BIO-214 #6 Artificial Selection & Agriculture
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
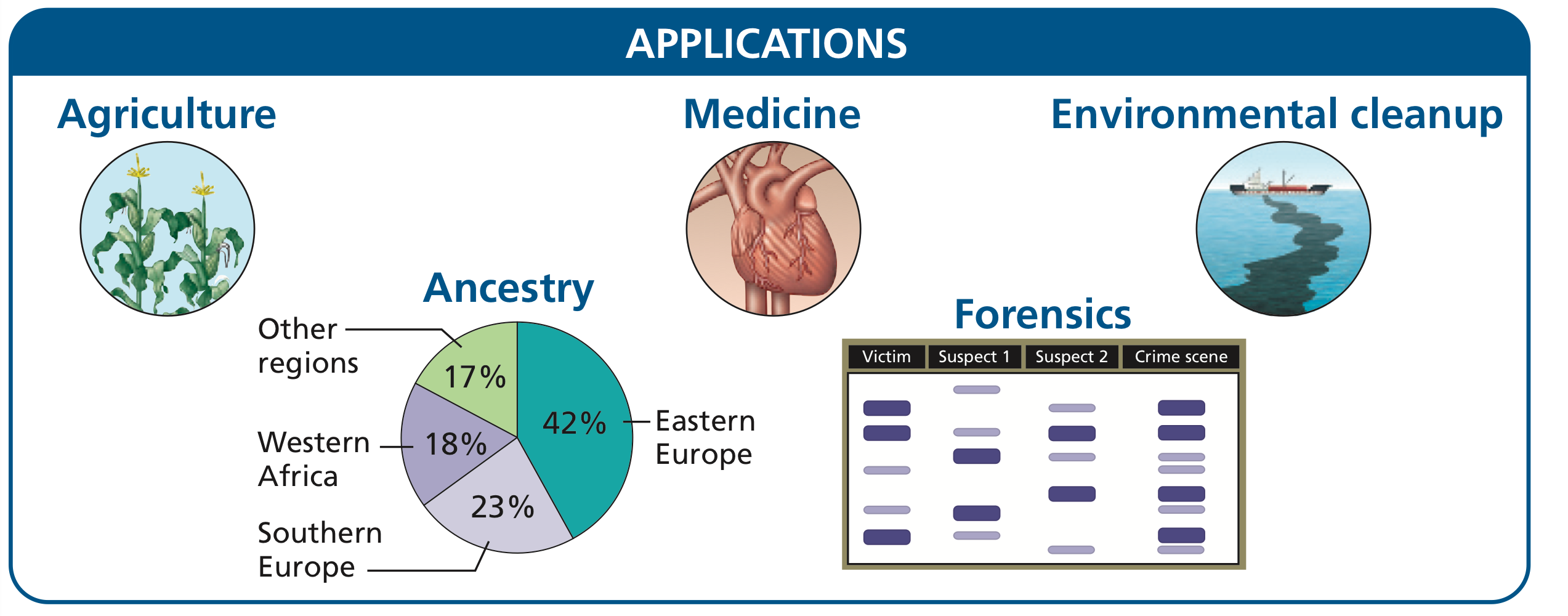
What is biotechnology?
What were the first uses of biotechnology?
How is biotechnology used in modern times?
The use of biological agents for technological advancement
Used for breeding livestock & crops
Modern times
Vaccine & antibiotic production
Agriculture
crop genetic modification to increase yeilds
Industrial Applications
Ferminatation
Treating oil spills
Promoting biofuels
What are the techniques of manipulating genetic material?
what is a lysis buffer? How is it used?
What enzymes are used
Isolate or extract DNA or RNA from the cells
Gel Electrophoresis
Nucleic Acid Fragment Amplification by Polymerase Chain Reaction
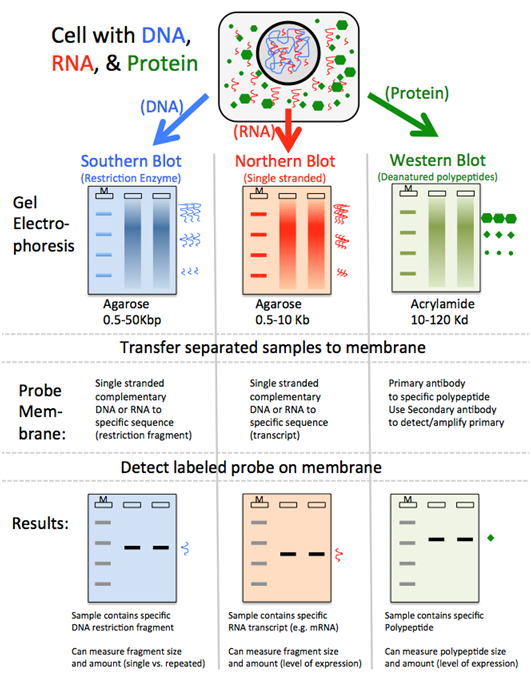
Hybridization, Southern Blotting, & Northern Blotting
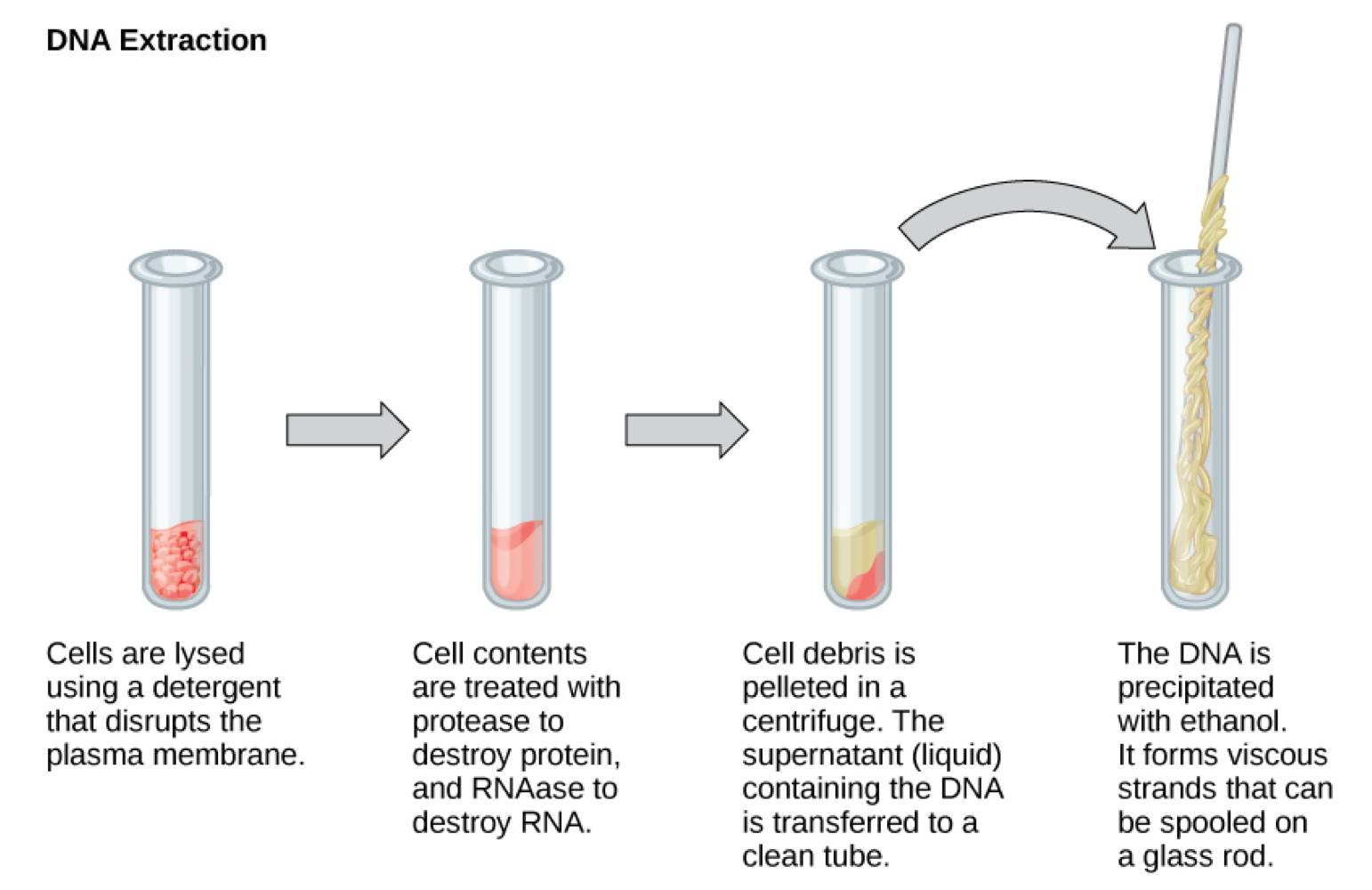
What is DNA & RNA Extraction
What buffer is used for extraction?
