2.1.1 Mind Matters HBS Human Body Systems PLTW Mr. Alasti WCHS
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Principal Investigator (PI)
Person in charge of a scientific research grant or clinical trial. The PI is considered the lead researcher, and their role is to manage and maintain the integrity or the study being conducted
Lab Manager
Person who generally oversees the lab, scheduling, ordering supplies, maintenance of equipment, and other tasks to keep the lab operating smoothly
Lab Technicians
People responsible for carrying out the hands-on work in the lab. They may collect specimens or samples, perform tests, calibrate equipment, collect data, or other tasks based on the work or research being conducted
Postdoctoral Students
PhD graduates continuing their education, research, and training beyond their doctoral studies
What are the two systems of the body involved in communication, response, and function regulation?
The nervous and endocrine systems
How does the nervous system communicate?
Using electrical signals
How does the endocrine system communicate?
Using hormones or chemical signals
Hormones
A signaling molecule produced by glands. A hormone induces a specific effect on the activity of cells
What are the two subsystems of the nervous system?
The central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Central nervous system (CNS)
The part of the nervous system which consists of the brain and spinal cord, where sensory impulses are transmitted and motor impulses pass out, supervising and coordinating the activity of the entire nervous system
Which subsystem of the nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord?
The central nervous system (CNS)
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
The part of the nervous system that is outside the central nervous system and comprises the cranial nerves excepting the optic nerve, the spinal nerves, and the autonomic nervous system
Which subsystem of the nervous system consists of a system of nerve cells that transmit information to and from the control center?
The peripheral nervous system (PNS)
How do the two subsystems of the nervous system work together?
They work together to ensure that important information gets to your brain to be processed and interpreted and that the correct response is generated
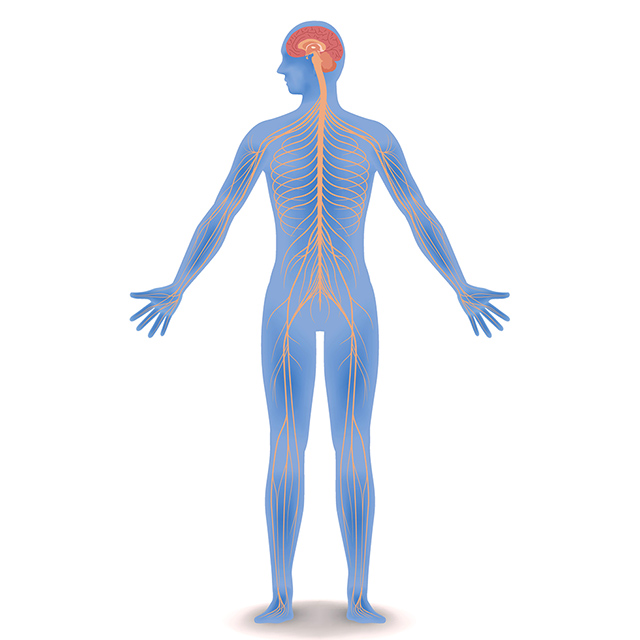
Which subsystem of the nervous system is pictured?
The central nervous system (CNS)
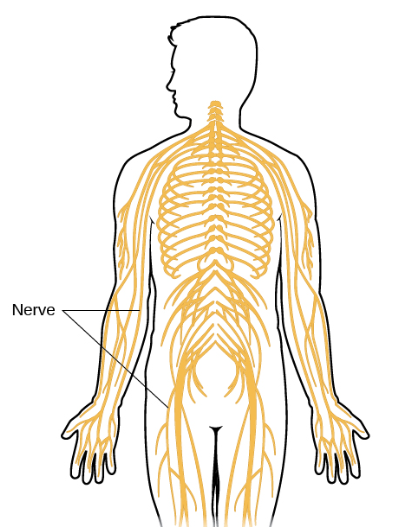
Which subsystem of the nervous system is pictured?
The peripheral nervous system (PNS)
What is the main organ of the nervous system?
The brain
Main functions of the brain
Allows you to move, breathe, make decisions, solve problems, feel emotions, and interact with the world
Key to communication in the human body
Allows you to communicate with and respond to your surroundings
What are the three distinct structures of the brain?
