Year 9 Body Coordination
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
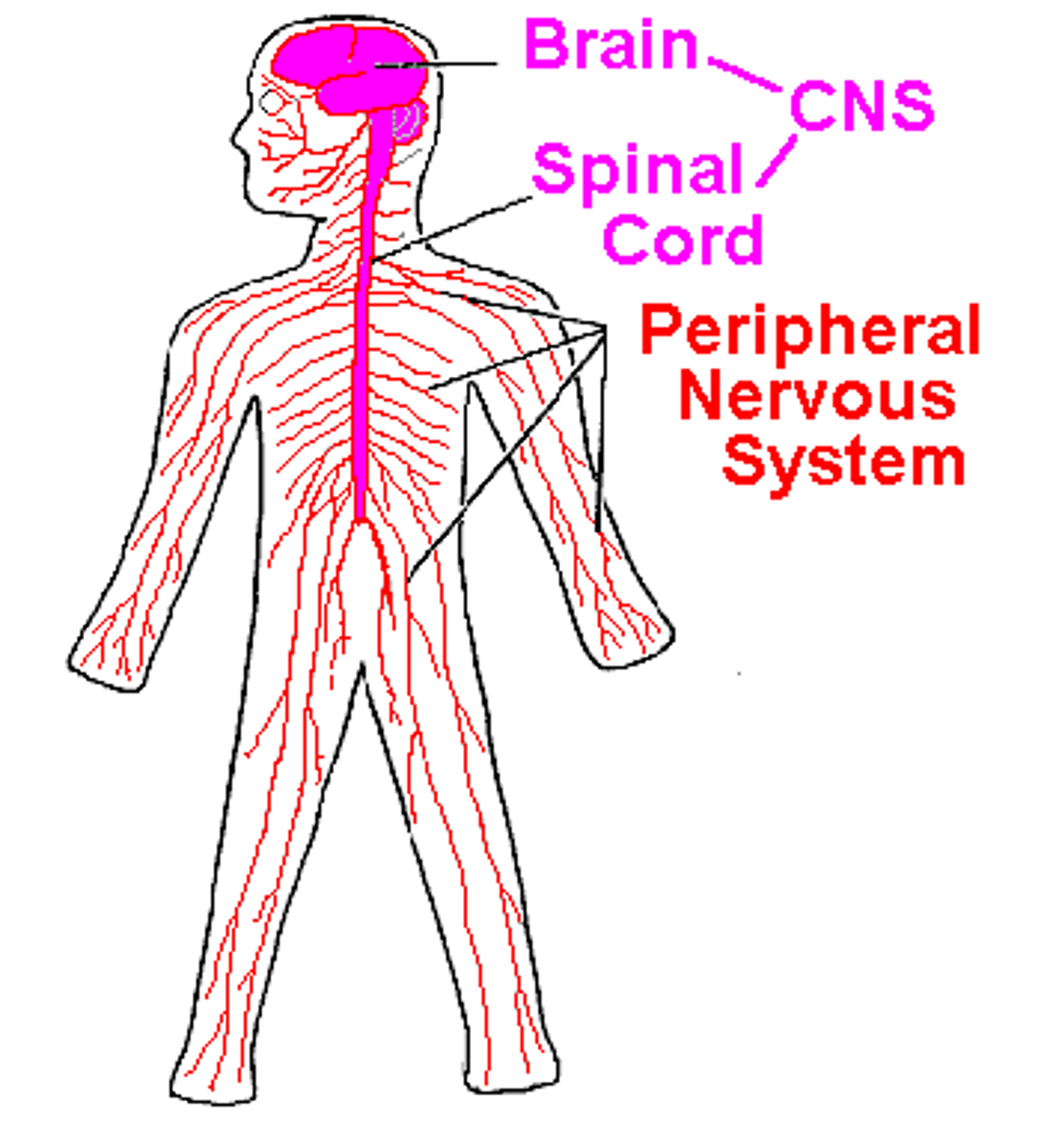
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
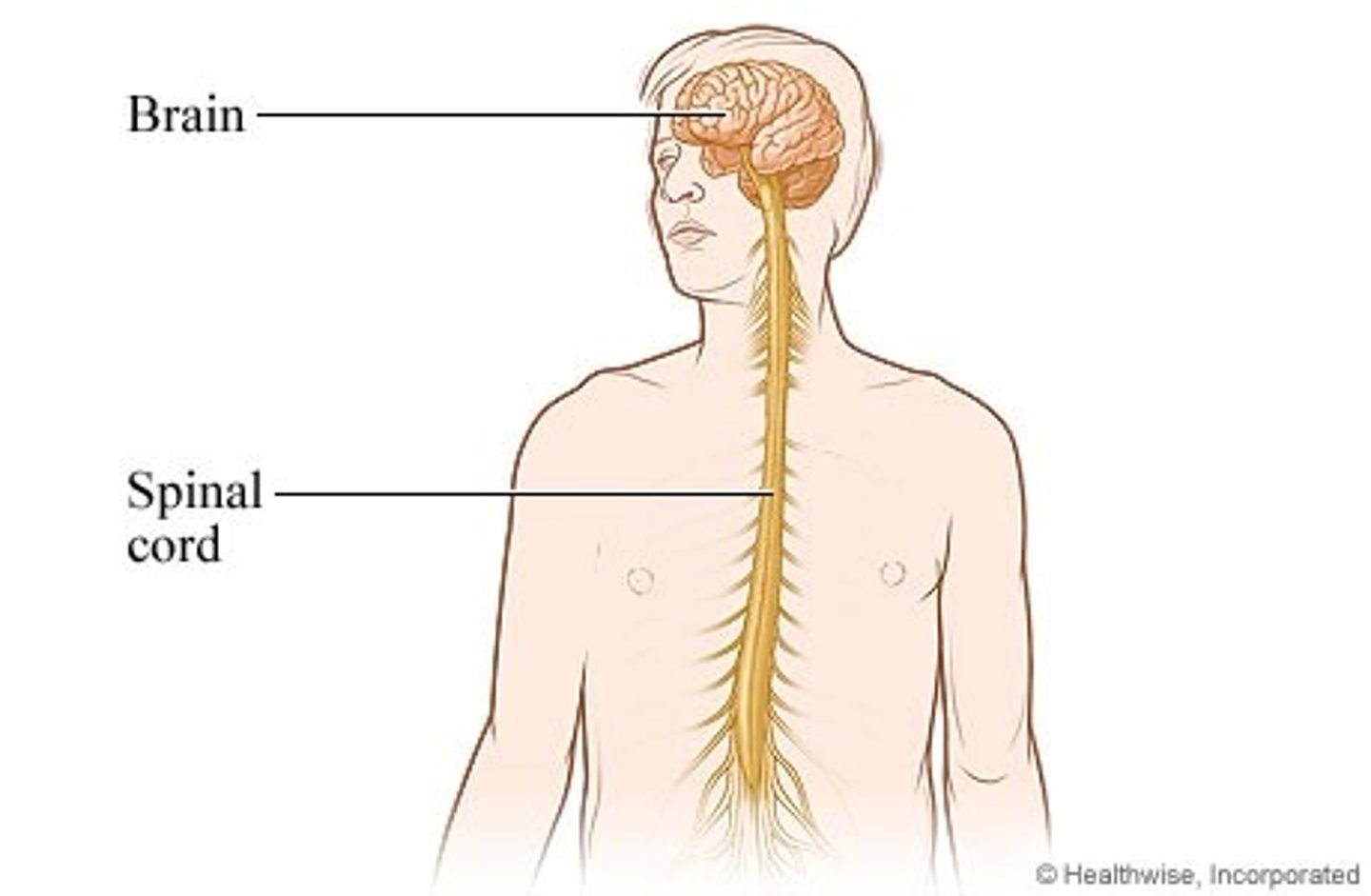
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body.
