Zoo-Lab (Sem-1) - Exercise 8: Histology
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
histology
the study of normal tissues
tissue
a group of cells which maybe associated by a common origin and by similarity of function or form
epithelial tissues
form the covering of all body surfaces, line body cavities and hollow organs, and are the major tissue in glands; specialized to protect, absorb, and secrete
glands
epithelial structures produced by epithelial tissues that perform secretory functions
intercellular substance
cements the cells together; very small amount in epithelial tissues
basement membrane
a condensation of the connective tissue at the surface of its contact with the epithelium where the epithelia rests upon
squamous
flat
cuboidal
squarish
columnar
rectangular
simple epithelia
consist of a single layer of cells all of which are in contact with the basement membrane
stratified epithelia
consists of several layers of cells superimposed one upon the other and only the cells at the basal layer come in contact with the basement membrane and only those at the superficial layer have free surfaces
basal layer
simple squamous epithelium
flattened, polygonal in shape; nucleus is round/oval and located at the center; boundary maybe irregular or smooth; cytoplasm is barely visible but maybe seen in the vicinity of the nucleus where it appears to bulge; found on the parietal layer of the Bowman’s capsule in the kidney/ lining of blood vessels, heart, and lymphatic ducts (endothelium)/ lining of the peritoneal, pleural, and pericardial cavities as serous membranes (mesothelium)
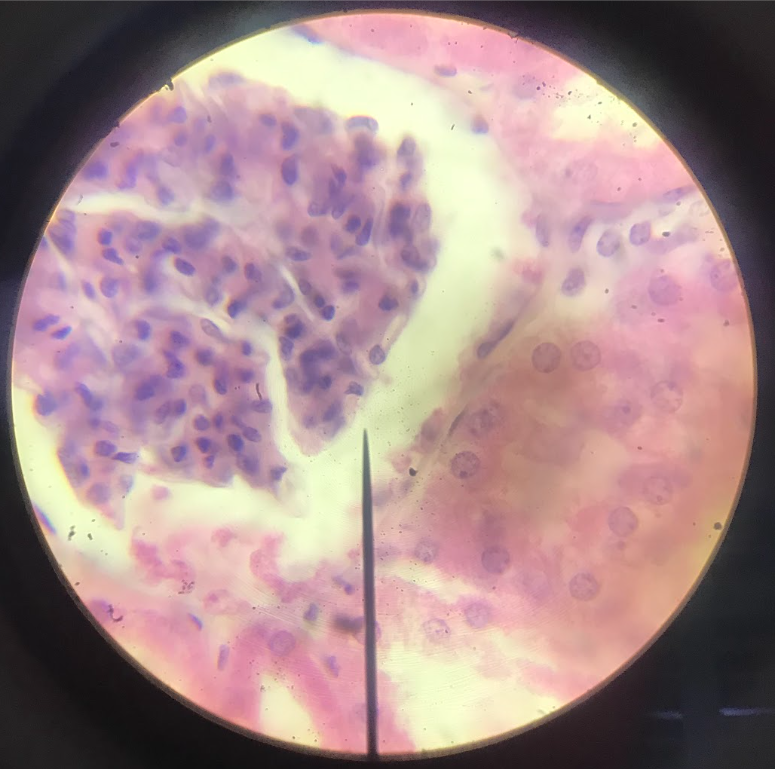
simple cuboidal epithelium
squarish cells w/ centrally located nucleus; nuclei are spherical and large
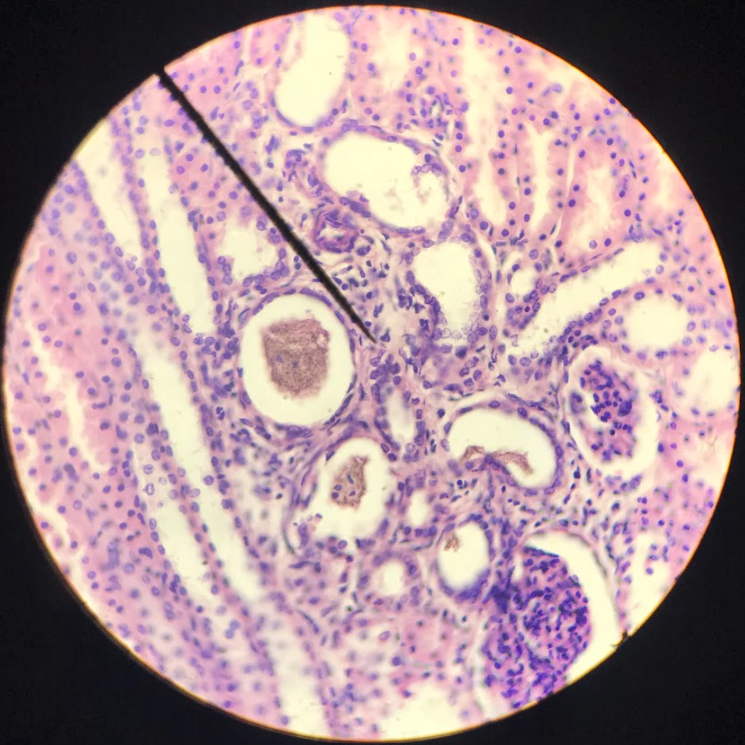
simple columnar epithelium
cells are taller than they are wide; nucleus is characteristically close to the base of the cell; found on the mucous lining of the stomach and intestine
simple columnar ciliated epithelium
on the free surface of the epithelial cells are ultrastructures, like the cilia, that helped the tissue in moving materials over it
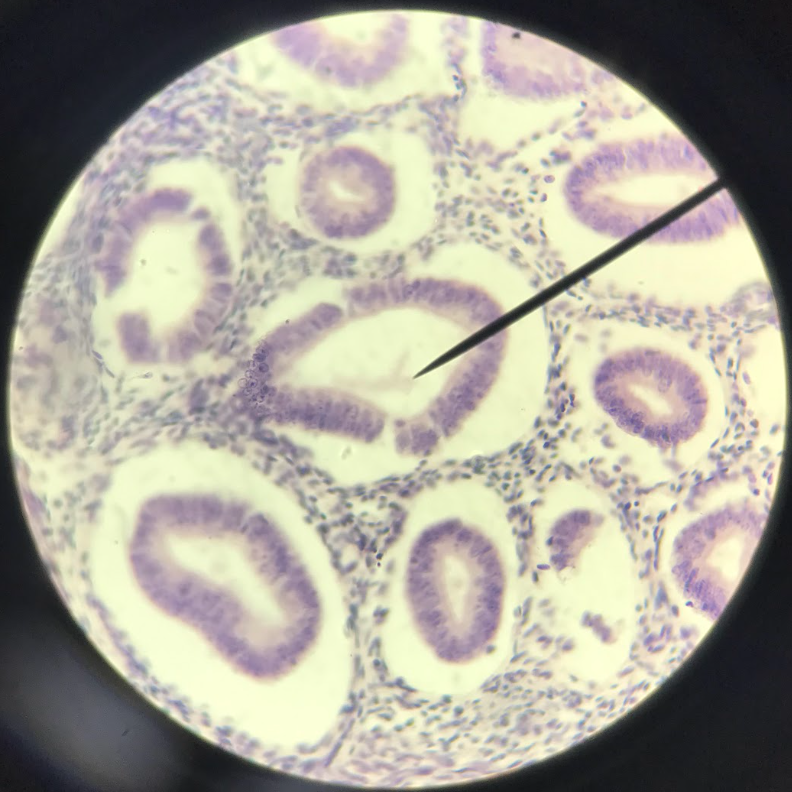
pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium
nucleus gives an impression of stratification/layering, but upon close examination, all of the cells are attached to the basement membrane; on the free surface of the cells are hair-projections called cilia
