Digestive System {Chapter 23]
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/118
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:31 PM on 11/1/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
1
New cards
What are other names for the digestive system
gastrointestinal tract, alimentary canal, gut
2
New cards
What are the major processes of the DI
Ingestion, Propulsion, Mechanical breakdown, Digestion, Absorption, Defecation
3
New cards
What is peristalsis?
wave-like muscle contractions
4
New cards
What is segmentation?
a type of mechanical breakdown; mixing in the small intestine
5
New cards
What is the visceral peritoneum?
covers the organs external surface
6
New cards
What is the parietal peritoneum
lines inside of abdominal cavity
7
New cards
Where is the peritoneal cavity
between visceral and parietal peritoneum
8
New cards
What is serosa
The thin, double-layered membrane that covers the walls of the ventral body cavity and the outer surfaces of the organs it contains.
9
New cards
What are the four layers of the alimentary canal
mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, serosa
10
New cards
What layer is the mucosa
the innermost layer
11
New cards
What does the mucosa do
secrets enzymes and mucus
absorption of nutrients
protects from infections
absorption of nutrients
protects from infections
12
New cards
What are the layers of mucosa
epithelium - lines lumen
lamina propria - supplies blood, nerves, MALT
muscularis mucosa - helps digestion/absorption
lamina propria - supplies blood, nerves, MALT
muscularis mucosa - helps digestion/absorption
13
New cards
What layer is the submucosa
the second layer
14
New cards
What is the histology of the submucosal layer
areolar C.T; contains blood, nerves, lymph
15
New cards
What layer is the muscularis externa
second most outer layer; Histology is Smooth muscle
16
New cards
What layer is the serosa
outermost layer; protects and supplies with blood
17
New cards
Mucosa (Picture)
B
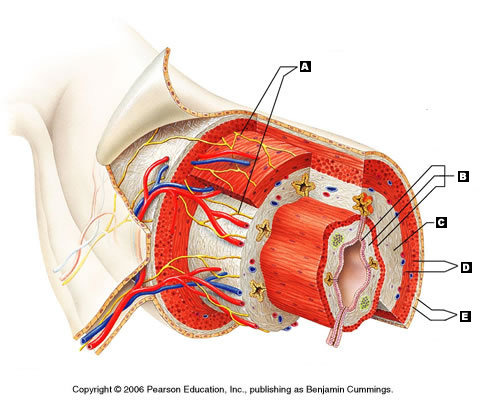
18
New cards
Submucosa (Picture)
C
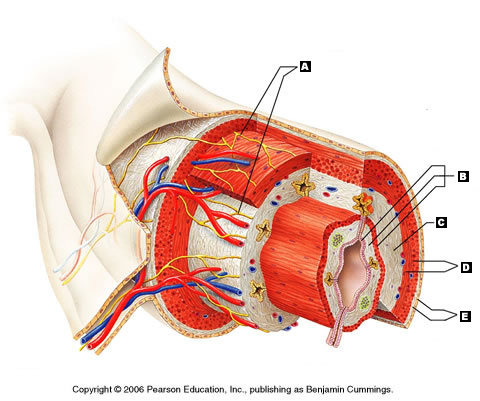
19
New cards
Muscularis externa (Picture)
D
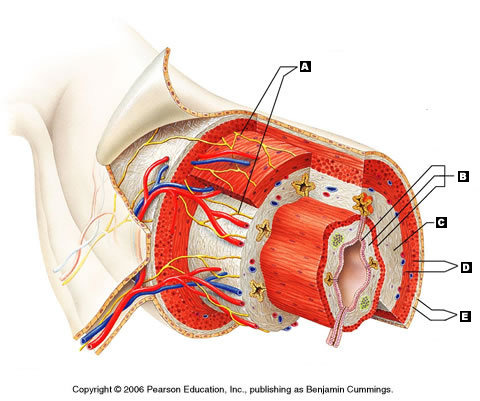
20
New cards
Serosa (Picture)
E
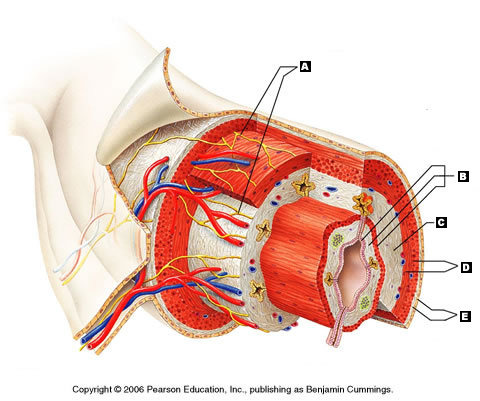
21
New cards
What is splanchnic circulation?
