Module 7 / working effectively and safely in n electrotechnical environment
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
What legislation has the government implemented to improve safe working practices and welfare for workers?
The Health and Morals of Apprentices Act of 1802.
The Factories Act of 1833.
The Electricity (Factories Act) Special Regulations, 1908 and 1944.
what are statutory laws and regulations?
Statutory laws and regulations tell us what the law is, but what they do not do is tell us how to comply with these laws. Guidance on how to fulfil their legal obligations is given by codes of practice and non-statutory regulations.
What is the health and safety at work act 1974?
This law is an “enabling act”, which means that it is a provision (the action of proving or supplying something for use) in a law that confers an appropriate officials power to implement or enforce the law. The HASAWA outlines a number of duties that employers have towards their employees.
Who and what does the electricity at work regulations apply 1998?
This came into force on the 1st April 1990. These regulations impose general health and safety requirements specifically relating to electricity at work, on employers, employees and the self-employed.
employee has the duty to co-operate with their employer, so far as is necessary, to enable the regulations to be complied with. Because these are STATUTORY regulations, penalties can be imposed on people found guilty of malpractice or misconduct.
These regulations refers to people as “duty holder”
Who and what does the Electricity safety, quality and continuity regulation 2002 apply to?
This is a statutory regulation which set out specific safety standards that are aimed at protecting the general public and consumers from danger. In addition, the regulations specify power quality and supply continuity requirements
Who and what does the provision and use of work equipment regulations (PUWER) 1998 apply to?
This replaced the provision and use of work equipment regulations 1992. These are statutory regulations. These regulations require that risks to people’s health and safety from equipment that they use at work must be prevented or controlled.
Why must employers in act control of substances hazardous to health and what substances may it include?
COSHH requires that employers control exposure to hazardous substances both to protect employees and any others who may be exposed to such hazards from work activities
substances may include:
Naturally occurring substances, e.g. bacteria, blood, or grain dust
Substances generated during work activities, e.g. fumes from soldering and welding
Substances that are used directly in work activities, e.g. cleaning agents, paints, or glues
COSHH is again a statutory requirement.
What does PPE stand for and what are some examples of it?
PPE stands for personal protective equipment.
PPE is equipment which is designed to be worn, or held, so as to protect against a risk to an individual’s health or safety. This is a statutory legislation
It includes most types of protective clothing and other items of equipment such as head, eye, hand, and foot protection, high visibility clothing, safety harnesses, life jackets, etc.
What does the BS7671 wiring regulations relate to?
The BS 7671 Wiring Regulations relate to the design, selection, erection, inspection and testing of electrical installations, both permanent and temporary, in and about buildings generally.
This regulation are non-statutory and covers installations operating voltages up to 1000V AC.
What does the workplace (health, safety and welfare) regulations 1992 in act?
These regulations apply to all workplaces, where a workplace is defined as being any premises or part of premises which are not domestic premises, and are made available to any person as a place of work.
The requirements of these regulations are imposed on every employer or any person who has, to any extent, control of a workplace in respect of the following matters:
Working environment, Safety, Facilities
These regulations are statutory.
When is construction (Design and management) regulations 2015 carried out and how?
These statutory regulations apply to all aspects of a construction site.
The general provision of the regulations is to set out minimum standards necessary to promote safety on site. The regulations place specific duties on clients, designers and contractors to rethink their approach to health and safety, so that it is taken into account throughout the life of a construction project, from its inception to its subsequent final demolition and removal.
The following are provided as some guidelines for safe working:
Observe all rules and instructions provided.
keep all equipment well maintained and in good condition.
Follow all manufacturer’s instructions and recommendations when using items of equipment.
Advise supervisors immediately if you observe any unsafe practices.
what are the guidelines for safely isolating a circuit from an electrical supply?
1. Identify the sources of the supply
2. Isolate the supply
3. Secure the isolation
4. Test the voltage indicator
5. Test system dead
6. Retest the voltage indicator
7. Begin work
Difference between switching off and isolation.
And how many poles are single, three and four phase installations isolated by using.
Switching off may involve the breaking of normal load current or even higher current due to overload or short circuit.
