MCAT Behavioral Sciences - Learning and Memory
1/133
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
134 Terms
learning
to the way in which we acquire new behaviors
stimulus
anything to which an organism can respond, including all of the sensory inputs
habituation
repeated exposure to the same stimulus can cause a decrease in response
subthreshold stimulus
a stimulus too weak to elicit a response
Dishabituation
the recovery of a response to a stimulus after habituation has occurred
Associative learning
creation of a pairing either between two stimuli or between a behavior and a response
Classical conditioning
type of associative learning that takes advantage of biological, instinctual responses to create associations between two unrelated stimuli
Ivan Pavlov
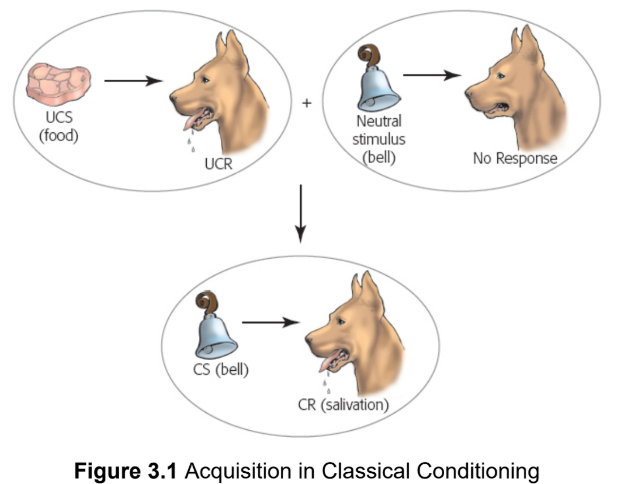
unconditioned stimulus
Any stimulus that brings about a reflexive response
unconditioned response
the innate or reflexive response to an unconditioned stimulus
neutral stimuli
stimuli that do not produce a reflexive response
conditioned stimulus
a normally neutral stimulus that, through association, now causes a reflexive response
conditioned response
the innate or reflexive response to an conditioned stimulus
acquisition
process of using a reflexive, unconditioned stimulus to turn a neutral stimulus into a conditioned stimulus
Extinction
loss of a conditioned response, and can occur if the conditioned stimulus is repeatedly presented without the unconditioned stimulus
spontaneous recovery
extinction of a response is not always permanent; after some time, presenting subjects again with an extinct conditioned stimulus will sometimes produce a weak conditioned response
Generalization
broadening effect by which a stimulus similar enough to the conditioned stimulus can also produce the conditioned response
e.g. Little Albert
(stimuli) discrimination
an organism learns to distinguish between similar stimuli
operant conditioning
the ways in which consequences of voluntary behaviors change the frequency of those behaviors
B.F. Skinner
behaviorism
the theory that all behaviors are conditioned
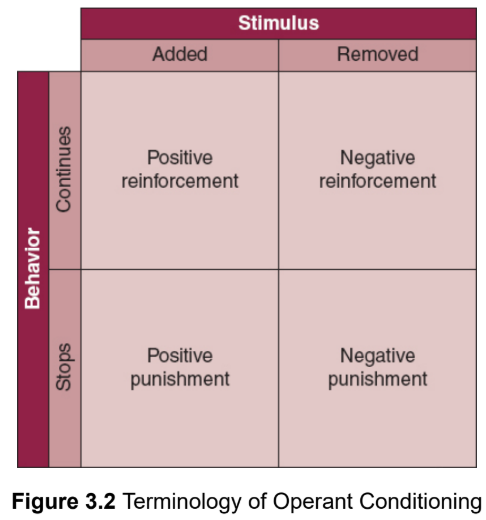
reinforcement
the process of increasing the likelihood that an animal will perform a behavior
reward-seeking behaviors
ways that organisms search for resources in their enironment
e.g. foraging, approach behaviours
Positive reinforcers
increase the frequency of a behavior by adding a positive consequence or incentive following the desired behavior
e.g. money
Negative reinforcers
increase the frequency of a behavior by removing something unpleasant
e.g. pain/painkillers
Escape learning
a situation where the animal experiences the unpleasant stimulus and, in response, displays the desired behavior in order to trigger the removal of the stimulus
avoidance learning
when the animal displays the desired behavior in anticipation of the unpleasant stimulus, thereby avoiding the unpleasant stimulus
primary reinforcer
stimulus that the subject responds to naturally
conditioned/secondary reinforcer
stimulus that the subject would not respond to naturally, but can be trained to respond to
discriminative stimulus
indicates that reward is potentially available in an operant conditioning paradigm
punishment
conditioning to reduce the occurrence of a behavior
Positive punishment
adds an unpleasant consequence in response to a behavior to reduce that behavior
e.g. fine
aversive conditioning
using something unpleasant to discourage a behavior
negative punishment
removing a stimulus in order to cause reduction of a behavior
e.g. grounding
reinforcement schedule
the rules that determine how often an organism is reinforced for a particular behavior
formal sanctions
a penalty, or some coercive measure, intended to ensure compliance; especially one adopted by several nations, or by an international body
e.g. rules and laws
informal sanctions
