Near East art History
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Agrarian Civilization: c. 3200 BCE – c. 1750 CE
An agrarian society means this society’s
economy is based on producing and
maintaining crops and farmland.
Mesopotamia: (means between rivers)
located on the plain between the Euphrates and Tigris Rivers,
now Iraq. Civilization developed in the Fertile Crescent,
benefiting from this agriculturally rich area.
Sumer
Considered the first civilization, c. 4,000 to 2350 BCE
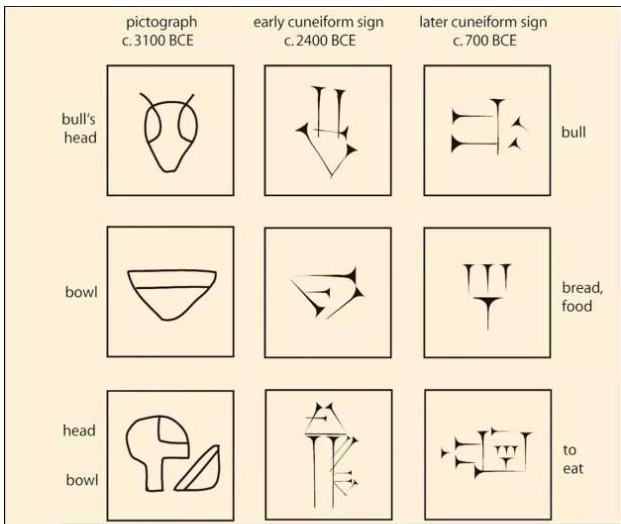
Cuneiform
First known language developed by seminarians
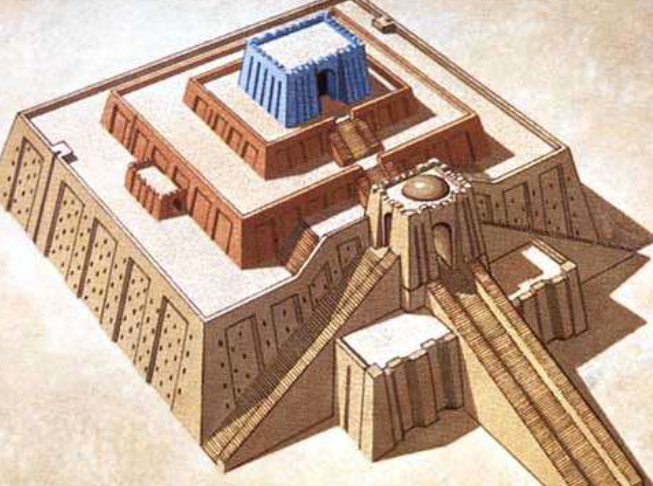
Ziggurat at Ur
eveloped in the Neo-Sumerian period (ca. 2150 – 2000 BCE).
• Materials:
Sun-dried bricks bonded with bitumen, reed matting, or rope,
finished with a weather-resistant exterior layer of kiln-fired bricks.
• Design:
1. Elevate the temples to the gods in the heavens;
2. Represent the mountains, where Sumerians and their
successors originally came from;
3. Protect the temples from flood waters;
4. Visually prominent in the city.
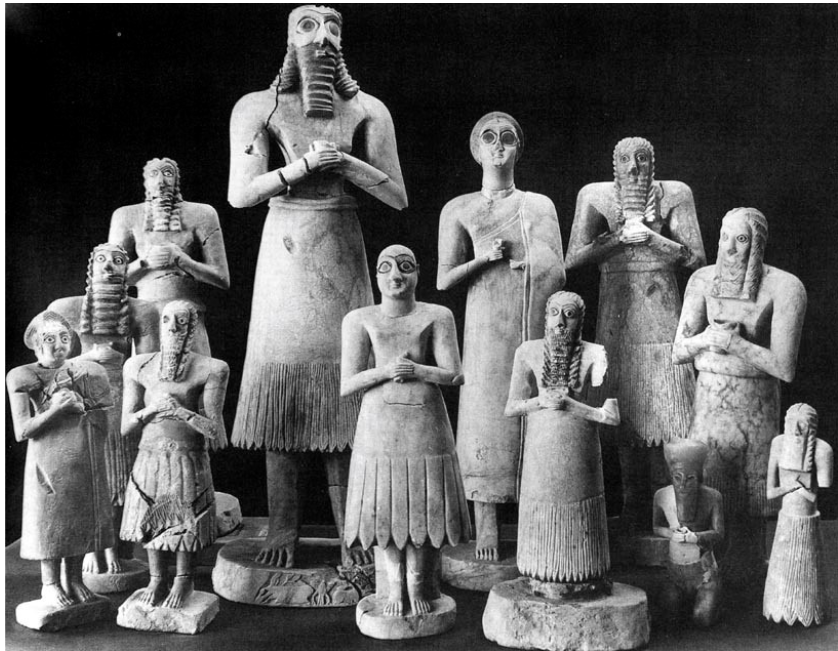
Votive figure
A statue of a man or
woman that is offered
to a god or goddess at a
sacred place, such as a
temple, to gain favor
with (or give thanks to)
the god or goddess.

