Medicinal Chem Exam 3
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
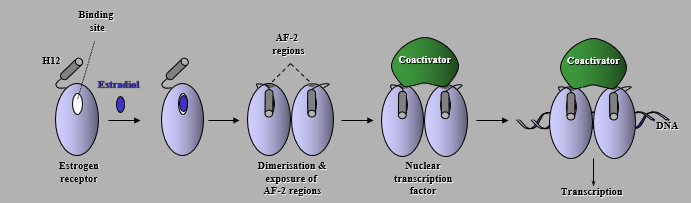
Action of Estrogen Receptor
Estradiol binds to the receptor binding site which causes dimerization and exposure of AF-2 reigons. The Coactivator Nuclear transcription factor then binds and allows transcription to occur
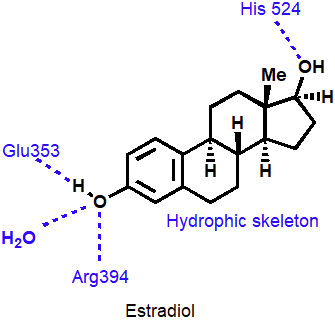
Binding interactions for estradiol
Phenol and alcohol of estradiol are important binding groups
Binding site is spacious and hydrophobic
Phenol group of estradiol is positioned in narrow slot
Orientates rest of molecule
Acts as agonist
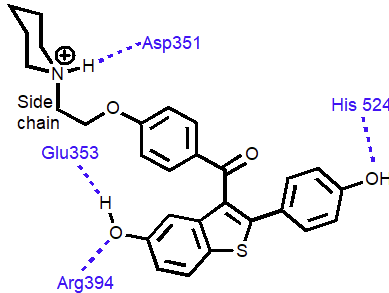
Raloxifene
Raloxifene is an antagonist (anticancer agent)
Phenol groups mimic phenol and alcohol of estradiol
Interaction with Asp-351 is important for antagonist activity
Side chain prevents receptor helix H12 folding over as lid
AF-2 binding region not revealed
Co-activator cannot bind
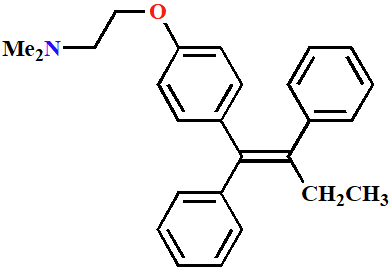
Tamoxifen
Antagonist for estrogen receptor
Anticancer agent
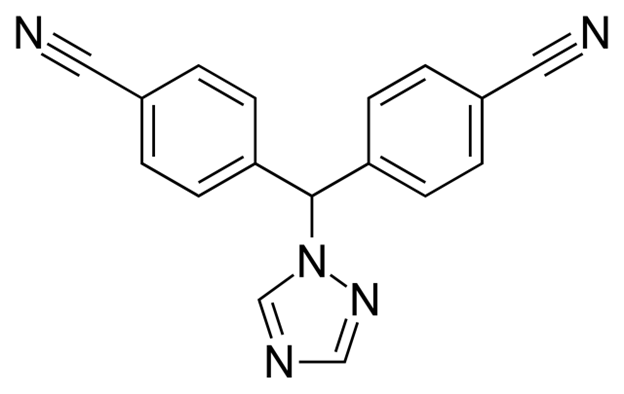
Letrazole
Aromatase Inhibitor
Treatment for estrogen positive breast cancer
Important for estradiol synthesis
Intercalating Agents Mechanism of action
They have planar aromatic or heteroaromatic ring systems that allow for them to slip between the layers of nucleic acid pairs and disrupt the helix shape.
Preference for minor or major groove
Prevents replication and transcription
Can inhibit topos
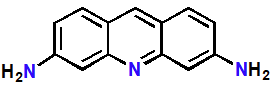
Proflavine
Intercalating Agents
Planar tricyclic system
Amino substituents are protonated and charged
Topical antibacterial during WWII
Targets bacterial DNA
Too toxic for systemic use
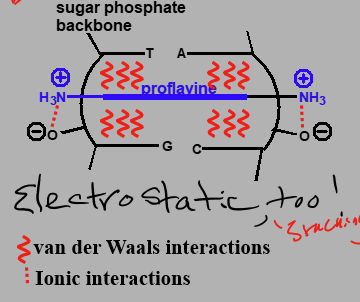
Proflavine interactions
Has van der Walls interactions between base pair and drug.