reactions of individuals and groups that bring about conformity to norms and laws
e.g. ostracization, praise, and shunning
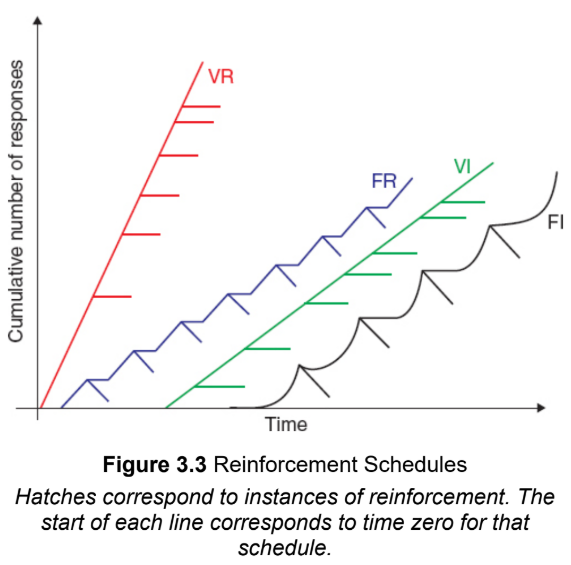
Fixed-ratio (FR) schedule
reinforce a behavior after a specific number of performances of that behavior
e.g. every third time
Continuous reinforcement
a fixed-ratio schedule in which the behavior is rewarded every time it is performed
Variable-ratio (VR) schedules
reinforce a behavior after a varying number of performances of the behavior, but such that the average number of performances to receive a reward is relatively constant
Fixed-interval (FI) schedules
reinforce the first instance of a behavior after a specified time period has elapsed
e.g. every 60 seconds
Variable-interval (VI) schedules
reinforce a behavior the first time that behavior is performed after a varying interval of time
effectiveness of various reinforecemnt schedules
variable-ratio works the fastest for learning a new behavior, and is also the most resistant to extinction (Very Rapid and Very Resistant)
e.g. gambling
shaping
process of rewarding increasingly specific behaviors that become closer to a desired response
latent learning
learning that occurs without a reward but that is spontaneously demonstrated once a reward is introduced
Problem solving
the ability to analyze the situation and respond correctly the first time without brute-force trial-and-error
preparedness
predisposition to learn certain behaviours based on natural abilities and instincts
instinctive/instinctual drift
When animals revert to an instinctive behavior after learning a new behavior that is similar
Observational learning
process of learning a new behavior or gaining information by watching others
Albert Bandura (social learning)
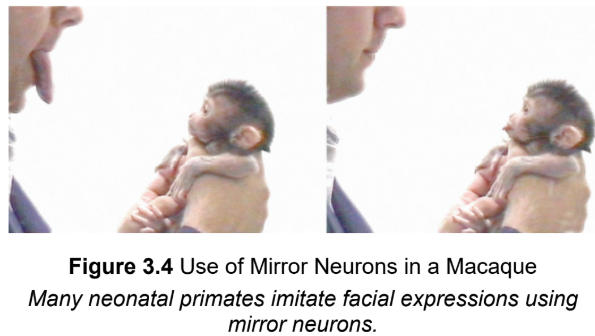
mirror neurons
located in the frontal and parietal lobes of the cerebral cortex; fire both when an individual performs an action and when that individual observes someone else performing that action; additionally are thought to be related to empathy and vicarious emotions; play a role in imitative learning
modeling
People learn what behaviors are acceptable by watching others perform them
memory
how we gain the knowledge that we accumulate over our lifetimes
Encoding
the process of putting new information into memory
automatic processing
Information gained without any effort; information is passively absorbed from the environment
controlled/effortful processing
active memorization; can become automatic with practice
visual encoding
store the way stimuli look
acoustic encoding
store the way stimuli sound
elaborative encoding
link information to knowledge that is already in memory
semantic encoding
put information into a meaningful context
self-reference effect
we tend to recall information best when we can put it into the context of our own lives
maintenance rehearsal
repetition of a piece of information to either keep it within working memory or to store it in short-term and eventually long-term memory
Mnemonics
often acronyms or rhyming phrases that provide a vivid organization of the information we are trying to remember
method of loci
associating each item in a list with a location along a route through a building that has already been memorized; “memory palace”
peg-word system
associates numbers with items that rhyme with or resemble the numbers
chunking/clustering
a memory trick that involves taking individual elements of a large list and grouping them together into groups of elements with related meaning
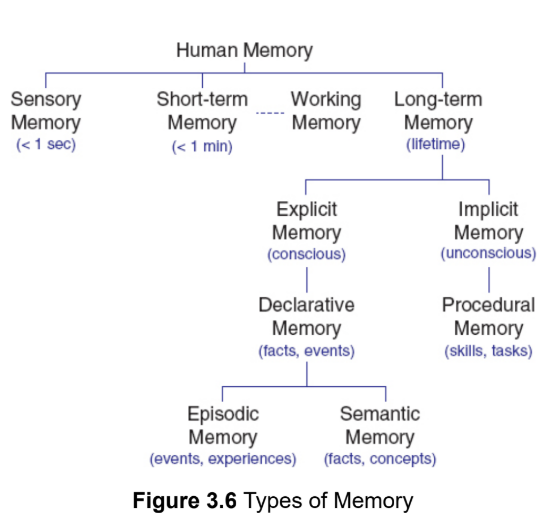
sensory memory
first and most fleeting kind of memory storage; preserves information in its original sensory form (auditory, visual, etc.) with high accuracy; lasts only a very short time (<1 s)
iconic memory
fast-decaying sensory memory of visual stimuli; occipital lobe
echoic memory
fast-decaying sensory memory of auditory stimuli; temporal lobe
haptic memory