Cerebrum (divided into 4 parts or lobes)
Cerebellum
Brain stem
Lobe
A division of a body organ marked off by a fissure on the surface
Brain Stem
The part of the brain that is composed of the midbrain, prons, and medulla oblongata and connects the spinal cord with the forebrain and cerebrum
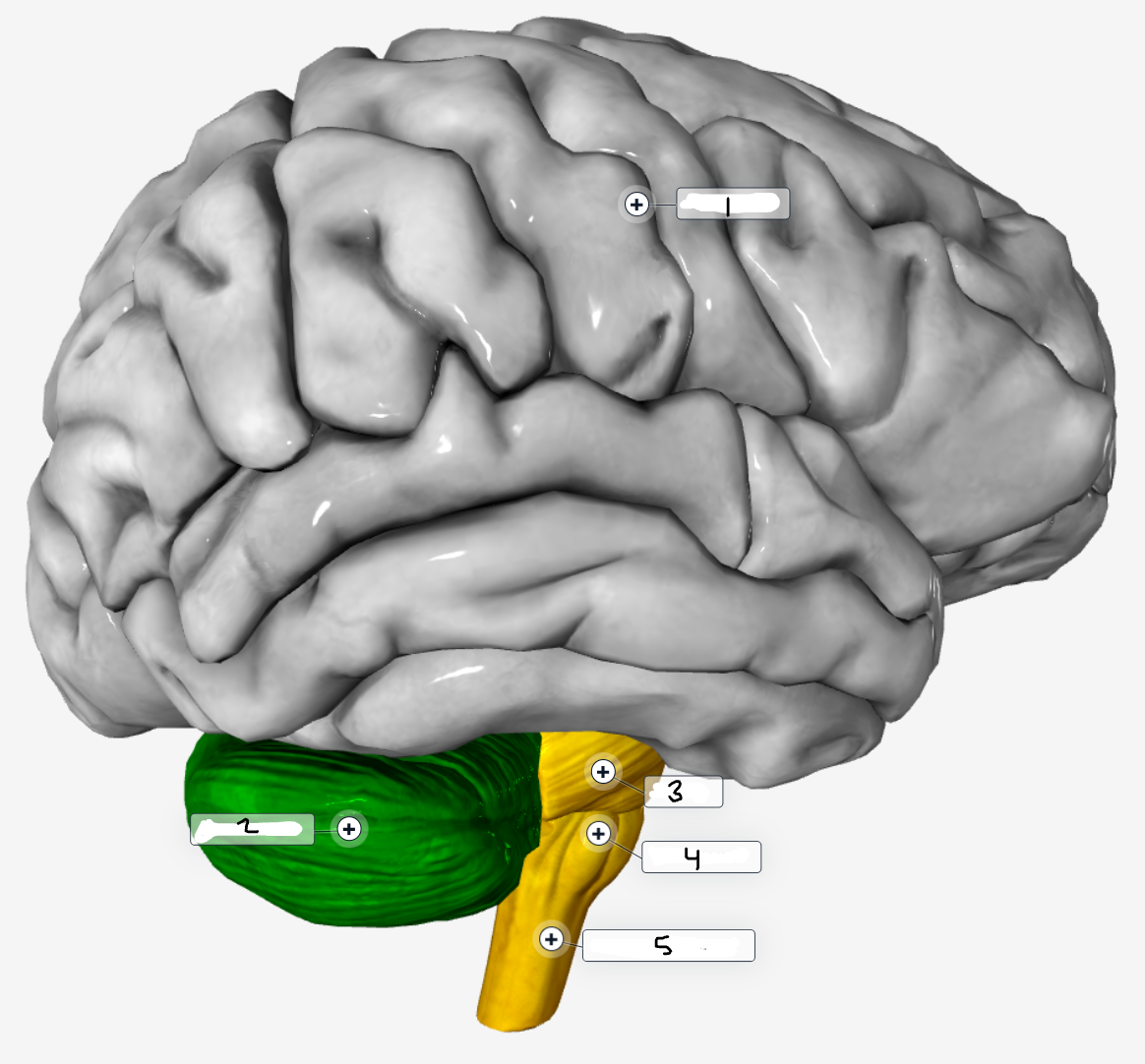
Label the outer brain structures
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
Pons
Brain Stem
Medulla Oblongata
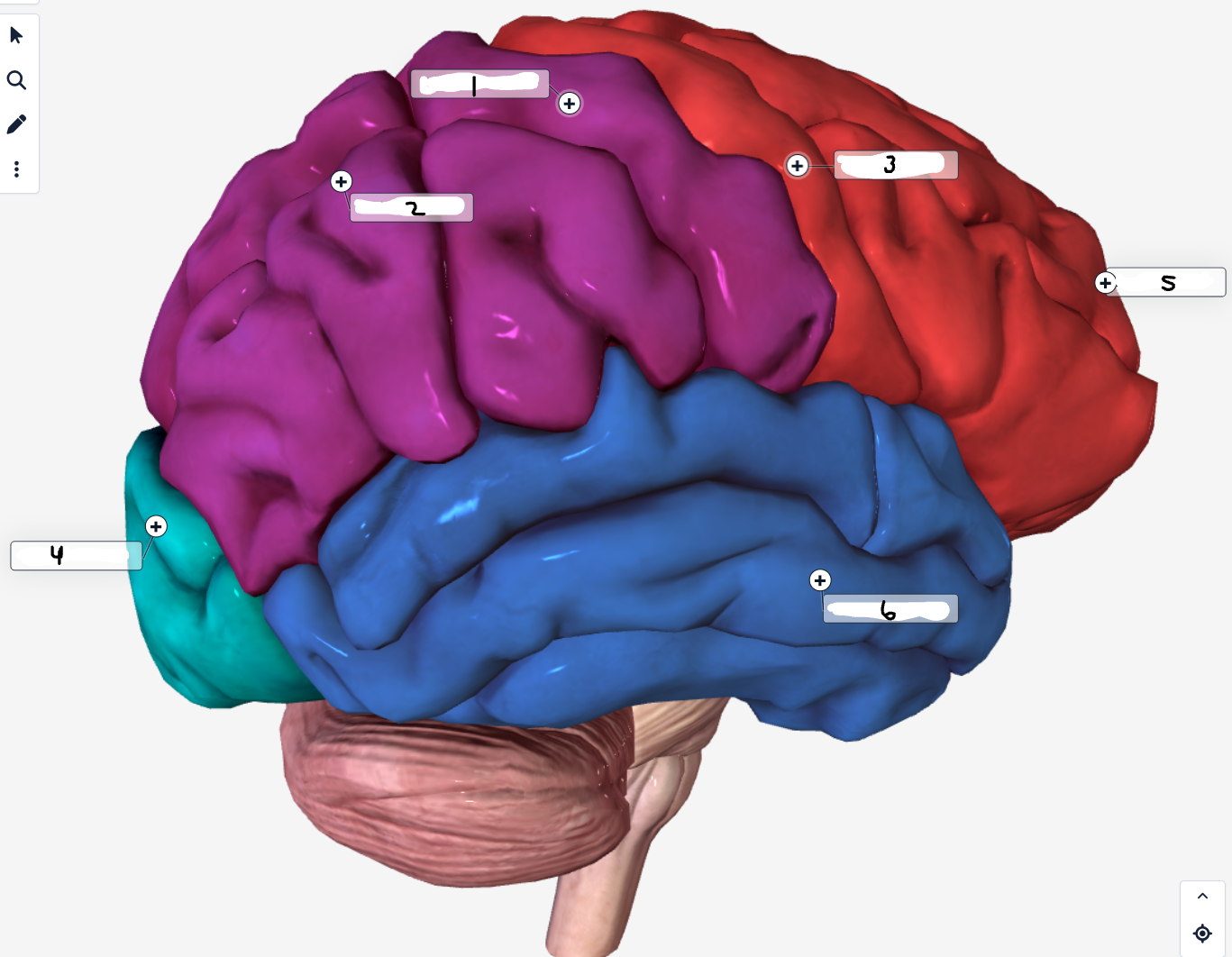
Label the lobes of the cerebrum
Sensory Cortex
Parietal Lobe
Motor Cortex
Occipital Lobe
Frontal Lobe
Temporal Lobe
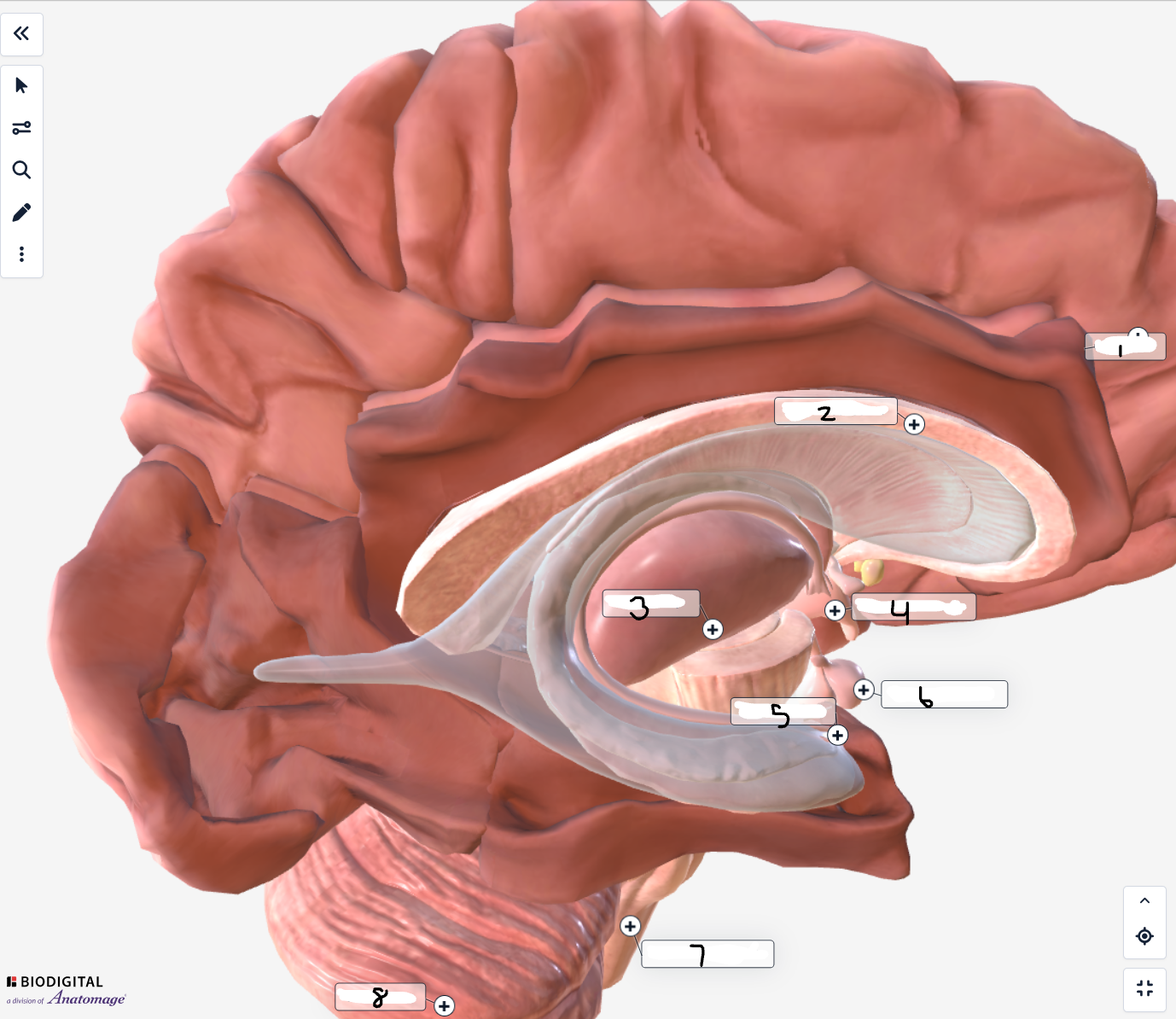
Label the inner brain structures
Cerebrum
Corpus Callosum
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Hippocamus
Pituitary Gland
Medulla Oblongata
Cerebellum
Cerebellum
The part of the brain at the back of the skull in vertebrates. Its function is to coordinate and regulate muscular activity
