Module 2: Sound Absorption, Reflection and Transmission
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Sound Absorption
the measure of the amount of energy removed from the sound wave as the wave passes through a given thickness of material.
Marble
— surfaces in churches creates a very reflective sound effect on users. Reverberation is too long that it affects the quality of sound.
Wood
aside from its beauty, it produces a very natural sound effects especially in residential buildings.
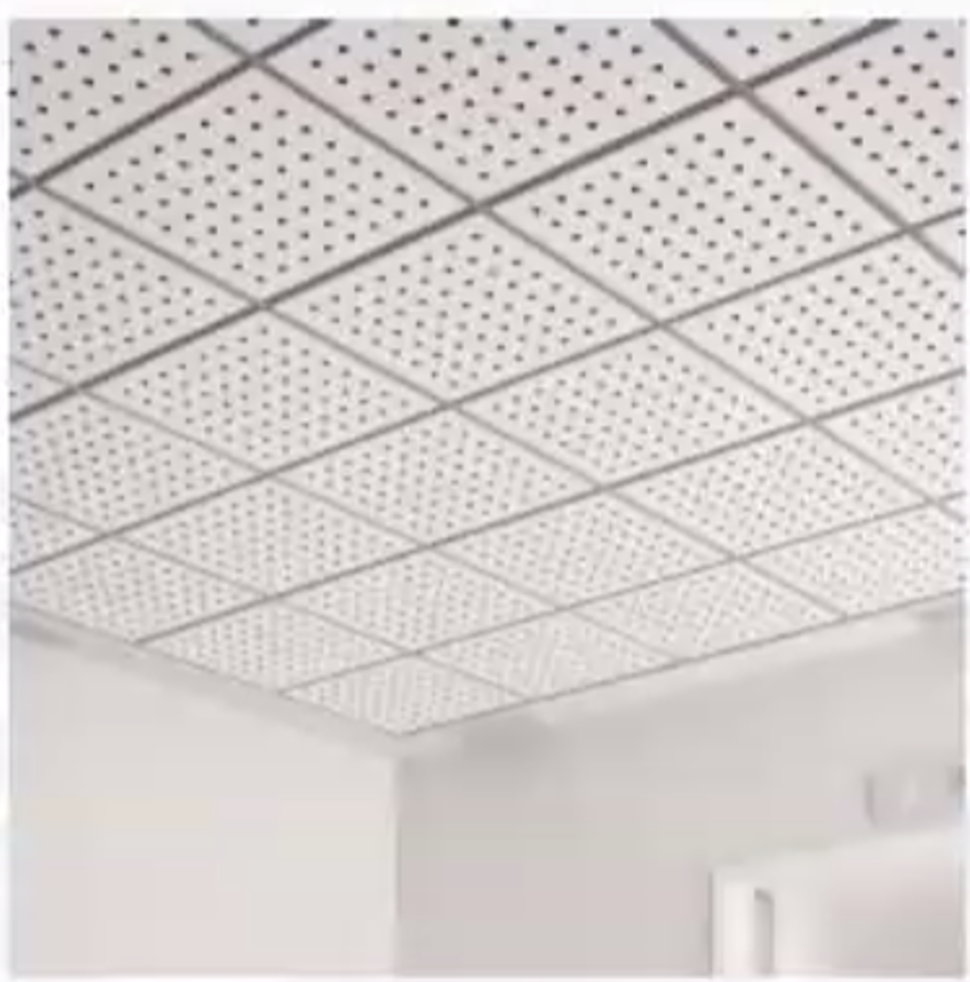
Acoustic ceiling boards
For best quality sound, we use —— (usually perforated gypsum boards or equal). This material can have a very large amount of sound absorption

Material’s Mass Density
To the same porous material, its ——- increases, the absorption efficiency to high frequency sound decreases
Material’s Thickness
Increasing the —— can enhance the absorption to low frequency sound, but it makes little difference to high frequency sound
Material’s Porosity
more pores in smaller sizes increases the sound absorption effect.
weak
Materials with bigger pores has —— sound absorption effect.
direct sound from source
indirect reflections from adjacent surfaces and objects
Sound in buildings is composed of:
transmission, absorption, or reflection of sound energy
The interaction of sound with a building component can result in ——- of sound energy
Sound Insulation
known as sound absorption
Sound Insulation
one of the most important features in building materials, with the purpose to maintain a living comfort, reducing noise and sound reflected by surfaces
Insulation materials
applied to walls to control their acoustic performance
Acoustic absorbers
have been extensively used in noise control to minimize the sound reflected by surfaces and have the ability to contrast sound transmission
Sound Reflection
Waves are reflected when the density of matter is too high for the wave to pass through or be absorbed
reflected
waves are —— when the density of matter is too high for the wave to pass through or be absorbed.
