Chemistry - Chapter 6
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
What is reaction rate?
Change in the amount of reactants or products over time
Can be expressed as a change in the amount of reactant consumed over time
OR
Can be expressed as change in amount of product produced over time
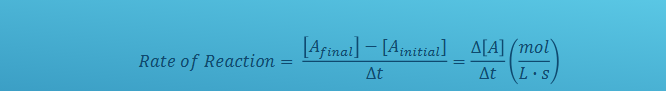
Explain this formula (finding reaction rate)
Rates of reaction are POSITIVE
Δ[A] is change of concentration of the reactant or product
[Afinal] is final conc of reactant or prodct
[Ainitial] is initial conc of reactant or product
t = change in time
always in mol/Ls
difference between change of concentration of a product and change of concentration of a reactant
IF PRODUCT:
Concentration increases over time
Δ[A] is positive, do not change sign
the change of concentration of a product is the rate at which that product is being produced
IF REACTANT:
Concentration decreases over time
Δ[A] is negative
rate = - Δ[reactant]/Δt
rate expression in terms of reactant must have negative sign in front
the change of concentration of a reactant is the rate at which that reactant is decreasing
True or false: reaction rates are typically constant
False. they are not usually constant
What is average rate of rxn
It is the slope of a secant on a Concentration-Time graph.
Gives you the average rate of reaction over a given
time interval
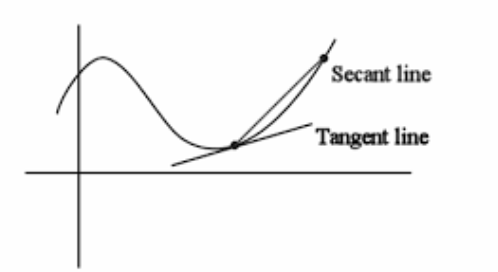
What is instantaneous rate of rxn
It is the slope of a tangent on a Concentration-Time graph.
Gives you the reaction rate at a
particular instant in time.
How is mass, pH, and electrical conductivity monitored, use a reaction as example (methods to measure rxn rate)
Consider rxn Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2
Monitoring mass: hdrogen gas is released, so mass decrease could be monitored by carrying out the reaction in an open vessel on an electronic balance
Monitoring pH: could be monitored as HCl is consumed
Monitoring electrical conductivity: could be monitored.
HCl is a mixture of hydronium ions and chloride ions. As MgCl2 is produced in this reaction, the concentration of ions increases (one Mg2+ and two Cl- ions).
this increase in ion concentration will increase in electrical conductivity over time
How to monitor pressure (method to measure rxn rate)
When a rxn produces gas in a closed system, the pressure of the system will increase and that change can be monitored to study rxn rate
How to monitor color (method to measure rxn rate)
a spectrophotometer can be used to measure the amount of visible light absorbed by a coloured solution.
The amount of light absorbed by a chemical compound is directly related to it’s concentration. (allows you to calculate concentration change over time in rxn)
How to monitor volume (method to measure rxn rate)
monitored when rxn produces gas
What are the 5 factors that affect reaction rates
temperature: increasing temp increases rxn rate
concentration: increasing the conc of reactants helps increase rate of rxn
catalyst: not consumed by reaction. increases rate of rxn
surface area: increasing the available surface area of a reactant INCREASES the rate
types of reactants: rate depends on what the reactants are
True or false: As the concentration of reactants increase in a chemical rxn, most often the rate of reaction increases
True
What is the rate law equation in reactions where the concentration of products does not affect the reaction rate?
Image
Rate=k[Reactant 1]m[Reactant 2]n
Rate laws are based on reactant concentrations.
If the reaction is irreversible or the reverse is negligible, product concentrations do not appear.
Why products don’t appear
Reaction rate depends only on the mechanism of the forward reaction.
The products don’t affect how fast reactants react (unless there’s a reverse reaction involved).
