Midterm 2 terms
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 8:30 PM on 7/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
154 Terms
1
New cards
monochromatic colour
single component of colour that cannot be refracted into different colours
2
New cards
problem of univariance
an infinite set of different wavelength-intensity combinations can elicit the same response from a single type of photoreceptor
one type of photoreceptor cannot discriminate colour based on wavelength
one type of photoreceptor cannot discriminate colour based on wavelength
3
New cards
scotopic
dim light
rods are sensitive
rods are sensitive
4
New cards
rhodopsin
photopigment in rods
5
New cards
Young-Helmholtz-Maxwell theory
colour vision is based on 3 photoreceptors sensitive to a particular ranges of wavelengths
trichromatic colour vision
trichromatic colour vision
6
New cards
Maxwell’s colour-matching technique
three colors can mix in different proportion to make other colours
additive explanation
additive explanation
7
New cards
s cones
420 nm “blue”
8
New cards
m cones
534nm “green”
9
New cards
l cones
565nm “red”
10
New cards
fovea
the _____ only has red and green cones
11
New cards
metamers
pair of stimuli that are perceived as identical though they are physically different
different mixtures of wavelengths can look identical
different mixtures of wavelengths can look identical
12
New cards
additive colour mixture
if lights are reflected, in perception they are added together
13
New cards
subtractive colour mixture
if pigments mix and light shines on them, what remains contributes to colour perception
14
New cards
hue
chromatic aspect of colour
15
New cards
saturation
chromatic strength of hue
16
New cards
brightness
distance from black in colour space
17
New cards
non spectral hues
don’t exist as pure light, only as mixtures of wavelengths
18
New cards
opponent colour theory
colour perception is based on red-green, blue-yellow, and black-white ratios
LGN has neurons that code differences between sets of cones
LGN has neurons that code differences between sets of cones
19
New cards
V1 colour system
blobs
20
New cards
V2 colour system
thin stripes
21
New cards
V4
colour area
22
New cards
achomatopsia
inability to perceive colours due to damage in CNS
23
New cards
ishiahara test
tests colour blindness
8% of males and 0.5% of females are colour blind
8% of males and 0.5% of females are colour blind
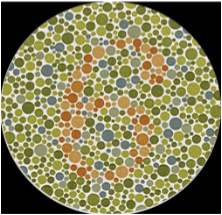
24
New cards
cone monochromat
only one type of cone
true colour blindness
true colour blindness
25
New cards
rod monochromat
no cones at all
true colour blindness
visual impairment in bright light
true colour blindness
visual impairment in bright light
26
New cards
deuteranope
colour anomalous people with no m-cones
27
New cards
protanope
colour anomalous people with no l-cones
28
New cards
tritanope
colour anomalous people with no s-cones
29
New cards
cultural relativism
different cultures describe colour differently and may perceive colours differently
30
New cards
unrelated colour
colour that can only be experienced in isolation
31
New cards
related colour
colour that can only be seen relative to other colours
example - brown & grey
example - brown & grey
32
New cards
colour constancy
tendency for surface to appear the same colour under a wide range on lumination
example - bees & goldfish
example - bees & goldfish
33
New cards
sensation equation
sensation = illuminant x reflectance
\[what we see\] = \[what we don’t and don’t care\] x \[what we don’t know and care about\]
12 = a\*b
\[what we see\] = \[what we don’t and don’t care\] x \[what we don’t know and care about\]
12 = a\*b
34
New cards
illuminant
what we don’t know and aren’t interested in
assumptions: 1 light source that is broadband, surface reflects broadband and has mutual reflections
assumptions: 1 light source that is broadband, surface reflects broadband and has mutual reflections
35
New cards
reflectance
what we don’t know but want to know
36
New cards
dichromats
two photoreceptors