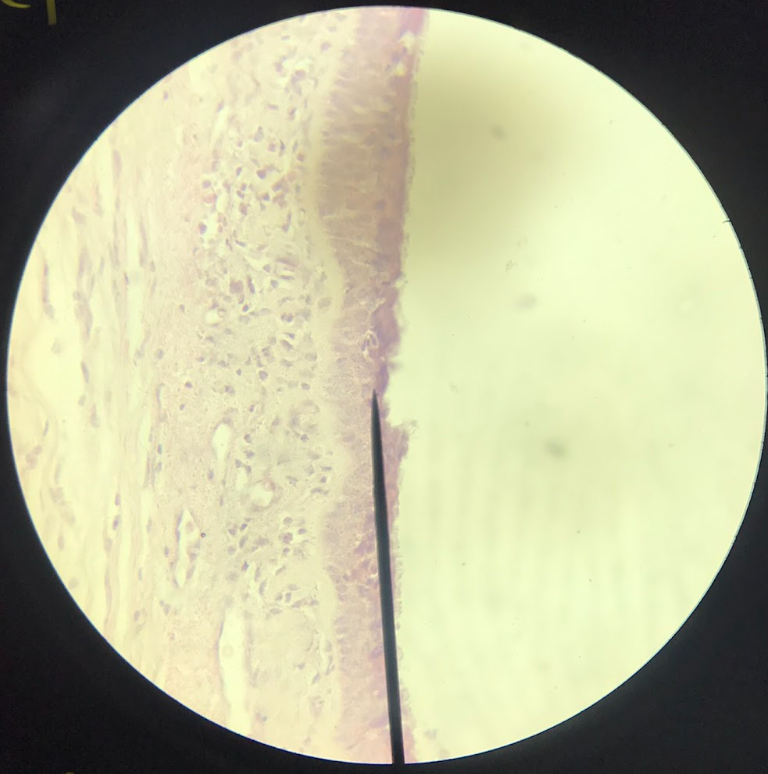
stratified squamous epithelium
found on the epidermis of the skin; thin outer layer (darkly stained) epidermis; thick inner layer (lightly stained) dermis;
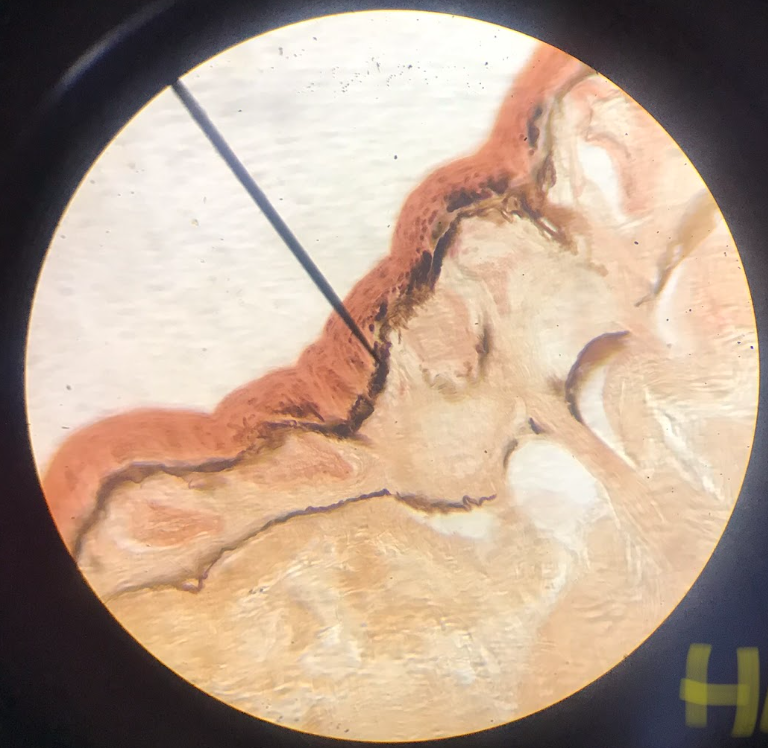
stratified columnar epithelium
corpus spongiosum; cells at the surface are columnar in form
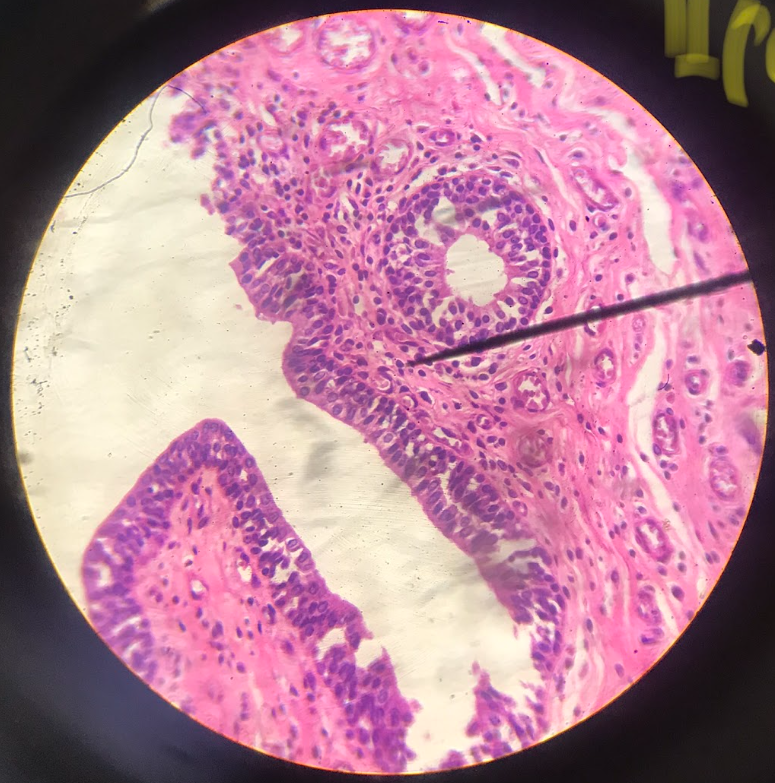
polyhedral cells
cells in the layer below the columnar cells until the basal layer
connective tissues
most diverse (bone, cartilage, and blood) supports, protects, and gives structure to other tissues and organs in the body
connective tissue proper
responsible for binding and connecting different organs of the body together; abundant intercellular substances; cellular elements are few and scattered called fibroblasts
collagenous (white) fibers
a type of connective tissue fiber; the most common; long, wavy, and unbranching; consist of bundles of fine fibrils called fibrillae, which lie parallel to each other and give the fiber its longitudinal striated appearance; resistant to a pulling force; each fiber is made of protein collagen
elastic (yellow) fibers
