Chapter 2 Mastery Training
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 2 - Cognitive Neuroscience
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
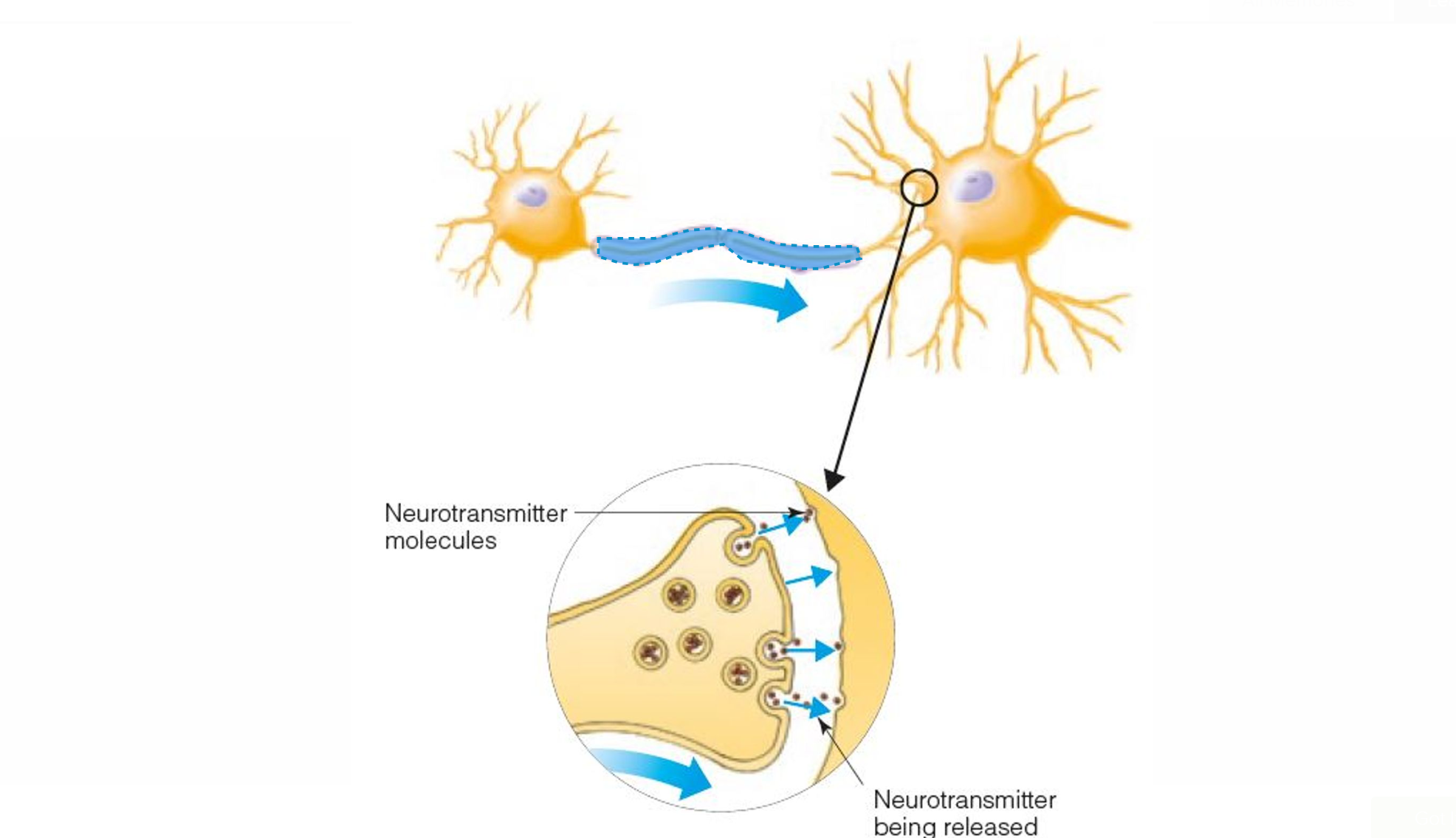
NERVE IMPULSE
An electrical response that is propagated down the length of an axon (nerve fiber) (also called an action potential)
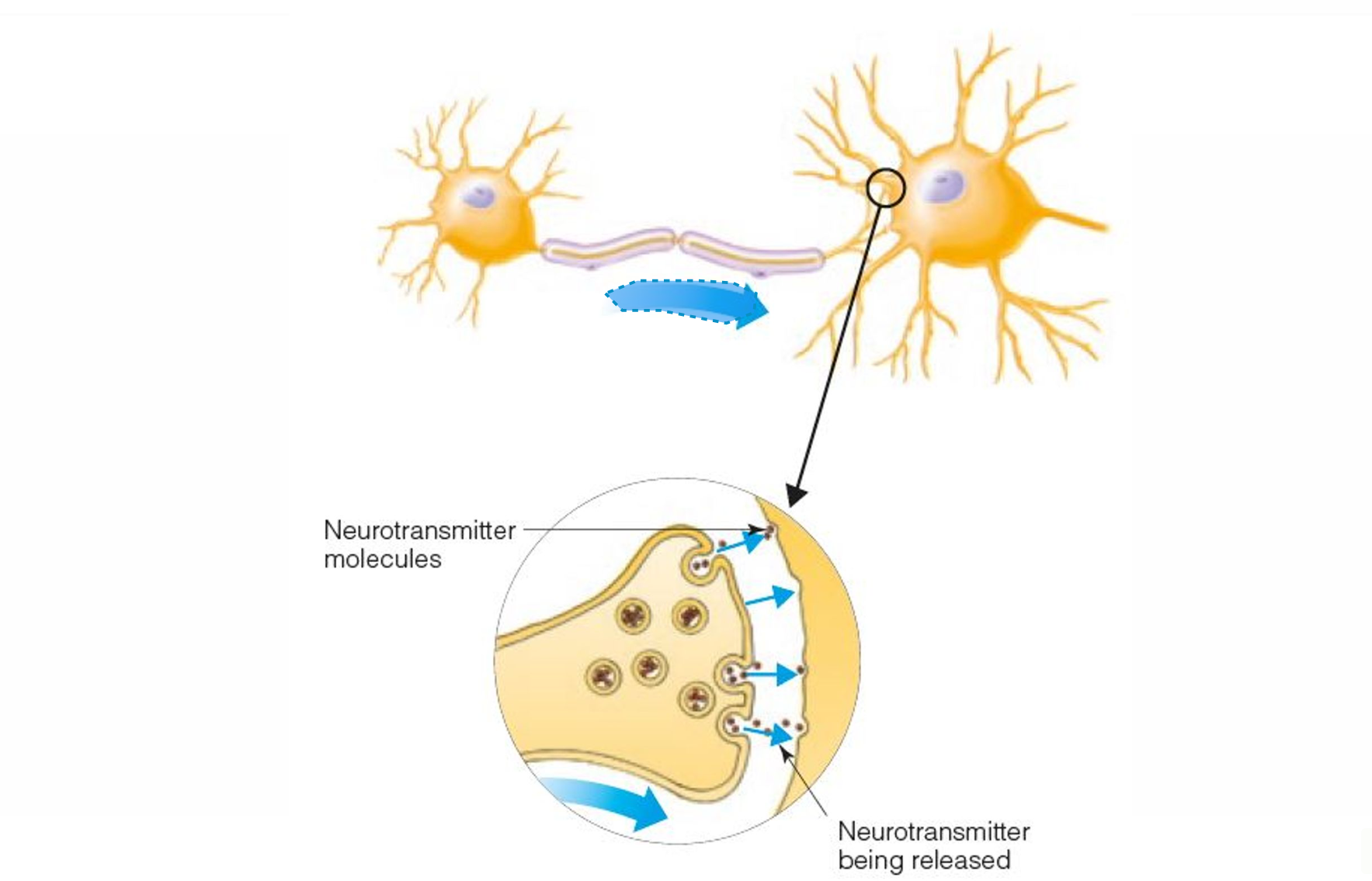
CELL IMPULSE
Part of a cell that contains mechanisms that keep the cell alive. In some neurons, the cell body and the dendrites associated with it receive information from other neurons
