BL3800 Mycology Identification and Objectives
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Fungi identification for Brigitte and Sarah's Mycology section. Includes microscopic, macroscopic, and colony images. Also includes descriptions of microscopic, macroscopic, and colony morphology (without images).
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
Which fungi are classified as Mucroales (aka Zygomycetes)?
Rhizopus spp.
Mucor spp.
Rhizomucor spp.
Lichtheimia spp.
Cunninghamella spp.
Which fungi has rhizoids directly opposite the sporangiophore and contains unbranched sporahgiophores connected by stolons?
Rhizopus spp.
Which fungi is the most common cause of mucormycosis?
Rhizopus spp.
Which fungi has white, cottony colonies that turn black or brown with a pale gray or brown underside?
Rhizopus spp.
Which fungi (usually) has tall, unbranched sporangiophores, no rhizoids or stolons, and round/ellipsoidal soorangiospores?
Mucor spp.
Which fungi has a white/pale gray colony that can sometimes be brown and fluffy?
Mucor spp.
Which fungi is the most common contaminant?
Mucor spp.
Which fungi has stolons and poorly developed rhizoids between sporangiophores?
Rhizomucor spp.
Which fungi has a colony that’s gray, brown, and fluffy?
Rhizomucor spp.
Which fungi has a funnel-shaped apophysis at the junction of the sporangium and the sporangiophore? This fungi also has sporangiophores between the rhizoids.
Lichtheimia spp.
Which fungi has a colony that resembles gray and brown cotton candy?
Lichthemia spp.
Which fungi has laterally branched sporangiophores with a large, “spiney” vesicle at the top?
Cunninghamella spp.
Which fungi colony is white or gray with a wooly texture?
Cunninghamella spp.
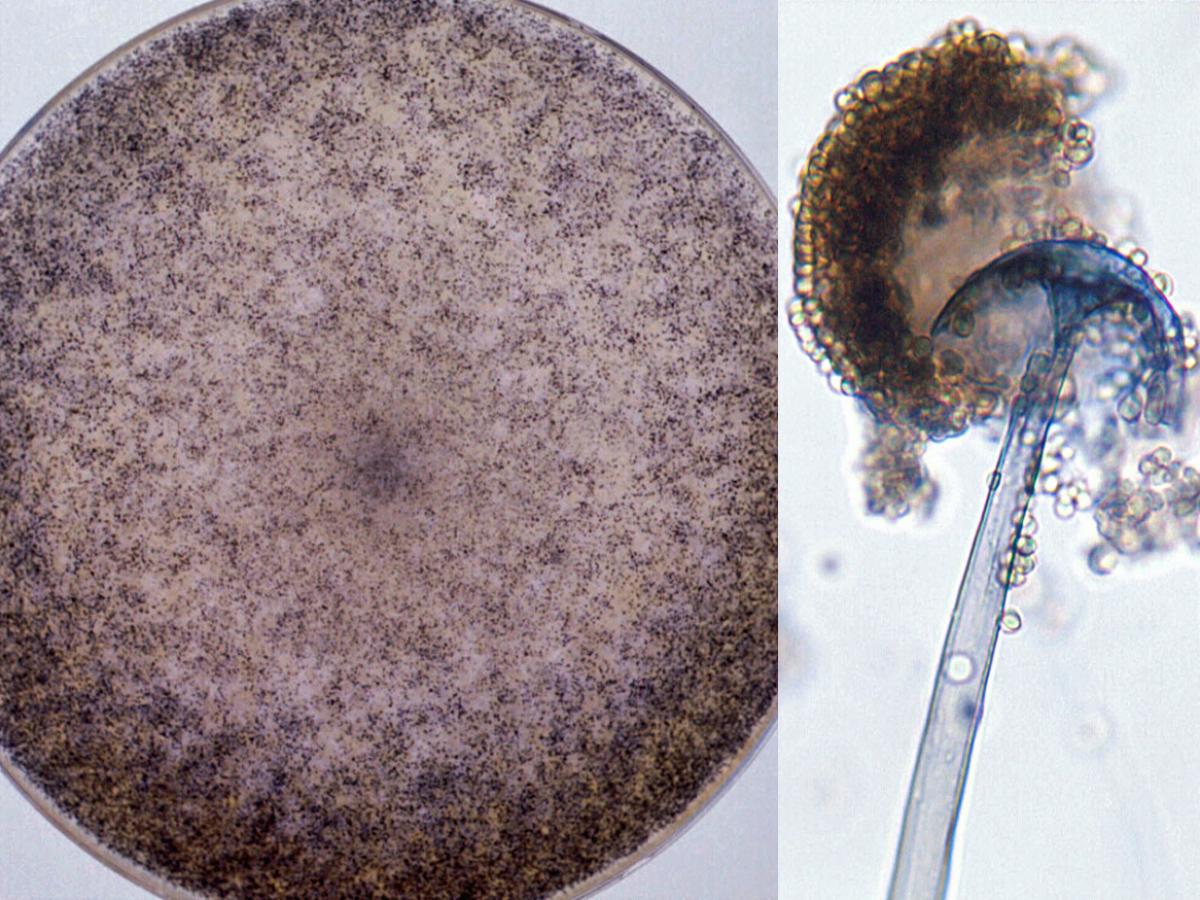
Identify this fungi
Rhizopus spp.
