Urine crystals and uroliths
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is found in urine sediment
Crystals e.g. calcium oxalate, struvite
Bacteria and WBCs
Yeast
Blood
Sperm
Epithelial cells
Neoplasia
What is the method for prepping sediment
Sediment samples should be spun via a centrifuge
1000-1500 for 5 minutes
Remove the supernatant and re-suspend sample
Pipette sample onto slide and place cover slip
Are RBCs in urine normal
<5 RBCs in field is normal
Must consider how we got sample as can have caused bleeding thru cysto and urinary catheter as are traumatic ways to get urine
Can be iatrogenic
What does iatrogenic mean
Relating to illness caused by medical examination or treatment
How to identify RBCs under microscope
All similar size
All similar colouring
Are WBCs in urine normal
<5 WBcs in field in normal urine
>5 is called Pyuria- inflammation, infection, trauma, neoplasia
Presence can be due to contamination depending on how we obtained urine sample
If cysto or catheter WBCs should not be there
What are the 4 different types of epithelial cells
Transitional
Squamous
Neoplastic
Neoplastic squamous
What are the characteristics of transitional epithelial cells
Common
Grainy cytoplasm
Central nucleus
Shouldn’t see loads
Where can we find squamous epithelial cells
In free catch sample
In expressed sample
Where can we find neoplastic epithelial cells
In transitional cell carcinomas
Where can we find neoplastic squamous cells
In squamous cell carcinomas
Example of neoplastic cells
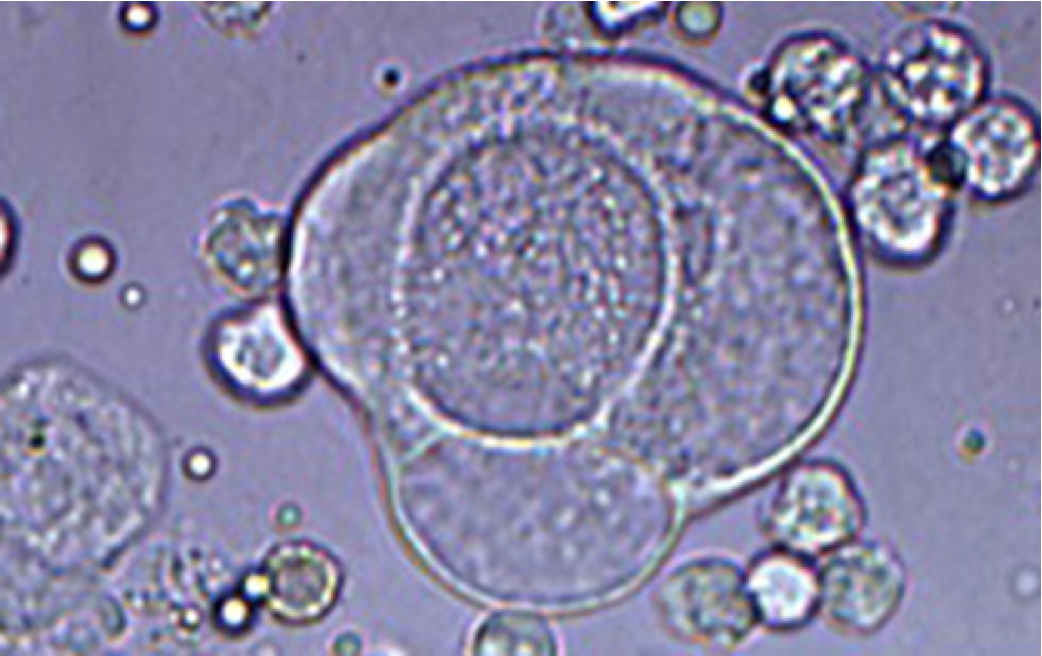
What are casts
Mucoproteins
Where can we see casts
Only on unstained slides
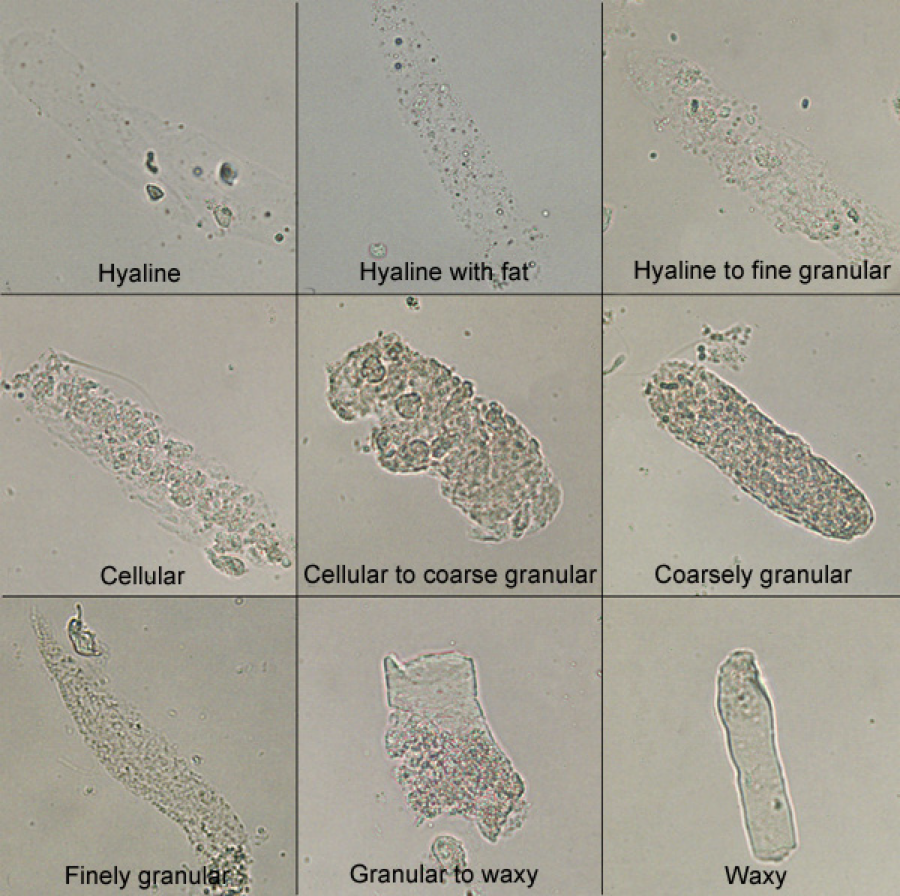
What are the 5 types of casts
Hyaline
Epithelial
Granular
Waxy
RBC and WBC
Fatty-lipid
What are the characteristics of hyaline casts
Parallel sides
Rounded ends
Mucoprotein
A few are normal
Associated with proteinuria
What are the characteristics of epithelial casts
Entrapment of sloughed cells in mucoprotein
Aka acute red tubular disease
What are the characteristics of granular casts
Degenerated epithelial cellular casts
Few is normal
Indicate acute renal disease/damage
What are the characteristics of waxy casts
Degeneration of granular/cellular casts
Never normal
What are the characteristics of RBC and WBC casts
Always abnormal
RBC-renal haemorrhage
WBC-renal inflammation
What are the characteristics of fatty lipid casts
Accumulate in kidneys
Cast images
UPLOAD IMAGE 49
What are the characteristics of bacteria
If cystocentesis is obtained and bacteria present—>infection
Free catch or expression= could be contamination but if large number and the same in appearance can be infection, will need more testing
Rods most easily identified
Confirm with gram stain or aerobic culture
What are the characteristics of yeast
Often result of contamination unless cysto or catheter then will indicate a yeast infection as there is no contaminated sample
Round to oval
