Thoracic Cavity, Viscera and VANs
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Boundaries of the Thorax (Bones)
Dorsal - Thoracic vertebrae
Laterally - Ribs and costal cartilage
Ventral - Sternum
Thorax Muscles
Diaphragm
Internal/External intercostal muscles
Fills spaces between ribs
Internal intercostal muscle = expiration
External intercostal muscle = inspiration
Transversus Thoracis
INSIDE of chest
Muscle of Expiration
Attaches to Sternum
Pulls sternum “in,” making chest cavity smaller
Chest cavity smaller => Volume smaller/Pressure increase => Expiration
Diaphragm
Main muscle of inspiration
Caudal wall of thoracic cavity (divides thorax/abdomen)
Musculotendinous structure
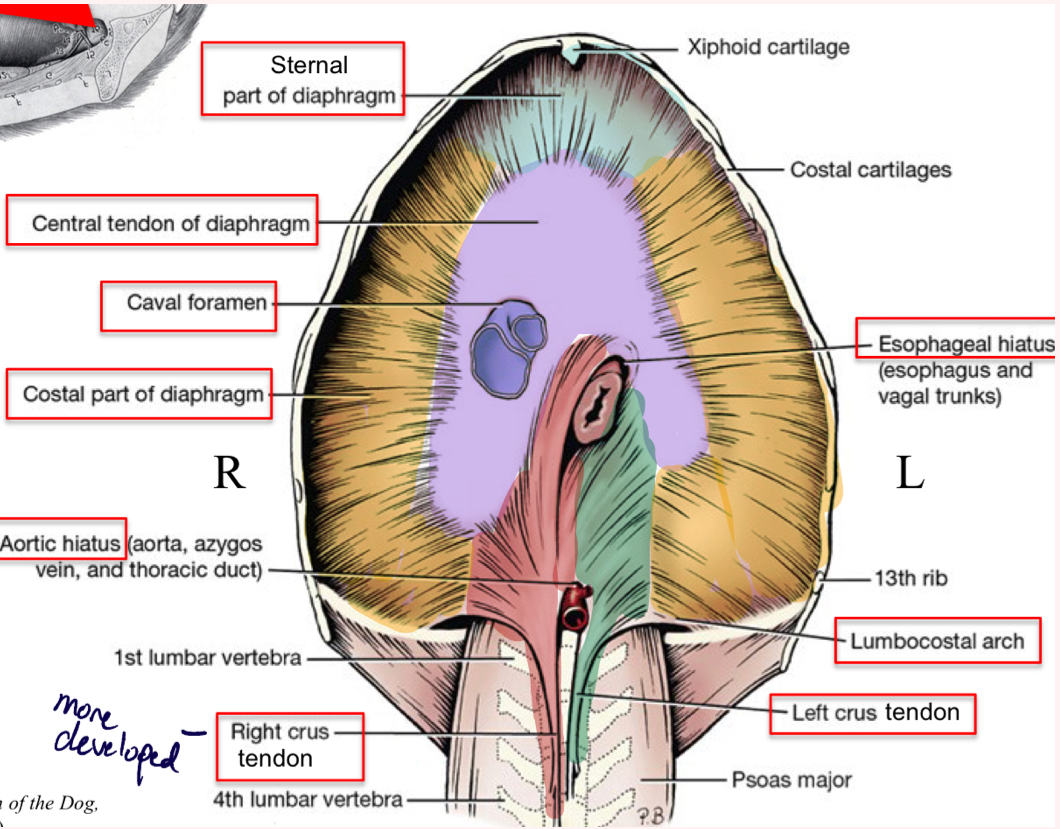
Diaphragm cranial view (from thorax)
Central tendon
Costal part
Sternal part
Right crus- more developed
Left crus
Caval Foramen
Esophageal hiatus
Aortic hiatus
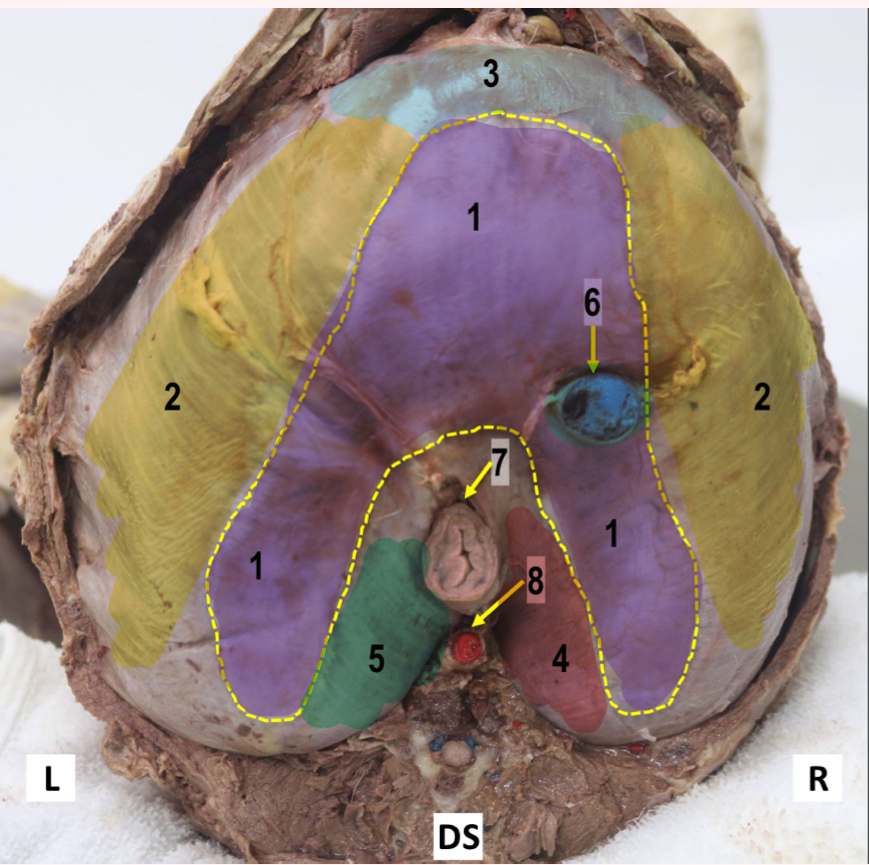
Diaphragm caudal view (from abdomen)
Central tendon
Costal part
Sternal part
Right crus- more developed
Left crus
Caval Foramen
Esophageal hiatus
Aortic hiatus
Serous membranes
every organ is surrounded by a serous membrane
inner wall = visceral
outer wall = parietal
Cavity
space between the visceral and parietal pleura
Pleura
Serous membrane for lungs
Pleural cavity
space between visceral/parietal pleura
Visceral pleura
directly on lungs
Parietal pleura
outer wall
Mediastinum
space between right/left pleural cavities
Pleural cavities
Left/right pleural cavities
Mediastinum between them
contains heart, esophagus, trachea
Plica vena cava
on right sight surrounding caudal vena cava
Mediastinal recess
between plica vena cava and right mediastinal pleura
*contains accessory lobe of right lung
Regions of Pleura
Costal pleura
Mediastinal pleura
Diaphragmatic pleura
Visceral pleura
Pleural cupula