occur singly (do not consist of fibrils); thin, straight, branching, and anastomose freely; they appear darker than the individual white fibrils; each fibril is made up of protein elastin; they can be stretched and returned to its original length
reticular fibers
fine, wavy, branching, and form a network; hard to distinguish or see in the specimen; components are identical with the collagenous fibers
areolar/loose connective tissue
serves as a filling tissue; contain less amount of fibers but with greater amount of ground substance, and greater number of cells
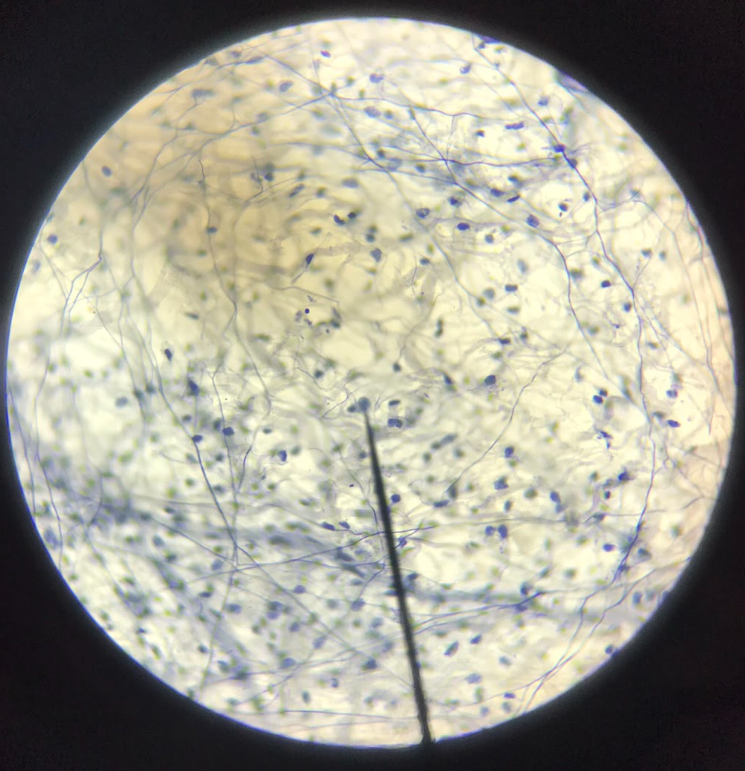
fibroblasts
responsible for the synthesis of fibers and ground substances which form the extracellular matrix; found along bundles of collagenous fibers; oval/fusiform-shaped; only nucleus is visible
mast cells
round/oval nucleus; cytoplasm is filled up w/ several hundreds of granules; believed to secrete histamine and heparin
fat/adipose cells
big cells containing a little amount of cytoplasm that surrounds a relatively big space which contained the fat globule; nucleus is flattened and displaced to one side of the cell; may occur singly but more often found in groups
dense connective tissue