What enzymes or substances are used? What are their functions?
Isolate or extract DNA/RNA from cells to study or manipulate nucleic acids
Lysis Buffer: breaks cells apart
Breaks apart lipid molecules in the cell & nuclear membranes
Enzymes & Subtances
Proteases: break down proteins & inactivates macromolecules
Ribonucleases: break down RNA
Alcohol: precipitates DNA
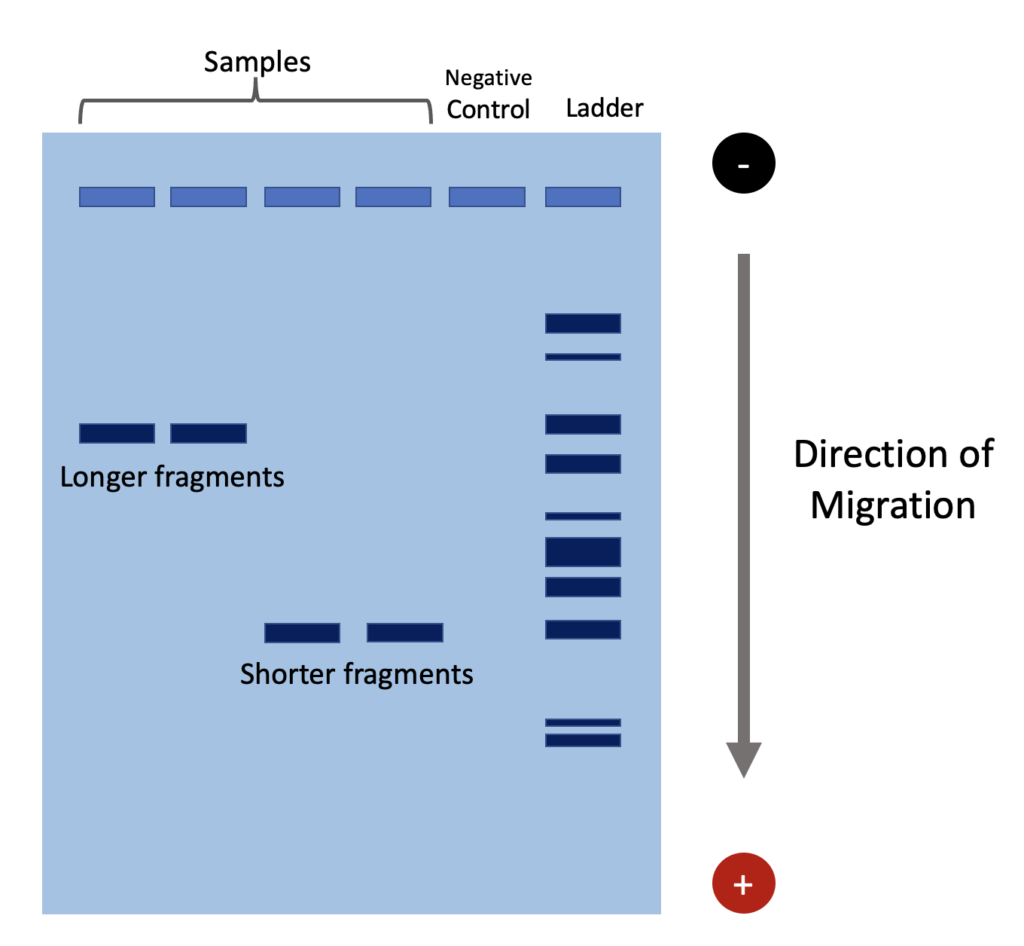
What is Gel Electrophoresis?
What does gel electrophoresis separate?
Technique used to separate molecules on the basis of size, using their charge
Smaller fragments move toward the positive electrode through the gel faster than larger fragments
Uses a dye to observe the fragments
Separates the nucleic acids as whole chromosomes or fragments
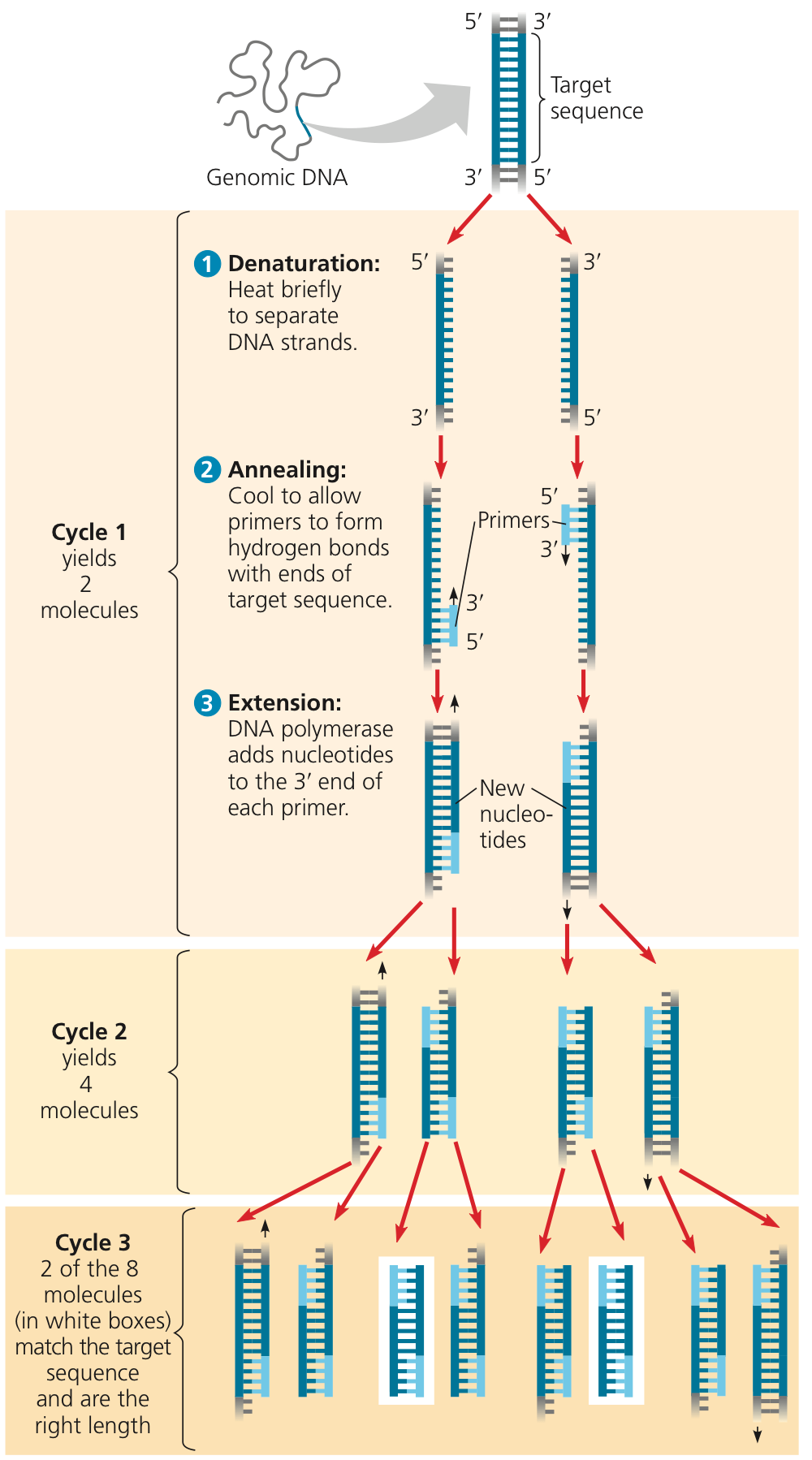
What is the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)?
What is it used for?
What are the steps for PCR?
What is reverse transcriptase PCR?
PCR is a technique used to amplify specific DNA regionsfor further analysis
Uses
Cloning gene fragments to analyze genetic diseases
Identifying contaminant foreign DNA
Amplifying DNA for sequencing
Determining paternity & detecting genetic diseases
Steps
Denaturation of DNA at high temp
Annealing (letting DNA cool slowly)
DNA synthesis
Reverse Transcriptase PCR
PCR technique that involves converting RNA to DNA by reverse transcriptase
also called reverse transcriptase
What is the blotting technique?
What are hybridization, southern blotting, and northern blotting?
How are they used?
Blotting: transfer fragmented DNA from a cell onto a nylon membrane
Definitions
Hybridization: identification of a specific DNA segment within a genomic DNA
Southern Blotting: DNA transfer from a gel to a nylon membrane
Used to detect the presence of certain DNA sequences in a given genome
Northern Blotting: transfer RNA to a nylon membrane
used to detect gene expression
What does reproductive cloning mean in biology?