Neurons
specialized nerve cells that transmit electrical signals called nerve impulses around your body
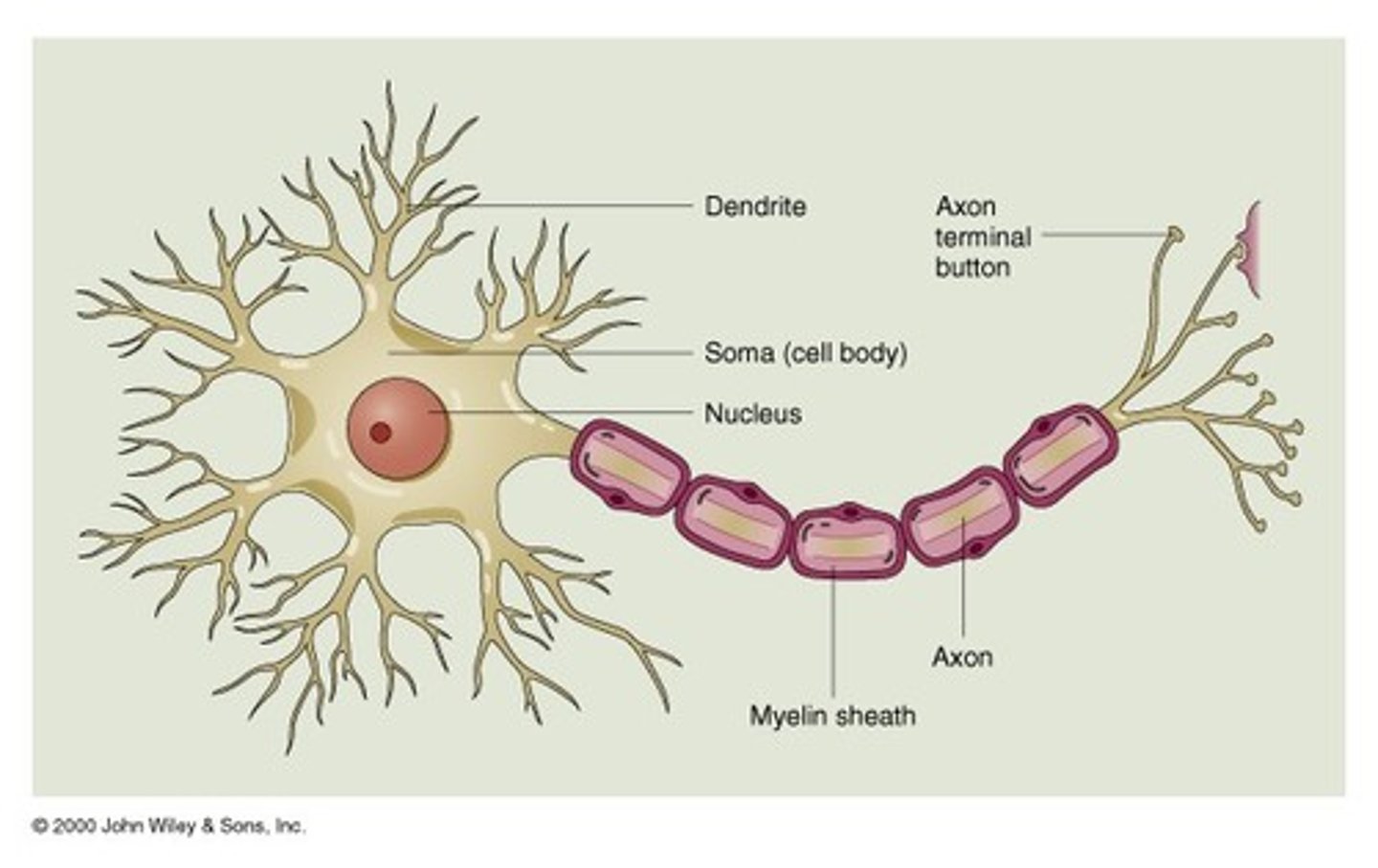
Dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
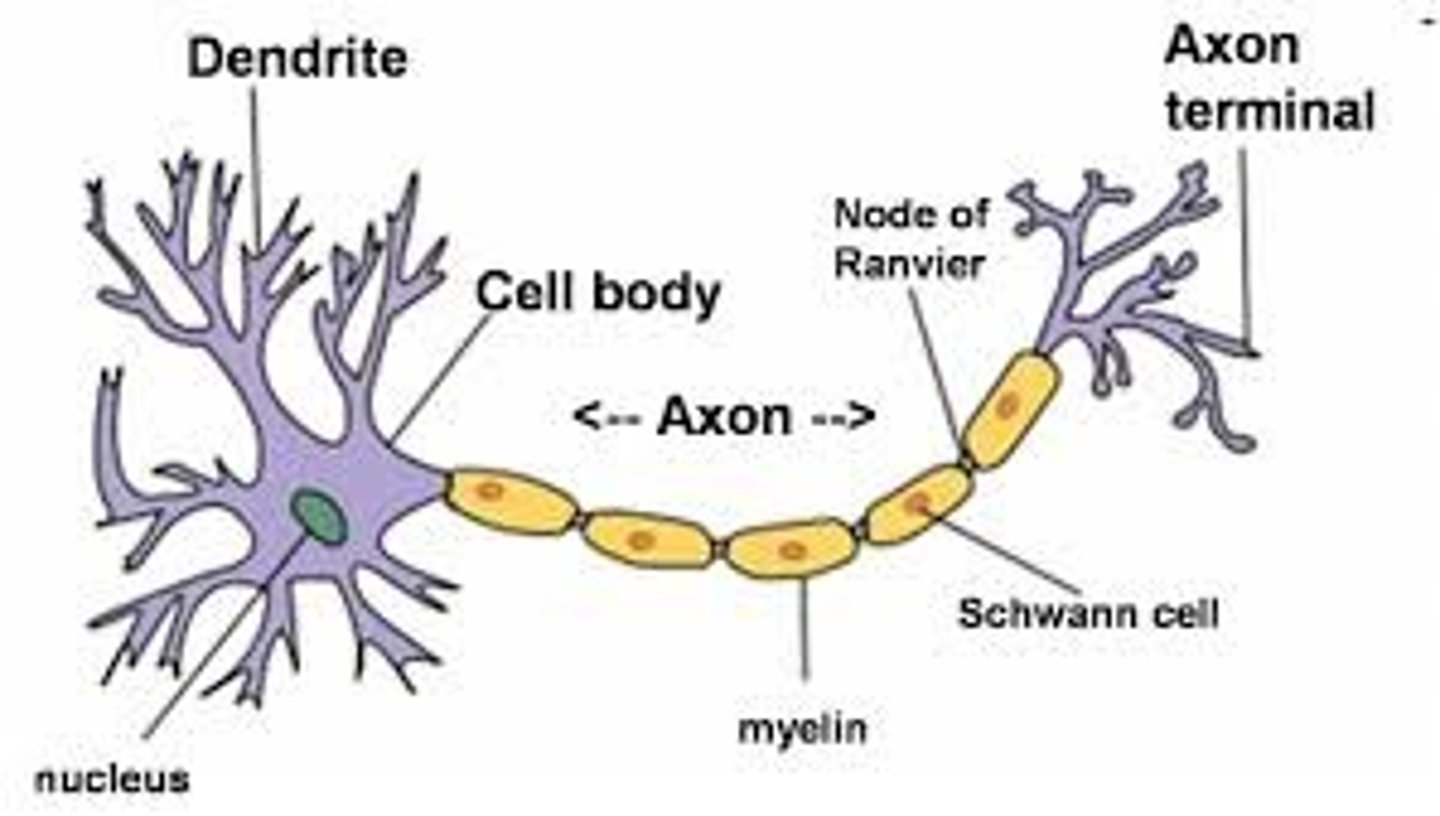
Axon
A threadlike extension of a neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body.
