K101 Final Exam
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/207
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
208 Terms
1
New cards
In a single molecule of water, the two hydrogen atoms are bonded to a single oxygen atom by
a. polar covalent bonds.
b. ionic bonds.
c. hydrogen bonds.
d. nonpolar covalent bonds.
a. polar covalent bonds.
b. ionic bonds.
c. hydrogen bonds.
d. nonpolar covalent bonds.
a
2
New cards
Stanley Miller's 1953 experiments demonstrated conclusively that
a. life arose on Earth from simple organic molecules, with energy from lightning and volcanoes.
b. the conditions on early Earth were conducive to the origin of life.
c. life arose on Earth 3.8 billion years ago from simple inorganic molecules.
d. organic molecules can be synthesized abiotically under conditions that may have existed on early Earth.
e. the conditions on early Earth were conducive to the abiotic synthesis of organic molecules.
a. life arose on Earth from simple organic molecules, with energy from lightning and volcanoes.
b. the conditions on early Earth were conducive to the origin of life.
c. life arose on Earth 3.8 billion years ago from simple inorganic molecules.
d. organic molecules can be synthesized abiotically under conditions that may have existed on early Earth.
e. the conditions on early Earth were conducive to the abiotic synthesis of organic molecules.
d
3
New cards
What do the four ‘elements of life’ -carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen-have in common?
a. They are equal in electronegativity
b. They are elements produced only by living cells
c. They all have the same number of valence electrons
d. Each element exists in only one isotopic form
e. They all have unpaired electrons in their valence shells.
a. They are equal in electronegativity
b. They are elements produced only by living cells
c. They all have the same number of valence electrons
d. Each element exists in only one isotopic form
e. They all have unpaired electrons in their valence shells.
e
4
New cards
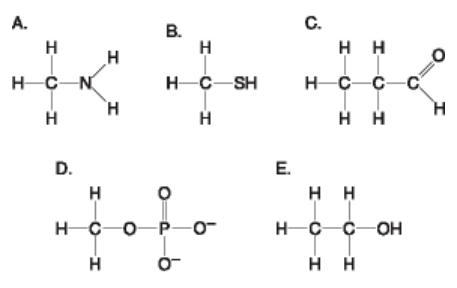
Using the functional group diagram at right answer A – E which of the following is incorrectly matched?:
a. A = amino group
b. B = thiol group
c. C = carbonyl (aldehyde)
d. D= organic phosphate
e. E= carboxyl group
a. A = amino group
b. B = thiol group
c. C = carbonyl (aldehyde)
d. D= organic phosphate
e. E= carboxyl group
e
5
New cards
Water is able to form hydrogen bonds because
a. the oxygen atom in a water molecule has a weak positive charge.
b. each of the hydrogen atoms in a water molecule is weakly negative in charge.
c. oxygen has a valence of 2.
d. the water molecule is shaped like a tetrahedron.
e. the bonds that hold together the atoms in a water molecule are polar covalent bonds.
a. the oxygen atom in a water molecule has a weak positive charge.
b. each of the hydrogen atoms in a water molecule is weakly negative in charge.
c. oxygen has a valence of 2.
d. the water molecule is shaped like a tetrahedron.
e. the bonds that hold together the atoms in a water molecule are polar covalent bonds.
e
6
New cards
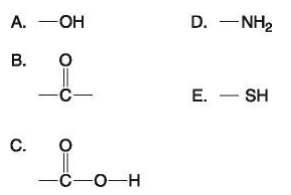
Which functional group shown at right is:
i) is an acidic functional group that can release H+ into a solution?
ii) a basic functional group that can accept H+?
iii) can exist as a ketone or aldehyde configuration?
iv) a characteristic of alcohols?
v) helps stabilize proteins by forming covalent cross-links within or between protein molecules?
i) is an acidic functional group that can release H+ into a solution?
ii) a basic functional group that can accept H+?
iii) can exist as a ketone or aldehyde configuration?
iv) a characteristic of alcohols?
v) helps stabilize proteins by forming covalent cross-links within or between protein molecules?
c
d
b
a
e
d
b
a
e
7
New cards
Which modifications of fatty acids will best keep triglycerides solid at warmer temperatures?
a. adding hydrogens and trans double bonds to the fatty acids
b. adding cis double bonds and trans double bonds to the fatty acids
c. creating cis double bonds to the fatty acids
d. adding hydrogens to the fatty acids
e. creating trans double bonds to the fatty acids
a. adding hydrogens and trans double bonds to the fatty acids
b. adding cis double bonds and trans double bonds to the fatty acids
c. creating cis double bonds to the fatty acids
d. adding hydrogens to the fatty acids
e. creating trans double bonds to the fatty acids
d
8
New cards
A comparison of saturated and naturally occurring unsaturated fats reveals that the unsaturated fats are __________ at room temperature and have _______:
a. Solids; cis double bonds
b. Liquids; trans double bonds
c. Liquids; single bonds
d. Liquids; cis double bonds
e. Solids; single bonds
a. Solids; cis double bonds
b. Liquids; trans double bonds
c. Liquids; single bonds
d. Liquids; cis double bonds
e. Solids; single bonds
d
9
New cards
A molecule with four joined rings that is the precursor of vertebrate sex hormones and is also found in the vertebrate phospholipid bilayer is:
a. estrogen
b. testosterone
c. glycerol
d. cholesterol
e. a phospholipid
a. estrogen
b. testosterone
c. glycerol
d. cholesterol
e. a phospholipid
d
10
New cards
A molecule with the formula C18H36O2 is probably a __, where one with the formula C6H12O6 is probably a ___
a. carbohydrate and fatty acid, respectively
b. fatty acid and monosaccharide, respectively
c. protein and monosaccharide, respectively.
d. nucleic acid and fatty acid, respectively.
e. fatty acid and nucleotide, respectively
a. carbohydrate and fatty acid, respectively
b. fatty acid and monosaccharide, respectively
c. protein and monosaccharide, respectively.
d. nucleic acid and fatty acid, respectively.
e. fatty acid and nucleotide, respectively
b
11
New cards
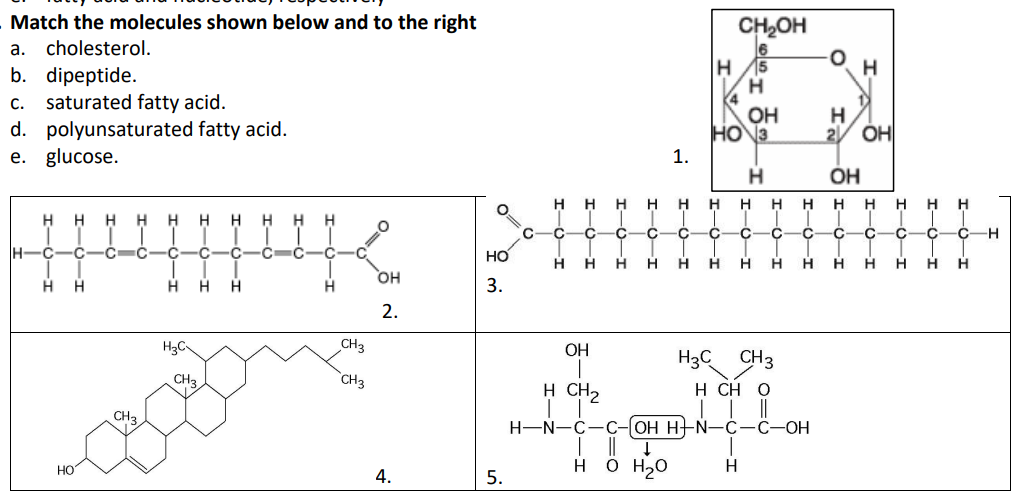
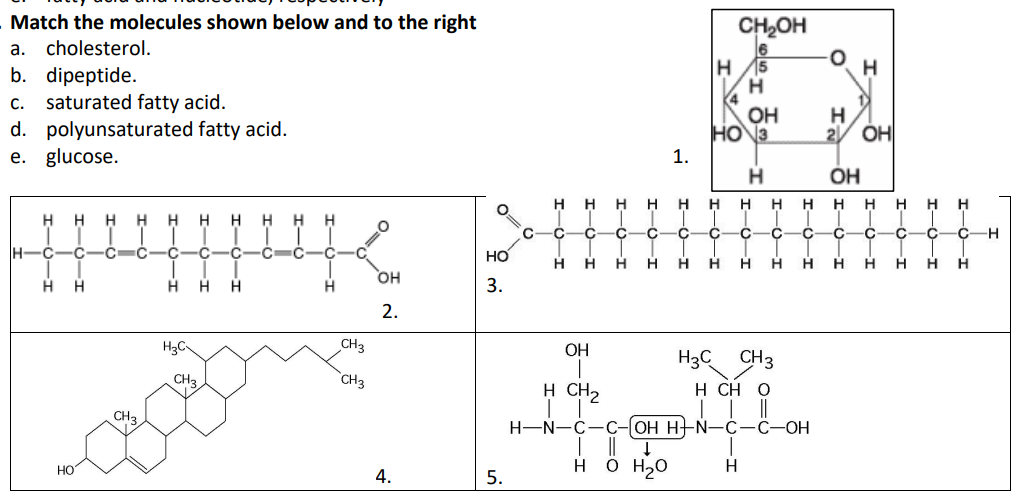
Match the molecules shown below and to the right
a. cholesterol.