because of that, the wave is — (or bounces off) and then moves in a different direction than it was originally traveling
echo or
reverberation
reflection of sound waves off of surfaces can lead to one of two phenomena:
echo
when sound waves are reflected, there is often an —- because the sound wave is traveling in various direction bouncing off matter
reverberation
the process of a sound wave repeatedly reflecting in a space
Echo
sound waves which have been reflected back to a listener with sufficient magnitude and time delay
echo
occur when a reflected sound wave reaches the ear more than 0.1 seconds after the original sound wave was heard
died out
if the elapsed time between the arrivals of the two sound waves is more than 0.1 seconds, then the sensation of the first sound will have —-
echo
the arrival of the second wave will be perceived as a second sound rather than the prolonging of the first sound
reverberation
the persistent of sound in an enclosed space as a result of repeated reflection or scattering of sound
Reverberation
often occurs in a small room with height, width, and length dimensions of approximately 17 meters or less
prolonged
If a reflected sound wave reaches the ear within 0.1 seconds of the initial sound, then it seems to the person that the sound is ——
reverberations
The reception of multiple reflection off of walls and ceilings within 0.1 seconds of each other causes ——— —the prolonging of sound
Flutter Echo
occur between hard parallel walls where the sound repeatedly bounces back and forth
Flutter Echo