example - dogs
example - dogs
37
New cards
tetrachromat
four colour receptors
example - chickens
example - chickens
38
New cards
motion aftereffect (MAE)
illusion of motion of a stationary motion after prolonged exposure to a moving object
due to imbalance in medial temporal
example - waterfall illusion, falls of Foyers
due to imbalance in medial temporal
example - waterfall illusion, falls of Foyers
39
New cards
reichardt detector
motion perception is discrete
delay causes motion perception in bugs
delay causes motion perception in bugs
40
New cards
apparent motion
illusionary impression of smooth motion resulting from the rapid alteration of objects that appear in different locations in rapid succession
41
New cards
correspondence problem
how do motion detection system know which feature is frame 2 corresponds to frame 1
42
New cards
aperture problem
the direction of motion is ambiguous when through a receptive field, the
partial view of object
partial view of object
43
New cards
global motion detector
integrates local motion information
44
New cards
magnocellular layers
lesions in _____________ __________ of LGN impair perception of large, rapidly moving objects
45
New cards
complex V1 cells
occipital neurons sensitve to motion
46
New cards
middle temporal lobe
brain region important for motion perception
47
New cards
medial temporal / MT / V5 / hMT
brain region that are selective for motion in a particular direction
48
New cards
global motion task
used to study motion perception in MT
normal monkeys can determine correct direct with 2-3% of cues being targets
lesioned monkeys need 10x more target cues to determine direction
normal monkeys can determine correct direct with 2-3% of cues being targets
lesioned monkeys need 10x more target cues to determine direction
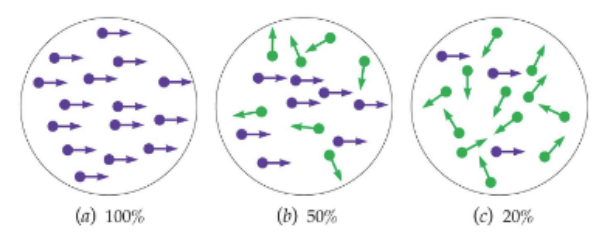
49
New cards
interocular transfer
adaption from one eye to the other after LGN
50
New cards
first order motion
motion of an object that is defined by change in luminance
51
New cards
second order motion
motion of an object is defined by contrast or texture
52
New cards
double dissociation
first and second order motion are independent which was discovered using _________ __________
53
New cards
optic flow
changing angular position of points as you move
54
New cards
biological movement
movement of living things
55
New cards
akinetopsia
individual has no perception of motion
medial temporal lesion
medial temporal lesion
56
New cards
Akiyoshi Kitaoki’s rollers illusion
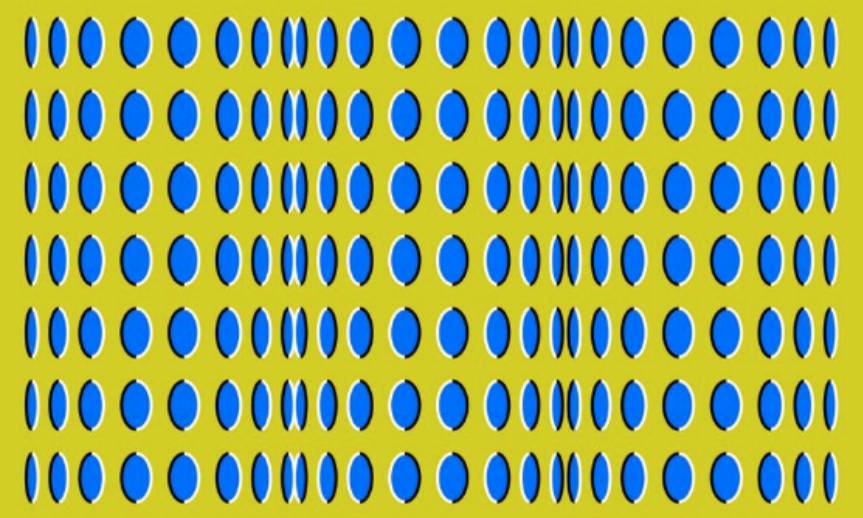
57
New cards
pinna illusion
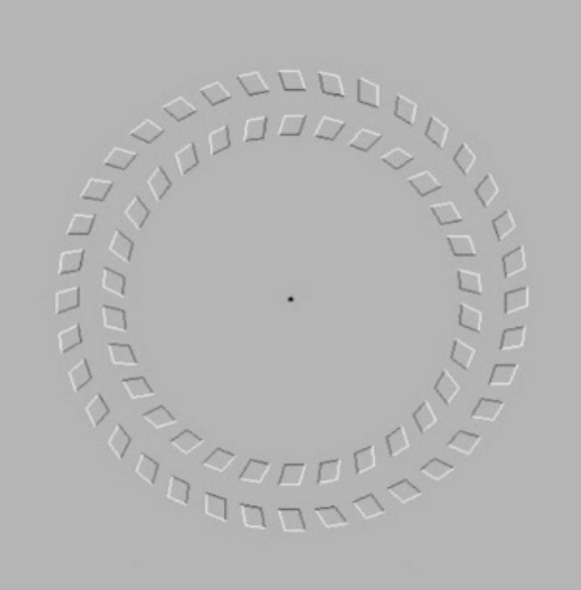
58
New cards
6
3
3
there are __ muscles attached to each eye paired into __ groups
superior/inferior oblique
inferior/superior/lateral/medial rectus
superior/inferior oblique
inferior/superior/lateral/medial rectus
59
New cards
3
eye muscles are controlled by ___ cranial nerves
60
New cards
superior colliculus
initiates and guides eye movement
61
New cards
smooth pursuit
eyes move smoothly to follow moving object
keep target stable and in fovea
keep target stable and in fovea
62
New cards
saccade
saccadic eye movement
saccadic eye movement
rapid eye movement when fixation changes from one object/location to another
move fovea to target as quickly as possible to reduce travel time
move fovea to target as quickly as possible to reduce travel time
63
New cards
vergence eye movements
two eyes move in opposite direction
looking at objects in depth so retinal images converge
looking at objects in depth so retinal images converge
64
New cards
fixational eye movement
65
New cards
microsaccades
66
New cards
spatial constancy
ability to the perceive the world as stable and continuous despite eye movement
allows us to discriminant movement from eye vs object movement
allows us to discriminant movement from eye vs object movement
67
New cards
compensation theory
perceptual system receives information about eye movement and discounts changes in retinal images that result from it
68
New cards
efference copy
corollary discharge