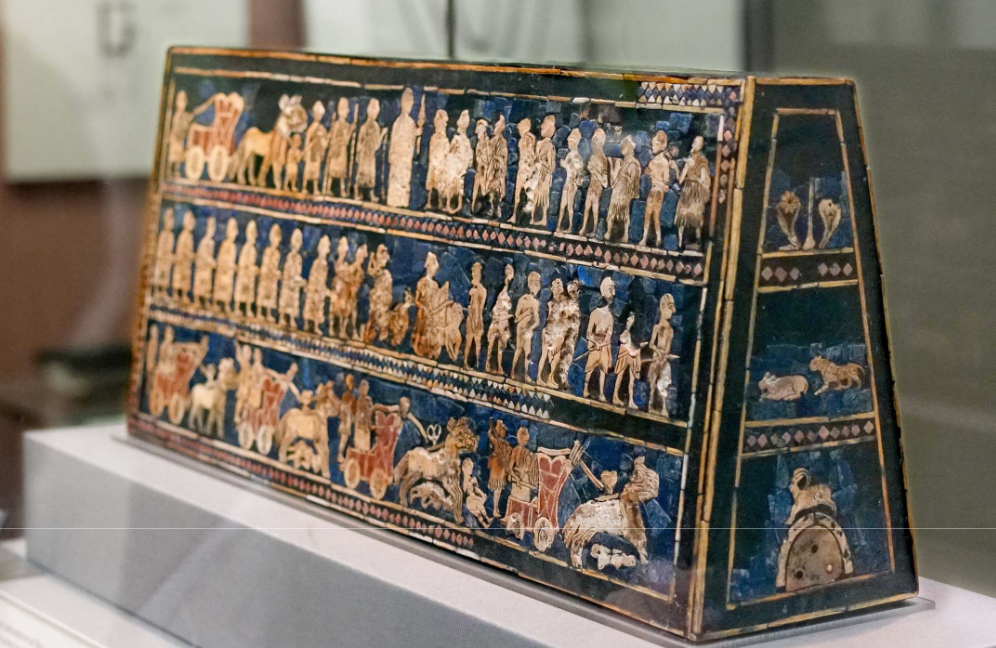
Standard of Ur from the Royal
Tombs at Ur
Rectangular
box-like object
• Wooden panels
decorated with
mosaic scenes

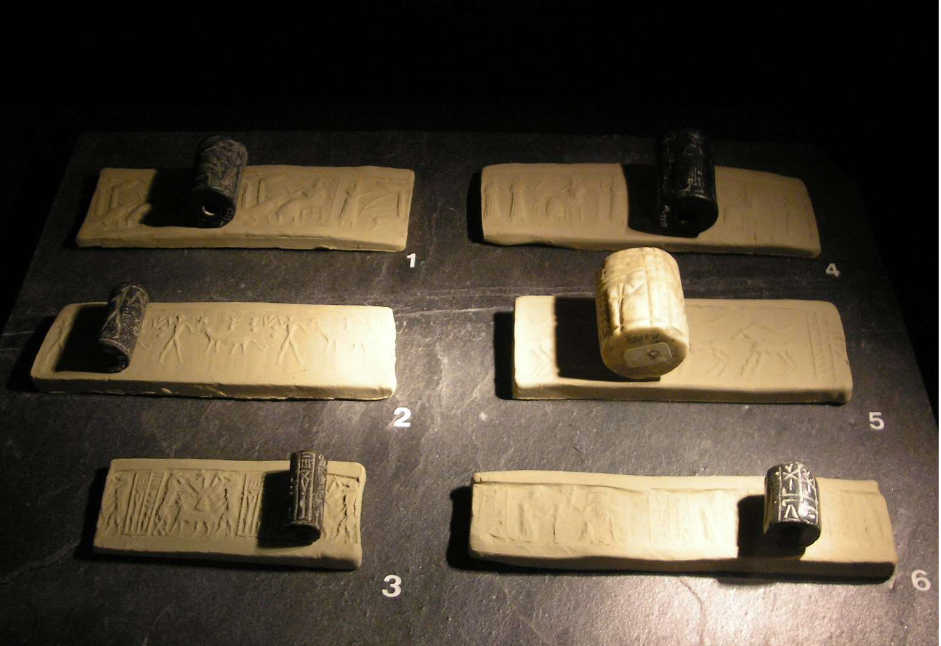
Cylinder seals

Victory Stele of Naram-Sin
2254-2218 B.C.E., Akkadian
A stele is a vertical stone monument or
marker often inscribed with text or relief
carving.

