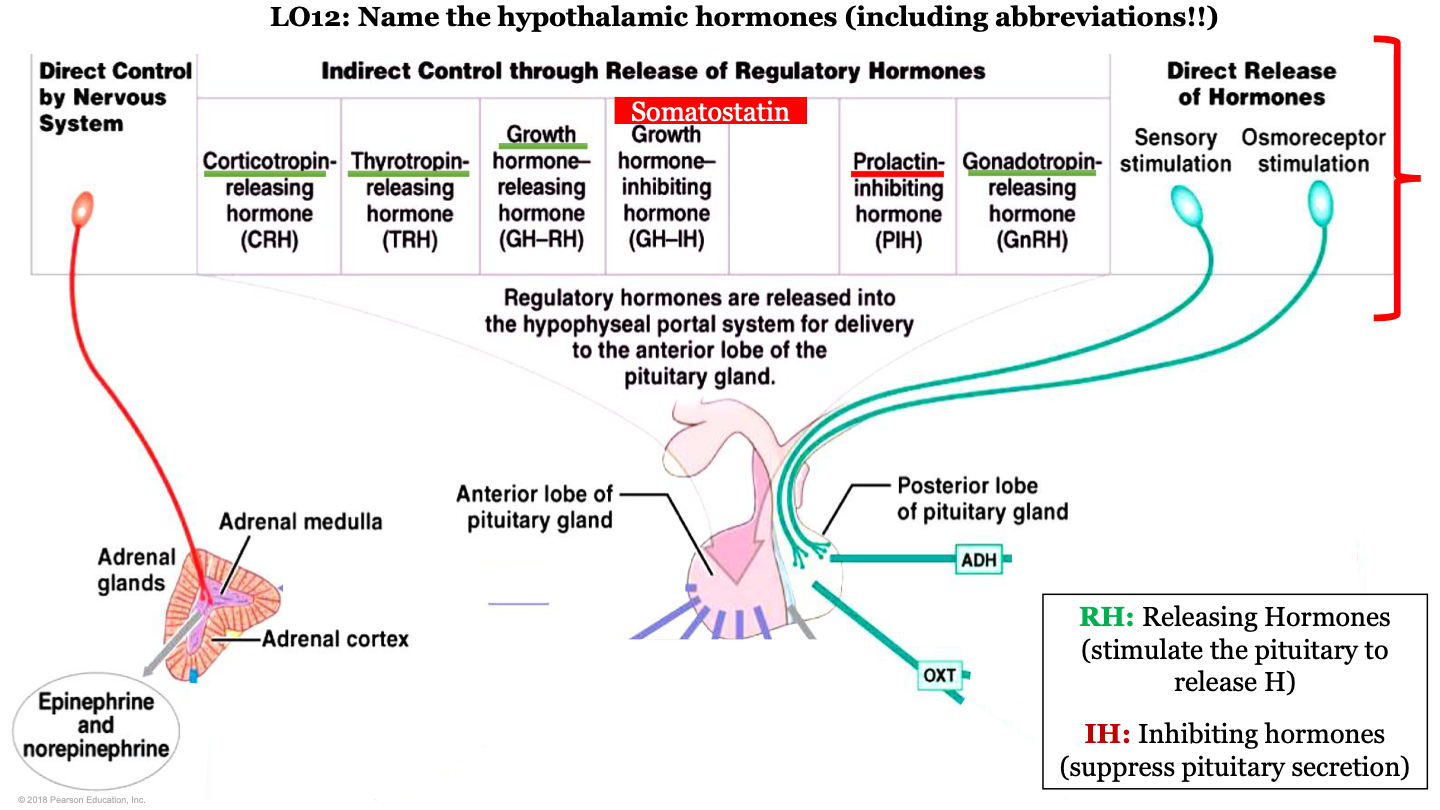
88
New cards
hypothalamic hormones - TRH
Thyrotropin releasing hormone; this is a releasing regulatory hormone
89
New cards
hypothalamic hormones - GH-RH
growth hormone releasing hormone; this is a releasing regulatory hormone
90
New cards
what do releasing hormones do?
stimulate the pituitary to release hormones
91
New cards
what do inhibiting hormones do?
suppress pituitary secretion
92
New cards
hypothalamic hormones - GH-IH
growth hormone inhibiting hormone; this is an inhibiting regulatory hormone
93
New cards
what is GH-RH AKA?
somatostatin
94
New cards
hypothalamic hormones - PIH
prolactin-inhibiting hormone; this is an inhibiting regulatory hormone
95
New cards
hypothalamic hormones - GnRH
gonadotropin-releasing hormone; this is a releasing regulatory hormone
96
New cards
which hormones are released by the posterior pituitary?