b. dipeptide.
c. saturated fatty acid.
d. polyunsaturated fatty acid.
e. glucose.
a. cholesterol.
b. dipeptide.
c. saturated fatty acid.
d. polyunsaturated fatty acid.
e. glucose.
4
5
3
2
1
5
3
2
1
12
New cards
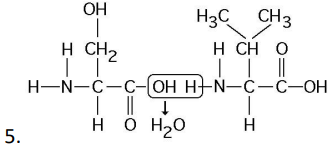
Which of the following statements is/are true regarding chemical reaction (5) illustrated above?
a. It is a hydrolysis reaction.
b. It results in a peptide bond.
c. It joins two fatty acids together.
d. It is a hydrolysis reaction and it results in a peptide bond.
e. It is a hydrolysis reaction, it results in a peptide bond, and it joins two fatty acids together
a. It is a hydrolysis reaction.
b. It results in a peptide bond.
c. It joins two fatty acids together.
d. It is a hydrolysis reaction and it results in a peptide bond.
e. It is a hydrolysis reaction, it results in a peptide bond, and it joins two fatty acids together
b
13
New cards
A bond that forms by joining monomers (such as nucleotides or amino acids) into polymers (such as DNA or insulin) is a(n):
a. Hydrogen bond
b. Ionic bond
c. Peptide bond
d. Covalent bond
a. Hydrogen bond
b. Ionic bond
c. Peptide bond
d. Covalent bond
d
14
New cards
Polysaccharides, triacylglycerides, and proteins are similar in that they
a. are synthesized from monomers by the process of hydrolysis.
b. are decomposed into their subunits by dehydration reactions.
c. all contain nitrogen in their monomer building blocks.
d. are synthesized from subunits by dehydration reactions.
e. are synthesized as a result of peptide bond formation between monomers.
a. are synthesized from monomers by the process of hydrolysis.
b. are decomposed into their subunits by dehydration reactions.
c. all contain nitrogen in their monomer building blocks.
d. are synthesized from subunits by dehydration reactions.
e. are synthesized as a result of peptide bond formation between monomers.
d
15
New cards
Match the following parts of the cell to its function
i) Nucleus
a. Sorting of proteins targeted for extracellular secretion
ii) Mitochondria
b. Site of cell-cell adhesion and cell recognition
iii) Nucleolis
c. Site of transcription of mRNA and tRNA for protein synthesis
iv) Rough ER
d. Synthesis of the steroid hormone testosterone
v) Golgi apparatus
e. Synthesis of ATP via oxidative phosphorylation
vi) Lysosome
f. Site of rRNA for protein synthesis
vii) Smooth ER
g. Intercellular digestion
viii) Extracellular Matrix
h. Synthesis of the insulin receptor, a transmembrane glycoprotein
i) Nucleus
a. Sorting of proteins targeted for extracellular secretion
ii) Mitochondria
b. Site of cell-cell adhesion and cell recognition
iii) Nucleolis
c. Site of transcription of mRNA and tRNA for protein synthesis
iv) Rough ER
d. Synthesis of the steroid hormone testosterone
v) Golgi apparatus
e. Synthesis of ATP via oxidative phosphorylation
vi) Lysosome
f. Site of rRNA for protein synthesis
vii) Smooth ER
g. Intercellular digestion
viii) Extracellular Matrix
h. Synthesis of the insulin receptor, a transmembrane glycoprotein
c
e
f
h
a
g
d
b
e
f
h
a
g
d
b
16
New cards
Proteins that are manufactured for secretion (export from the cell):
a. are made in the cytosol and transported across the ER membrane
b. are threaded through special pores in the plasma membrane
c. are made in the smooth ER and packaged in transport vesicles
d. have carbohydrates covalently added when the proteins are in transport vesicles
e. are made in the rough ER and packaged in transport vesicles
a. are made in the cytosol and transported across the ER membrane
b. are threaded through special pores in the plasma membrane
c. are made in the smooth ER and packaged in transport vesicles
d. have carbohydrates covalently added when the proteins are in transport vesicles
e. are made in the rough ER and packaged in transport vesicles
e
17
New cards
Mammalian blood contains the equivalent of 0.15 M NaCl. Seawater contains the equivalent of 0.45 M NaCl. What will happen if red blood cells are transferred to seawater?
a. The blood cells will take up water, swell, and eventually burst.
b. NaCl will passively diffuse into the red blood cells.
c. Water will leave the cells, causing them to shrivel and collapse.
d. NaCl will be exported from the red blood cells by facilitated diffusion.
e. The blood cells will expend ATP for active transport of NaCl into the cytoplasm.
a. The blood cells will take up water, swell, and eventually burst.
b. NaCl will passively diffuse into the red blood cells.
c. Water will leave the cells, causing them to shrivel and collapse.
d. NaCl will be exported from the red blood cells by facilitated diffusion.
e. The blood cells will expend ATP for active transport of NaCl into the cytoplasm.
c
18
New cards
All of the following are functions of integral membrane proteins except
a. Synthesis of hormones.
b. Active transport of ions.
c. Cell – cell adhesion.
d. Reception of hormone signals like epinephrine.
e. Attachment to the extracellular membrane.
a. Synthesis of hormones.
b. Active transport of ions.
c. Cell – cell adhesion.
d. Reception of hormone signals like epinephrine.
e. Attachment to the extracellular membrane.
a
19
New cards
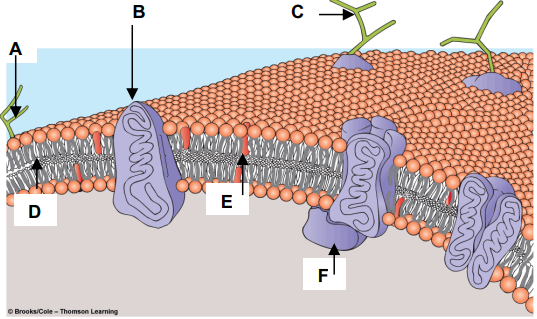
Match the components of the plasma membrane with the letters in the figure at right.
a. Cholesterol -
b. Glycolipid -
c. Integral Membrane Protein -
d. Peripheral Membrane Protein -
e. Glycoprotein –
a. Cholesterol -
b. Glycolipid -
c. Integral Membrane Protein -
d. Peripheral Membrane Protein -
e. Glycoprotein –
E
A
B
F
C
A
B
F
C
20
New cards
Which of the following types of reactions would decrease the entropy within a cell?
a. anabolic reactions
b. hydrolysis
c. respiration
d. digestion
e. catabolic reactions
a. anabolic reactions
b. hydrolysis
c. respiration
d. digestion
e. catabolic reactions
a
21
New cards
SELECT ALL THAT APPLY: Why is ATP an important molecule in metabolism?
a. Its hydrolysis provides an input of free energy for exergonic reactions.