includes arteries that branch off the abdominal aorta to serve digestive organs and the hepatic portal circulation
22
New cards
How much of cardiac output does splanchnic circulation receive
25%, and more after eating
23
New cards
What is the nervous supply for the digestive system
Enteric nervous system
24
New cards
What is the function of lips and cheeks
keep food between teeth
25
New cards
What is the gross anatomy of the mouth
Oral cavity, Lips, Cheeks, Hard/Soft palate, Tongue
Parotid/Sublingual/Submandibular salivary glands
Teeth, Pharynx, Esophagus
Parotid/Sublingual/Submandibular salivary glands
Teeth, Pharynx, Esophagus
26
New cards
Which palate is hard
The anterior
27
New cards
Which palate is soft
The posterior
28
New cards
What is the function of the palates
create a barrier to keep food from entering the nasal cavity/ nasopharynx
29
New cards
What is a bolus
ball of food
30
New cards
Parotid salivary gland (Picture)
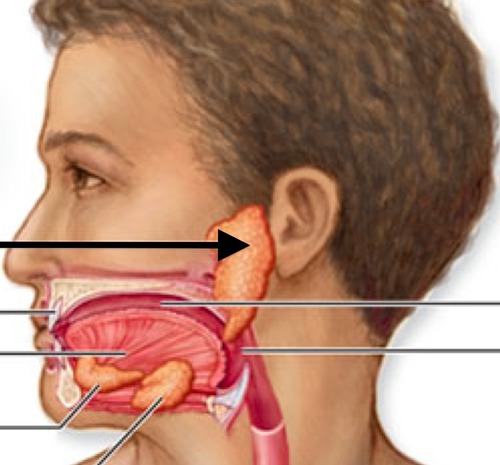
31
New cards
Sublingual salivary gland (Picture)
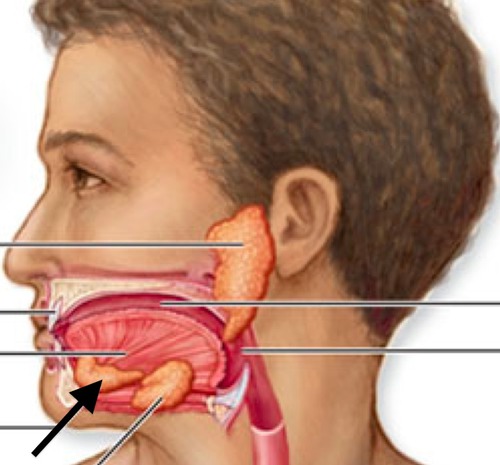
32
New cards
Submandibular salivary gland (Picture)
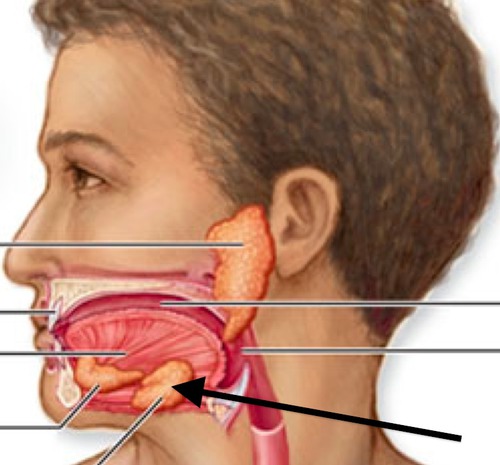
33
New cards
What is the function of saliva
Dissolves food for tasting, moistens food, contains amylase/lipase/lysozyme
34
New cards
How much saliva is produced per day?