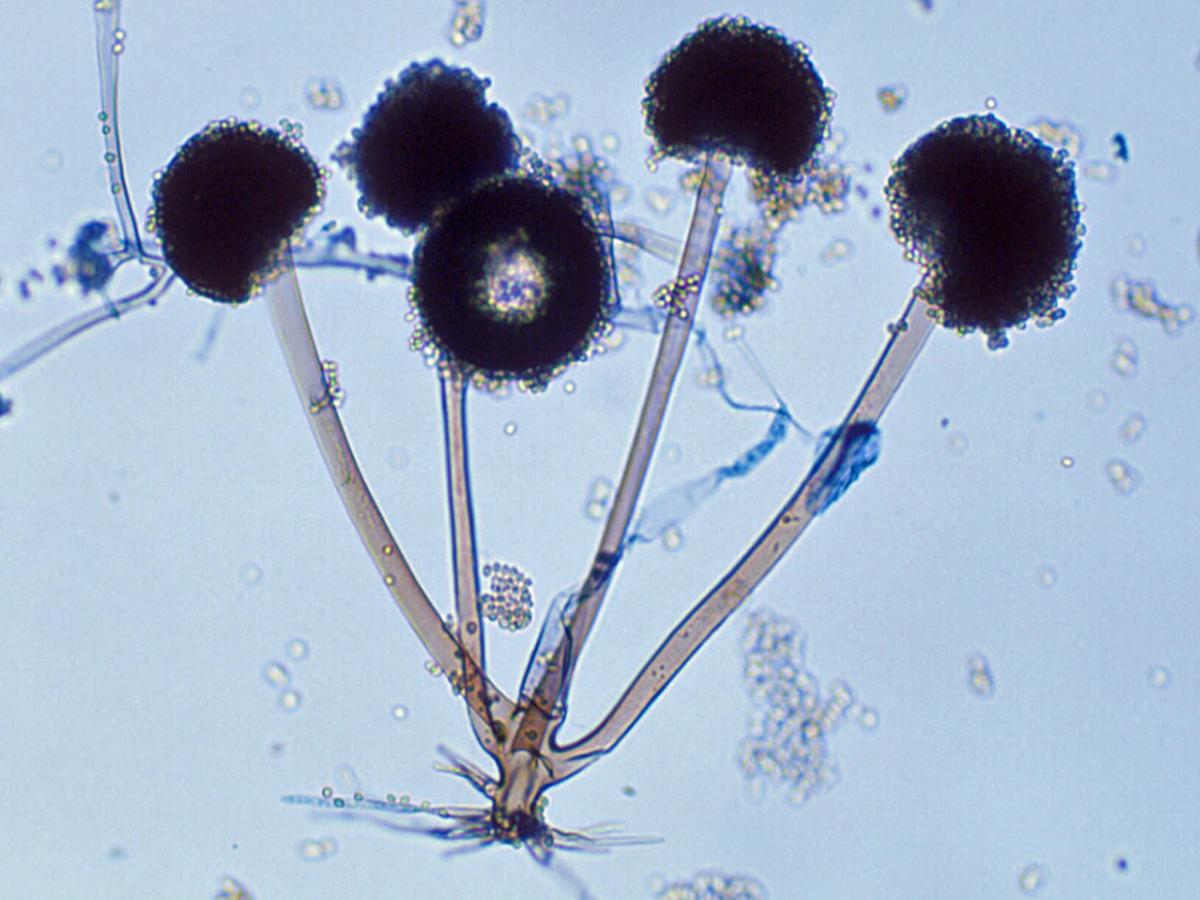
Identify this fungi
Rhizopus spp.
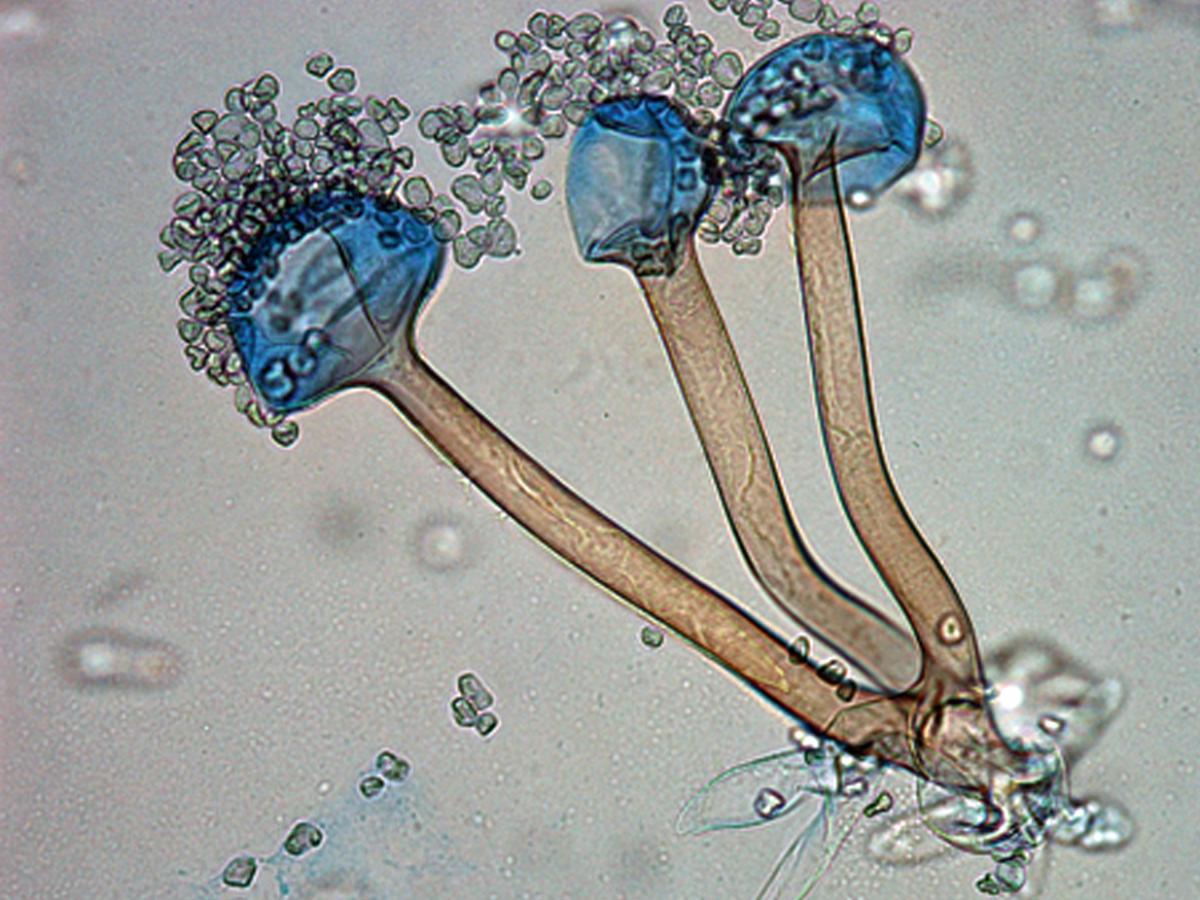
Identify this fungi
Rhizopus spp.