b. It provides energy coupling between exergonic and endergonic reactions.
c. Its terminal phosphate group has unusually strong covalent bonds that generate free energy
a. Its hydrolysis provides an input of free energy for exergonic reactions.
b. It provides energy coupling between exergonic and endergonic reactions.
c. Its terminal phosphate group has unusually strong covalent bonds that generate free energy
a, b
22
New cards
Increasing the substrate concentration in a reaction could overcome which of the following?
a. denaturation of the enzyme
b. allosteric inhibition
c. competitive inhibition
d. saturation of the enzyme activity
e. insufficient cofactors
a. denaturation of the enzyme
b. allosteric inhibition
c. competitive inhibition
d. saturation of the enzyme activity
e. insufficient cofactors
c
23
New cards
SELECT ALL THAT APPLY: The primary way that cells do work is called energy coupling, using ATP. Which statements below statements accurately defines energy coupling?
a. Anabolic reactions drive catabolic reactions.
b. Exergonic reactions drive endergonic reactions.
c. Endergonic reactions drive exergonic reactions.
d. ATP hydrolysis releases free energy that can be coupled to an endergonic reaction via the formation of a phosphorylated intermediate.
e. Endergonic and exergonic reactions occur independently of each other.
a. Anabolic reactions drive catabolic reactions.
b. Exergonic reactions drive endergonic reactions.
c. Endergonic reactions drive exergonic reactions.
d. ATP hydrolysis releases free energy that can be coupled to an endergonic reaction via the formation of a phosphorylated intermediate.
e. Endergonic and exergonic reactions occur independently of each other.
b, d
24
New cards
The general name for an enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to a protein is
a. phosphorylase.
b. phosphatase.
c. protein kinase.
d. ATPase.
e. protease.
a. phosphorylase.
b. phosphatase.
c. protein kinase.
d. ATPase.
e. protease.
c
25
New cards
In liver cells, the inner mitochondrial membranes are about five times the area of the outer mitochondrial membranes. What purpose must this serve?
a. It allows for an increased rate of glycolysis.
b. It allows for an increased rate of the citric acid cycle.
c. It increases the surface area for oxidative phosphorylation.
d. It increases the surface for substrate-level phosphorylation.
e. It allows the liver cell to have fewer mitochondria.
a. It allows for an increased rate of glycolysis.
b. It allows for an increased rate of the citric acid cycle.
c. It increases the surface area for oxidative phosphorylation.
d. It increases the surface for substrate-level phosphorylation.
e. It allows the liver cell to have fewer mitochondria.
c
26
New cards
Why is the Calvin cycle said to be dependent on the light reactions?
a. The light reactions generate the molecular oxygen needed for the production of sugars in the Calvin cycle.
b. G3P produced in the light reactions is oxidized in the Calvin cycle.
c. The light reactions produce the ATP energy and NADPH for sugar production in the Calvin cycle.
d. RuBP produced in the light reactions facilitates CO2 fixation in the Calvin cycle.
e. Photons of light that are byproducts of the light reactions provide the energy for the Calvin cycle
a. The light reactions generate the molecular oxygen needed for the production of sugars in the Calvin cycle.
b. G3P produced in the light reactions is oxidized in the Calvin cycle.
c. The light reactions produce the ATP energy and NADPH for sugar production in the Calvin cycle.
d. RuBP produced in the light reactions facilitates CO2 fixation in the Calvin cycle.
e. Photons of light that are byproducts of the light reactions provide the energy for the Calvin cycle
c
27
New cards
One function of alcohol and lactic acid fermentation is to
a. reduce NAD+ to NADH.
b. reduce FAD+ to FADH2.
c. oxidize NADH to NAD+.
d. reduce FADH2 to FAD+.
a. reduce NAD+ to NADH.
b. reduce FAD+ to FADH2.
c. oxidize NADH to NAD+.
d. reduce FADH2 to FAD+.
c
28
New cards
When skeletal muscle cells undergo anaerobic respiration, they become fatigued and painful. This is now known to be caused by
a. buildup of pyruvate.
b. buildup of lactate.
c. increase in sodium ions.
d. increase in potassium ions.
e. increase in ethanol.
a. buildup of pyruvate.
b. buildup of lactate.
c. increase in sodium ions.
d. increase in potassium ions.
e. increase in ethanol.
b
29
New cards
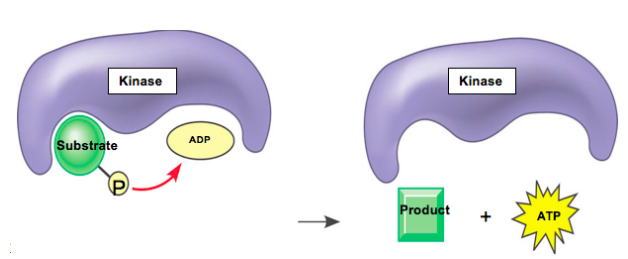
SELECT ALL THAT APPLY: Which of the 4 kinase enzymes in glycolysis might be the enzyme shown below?
a. Hexokinase
b. Pyruvate Kinase (PK)
c. Phosphofructokinase (PFK)
d. Phosphoglycerokinase (PGK)
a. Hexokinase
b. Pyruvate Kinase (PK)
c. Phosphofructokinase (PFK)
d. Phosphoglycerokinase (PGK)
b, d
30
New cards
Photosynthesis and respiration: Match with the correct location in the cell
a. Krebs cycle
i) Thylakoid membrane
b. Calvin cycle
ii) Thylakoid lumen
c. Light reactions
iii) Mitochondrial inner membrane space
d. Proton Gradient in aerobic respiration
iv) Chloroplast stroma
e. Proton Gradient in light reactions
v) Mitochondrial matrix
a. Krebs cycle
i) Thylakoid membrane
b. Calvin cycle
ii) Thylakoid lumen
c. Light reactions
iii) Mitochondrial inner membrane space
d. Proton Gradient in aerobic respiration
iv) Chloroplast stroma
e. Proton Gradient in light reactions
v) Mitochondrial matrix
5
4
1
3
2
4
1
3
2
31
New cards
Substrate-level phosphorylation accounts for approximately what percentage of the ATP formed during glycolysis?
a. 0%
b. 2%
c. 10%
d. 38%
e. 100%
a. 0%
b. 2%
c. 10%
d. 38%
e. 100%
e
32
New cards
A C4 plant initially fixes CO2 into ____ where a C3 plant fixes CO2 into _______
a. Oxaloacetic acid using PEP carboxylase, PGA using Rubisco.
b. G3P using PEP carboxylase, PGA using Rubisco
c. Malic acid using Rubisco, PGA using PEP carboxylase.
d. RuBP using Rubisco, Oxaloacetic acid using PEP carboxylase
e. ATP using PEP carboxylase, PGA using Rubisco.
a. Oxaloacetic acid using PEP carboxylase, PGA using Rubisco.
b. G3P using PEP carboxylase, PGA using Rubisco
c. Malic acid using Rubisco, PGA using PEP carboxylase.
d. RuBP using Rubisco, Oxaloacetic acid using PEP carboxylase
e. ATP using PEP carboxylase, PGA using Rubisco.
a
33
New cards
Which of the following statements describes the results of this reaction? 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
a. C6H12O6 is oxidized and O2 is reduced.
b. O2 is oxidized and H2O is reduced.
c. CO2 is reduced and O2 is oxidized.
d. CO2 is reduced and H2O is oxidized.
e. O2 is reduced and CO2 is oxidized.
a. C6H12O6 is oxidized and O2 is reduced.
b. O2 is oxidized and H2O is reduced.
c. CO2 is reduced and O2 is oxidized.
d. CO2 is reduced and H2O is oxidized.
e. O2 is reduced and CO2 is oxidized.
d
34
New cards
The oxygen consumed during aerobic cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event?
a. glycolysis
b. accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain
c. the citric acid cycle
d. the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
e. the phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP
a. glycolysis
b. accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain
c. the citric acid cycle
d. the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
e. the phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP
b
35
New cards
Which of the following is NOT true about Rubisco?