Costodiaphragmatic recess
*pleural taps/thoracocentesis
Endothoracic fascia
“Glue” that holds parietal pleura to the throracic wall
Lungs
Heart on left side of chest, more room for lungs on right side
Right lung
4 lobes
Cranial, middle, caudal, and accessory lobes
Left lung
2 lobes
Cranial, caudal
Costal surface
touch ribs
Diaphragmatic surface
touch diaphragm
Basal margin
border of the base of the lungs
Hilus
where everything goes into the lungs
Bronchi
Pulmonary artery
Pulmonary veins
“Root of lung”
Pulmonary artery
carries deoxygenated blood
supplies lungs with blood
Pulmonary veins
carries oxygenated blood
drains lungs
Lung lung lobation
Cranial lobe
cranial and caudal parts
Caudal lobe
Right lung lobation
Cranial lobe
Middle lobe
Caudal lobe
Accessory lobe (in mediastinal recess)
*right cardiac notch
Right cardiac notch
4th intercostal space (between ribs 4 and 5), between cranial and middle lobes
access to heart
Medial view of right lung
Accessory lobe: in mediastinal recess
has a groove for the caudal vena cava
Trachea
In mediastinum divides into two principal/main bronchi
Bronchi
Principal bronchi → Lobalar bronchi → Segmental bronchi, conducting air to lungs
Carina
where trachea branches into principal bronchi
Brochoesophageal artery
supplies bronchial tree
actual nutritional blood that the lungs need
Tracheobronchial lymph nodes
lymph nodes associated with trachea and bronchi
Major Thoracic arteries
Aortic arch
Brachiocephalic trunk
L/R common carotid aa
Right subclavian a
Left subclavian
Descending aorta
Left subclavian
own branch off of brachiocephalic trunk
Descending aorta
continuation of aortic arch to abdomen
Subclavian arteries (L/R)
R/L Subclavian aa. have identical branches but come off aortic arch differently
4 branches:
Costocervical trunk
Vertebral a
Superficial cervical a
Internal thoracic a.