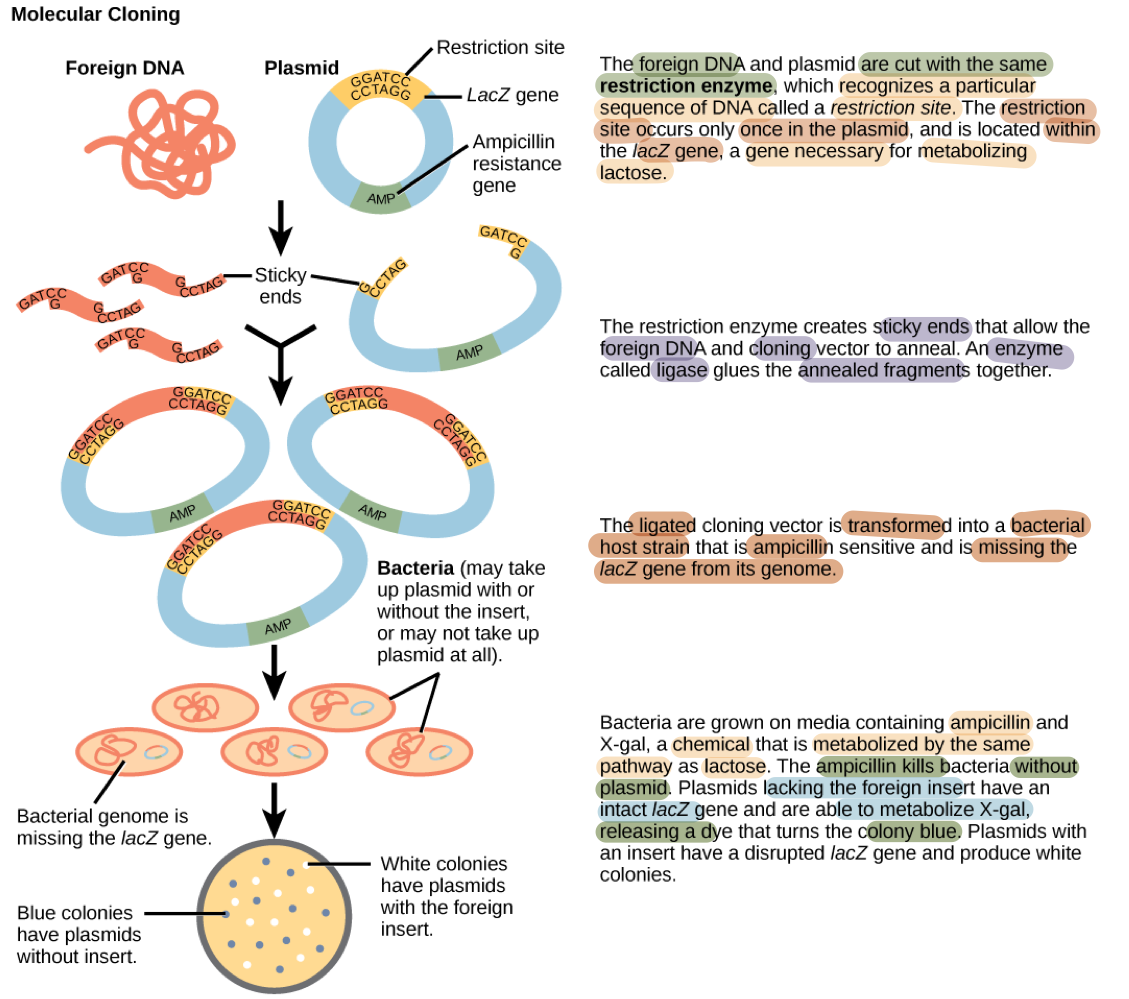
What is molecular cloning?
How does cloning genome fragments help researchers?
The recreation of a whole organism
Molecular Cloning: Reproduce desired regions/fragments of the genome
Cloning Applications
Allows researchers to manipulate & study:
Specific genes
Their protein producuts
noncoding regions
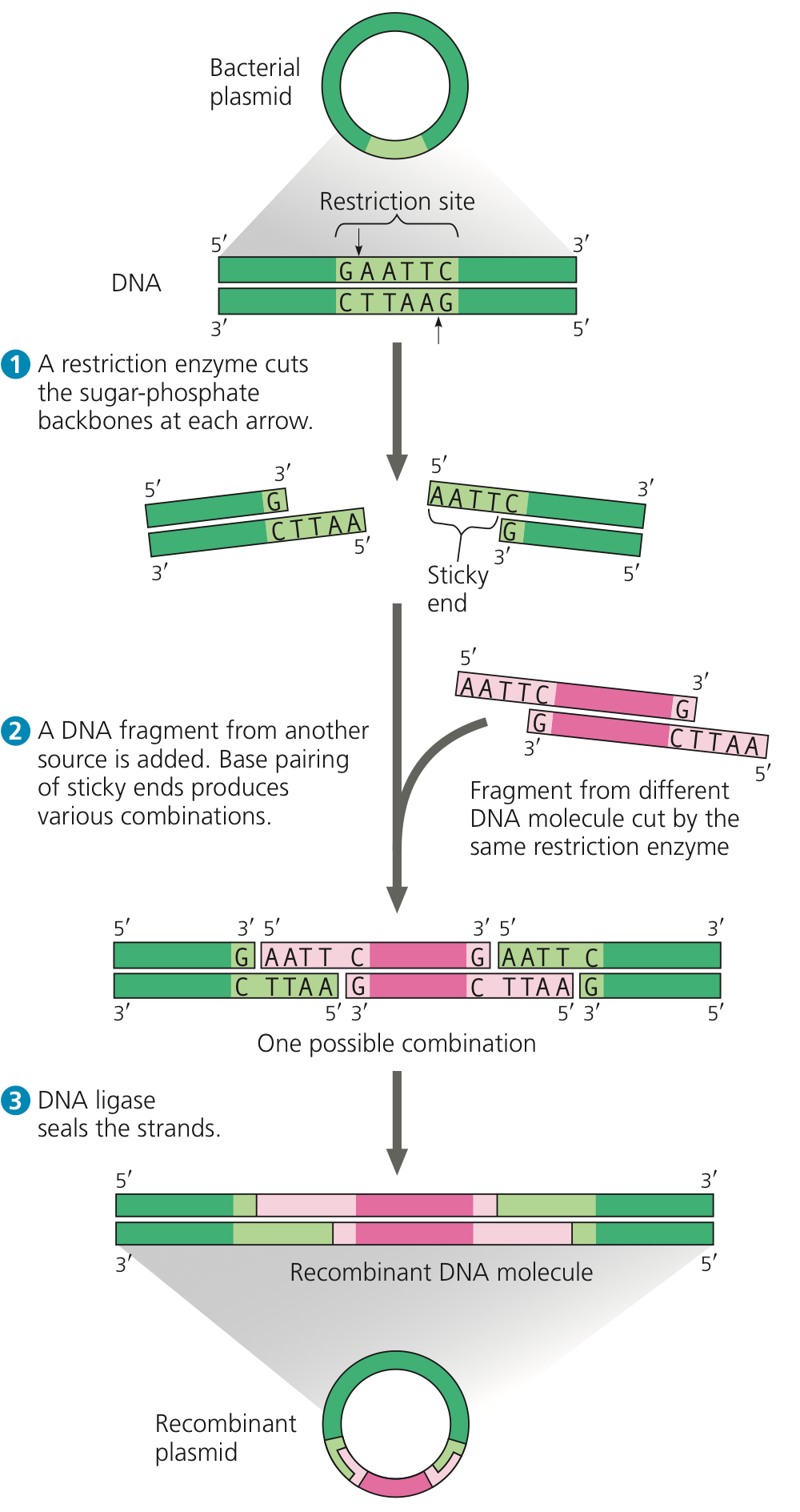
What is a plasmid/vector?
How are plasmids used in cloning?
What plasmid vector structure is essential for cloning?
What is a restriction endonuclease?
What does DNA ligase do?
Plasmid: small circular DNA molecule that replicates independently of the chromosomal DNA
Plasmids are used to transfer foreign DNA into a cell
Used for the large-scale production of important reagents: insulin & human growth hormone
Special plasmid feature: Multiple cloning site (MCS)
short DNA sequence containing multiple sites that different restriction enzymes can cut
Restriction endonuclease: enzyme that can recognize and cleave specific DNA sequences
naturally produced as a defense mechanism against foreign DNA
“sticky ends: complementary overhangs
DNA ligase: permanently joins the DNA fragments
What is antibiotic resistance?
The ability of an organism to be unaffected by an antibiotic’s actions
What are recombinant DNA molecules?
What’s another name for recombinant DNA?
What are recombinant proteins?
