Anatomy Units 1-4 Test
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Anatomy
study of structure
Physiology
Study of function - how the body works and carries out its functions
Describe from simple to complex the levels of a human organism
atoms → molecules → cells →tissue → organ → organ system
Gross Anatomy
study of large body structures visible to naked eye. Heart, kidneys, lungs etc
Surface Anatomy
Studies external features of body, without dissection or visual assistance
Systemic Anatomy
Studies how body systems work ex digestive system, cardiovascular, etc
What are the subdivisions of microscopic anatomy?
Histology, cytology, virology
Virology
Study of viruses
Developmental Anatomy
changes that occur throughout life
Embryology
Developments that occur before birth
Renal physiology
kidney function
Integumentary System
hair, nails, skin. Synethesizes Vitamin D when exposed to UV light. Houses cutaneous receptors, sweat glands, oil gland
Skeletal System
Bones of body. Protects and support organs. Provides frame muscles can pull on. Stores calcium
Muscular System
Skeletal muscles. Allows manipulation of environment, locomotion and facial expression, maintains posture and produces heat
Lymphatic System
Red bone marrow, thymus, lymphatic vessels, thoracic duct, spleen, lymph nodes. Disposes of debris in lymphatic stream, houses lymphocytes that are involved in immunity
Respiratory System
Lungs, trachea, larynx, bronchus, pharynx, nasal cavity. Supplies blood with oxygen, removed carbon dioxide
Digestive System
Oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, large/small intestines, rectum, anus. Breaks down food, removes waste
Nervous System
Brain, spinal cord, nerves. Control system of body. Responds to stimuli by activating muscles/glands
Endocrine System
pineal gland, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal gland, pancreas, testis, ovaries. Hormones regulate processes such as growth, production, metabolism
Cardiovascular System
Blood vessels, heart. Heart pumps blood, blood vessels transport blood, removing waste
Urinary System
Kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra. Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from body, regulates water, electrolytes, and acid base balance of blood
Female Reproductive System
mammary glands, ovary, uterus, vagina, uterine tube. Produces eggs and sex hormones. Development of the fetus. Mammary glands produce milk
Male Reproductive System
Prostate, penis, testis, scrotum, ductus deferens. Produces sperm and male sex hormone
What characteristics are needed to maintain life?
Maintaining boundaries, movement, responsiveness, digestion, metabolism, excretion, reproduction, growth
Catabolism
breaking substances down into simpler components
Anabolism
Synthesizing complex structures from simpler components
Survival Needs
Nutrients, oxygen, water, normal body temperature, appropriate atmospheric pressure
Normal Body Temperature
98.6 degrees F, 37 degrees C
Homeostasis
maintaining stable internal conditions despite outside changing environment.
Maintained through negative/positive feedback loops.
Regulated by nervous and endocrine systems
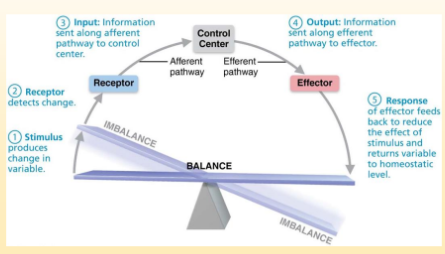
Receptor
Monitors environment and detects change. Sends information along Affarent (Away from brain) pathway to the control center.
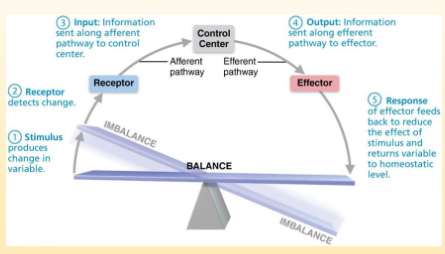
Control Center
decides how to react to an Affarent pathway. The output moves along the Efferent pathway (towards the brain)
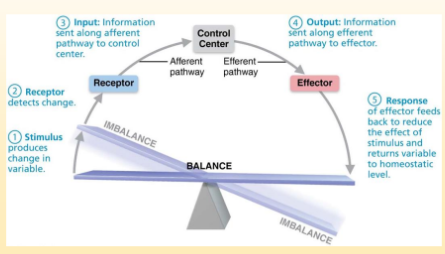
Effector
Carries out control centers response to the stimulus. Effectors carried out by glands or muscles
Positive Feedback
Enhances stimulus
Less frequent
Ex: childbirth, lactation, blood clotting
Negative Feedback
Reduces, reverses, shuts off original stimulus.