Isolation is concerned with keeping the already dead circuit dead, so that re-closing the switch is not unintentionally possible.
A single-phase installation may be isolated using a double-pole device or a single pole device. An installation supplied with a three-phase or a four-wire system may be isolated using a three-pole or four-pole switch. A semi-conductor device, e.g. a dimmer, cannot be used for isolation.
How to test that the equipment and system are dead.
First, test the voltage indicator on a known supply or proving unit before use.
Then test between line and neutral, line and earth, and neutral and earth for single-phase supplies.
For three phase supply test between Blue, black, grey and yellow/green.
What are all types of signs on a construction site?
Prohibition signs
Warning signs
Information signs
Mandatory signs
In the event of you discovering someone who has had an accident it is important that you check what?
Check for further danger to yourself and the casualty
Make an assessment of the casualty – are they bleeding, are they breathing, are they unconscious
Only move the casualty if it is really necessary;
for serious injuries the casualty should remain still until professional medical help has arrived
All accidents must be reported to the employer and details recorded into the accident book. To do so what do I need to record?
The date and time of the accident.
The details of what happened.
The details of the person injured.
The details of the injury sustained.
The details of any witnesses.
The name and signature of the person reporting the accident.
What to do in event of an electric shock.
Check your own safety. Ensure that you would not put yourself in any danger by helping the casualty.
Break the electrical contact by either switching off the supply, or removing the plug (if it is undamaged).
a) If necessary pull the cable free (only attempt this if the cable and plug, etc. are undamaged) or;
b) Break the contact by pushing or pulling the casualty free using non-conductive material, e.g. a wooden broom.
Check whether the casualty is conscious. If they are and it is possible, guide them to a safe place, making sure that further injuries are not sustained, e.g. banging their head falling down, etc.
How AVPU checks are carried out on a casualty?
Alert;
Responsive to voice;
Talk to and gently shake the casualty to gauge their level of response.
Responsive to pain;
Unconscious.
How do you check for open airways during an ABC check on a casualty?
To open the airway, remove any obvious obstruction from the mouth. Place two fingers under the point of the casualty’s chin, and lift the jaw. At the same time, place your other hand on the casualty’s forehead and tilt the head well back.
How do you check for breathing during an ABC check on a casualty?
Put your face close to the casualty’s mouth. Listen for the sound of breathing and look for chest movements. Feel for breath on your cheek. Look, listen and feel for 10 seconds before deciding that breathing is absent.
How do you check for signs of circulation during an ABC check on a casualty?
Current thinking is to listen to the patient’s chest instead. Check for about 10 seconds to see whether a pulse is present. If the casualty is breathing, place them in the recovery position.
How do you put someone into a recovery position?
Use your free hand to bend the person's knee farthest away from you to a right angle. Carefully roll the person onto their side by pulling on the bent knee towards you. Their bent arm should be supporting the head, and their extended arm will stop you rolling them too far. Make sure their bent leg is at a right angle.
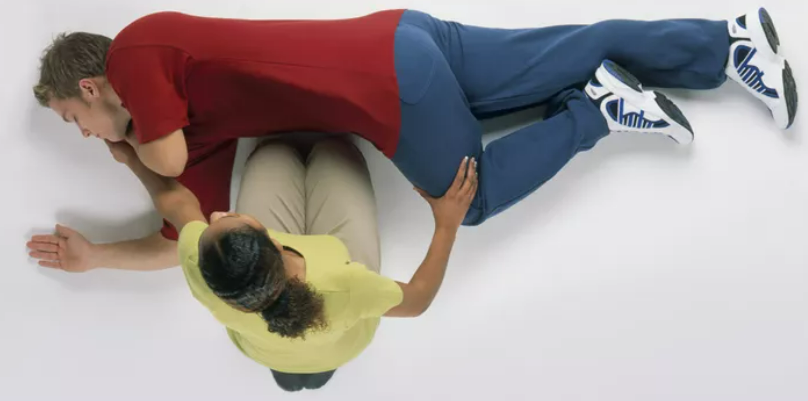

How do you perform mouth to mouth?