Recombinant DNA molecules: artificially created plasmids with foreign DNA
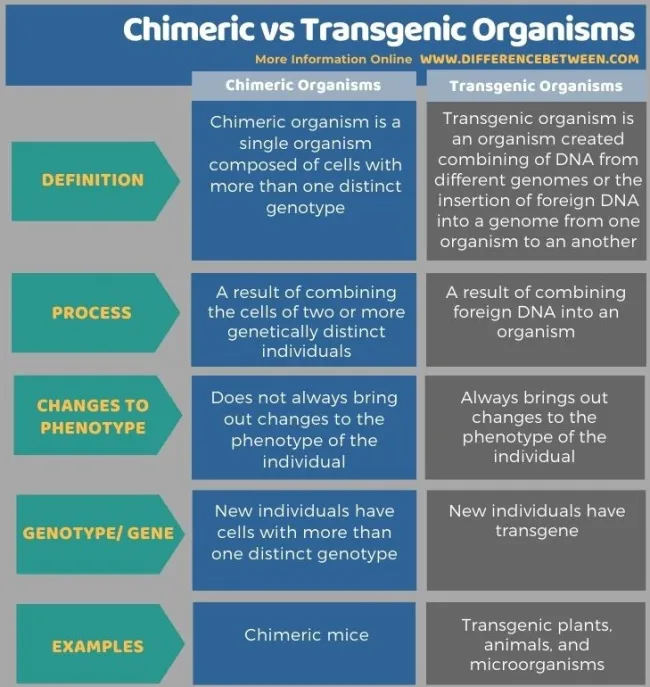
Chimeric molecules: Recombinant DNA
The origin of different molecule parts come from different species
Recombinant proteins: proteins that are expressed from recombinant DNA
What is cellular cloning?
Production of identical cell populations by binary fission (asexual reproduction)
Used by uncellular organisms (bacteria & yeast)
Occurs via mitosis (identical daughter cells)
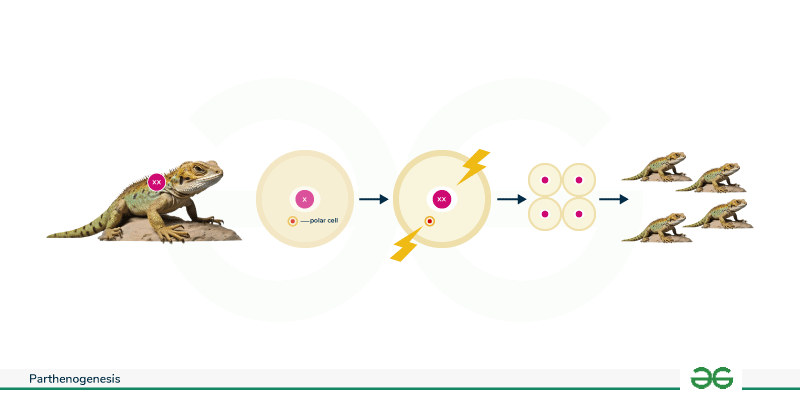
What is parthenogenesis?
Give examples
an asexual reproduction in which a female can produce an embryo without fertilizing an egg with sperm
Examples
A female lays an egg
Fertilized egg: Diploid → develops into a female
Unfertilized egg: remains a haploid egg → develops into a male
virgin egg
sea stars, fish, snakes
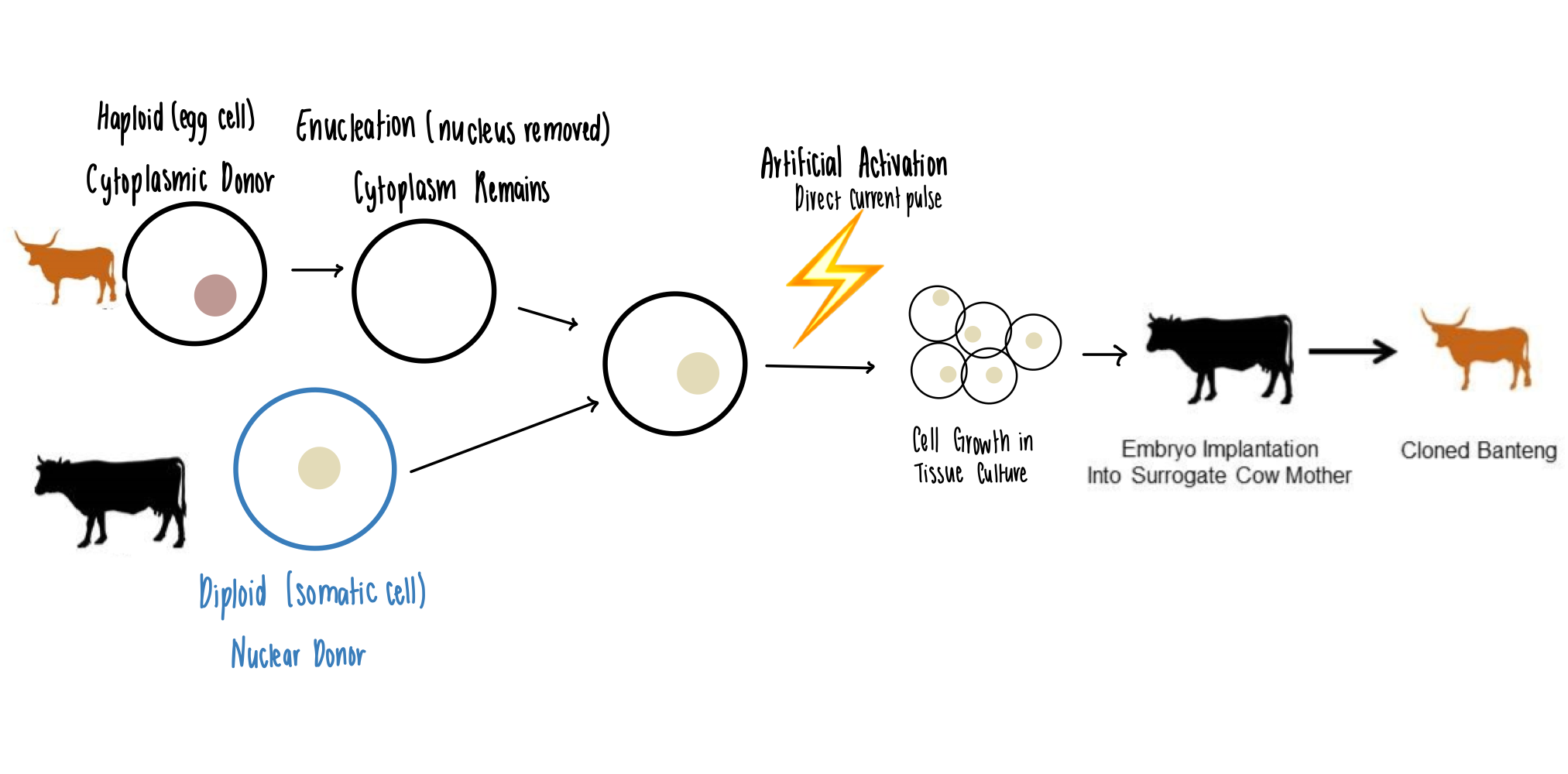
What is an enucleated egg?
What is somatic cell nuclear transfer? What is it used for?
How does somatic cell nuclear transfer work?
Enucleated egg: egg cell that had its nucleus removed
Somatic cell nuclear transfer:
Technique of transferring a diploid nucleus into an enucleated egg
Application
Therapeutic cloning
Reproductive cloning
Process: diagram
What is Genetic Engineering?
What technique is used for genetic engineering?
What is a genetically modified organism?
What is a transgenic organism?
Genetic Engineering
The alteration of an organism’s genotype using recombinant technology to modify an organism’s DNA to achieve desirable traits
Technique: molecular cloning
adding foreign DNA in the form of recombinant DNA vectors/plasmids
GMO: receives the recombinant DNA
Transgenic organism: an organism with foreign DNA
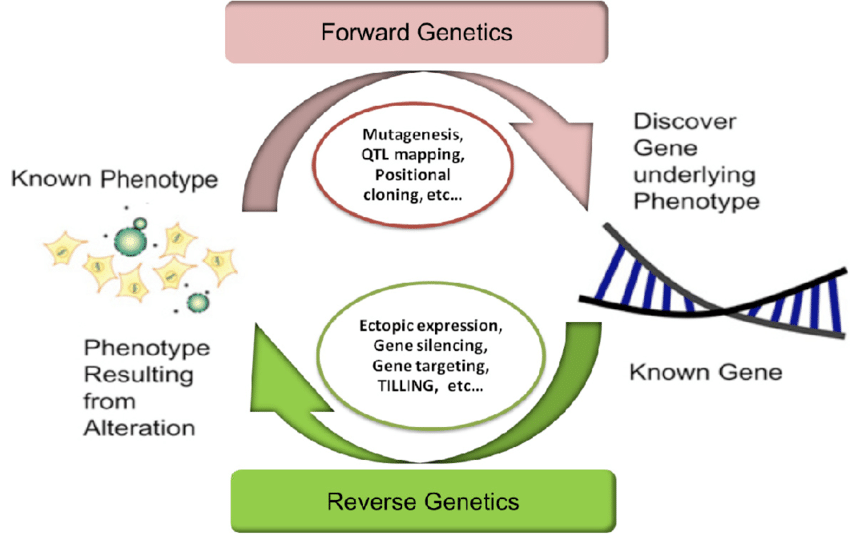
What is reverse genetics?