Most used feedback loop in body
Ex: blood glucose regulation, body temp regulation, heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen/CO2 levels
True or False
If negative Feedback mechanisms fail, destructive positive feedback mechanisms occur.
True
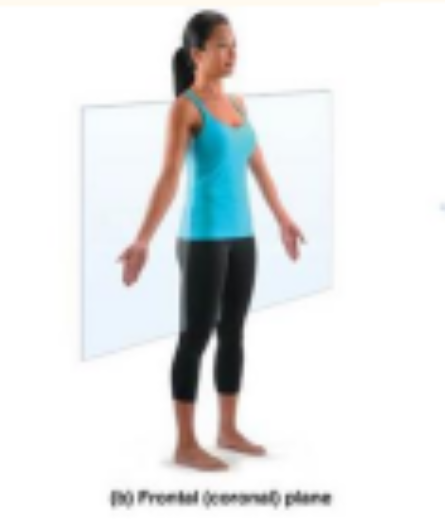
frontal plane
divides body into anterior and posterior parts

midsagittal Plane
exactly in middle, symmetrical

Transverse/Horizontal Plane
divides body into superior and inferior parts

parasagittal
offset from the midline, asymmetrical
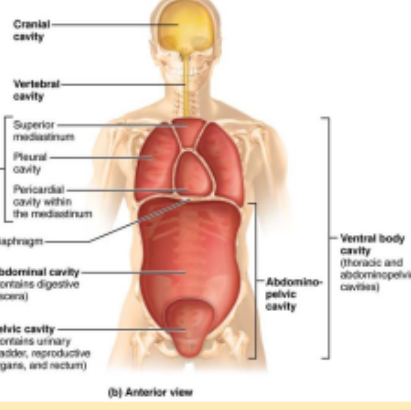
Dorsal Body Cavity
protects the nervous system, has 2 subdivisions: cranial cavity, vertebral/spinal cavity
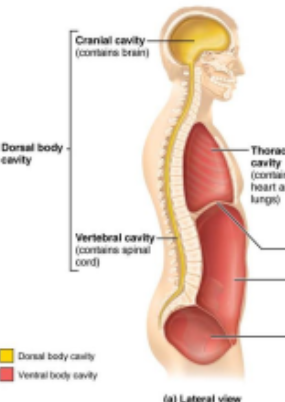
Ventral Body Cavity
more anterior and larger.
Contains Thoracic cavity which has the pleural cavities, mediastinum.
Abdominopelvic cavity - inferior to thoracic. Houses abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity
Parietal Serosa
Thin double layered membrane called serosa or serious membrane. Lines the cavity wall.