Cerebrum
The most anterior part of the brain, located in the front area of the skull and consists of two hemispheres, left and right. It is responsible for the integration of complex sensory and neural functions and the initiation and coordination of voluntary activity in the body
Medulla Oblongata & Pons
Part of the brainstem
Temporal Lobe
Responsible for processing smell and sound, as well as the ability to recognize and understand words and language. They are also involved in visual memory
Frontal Lobe
Plays a large role in your behavior and personality, such as planning, voluntary muscle movements, mood, emotions, and social interactions, and attention, and are also involved in memory retrieval and storage
Parietal Lobe
Responsible for sensing touch, spatial processing (being able to tell where objects are in space), language, and memory
Occipital Lobe
Primarily responsible for visual perception and are involved in some forms of visual, short-term memory
Motor Cortex
Where nerve impulses initiate voluntary muscular activity
Sensory Cortex
All received sensory input signals, such as touch and taste, are sent through neurons to the sensory cortex to be processed
Thalamus
One of two masses of gray matter lying between the cerebral hemispheres, relaying sensory information and acting as a center for pain perception
Pituitary Gland
A tiny organ that serves as the primary gland for the body, producing several hormones and activating other glands to produce hormones
Hypothalamus
Located below the thalamus and coordinated the autonomic nervous system and the activity of the pituitary, controlling body temperature, thirst, hunger, and other homeostatic systems, and involved in sleep and emotional activity
What greatly increase the brain’s surface area?