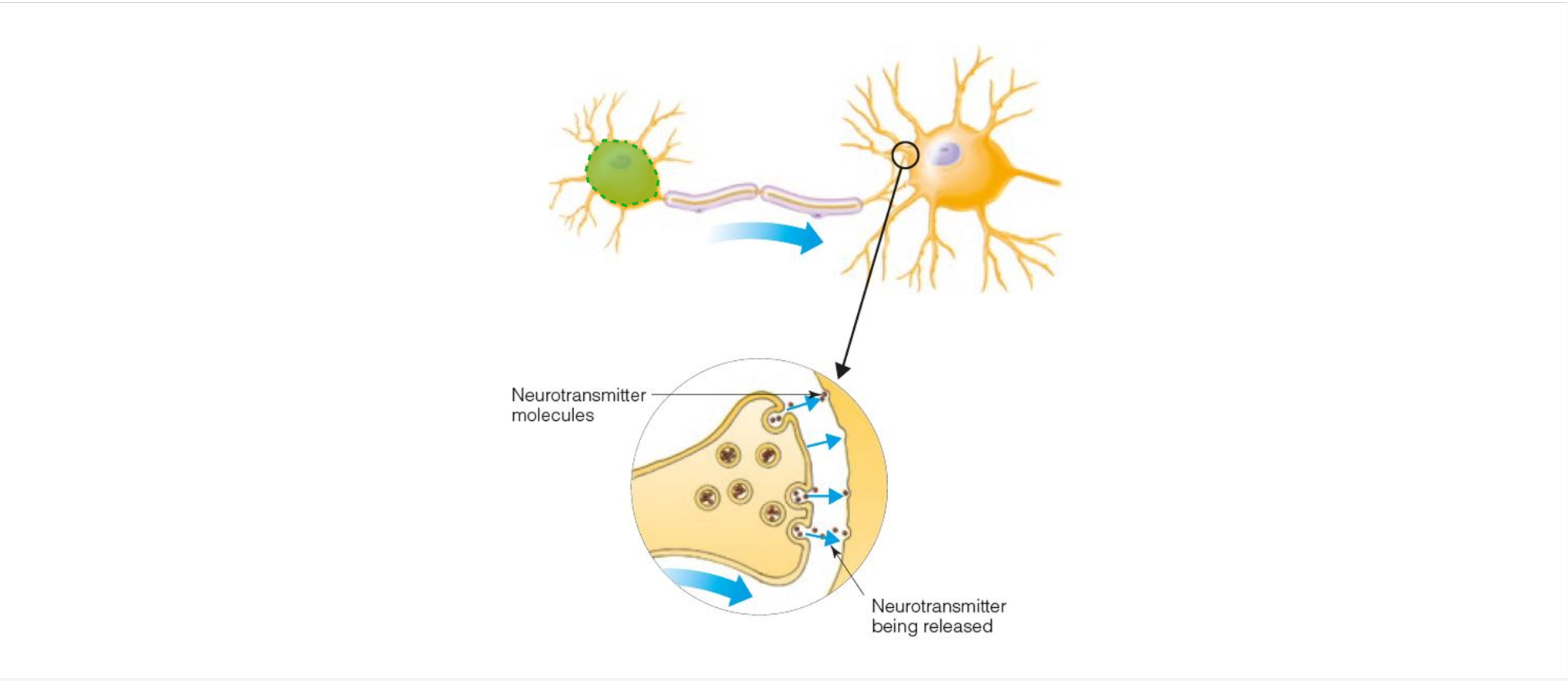
AXON(S)
Part of the neuron that transmits signals from the cell body to the synapse at the end of the axon

NERVE NET
Network of continuously interconnected neuron fibers
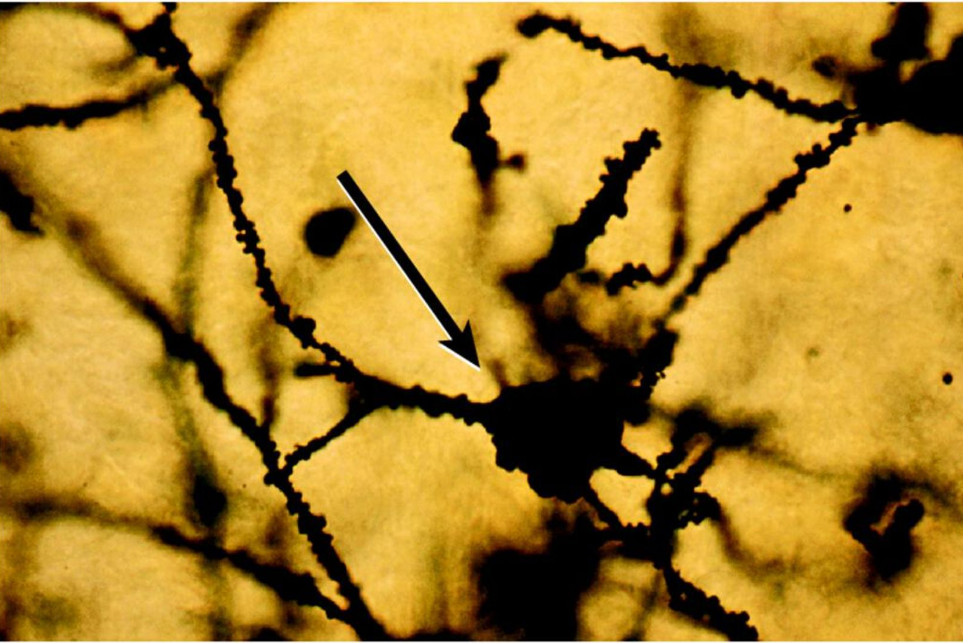
NEURON
Cell that is specialized to receive and transmit information in the nervous system
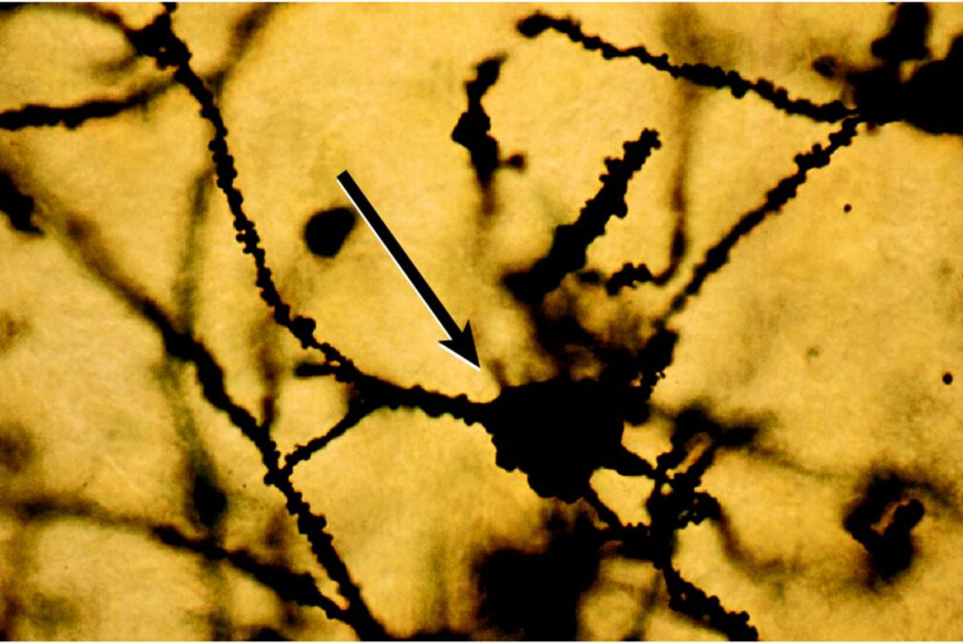
DENDRITE
Structure that branches out from the cell body to receive electrical signals from other neurons