divided into dense irregular (fiber bundles are randomly oriented) and regular (fibers oriented parallel to each other) tissues
dense irregular connective tissue
dermis; pinkish bundles of fibrillar structures are the collagenous fibers; small, dark blue in color are the nuclei of fibroblasts
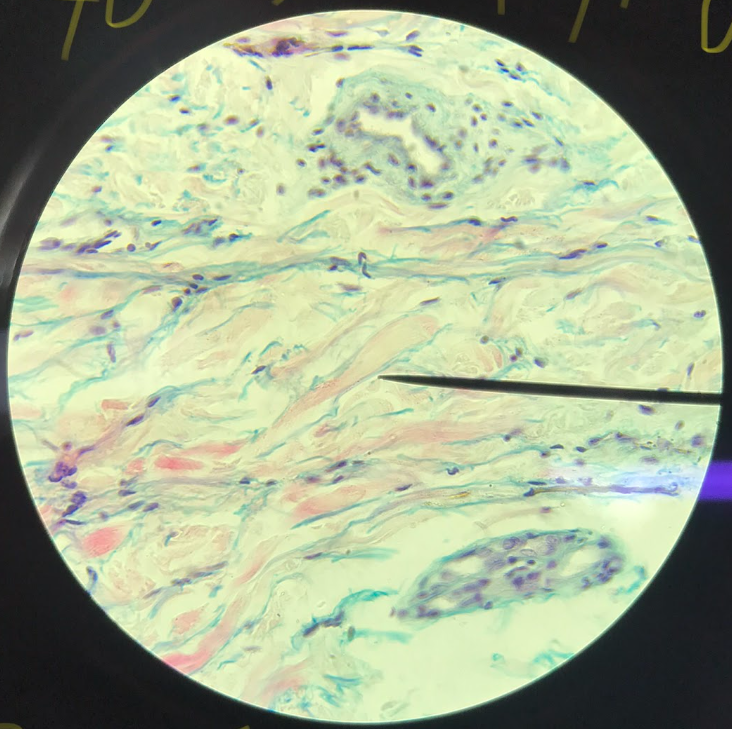
dense regular connective tissue
tendon; parallel arrangement of collagenous fibers; fibroblast nuclei are located between the bundles of collagenous fibers
specialized connective tissue
perform other functions than connecting and binding tissues and organs together
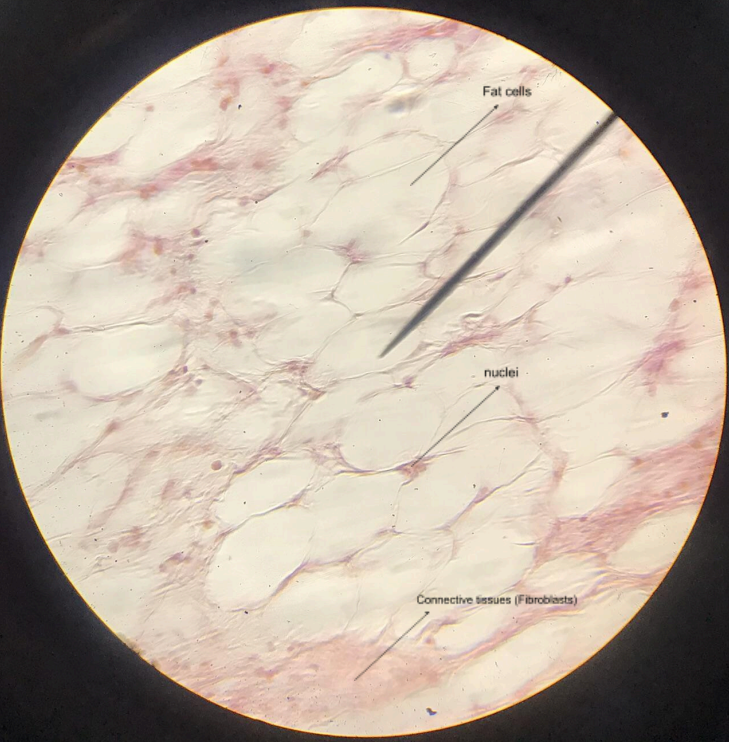
adipose tissue
human skin; resemble signet rings; abundant in the subcutaneous layer (hypodermis) beneath the dermis; nuclei are located at the basal side of the cells
supporting tissues
these tissues form the framework of the body, including cartilages and bones
cartilages
soft, pliable, translucent, and avascular; form skeletal framework; cover the ends of long bones, forming articular surfaces, and protect the nose, larynx, trachea, and bronchi
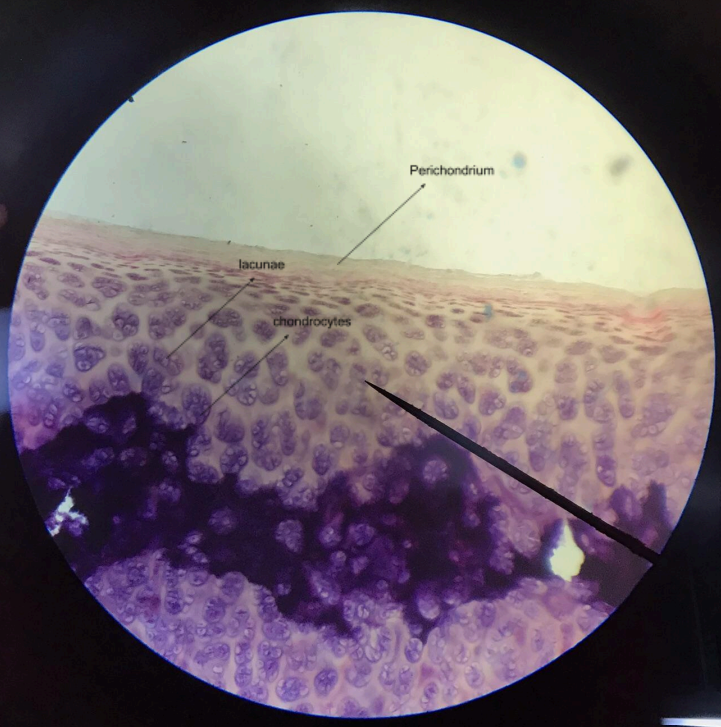
hyaline cartilage
matrix is predominated by glass-like ground substance called hyaline; scattered around the matrix are spaces called lacunae, and lodged between them are the chondrocytes; the connective tissue covering the cartilage is the perichondrium