a. It is a carboxylase
b. It is an oxygenase
c. It is a kinase
d. It is the most abundant protein in the world
e. It fixes carbon dioxide into an organic form
a. It is a carboxylase
b. It is an oxygenase
c. It is a kinase
d. It is the most abundant protein in the world
e. It fixes carbon dioxide into an organic form
c
36
New cards
Up to 60% of all medicines used today influence what structures in the cell membrane?
a. Receptor tyrosine-kinases
b. Epinephrine receptors
c. Growth factors
d. G-protein linked receptors
e. Steroid hormone receptors
a. Receptor tyrosine-kinases
b. Epinephrine receptors
c. Growth factors
d. G-protein linked receptors
e. Steroid hormone receptors
d
37
New cards
How does adenylyl cyclase help transmit signals within a cell?
a. Adenylyl cyclase converts cAMP to phosphodiesterase, which then amplifies the signal throughout the cell.
b. Adenylyl cyclase activates a G protein after binding to an extracellular ligand.
c. Adenylyl cyclase activates phospholipase C, releasing IP3and DAG from membrane lipids.
d. Adenylyl cyclase converts ATP to cAMP, which then amplifies the signal throughout the cell.
e. Adenylyl cyclase is responsible for the initial dimerization of R-TK proteins .
a. Adenylyl cyclase converts cAMP to phosphodiesterase, which then amplifies the signal throughout the cell.
b. Adenylyl cyclase activates a G protein after binding to an extracellular ligand.
c. Adenylyl cyclase activates phospholipase C, releasing IP3and DAG from membrane lipids.
d. Adenylyl cyclase converts ATP to cAMP, which then amplifies the signal throughout the cell.
e. Adenylyl cyclase is responsible for the initial dimerization of R-TK proteins .
d
38
New cards
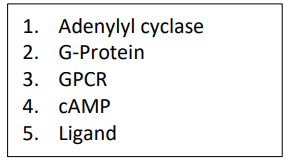
MATCHING: Match the following components related to cell signaling
a. Epinephrine
b. Intergral membrane protein receptor
c. Intergral membrane protein enzyme
d. Peripheral membrane protein that binds GTP
e. Second messenger generated from ATP
a. Epinephrine
b. Intergral membrane protein receptor
c. Intergral membrane protein enzyme
d. Peripheral membrane protein that binds GTP
e. Second messenger generated from ATP
5
3
1
2
4
3
1
2
4
39
New cards
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are found at high levels on various cancer cells. A protein, Herceptin, has been found to bind to an RTK known as HER2 if which of the following is true?
a. If Herceptin is found in the breast lymph nodes of the patient.
b. If HER2, administered by injection, is in sufficient concentration.
c. If the patient's breast cancer cells have detectable HER2.
d. If the patient's genome codes for the HER2 receptor.
e.If the patient's genome codes for the manufacture of Herceptin
a. If Herceptin is found in the breast lymph nodes of the patient.
b. If HER2, administered by injection, is in sufficient concentration.
c. If the patient's breast cancer cells have detectable HER2.
d. If the patient's genome codes for the HER2 receptor.
e.If the patient's genome codes for the manufacture of Herceptin
c
40
New cards

MATCHING: Enzyme Roundup: Cell Signaling
a. Converts ATP to cAMP after G-protein signaling
b. Converts cAMP to AMP; inhibited by caffeine
c. Converts membrane lipids to IP3 and DAG
d. Phosphorylates relay molecules after activation and dimerization
a. Converts ATP to cAMP after G-protein signaling
b. Converts cAMP to AMP; inhibited by caffeine
c. Converts membrane lipids to IP3 and DAG
d. Phosphorylates relay molecules after activation and dimerization
4
1
2
3
1
2
3
41
New cards
The activation of receptor tyrosine kinases (R-TKs) is always characterized by
a. Dimerization and auto-phosphorylation.
b. Activation of adenylyl cyclase
c. A phosphorylation cascade.
d. GTP hydrolysis.
e. Phosphorylation of Protein Kinase A .
a. Dimerization and auto-phosphorylation.
b. Activation of adenylyl cyclase
c. A phosphorylation cascade.
d. GTP hydrolysis.
e. Phosphorylation of Protein Kinase A .
a
42
New cards
If the DNA content of a diploid cell in the G1 phase of the cell cycle is x, then the DNA content of the same cell at metaphase of meiosis I would be
a. 0.25x.
b. 0.5x.
c. x.
d. 2x.
e. 4x.
a. 0.25x.
b. 0.5x.
c. x.
d. 2x.
e. 4x.
d
43
New cards
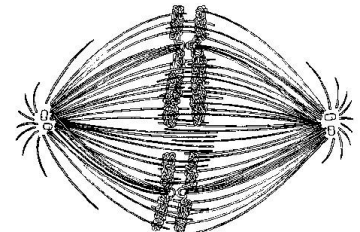
If the cell whose nuclear material is shown at right continues toward completion of mitosis, which of the following events would occur next?
a. cell membrane synthesis
b. spindle fiber formation
c. nuclear envelope breakdown
d. formation of telophase nuclei
e. synthesis of chromatids
a. cell membrane synthesis
b. spindle fiber formation
c. nuclear envelope breakdown
d. formation of telophase nuclei
e. synthesis of chromatids
d
44
New cards
Observations of cancer cells in culture support the hypothesis that cancer cells _____
a. have altered plasma membranes and cytoskeletal proteins
b. have mutations or deletions in tumor suppressors like p53
c. have the ability to stimulate new blood vessel formation
d. do not exhibit density-dependent inhibition of growth
e. all of the above
a. have altered plasma membranes and cytoskeletal proteins
b. have mutations or deletions in tumor suppressors like p53
c. have the ability to stimulate new blood vessel formation
d. do not exhibit density-dependent inhibition of growth
e. all of the above
e
45
New cards
SELECT ALL THAT APPLY: Which of the following occurs in meiosis, but not mitosis?
a. The cells formed have the same combination of genes as found in the initial cell.
b. Homologous chromosomes separate.
c. The nuclear envelope disappears.
d. Sister chromatids undergo disjunction.
e. A spindle apparatus forms.
a. The cells formed have the same combination of genes as found in the initial cell.
b. Homologous chromosomes separate.
c. The nuclear envelope disappears.
d. Sister chromatids undergo disjunction.
e. A spindle apparatus forms.
b
46
New cards
In a plant with a diploid chromosome number of 2n = 46, how many pairs of homologous chromosomes are present in a cell that has just entered Meiosis II? (We want everyone correct!)
a. 0
b. 2
c. 23
d. 46
a. 0
b. 2
c. 23
d. 46
a
47
New cards
Using a microscope to examine the skin cells from a female, it is apparent that each nucleus has two Barr bodies. From this karyotype, it can be concluded that the woman’s chromosomal condition is
a. 47, XXX
b. 46, XX
c. 45, XX
d. 45, XO
e. 47, XXY
a. 47, XXX
b. 46, XX
c. 45, XX
d. 45, XO
e. 47, XXY
a
48
New cards
At what stage of meiosis do cells become haploid?
a. Prophase I
b. Prophase II
c. Telophase I
d. Telophase II
a. Prophase I
b. Prophase II
c. Telophase I
d. Telophase II
c
49
New cards
After Telophase I of meiosis, the chromosomal makeup of each daughter cell is
a. diploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of a single chromatid.
b. diploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
c. haploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of a single chromatid.
d. haploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
e. tetraploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
a. diploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of a single chromatid.
b. diploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
c. haploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of a single chromatid.
d. haploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
e. tetraploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
d
50
New cards
Homologous chromosomes synapse or pair during:
a. anaphase I.
b. prophase I.
c. anaphase II.
d. telophase II.
e. prophase II.
a. anaphase I.
b. prophase I.
c. anaphase II.
d. telophase II.
e. prophase II.
b
51
New cards
Mendel's law of independent assortment has its basis in which of the following events of meiosis?
