Network Devices
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Physical Appliances
Dedicated hardware devices focused on specific network functions, with high performance and reliability, but with higher cost and space requirements
Virtual appliances
Software-based solutions that run on virtual machines, providing similar functionalities with greater flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency, but potentially at the expense of raw performance
Router
Operates at the network layer, directing data packets between different networks based on IP addresses. Uses routing tables to determine the best path for forwarding packets to their destination, connecting multiple networks together, such as a local network to the internet
Also provides security features, like firewalls and VPN support
What breaks up a broadcast domain?
Router; implementing subnets
What breaks up collision domains?
A switch
Switch
Operates at the data link layer, forwarding data based on MAC addresses. Creates separate collision domains for each port, improving network efficiency by reducing collisions.
Layer 2 switches are used to connect devices within the same network or VLAN (can use a switch to create VLANs as well)
Has a MAC address table, creates a broadcast and uses ARP to resolve an IP address to a MAC address
IDS
Intrusion Detection System: can detect malicious network activity
Uses signature identification techniques like antimalware
Can detect malicious activity based on anomalous behavior
IPS
Intrusion Prevention System: used to actively drop packets or connections that are identified as malicious
Rules must be configured on an IPS for it to be able to identify traffic as malicious
These devices can operate on multiple layers
Load Balancer
Distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure no single server becomes overwhelmed, improving reliability and availability of applications. Can be hardware or software
Operates at various layers of the OSI model, makes decision based on IP addresses, TCP/UDP ports, or application-level content to optimize resource use, maximize throughput, minimize response time, and avoid overload of any single resources
Proxy server
Acts as an intermediary between a user’s device and the internet, receiving requests from clients, forward them to the relevant server, and returning the server’s response to the client.
It can provide additional functionality such as content caching, access control, and filtering, enhancing security and performance
Most proxy servers are firewall. Can choose which sites users can access
NAS
Network-Attached Storage, dedicated file storage device connected to a network, allowing multiple users and client devices to retrieve and store data from a centralized location.
Designed for easy file sharing, data backups, and centralized data management, supporting a variety of file-based protocols, such as NFS, SMB/CIFS, and AFP
Offers a scalable and cost-effective solution for businesses and home users needing to share files across different platforms and devices
SAN
Storage Area Network. A dedicated, high-speed network that provides access to consolidated, block-level data storage.
Designed to handle large volumes of data transfers, improving the availability and performance of applications by offloading storage functions and direct access to multiple storage devices
Commonly used in enterprise environments to enhance storage solutions and data management
Wireless LAN Controller
Manages wireless access points in a network, centralizing control of the wireless LAN (WLAN).
Simplifies the deployment and management of wireless networks, including configuration, security policies, and managing guest access, enhancing the efficiency and security of wireless networks
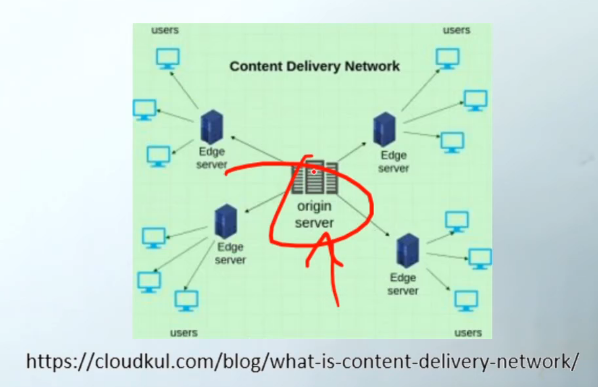
Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A globally distributed network of proxy servers and data centers designed to deliver internet content rapidly to users.
CDNs cache content like web pages, videos, and images in multiple locations around the world to reduce latency and improve access speed for users regardless of their location. Allows users to access content straight from the server and not through the variety of different locations the videos are uploaded from
TTL
Time to Live is a field in the header of IP packets that specifies the maximum time or number of hops a packet is allowed to traverse before being discarded by a router.
TTL helps prevent packets from looping indefinitely in the network, with each router decrementing the TTL value by one until it reaches zero, at which point the packet is dropped
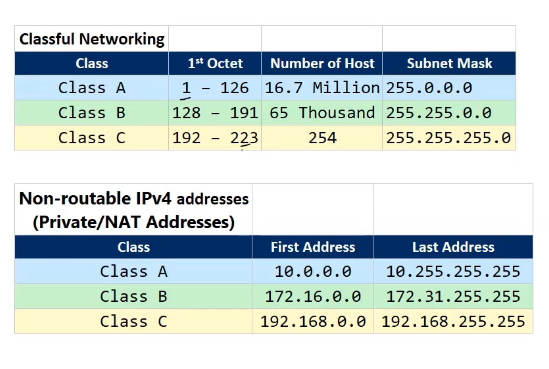
IP Classes
Network ID
Determined by the IP address and subnet mask. Wherever there’s zeroes for the subnet mask, the Network ID has zeroes as well. ex: 192.154.10.3 = Class C address = 255.255.255.0 subnet mask, so Network ID = 192.154.10.0
Network IDs determine which devices can talk to each other. If they have the same Network ID, they can communicate
Class C = can only change the last number to maintain the same Network ID
Class B = can change the last two numbers
Class A = can change last 3 numbers