1.5 liters
35
New cards
What is Amylase
Amylase is an enzyme that catalyses the breakdown of starch into sugar
36
New cards
what is lipase
enzyme that breaks down lipids
37
New cards
What is lysozyme
enzyme that kills bacteria
38
New cards
what promotes salivation
Chemoreceptors and mechanoreceptors
39
New cards
How many deciduous teeth are there?
20
40
New cards
How many permanent teeth are there?
32
41
New cards
Incisors (Picture)
A, used for cutting
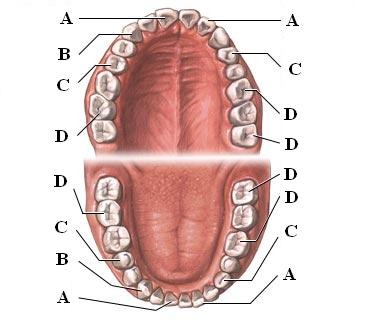
42
New cards
canines (Picture)
B, used for piercing/tearing
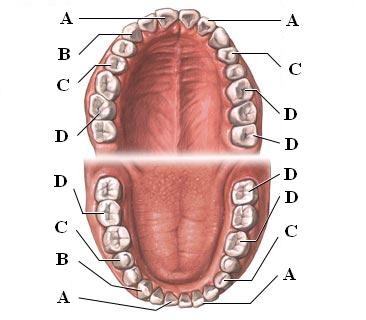
43
New cards
premolars [bicuspids] (Picture)
C, grinding
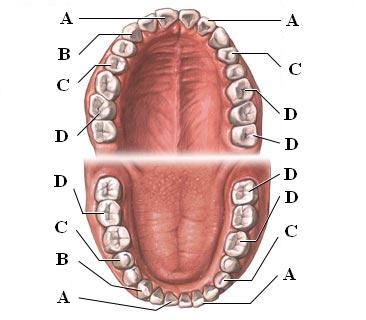
44
New cards
Molars (Picture)
D, grinding
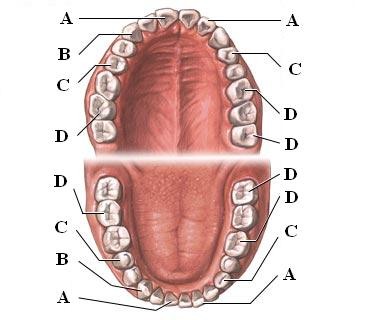
45
New cards
What is the inner histology of the esophagus
Stratified Squamous epithelium
46
New cards
Cardiac sphincter (Picture)
C
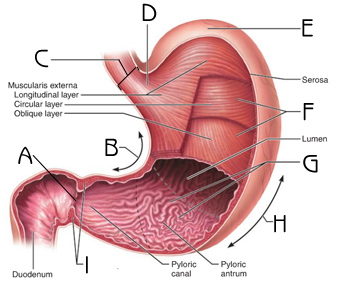
47
New cards
pyloric sphincter (Picture)
A
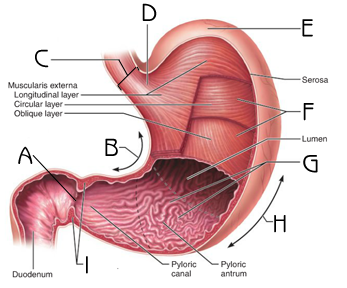
48
New cards
What are the function of the stomach
Storage, mechanical breakdown, initial digestion
49
New cards
How much does the stomach hold
50 ml empty
4 L full
4 L full
50
New cards
What do mucous neck cells secrete?
acidic mucus
51
New cards
What do parietal cells secrete?
HCl and intrinsic factor
52
New cards
What does intrinsic factor do?
absorbs vitamin B12
53
New cards
What does HCl do in the stomach?
Kills microbes
54
New cards
What type of gland cells are in the stomach
Mucous Neck cells
Parietal Cells
Chief cells
Enteroendocrine cells
goblet
Parietal Cells
Chief cells
Enteroendocrine cells
goblet
55
New cards
What do chief cells secrete?