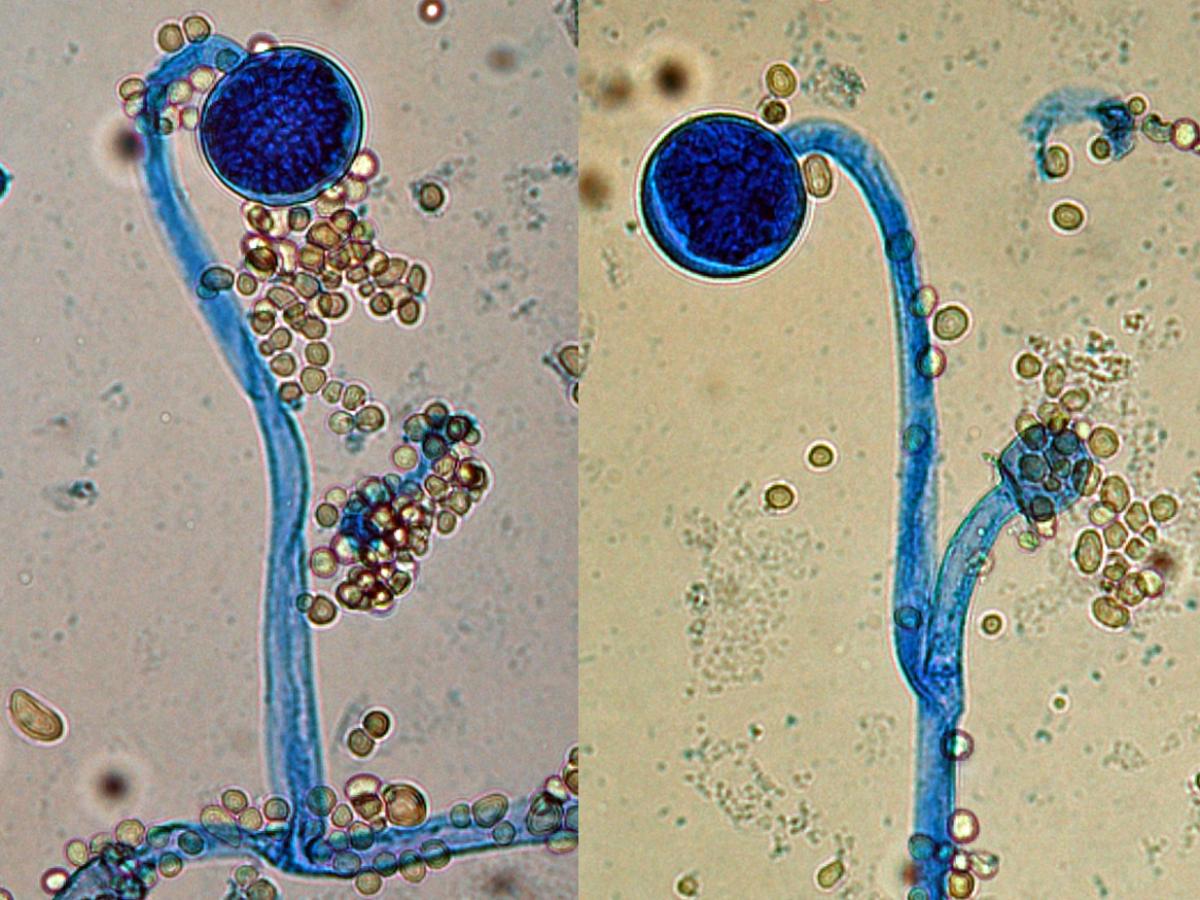
Identify this fungi
Mucor spp.
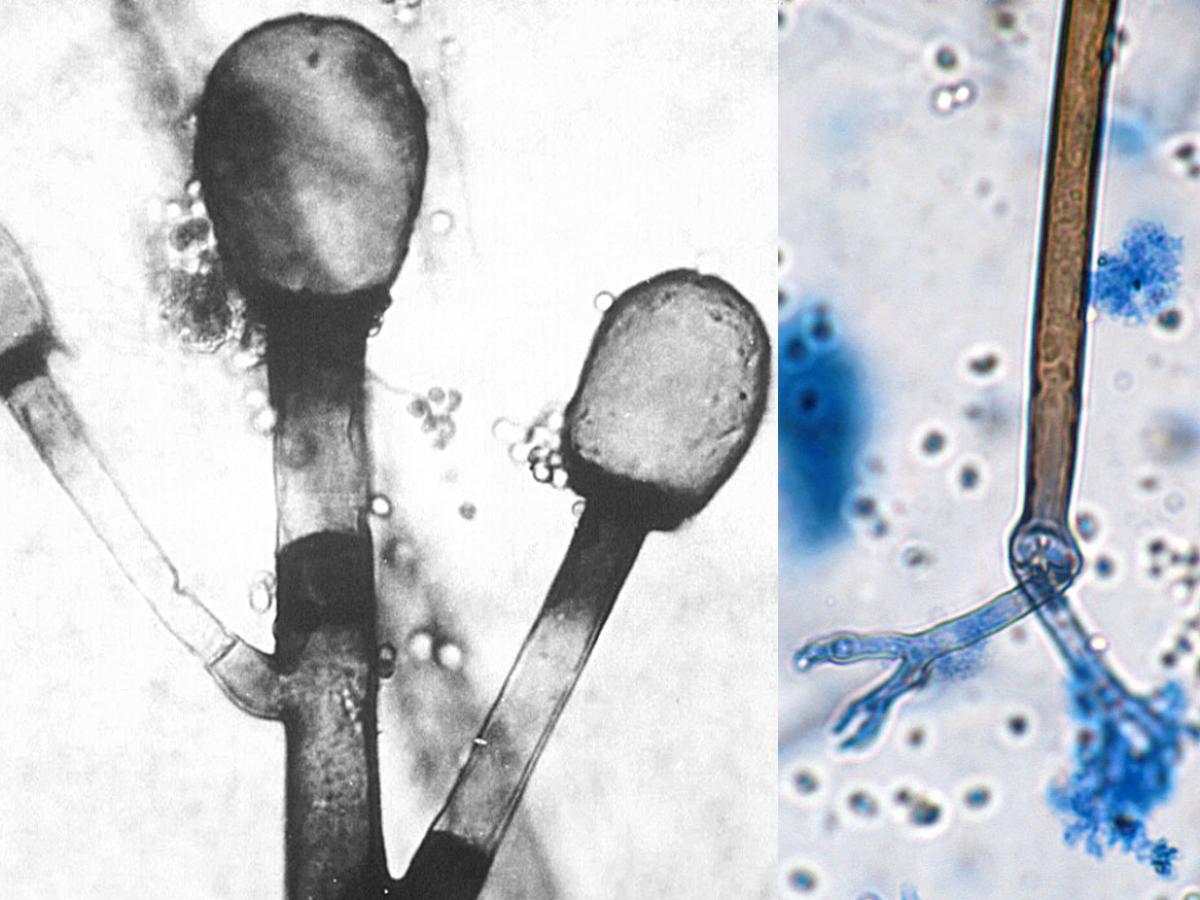
Identify this fungi
Rhizomucor spp.
