2.2 glucose metabolism
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
overview diagram of metabolism
single glucose molecule yields up to 38 atp
glycolysis - 2
fermentation or respiration - 2
etc - 34

cellular respiration diagram

cellular respiration step by step
aerobic pathway, eventually require oxygen
glycolysis, pyretic
into intermediate (acetyl coa)
citric acid or tca, or Krebs
electron transport chain, final receptor oxygen
fermentation option
glycolysis
first step of respiration,
turns one glucose into 2 pyruvate
anaerobic
in cytoplasm
energy investment (split glucose) (donate to glucose 6 phosphate) and energy pay off (generate atp and nah)
pyruvate moves onto citric acid)
invested two molecules of atp

energy investment and payoff glycolysis

fermentation
allows for the catabolism in the absence of oxygen as the final electron acceptor
yields less energy
recycles nad+
electron acceptors are ethanal (alcoholic fermentation) and pyruvate (lactic acid fermentation)

utilizing fermentation

cellular respiration vs fermentation

Tricarboxylic Acid /Krebs/ Citric Acid cycle
Intermediate step converts pyruvate into Aceytlcoa, enters tca cycle
transfers energy in acetylCoA, to activated carriers NAD+ and FAD
cycle bc series of 8 steps regenerates starting material
occurs in mitochondrial matrix
Krebs cycle simplified diagram
two molecules of acetyl per glucose molecules, goes around Krebs twice,
makes 2 atp, 6 nadh, 2 fadh2

where is cellular respiration?
mitochondria

Electron transport system or chain
ETC uses chemiosmosis (coupling of electron transport and movement of h+ (protons))
electron transport carriers oxidize activated carriers nada and fadh2
energy produced moves hydrogen ions against their concentration gradient from mitochondrial matrix into inter membrane space setting up a proton gradient
hydrogens flow back down the concentration gradient through the enzyme atp synthetase
catalyzes reaction ADP + Pi into atp
occurs with oxygen
ETC diagram
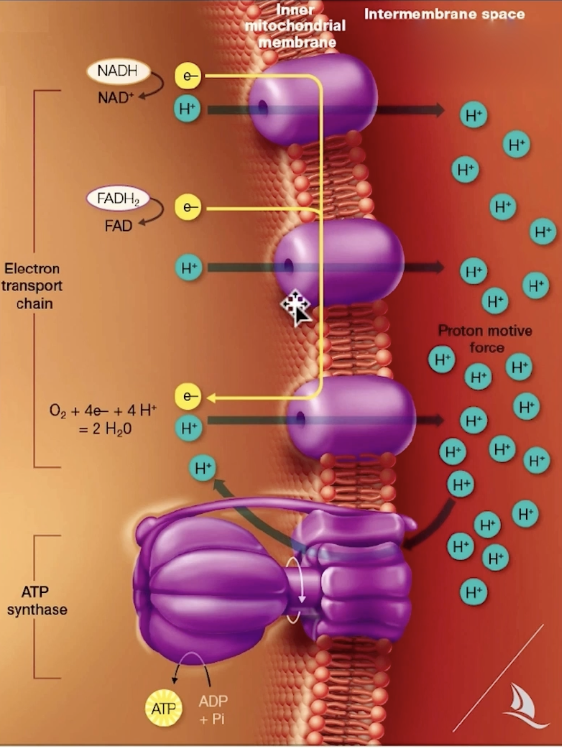
ETC key concepts
electrons move in a sequential chain losing energy with each step in the transfer
electron’s energy is used for pumping H+ ions across the membrane to set up the gradient
oxygen is the final electron acceptor, ending the reaction
etc located in plasma membrane of prokaryotic organism
cellular respiration overall image

yield table

cellular pathway comparisons

fad/fadh
Flavin adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme from riboflavin (B2 vitamin). It is an energy carrier involved in transferring electrons.
cellular respiration
The catabolic reactions that release electrons from molecules and shuttle them via electron carriers to the final electron acceptor, O2, producing H2O, energy, and CO2
metabolism
The chemical reactions an organism uses to breakdown macromolecules to release energy and then harness it to build new ones
energy carrier
Coenzymes (riboflavin and niacin – B vitamins) that pick-up electrons released in one reaction and bring them to another.
nad/nadh
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is a coenzyme from niacin, a B3 vitamin. It is an energy carrier involved in transferring electrons