Pepsinogen and Lipases
56
New cards
What does pepsinogen do?
becomes pepsin in acid
57
New cards
What does pepsin do?
breaks down proteins
58
New cards
What do enteroendocrine cells secrete?
hormones/molecules to help digestion
59
New cards
What is the mucosal barrier?
The physical defense of the stomach lining that prevent self-digestion. Bicarbonate rich mucus and tight junctions between epithelial cells
60
New cards
How do ulcers form?
when Helicobacter pylori destroys mucus
61
New cards
How much gastric juice is produced per day?
3 L
62
New cards
What is the cephalic phase?
Smell, sight, and though of food triggers gastric secretions
63
New cards
What is the gastric phase?
When food reaches stomach, dramatically increases secretions
64
New cards
What is the intestinal phase?
As food enters duodenum
65
New cards
What is the alkaline tide?
Blood pH increases leaving stomach due to H_ ions entering stomach causing HCO3- ions to enter the blood
Blood becomes basic
Blood becomes basic
66
New cards
What is chyme
a mixture of partially digested food, water, and gastric juices
67
New cards
How does food enter the duodenum
The pyloric sphincter squirts 3 ml of chyme
68
New cards
What supplies the liver with blood
The Hepatic Artery=Ox blood from Aorta
Hepatic Portal Vein=Nutrient rich blood from GI
Hepatic Portal Vein=Nutrient rich blood from GI
69
New cards
Where does bile leave the liver from
common hepatic duct
70
New cards
What forms the bile duct?
common hepatic duct and cystic duct
71
New cards
What WBC cleans blood within the liver
Hepatic Macrophages
72
New cards
What cells are arranged in lobules in the liver
Hepatocytes
73
New cards
What are hepatocytes
functional cells of the liver
74
New cards
What do hepatocytes do?
Produce bile, detoxify blood, store vitamins, and process nutrients
75
New cards
What is bile
fat emulsifier, made of bile salts and phospholipids
alkaline
alkaline
76
New cards
What is Hepatitis
inflammation of the liver
77
New cards
What is cirrhosis?
a chronic disease of the liver marked by degeneration of cells, inflammation, and fibrous thickening of tissue. It is typically a result of alcoholism or hepatitis.
78
New cards