What is the classical genetic method?
How does mutating/deleting genes help researchers?
What is gene targeting?
Reverse Genetics: find out what phenotypes are controlled by particular genetic sequences
Similar to damaging a body part to determine its function
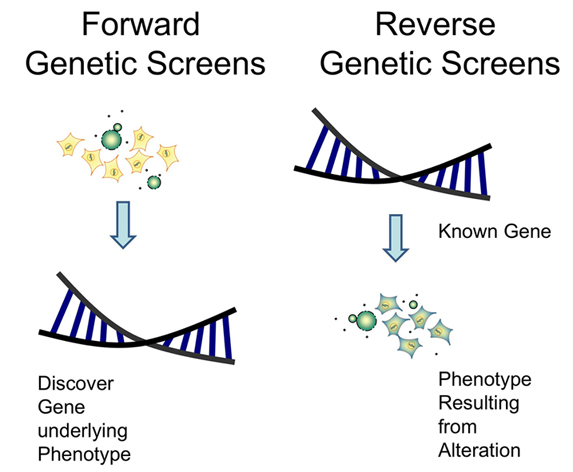
Classical Genetic Method: find the genetic basis of a phenotype/trait
Mutations
Provides with clues about the mutated/deleted gene function
Gene Targeting
Use of recombinant DNA vectors to alter a particular gene’s expression
Introducing mutations in a gene
Eliminating a gene’s expression (deleting a part/all of the gene sequence from an organism’s genome)
What are the applications of biotechnology in agriculture?
Disease resistance
Insect resistance
Herbecide resistance
Environmental stress
Drought tolerance
Hardiness (cold tolerant)
Improve crop yield & quality
Better nutritional value
What is genetic diagnosis?
What is genetic testing?
What is gene therapy?
How does gene therapy work?
Genetic diagnosis
Diagnosis of the potential for disease development by analyzing disease-causing genes
Genetic Testing
Process of testing for the presence of disease-causing genes
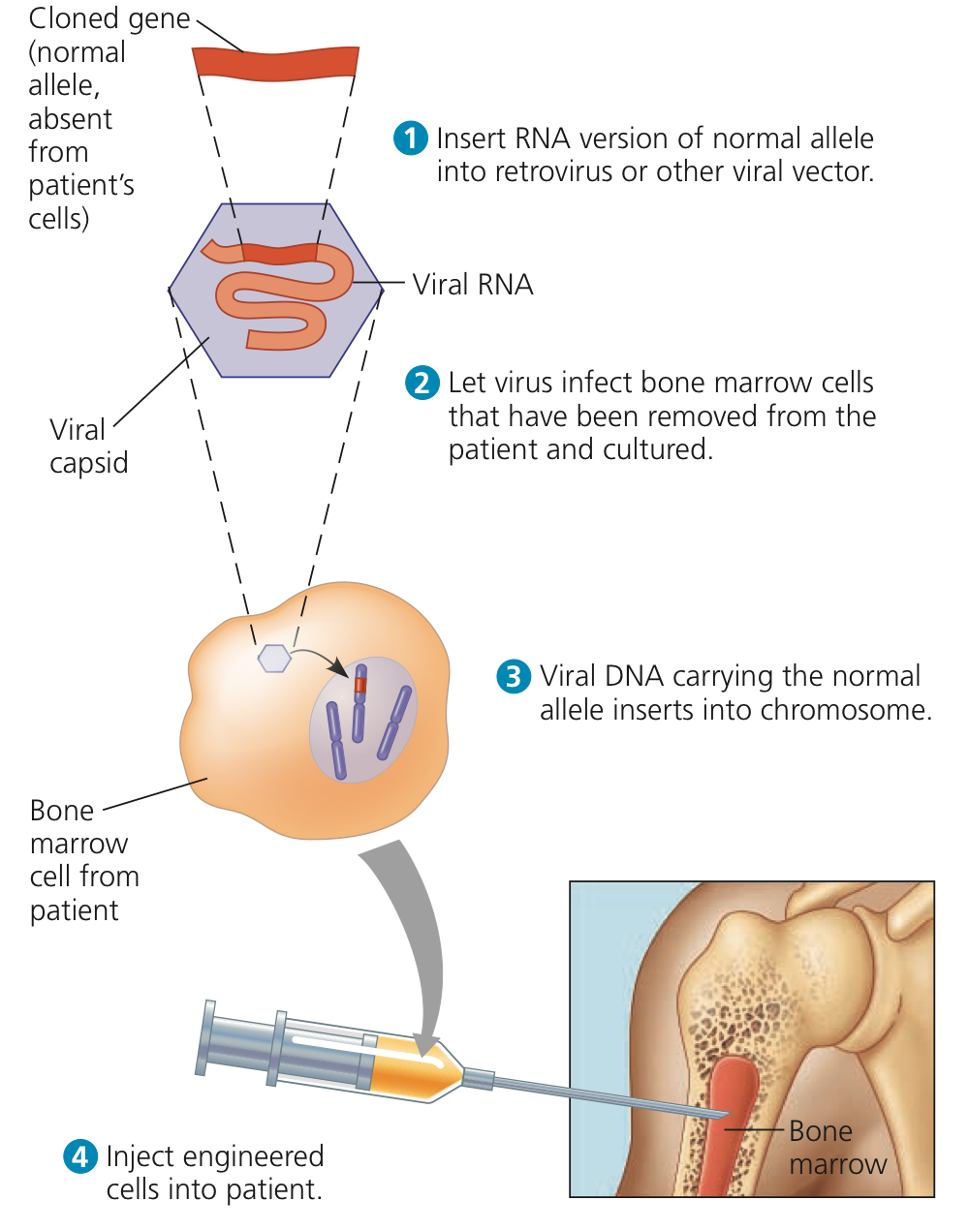
Gene therapy
Genetic engineering technique used to cure inheritable diseases by replacing mutant genes with good genes
Gene therapy process
good gene is introduced to diseased cells as part of a vector transmitted by a virus that can infect the host cell & deliver the foreign DNA
Tries to correct the mutation at the original site in the genome
What are the traditional vaccination strategies?
Use weaked or inactive forms of microorganisms to mount the initial immune response
Genes of microorganisms are cloned into vectors to mass-produce the desired antigen
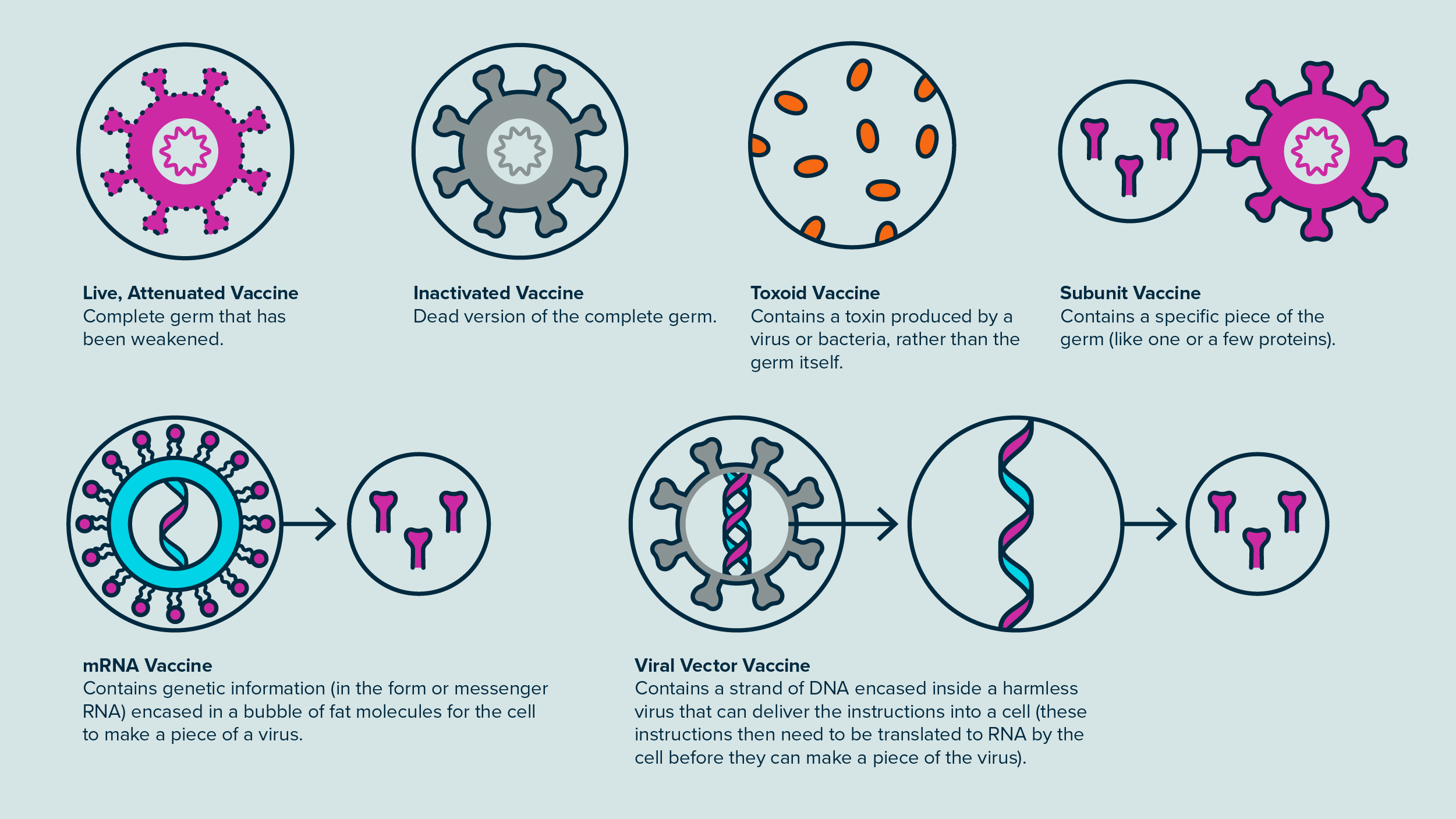
What are antibiotics?