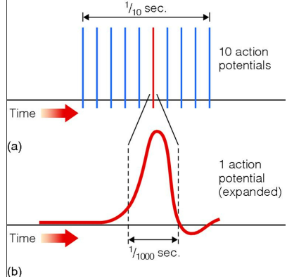
ACTION POTENTIAL
Impulse responsible for transmitting neural information and for communication between neurons
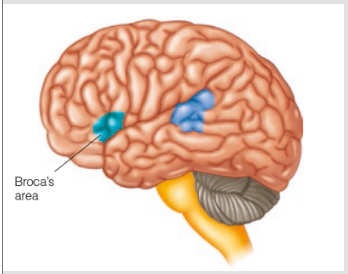
BROCA’S AREA
Region in the frontal lobe associated with the production of language

WERNICKE’S AREA
Region in the temporal lobe associated with understanding language
EXTRASTRIATE BODY AREA (EBA)
Region in the temporal cortex activated by pictures of the human form, not by faces
NEURAL CIRCUIT
Group of interconnected neurons that are responsible for processing
SYNAPSE
Space between the end of an axon and the cell body or dendrite of the next axon
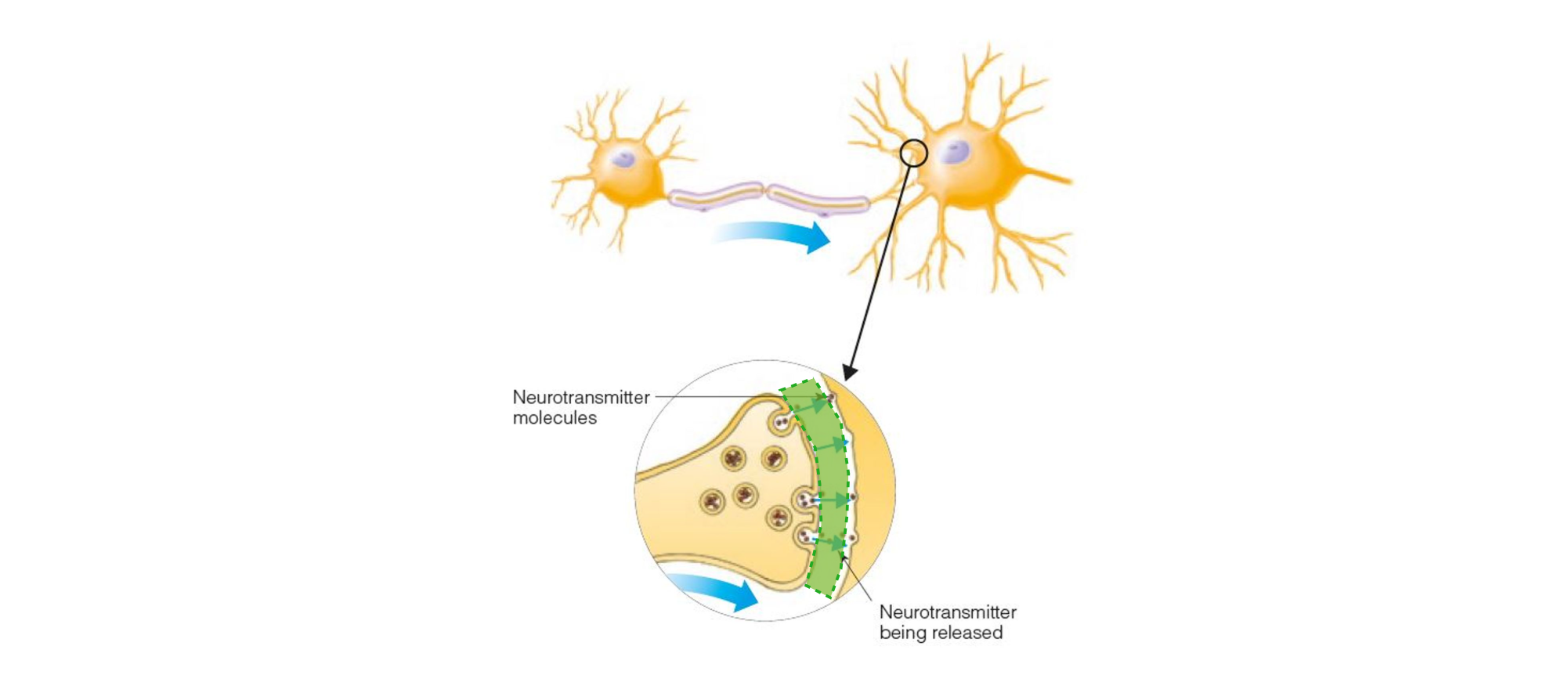
RECEPTOR
Specialized neural structure that responds to environmental stimuli, mechanical stimulation, or chemical stimuli
NEUROTRANSMITTER
Chemical that is released at the synapse in response to incoming action potentials
FEATURE DETECTORS
Neurons that respond to specific stimuli such as orientation, movement, and length
EXPERIENCE-DEPENDENT PLASTICITY
Characteristic of the brain in which its structure is changed by experience