Ionic interactions between NH3 and O- of backbone
Electrostatic possible from stacking
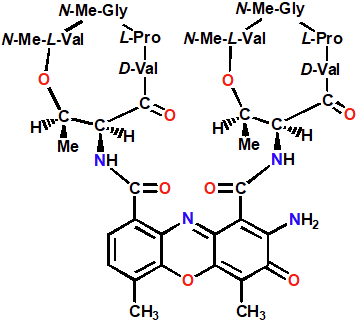
Dactinomycin
Intercalating Agents
Extra binding to sugar phosphate backbone by cyclic peptides
Intercalates by minor grooves
Prevents DNA unwinding
Blocks transcription by blocking DNA-dependent RNA pol
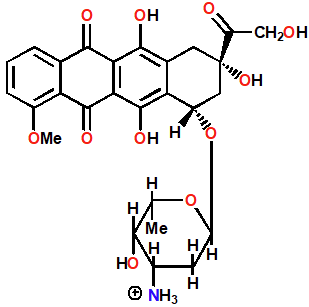
Doxorubicin (Adriamycin)
Intercalating Agents
Extra binding to sugar phosphate backbone by NH3
Intercalates via major groove
Blocks action of topo II by stabilizing DNA-Enzyme complex
Topo poison
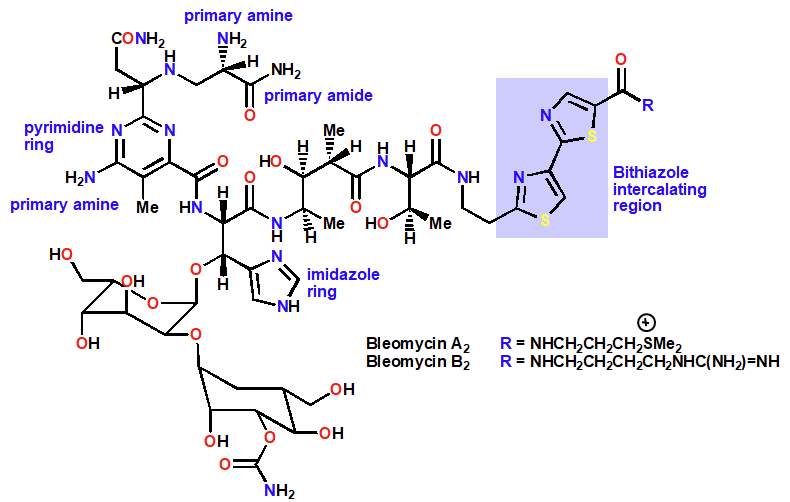
Bleomycin
Intercalating Agent & chain cutter
Anticancer Agent- Skin cancer
Intercalated by means of bithiazole ring system
Ferrous ion Fe2+ then chelated by nitrogens of primary amines, amide & pyrimidine ring
Reaction with O2 results in Fe2+ ion and ROS
Results in radical formation (from abstracting H from DNA) and chain cutting
Prevents DNA ligase from repairing damage
Etoposide
Topo poison- non intercalating
Stabalizes complex between DNA & Topo enzymes
Anticancer agent
Causes Chain cutting
Teniposide
Topo poison- non intercalating
Stabalizes complex between DNA & Topo enzymes
Anticancer agent
Causes Chain cutting
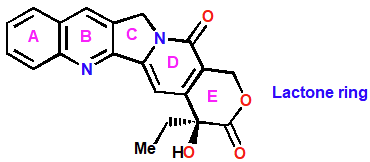
Camptothecin
Topo poison- non intercalating
Stabalizes complex between DNA and topo I
Single-Strand breaks accumulate in the chain
Irreversible double-strand breaks occur during transcription
Semi-synthetic analogs used as anticancer agents
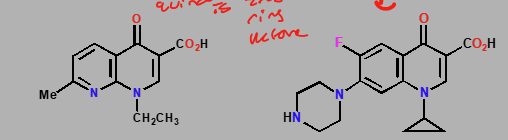
Quinolones & Fluoroquinilones
Nalidixic acid & Ciprofloxacin
Topo poison- non intercalating
Synthetic agents used as antibacterials
Stabalizes complex between bacterial DNA & Topo
Binding site for agents revealed once DNA strands are nicked
Quinolones and fluoroquinilones
Four drug molecules are stacked in the bound complex
Bound to DNA and enzyme by hydrogen binding & ionic interactions - no stacking
Alkylating Agents
Contains highly electrophilic groups
Forms covalent bonds to nucleophilic groups in DNA
Prevents replication and transcription
Anticancer agents but could have toxic side effects
Can cause interstrand and intrastrand crosslinking if two electrophilic groups are present
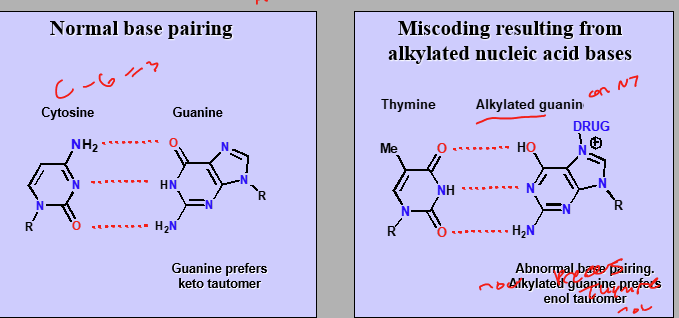
Can result in miscoding
Nucleophilic groups on nucleic acid bases
Miscoding
Alkylated nucleic acid guanine prefers enol tautomer while regular G prefers keto tautomer. These differences cause incorrect binding instead of G-C it is G-T