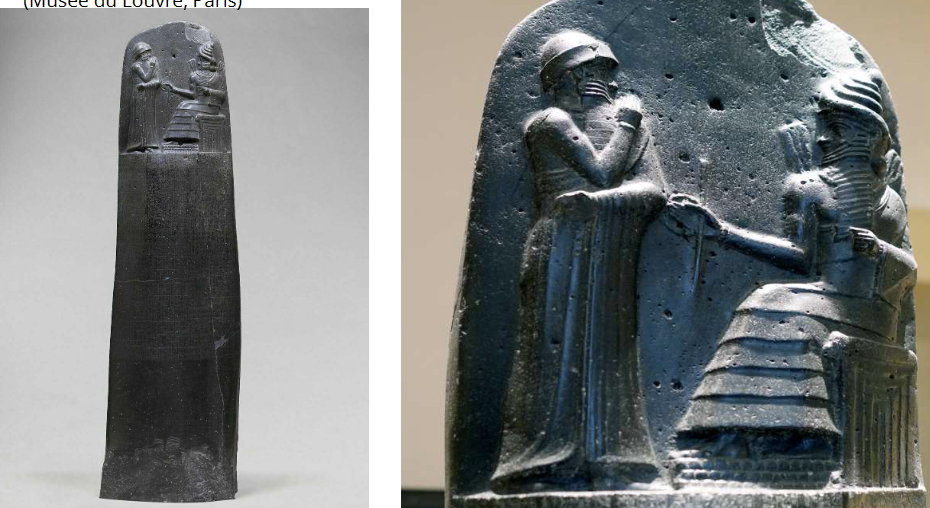
Law Code Stele of King Hammurabi

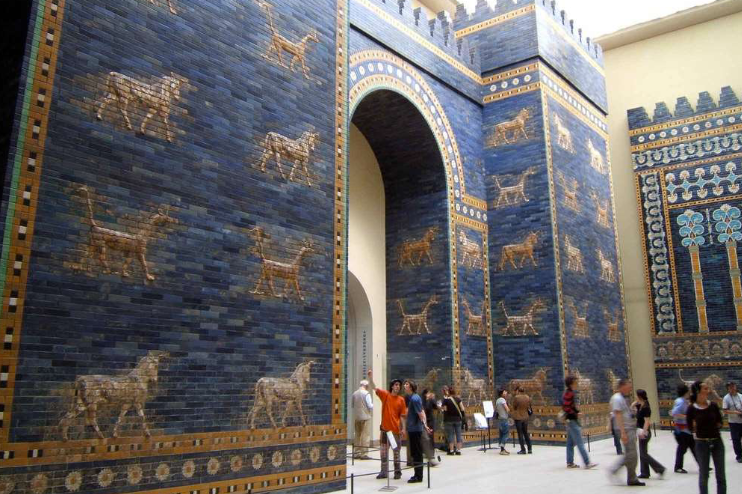
Gate of Ishtar

The Processional Way:

Lamassu, the citadel of Sargon II,
Khorsabad, Iraq

Ashurbanipal Hunting Lions,
North Palace, Ninevah

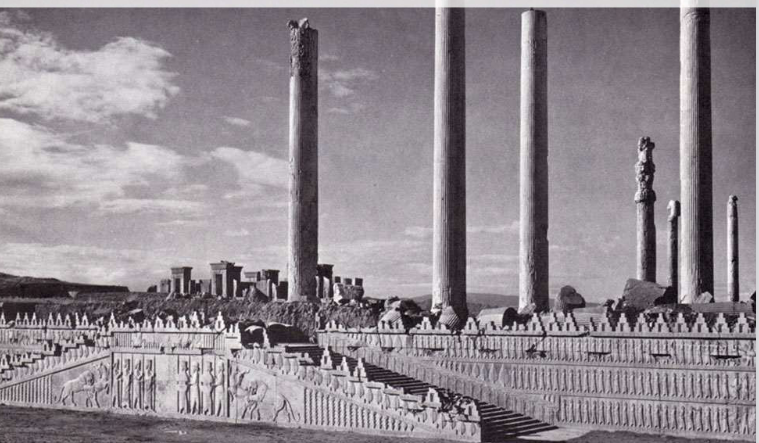
Palace in Persepolis

The Apādana / Audience Hall of Darius and Xerxes,
c. 520-465 B.C.E

Hypostyle
Literally means
“under pillars,” it is
a structure whose
roof is supported by
rows of pillars or
columns. This
design allows for
the construction of
large spaces without
the need for arches