![<p>Image<br><br><span>Rate=k[Reactant 1]m[Reactant 2]n</span><br><br>Rate laws are based on <strong>reactant concentrations</strong>.</p><ul><li><p>If the <strong>reaction is irreversible</strong> or the reverse is negligible, <strong>product concentrations do not appear</strong>.</p></li></ul><p><strong>Why products don’t appear</strong> </p><ul><li><p>Reaction rate depends <strong>only on the mechanism of the forward reaction</strong>.</p></li><li><p>The <strong>products don’t affect how fast reactants react</strong> (unless there’s a reverse reaction involved).</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/260f89c7-64f7-4015-a92e-2f1a821d09fe.png)
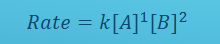
True or false: The values of the rate law exponents determine the order of the reaction
True
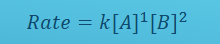
What does this mean? break it down in terms of order
The reaction order is first in A, second order in B. the reaction is third order OVERALL
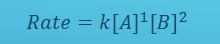
What does this mean? break it down in terms of k
Definition of k: magnitude of rate constant. helps indicate speed of reaction
— a first order reaction with k = 10² s^-1 will be complete in less than 0.10 s
— a first order reaction with k=10^-3 s^-1 will take about 2 hours
What happens to k when conditions remain constant
k stays the same
what happens to k when conditions change, such as if temperature increases
k will increase
** k must be stated with the temperature at which the reaction occurred
Why does reaction rate decrease over time
As a reaction proceeds, the conc of reactants decreases
Since rate = k[reactant]^m [reactant]^n, a lower conc leads to a slower rate
Why do chemists use initial rates method
To determine rate law exponents by comparing initial reaction rates at different reactant concentrations
Reaction does not need to go to completion since only rxn data from the beginning of the reaction is used in initial rates method
— means you only need to measure how fast the rxn starts, not how long it takes to finish
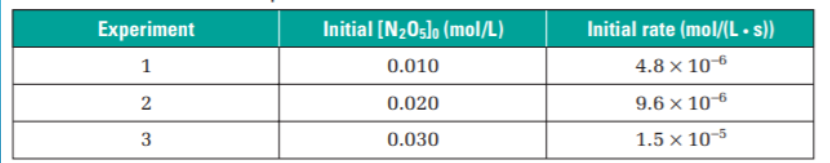
How to tell the overall order of reaction using table of datAA
In example: when concentration doubles the rate doubles
When concentration triples the rate triples
This is a first order reaction
THIS METHOD IS ONLY FOR FIRST ORDER REACTION (EYEBALLING AND PROPORTIONALITY OTHERWISE U HAVE TO SOLVE USING LOG)
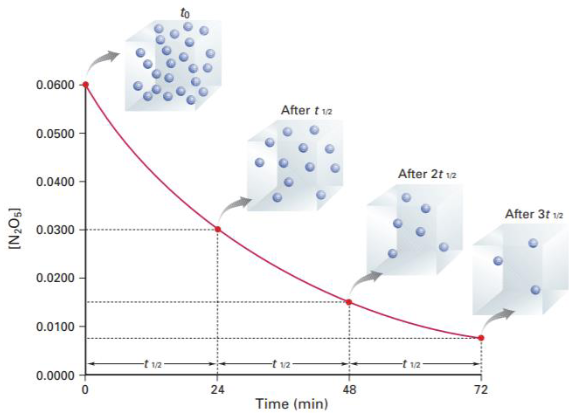
What is half-life of reaction and explain the graph
Half-life, t1/2
→ the time needed for the initial reactant mass or conc to reduce to HALF
ex graph: shows [N2O5] vs time for 3 half-lives at 44 degree celsius
How is half-life calculated for any first order reaction
This
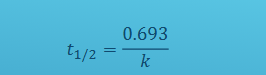
What is collision theory (theory of rxn rate)
In order for a rxn to occur, reactant particles must collide with each other (necessary first step)
How does concentration make rxn rate increase (concentration is a theory of rxn rate)
If the concentration of reactants increases, there will be more collisions betwen particles —> rxn rate increases (faster rate and reaction - means reaction finishes faster)
How does surface area make rxn rate increase (theory of rxn rates)
If the surface area of a solid state reactant increases, this will increase the number of collisions → rxn rate increases
True or false: Every collision between particles results in a rxn (beyond collision theory)
False, not every collision between particles results in a rxn (some collisions will fail and some will succeed- the ones that do will allow rxn to occur)
btw: collision theory is still true on its own, reactant particle smuset collide w each other for reaction to occur (foirst step). Some of the collisions will not be successful however, causing these collisions to fail to cause a rxn to occur. this is what this card is talking about (its just the second step after collision theory is applied)
True or false: in order for a rxn to occur, the collision must be effective (successful)
True
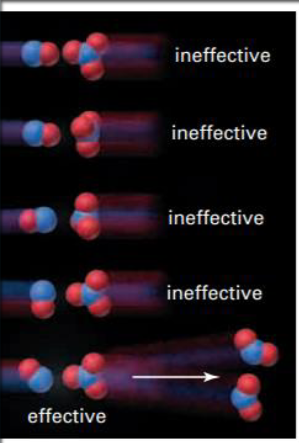
What is an effective collision (successful)
Has correct orientation of reactants and sufficient energy
Only collisions with enough energy and proper orientation will actually form products.