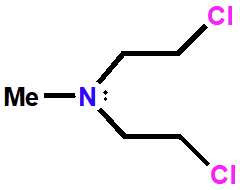
Chlormethine (nitrogen mustard)
Alkylating Agent
Used in 1942
Causes intra & interstrand linking
Prevents replication
Mono-alkylation of guanine possible
Analogues with better properties have been prepared
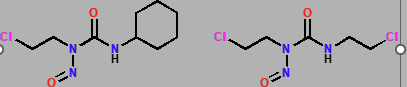
Nitrosoureas
Lomustine & Carmustine
Alkylating Agent
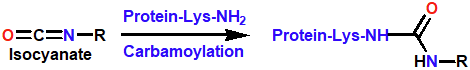
Decomposes in body to form an alkylating (Cl-CH2-CH2+) agent and carbamoylating agent (O=C=N-R)
Alkylating agent unlikely, R-N+=- N more likely
Nitrosoureas Alkylating Agent
Causes interstrand crosslinking between G-G or G-C
Nitrosoureas carbamoylating agent
Reacts with lysine residues on proteins, may inactivate DNA repair enzymes
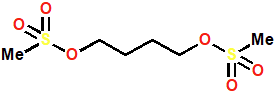
Busulfan
Alkylating Agent
Synthetic agent used as an anticancer agent
Causes interstrand crosslinking
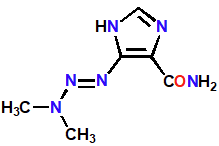
Dacarbazine
Alkylating Agent
Prodrug activated by demethylation in liver
Decomposes to form methyldiazonium ion (N=-N+-CH3)
Alkylated guanine groups
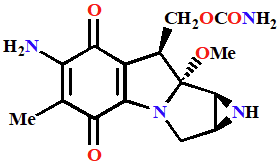
Mitomycin C
Alkylating Agents
Prodrug activated in the body to form an alkylating agent
One of the most toxic anticancer drugs in clinical use
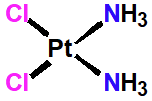
Cisplantin
Metallating Agent
Neutral inactive molecule acting as prodrug
Platinum covalently inked to chloro subsitiuents
Ammonia acts as ligands
Activated in cells with low chloride ion conc.
Chloro subs replaced with neutral water ligands
Produced positively charged species
Binds to DNA in G rich reigons
Intrastrand links
Localized unwinding of DNA helix
Inhibits transcription
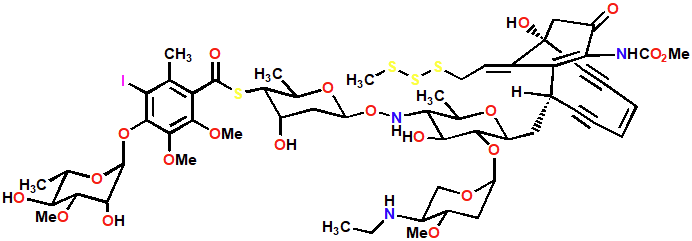
Calicheamicin y1
Chain cutter
Antitumor agent
Generates DNA diradical that reacts with oxygen and results in chain cutting
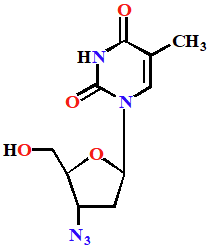
Azidothymidine (AZT)
(Zidovudine;Retrovir)
Chain terminator
Prodrug used to treat HIV
Phosphorylated to triphosphate in body
Has two mechs of action: inhibit a viral enzyme (reverse transcriptase) & is added to growing DNA chain and acts as a terminator
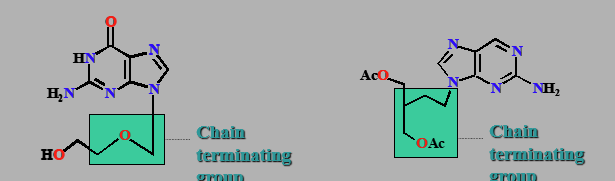
Aciclovir (Zovirax) & Famciclovir
(Famvir)
Chain terminators
Prodrug used as antiviral
Same mech as AZT
Used on herpes simplex & shingles
Chain termination mechanism
Instead of base binding to growing strand and have OH substituent, the drug binds with an H substituent which keeps more bases from being able to be added.