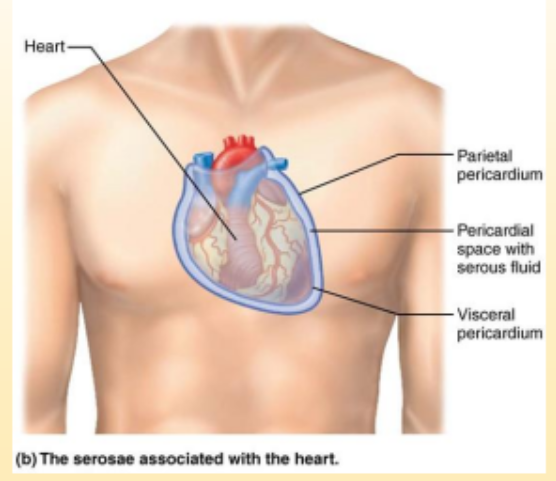
Visceral Serosa
covers the organ
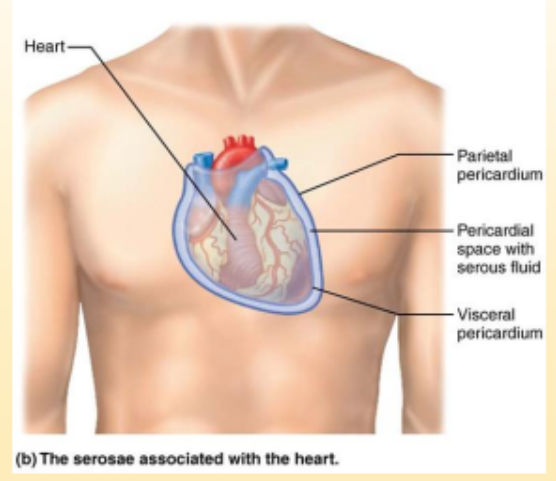
Serous fluid
in between two serosa is a lubricating fluid that prevents friction
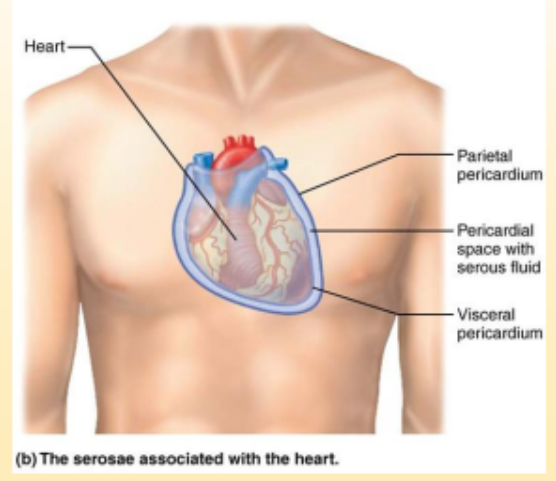
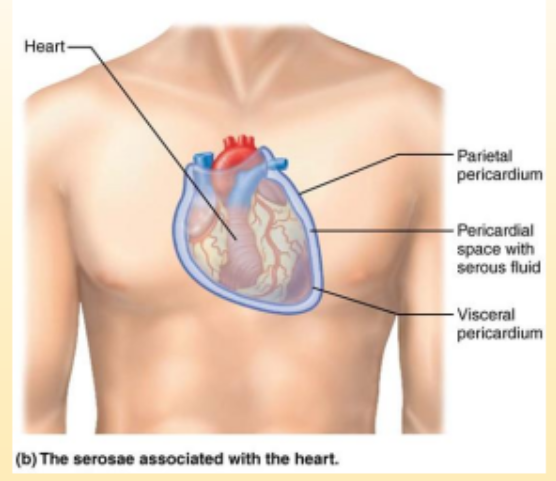
Parietal Pericardium
lines the pericardial cavity
Visceral Pericardium
covers the heart
Pericardial space
space between the two pericardiums that secrete serous fluid
Eukaryotic Cell
have a nucleus, organelles, in animals, plants, fungi, protists
Cellular Respiration
includes 4 steps glycolysis, bridge reaction, krebs cycle, electron transport chain
Cellular respiration reaction formula
C6H12O6 + 6O2 →6H2O + 6CO2+ 32ATP + heat
What organs are in the right hypochondriac region?
liver, gallbladder
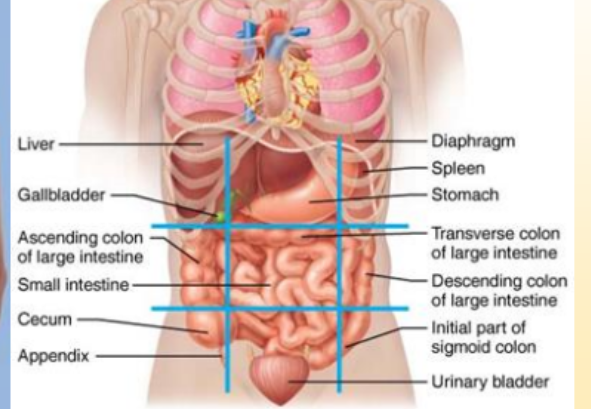
What organs are in the left hypochondriac region?
diaphragm, spleen,
What organs are in the epigastric region?
stomach
What organs are in the right lateral/lumbar region?
