Mental Health Exam #1 part 1
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
What were the beliefs around mental illness before 800 BCE?
It was devine/demonic
Religions were involved
What is the importance of Hippocrates in regards to mental health?
He was one of the first to study mental disorders
What is the importance of Aristotle in regards to mental health?
He connected the relationship of physical disorders to mental disorders
What was Trephination?
It was used to treat mental health disorders a long time ago
It involved cutting a piece of the skull out and leaving it open so the bad spirits could leave
What is the importance of St. Augustine in regards to mental health?
They proposed that mental illness was caused by demons
What were Asylums originally run by?
Religious orders
What was the importance of Englads hospital of St. Mary of Bethlehem?
It was VERY inhumane
Patients were abused and tours were given for entertainment
What is the importance of Benjamin Franklin in regards to mental health?
He founded the first hospital for the mentally ill
What is the importance of Benjamin Rush in regards to mental health?
Is considered the father of American Psychiatry
Showed that the psychicians/patient relationship can be curative (nurses can be healing!)
Faulty blood curculation to the brain
What is the importance of Borthea Dix in regards to mental health?
Wanted humame, but isolated treatment
T/F: Scientific racism was used to justify slavery and is still evident in healthcare today
TRUE!
What is Drapetomania?
Treatable “mentall illness” that caused black slaves to flee captivity (considered this until 1914)
How was Schizophrenia impacted by scientific racism?
It started out as a neurosis of middle class houswives
Became a “violent social disease”, now black men are 4 times more likely to be diagnosed with this and it is seen as scary.
What did early mental health instisutions in Iowa believe in regards to treatment?
Keep the patients alive and dont let them hurt eachother
Self contained communities where patients work supported themselves
Minimal to no oversight- male nurses
What treatments were used in the early institutions?
Lobotomies
ECTs (no sedation)
Insulin shock therapy
Ice water therapy
Restrains and seclusion
How did psychosocial rehabilitation evolve?
Many mentally ill pts were in public hospitals
Outpatient clinics were created
Chlorpromazine and lithium were introduced as anitpsychotcis (big change!)
Joint commision of mental health and community mental health centers
T/F: Iowa is ranked in the top 10 for best mental health
FALSE!
Iowa has been ranked one of the WORST states in the nation for mental health
What needs fixing in regards to mental health in iowa now?
Lack of treatments space available and lack of providers both inpatient and outpatients
What are intensive outpatient programs?
The patient comes in, 9-5 therapy, then goes home
What is the Crisis Stabilization Unit?
Keeps patients safe in times of crisis while nurses set up what they need. Intended for short term
What is the Housing First Initiative in Iowa City?
Gives people housing which increases their liklihood to recieve treatment for mental health.
Homelessness + stess= may turn to substances
What is the GuideLink Center?
Mental health access center
Sobering unit here so they can safely come off alcohol and come home
What are the myths around mental illness?
Mentally ill people always violate social norms
People without mental illness are always logical and rational
Mentally ill people have violent tendencies and are dangerous
T/F: Mental illness is a physical illness
True! The brain is an organ
T/F: Awareness had grown so much in mental health and there is no longer prejudice
False! Awareness has grown so it is less stigmatied, but there is still prejudice.
_______ safety before emotional safety
Physical
What are the seven signs of mental wellness
Happiness
Control over behavior
Apprasial of reality
Effectiveness in work
Health self-concept
Satisfying relationships
Effective coping strategies
What is the DSM-5 used for?
This is the main tool used to diagnosed mental disorders
What does the DSM-5 say about mental disorders?
Mental disroders are considered a manifestation of a behavioral, psychiological, and/or biological dsyfunction of the individual
Psychological is hard to determine besides subjective reports, no way to measure biological in a living person, vast majority is behavioral.
The term _________ should be used rather than “average” or “normal”
Baseline (it is the general bell average)
Mild to Moderate
Lifes normal up and downs
Movements is often mild to moderate then back to baseline with no or some treatment
Usually pretty functional
Ex: Psychological responses to illness, greiving a loss
Moderate to Severe
The patient goes back and forth, these are chronic illnesses that arent necessarily curable but treatable
Ex: Anxiety disorders, Personality disorders, Eating disorders
Severe to Psychotic
Movement is chronic and often progressive
Generally not curable but working on management
Ex: Mood disorders (bipolar, depression), thought disorders (schizophrenia), cognitive disorders (dementia)
What is Psychosis?
A detachment from reality. It can have 2 different symptoms
Hallucinations
Delusions
Hallucinations vs Delusions
Hallucinations are sensory based
Delusions are are thought processes (ex: pt thinks they are jesus)
________% of the adult population had any mental illlness in 2020
21%
Do more men or more women have any mental illness?