corollary discharge
copy of motor command that was sent to eyes gets sent to visual system / comparator
69
New cards
comparator
area of the visual system that compensates for changes due to eye movement inhibiting other visual areas to perceive it as motion
70
New cards
saccadic suppression
reduction of visual sensitivity when moving eyes in saccade
eliminates smear during eye movement
eliminates smear during eye movement
71
New cards
Euclidian geometry
parallel lines remain parallel as they extend into space
72
New cards
parallax
placement of observer causes changes in POV
result of two retinal images in a 3D world
result of two retinal images in a 3D world
73
New cards
binocular disparity
differences between the two retinal images due to parallax
basis of stereopsis
basis of stereopsis
74
New cards
stereopsis
vivid perception of 3D world not available with monocular vision
“popping out in depth’
“popping out in depth’
75
New cards
binocular cues
convergence, stereopsis, ability to see more of an object
76
New cards
monocular cues
occlusion, relative size, position cues, familiar size, aerial perceptive, linear perceptive, motion cues
77
New cards
occlusion
cue relative to depth order, one object obstructs the view of another
78
New cards
nonmetrical depth cue
provides information about depth order but not magnitude
79
New cards
metrical depth cue
provides quantitative information about distance
ex - meters, yards
ex - meters, yards
80
New cards
relative size
comparison of size between items without knowing the absolute size of either
81
New cards
texture gradient
depth cue based on fact that items appear smaller the farther away they are
82
New cards
relative height
objects at different distances from the viewer on the ground plane will form images at different heights in retinal image
83
New cards
natural scene statistics
statistical properties and regularities in natural environment
common distribution and relationship between features of an image
common distribution and relationship between features of an image
84
New cards
familiar size
depth cue based on knowledge of typical size of an object
ex - size of a quarter, a hand, a book, etc.
ex - size of a quarter, a hand, a book, etc.
85
New cards
aerial perspective
depth cue based on fact that light is scattered by atmosphere
objects farter away appear bluer
ex - haze
objects farter away appear bluer
ex - haze

86
New cards
linear perspective
depth cue based on fact that parallel lines in 3D converge in 2D
87
New cards
vanishing point
apparent point in which parallel lines converge
88
New cards
foreshortening
visual effect where an object appears shorter because it is angled towards screen/retina/plane
89
New cards
anamorphism
distorted projection or perspective requiring the viewer to use a special device or vantage point to reconstitute the image
90
New cards
motion parallax
objects moving at constant speed across retina will appear to move faster the closer they are to the observer
91
New cards
convergence
turn eyes inward to focus on something close
92
New cards
divergence
turn eyes outward to focus on something far
93
New cards
corresponding retinal points
zero binocular disparity
zero binocular disparity
points of retinal images that have the same distance from the fovea
94
New cards
horopter
location of objects in space whose images lie on corresponding points
surface of zero disparity
surface of zero disparity
95
New cards
panum’s fusion area
region of space in front and behind horopter where binocular single vision is possible
96
New cards
diplopia
double vision for points outside Panum’s fusion area
97
New cards
absolute disparity
difference in actual retinal coordinates in both eyes of the feature in the visual scene
98
New cards
relative disparity
difference in absolute disparities of two elements in the visual scene
99
New cards
free fusion
technique of converging or diverging the eyes
crossing you eyes
crossing you eyes
100
New cards
stereoblindness
inability to make use of binocular disparity as depth cues