a. synapsis of homologous chromosomes
b. crossing over in prophase
c. alignment of tetrads at the equator in metaphase
d. separation of homologs at anaphase
e. separation of cells at telophase
a. synapsis of homologous chromosomes
b. crossing over in prophase
c. alignment of tetrads at the equator in metaphase
d. separation of homologs at anaphase
e. separation of cells at telophase
c
52
New cards
In a population with two alleles for cystic fibrosis, C and c, the frequency the recessive allele is 0.6. What percent of the population would be heterozygous carriers for cystic fibrosis if the population is in HardyWeinberg equilibrium?
a. 16%
b. 36%
c. 40%
d. 48%
e. 64%
a. 16%
b. 36%
c. 40%
d. 48%
e. 64%
d
53
New cards
Black fur in mice (B) is dominant to brown fur (b). Short tails (T) are dominant to long tails (t). What fraction of the progeny of crosses BbTt × BBtt will be expected to have black fur and long tails?
a. 1/16
b. 3/16
c. 3/8
d. 1/2
e. 9/16
a. 1/16
b. 3/16
c. 3/8
d. 1/2
e. 9/16
d
54
New cards
SELECT ALL THAT APPLY: Blood Type: What are the probabilities for blood types in the offspring of individuals who both have type AB blood?
a. Type A = 25%
b. Type B = 25%
c. Type AB = 25%
d. Type AB = 50%
e. Type O = 25%
a. Type A = 25%
b. Type B = 25%
c. Type AB = 25%
d. Type AB = 50%
e. Type O = 25%
a, b, d
55
New cards
Epistasis: A black Labrador retriever (BbEe) is crossed with a chocolate Lab (bbEe). In a litter of 16 F1 puppies, what are the likely proportions of black, chocolate or yellow Labs?
a. 9 Black, 3 Chocolate, 4 Yellow
b. 8 Black, 4 Chocolate, 4 Yellow
c. 6 Black, 2 Chocolate, 8 Yellow
d. 6 Black, 6 Chocolate, 4 Yellow
e. 8 Black, 6 Chocolate, 2 Yellow
a. 9 Black, 3 Chocolate, 4 Yellow
b. 8 Black, 4 Chocolate, 4 Yellow
c. 6 Black, 2 Chocolate, 8 Yellow
d. 6 Black, 6 Chocolate, 4 Yellow
e. 8 Black, 6 Chocolate, 2 Yellow
d
56
New cards
Sex linkage: SELECT ALL THAT APPLY: Hemophilia is an X-linked, recessive trait. If a male has hemophilia (Xf Y), and his spouse is heterozygous for blood clotting factors (XF Xf ),
a. There is a 50% chance that their sons will have hemophilia
b. There is a 50% chance that their daughters will have hemophilia
c. There is a 50% chance that their daughters will be carriers for hemophilia
d. All of their daughters will have hemophilia
e. All of their sons will have hemophilia
a. There is a 50% chance that their sons will have hemophilia
b. There is a 50% chance that their daughters will have hemophilia
c. There is a 50% chance that their daughters will be carriers for hemophilia
d. All of their daughters will have hemophilia
e. All of their sons will have hemophilia
a, b, c
57
New cards
Match the following human genetics disorders with their inheritance patterns? Answers (a-e) may be used more than once
i) Marfan’s
a) Autosomal recessive condition
ii) Tay Sachs
b) Autosomal dominant condition
iii) Cystic Fibrosis
c) X-linked condition
iv) Hemophilia
d) Multifactorial condition
v) Achondroplasia
vi) Schizophrenia
vii) Polydactyly
i) Marfan’s
a) Autosomal recessive condition
ii) Tay Sachs
b) Autosomal dominant condition
iii) Cystic Fibrosis
c) X-linked condition
iv) Hemophilia
d) Multifactorial condition
v) Achondroplasia
vi) Schizophrenia
vii) Polydactyly
b
a
a
c
b
d
b
a
a
c
b
d
b
58
New cards
Maize (corn) plants are tall if they have the genotype HH or Hh, and they are short if they have genotype hh. If a tall plant is mated with a short plant as a Test Cross, which outcome would indicate that the tall parent corn plant was heterozygous?
a. The ratio of tall offspring to short offspring is 1:1. (50%:50%)
b. All of the offspring are short. (100%)
c. All of the offspring are tall. (100%)
d. The ratio of tall offspring to short offspring is 3:1 (75%:25%).
a. The ratio of tall offspring to short offspring is 1:1. (50%:50%)
b. All of the offspring are short. (100%)
c. All of the offspring are tall. (100%)
d. The ratio of tall offspring to short offspring is 3:1 (75%:25%).
a
59
New cards
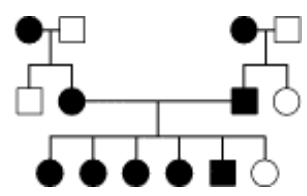
The trait found in the individuals is represented by the shaded symbols. Which of the following patterns of transmission for this gene is/are consistent with this pedigree?
a. autosomal recessive
b. autosomal dominant
c. X-linked recessive
a. autosomal recessive
b. autosomal dominant
c. X-linked recessive
b
60
New cards
Cystic fibrosis affects the lungs, the pancreas, the digestive system, and other organs, resulting in a range of symptoms. Which of the following terms best describes this?
a. incomplete dominance
b. multiple alleles
c. pleiotropy
d. epistasis
e. codominance
a. incomplete dominance
b. multiple alleles
c. pleiotropy
d. epistasis
e. codominance
c
61
New cards
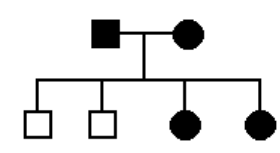
The pedigree at right shows a family with a disease pattern indicated by shaded symbols. Which of the following patterns of transmission for this gene are consistent with this pedigree?
a. autosomal recessive
b. autosomal dominant
c. X-linked recessive
a. autosomal recessive
b. autosomal dominant
c. X-linked recessive
b
62
New cards
A scientist removed the AAC nucleotides at the 3' end of the tRNA corresponding to the amino acid methionine. Which of the following describes the most likely result?
a. tRNA will not form a cloverleaf.
b. The nearby stem end will pair improperly.
c. The amino acid methionine will not be able to bind to the tRNA.
d. The anticodon will not bind with the mRNA codon.
e. The aminoacylsynthetase will not be formed.
a. tRNA will not form a cloverleaf.
b. The nearby stem end will pair improperly.
c. The amino acid methionine will not be able to bind to the tRNA.
d. The anticodon will not bind with the mRNA codon.
e. The aminoacylsynthetase will not be formed.
c
63
New cards
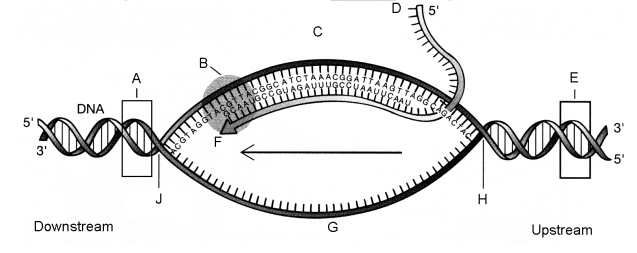
In the figure to the right, mRNA transcription process initiates at the area labeled _______, The messenger RNA transcript in the figure is labeled_____, and the template strand is labeled ______: fill up in the blank
a. E; D; C
b. E G, D
c. A; D; C
d. A; C; D
e. A; E C
a. E; D; C
b. E G, D
c. A; D; C
d. A; C; D
e. A; E C
a
64
New cards
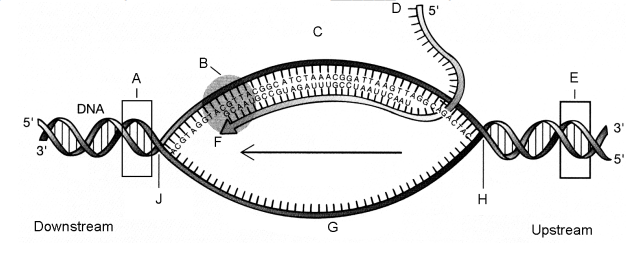
The component labeled B in the figure at right is:
a. DNase.
b. RNA primase.