Control of Gene Transcription
Design of synthetic molecules than can recognize and bind to specific base pairs
Hairpin polyamides containing heterocylic rings can bind to minor grooves
Binding involves amide groups and heterocycles
Particular patterns of heterocyclic rings allow recognition of particular base pairs
Capable of inhibiting transcription
Designed to bind to regulatory element of a gene
Drugs acting on rRNA
Antisense Therapy Advantages
Same effect as an enzyme inhibitor or receptor antagonist
Highly specific where the oligonucleotide is 17 nucleotides or more
Smaller dose levels required compared to inhibitors or antagonists
Potentially less side effects
Antisense Therapy disadvantages
‘Exposed’ sections of mRNA must be targeted
Instability and polarity of oligonucleotides (pharmacokinetics)
Short lifetime of oligonucleotides and poor absorption across cell membranes
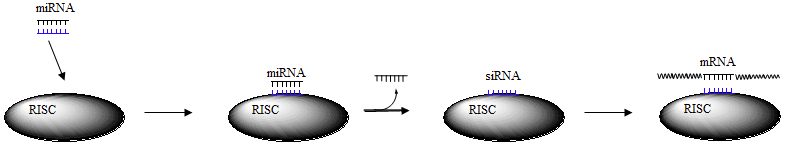
Micro-RNA (miRNA)
Short segments of double stranded RNA
Recognized by enzyme complex RISC to produce single stranded RNA - small interfering or small inhibitory RNA (siRNA)
Binds to complementary region of mRNA
mRNA is cleaved by enzyme complex
miRNA advantages
siRNAs have potential to be used in gene therapy
Greater efficiency in silencing mRNA than conventional antisense therapy
One siRNA could lead to cleavage of several mRNA molecules
miRNA disadvantages
siRNAs need to be metabolically stable
Need to reach target cells
Need to enter target cells
Agents Blocking Transport Proteins
Agents binding to transport proteins prevents the re uptake of neurostransmitters
Results in increased levels of affected neurostransmitters
Result is similar to using an agonist
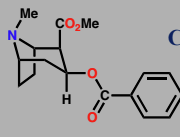
Cocaine
Reuptake inhibitor for dopamin in CNS
Causes euphoric effects
Reuptake inhibitor of noradrenaline in peripheral system
suppresses hunger
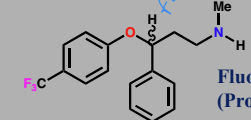
Fluoxetine (Prozac)
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI)
Antidepressant
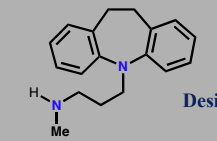
Desipramine
Tricyclic antidepressant
Non-selective reuptake inhibitor for noradrenaline
Principle treatment for depression from 60s-80s
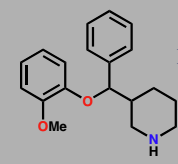
Reboxetine
Selective noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor (SNRI)
antidepressent uses since 2003
Not marketed in US
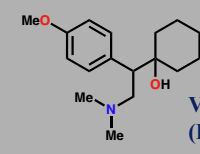
Venlafaxine
Dual noradrenaline & serotinin reuptake inhibitor
Antidepressant
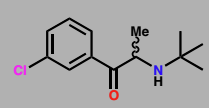
Bupropion (Wellbutrin)
Reuptake inhibitor for noradrenaline & dopamine
Antidepressant & aid smoking cessation
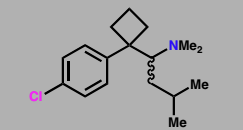
Sibutramine (Meridia)
Reuptake inhibitor of serotonin, noradrenaline & dopamine
Anit-obesity agent
Methylphenidate (Ritalin)
Reuptake inhibitor for noradrenaline & dopamine
Used for ADHD
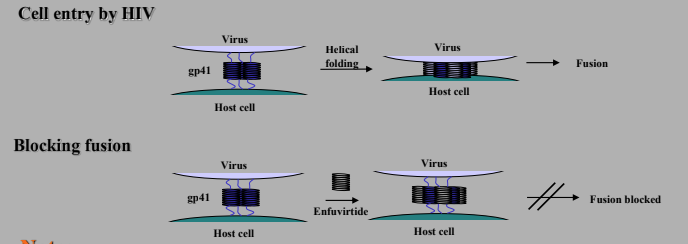
Agents binding to a viral structural protein
gp 41 helices fold over on each other to form twice as many helices that are half as long, this draws virus and host cell together leading to fusion.
Enfuvirtide is a polypeptide with 36 AA used for HIV since 2003. It acts as a fusion inhibitor by binding gp41 and preventing folding, so the cells aren’t pulled together and fusion is blocked.
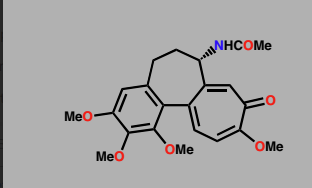
Colchicine
Inhibitor of tubulin polymerization
used in gout
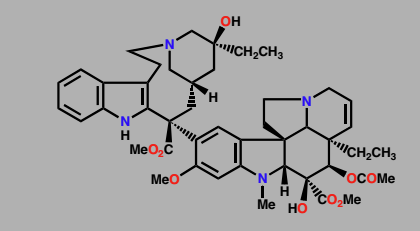
Vinblastine
Inhibitor of tubulin polymerization
anticancer agent
Tubulin polymerization
Microtubules are long hollow cylinders made up of polymerizaed a & b tubulin dimers. These polymerize end to end in protofilamnets, which are the building blocks for microtubule structures
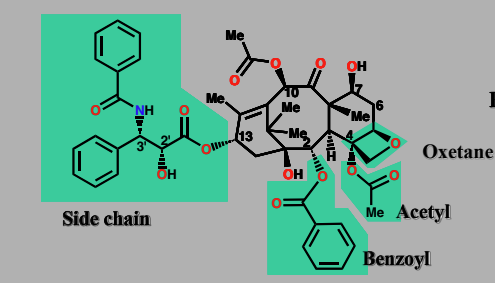
Paclitaxel (Taxol)
inhibitor of tubulin deplolymerization
Important anticancer agent isolated from yew tree
accelerates tubulin polymerization and stabilizes microtubules
Cell division cycle halted
Binds to tubulin via side chain, acetyl, benzoyl & oxetane
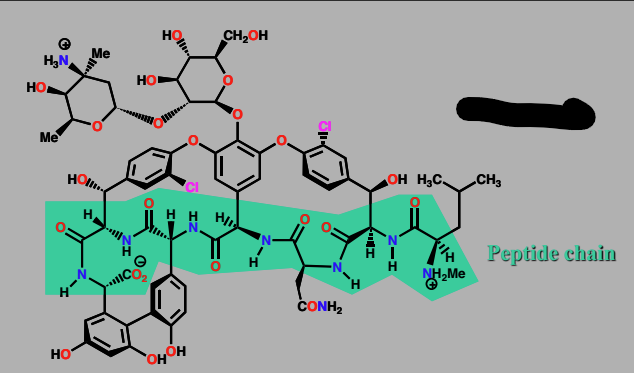
Vancomycin
Agent acting on Biosynthetic Building blocks
antibacterial agent
caps the building block used in synthesis of bacterial cell wall
contains a peptide chain which forms H-bond to the target
acts as a receptor for building blocks
Binds to D-Ala-D-Ala peptide chain and caps it, disguises building block from enzyme
Cell Wall Synthesis
Building blocks are partially constructed in the cytoplasm from sugar (NAM) and peptide chain. This is then transported across the cell membrane and completed (NAM + glycines)
Linked to growing cell wall by enzyme (transglyconsidation)
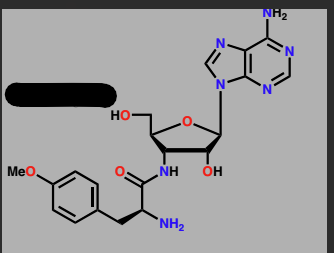
Puromycin
Protein synthesis chain terminator
antibiotic
acts as a chain terminator during translation
mimics aminoacyl-tRNA molecules used during translation
Binds to ribosome instead of the tRNA and interacts with the bound tRNA that has the attached protein chain, which is transferred to the drug.