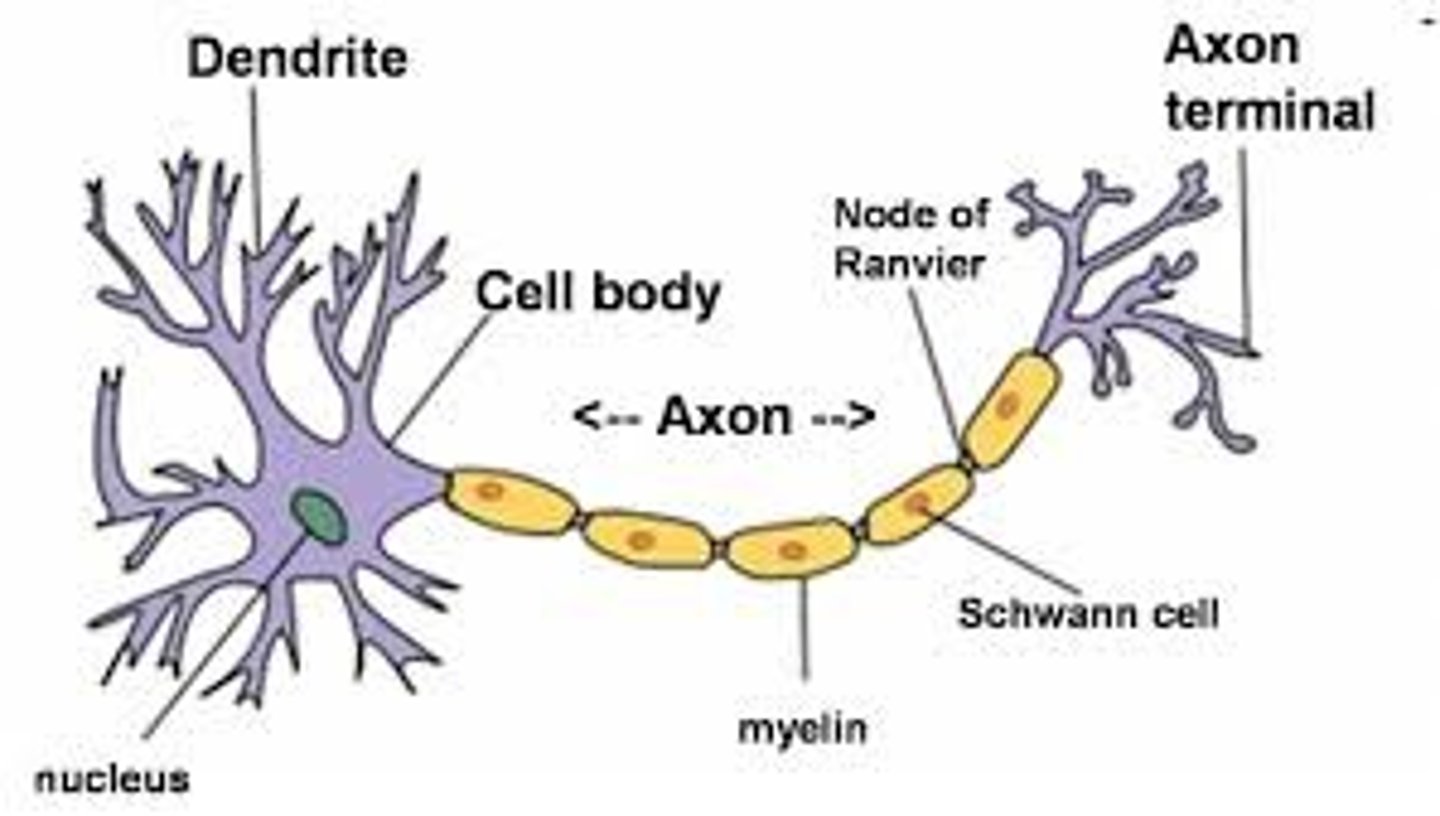
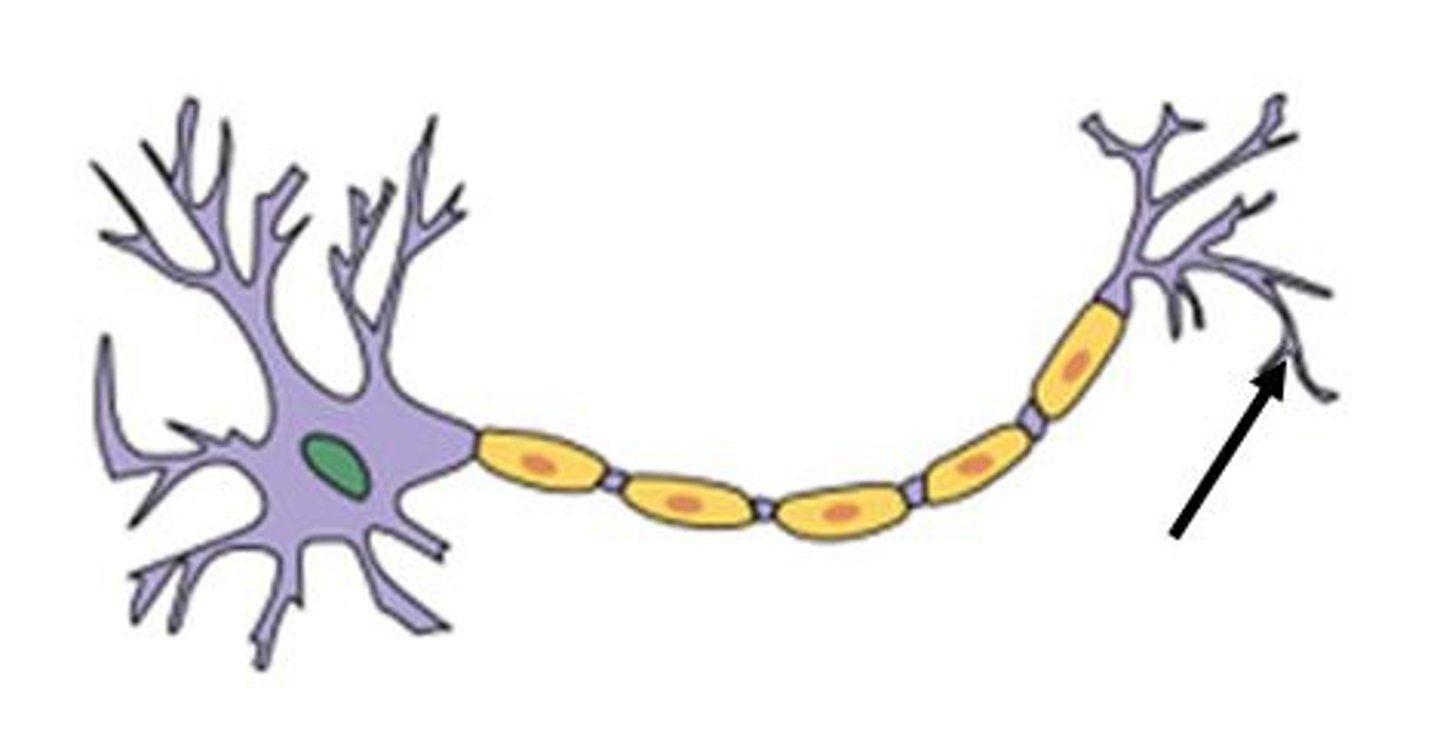
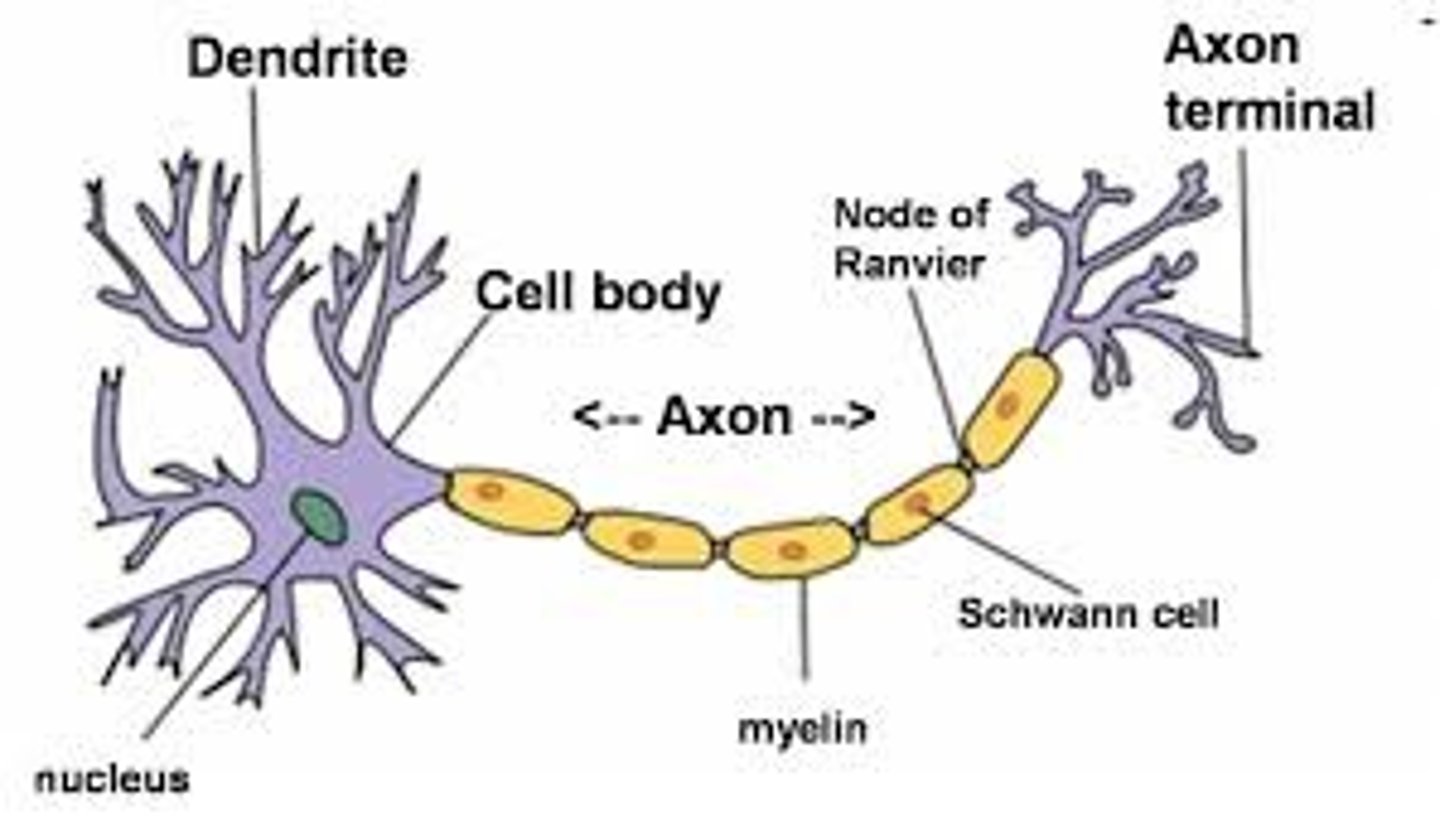
Axon terminal
The endpoint of a neuron where neurotransmitters are stored
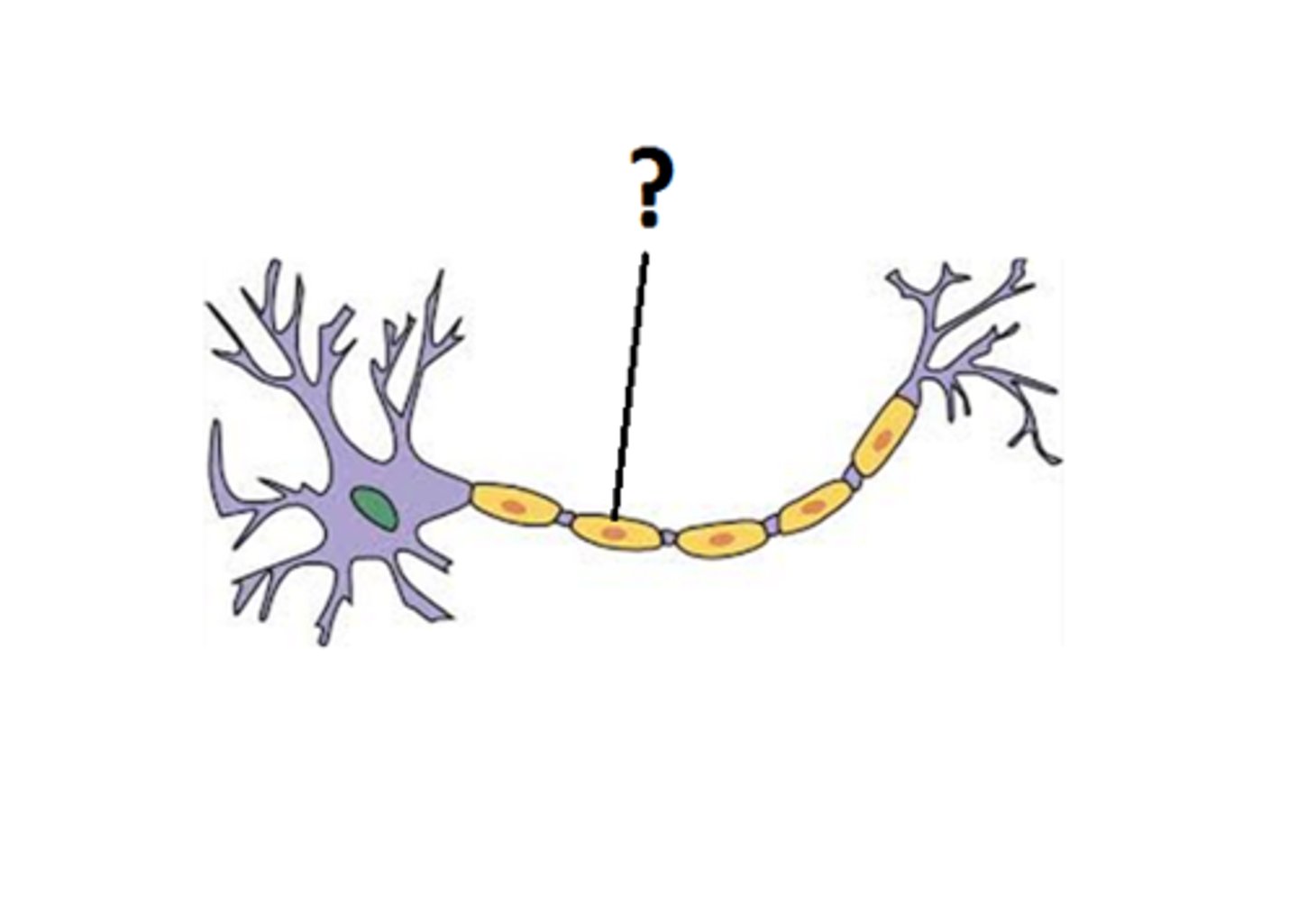
Schwann cells
Fatty cells responsible for the formation of myelin.