Which organisms produce them?
Biotechnological product to fight bacterial infections
Micoorganisms
Fungi: Naturally produce them to attain an advantage over bacterial populations
cultivating & manipulating fungal cells produce antibodies
How was insulin first produced?
How was human growth hormone (HGH) created?
Insulin production: using reecombinant DNA tech
HGH: cloned from a cDNA libray & inserted into E.coli by cloning it into a bacterial vector
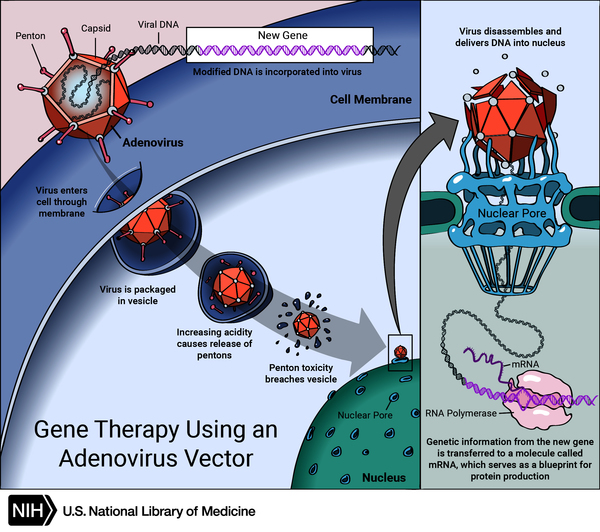
What are transgenetic animals?
How does the government monitor transgenetic plants?
Animals that have been modified to express recombinant DNA
Government regulation
Fit for human consumption
Don’t endanger other plant & animal life
Extensive testing for ecological stability (foreign genes can spread to other species in the environment)
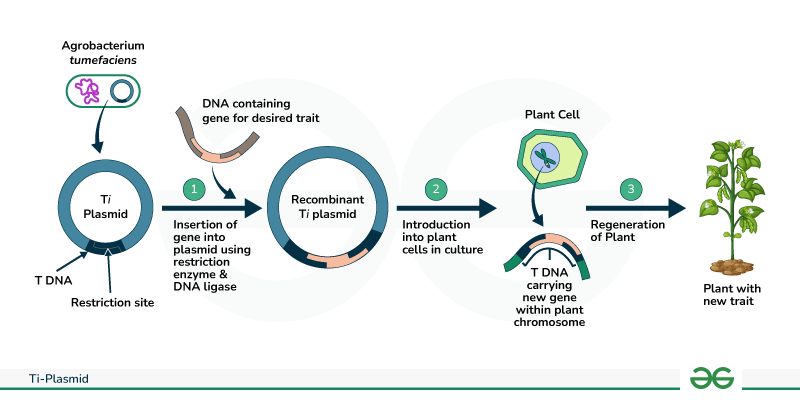
How do plants use Agrobacterium tumefaciens to transform?
How does the bacterium affect the plant?
Is artificially introducing DNA into plant cells more or less challenging than in animal cells?
The bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens causes tumors by DNA transfer (from bacterium to plant)
Tumors student the plants → plants become more susceptible to harsh environmental conditions
More challenging to introduce DNA into plant cells
Thick plant cell wal

What are Ti plasmids?
What do these plasmids carry?
Ti plasmids: Tumor-inducing plasmids that are derived from Agrobacterium tumefaciens & used to introduce foreign DNA into plant cells
Carry antibiotic resistance genes to aid selection
What was the organic insecticide called?
How does the insecticide work?
Bacillus thuriengsis
Produces protein crystals during sporulation that are toxic to many insect species that affect plants
insects need to ingest Bt toxin to DIE
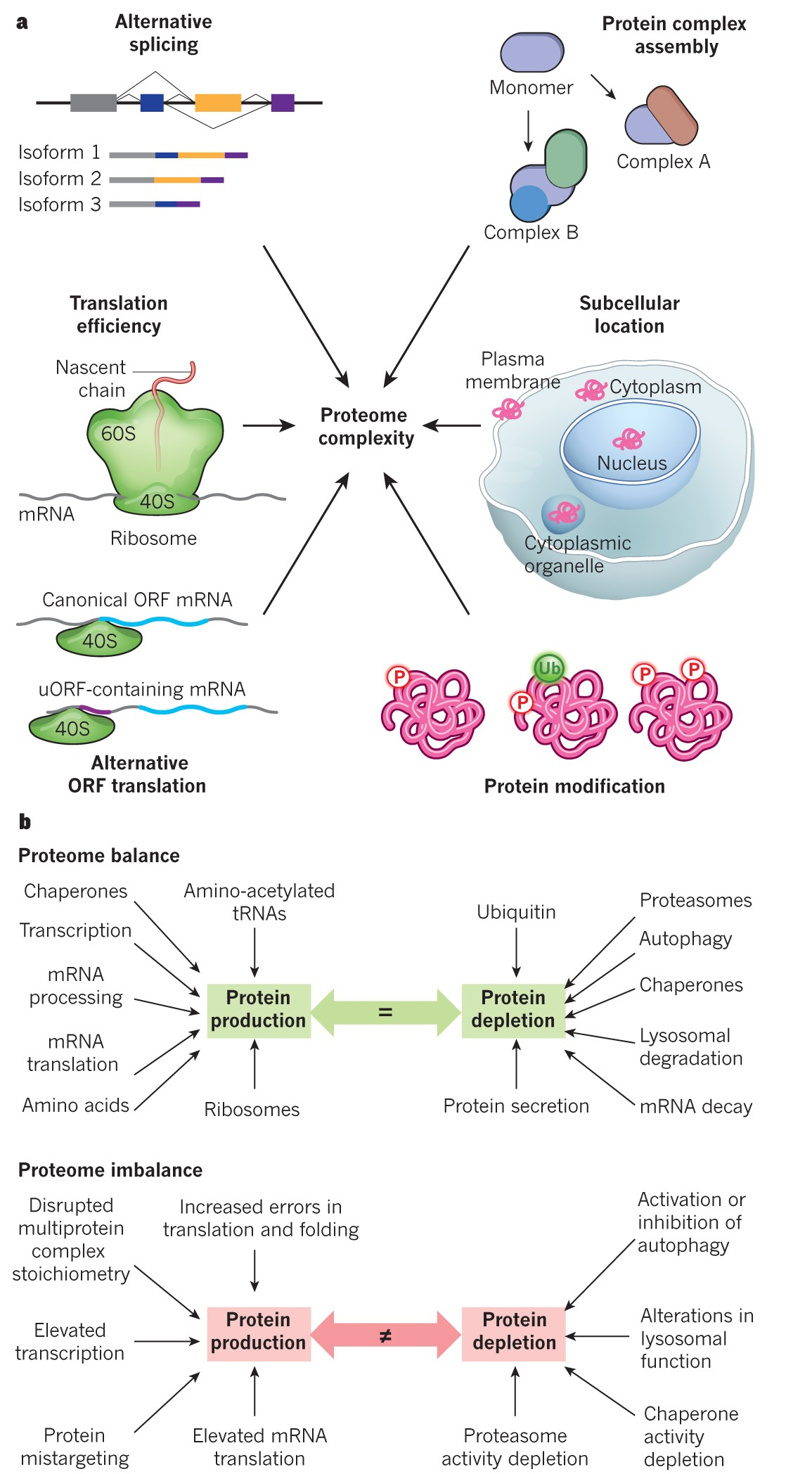
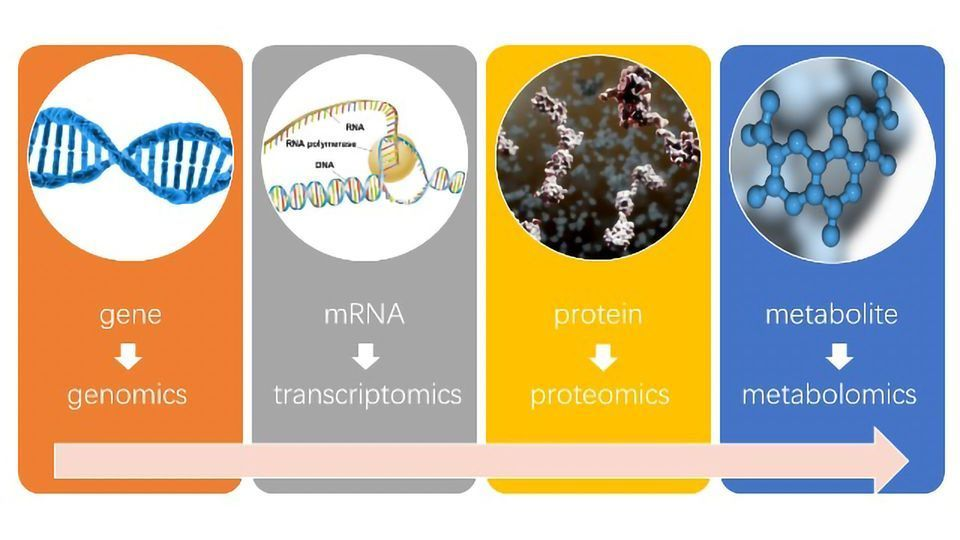
What is a proteome?