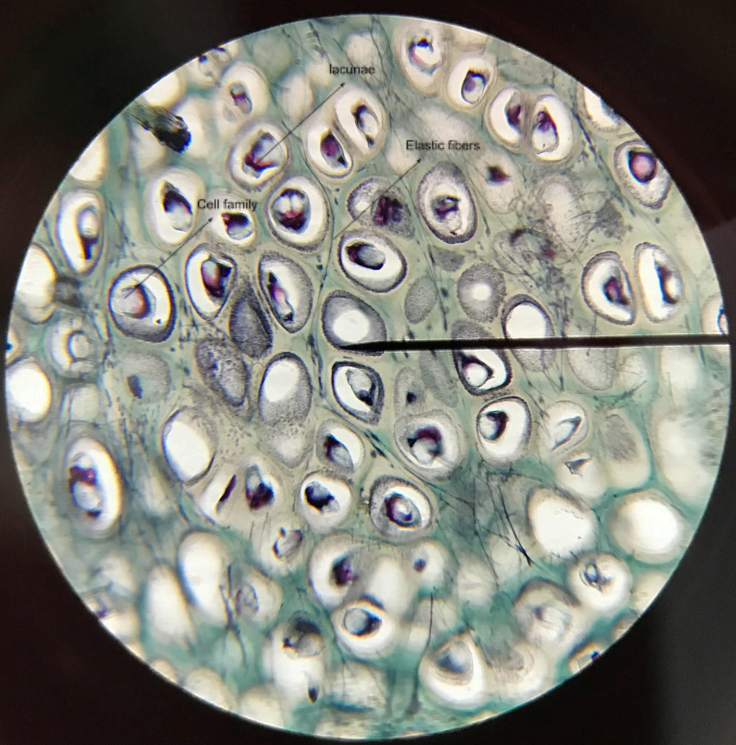
elastic cartilage
similar to hyaline cartilage; lacunae are scattered in isogenous groups of two or four cells called cell family; difference with the hyaline cartilage is this one has elastic fibers permeating
bones
rigid, hard, and brittle; hardness is caused by the deposition of inorganic salts, primarily calcium phosphate; storage depot of minerals and site of red blood cell formation
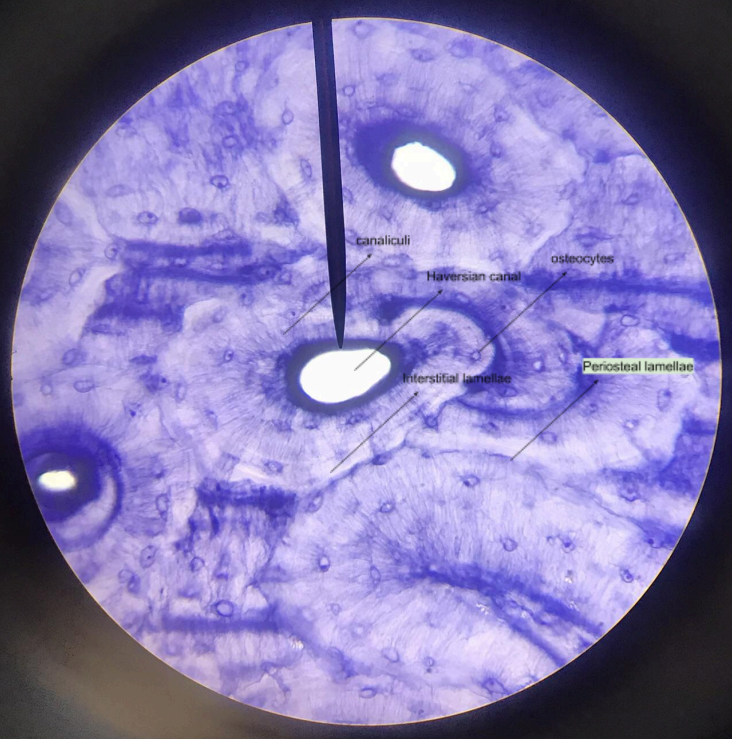
osteocytes
bone cells
lamellae
well-defined layers within a bone
periosteal lamellae
outermost bony layer
Haversian canal system/osteon
structural unit of the bone tissue; concentric lamellae-rings; canaliculi-tiny tubules; Haversian canal-center; osteocytes (within lacunae)-cells
interstitial lamellae
bony substance between the Haversian canal systems/osteon
vascular/circulating tissue
blood is a specialized connective tissue that transports oxygen, nutrients, and hormones into the cells
plasma
fluid matrix
frog’s blood
with nucleus
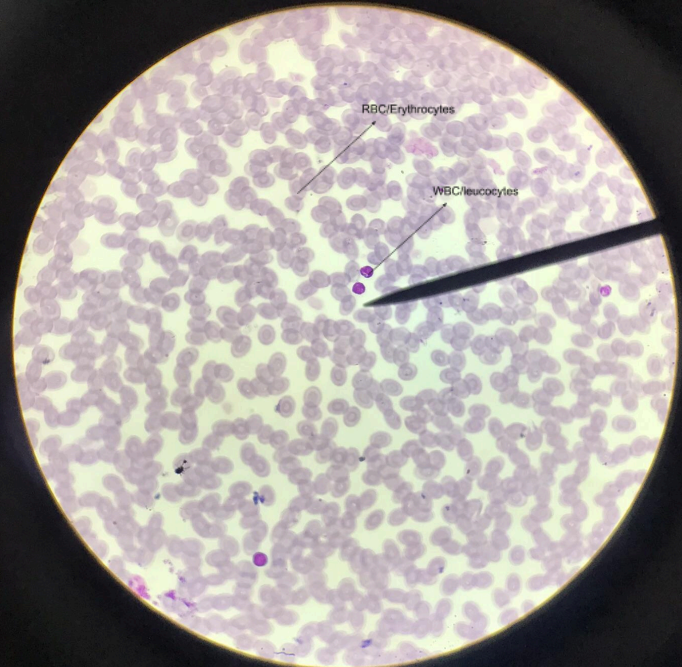
erythrocytes
red blood cells
leucocytes