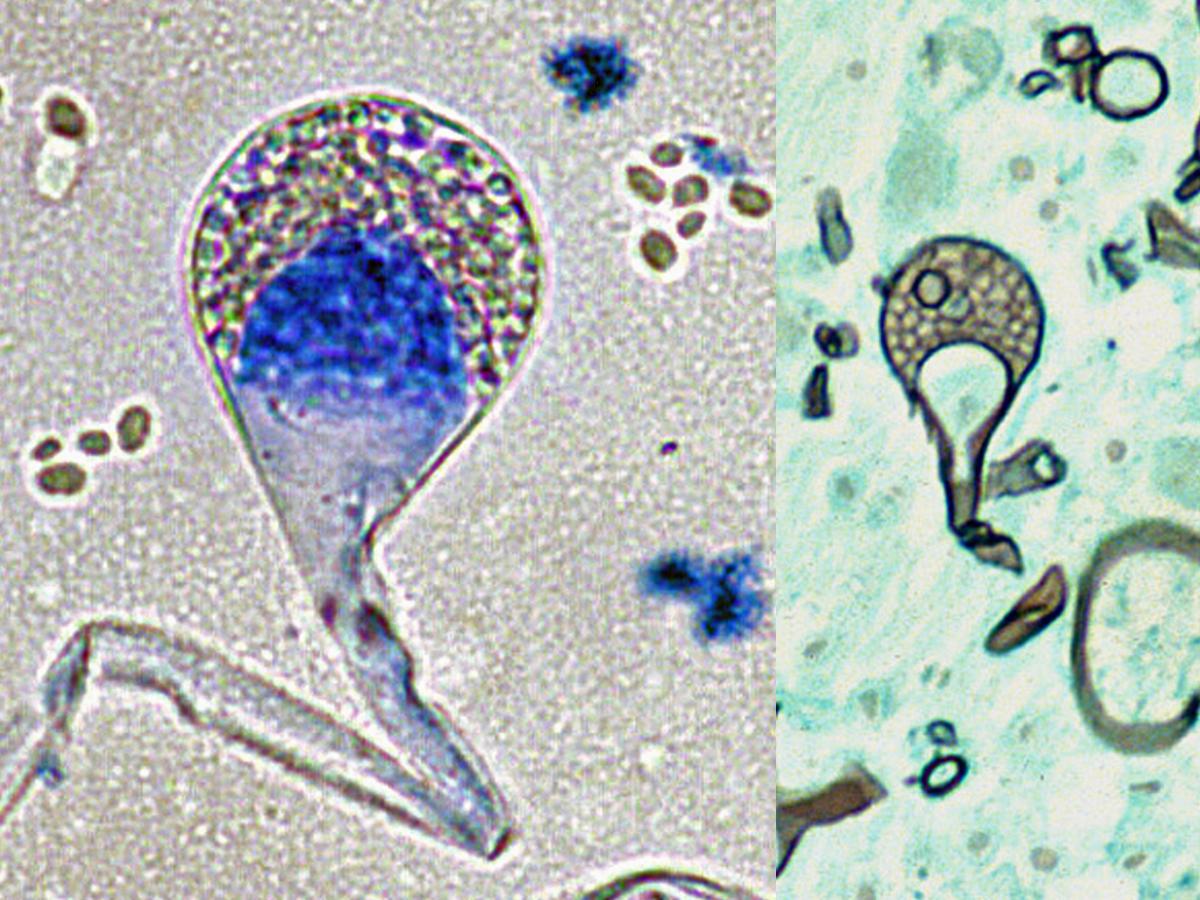
Identify this fungi
Lichtheimia spp.
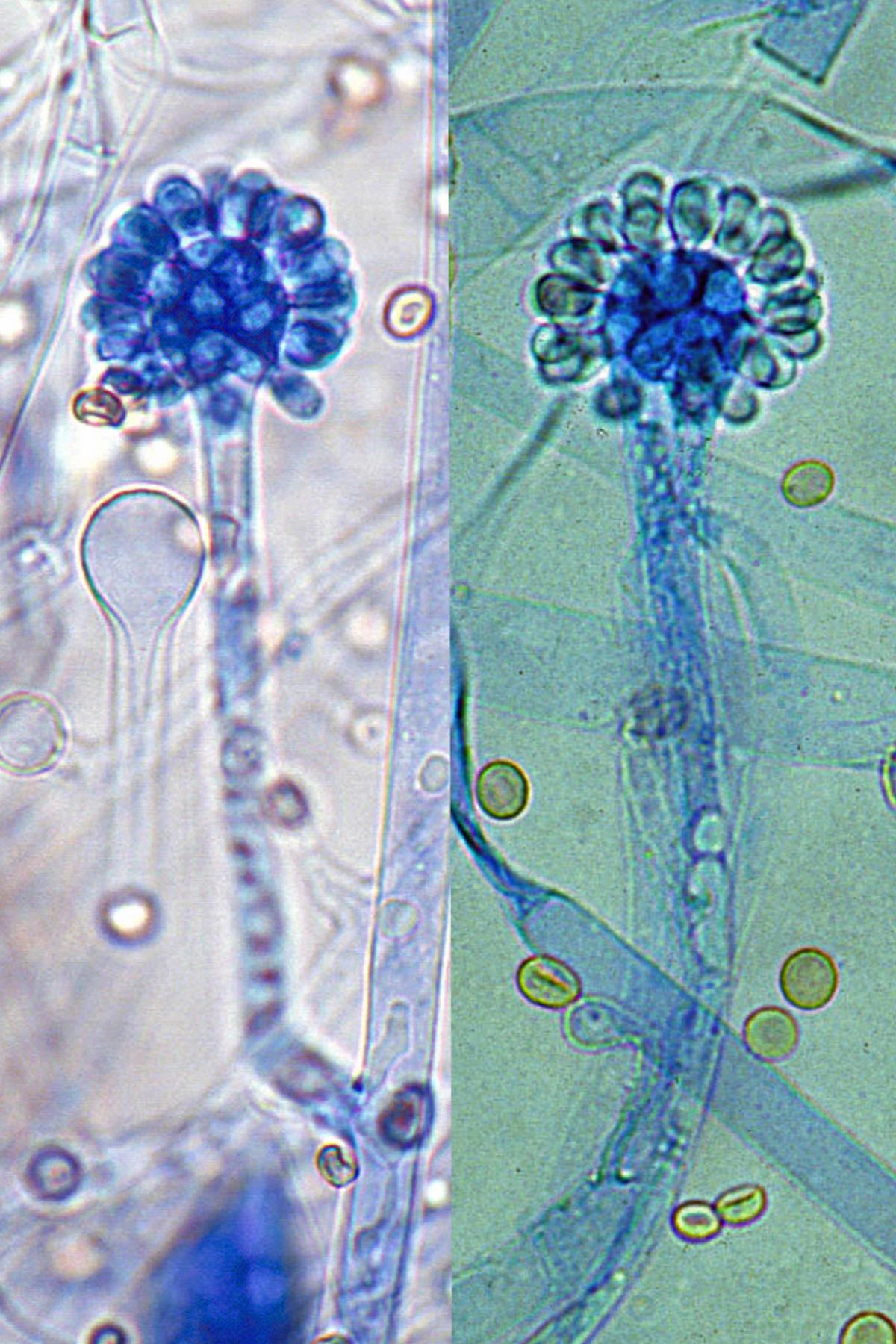
Identify this fungi
Cunninghamella spp.
List general features of fungi that separate them from plants and animals.
Fungi have a cell wall, but lack chloroplasts and chlorophyll. They gain energy through decomposition, but they absorb nutrients rather than ingesting them. They reproduce via budding, spores, and fragmentation, not seeds. They have ergosterol (not cholesterol) in the cell membrane.
Define hyphae
Filaments that make up multicellular fungi
Define mycelium
A mass of hyphae
Define spores
Sexual reproductive method
Define sporangia
A receptacle where asexual spores are formed
Define conidia
Asexual reproductive method
Define rhizoids
Hyphae that function like roots
Define stolons
Lateral (left-right) hyphae above the surface
List three ways fungi might reproduce
Budding, spores, and fragmentation
Name the six groups of medically relevant fungi
Yeasts, Mucroales, hypomycetes, dermatophytes, dematiaceous, hyaline
Which group(s) of fungi are single-celled?
Yeasts
Which group(s) of fungi are pigmented?
Hyaline
Which groups of fungi use sporangia to reproduce?