True or false: 1 in 16 collisions between NO and NO3 will result in a rxn
False, only 1 in 5 collisions
True or false: reactants must collide with sufficient energy to break bonds in reactants and form new bonds in the products
True
What is activation energy (Ea)
Minimum collision energy required for a successful reaction
True or false: Collision energy is independent of the kinetic energy of the particles of a substance
False, it depends on the kinetic energy of the particles of the substance (temperature is the average kinetic energy of a substance)
For maxwell boltzmann distribution, what is the independent and dependent variables on the graph
Number of collisions (aka fraction of collisions) = y axis
kinetic energy of each collision at a given temperature (aka energy) = x axis
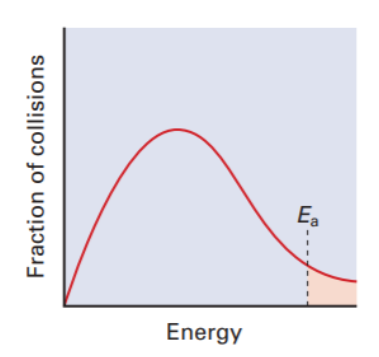
Analuze the graph: what is Ea and what does the shaded region represent
Ea = activation energy
Shaded region represents the fraction of molecules that have enough energy to react
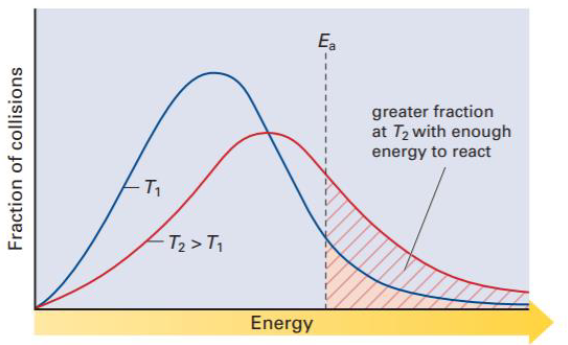
Analyze this second graph (maxwell-boltzmann distribution)
As temp increases, more particles collide with enough energy to react.
