Ionic equilibrium
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Buffer solution
Ek aisa solution jiska pH value lagbhag constant rehta hai, yaani zyada change nahi hota, chahe usme thodi si acid ya base daal di jaye, usse buffer solution kehte hain.
Acidic buffer solution
"Equimolar mixture of a weak acid and its salt with a strong base."
Ye acidic buffer solution ka ek standard definition hai. Iska matlab samajhne ke liye, isko tod kar samajhte hain:
1. Equimolar mixture → Matlab equal moles ka mixture.
2. Weak acid → Aisa acid jo partially ionize hota hai, jaise acetic acid (CH₃COOH).
3. Its salt with a strong base → Matlab weak acid ka salt, jo ek strong base ke reaction se banta hai. Yahaan sodium acetate (CH₃COONa) diya gaya hai, jo acetic acid aur NaOH se banta hai.
Samajhne ka tareeqa:
Jab acetic acid (CH₃COOH) aur sodium acetate (CH₃COONa) ko equimolar amount me mix karte hain, toh ek buffer solution banta hai.
CH₃COOH ek weak acid hai, jo partially ionize hota hai:
CH₃COOH ⇌ CH₃COO⁻ + H⁺
CH₃COONa → CH₃COO⁻ + Na⁺
Conclusion:
Agar kisi solution me weak acid + uska salt (jo strong base se bana ho) ka equimolar mixture ho, toh wo ek acidic buffer banta hai.
Basic buffer solution
"Equimolar mixture of a weak base and its salt with a strong acid."
1. Equimolar mixture → Matlab equal moles ka mixture.
2. Weak base → Aisi base jo partially ionize hoti hai, jaise ammonium hydroxide (NH₄OH).
3. Its salt with a strong acid → Matlab weak base ka salt, jo strong acid ke reaction se banta hai. Yahaan ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl) diya gaya hai, jo NH₄OH aur HCl ke reaction se banta hai.
Samajhne ka tareeqa:
Jab NH₄OH aur NH₄Cl ko equimolar amounts me mix karte hain, toh ek basic buffer solution banta hai.
NH₄OH ek weak base hai, jo partially ionize hoti hai:
NH₄OH ⇌ NH₄⁺ + OH⁻
NH₄Cl → NH₄⁺ + Cl⁻
Conclusion:
Agar kisi solution me weak base + uska salt (jo strong acid se bana ho) ka equimolar mixture ho, toh wo basic buffer banta hai.
Common ion effect
1. Kya Hai Common Ion Effect?
Imagine tumhare paas ek weak acid hai, jaise acetic acid (CH₃COOH). Ye thoda-bahut dissociate hokar H⁺ ions aur acetate ions (CH₃COO⁻) deta hai:
Ab agar hum isme sodium acetate (CH₃COONa) add karein (jo ek salt hai), toh ye pura dissociate hokar CH₃COO⁻ ions dega.
Common Ion: Sodium acetate aur acetic acid dono CH₃COO⁻ ions dete hain. Isliye, sodium acetate add karne se solution mein CH₃COO⁻ ki concentration badh jati hai.
2. Equilibrium Par Kya Asar Padta Hai?
Le Chatelier ka Principle: Agar kisi reaction ke product ki concentration badha di jaye, toh equilibrium reverse direction (left) shift ho jata hai.
Example:
Acetic acid dissociation:
Sodium acetate add karne se CH₃COO⁻ ions badh gaye → Equilibrium left shift hoga.
Matlab: Acetic acid kam dissociate hoga → H⁺ ions kam banenge.
3. Real-Life Example Samjho:
Case 1: Agar acetic acid mein HCl (strong acid) add kiya, toh HCl pura dissociate hokar H⁺ ions dega. Ye H⁺ ions acetic acid ke dissociation ko suppress karenge (kyuki H⁺ ek product hai).
Case 2: Agar ammonium hydroxide (NH₄OH) mein NH₄Cl (salt) add kiya, toh NH₄Cl se NH₄⁺ ions aayenge → NH₄OH ka dissociation kam hoga.
4. Key Points:
Common Ion Effect Ka Result:
Weak acid/base ka dissociation suppress ho jata hai.
Solution ka pH change nahi hota easily (buffer ki tarah kaam karta hai).
Mathematical Connection:
Agar acetic acid (c₁) aur sodium acetate (c₂) mix kiya, toh:
Isko Henderson-Hasselbalch equation mein use karte hain:
5. Common Ion Effect ka Fayda?
Buffer Solutions: Ye effect use hota hai pH ko stable rakhne ke liye. Jaise blood ka pH 7.4 par stable rehta hai, partially common ion effect ki wajah se.
Lab Experiments: Reactions ko control karne ke liye, jaise precipitate banane ya rokne mein help karta hai.
TL;DR:
Common ion effect = Jab ek hi ion ko do sources se add karo, toh weak acid/base ka dissociation kam ho jata hai.
Example: Acetic acid + Sodium acetate → Ac
etic acid kam dissociate hoga.
Iska use pH control karne mein hota hai! 🔥
Mechanism of buffer solution/Buffer action
Acidic Buffer solution (CH3COOH+ CH3COONa)
Doubt Cleared:
🔍 Situation: Base add kar rahe ho buffer mein
Buffer solution:
Weak acid: CH₃COOH
Salt (conjugate base): CH₃COONa → gives CH₃COO⁻
📌 Jab base (OH⁻) daala buffer mein:
OH⁻ ions kya karta hai?