What is proteomics?
Even though all multicellular organisms’ cells have the same set of genes, the set of ________ produced in different tissues is different and dependent on ________ expression.
If the genome is constant, is the proteome the same?
Proteome: the entire set of proteins that a cell type produces
Proteomics: study of proteome’s function
Identify/compare the proteins expressed from a given genome under specific conditions→ study those interactions between proteins & use that info to predict cell behavior/develop drug targets
Fill in blank:
proteins, gene
No, the proteome is NOT the same, it varies
RNA can be alternately spliced & many proteins modify themselves after translation

What is metabolmics?
What is a metabolome?
Metabolomics: study of small molecule metabolites in an organism
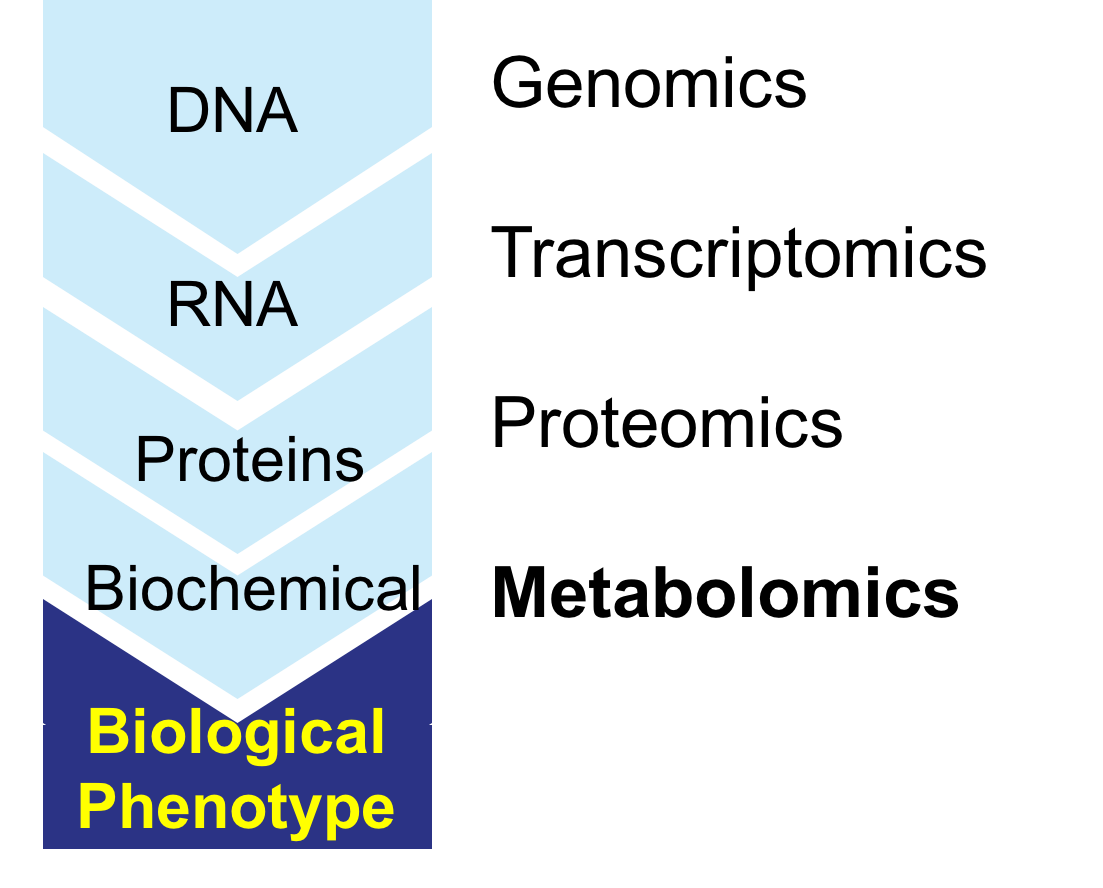
Compares genetic makeup & physical characteristics
Compares genetic makeup & environmental factors
Metabolome: a complete set of metabolites that are related to an organism’s genetic makeup
Identify, quantify, & catalogue all the metabolites in living organisms’ tissues & fluids

What is the basic technique for protein analysis?
What technique allows scientists to determine a protein’s 3D structure?
What is nuclear magnetic resonance?
Mass spectrometry
Identifies and determines a molecule’s characteristics
X-ray crystallography
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
uses atom's’ magnetic properties to determine a protein’s 3D structure in aq solns
What is systems biology?
How are proteomes used in systems biology?
What do pharmaceutical drug trials target?
study of whole biological systems (genomes & proteomes) based on interactions within the system
Proteomes
used to compare the protein profiles of different cells to identify proteins & genes involved in disease processes because proteins are direct products of genes & reflect activity at the genomic level
They target proteins
info from proteomics → identify novel drugs → understand protein mechanism of function
How do researchers use proteins when detecting cancer?
What is a biomarker?
What is a protein signature?
How much can biomarker/protein signatures be detected?
How are biomarkers/protein signatures inaccurate?
They identify proteins (a biomarker) whose expression indicates the disease process
Biomarker: individual protein that is uniquely produced in a diseased state
Protein signature: set of proteins with altered expression (in the diseased state)
Biomarker/protein signature must be secreted in body fluids (sweat, blood, or urine) (of non-invasive screening)
They produce a high rate of false negatives (cancer goes undetected)
Test should’ve been positive
Why is implementing proteomic analysis difficult?
Difficult to detect small protein quantities
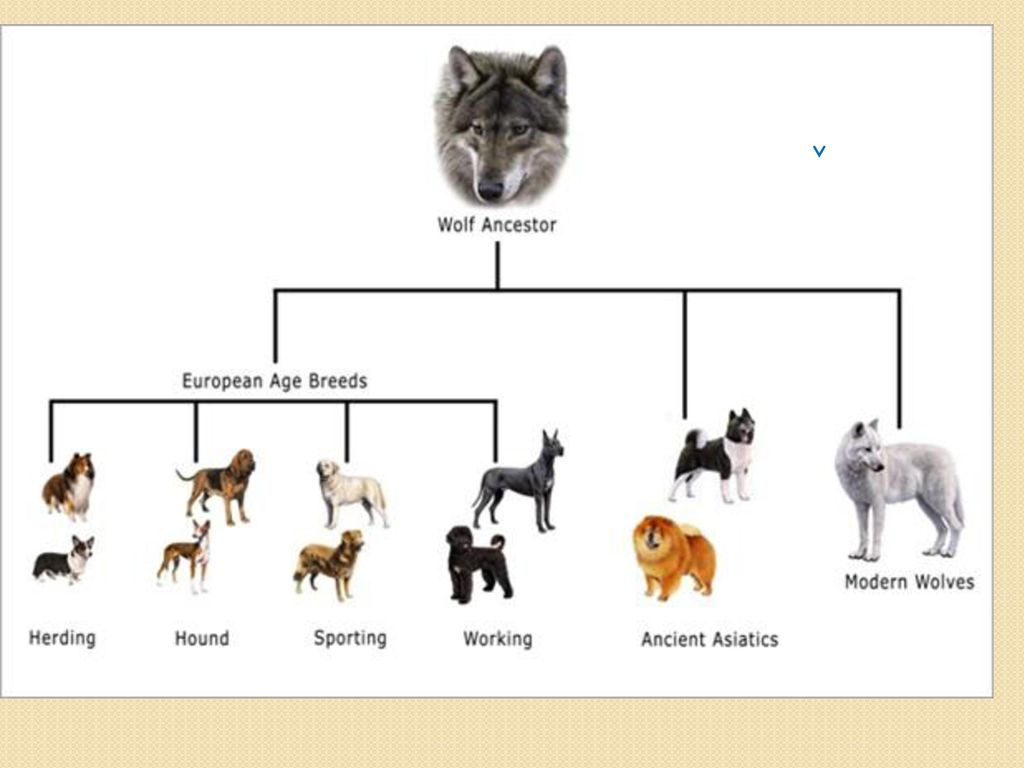
What is artificial selection?