More women (however it is probably more equal but it is less socially acceptable for men to express this so they may be less likely to report)
The prevalence of any mental illness is highest from the ages of _______ to _______ and decreases with________.
18-25 years old
the older population
Any mental illness is highest in what demographic (besides age)?
Multiracial people
What is the average delay between onset of symptoms and treatment?
10 years!
How does the prevalence of severe mental illness compare to any mental illness?
The same
Higher in women than men
Highest in 18-25 year olds
When does the onset of a severe mental illness (such as psychotic disroders, bipolar, etc) occur?
Onset is often in the early 20s
Generally the more severe an illness the ________ common it is
Less
What are the influences on mental health?
Biology (bipolar is one of the most inherited illnesses)
Support systems
Family influences (different dynamics)
Developmental events (trauma at young age)
Cultural beliefs and values (is mental health discussed?)
Health practices
Negative influences
What are the influences of episodic mental illness?
A combination of biology and other influences (environmental)
Ex: panic attacks, depression, etc
What are the influences of severe and chronic mental illness?
Biology is usually the most influential factor
What must nurses know in regards to mental health?
DSM-5
Recognize the signs/symptoms
Possible influences
Techniques to assess, diagnose, and intervene for disorders
Adapt for the individual
Erickson
8 stages of development (personality develops throughout life and a failure in one stage can be recified at another stage)
Helps determine what types of interventions are most likely to be effective (different interventions based on their stage in development)
Trust vs mistrust
0-1.5 years
Connecting with others
Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt
1.5-3 years
Learnig to be independent
Initiative vs. Guilt
3-5 years
Industry vs. Inferiority
5-12 years
taking initiative in things, or are they dependent on others and feel lesser than
Identity vs. Role Confusion
12-18 years
Period of time where we have adult impulses and child frontal lobes, messy!
Intimacy vs. Isolation
18-40 years
Generativity vs. Stagnation
40-65 years
Ego Integrity vs Despair
65+ years
What are Maslows Hierarchy of needs?
If the lower needs are not met, other higher up needs may not be met
Ex: If someone is having a panic attack, they probably are not concerned about other things until the problem is resolved
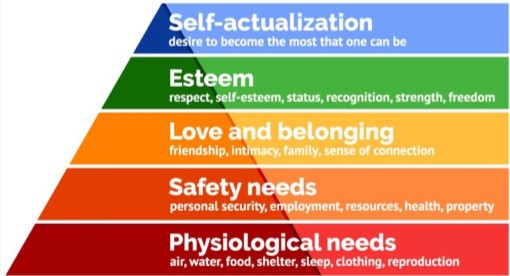
What was Maslows Theory and how did it relate to nursing?
Emphasis on human potential and the patients strengths
Prioritizing nursing actions in the nurse-patient relationship
Focus on physiological and safety needs first when patients are acutely ill
What is Peplau’s influence on nursing?
Interpersonal Relations in Nursing (book)
Changes nurses from being the “custodians” in healthcare to doing work to help the patient heal—> Nurse using theraputic communication is a DIRECT means to help them recover
Orientation phase of the nurse vs patient
Nurse: Introduce self, set contract, build trust, set goals, assess patient
Patient: Meet nurse, agree to contract, understand expectations, participate in goal setting
Working phase of the nurse vs patient
Nurse: Maintain relationship, facilitate expression
Foster change
Patient: Examine own worldview, test new behaviors, try alternate solutions
Termination phase of the nurse vs patient
Nurse: Summarize achievements, validate expereincee, maintain limits
Patient: Examine thoughts, discuss plans, accept termination
Neurons
Responds to stimuli and release chemicals called neurotransmitters
Presynaptic neuron —> synapse —→ postsynaptic neuron
How are neurotransmitters destroyed
Enzymes
Reuptake
How does mental illness relate to neurotranmitters?
Many hypothesis that mental illness has to do with low/high levels of different neurotranmitters however it is not that simple
Other things can cause mental illness, its not consistent, there are many theories
Why do side effects occur for psychotropic medications?
A particular transmitter is often used by different neurons to carry out different activities. Taking medication can alter these activities
What are side effects of psychotropic medications?
Alterations to mental status
Changes in sleep patterns
Changes in body movement
Changes in autonomic functions (temp regulation)
What is the purpose of psychiatric assessment?
Establish rapport with patient
Obtain understanding of the problem
Assess psychological functioning
Identify goals
Perform mental status exam
Identify areas to be modified to effect positive changes
What is important when establishing rapport with a patient?