First remove any obstructions form the airways, tilt head back and lift the chin. close the casualty’s nose, take a full breath and place your lips on the casualty’s mouth ensuring a good seal. Blow into the mouth and watch their chest inflate. Remove your mouth and allow their chest to unflatten and repeat. Keep going unless their is a response, if there is place the casualty into a recovery position.
How do you perform chest compressions on a casualty?
Place the heel of your hand on the centre of the person's chest, then place the palm of your other hand on top and press down by 5 to 6cm (2 to 2.5 inches) at a steady rate of 100 compressions a minute. After every 30 chest compressions, give 2 rescue breaths.
How a casualty should be treated for shock if circulatory system fails?
Lay the casualty down, keeping the head low. Loosen tight clothing, braces, straps or belts to reduce constriction at the neck, chest and waist. Stop external bleeding if there is any. The most effective way to stop bleeding is to apply a clean, lint free dressing or cloth to the wound and apply pressure. Raise and support the legs but be careful if you suspect a fracture. Keep the casualty warm by wrapping them in a blanket or coat. Continue to check and record breathing, pulse and level of response. Be prepared to resuscitate if necessary.
How to generally treat burn areas?
Remove any pieces of clothing, jewellery etc. Run cool water over the burn area for at least 20 mins. this will halt the burning process, relieve pain, and help to minimise the infection.
How to treat a casualty for smoke and fumes inhalation?
Get them outside into the fresh air as soon as possible, provided that it is safe to do so. Loosen any clothes around their neck or chest that may impair their breathing. Call the emergency services and refer to the first aid section of this book regarding the ABC procedure.
What does a blue coloured fire extinguisher contain and what is it used for?
Blue fire extinguishers contain powder and are to be used on most kinds of fire, especially on burning solids and burning liquids.
What does a red coloured fire extinguisher contain and what is it used for?
Red fire extinguishers contain water and is to be used on solids like wood or paper. Never use on electrical fires or fat and oil.
What does a black fire extinguisher contain and what is it used for?
Black fire extinguisher contains oxygen with CO2 which is a non flammable gas. Good for electrical fires as they do not leave residue.
What does a white or cream fire extinguisher contain and what is it used for?
White or cream fire extinguishers contains a conventional foam. AFFF is very effective on most fires except electrical and chip-pan fires. This extinguisher works by forming a blanket or film on the surface of a burning liquid.
What is a fire and what are types of fire fighting equipment?
A fire is essentially a rapid oxidation which is a chemical combustion with oxygen. Fire fighting equipment includes portable appliances such as buckets of sand or water, fire-resistant blankets, and extinguishers. In larger premises, you may find hose reels, automatic sprinklers, and hydrant systems.
What does the electrotechnical industry encompass?
It encompasses a number of specialisms which range from things like electrical maintenances and repairs to public lighting installations.
What does maintenance cover in the construction industry?
This covers the repair, refurbishment and restoration of existing buildings and structures.
What does civil engineering cover in the construction industry?
Civil engineering involves the construction and installation of services for large structures such as bridges, roads, motorways, docks, harbours and mines.
What does building and structural engineering cover in the construction industry?
This type of company broadly covers the construction and installation of services for buildings such as factories, offices, shops, leisure centres, hospitals, schools, and of course, houses. Specialist contractors are normally the people who operate in this field.
What are different types of specialist jobs for an electrician?
Highway electrical systems
cable jointing
electrical maintenance
Electrical machine drive installations
panel building
instrumentations
How a design stage works for projects?
The architect, consulting engineer, quantity surveyor and clerks of works are traditionally part of the architect’s design team.
In smaller firms, the client expects the electrician to ensure that the installation is properly designed and carried out.
In larger firms, they might have an internal architect team that makes things simpler and possibly cheaper.
What is a tendering process?
Tendering is the process by which a contractor works with the drawings and specifications issued by the consulting engineer and submits in writing, in competition with others, a total estimated cost for carrying out the work (i.e. materials, tools, equipment and labour).
What does an estimator do?
The estimator’s task is to calculate the total cost that will be given in the tender.
How can all types of information be stored?
Email (most used way)
Printers
Fax machine
Telephone
written messages ( hand written notes)
USB flash memory drives
Electronic file server
external flash drives
optical media (CDs)
microforms (stores images)
Printed materials (papers)
What is an assembly drawing?