myelin sheath
A fatty layer made up of schwann cells that insulates some axons to allow for faster movement of electrical impulses along the axon
sensory neurons
neurons that receive information from the external world and convey this information to the CNS
relay neurons
These connect the sensory neurons to the motor or other relay neurons. They have short dendrites and short axons.
motor neurons
neurons that carry outgoing information from the CNS to the muscles and glands
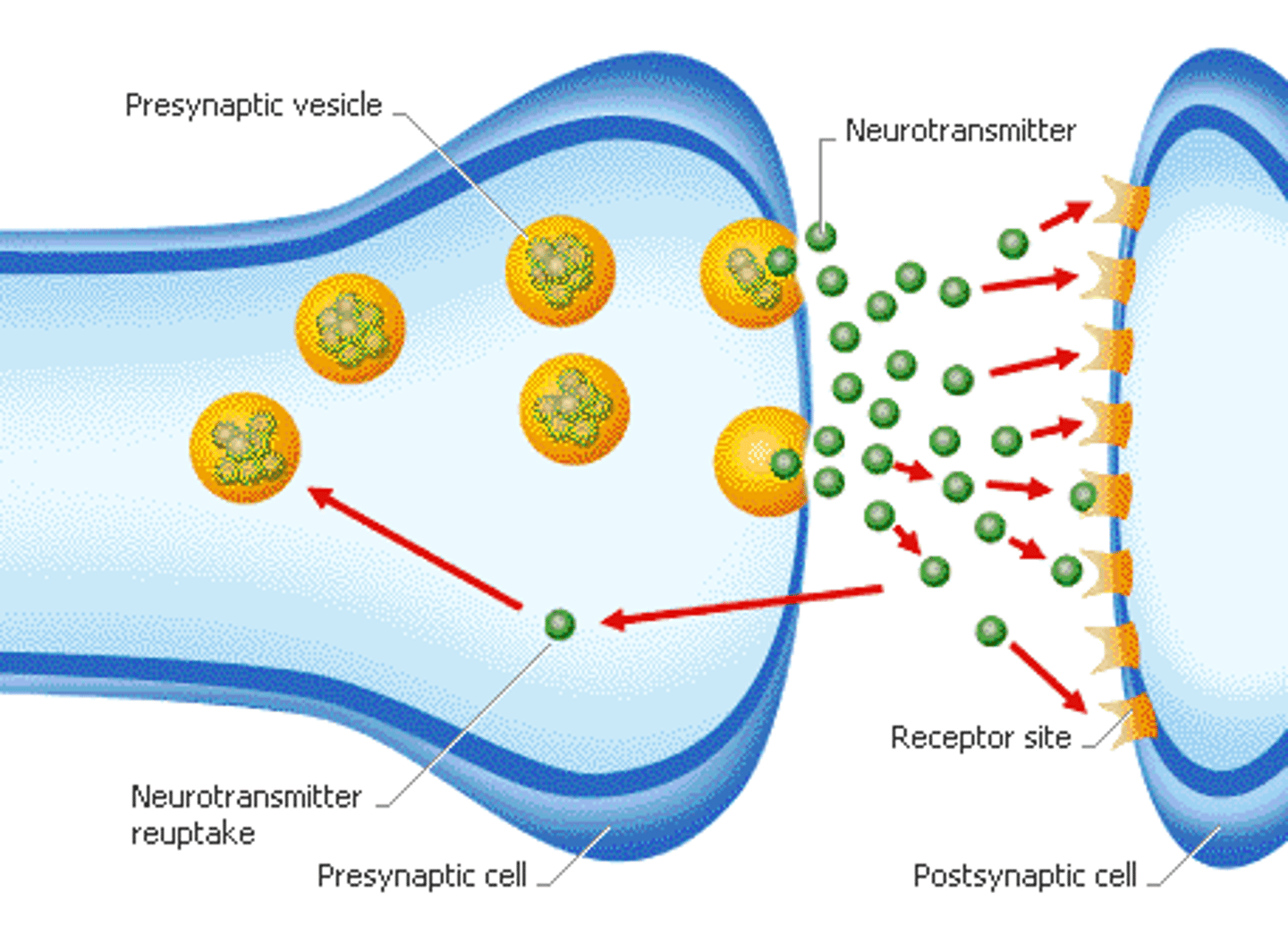
Synapse
Gap between axon terminal of one neuron and the dendrites of the next neuron
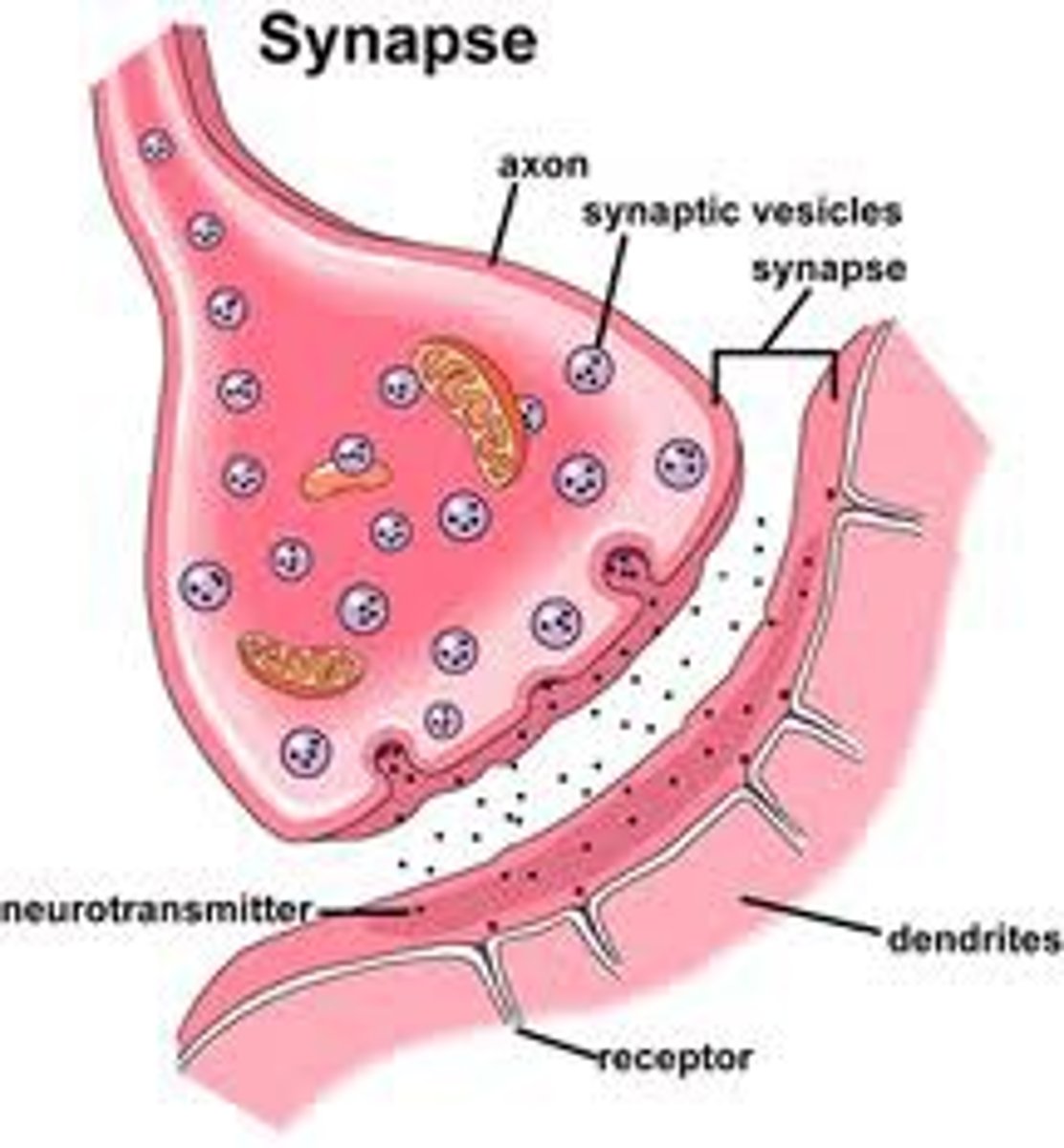