HIERARCHIAL PROCESSING
Neural movement that occurs in a progression from lower to higher areas of the brain
POPULATION CODING
Neural representation of a stimulus by the pattern of firing of many neurons
LOCALIZATION OF FUNCTION
Idea that specific areas of the brain are responsible for specific operations
CEREBRAL CORTEX
Outer layer of the brain that contains the mechanisms responsible for higher mental functions
CORTICAL EQUIPOTENTIALITY
Idea that the brain operates as an indivisible whole
BROCA’S APHASIA
Condition caused by frontal lobe damage that is characterized by slow, labored, ungrammatical speech
PROSOPAGNOSIA
Condition caused by temporal lobe damage that is characterized by an inability to recognize faces
DOUBLE DISSOCIATION
Process by which it is determined that different functions are served by different mechanisms
BRAIN IMAGING
Technique that creates pictures of neural structures
FUNCTIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING (fMRI)
Technique that measures how blood flow changes in response to cognitive activity
VOXEL
Small cube-shaped area in the brain used in analyzing data from brain scanning experiments
FUSIFORM FACE AREA (FFA)
Region in the brain responsible for recognizing human features
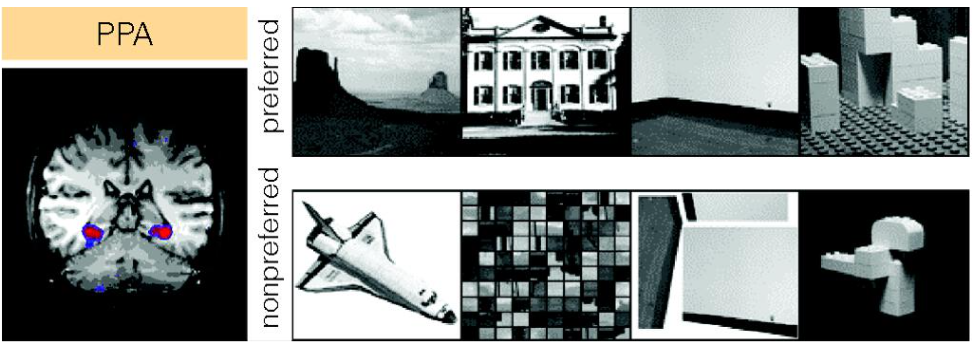
PARAHIPPOCAMPAL PLACE AREA (PPA)
Region in the brain containing neurons selectively activated by pictures of indoor and outdoor scenes
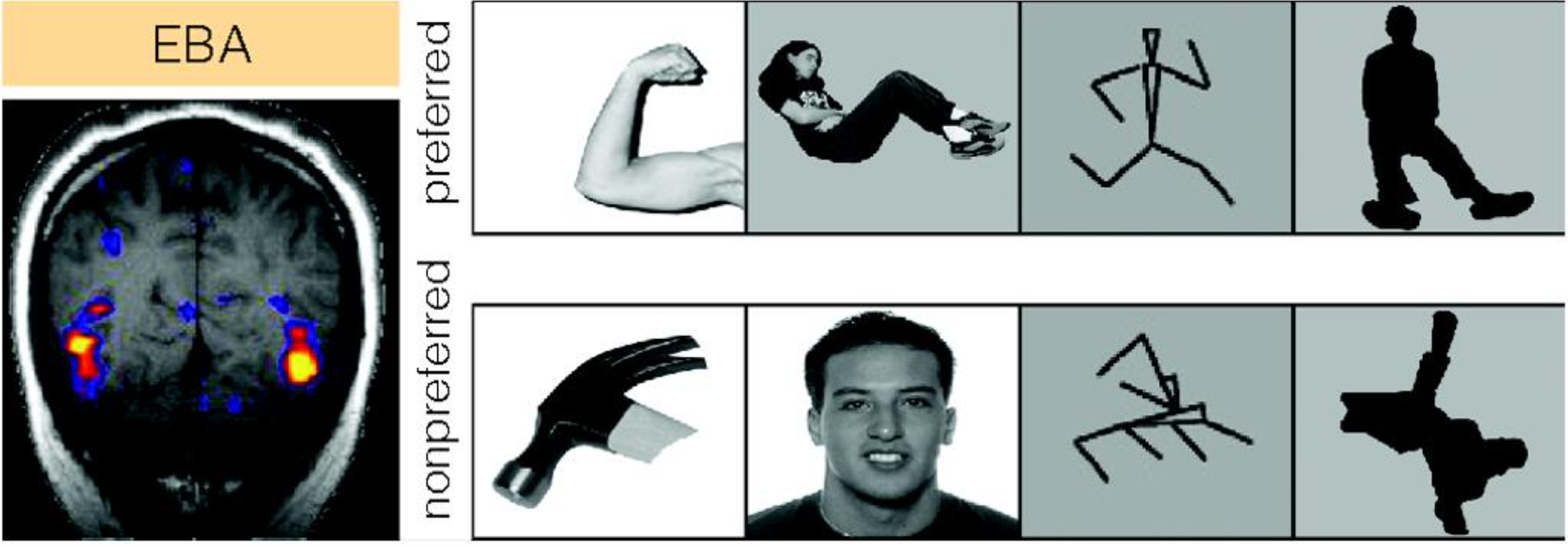
EXTRASTRIATE BODY AREA (EBA)
Region in the temporal cortex activated by pictures of the human form, not by faces