➡ OH⁻ reacts with H⁺ ions in solution:
\text{OH}^- + \text{H}^+ \rightarrow \text{H}_2\text{O}
➡ pH badhne wala tha kyunki H⁺ kam ho gaya
Lekin...
⚖ Le Chatelier's Principle:
> “Jab system ka equilibrium disturb hota hai, toh woh us disturbance ko cancel karne ki koshish karta hai.”
Aapke case mein:
H⁺ ions kam ho gaye hain (OH⁻ ne use up kar liya)
Equilibrium:
\text{CH}_3\text{COOH} \rightleftharpoons \text{H}^+ + \text{CH}_3\text{COO}^-
➡ System ka equilibrium right shift karega
➡ Aur CH₃COOH toot kar aur H⁺ banayega
➡ Taa ki lost H⁺ ions ko compensate kiya jaa sake
✅ Result:
Naye H⁺ ions ban jaate hain
pH zyada change nahi hota
Isiliye hum kehte hain "buffer resists change in pH"
💡 Final Hinglish Summary:
> Jab base add kiya, OH⁻ ne H⁺ ko le liya → pH badhne laga.
Lekin system ne equilibrium ko right shift karke aur CH₃COOH ko dissociate karwaya → naye H⁺ aaye → pH wapas stable ho gaya.
Isiliye buffer ka pH constant rehta hai (zyada change nahi karta).

Mechanism of buffer solution/Buffer action
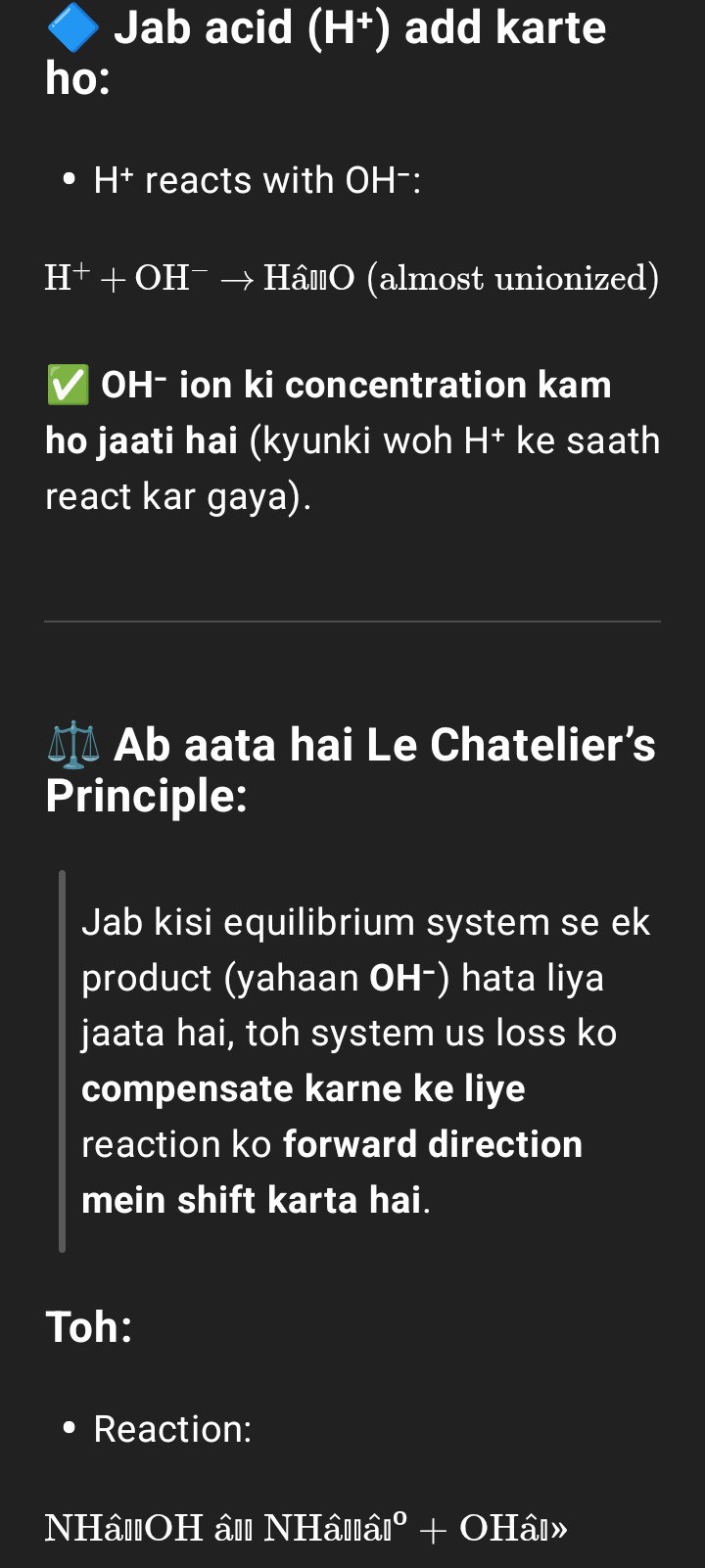
Basic buffer solution
When a small amount of acid is added to the above buffer solution, the H⁺ ions given by the acid combine with the OH⁻ ions released by NH₄OH to form H₂O (which is almost unionized).
As a result, more NH₄OH dissociates slightly to replace the OH⁻ ions used up, thereby maintaining the pH of the solution nearly constant.
Simple table to clear double

Henderson equation for acidic buffer solution