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that diffuse across the synaptic gaps between neurons
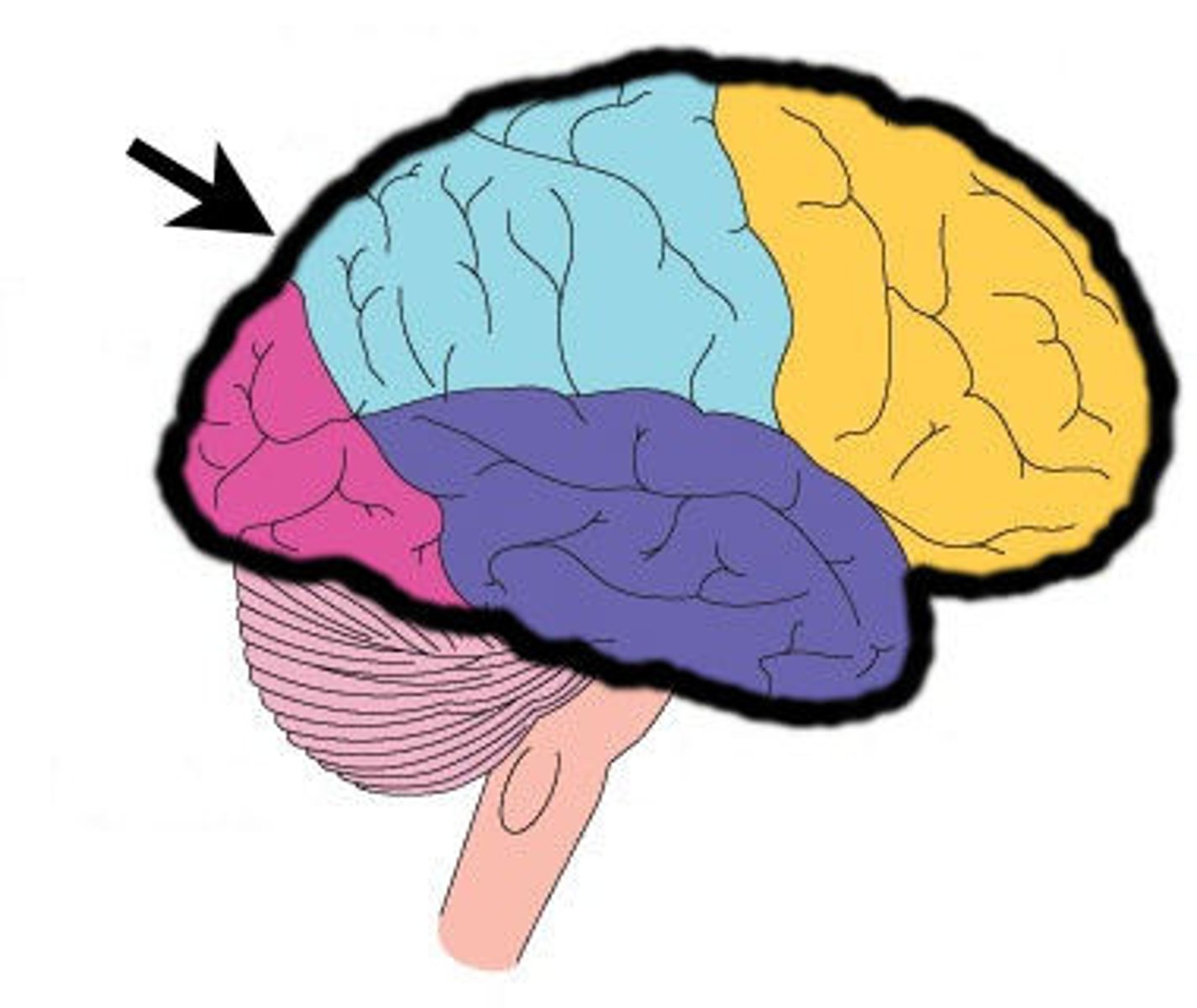
Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain; responsible for voluntary movement, processing sensory information, and complex thought.