Intentional human modification of species over many generations by selecing & breeding individuals that posses desirable traits
What traits do humans modify in animals?
Muscle Mass
Milk production
Growth rate
Intelligence
Number of eggs
Amount of feathers
Behavioral conditions
Health Conditions
What traits do humans breed in plants and animals?
Hardiness
Tolerates extreme weather
Temperament
behavior (cattle)
Aesthetics
Gardening
Shape
Size
Harvest yield
Producing more fruit
Larger grains
Flavor
spiciness
Sweetness
Health
tolerance to dieases & molds
Examples of artifiical selection on livestock
Sheep
Horses
Goat
Cows
Chickens
What traits are pets bred for?
What are the consequences of breeding pets?
Traits
Behavior
Protection
Muscle Mass
Eye color
Claws
Hunting
Farming: guarding, herding
Companionship
Consequences
Health outcomes
Recessive mutations are being expressed
Some genes are linked and, when expressed, cause detrimental health outcomes
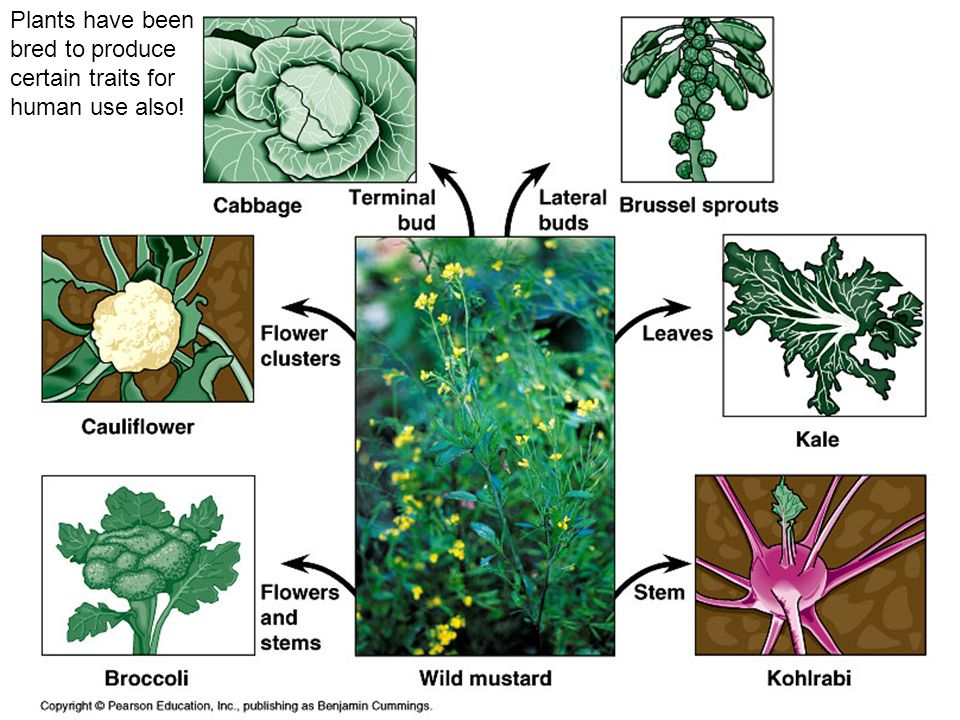
Artifiical selected traits for gardening plants
Shape
Size
Hardiness
Leaf strips
Color
Size of flower cluster
Thorns
Stems
longer, straighter, stronger
Flower perfume/smell isn’t potent
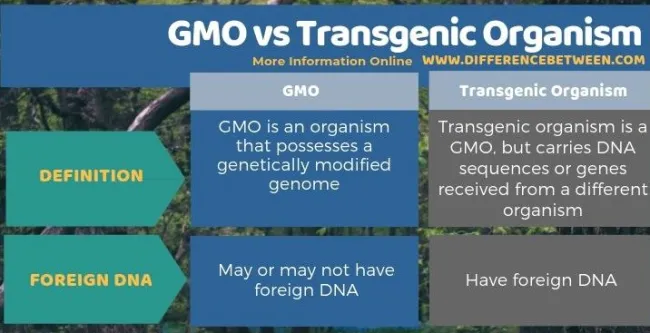
Difference between GMOs and trangenetic organisms
GMOS
faster results than artificial selection (application of both genetics and technology
contains genes from a naturally occurring gene pool selected by genesis for specific traits
Transgenic organisms
artificially added foreign genes from a different species in a lab
“trans”: across (genes are travelling across species)
Ex: adding biolumeniscience gene to mice & rabbits

Chimeric vs trangenic organisms
Concerns about GMOS
Are they safe?
For humans?
Increasing essential nutrients (K+, minerals, protein, etc)
golden rice for
Safe for people, the environment, and getting plentiful nutrients
For the environment?
RoundUp Ready pesticides & herbicides
Are there GMOS in this product?
labeling/ingredient list
What about human GMOs?
Gene therapy
What’s the big deal about RoundUp Ready?
Created a genetic strain that secreted pesticides & herbicides into their tissues & soils
The wind dispersed GMO seeds & their pollen ended up to wild habitats
Ecological damage
Farming damage
How is gene therapy used in humans/application of GMOs in humans?
Aims to fix a faulty gene or replace it with a healthy gene to cure a disease
Turn off genes that cause Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s disease, cancers, etc
Create essential neurotransmitters & hormones
Testestorone
Serotonin
Insulin
Oxytocin
Esterogen
How much do Californian farms produce?
What agricultural products are produced only in California?
How is California ranked among dairy production?
Californian farms produce nearly half of vegetables, fruits, & nuts grown in the USA
Almonds, artichokes, olives, walnuts, & figs
Ranked first in dairy production
What is Land Conversion?
What factors drive land conversion?
Land Conversion
development & conversion of farmland to urban use
Land conversion factors
Rising populations
Higher land prices (places pressure on farmland)
What challenges do farmers face?
Increased willingness to sell off family farms
Children want to pursue other careers
Farming is less profitable
Significant losses in prime farmland (1982-2007) but has since stabilized
Planners advocating for higher density residential areas
Agricultural conservation easements
Novel financing arrangements to help farmers keep their land
Water Use
How much water does agriculture use?
Where are Californian farms located?
How do these farms access water?
How are farms being supported?
50-90% of California’s fresh water
Farms & ranch land located in the drier Southern hlaf of the state
A high percentage of water used in these southern farms is conveyed via aqueducts & dams from the north
Support via:
Federal government
Water subsidies that benefit large industrial growers
What are the ecological concerns about agricultural water use?
What effect does water use have during the dry season?
How does agricultural water contaminate neighboring ecosystems?
Coastal summer agricultural water needs are met by tapping riparian and groundwater resources
Decreases stream flow during dry season
Surface water by surface runoff of fertilizer & pesticides contaminate aquatic life
Can also enter ground water & degrades sources of drinking water

How can we practice sustainable agriculture?
Supply & maintain open space
Refuge for wildlife
letting the land rest from heavy agricultural usage
Soil can recupriate nutrients
Wildlife will return nutrients to farms
Possibility of locally based food systems
Buy local to reduce our carbon footprint
How does sustainable agriculture integrate three main goals from traditional agriculture?
Environmental health
Economic profitability
Social/economic equity
What approaches does sustainable agriculture use?
Selection of species & varieties well suited to the site
Climate & crop hardiness
Seasonal crop rotation
Native pollinators & nutrient turnover
Diversification of crops (including livestock)
Management of the soil to protect & enhance its quality
Efficient & humane use of animals
Consideration of farmers’ goals & lifestyle choices