True or false: For all reactions, the rate roughly doubles for every 10 degree celsius increase in temperature
False, for many, not all
True or false: When reactions occur at a lower temperature, more particles have enough energy to react so the reaction rates increases
False, when reactions occur at high temperatures, more particles have enough energy to react so the reaction rate increases
Why do chemists carry out reactions under elevated temperatures
To increase reaction rates
What is a reflux apparatus purpose
To prevent vapour loss, a condenser tube is attached so vapours return to the reaction vessel
What is transition state theory
When molecules collide, kinetic energy is transferred into potential energy as the reactants collide
This increase in potential energy can be represented using a potential energy diagram
Fast reactions have a low Ea
Slow reactions have a high Ea
The overall difference in potential energy is the ∆H, enthalpy change
For exothermic reactions Ea(rev) = Ea(fwd) + ∆H
For endothermic reactions Ea(rev) = Ea(fwd) - ∆H
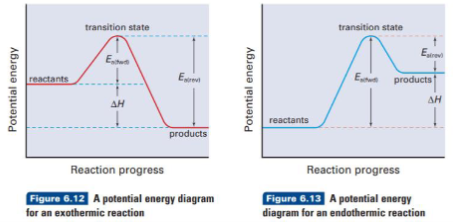
True or false: Reactions can take place in either direction
True
True or false: When a reaction takes place in either direction, enthalpy change for each reaction is the same, but opposite signs
True
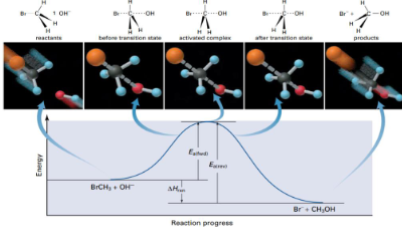
Analyze this diagram of the reaction: 𝐵𝑟𝐶𝐻3 + 𝑂𝐻− → 𝐶𝐻3𝑂𝐻 + 𝐵𝑟−
Describe where the transition state is on the diagram, what is the activated complex?
Transition state: At the top of the Ea barrier. It is the turning point of the reaction. The highest potential energy
Activated complex: The chemical species that exists at the transition state
Neither reactant or produce. The activated complex refers to a range of configurations near the transition state. Activated complex contains partial bonds and is highly unstable
For a successful reaction to take place OH- must approach the BrCH3 from the side opposite the Br atom
Partial bonds exist between OH- and C and the Br - C bond is weakened. At this point, the reaction could go either way - form products or re-form reactants
What is reaction mechanism (definition)?
Involves a series of elementary reactions that are determined using indirect evidence (they cannot be directly observed, they are proposed by providing evidence of reaction intermediate)
What are elementary reactions?
Involve a single molecular event, meaning it cannot be broken down into simpler steps (than that single, individisble step). Can involve the formation of different molecules or ions or a change in the energy or geometry of starting molecules.
What is reaction intermediate?
Appears for a short period of time and cannot be isolated
How are reaction intermediates detected
May be detected if they are colored (for example). A spectrophotometer may show this or the intermediate color change may be seen with the unaided eye.
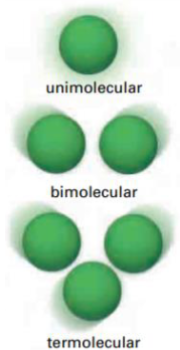
What is molecularity
Refers to the number of reactant particles involved in an elementary reaction
What is bimolecular reaction
Two reactant molecules collide with one another
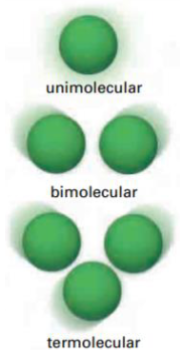
What is unimolecular reaction and think of an example
When one molecule reacts
Ex. Cl2 (g) breaking down in the presence of UV light
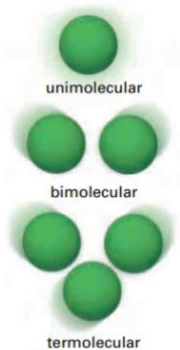
What is termolecular reaction? Is it rare or no?
Three reactant molecules will collide.