ADH and oxytocin; this is a direct release of hormones from sensory stimulation and osmoreceptor stimulation
97
New cards
which hormones are released by the adrenal medulla
epinephrine and noepinephrine; this is under direct control by the nervous system
98
New cards
what does the ovulation test detect?
a rise in luteinizing hormone (LH) in the urine; a rise in this hormone signals the ovary to release the egg; this test is used by women to predict egg release (this is when pregnancy is most likely to occur)
99
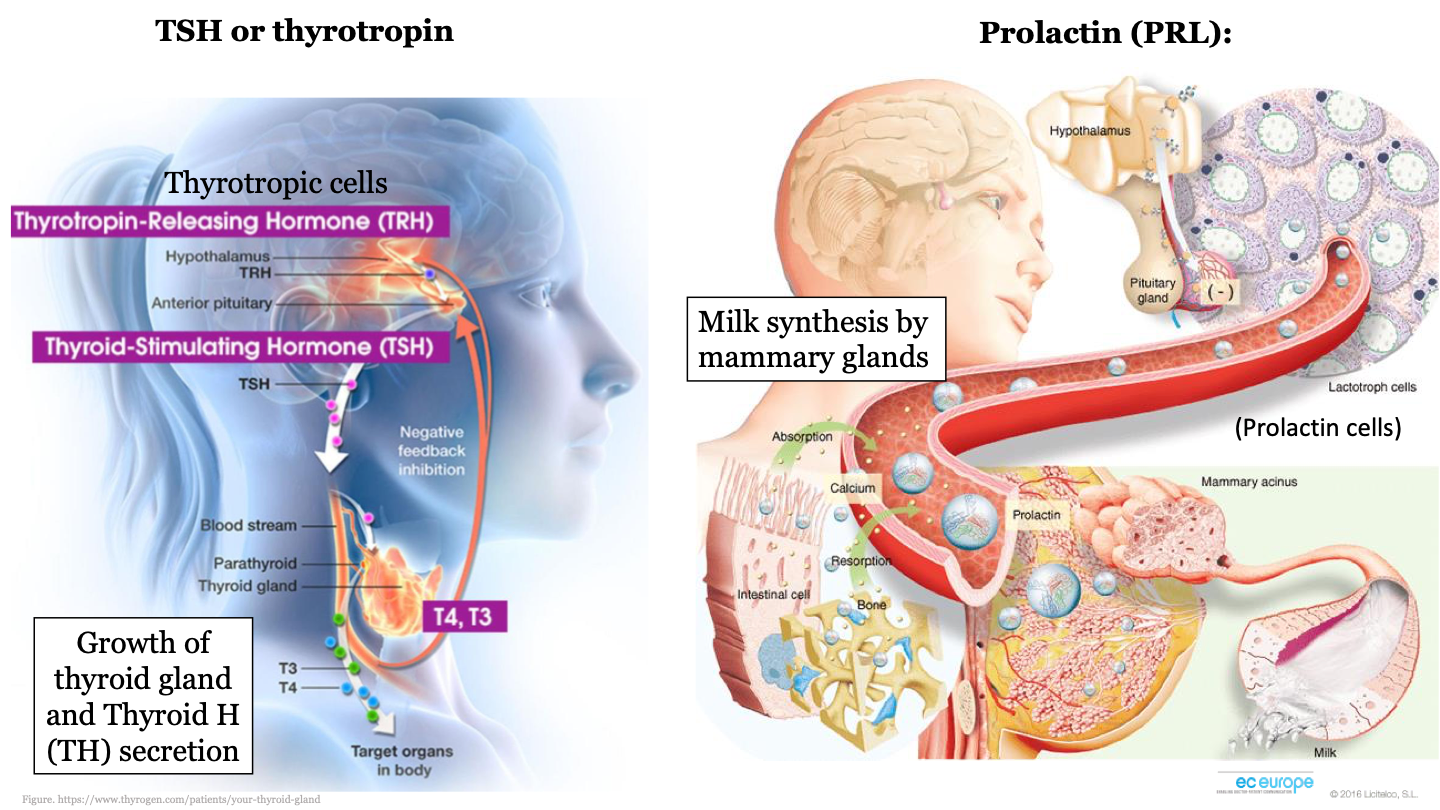
New cards
what stimulates the release of prolactin?
TSH (thyrotropin)
100
New cards
abbreviation for prolactin
PRL