Costocervical trunk
Supplies dorsal intercostal spaces 1-3, muscles of neck
Supplies ribs and neck
Vertebral a
shoots up neck through transverse vertebral foramina
Supplies brain and spinal corf
Vertebral a goes through vertebrae
Superficial cervical a
Supplies superficial structures of neck
Internal thoracic
Most important branch of subclavian a
Runs down to diaphragm
-Gives off: Ventral intercostal aa
-Musculophrenic a- to diaphragm
-Continues as cranial epigastric a
Branches off as the superficial cervical a
Veins of the thorax
Right azygos v
Caudal vena cava
Cranial vena cava
Right azygos v
drains thorax
in dogs, only have a right azygos
Ox has right and left azygos
Drains the coastal walls, the bronchial tree, and the esophagus
Caudal vena cava
drains caudal to thorax
drains pelvic limb, abdomen
Cranial vena cava
drains cranial to thorax
Drains head, thoracic limb
Thoracic duct
The largest lymphatic vessel in the body
Originates in the cisterna chyli in the abdomen
*Drains into the L brachiocephalic v, which drains into the cranial vena cava
Often see with right azygos v
Central Nervous System
Brain and Spinal cord
Brain: white matter central, gray matter out
Spinal cord: gray matter central, white matter outer
Integrating issuing commands
Peripheral Nervous System
Nerves and Ganglia
Sensory, motor output from CNS
Sensory
Afferent nerves, take impulse to CNS
Motor
Efferent nerves, take impulse away from CNS
Mixed Nerves
nerves seen carrying both sensory and motor fibers.
Spinal Nerves
Come from spinal cord/vertebrae
All spinal nerves are mixed
Motor/Efferent Nerves
Either visceral or somatic
somatic to voluntary skeletal/ striated muscle
1 neuron system
Visceral (Autonomic Nervous System)
involuntary
2-neuron system
1 in CNS and 1 in peripheral ganglion
Autonomic Nervous System/ Visceral Motor Nerves
2 divisions:
Parasympathetic and Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
Craniosacral system
Nerves from cranial/sacral spinal cord
Sympathetic
Thoracolumbar system
Nerves from thorax/lumbar spinal cord
Spinal Cord
Dorsal Root- Sensory
Dorsal root ganglion (synapse)
Ventral Root- Motor
No ganglion
Spinal Nerves
Mixed nerves: Motor and Sensory
Branches into: Dorsal ramus, Ventral ramus, communicating branch
Dorsal Ramus
to epaxial structures
Ventral ramus
to all other structures
Communicating branch
sympathetic trunk
Cervical Spinal Nerves
8 cervical nerves
CN1: comes out of lateral vertebral foramen of Atlas
CN2 out intervertebral foramen between Atlas/Axis
CN3 between Axis/C3
CN8 between C7/T1
*Vertebrae after nerve
Phrenic Nerve
Made from ventral branches of C5, C6, C7
Somatic motor and sensory to diaphragm
Left phrenic n crosses the heart
Thoracic/Lumbar Numbering
Different from Cervical
Nerve after vertebrae
TN1 between T1/T2
TN13 between T13/L1
Thoracic Nerves
Intercostal nerves
located directly caudal to ribs
run with intercostal arteries/veins
T13 - costoabdominal n
makes sense - last nerve between ribs (costo) and abdomen
Lumbar Nerves
Innervate abdominal walls:
a. T13: Costoabdominal n
b. L1: Crainal iliohypogastric n
c. L2: Caudal iliohypogastric n
d. L3: Ilioinguinal n
e. L4: Lateral cutaneous femoral n.
Nerves on transversus abdominis
Sacral Nerves
S1 and S2: No intervertebral foramina (fused)
Dorsal branches out of dorsal sacral foramina
Ventral branches out of pelvic sacral foramina
S3 through intervertebral formina between sacrum and Cd1