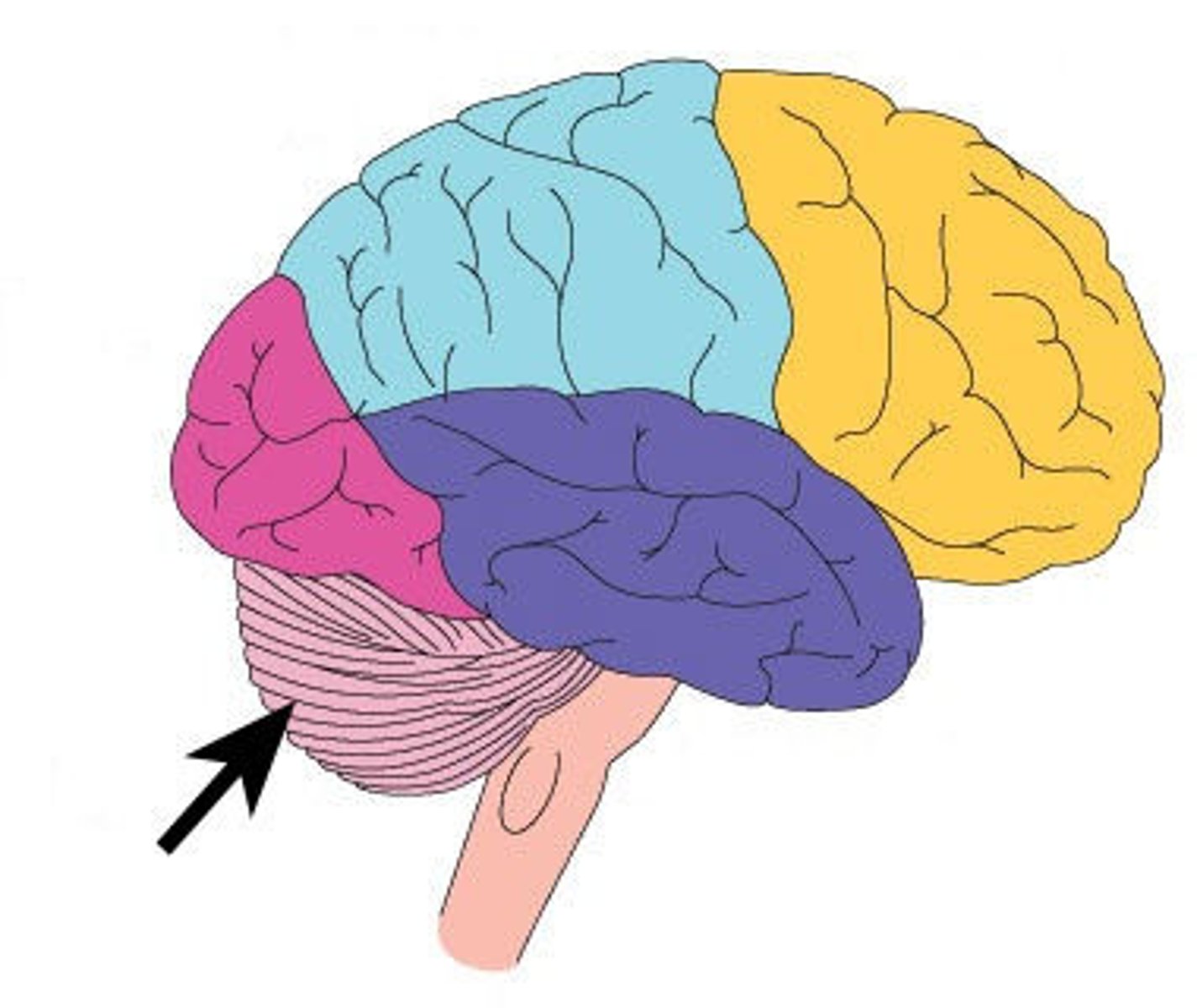
Cerebellum
Balance and coordination
Brainstem / Medulla
responsible for automatic survival functions e.g. breathing, heart rate, blood pressure