Mucroales
Which groups of fungi use conidia to reproduce?
dermatophytes, hyaline, dematiaceous
Which groups of fungi are considered opportunistic?
Hyaline and dematiaceous
Which groups of fungi are strictly parasites?
Dermatophytes
Describe the type of patients who are most susceptible to fungal infections?
Immunocompromised people
Describe what it means for a fungal infection to be superficial
Skin or surface level infection
Describe what it means for a fungal infections to be subcutaneous
Deep skin or tissue infection
Describe what it means for a fungal infection to be systemic
Infects everywhere in the body, it spreads through your entire system
Describe what it means for a fungal infections to be opportunistic
Not super harmful, but attacks when given the opportunity (aka when immune system is weak)
Which fungi are classified as Thermally Dimorphic, aka systemic mycoses?
Histoplasma capsulatum
Blastomyces dermatitidis
Coddidiodes spp.
Paracoddidioides brasiliensis
Sporothrix schenckii
Which fungi’s mold phase has septate hyphae with a round or pear-shaped microconidia? Macroconidia can form after several weeks and give a prickly-looking surface.
Histoplasma capsulatum
Which fungi’s yeast phase has simple, round or oval budding cells?
Histoplasma capsulatum
Which fungi’s mold colony looks gray-white with a delicate or cobweb appearance?
Histoplasma capsulatum
Which fungi’s yeast colony looks most, white, and yeast-like?
Histoplasma capsulatum
This fungi is endemic to the eastern US, Central & South America, and West Africa, and is transmitted via aerosols (inhaled) from soil to humans. It can be contracted from bird roots, guano of bats and birds, and in caves.
Histoplasma capsulatum
This fungi causes a chronic, granulomatous infection that infects the lungs (also lymph nodes, spleen, liver, and bone marrow), and is mostly asymptomatic (but can have flu-like symptoms). Ulcerative lesions are possible in the upper respiratory tract. Name the fungi and the disease is causes.
Histoplasma capsulatum, histoplasmosis
This fungi’s mold phase resembles lollipops, and has septate, hyaline hyphae with round or pear-shaped conidia.
Blastomyces dermatitidis
This fungi’s yeast phase has cells with a budding base and thick walls.
Blastomyces dermatitidis
This fungi’s mold colony has a white or brownish colony with a cottony texture. It resembles a fried egg.
Blastomyces dermatitidis
This fungi’s yeast colony is creamy or wrinkled and is cream or tan in color.
Blastomyces dermatitidis
This fungi is endemic to the Mississippi river basin, the great lakes, and the southeast US. It is transmitted via aerosols, which are inhaled. It’s more common in males than females, associated with outdoor jobs and activities, and dogs are 10x more susceptible.
Blastomyces dermatitidis
This fungi causes an acute and chronic granulomatous infection, or a suppurative infection. It brings flu-like symptoms and sometimes pulmonary mass lesions. It can also disseminate to other parts of the body, like the skin.
Blastomyces dermatitidis
This fungi’s mold phase has chains of alternate-staining dysjunctor cells and barrel-shaped arthroconidia.
Coccidioides spp.
This fungi’s yeast phase is round and forms spherules in tissues.
Coccidioides spp.
This fungi’s mold colony can be white, gray, brown, or yellow. It appears like a dense cotton with a tan or brown underside.
Coccidioides spp.
This fungi does not have a yeast phase growth when put on a plate.
Coccidioides spp.
This fungi is endemic to the southwest US, northern Mexico, and other desert soils. Spores are blown in the dust, found in the burrows of desert rodents, and other decaying carcasses. It’s transmitted via aerosols, and is one of the MOST infectious fungi.
Coccidioides spp.
This fungi causes a disease which is mostly asymptomatic, can create spherules in the lungs, and disseminate to the organs, bone, skin, lymph nodes, or other subcutaneous tissues. Name the fungi and the disease.
Coccidioides spp, coccidioidomycosis
This fungi’s mold phase looks similar to Blastomyces dermatitis, with oval or round conidia.
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis
This fungi’s yeast phase looks like a mariner’s (ship’s) wheel.
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis
This fungi’s mold colony looks flat and wrinkled or folded, appearing white or brown in color, with a tan or brown underside.
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis
This fungi’s yeast colony is white or tan, moist-looking, and can become wrinkled or folded.
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis
This fungi is endemic to Central and South America, and is most likely transmitted via aerosols. When in the lungs, conidia turn to yeast with multiple buds. Men are 15x more susceptible to this converstion because estrogen is protective.
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis
This fungi causes a chronic granulomatous infection, which can become become pulmonary. It produces ulcerative lesions of mucous membranes, and can disseminate to the lymph nodes, spleen, intestines, liver, brain, and adrenal glands. Name the fungi and the disease is causes.
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis, paracoccidioidomycosis
This fungi’s mold phase has rosette-like conidia that appear round or tear-shaped. There are septate, narrow, hyaline hyphae with slender and branching conidiophores containing many conidia.
Sporothrix schenckii
This fungi’s yeast phase has budding cells that look like cigar bodies or floppy rabbit ears.
Sporothrix schenckii
This fungi’s mold colony starts white, and then goes to a pale orange, and then becomes dark. It appears wrinkled, leatherly, or velvety.
Sporothrix schenckii
This fungi’s yeast colony is cream or tan-colored, smooth, and yeast-like.
Sporothrix schenckii
This fungi is found worldwide and is a hazard for farmers, gardeners, florists, and miners. It can be found in living or dead vegetation, and is transmitted via trauma (splinters, bites, thorns, scratches) on the arm, hand, or leg. Name the fungi and the disease is causes.
Sporothrix schenckii, sporotrichosis (aka Rose Gardener’s disease)
This fungi is known for producing a chronic subcutaneous infection and the primary lesion is small and non-healing, typically found on an index finger or back of hand. Nodular lesions form afterwards, usually involving lymphatic vessels and nodes. The disease rarely disseminates.