Drug departs from the ribosome carrying away stunted protein
Protein-Protein binding inhibitors
These interactions are important to biochem mechanisms and sometimes involve relatively few AA on each protein.
Small molecules that mimic these groups on one of the proteins can be designed and should be capable of binding to the other protein and prevent the interaction.
Ex) drugs interacting with tubulin
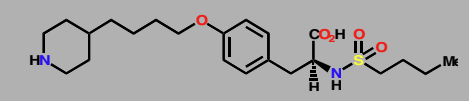
Tirofibrin
Protein-Protein binding inhibitor
Mimic a tripeptide sequence (Arg-Gly-Asp) found in fibrinogen
Binds to an integrin that normally binds fibrinogen and blocks their interactions
Anticoagulant
p53
restricts cell growth or produce cell death in damaged cells or cells under stress (cancer).
It is normally supressed by interactions with MDM2
Some cancer have excess MDM2
3 residues on p53 are like fingers that fit into the 3 binding pockets of MDM2 protein
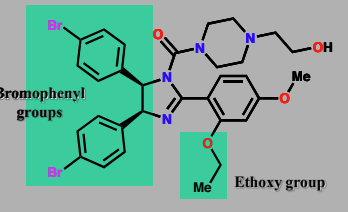
Nutlin-2
protein-protein binding inhibitor
anticancer agent
mimics the 3 amino acids (Leu, Trp, Phe) found in p53 mimicked by Bromophenyl groups and ethoxy in nutlin
p53 as a Cancer Drug Target
p53 is a tumor suppressor gene and encodes a transcription factor
Master regulator of cellular response to DNA damage, inappropriate oncogene activation, hypoxia, inadequate nucleotide supply and defects in DNA methylation
Mutated in half of human cancers
function is frequently inactivated in remaining cancers
MDM2 as a Cancer Drug Target
Binds to p53 transactivation domain and inhibits p53 mediated transcription.
Contains signal sequence similar to nuclear export signal of various viral proteins and after binding it induces p53 nuclear export. p53 can no longer carry out its nuclear functions
Uniquitin ligase. able to target p53 for degradation by proteasome
Overexpression blocks p53 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
Amplified or over expressed in many cancers
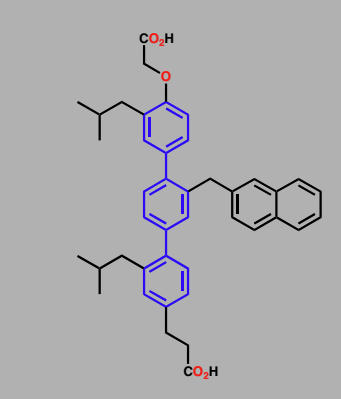
Terphenyl-based structure
Binds to protein BCl-x1- plays an important role in suppressing apoptosis