large intestine
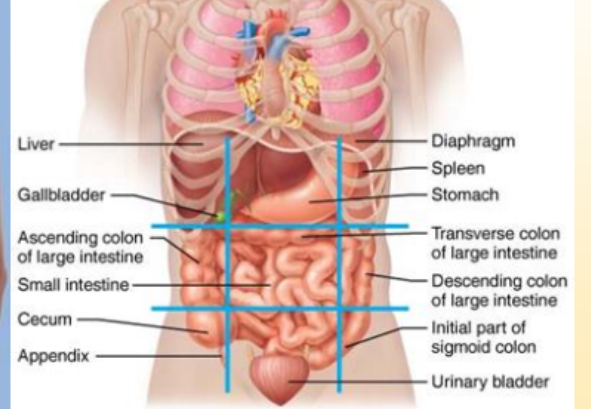
What organs are in the left lumbar/lateral region?
descending colon of large intestine
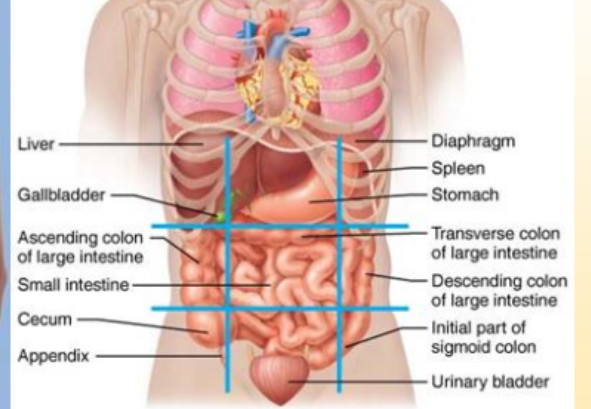
What organs are in the umbilical region?
small intestine
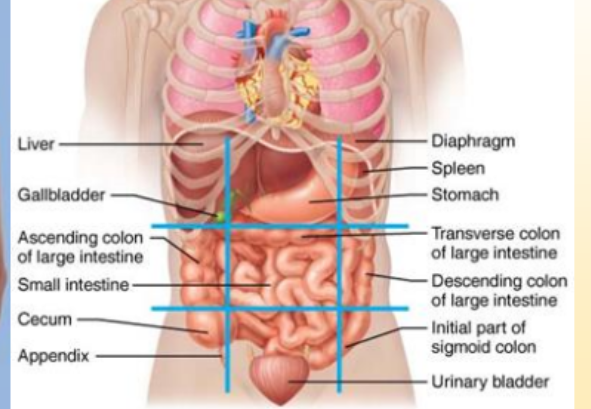
What organs are in the right iliac region?
appendix, cecum
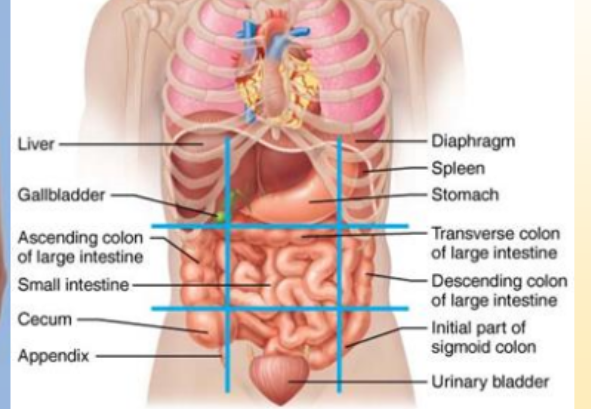
What organs are in the left iliac region?
initial part of sigmoid colon
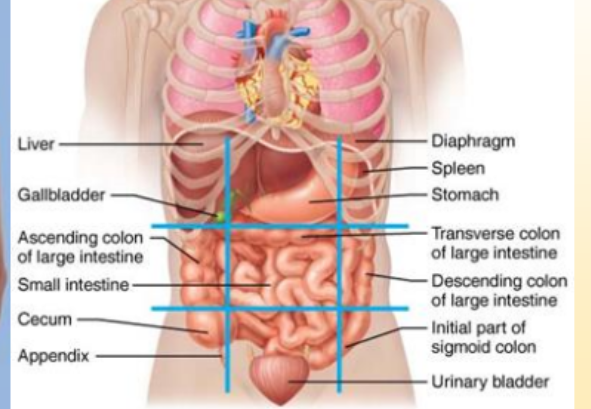
What organs are in the pubic/hypogastric region?
