Unit 1: Hydrosphere study guide
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:45 PM on 10/9/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
1
New cards
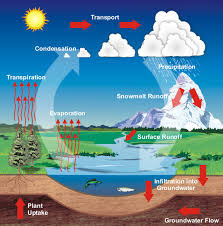
Fill in the blank next to each number with corresponding water cycle process.
1. Evaporation, 2. Advection, 3. Condensation, 4. Precipitation, 5. Rivers & streams, 6. groundwater
2
New cards
What percent of the Earth's surface is covered with water? where is most of it found?
70% & oceans.
3
New cards
3 of the water's most unique qualities
LIquid, Solid, & gas
4
New cards
Substances in order of least to greatest permeability
Clay, Silt, plastic, sand, & gravel
5
New cards
what is the difference between direct & indirect use? give an example of both.(direct)
Direct-using a faucet or hose(example: bathing, drinking, & cooking.
6
New cards
what is the difference between direct & indirect use? give an example of both.(indirect)
indirect use- water used to produce the goods & services(example: cotton, paper, & more.
7
New cards
Porosity
amount of space available to hold water(depends on size & sorting of particles.
8
New cards
Permeability
Ability of rock or soil to allow water to flow through it
9
New cards
saturated zone
the area of permeable rock or soil that is totally filled or saturated with water
10
New cards
unsaturated zone
both oxygen & water fill the spaces between sediment that is not saturated
11
New cards
Water table
The top of the saturated zone & separates it from the zone of aeration.
12
New cards
Aquifer
zones of Earth's crust in which water can easily move.
13
New cards
Artesian well
Well from which water flows on its own without pumping
14
New cards
Watershed
the entire land area that drains to a given river, stream, wetland, or lake.
15
New cards
Divide
the boundary of a watershed that is characterized by the highest point in a particular region.
16
New cards
Groundwater
the water that is beneath Earth's surface
17
New cards
Heat capacity
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of a substance
18
New cards
Infiltration
the movement of surface water into rock or soil through cracks and pore spaces
19
New cards
Evaporation
the process by which water is converted from a liquid to a gas or vapor.
20
New cards
Advection
the transfer of heat or matter by the flow of a fluid, especially horizontally in the atmosphere or the sea.
21
New cards
Condensation
The change of state from a gas to a liquid
22
New cards
Precipitation
water released from clouds in the form of rain, freezing rain, sleet, snow, or hail
23
New cards
Surface runoff
water that flows over land surface rather than infiltrating into the ground
24
New cards
Transpiration
the release of water vapor to the atmosphere by plants
25
New cards
Adhesion
attraction between molecules of different substances
26
New cards
Cohesion
an attraction between molecules of the same substance
27
New cards
Surface tension
property of liquid surface that allows it to resist an external force.
28
New cards
Water as a solvent
a substances capable of dissolving other polar molecules & ionic compounds.
29
New cards
Mouth(of river)
place where a stream or river flows into a larger body of water
30
New cards
Tributaries
small river or stream that flows in to a larger river or stream; a branch of the river
31
New cards
Erosion
a process that wears away surface materials & moves them from one place to another.
32
New cards
Deposition
Process in which sediment is laid down in new locations.
33
New cards
River upper course
when a river runs over alternating layers of hard & soft.
34
New cards
River middle course
found on gently sloping land, & is typically identified by it's meandering path( the sweeping side to side curves.
35
New cards
River lower course
has a low energy level & the process of deposition takes place.
36
New cards
Delta
flat, low-lying land plain that sometimes forms at the mouth of a river from deposits of sediment.
37
New cards
Why is sediment deposited at the mouth of a river?
It's because of the river slows down at the mouth, so it doesn't have the energy to carry all the silt, sand, & clay anymore.
38
New cards
Summarize the erosion & deposition characteristics of the 3 different courses of a river. (upper course)
Vertical erosion is the main process in the upper course of the river, as the river wants to get to sea level. This process created 5 unique features; a v-shaped valley, interlocking spurs, gorges, & rapids
39
New cards
Summarize the erosion & deposition characteristics of the 3 different courses of a river. (middle course)
The river has more energy & a high volume of water. The gradient is gentle & lateral(sideways) erosion has widened the river channel. It created wider, shallower valleys, meanders & oxbow lakes.
40
New cards
Summarize the erosion & deposition characteristics of the 3 different courses of a river. (lower course)
The river has high volume & a large discharge. The river channel is now deep, wide, & the landscape around it is flat, As a river reaches the end of its journey , energy levels are low & deposition takes place. It created wide flat-bottomed valleys, floodplains, & deltas.
41
New cards
explain the relationship between river/stream velocity & the size of sediment that can be transported.
Both the size & amount of sediment transported in a stream are determined by the speed of the stream. Higher velocities equal the stream has more kinetic energy, As a result, higher velocities carry larger sediments.