Sporothrix schenckii
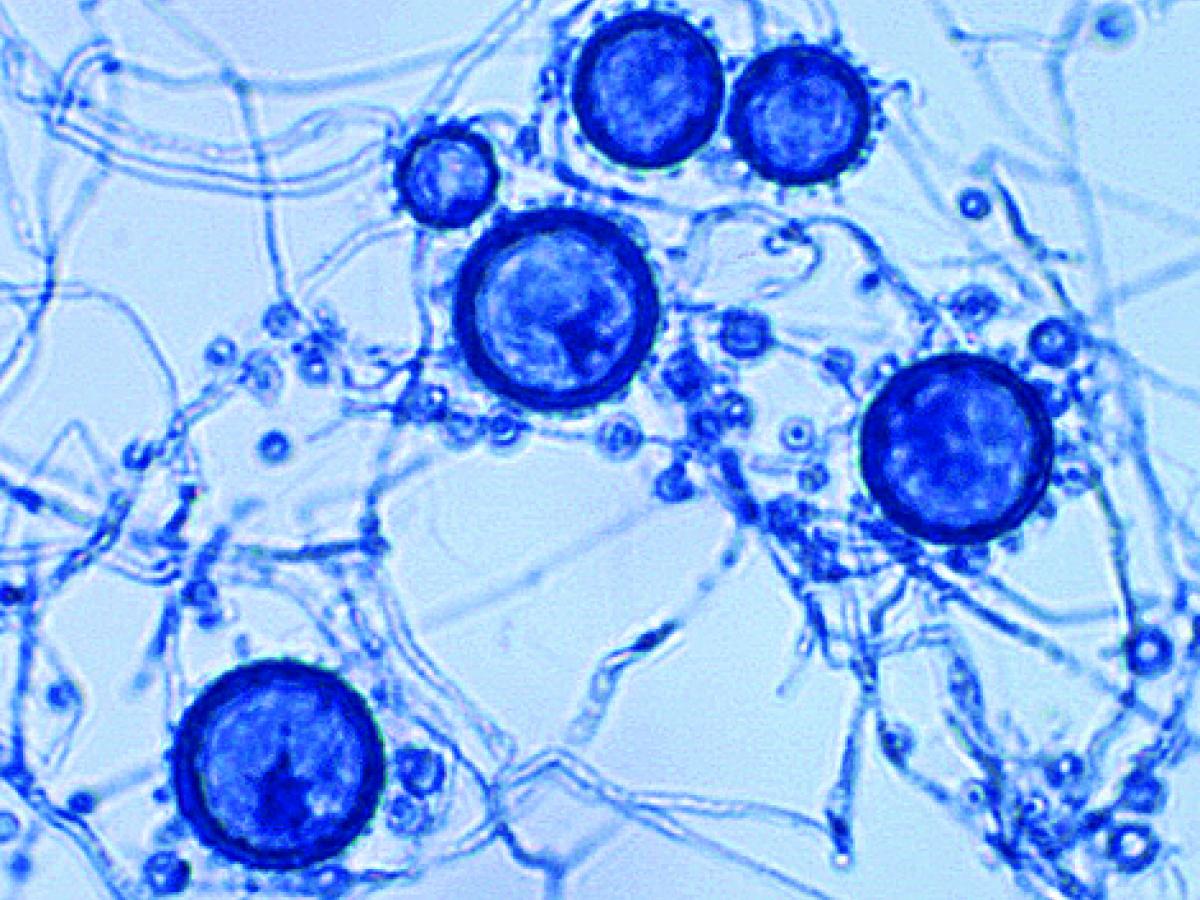
Identify this fungi
Histoplasma capsulatum
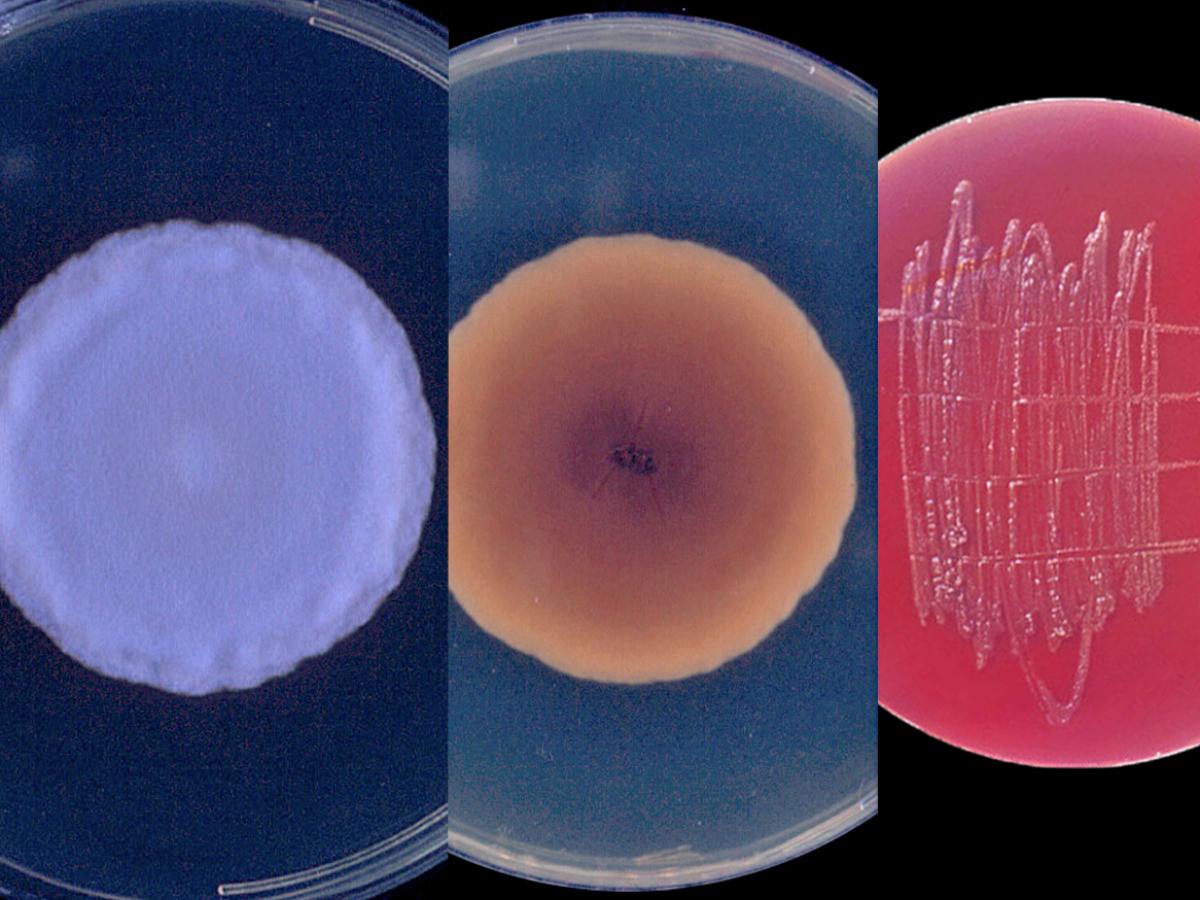
Identify this fungi
Histoplasma capsulatum
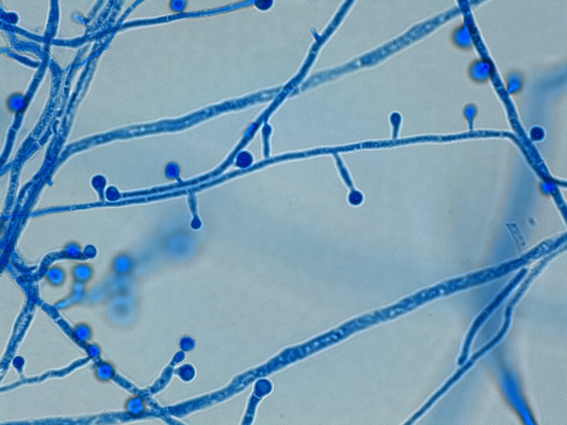
Identify this fungi
Blastomyces dermatitidis
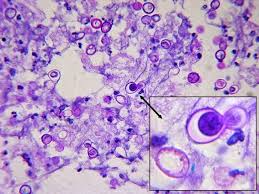