c. Reverse transcriptase.
d. DNA polymerase.
e. RNA polymerase.
a. DNase.
b. RNA primase.
c. Reverse transcriptase.
d. DNA polymerase.
e. RNA polymerase.
e
65
New cards
The most commonly occurring mutation in people with cystic fibrosis is a deletion of a single codon. This results in
a. a base-pair substitution.
b. a nucleotide mismatch.
c. a frameshift mutation.
d. a polypeptide missing an amino acid.
e. a nonsense mutation.
a. a base-pair substitution.
b. a nucleotide mismatch.
c. a frameshift mutation.
d. a polypeptide missing an amino acid.
e. a nonsense mutation.
d
66
New cards
A part of an mRNA molecule with the following sequence is being read by a ribosome: 5' CCG-ACG 3' (mRNA). The dipeptide that will form will be
a. cysteine-alanine.
b. proline-threonine.
c. glycine-cysteine.
d. alanine-alanine.
e. threonine-glycine.
a. cysteine-alanine.
b. proline-threonine.
c. glycine-cysteine.
d. alanine-alanine.
e. threonine-glycine.
b
67
New cards
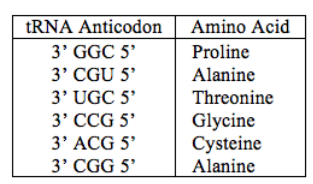
The anticodon loop of a tRNA that will complement this mRNA: 5’ CCG 3’ is
a. 3’GGC 5’
b. 5’GGC 3’
c. 5’ACG 3’
d. 5’UGC 3’
e. 3’UGC 5’
a. 3’GGC 5’
b. 5’GGC 3’
c. 5’ACG 3’
d. 5’UGC 3’
e. 3’UGC 5’
a
68
New cards
When translating secretory or membrane proteins, ribosomes are brought to the ER membrane by
a. a specific characteristic that identifies it as a “bound” ribosome itself.
b. a signal-recognition particle that brings ribosomes to a receptor protein in the ER membrane.
c. moving through a specialized channel of the nucleus.
d. a chemical given off by the ER.
e. a signal sequence of RNA that precedes the start codon of the message
a. a specific characteristic that identifies it as a “bound” ribosome itself.
b. a signal-recognition particle that brings ribosomes to a receptor protein in the ER membrane.
c. moving through a specialized channel of the nucleus.
d. a chemical given off by the ER.
e. a signal sequence of RNA that precedes the start codon of the message
b
69
New cards
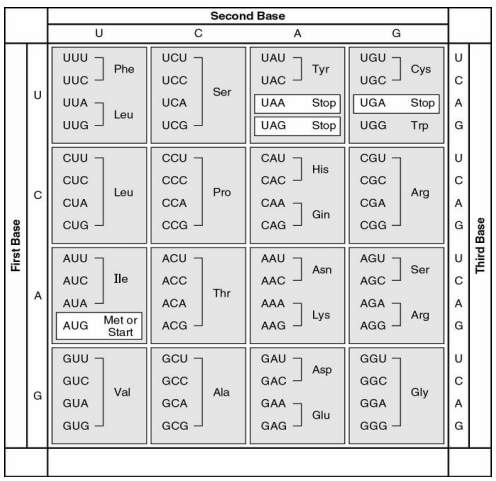
What amino acid sequence will be generated, based on the following mRNA codon sequence? 5' AUG-UCU-UCG-UUA-UCC-UUG 3'
a. met-arg-glu-arg-glu-arg
b. met-glu-arg-arg-glu-leu
c. met-ser-leu-ser-leu-ser
d. met-ser-ser-leu-ser-leu
e. met-leu-phe-arg-glu-glu
a. met-arg-glu-arg-glu-arg
b. met-glu-arg-arg-glu-leu
c. met-ser-leu-ser-leu-ser
d. met-ser-ser-leu-ser-leu
e. met-leu-phe-arg-glu-glu
d
70
New cards
RNA molecules with enzymatic functions (such as peptidyltransferase) are called __________.
a. RNA polymerases
b. transfer RNAs
c. polysomes
d. ribozymes
e. aminoacyl-RNA synthetases
a. RNA polymerases
b. transfer RNAs
c. polysomes
d. ribozymes
e. aminoacyl-RNA synthetases
d
71
New cards
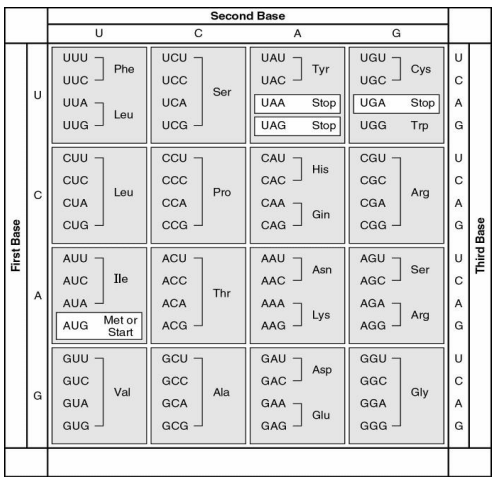
Using the Codon Chart, match the designation with the following 3 mutations
a. GAA à GUA (Sickle Cell Anemia)
x. Silent Mutation
b. UGC à UGA (Phenylketoneuria, or PKU)
y. Missense Mutation c. AAU à AAC (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism, or SNP)
z. Nonsense Mutation
a. GAA à GUA (Sickle Cell Anemia)
x. Silent Mutation
b. UGC à UGA (Phenylketoneuria, or PKU)
y. Missense Mutation c. AAU à AAC (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism, or SNP)
z. Nonsense Mutation
y
z
x
z
x
72
New cards
The 5’ end of a DNA strand always has a free ______ group while the 3’ end always has a free _______ group.
a. phosphate; hydroxyl
b. hydroxyl; phosphate
c. phosphate; amine
d. amine; phosphate
e. phosphate; acidic
a. phosphate; hydroxyl
b. hydroxyl; phosphate
c. phosphate; amine
d. amine; phosphate
e. phosphate; acidic
a
73
New cards
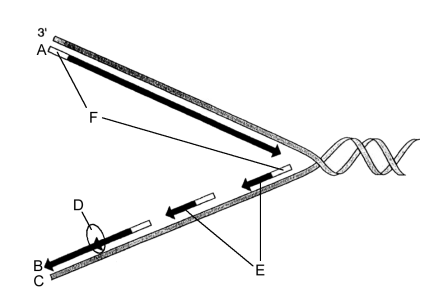
Match the following aspects of DNA replication (A-F) to their correct descriptions
i) Site of action of DNA Ligase
ii) Leading Strand
iii) Okasaki Fragments
iv) Lagging Strand
v) RNA primers
vi) DNA Template Strand
i) Site of action of DNA Ligase
ii) Leading Strand
iii) Okasaki Fragments
iv) Lagging Strand
v) RNA primers
vi) DNA Template Strand
D
A
E
B
F
C
A
E
B
F
C
74
New cards
SELECT ALL THAT APPLY: The human Crystalline gene is contained in the genome of every cell of a human, but is only expressed (made into protein) in the lens of the eye. This is because
a. The crystalline gene is spliced out of the genome early in development in all cells in the body except lens cells
b. Activator proteins (transcription factors) that bind to regulatory regions of the crystalline gene are only found in the lens cells
c. The crystalline gene has specific promoter and enhancer control elements that bind to only lens-specific activators
a. The crystalline gene is spliced out of the genome early in development in all cells in the body except lens cells
b. Activator proteins (transcription factors) that bind to regulatory regions of the crystalline gene are only found in the lens cells
c. The crystalline gene has specific promoter and enhancer control elements that bind to only lens-specific activators
b
75
New cards
Which of the following is the attachment site for RNA polymerase?
a. the small subunit of the ribosome
b. the TATAAA box
c. the enhancer
d. the Upstream Promoter Elements
e. the AUG codon
a. the small subunit of the ribosome
b. the TATAAA box
c. the enhancer
d. the Upstream Promoter Elements
e. the AUG codon
b
76
New cards
Upstream (proximal) promoter elements in eukaryotes are:
a. nucleotide sequences that act as binding sites for RNA polymerase.