Assembly drawings are technical drawings that illustrate how multiple components fit together to form a complete product or structure, showing the arrangement and relationship of parts
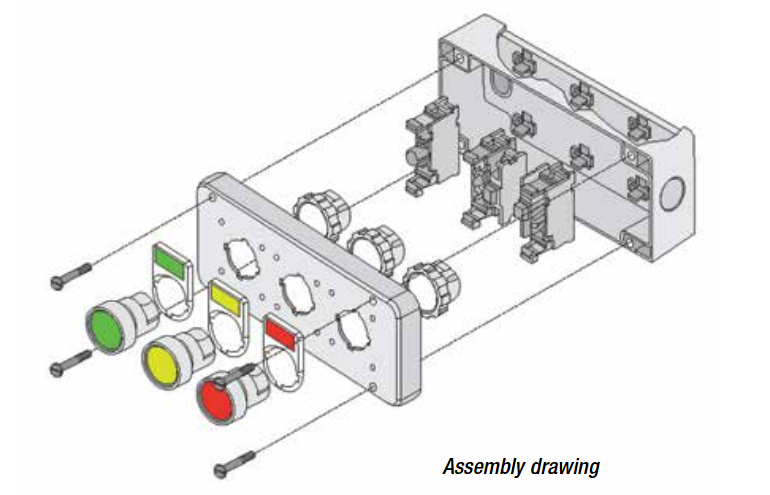
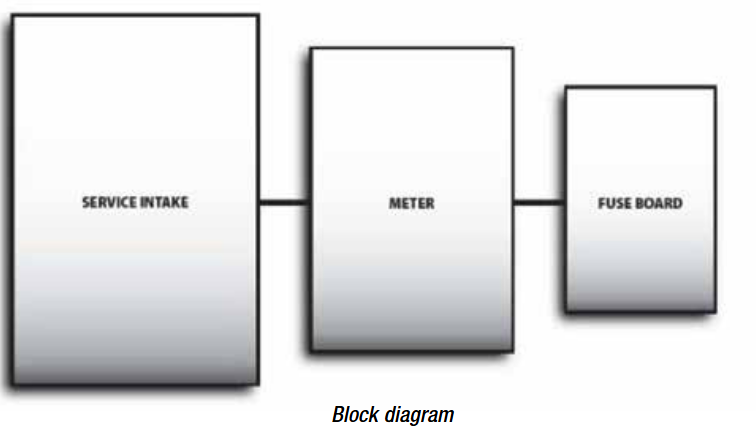
What is a block diagram?
A block diagram can be used to relate information about a circuit without giving details of components or the manner in which they are connected. In block diagrams, the various items are represented by a simple figure or symbol, such as square or rectangle, labelled to indicate its purpose.
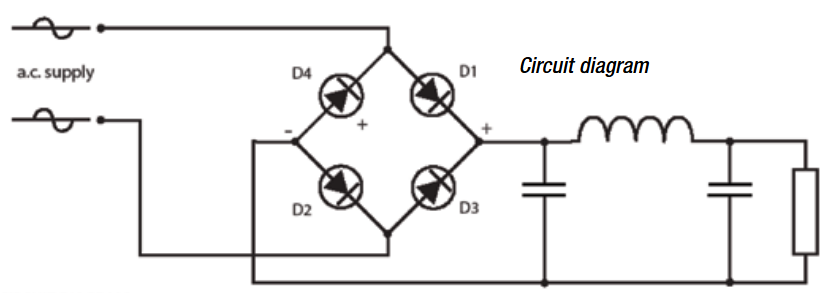
What is a circuit diagram?