The gyri and sulci
Gyrus
A convoluted ridge between anatomical grooves
Sulcus
A shallow furrow on the surface of the brain separating adjacent gyri
What are the major nerves?
Brachial plexus
Radial nerve
Ulnar nerve
Spinal nerves
Median nerve
Sciatic nerve
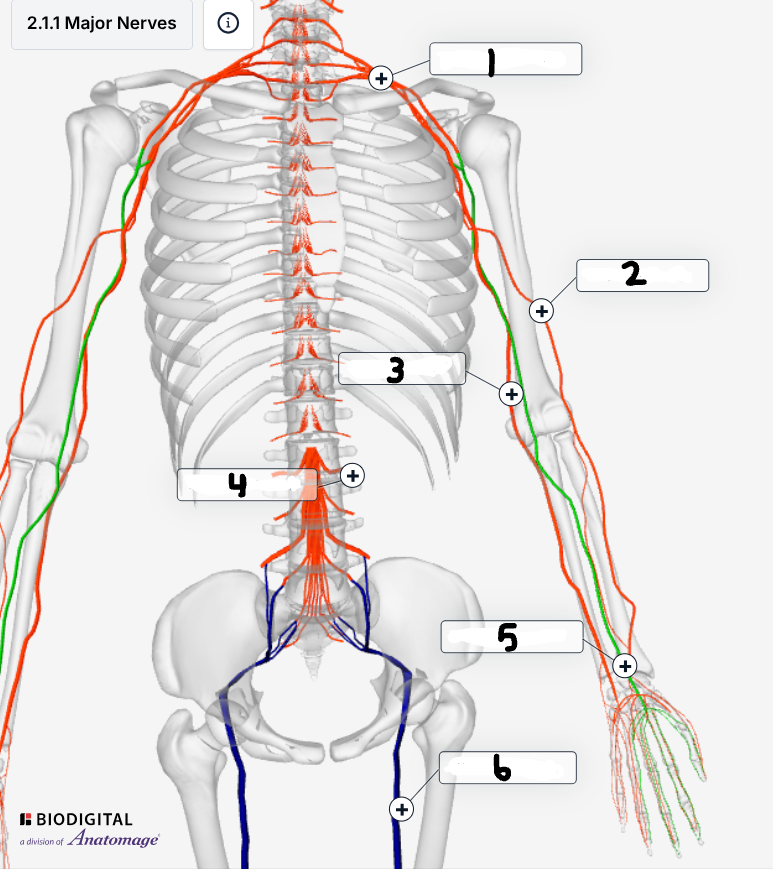
Label the major nerves
Brachial plexus
Radial nerve
Ulnar nerve
Spinal nerves
Median nerve
Sciatic nerve
Brachial plexus
Located near the shoulder area, extending down the arms
Radial nerve
Runs along the outer side of the arm
Median nerve
Runs down the middle of the arm
Sciatic nerve
Extends from the lower back down to each leg
Spinal nerves
Branch out from the spinal cord, extending to various parts of the body
Ulnar nerve
Positioned along the inner side of the arm