white blood cells
human blood (erythrocytes and leucocytes)
RBC - flat cells with bioconcave discs devoid of nuclei/carriers of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood; WBC - lack of color, true cells with nucleus, divided to 2 groups: non-granular/agranulocytes and granular/granulocytes
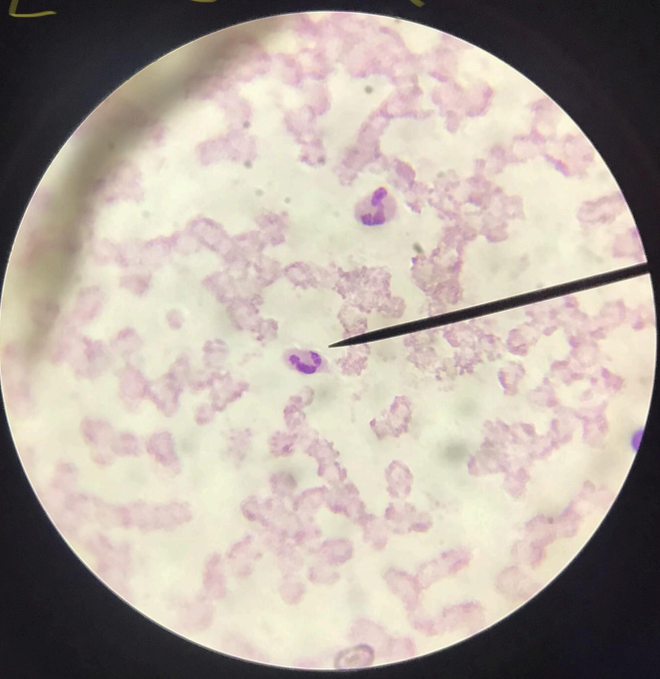
monocytes
a type of agranulocyte; much bigger than lymphocytes; nucleus is indented and kidney-shaped/horseshoe-shaped
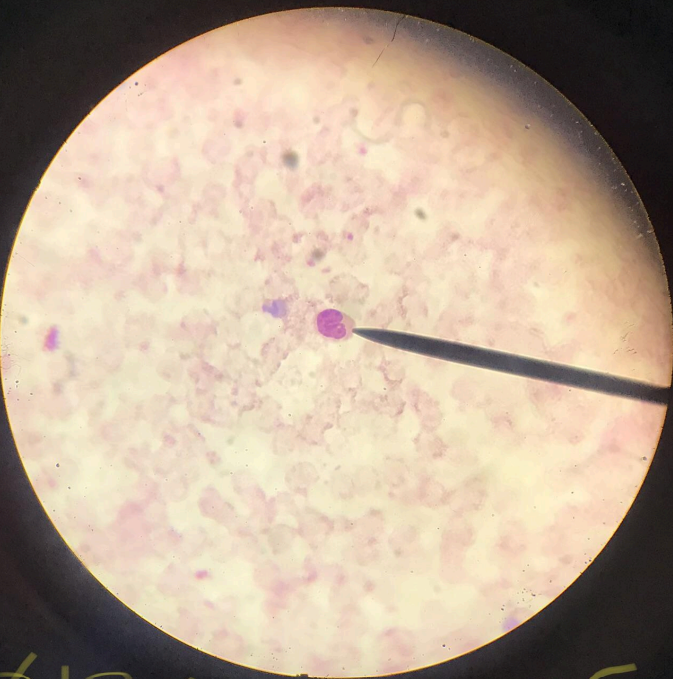
lymphocytes
a type of agranulocyte; larger than erythrocytes; big nucleus which stains deep blue; mechanism of immunity
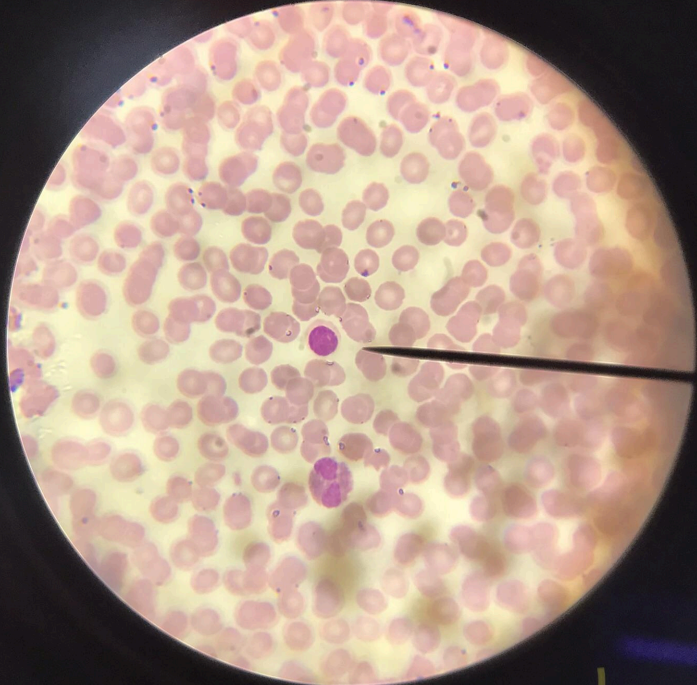
acidophils/eosinophils
spherical in shape; cytoplasm stains bright red with acid dyes; nucleus is two oval bodies connected via thin chromatin thread; detoxification role
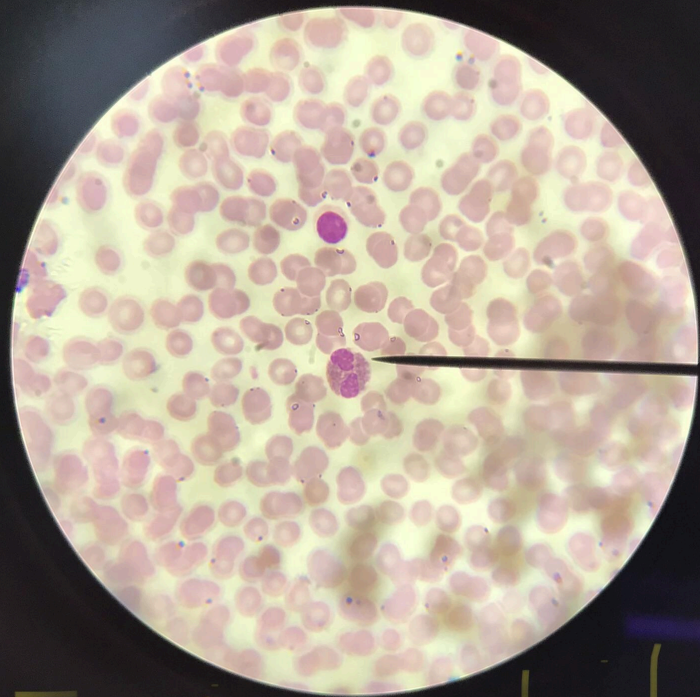
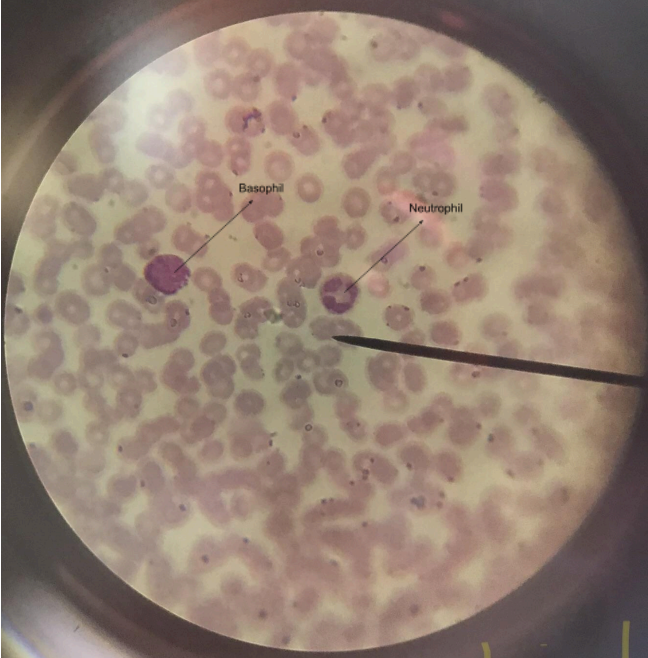
basophiles and neutrophils
basophils - difficult to find in the human bloodm(0.5-1% of leucocytes), granules of cytoplasm will stain dark blue; nucleus is polymorphic; neutrophils - spherical cells with cytoplasm that is not strongly acidic nor basic in its reaction; cytoplasmic granules will stain light pink/lavender; nucleus is elongated; phagocytes (kill bacteria)
