Unit 4 chem quiz 2
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
good luck minions of Mrs Olar 😢
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Metals
Hard solids
Hugh electrical conductivity
High melt/boiling points
How do we apply thomsons model to compounds?
Electrical forces are involved in holding the particles that make up pure substances
Charge of neutral atoms
have equal amount of both positive and negative charge
Charged pieces of tape interaction with other objects
When two objects of diff substances come into contact, some electrons move from one substance to the other.
The top tape becomes + charged bc electrons are transferred to the bottom tape.
Two ways materials conduct electricity
If electrons move around freely, or ions can move around freely
Non metals
Softer
Colorful elements
Lower melt/boiling levels than most metals
Poor conduction of heat/electricty
Ionic compounds
Compounds composed of ions, charged particles that form when an atom loses or gains electrons. They are NOT molecules.
covalent/molecular compounds
Compounds form when elements share electrons in a covalent bond to form molecules.
Molecular compounds are electrically neutral.
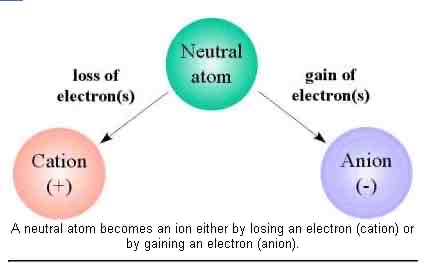
How does neutral atom become a positive ion?
A neutral atom must lose electrons to become a positive ion (cation)
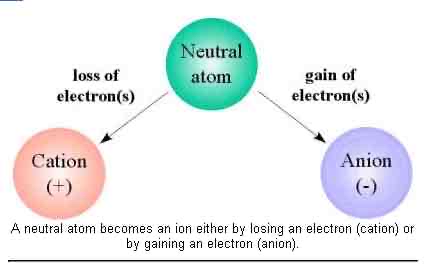
How does a neutral atom become a negative ion?
A neutral atom must gain electrons to become a negative ion (anion)
Why do some things conduct electricity while others do not?
if electrons can move around freely and if ions can move around freely then electricity can be conducted.
Electrolyte
Conducts electricity when dissolved in water
What are cathode rays?
Negatively charged electrons (smaller than atoms)
Ionic
Metals + non metals
Covalent
Non metals only
Metallic
Metals only
In the sticky tape activity, we stuck two uncharged pieces of tape together and then pulled them apart. Explain how you knew the two pieces of tape had different charges after pulling them apart.
Support your answer with your observations and data from the activity!
When the two pieces of tape were palled apart, electrons from the top tape transferred onto the bottom tape, which gained more electrons. Thus, the top tape had a positive charge while the bottom tape had a negative charge. Then, we made both the top tape and bottom tape come in contact with neutral objects such as paper, aluminum, and fur. One notable difference was that the fur was attracted to the top tape, but was repelled by the bottom tape. Therefore, the two pieces of tape had different charges when pulled apart
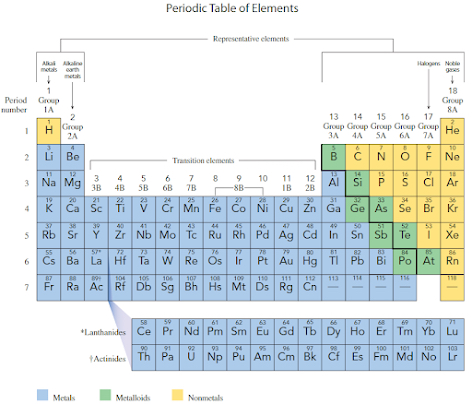
Periodic chart
Yellow - non metal
Green - metalloids
Blue - metals
Structural formulas
Explain how atoms become ions using thomsons plum pudding model
For an atom to become an ion, it has to gain or lose electrons. This can be similar to plucking out or adding “plums” (electrons) to the positive charged sphere.
How do you predict the conductivity of a solution based on the composition of the compound dissolved in water (idk if this will be on the quiz)
The more ions and the more easily electrons are able to move around freely, the high the electrical conductivity.
Explain how an object becomes polarized (electrically charged)
separation of positive and negative charges.
Rubbing (transfer) , induction (repel/attract), and contact with a charged object
Diffrientiate between elements, compounds, and mixtures
Elements - pure substances of one atom
Compounds - chemically combining of two or more elements
Mixtures - physically combing two or more substances
ions
An atom that carries a positive or negative charge as a result of losing or gaining electrons.
Copper ions have a positive charge because
copper metal formed on the negative electrode
Anion
Negatively charged ion. Must lose electrons to become a neutral atom. Attracted to anode.
Cation
Positively charged ion. Attracted to cathode.
Polarization
The Disortion of negatively charged electrons by a positively charged electron. This effect caused electrons in neutral objects to changed direction temporarily, even though the overall object remains neutral.
Anode
Electrode that’s Usually on the positive side
Cathode
An electrode that’s usually on the negative side.
Compare differences and similarities of elements, mixtures, and compounds
(This was on last quiz I think, tests target 4.2)