Hepatic duct (Picture)
79
New cards
common bile duct (Picture)
80
New cards
What is the common bile duct
duct where exocrine secretions from the liver, pancreas and gall bladder enter the small intestine
81
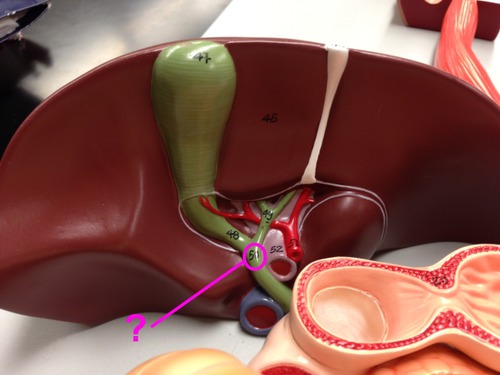
New cards
Portal triad (Picture)
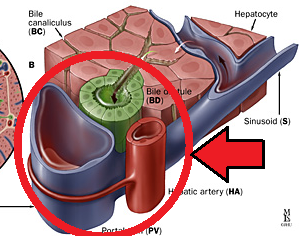
82
New cards
Portal triad (Slide Picture)
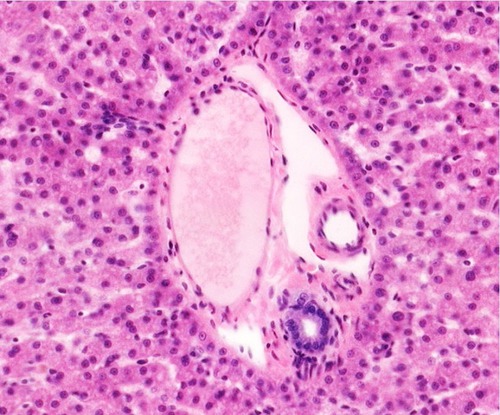
83
New cards
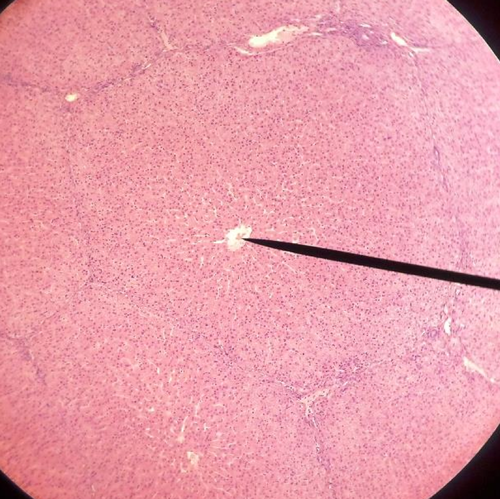
Hepatic vein (Picture)
84
New cards
Liver lobules (SLide Picture)
85
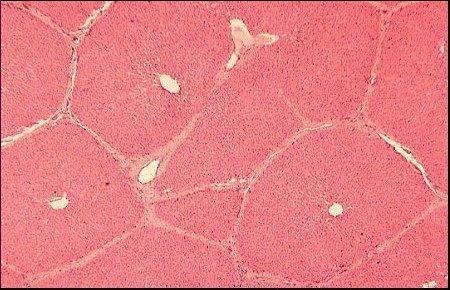
New cards
Lobule central vein (Slide Picture)
86
New cards
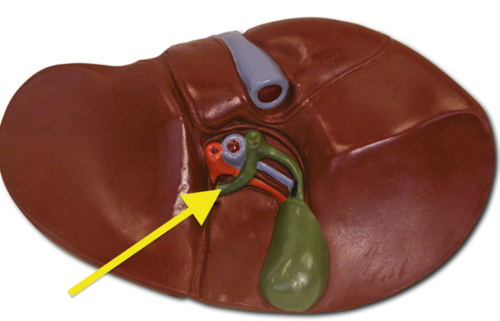
Gall bladder (Picture)
D
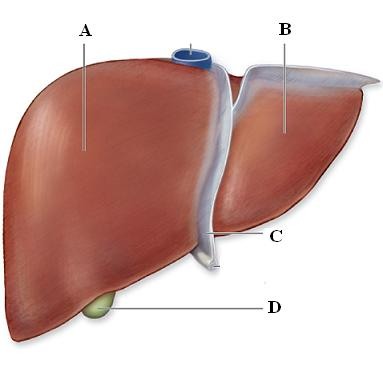
87
New cards
What is the function of the gallbladder
bile storage and release
88
New cards
What causes gallstones?
too much cholesterol or too few bile salts
89
New cards
How much pancreatic juice is produced per day?
1.5 L
90
New cards
What enzymes makes up pancreatic juice
Proteases [Tripsin, Carboxypeptidase, Chymotrypsin]
Amylase
Lipase
Nucleases
Amylase
Lipase
Nucleases
91
New cards
What converts trypsinogen to trypsin?
enteropeptidase from duodenum
92
New cards
What does trypsin activate?
chymotrypsin and carboxypeptidase
93
New cards
What does trypsinogen activate into
Trypsion
94
New cards
What is the order of sections in the small intestine
Duodenum (25 cm)
Jejunum (2.5 m)
Ileum (3.6 m)
Jejunum (2.5 m)
Ileum (3.6 m)
95
New cards
What is the function of villi and microvilli
increase surface area for absorption
96
New cards
What are intestinal crypts
They are pits between intestinal villa that contain cells that make intestinal juice
97
New cards
What are the secreationatory cells within the small intestine
Goblet cells
Enteroendocrine cells
Paneth cells
Duodenal Glands
Enteroendocrine cells
Paneth cells
Duodenal Glands
98
New cards
What are enterocytes?
basic epithelium cells, intestinal absorptive cells
99
New cards
What are enteroendocrine cells?
hormones and paracrine messengers that aid in digestion activity
100
New cards
What are paneth cells?
They are located at the base of the crypts and produce antibiotic peptides and proteins.