Compound may be useful in promoting apoptosis in tumor cells
Similar compounds synthesized in Hamiltons lab at yale for MDM2
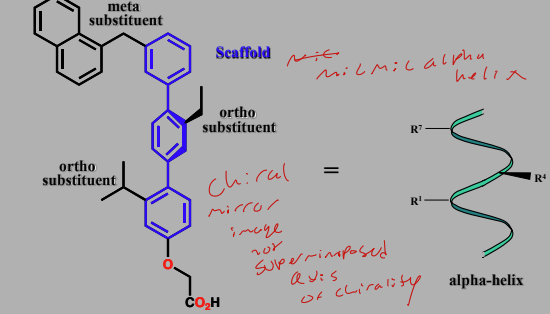
Terphenyl-based structures
Have a scaffold design that mimics backbone of an alpha helix
Substituents mimic AA residues at 1,4,7 residues of helix
Antagonist for calmodulin
Varying substituents varies target proteins
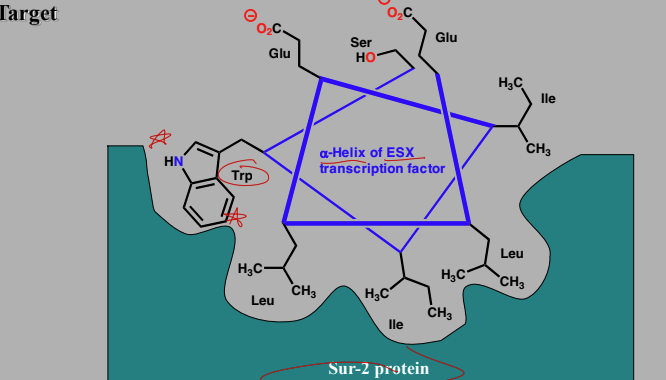
Targeting transcription factor-coactivator interactions
Interactions between the ESX transcription factor and the co-activator protein Sur-2 involved 8 AA a-helix of ESX
Trp forms a particular important interaction
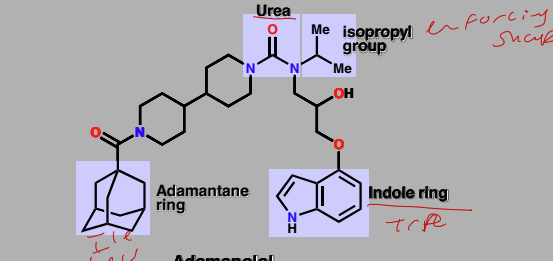
Adamanolol
Lead compound for targeting transcription factor-coactivator interactions
Searched for lead compounds contain indole ring to mimic Trp
Adamantane though ti mimic Ile and Leu residues
Isopropyl group for enforcing shape

Wrenchnolol
Drug optimized for trageting transcription factor-coactivator interactions
More active and water soluble
Two hydrophobic jaws and polar handle
Amphiphilic molecule mimicking alpha helix
non-polar components cluster on one face
Jaws mimic Trp, Leu & Ile
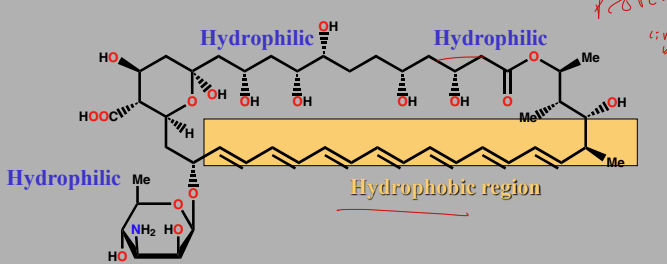
Amphotericin B
Antifungal that acts on cell membrane lipids
builds tunnels through membrane and drains cell
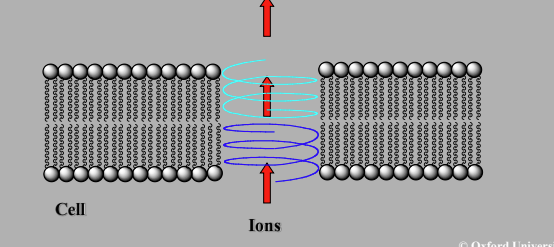
forms polar tunnel that is an escape route for ions
Gramicidin
Interacts with cell membrane lipids
Peptide antibiotic thought to form a helix in membrane
Two helices align end to end to form escape tunnel
Hydrophobic exterior interacts with lipids, interior allows ion passage
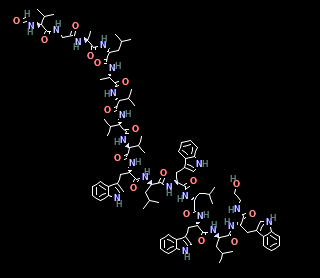
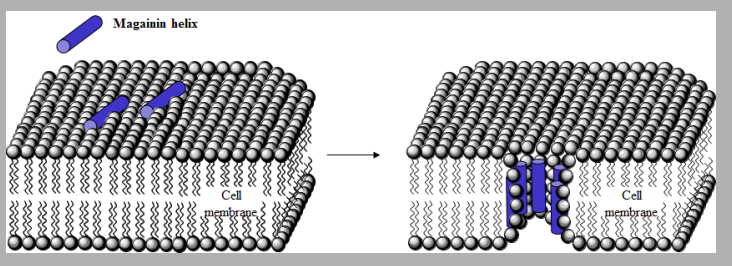
Magainins
Polypeptide antibiotics containing 23 AA.
Form helices in cell membrane
Interact with polar head groups of cell membrane lipids
Create wormholes that disrupt permeability
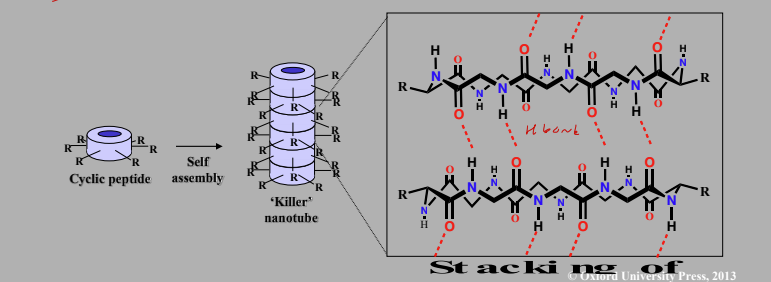
Killer nanotubes
Synthetic cyclic peptides that self assemble in bacterial cell membranes to form nanotubes alternating L- & D- AA.
