Basics of Chemistry
1/34
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Matter is …
anything with mass
Matter can be classified into…
Pure: elements, compounds
Mixture: homogeneous, heterogenous
An element is…
made up of 1 type of atom
Compounds are…
made up of 1 or more different elements
Homogeneous mixtures…
are a blend of different chemicals but appear to be uniform to the naked eye
Heterogenous mixtures are..
not uniform and visibly different
In the modern periodic table, elements are arranged by…
atomic number
A period in a periodic table represents…
a row
A group in the periodic table represents…
A column
A valence shell is
the outermost shell of an atom
Valence electrons are
electrons on the valence shell
A period number refers to
the number of shells and atom has
There are 3 types of elements. They are
metals, non-metals, and metalloids.
Metals are
solid(ex mercury), ductile, malleable, shiny, good conductors, and silver ish
Non-metals are
brittle, dull, poor conductors, solid or gas(ex bromine)
Metalloids are
solid, shiny, brittle, good conductors of electricity but bad conductors of heat
All matter is made up of
atoms
Atoms are made up of 3 sub-atomic particles. They are
protons- positive charge, mass=1
neutrons- no charge, mass=1
electrons- negative charge, mass=1/2000
The atomic number shows
the number of protons
The number of protons and electrons are _______ in a neutral atom
equal
To find the number of neutrons,
subtract the atomic number from the atomic mass
There are 6 chemical families. They are
alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, halogens, noble gases, and hydrogen
Alkali metals are
the first group of the periodic tables
Malleable, low density, low melting point, very reactive, silver or grey
They are especially reactive with water and form hydrogen gas and oxides
Alkaline earth metals are
the second group of the periodic table
somewhat malleable, high density, high melting point
used in fireworks and construction materials
Transition metals are
groups 3-12 of the periodic table
dense, durable, high melting points, very good conductors, solid
They are particularly precious and valuable
Halogens are
group 17 of the periodic table
exist in all 3 states, very electronegative, very reactive
Nobel gases are
group 18 of the periodic table
colorless, odorless, non-flammable, non-reactive, stable
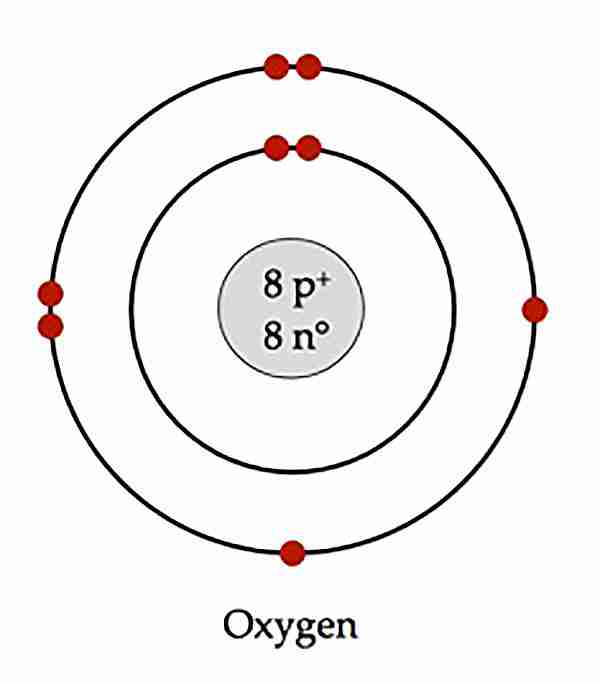
In atomic diagrams, there are certain limits to how many electrons you can put in each shell.
Shell 1: 2 electrons
Shell 2: 8 electrons
Shell 3: 8 electrons
A Bohr-Rutgerford diagram looks like
A lewis dot diagram
is only concerned with the valence electrons
Ions are
elements with empty spots in their valence shell
Atoms with empty valence shells are ______ and become _______ by _________ or _________ __________.
1) unstable
2) stable
3) giving away
4) taking in
5) electrons
Atoms with less than 4 missing spots ______ electrons and form _______.
1) give away
2) cations
Atoms with more than 4 empty spots ________ electrons and form ______.
1) take in
2) anions