Colourless
Usually treated with long term antibiotics
What are the characteristics fungal hyphae
Very rare
Most commonly due to contaminates overgrowth
Fungal infection can occur with aspergillus terreus-systemic infection including renal pelvis colonization
What are the characteristics of lipids
Common
Can be mistaken for RBCs
Vary in size
Most common in cats
Where can you find sperm in urine
Males
Recently bred females
Where can you find plant material
Debris in contaminated samples
samples collected from floor or litter trays
What affects crystal formation
Urine pH
Concentration of crystal forming minerals
Urine temp
Length of time between collection and examination
Not necessarily pathologic
What are the 7 types of crystals
Struvite
Calcium oxalate
Calcium carbonate
Ammonium urate
Uric acid
Cysteine
Billirubin
What are the properties of struvite crystals
Forms in alkaline urine
Common in cats and dogs
Dogs have a bacterial element to struvite crystals but cats don’t
In dogs- struvite+UTI—>urolith
Felines don’t get UTI (no bacterial element)—> no urolith
Coffin lid/prism shaped
Can treat with acidifying diets
What is the veterinary name for struvite crystals
Magnesium ammonium phosphate
What are the properties of calcium oxalate crystals
Normally formed in acidic urine
Common in healthy horses but less common in SA
Form in stored urine
Increased risk of urolith formation
Can occur due to hypercalcemia and or renal injury
What s the veterinary name for calcium oxalate crystals
Dihydrate
What are the properties of calcium carbonate crystals
Horses, rabbits and guinea pigs
Alkaline pH
Cause uroliths in guinea pigs
Rare in dogs/cats
Large circular crystals
Smaller-pairs/tetrads
Slightly brown
What are the properties of ammonium urate crystals
Acidic urine
Never normal
Birds, dogs, reptiles
Caused by liver disease (e.g. PSS)
Certain breeds e.g. Dalmatians, bulldogs, Black Russian terriers
Yellow/brwon
Irregular, spiny projections
What are the properties of uric acid
Formed in acidic urine
Dalmatians are predisposed as can’t convert uric acid to allantoin (purine metabolism)
What are the properties of cysteine crystals
Acidic urine
Many breeds of dogs, ferrets
Rarely cats
Proximal tubular defect in amino acid resorption
Six sided
Variable in size
What are the properties of bilirubin
Normal in dogs, cats
Due to bilirubinuria—> due to cholestasis or haemolysis
Detected on dipstick
Brown
Urchin shaped crystals
What are the 4 types of uroliths
Struvite
Calcium oxalate
Urate
Cysteine
Where are struvite uroliths most common
Female dogs (associated with infection)
Male cats
Where are calcium oxalate uroliths most common
MN, obese dogs, monohydrate
MN, obese cats, dihydrate
Where are urate uroliths most common
Males
What are properties of urate uroliths
Uric acid
Xanthine
Very uncommon
Normally dogs treated with allopurinol
Where are cysteine uroiths most common
Male dogs
Middle aged terriers