Amide groups perpendicular to plane of cyclic peptides
Allows H bonding between each layer of cyclic peptide
Residues sticking out in the same plane do not interfere
Lysine aids selectivity for bacterial cells which have a negatively charged surface – the lysine side chain is positively charged
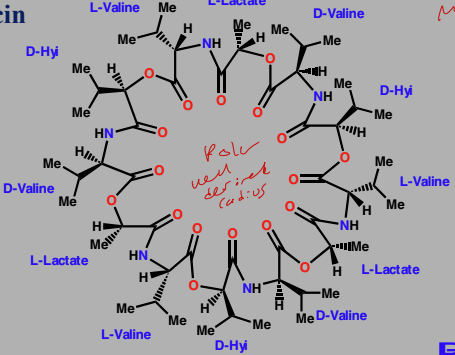
Valinomycin
Agent interacting with cell membrane lipid
Alternating ester and amide links
Hydrophobic residues on exterior
Polar carbonyl groups inside
Killer Nanotubes Mech of Action
Acts as an ion carrier
Hydrophobic groups on exterior interact with membrane lipids
Carbonyl groups interact with potassium ion
Allows uncontrolled escape of potassium ions from cell
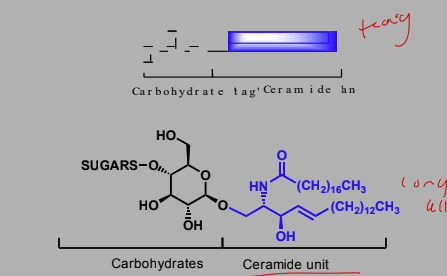
Carbohydrates
Carbs play a role in cell recognition, regulation and growth
Targets of treatment of bacterial and viral infections, cancer and autoimmune disease
Act as antigens
Carb tags
Ceramide unit is in the cell membrane and a carb tag sticks out of the membrane.
Ceramide made up of fatty acid and sphingosine
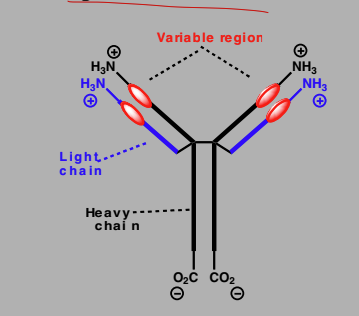
Antibodies
Proteins produced by immune system
Recognizes and binds to foreign antigens
Y-shaped molecules consisting of 2 heavy and two light chains
variable region at tips of the arms
Bind to foreign antigens on foreign cells and mark it for destruction.
Cell destroyed by immune system
Antibodies have been designed as anticancer agents
Pharmacokinetics
Factors affecting whether a drug will reach its target
Active drugs in vitro may be inactive in vivo
most potent drug at its target may be useless clinically
drug design should consider binding interactions and pharmacokinetics
Consider ADME factors: Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism & Excretion
Drug Absorption
Orally taken drugs must cross the gut wall to reach blood supply, so they have to pass through cell lining. Pass through two fatty acid cell membranes which requires the balance of hydrophilic/phobic character.
Polar drugs can be administered through injection or can be used to target gut infections
Lipinski’s Rule of Five
Orally active drugs generally show a balance of hydrophilic / hydrophobic properties and obey at least three of the following rules:
MW< 500
No more than 5 HBD groups (H attached to O/N)
No more than 10 HBA groups (O/N groups)
log P< +5- partition coefficent
guidelines many exceptions
Lipinski’s Rule of Five Exceptions
Small polar molecules (MW <200) that cross the gut wall through small pores between cells
Polar molecules carried across the membrane by transport proteins - amino acids, nucleic acid bases and some drugs (e.g. lisinopril)
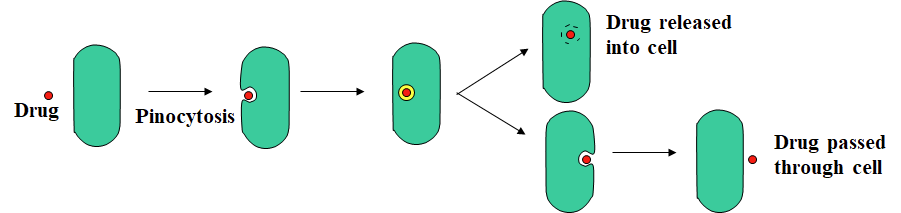
Pinocytosis
A process allowing passage of large polar drugs into a cell without actually crossing the cell membrane
Drug Metabolism
Foreign chemicals are modified by enzyme-catalyzed reactions, mostly in the liver - detoxification
Rxns can also occur in blood, gut wall and other organs
Drug metabolites are products formed from metabolism, usually less active or inactive (exception- prodrugs)
Modification of a structure may interfere or prevent binding interactions with a target (pharmacodynamics)
Orally absorbed compounds generally pass through the liver before distribution to the rest of the body
First Pass effect
A percentage of orally absorbed drug is metabolized in the liver prior to distribution round the body
Non orally absorbed drugs
Compounds absorbed by other routes avoid the first pass effect and circulate round the body before reaching the liver
A percentage of non-orally absorbed compounds never reaches the liver due to distribution into fat, cells and tissue)
Phase I & II reactions