urinary bladder
glycolysis
breaks down glucose into 2 pyruvate molecules. 2 ATP produced. Takes place in cytoplasm
Bridge Reaction
converts 2 pyruvate to 2 acetyl CoA. 0 ATP prduced. in mitochondria
Krebs Cycle
Series of reactions to refine molecule to enter ETC 2 ATP produced. takes place in mitochondria
Electron Tranport Chain
oxygen is final electron acceptor. Produces most ATP, occurs in cristae of mitochondria
Cell Theory
A cell is the structural/functional unit of life
How well the entire organism functions depends on cells activities
Structure and function are complementary
Continuity of life has cellular basis
3 Main Components of Cell Theory
1) Cell is smallest unit of life
2) All organisms are made of cells
3) Cells arise only from other cells
Progenitor Cells
derivative of stem cells that are already differentiated.
Can be unipotent, or oligopotent
Main difference between Stem and Progenitor Cells
Progenitor Cells cant make more of themselves when they divide. They can be used if damage keeps occurring.
Stem cells duplicate themselves
hyperplasia
accelerated growth that increases cell numbers when needed
atrophy
decrease in size that results from loss of stimulation or use
Hypertrophy
Increase in size that results from gain of stimulation or use
Extracellular fluids (body fluids)
Interstitial fluid, blood plasma, cerebroespinal fluid, cellular secretions
Interstitial fluid
fluid filling space around cells in a tissue
Blood plasma
liquid component of blood, 90% water
Cerebroespinal fluid
cushions, protects, and nourishes the brain and spinal cord
Cellular Secretions
Made inside the cell then pushed outside cell- ex: saliva, mucus, gastric fluid
glycocalyx
cell to cell recognition. allows immune system to distinguish between self tissue and potential pathogenic tissue
membrane proteins
make up half the plasma membrane, have specialized functions
includes integral proteins and peripheral proteins
integral proteins
embedded in cell membrane. travel through thickness of membrane
Peripheral proteins
Attached to surface of cell membrane.
travel partially through cell membrane or attached to integral protein
why do cells divide
growth, repair, development
Cell junctions
tight junctions, desmosomes, gap junctions
how cells are bound together to form tissues/organs
tight junctions
tight permeable membrane seal. Prevents fluid from squeezing between cells.
Ex: urinary bladder, intestines, blood brain barrier
Desmosomes
hook shaped proteins that link adjacent cells together
Linker protein called plaques
Ex: myocardium, skin
Stem cells
have the ability to specialize into different types of cells.
3 different types
Totipotent, pluripotent, multipotent
gap junctions
pores between cells, allows substances to pass between calls.
Transmembrane proteins (connexons)
Ex: n cardiac/smooth muscle cells
Active Transport
how substance passes plasma membrane, energy is required, ATP
Passive Transport
No energy required for substances to cross plasma membrane
3 types of passive transport
Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis
simple diffusion
non-polar hydrophobic substances diffuse directly through phospholipid bi-layer
EX: oxygen, carbon dioxide, steroid hormones, fatty acids
Facilitated diffusion
Carrier mediated- substances bind to protein carriers
Channel mediated- substances move through water filled channels called aquaporins
Active Transport
Primary and secondary active transport
hydrostatic pressure
outward pressure exerted on cells size of membrane caused by increase in volume of cell due to osmosis
osmotic pressure
inward pressure
primary active transport
must occur first
energy to do work comes from hydrolysis of ATP by pumps
energy from ATP hydrolysis cause change in shape of pump
Secondary active tranport
energy stored in concentration gradients of ions created by primary active transport pump
always move more than one substance at a time using cotransport protein
do not directly require energy
Vesicular transport
involves Tranport of large particles, macromolecules, and fluid in vesicles
Includes endocytosis, exocytosis, transcytosis, vesicular trafficking
endocytosis
transport into the cell
Inlcudes Phagocytosis: sold, “cell eating”
Pinocytosis- Liquid “cell drinking”
Exocytosis
transport out of cell
Transcytosis
moves substances into, across then OUT of cell
vesicular trafficking
moves substances across the cell