b. nucleotide sequences that regulate the efficiency of transcription initiation.
c. nucleotide sequences that contain the TATA box.
d. proteins that are required for RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter.
e. proteins that inhibit RNA polymerase binding to the promoter.
a. nucleotide sequences that act as binding sites for RNA polymerase.
b. nucleotide sequences that regulate the efficiency of transcription initiation.
c. nucleotide sequences that contain the TATA box.
d. proteins that are required for RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter.
e. proteins that inhibit RNA polymerase binding to the promoter.
b
77
New cards
Which of the following is most likely to be ubiquitinated (ie: tagged with ubiquitin)?
a. a cyclin that usually acts in G1, now that the cell is in G2
b. a cell surface protein that requires transport from the ER
c. an mRNA that is leaving the nucleus to be translated
d. a regulatory protein that requires sugar residues to be attached
e. an mRNA produced by an egg cell that will be retained until after fertilization
a. a cyclin that usually acts in G1, now that the cell is in G2
b. a cell surface protein that requires transport from the ER
c. an mRNA that is leaving the nucleus to be translated
d. a regulatory protein that requires sugar residues to be attached
e. an mRNA produced by an egg cell that will be retained until after fertilization
a
78
New cards
Alternative RNA splicing
a. is a mechanism for increasing the rate of transcription.
b. can allow the production of proteins of different sizes from a single mRNA.
c. can allow the production of similar proteins from different RNAs.
d. increases the rate of transcription.
a. is a mechanism for increasing the rate of transcription.
b. can allow the production of proteins of different sizes from a single mRNA.
c. can allow the production of similar proteins from different RNAs.
d. increases the rate of transcription.
b
79
New cards
In eukaryotes, histone methylation ________, while histone acetylation __________.
a. marks genes for destruction, promotes transcription
b. promotes transcription, represses transcription
c. imprints genes; inactivates genes
d. inactivates genes; reduces the size of the genome
e. represses transcription, promotes transcription
a. marks genes for destruction, promotes transcription
b. promotes transcription, represses transcription
c. imprints genes; inactivates genes
d. inactivates genes; reduces the size of the genome
e. represses transcription, promotes transcription
e
80
New cards
In human females, one X chromosome per cell is randomly inactivated during early embryonic development, forming a Barr Body. Much of the DNA in this chromosome is then in the form of
a. Introns
b. Chromosome puffs
c. Heterochromatin
d. Euchromatin
e. Tetrads
a. Introns
b. Chromosome puffs
c. Heterochromatin
d. Euchromatin
e. Tetrads
c
81
New cards
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) both function to "silence" genes, by,
a. Causing chromatin de-acetylation and tight winding of the DNA
b. Acting as a release factor to cause ribosome disassembly
c. Activating the Dicer enzyme to rapidly degrade the mRNA
d. Binding to complementary RNA sequences to prevent translation
e. Binding to complementary DNA sequences to prevent transcription
a. Causing chromatin de-acetylation and tight winding of the DNA
b. Acting as a release factor to cause ribosome disassembly
c. Activating the Dicer enzyme to rapidly degrade the mRNA
d. Binding to complementary RNA sequences to prevent translation
e. Binding to complementary DNA sequences to prevent transcription
d
82
New cards
Which of the following occurs in eukaryotic, but not prokaryotic, gene expression?
a. mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA are transcribed.
b. RNA polymerase binds to the promoter.
c. A poly-A tail is added to the 3' end of an mRNA and a cap is added to the 5' end.
d. Transcription can begin as soon as translation has begun even a little.
e. RNA polymerase requires a primer to elongate the molecule.
a. mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA are transcribed.
b. RNA polymerase binds to the promoter.
c. A poly-A tail is added to the 3' end of an mRNA and a cap is added to the 5' end.
d. Transcription can begin as soon as translation has begun even a little.
e. RNA polymerase requires a primer to elongate the molecule.
c
83
New cards
Muscle cells differ from nerve cells mainly because they:
a. Express different genes.
b. Contain different genes.
c. Use tissue-specific tRNAs to create different amino acid sequences from the same gene
d. Have unique ribosomes.
e. Have different chromosomes.
a. Express different genes.
b. Contain different genes.
c. Use tissue-specific tRNAs to create different amino acid sequences from the same gene
d. Have unique ribosomes.
e. Have different chromosomes.
a
84
New cards
The functioning of enhancers is an example of:
a. Transcriptional control of gene expression.
b. A post-transcriptional mechanism to regulate mRNA.
c. The stimulation of translation by initiation factors.
d. Post-translational control that activates certain proteins.
e. How efficiently the mRNA can bind to the ribosome.
a. Transcriptional control of gene expression.
b. A post-transcriptional mechanism to regulate mRNA.
c. The stimulation of translation by initiation factors.
d. Post-translational control that activates certain proteins.
e. How efficiently the mRNA can bind to the ribosome.
a
85
New cards
Viruses that attack bacteria are called:
a. phages.
b. bacteroids
c. prions.
d. virons.
e. viroids
a. phages.
b. bacteroids
c. prions.
d. virons.
e. viroids
a
86
New cards
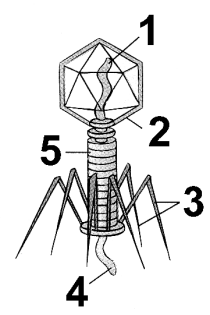
In the bacteriophage shown above, the functions of the structures labeled 2 and 3 are
a. 2= protection of the genetic material, 3= locomotion.
b. 2= mate recognition, 3= attachment to a host cell
c. 2= protection of the genetic material, 3= replication.
d. 2= to take over host cell mechanisms, 3= attachment to a host cell.
e. 2= protection of the genetic material, 3= attachment to a host cell
a. 2= protection of the genetic material, 3= locomotion.
b. 2= mate recognition, 3= attachment to a host cell
c. 2= protection of the genetic material, 3= replication.
d. 2= to take over host cell mechanisms, 3= attachment to a host cell.
e. 2= protection of the genetic material, 3= attachment to a host cell
e
87
New cards
Retroviruses like the HIV virus differ from other viruses by:
a. Using the enzyme reverse transcriptase to copy their RNA into DNA.
b. the shape of their capsid.
c. the way they infect their host cells.
d. the sugar coating on their capsids.
e. lytically destroying their hosts.
a. Using the enzyme reverse transcriptase to copy their RNA into DNA.
b. the shape of their capsid.
c. the way they infect their host cells.
d. the sugar coating on their capsids.
e. lytically destroying their hosts.
a
88
New cards
All of the following are DNA viruses except:
a. The Herpes virus that causes cold sores
b. The Influenza virus that causes the ‘flu.
c. The Pox-viruses that cause chicken pox
d. The Human Papilloma virus that causes cervical cancer
e. The Parvoviruses that cause the common cold
a. The Herpes virus that causes cold sores
b. The Influenza virus that causes the ‘flu.
c. The Pox-viruses that cause chicken pox
d. The Human Papilloma virus that causes cervical cancer
e. The Parvoviruses that cause the common cold
b
89
New cards
During the lytic life cycle of phages, which of the following occurs?
a. The phage capsid fuses with the host cell, allowing the viral genome to be inserted into the host nucleus.
b. The host cell often dies, releasing many newly assembled copies of the virus.
c. The host cell usually lives and secretes the copies of the virus.
d. The phage enters the host cell intact during infection.
e. The host cell lives, with the viral genome becoming incorporated into the host cell’s own genome
a. The phage capsid fuses with the host cell, allowing the viral genome to be inserted into the host nucleus.
b. The host cell often dies, releasing many newly assembled copies of the virus.
c. The host cell usually lives and secretes the copies of the virus.
d. The phage enters the host cell intact during infection.