DISTRIBUTED REPRESENTATION
Characteristic of the brain in which looking at a face activates many areas
NEURAL NETWORK
Group of structures that are connected together
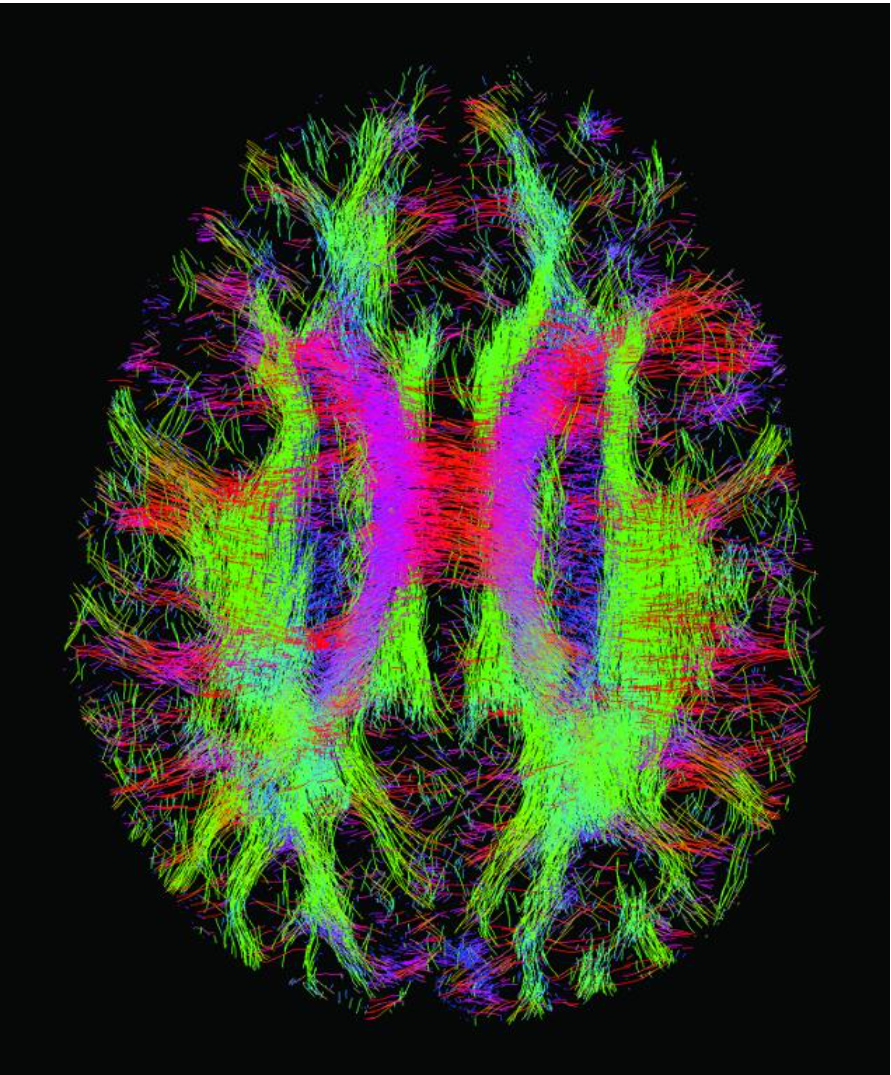
CONNECTOME
Structural description of the network of elements and connections forming the human brain
DEFAULT MODE NETWORK (DMN)
Network of structures that respond when a person is not involved in specific tasks
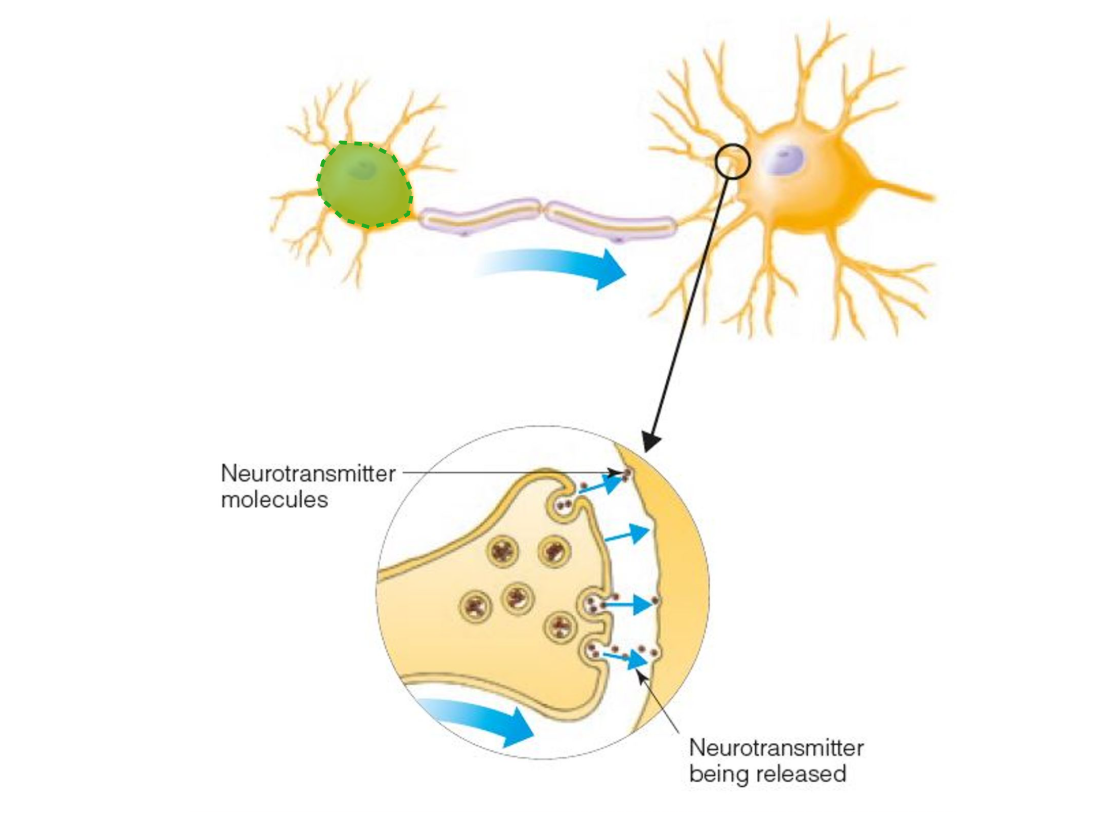
CELL BODY
Part of a cell that contains mechanisms that keep the cell alive