Identify this fungi
Blastomyces dermatitidis
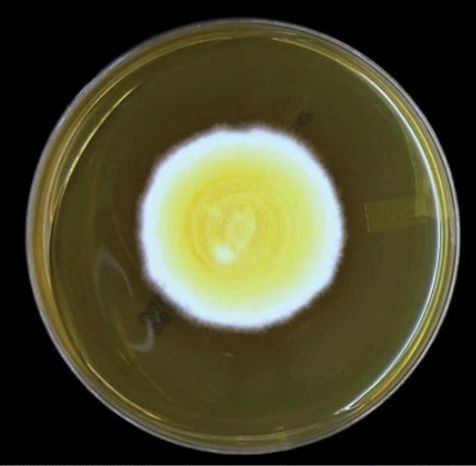
Identify this fungi
Blastomyces dermatitidis
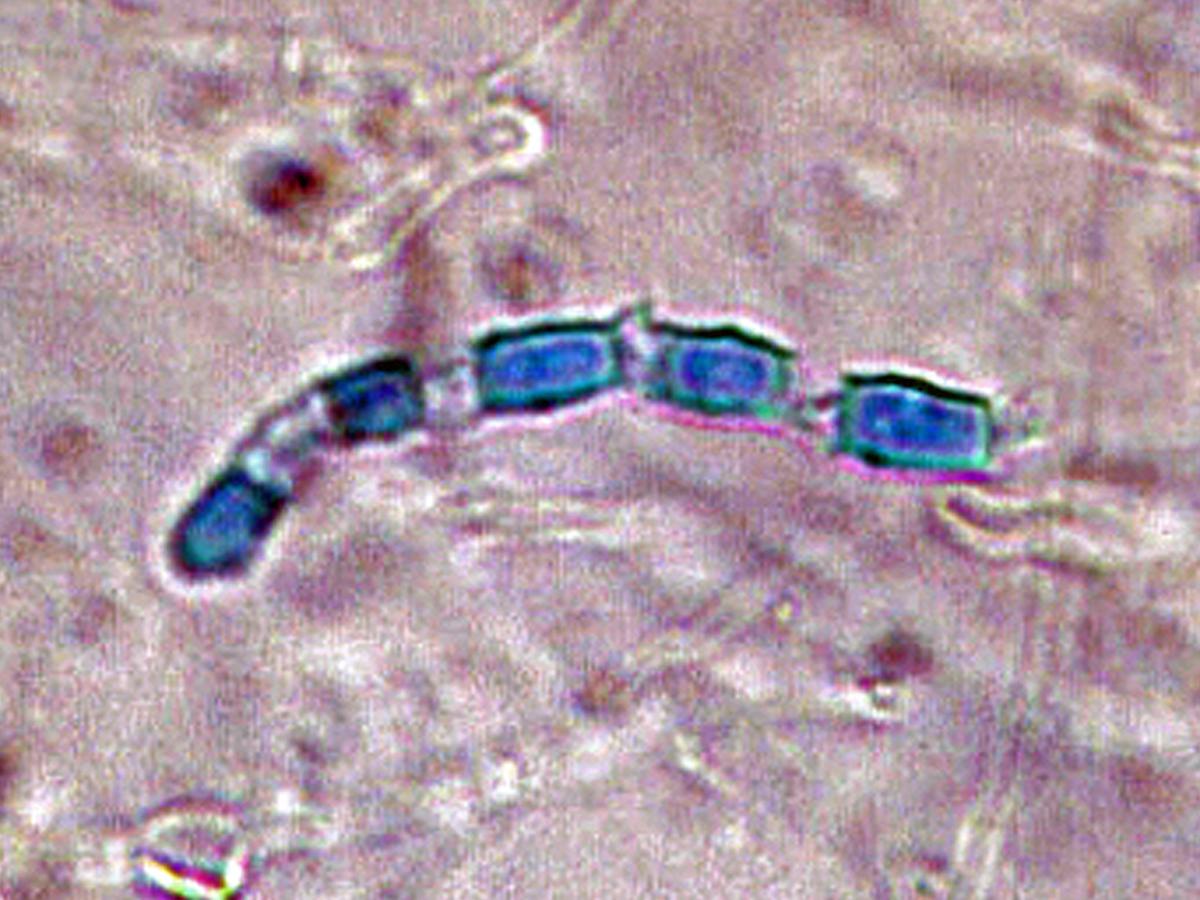
Identify this fungi
Coccidioides spp.
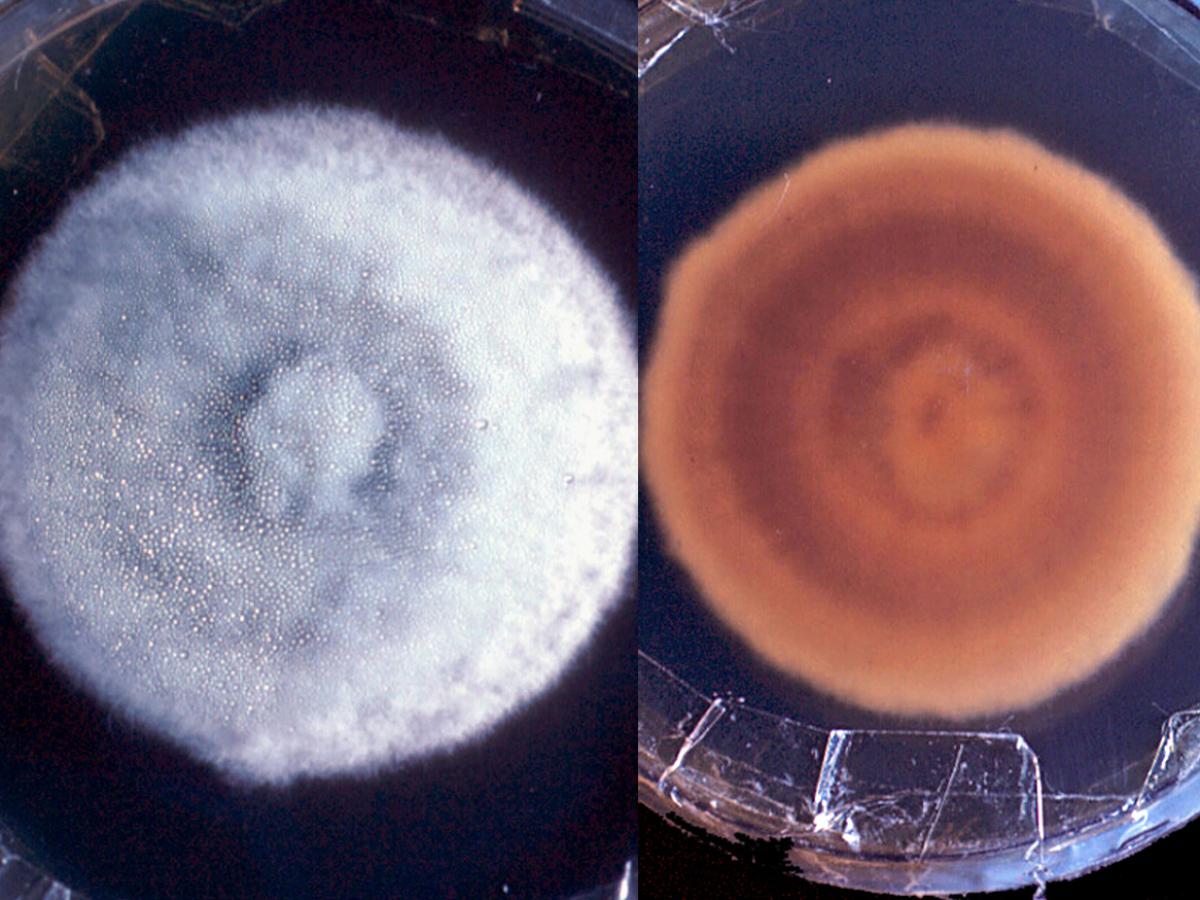
Identify this fungi
Coccidioides spp.