fast-decaying sensory memory of touch stimuli; somatosensory cortex
whole-report
a method used in studies of iconic memory in which the participant attempts to recall all of the presented information
partial-report
a method of testing memory in which only some of the total information presented is to be recalled
Eidetic memory
the ability to recall, with high precision, an image after only a brief exposure; may represent an extreme example of iconic memory that endures for a few minutes; generally not observed in adults, but reported in a small percentage of children
short-term memory
the reproduction, recognition, or recall of a limited amount of material; memory fades quickly (~30 s w/o rehearsal)
memory capacity
the number of items we can hold in our short-term memory at any given time
7 ± 2 rule
hippocampus
memory center of brain; both short- and long-term memory
Working memory
enables us to keep a few pieces of information in our consciousness simultaneously and to manipulate that information; integrate short-term memory, attention, and executive function; mental math
long-term memory
an essentially limitless warehouse for knowledge that we are then able to recall on demand
elaborative rehearsal
association of the information to knowledge already stored in long-term memory
cerebral cortex
holds very long-term memories
visuospatial sketchpad
aspect of working memory; stores and manipulates visual and spatial information
Baddeley and Hitch working memory model
central executive
visuospatial sketchpad
phonological loop
episodic buffer
Implicit/nondeclarative memory
skills, habits, and conditioned responses, none of which need to be consciously recalled
procedural memory
unconscious memory of the skills required to complete procedural tasks
priming
the presentation of one stimulus affecting perception of a second
Positive priming
exposure to the first stimulus improves processing of the second stimulus; decreased response time or decreased error rate
negative priming
the first stimulus interferes with the processing of the second stimulus, resulting in slower response times and more errors
explicit/declarative memory
memories that require conscious recall
episodic and semantic
episodic memory
recollection of life experiences
semantic memory
ideas, concepts, or facts that we know, but are not tied to specific life experiences
Autobiographical memory
explicit memories about our lives and ourselves, and includes all of our
episodic memories of our own life experiences, but also includes semantic
memories that relate to our personal traits and characteristics
flashbulb memory
the detailed recollection of stimuli immediately surrounding an important (or emotionally arousing) event
retrieval
to the process of demonstrating that something that has been learned has been retained
recall
the retrieval and statement of previously learned information
recognition
process of merely identifying a piece of information that was previously learned
Relearning
second time memorising/learning is much faster than first
spacing effect
the longer the amount of time between sessions of relearning, the greater the retention of the information later on
semantic network
concepts are linked together in the brain based on similar meaning
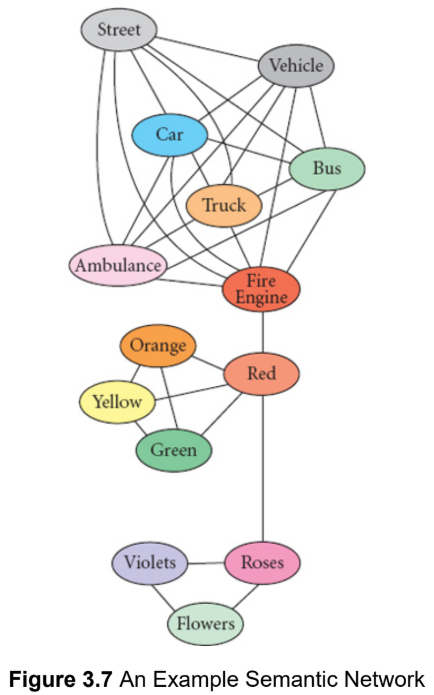
spreading activation
When one node of our semantic network is activated, the other linked concepts around it are also unconsciously activated
recall cue
a word or phrase that is close to the desired semantic memory.
context effect
where memory is aided by being in the physical location where encoding took place
source monitoring
part of the retrieval process that involves determining the origin of memories, and whether they are factual (real and accurate) or fictional (from a dream, novel, or movie)
State-dependent memory/effect
is a retrieval cue based on performing better when in the same mental state as when the information was learned