Whispering Gallery
If you stand facing the wall in any of the four corners, and whisper, your words will be carried to the corner diagonally across from you and can be heard by someone in that corner

Long Reflective Hallways

Flutter Echo in a modern plastered room
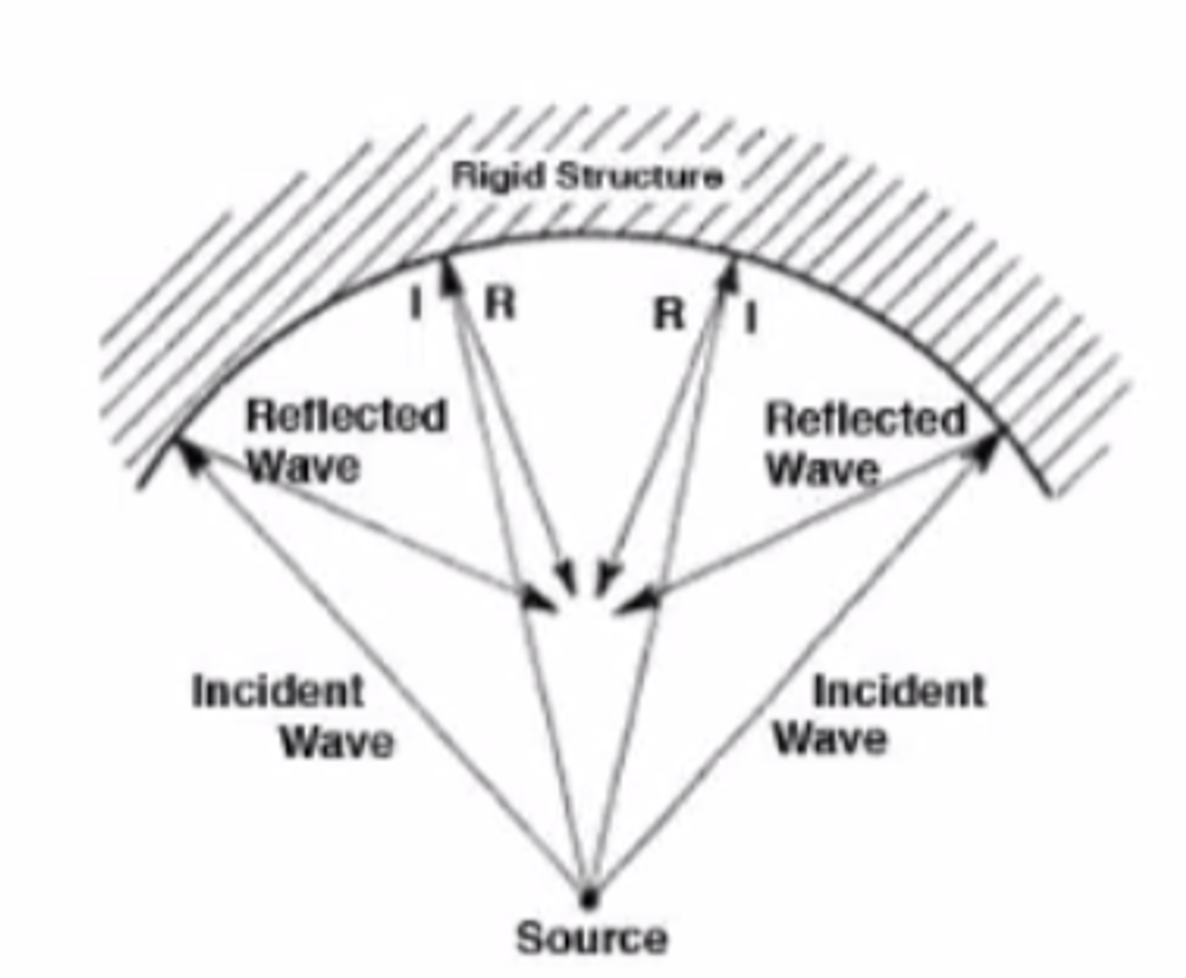
Concave Reflector
Focuses Reflections
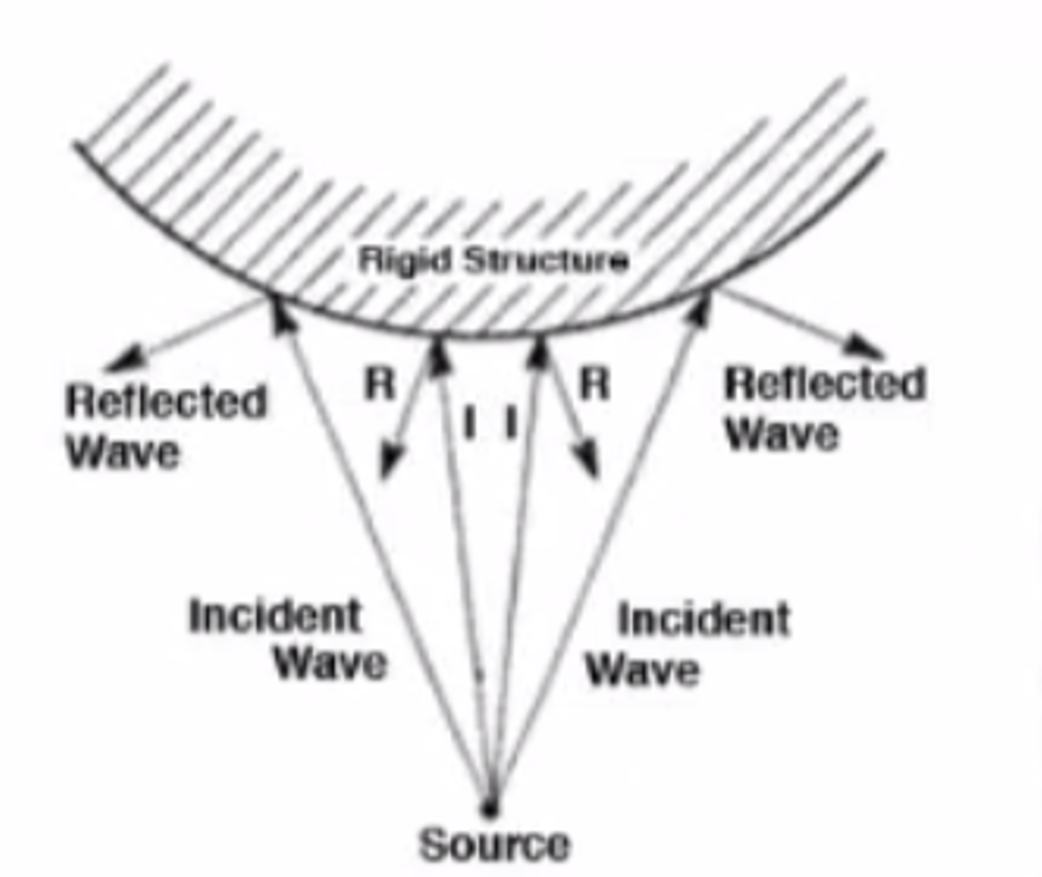
Convex Reflector
Scatters Reflections
Attenuation and sound insulation
descriptive terms used to denote performance in reducing sound transmission
Transmission loss
____ of a wall or a floor is a number of decibels by which the level of air-borne sound is decreased in passing through the structure
Air-borne transmission
produced by sources that radiate directly into the air
Impact transmission
produced by a direct mechanical impact such as footsteps, a slam
Sound Transmission Class
a single number used to characterize the air-borne isolation properties of a partition
Sound Transmission Class
determined from the measure Transmission Loss of a partition at different frquencies.
Mass Law
the degree of variation of the energy of sound transmission through a partition will depend first of all on the mass or weight or unit area of a panel. (Porous materials_
Sound absorption coefficient
defined as the ratio of the sound energy absorbed by a surface to the sound energy incident on that surface, taking values between 0 and 1
Sound absorption coefficient
The ratio of the absorbed sound energy to the incident energy
Noise reduction coefficient
the descriptor most often used