muscle tissues
composed of cells that have the special ability to shorten or contract in order to produce movement of the body parts
myofibrils
contractile fibrillar components
location
movement from one place to another
motion
movement of various parts of the body with respect to one another
skeletal muscle tissues
striated, voluntary muscles; cylindrical and multinucleated; with a thin membrane (sarcolemma) and liquid cytoplasm (sarcoplasm)
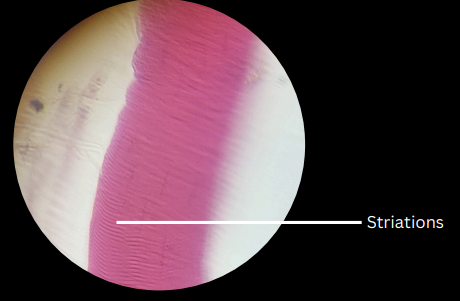
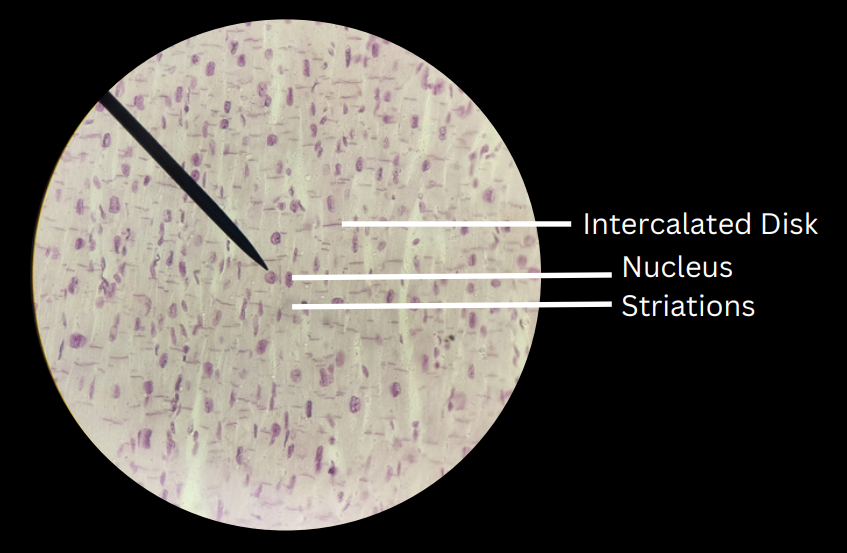
cardiac muscle tissues
striated, involuntary muscles; separated by intercalated/intercalary disks
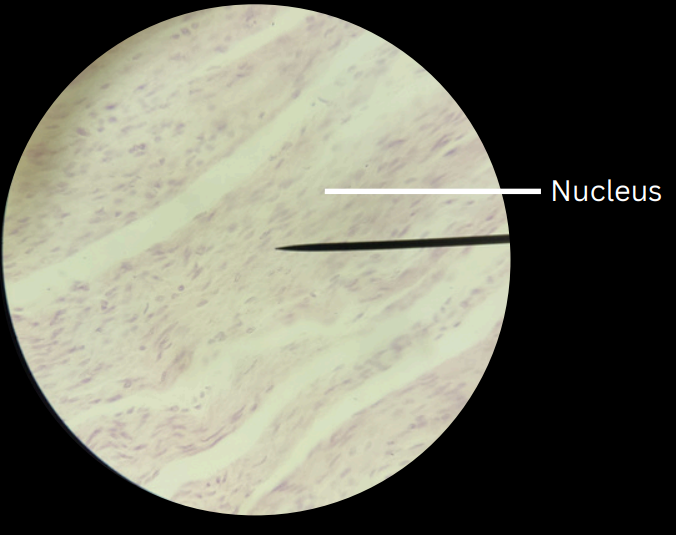
smooth muscle tissueun
unstriated, involuntary muscles
nervous tissues
found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves
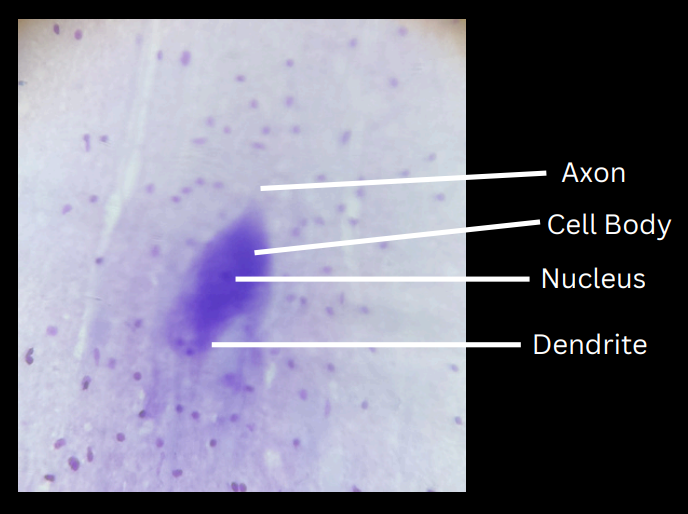
neuron/nerve cell
structural and functional unit of nervous tissue
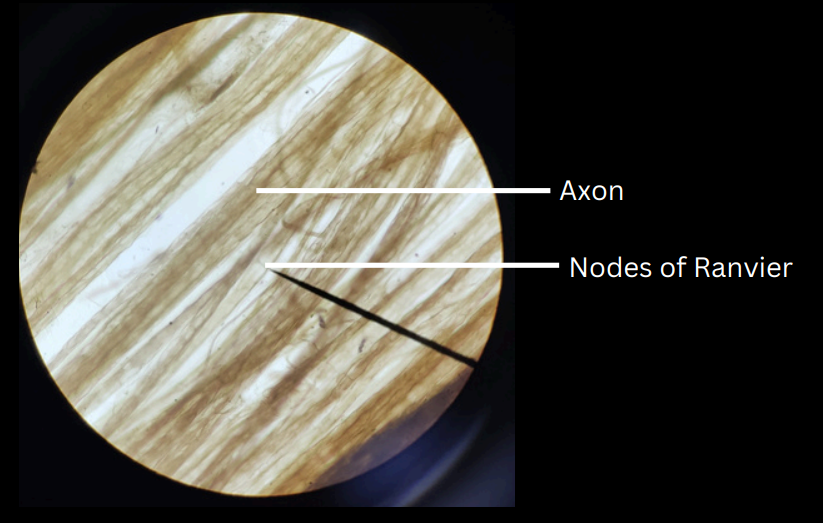
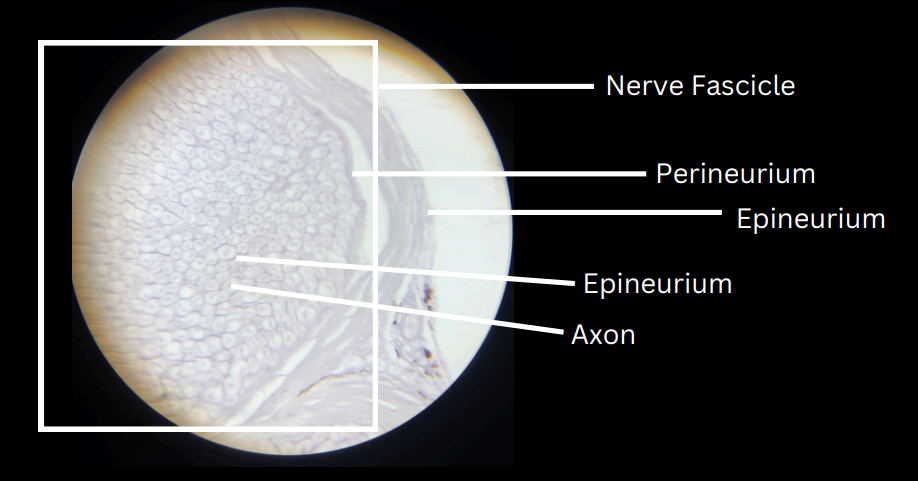
nerve/nerve trunk
composed of one or more bundles or groups of nerve fibers bound together by a connective tissue
nerve fiber
fibers in the nerve