Metabolic reactions are defined as phase I or phase II
Most phase I reactions add a polar ‘handle’ to the molecule
Phase II reactions are often carried out on functional groups which have been added by Phase I reactions
Increasing the polarity of a compound increases the rate of drug excretion (see drug excretion)
Cytochrome P450 enzymes catalyze phase
Cytochrome P450 enzymes
Located in liver
At least 12 families in human biochemistry
Individuals differ in types of Cyt. P450 enzymes present
Patient variability in drug metabolism complicates dose levels and leads to different susceptibilities to drugs
Drugs which affect the activity of Cyt. P450 enzymes may affect the activity of other drugs (drug-drug interactions)
Phase I Reactions Part 1
Oxidations (catalysed by cytochrome P450 enzymes)
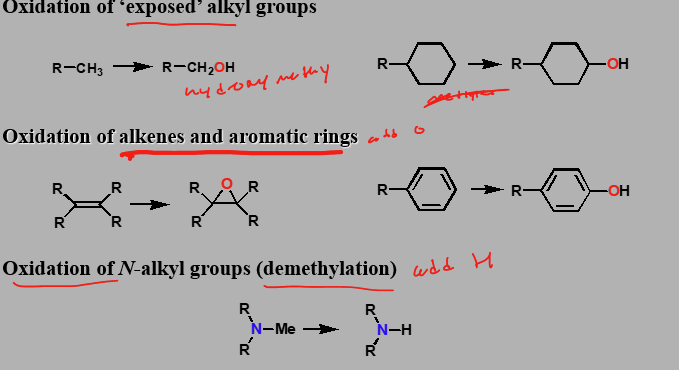
Phase I Reactions Part 2
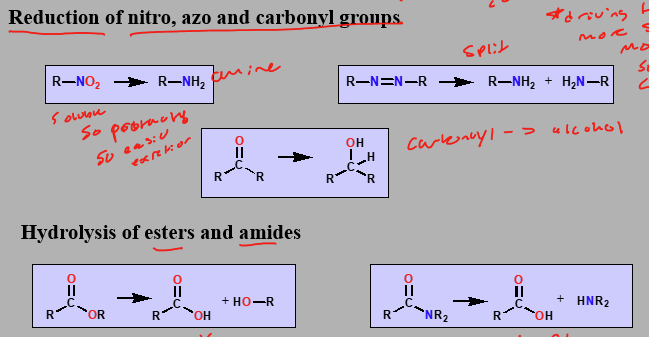
Discovery of Anti-cancer Drugs
First select a suitable biochemical target involved in tumor progression and metastasis
Discover small molecule that can interact with target
Optimize interaction of lead compound for increase binding affinity, selectivity and optimum ADME
Discover compound that can be tested in human clinical trails
Drug Design and Development
Identify target disease
Identify drug target
Establish testing procedures
Find lead
Structure Activity Relationship (SAR)
Identify Pharmacophore
Optimize target interactions
Optimized pharmacokinetic properties
Toxicology and Safety
Chemical development & production
Patenting and regulations
Clinical trials
Target Disease Pharm Industry Priority
Can the profits from marketing a new drug outweigh the cost of developing and testing that drug?
Target Disease Addressed Questions
Is the disease widespread? (e.g. cancer, cardiovascular disease, ulcers, malaria)
Does the disease affect the first world? (e.g. cardiovascular disease, ulcers)
Are there drugs already on the market? If so, what are there advantages and disadvantages? (e.g. side effects)
Can one identify a market advantage for a new therapy?
Drug Targets
LIPIDS: Cell Membrane Lipids
PROTEINS: Receptors, Enzymes, Carrier Proteins. Structural Proteins (tubulin)
NUCLEIC ACIDS: DNA, RNA
CARBOHYDRATES: Cell surface carbohydrates, Antigens and recognition molecules
Drug Target Selectivity Between Species
Antibacterial and antiviral agents
Identify targets which are unique to the invading pathogen
Identify targets which are shared but which are significantly different in structure
Drug Target Selectivity within the body
Selectivity between different enzymes, receptors etc.
Selectivity between receptor types and subtypes
Selectivity between isozymes
Organ selectivity
Testing Drugs
Tests are required in order to find lead compounds and for drug optimization
Tests can be in vivo or in vitro
A combination of tests is often used in research programs
In vivo Tests
Tests on live animals or humans.
Measures an observed physiological effect, a drug’s ability to interact with target and its ability to reach target.
Can identify side affects
Rationalization of results can be difficult
Transgenic animals
genetically modified animals
Drug Potency
concentration of drug required to produce
50% of the maximum possible effect
Therapeutic ratio/index
compares the dose level of a drug required to produce a desired effect in 50% of the test sample (ED50) versus the dose level that is lethal to 50% of the sample (LD50)
In vitro tests
Carried out on target molecules, cells, tissues, organs, micro-organisms
Suitable for routine testing
Used in high throughput screening (HTS)
Measures interaction of drug with target but not ability to reach target
Results are easier to rationalize
Can’t identify effective prodrugs