Very rare - highly unlikely that three molecules will collide at the same time with sufficient energy and corrwect orientation to react
True or false: rate law equations must be determined experimentally for overall reactions and exponents do not correspond to the stoichiometric coefficients of the overall chemical equation
True
True or False: For elementary reactions, the exponents in the rate law equations are not equal to the stoichiometric coefficients for each reactant
False. For SPECIFICALLY elementary reactions, the exponents in rate law equations are equal to the stoichiometric coefficients for each reactant
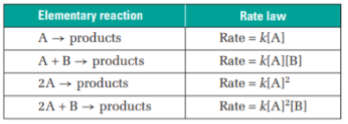
Summary of the elementary reaction and rate law
What are 3 points you need to remember about proposing and evaluating mechanisms
elementary steps must combine to give the overall reaction
Steps must be reasonable
MEchanisms must support the experimentally determined rate law
True or false: Elementary reactions have the same rates
False, they have different rates
What is rate-determining step
When one rate (step) is much slower than the other
How to figure out if the proposed reaction mechanism seems reasonable
Steps add up to overall reaction (HEss law)
Both steps are same molecular reaction (ex. bimolecular)
If the rate law for the slow step matches the experimentally determined rate law for the overall reaction
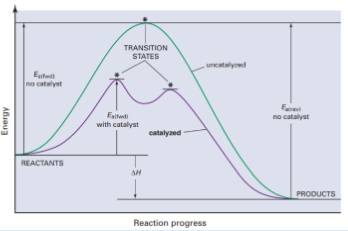
What is a catalyst? What is its purpose
Increases the rate of a chemical rxn without being consumed
Purpose: lowers the activation energy (Ea) for a rxn. this means that more reactants will have effective collisions in order to react.
How do catalysts lower the Ea for the rxn
They provide an alternate mechanism for the reaction
two mech in rxn
catalyzed mech: new rxn path provided by catalyst
uncatalyzed mech” original rxn path
How can a catalyst increase the rate of of a chemical reaction? Does it change the overall rxn?
Consider a one step bimolecular reaction:
A+B→ AB
Catalyst can increase the rate by providing an alternative mechanism that lowers the Ea of the rxn
(catalyst and intermedite both do not appear in overall rxn)
Intermediate - produced first, consumed later
Catalyst - used temporarily, then regenerated as product
A+catalyst → A-catalyst
A-catalyst+B → AB + catalyst
The reaction intermediate A-catalyst is produced in step 1 but consumed in step 2. the catalyst is regenerated as a product in step 2. Thus, it does not get consumed by the reaction, not changing the overall rxn.
(catalyst coming out the same way it came in = regeneration = not consumed, returns to original state after participating temporarily to form intermediates) - it is unchanged at the end
catalyst not consumed = does not change overall rxn
Potential energy diagram for catalyzed vs uncatalyzed
What are homogeneous catalysts? What is their purpose? Give an example using zinc chloride catalyst
They are the same phase as the reactants.
They most often catalyse aqueous and gaseous reactions
Ex. zinc chloride is used to catalyze the reaction between the 2 reactants in the image:
This reaction takes place in solution, zinc chloride is soluble. Thus zinc chloride is a homogeneous catalyst
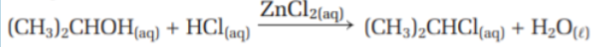
What are heterogeneous catalysts? Give an example using solid palladium catalyst
Definition: Exists in a phase that is different from the phase of the rxn it catalyzes
Ex. From the image, the hydrogenation of ethylene gas is catalyzed by solid palladium
The ethylene and hydrogen molecules form bonds with the metal surface, this weakens the bonds of the hydrogen (H-H) and ethylene (C=C) Hydrogen atoms are somewhat stable because of their attraction the metal
What are enzymes (not needed)
Catalysts in biological processes. They are very large protein molecules (15 000 to 1000 000 g/mol)
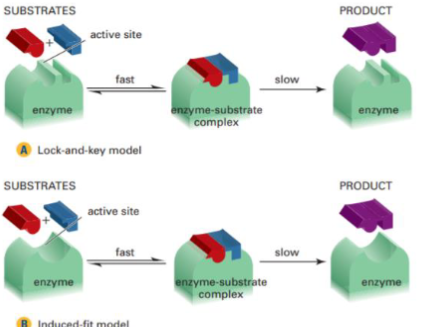
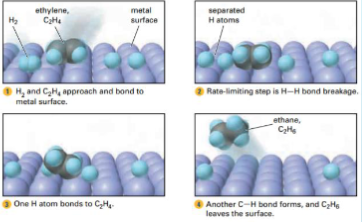
What is this process (not needed)
Catalytic hydrogenation (of ethylene)
know Arrhenius eq