Circuit diagrams use symbols to represent all circuit components and shows how these are connected. A circuit diagram should be as clear as possible and follow a logical progression route from supply to output. In all other respects, the circuit diagram cannot be regarded as a direct source of information. This is because it does not represent the physical outline of the circuit
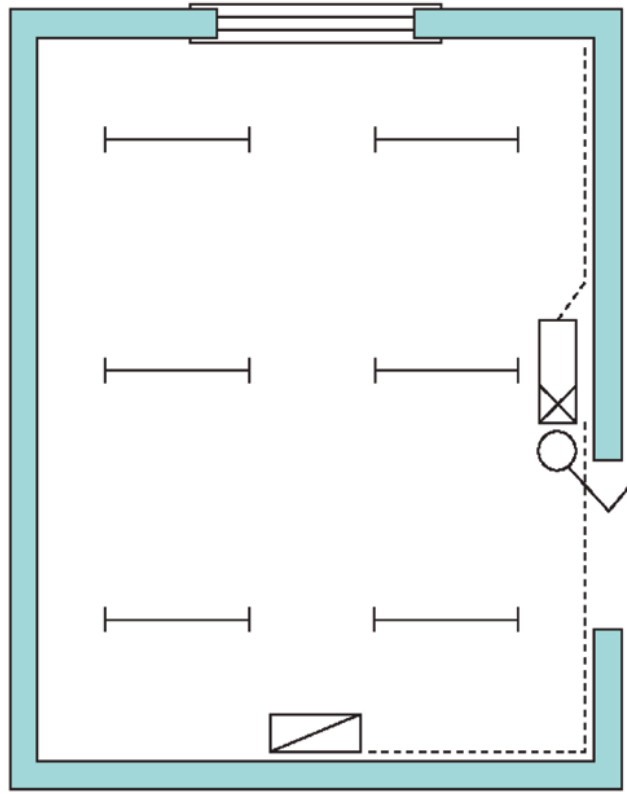
What is a lay out diagram?
They are often based upon architects’ drawings of the building in which the electrical system is to be installed. This type of drawing shows the required position of all equipment, metering and control gear, and they normally show the plan view of the installation.
Why is recording of drawing changes so important?
In an ideal world, every installation would exactly follow the architect’s, designer’s, or consulting engineer’s original plans. In reality, however, everyone knows that problems can occur which will mean that cables must be routed in another way, or conduit must be fixed in a different position. These changes must be recorded so that, in future, when maintenance or alterations are needed, the actual layout of the installation is known.
What is a schematic diagram?
These diagrams do not show precisely how to wire components but they do show how the circuit is intended to work. Schematic diagrams tend to be used for larger, more complicated electrical installations such as control systems for motor starters and heating systems (Like a standard circuit diagram with symbols).
What is a site plan?
A site plan will show the entire area that is being worked upon. In terms of a house, for example, the site plan would not just show a single room or a floor but the whole dwelling, including all the land and gardens up to and including the property boundary.
What is a Wiring diagram?
The physical layout is taken into consideration. The components and connections show a pictorial version of those found in the actual circuit. Wiring diagrams can be used to carry information of a specific nature relating to the connection or wiring of components.
How are manufacturers data and service manuals used?
Almost all equipment will be supplied with manufacturers’ fitting instruction and other technical data or information sheets. These should be read and understood. Occasionally you may need more details about an item. You can get this from the manufacturer’s catalogue or datasheets, website, or by speaking directly to the manufacturer. Once the installation of the item is complete, they should be kept safely in a central file then to be given to the customer once the installation is installed.
What is a Gantt chart used for and how does it work?
A Gantt chart shows jobs or activities (normally in one colour) and when it is due to happen and for how long it will take. Main contractors use this sort of chart as it shows when individual trades are coming into a site. Another line of colour can be added underneath the certain trade to show weather it is on time or behind schedule.
How do scales work when designing?
Layout, assembly and site drawings give information about physical objects, such as the floor layout in a building, or a mechanical object. If the drawing were the same size as the object, the drawings would often be far too big to handle.
To find a measurement on the actual physical object, you measure the distance on the drawing and multiply it by the scale.
1:100 means in reality the object is 100 times bigger than on paper. Where as, 100:1 means the object is magnified 100 times bigger on paper than in reality. Any types of units can be used.
What must scaffolding that is built to a height greater than 2 m have?
Toe boards and guard rails
Actual full-size measurements calculated by taking measurements from the drawing and multiplying them by?
100
What is the difference between schematic and circuit diagrams?
A schematic diagram focuses on the logical function of an electrical circuit, showing how components are connected and how the circuit is supposed to behave.
A circuit diagram, on the other hand, is a more detailed representation that includes the physical layout of components and wiring, including specific wire colours.