Be respectful
Be genuine
Be trustworthy
T/F: Nurses know better than the patient
False
What should be looked for during an assessment in mental health?
LOC
Physical appearance (look for baseline, does clothing make sense)
Behavior
Cognitive/intellectual abilities
Psychosis
Potential for violence
Suicide risk
Mood vs Affect
Mood: subjective from the patient, how they feel
Affect: what the nurse is observing
Mini Mental Status Exam (MMSE)
Screening tool
Asseses orientation to time/place, attention span, ability to calculate counting backwards, recall ability, language
Glasgow Coma Scale
Screening tool
Assesses basline LOC by ear, verbal and motor responses
MOCA exam
Cognitive exam to assess fuctionality
Why is self-assessment important as a nurse?
Know biases/feelings/fears as a nurse and how this may impact care for a patient
Ex: if working with a pedophile, must still give the patient care like others
Difference between a friendhsip and a patient realationship
Friendship: Both people connect and talk about personal experiences
Patient relationship: We talk about then, dont bring up similar experiences if you have had them
T/F: It is not worth building a theraputic relationship and positiv raport if the nurse will only be with the patient for a short time
False! Even time limited can have a positive impact
Positive factors of a nurse
Consisent approach to interaction (scripting)
Adjustment of pace to patients needs
Attentive listening
Positive inital impressions
Comfort level during relationship
Self awareness of own thoughts and feelings
Consistent availability
Positive factors of a patient
Trusting attitude
Willingness to talk
Active participation
Consistent availability
Empathy vs sympathy
Empathy: Ability to understand how someone feels and sit with them while they feel. This takes energy!
Sympathy: Feeling pity, relief of not having the same probelsm
What is Transference?
The patient veiws the nurse as having characteristcis of another person who has been significant in the patients life
Includes expective exclusive serivce from nurse, jealousy, compares nurse to former authority figures
Ex: calling a nurse mom
Not healthy!
What is Countertransference?
Nurse displays characteristics on the patient
Includes nurse over-identifying with the patient, competes with the patient, argues with the patient
The more stressed someone is the __________ their bubble of personal space may be.
Bigger
Important components of nursing patient relationships
Time
Active listening
Caring attitude
Honesty
Trust
Empathy
Non-judgemental attitue
Theraputic Communication Techniques
Validation
Silence
Active Listening
Open ended questions
Close ended questions
Projective questions
Presupposition questions
Restating
Reflecting
Paraphrasing
Exploring
General leasa dn brod opening statements
Acceptance
Focusing
Giving information
Presenting realtiy
Summarizing
Offering Self
Making observation
Encouraging
Voicing doubt
Fomulating a plan of action
Validation
Acknowledging emotions without judegement
Separate from action
If dont use empathy it will come off as sarcastic
Example: “You are feeling______” or “that makes sense”
How can using silence and activie listening be helpful?
This spaces out the conversation. People often dont like silence so they may try to talk to fill it
How are open ended questions helpful?
It allows for spontaneous responses and a more interactive discussion
Most questions should be this
Ex: “how are you feeling today”
How are close ended questions helpful?
Helpful if used sparingly to obtain specific information
Ex: are you feeling suicidal?
How are projective questions helpful?
It uses “what if” to assist in exploring feelings
Ex: “if i could give you a pill to fix your biggest problem, what would it be”
How are presupposition questions helpful?
Explores motivations and goals with hypothetical questions in which the patient does not have a mental illness
Ex: “What would you bring with you on a deserted island”
Restating
Uses the patients exact working
Lets them known whether they have een undertood and that you are paying attention
If they correct you, you are still using it right
Reflecting
Mirroing with different wording
Directs the questions/feelings back to the patient so they may be recognized and accepted
Paraphrasing
Restates thoughts and feelings to confirm what has been communicated
Exploring
Delving further into a subject, idea, experience or relationship
Gathering and organizing information about the patient
Ex: use a word/phrase that sticks out to you- “you said you feel lonely, can you tell me more about that”
Offeing general leads and broad opening statements is helpful because
Allows the patient to select a topic
Leading: “slept well last night” this implies there is a correct answer
Broad opening: “how did you sleep last night” this allows them to decide
Showing acceptance is helpful because
It conveys positive regard
Regardless of their choice, you will care about them
Importance for abuse
How is focusing helpful
Taking notice of a single idea of single word
Bas for anxiety
How is giving information helpful?
Provides details the patient may need to make a decision
Ex: asking about the side effects of a medication, the nurse gives info and not advice