e. The host cell lives, with the viral genome becoming incorporated into the host cell’s own genome
b
90
New cards
MATCHING Match the RNA viruses with the diseases they cause
a. Polio and Hepatitis A
w. Filovirus
b. West Nileand Hepatitis C
x. Picornaviruses
c. Measles and Mumps
y. Flavivirus
d. Ebola and other hemorrhagic fevers
z. Paramyxoviruses
a. Polio and Hepatitis A
w. Filovirus
b. West Nileand Hepatitis C
x. Picornaviruses
c. Measles and Mumps
y. Flavivirus
d. Ebola and other hemorrhagic fevers
z. Paramyxoviruses
x
y
z
w
y
z
w
91
New cards
The Prion Hypothesis (Dr. Stanley Pruissner) states that
a. Mad cow disease is caused by eating beef tainted with abnormally folded prion proteins.
b. Cooking beef or lamb infected with prion proteins will destroy the prions, making the meat safe to eat.
c. Kuru, a transmissible spongiform encephalopathy in humans, can be caused by the religious practice of ritual cannibalism.
d. Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies result from the conversion of normal PrP-c to an abnormally folded PrP-sc state
e. Prion particles infect cells of the brain and redirect the cell’s protein synthesis machinery to replicate new prion particles in the neurons responsible for memory
a. Mad cow disease is caused by eating beef tainted with abnormally folded prion proteins.
b. Cooking beef or lamb infected with prion proteins will destroy the prions, making the meat safe to eat.
c. Kuru, a transmissible spongiform encephalopathy in humans, can be caused by the religious practice of ritual cannibalism.
d. Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies result from the conversion of normal PrP-c to an abnormally folded PrP-sc state
e. Prion particles infect cells of the brain and redirect the cell’s protein synthesis machinery to replicate new prion particles in the neurons responsible for memory
d
92
New cards
Prion diseases of humans include:
a. Kuru.
b. Scrapie.
c. Mad Cow Disease.
d. Variant Creutfeld-Jacob disease (vCJD).
e. A and D
a. Kuru.
b. Scrapie.
c. Mad Cow Disease.
d. Variant Creutfeld-Jacob disease (vCJD).
e. A and D
e
93
New cards
Which of the following characteristics, structures, or processes is common to bacteria, viruses and prions?
a. Proteins
b. Cell division
c. Nucleic acids
d. Ribosomes
e. Metabolism
a. Proteins
b. Cell division
c. Nucleic acids
d. Ribosomes
e. Metabolism
a
94
New cards
Which of the recombinant DNA drugs is incorrectly matched with its indication (the disease it is prescribed to treat)?
a. Humulin (Lilly): Diabetes (Insulin)
b. Epogen (Amgen): Anemia (Erythropoetin)
c. Neupogen (Amgen): Multiple sclerosis (interferon)
d. Activase/TNKase (Genentech): AMI - Acute myocardial infarction (heart attack)
e. Regranex (Novartis): Diabetic foot ulcers (PDGF)
a. Humulin (Lilly): Diabetes (Insulin)
b. Epogen (Amgen): Anemia (Erythropoetin)
c. Neupogen (Amgen): Multiple sclerosis (interferon)
d. Activase/TNKase (Genentech): AMI - Acute myocardial infarction (heart attack)
e. Regranex (Novartis): Diabetic foot ulcers (PDGF)
c
95
New cards
Where would Biotech be without these scientists? Briefly describe the contribution (experiment, technique) of these scientists in the timeline of Biotechnology
i) Ian Wilmut
a. First Human Gene Therapy
ii) Jennifer Doudna
b. Dideoxy DNA Sequencing
iii) W. French Anderson
c. Isolation of Bacterial Plasmids
iv) Shinya Yamanaka
d. Cloning of Dolly the Sheep
v) Stanley Cohen
e. Derivation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells
vi) Kary Mullis
f. Whole Genome Shotgun Sequencing
vii) Herb Boyer
g. CRISPR Cas9
viii) James Thompson
h. Isolation of Restriction Enzymes, Founder of Genentech
ix) Fred Sanger
i. Polymerase Chain Reaction
x) Craig Venter
j. Induced Pleuripotent Stem Cells
i) Ian Wilmut
a. First Human Gene Therapy
ii) Jennifer Doudna
b. Dideoxy DNA Sequencing
iii) W. French Anderson
c. Isolation of Bacterial Plasmids
iv) Shinya Yamanaka
d. Cloning of Dolly the Sheep
v) Stanley Cohen
e. Derivation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells
vi) Kary Mullis
f. Whole Genome Shotgun Sequencing
vii) Herb Boyer
g. CRISPR Cas9
viii) James Thompson
h. Isolation of Restriction Enzymes, Founder of Genentech
ix) Fred Sanger
i. Polymerase Chain Reaction
x) Craig Venter
j. Induced Pleuripotent Stem Cells
d
g
a
j
c
i
h
e
b
f
g
a
j
c
i
h
e
b
f
96
New cards
In the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique, a heating phase and a cooling phase alternate in cycles. An original sample of DNA would have to pass through how many total cycles to amplify the DNA \~1 billion times? (What about 2 billion times? What about 1 trillion times?)
a. 20
b. 21
c. 30
d. 31
e. 40
a. 20
b. 21
c. 30
d. 31
e. 40
c
97
New cards
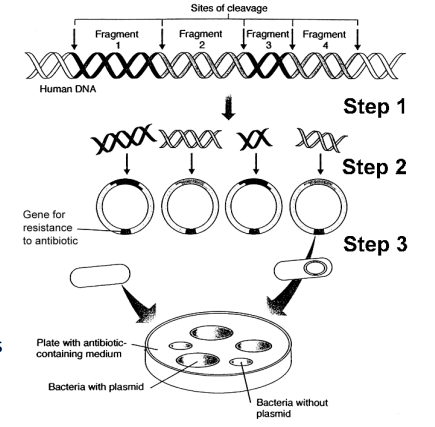
This figure shows the steps in cloning the human insulin gene. What process or enzyme was used for Step 1?
a. ligase
b. transcriptase
c. a restriction enzyme
d. RNA polymerase
e. DNA polymerase
a. ligase
b. transcriptase
c. a restriction enzyme
d. RNA polymerase
e. DNA polymerase
c
98
New cards
Gene Therapy treatments with new drugs like Kymriah and Yescarta (select all that apply)
a. Provide a safer bone marrow transplant procedure using matched donors
b. Are the first FDA-approved drugs for personalized immunotherapy to treat specific leukemias
c. Involve the use of a genetically engineered Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell to recognize proteins like CD19 on cancer cells
d. Require the formation of a blastocyst that is then used for gene editing
e. Can cure autoimmune disorders like diabetes and multiple sclerosis
a. Provide a safer bone marrow transplant procedure using matched donors
b. Are the first FDA-approved drugs for personalized immunotherapy to treat specific leukemias
c. Involve the use of a genetically engineered Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell to recognize proteins like CD19 on cancer cells
d. Require the formation of a blastocyst that is then used for gene editing
e. Can cure autoimmune disorders like diabetes and multiple sclerosis
b, c
99
New cards
Match the mAb (monoclonal Antibody) drug with the disease it is intended to treat
a. Herceptin
(1) RSV (Respiratory syncytial Virus
b. Rituxin
(2) Cancer (anti-VEGF, anti angiogenesis)
c. Enbrel
(3) HER-2+ breast cancer
d. Synagis
(4) CD20+ Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma
e. Avastin
(5) T-cell autoimmune diseases like Rheumatoid arthritis and Psoriasis
a. Herceptin
(1) RSV (Respiratory syncytial Virus
b. Rituxin
(2) Cancer (anti-VEGF, anti angiogenesis)
c. Enbrel
(3) HER-2+ breast cancer
d. Synagis
(4) CD20+ Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma
e. Avastin
(5) T-cell autoimmune diseases like Rheumatoid arthritis and Psoriasis
3
4
5
1
2
4
5
1
2
100
New cards
In the pGLO lab, how could you confirm that a transformed cell was expressing the bla gene?
a. It would fluoresce green
b. It would grow on Amp plates
c. It would not grow on ‘LB only’ plates
d. It would only grow on ‘LB only’ plates
a. It would fluoresce green
b. It would grow on Amp plates
c. It would not grow on ‘LB only’ plates
d. It would only grow on ‘LB only’ plates
b