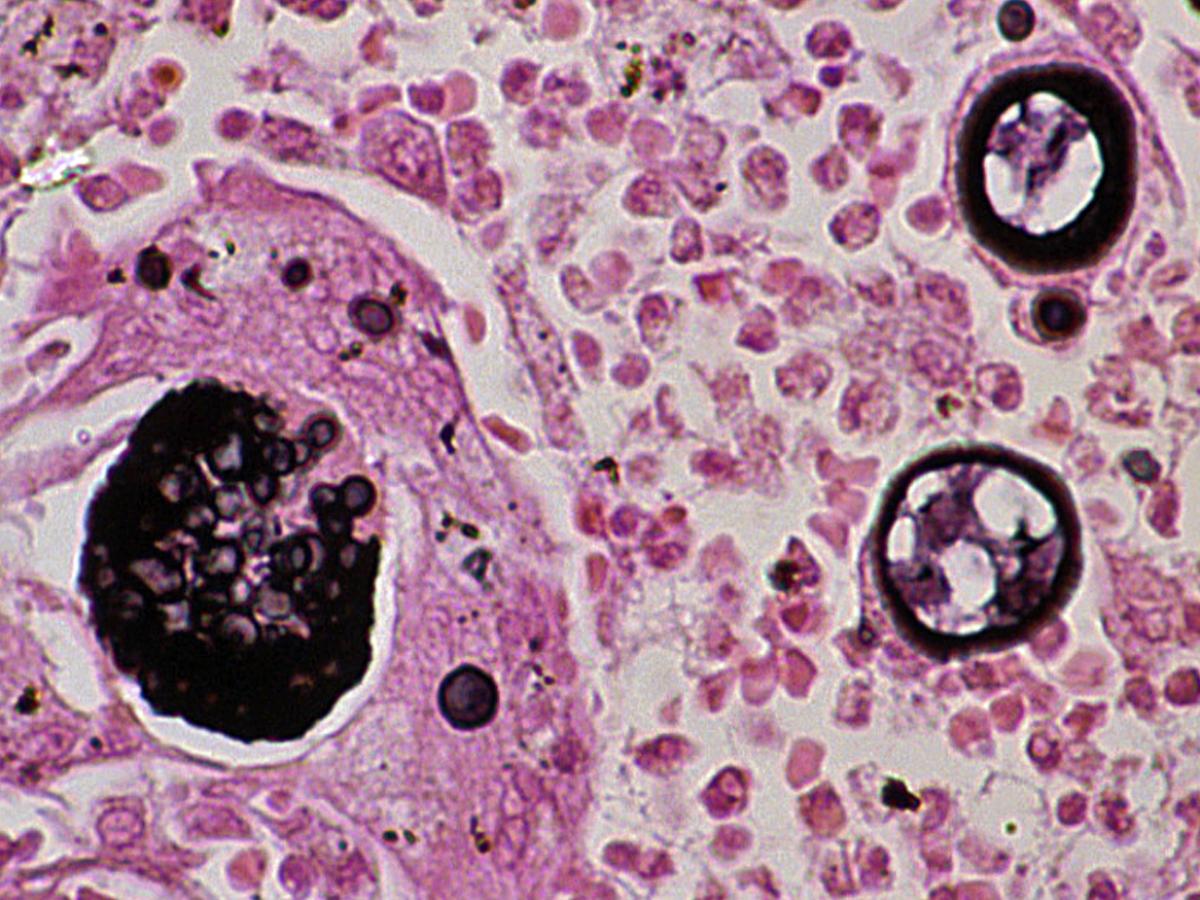
Identify this fungi
Coccidioides spp.
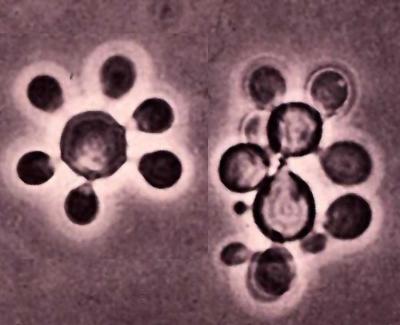
Identify this fungi
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis
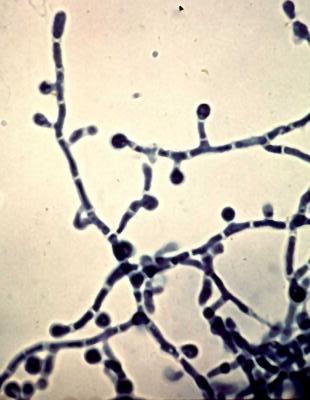
Identify this fungi
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis

Identify this fungi
Sporothrix schenckii
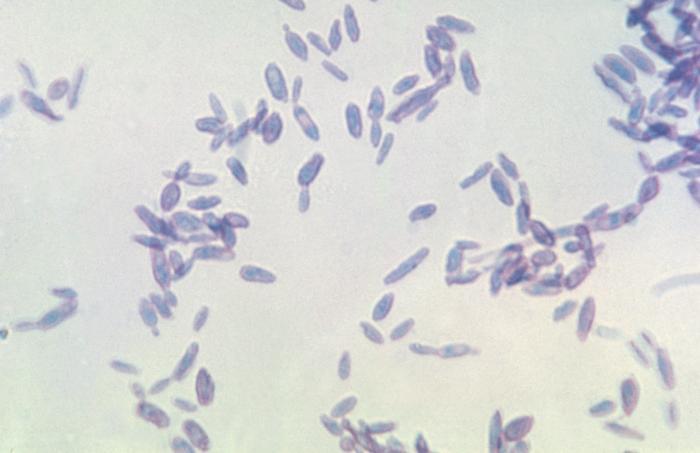
Identify this fungi
Sporothrix schenckii
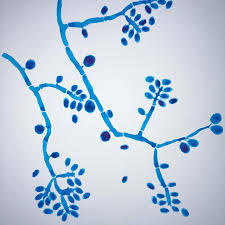
Identify this fungi
Sporothrix schenckii