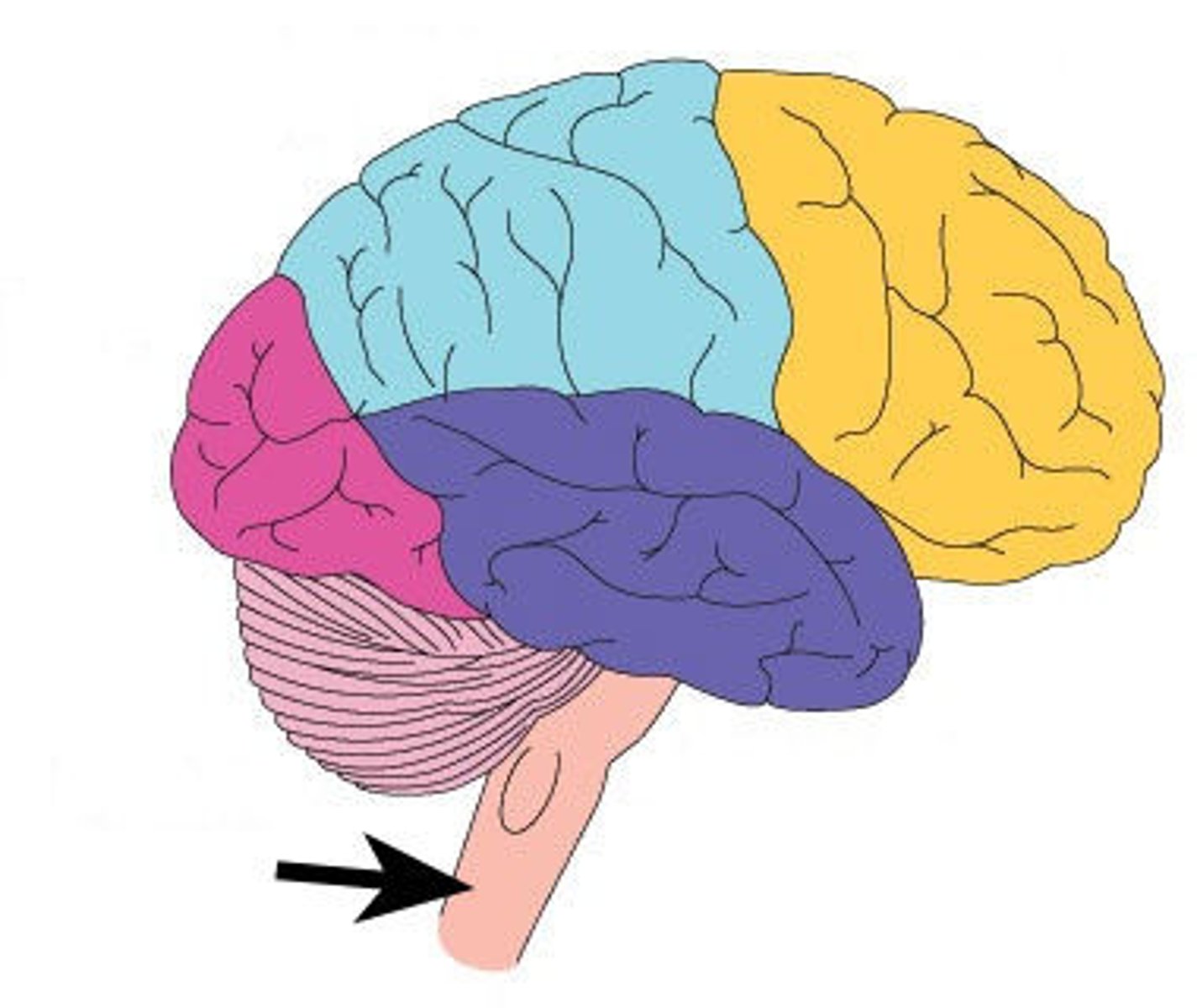
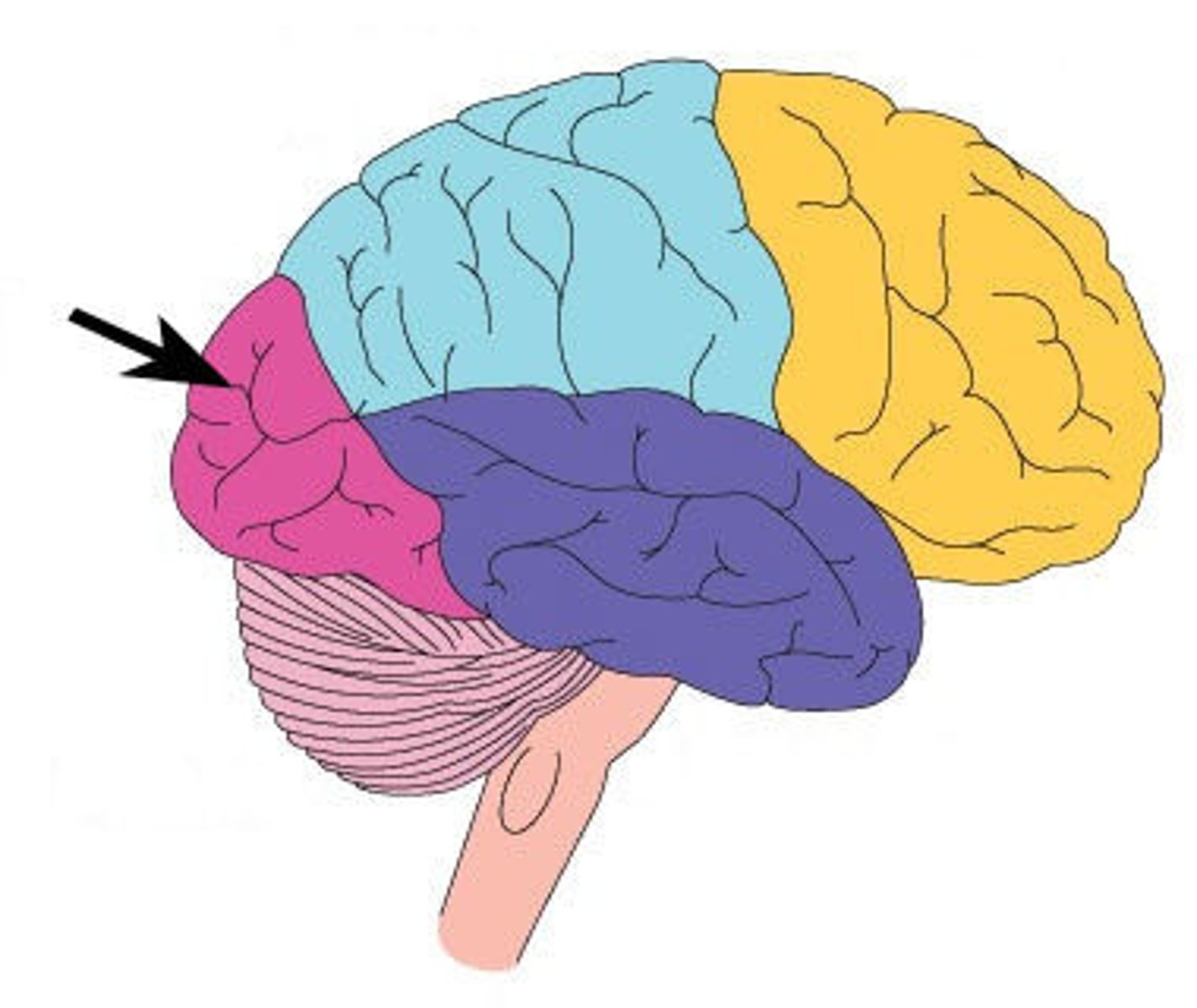
frontal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that controls movement, higher order thinking, problem solving and emotion
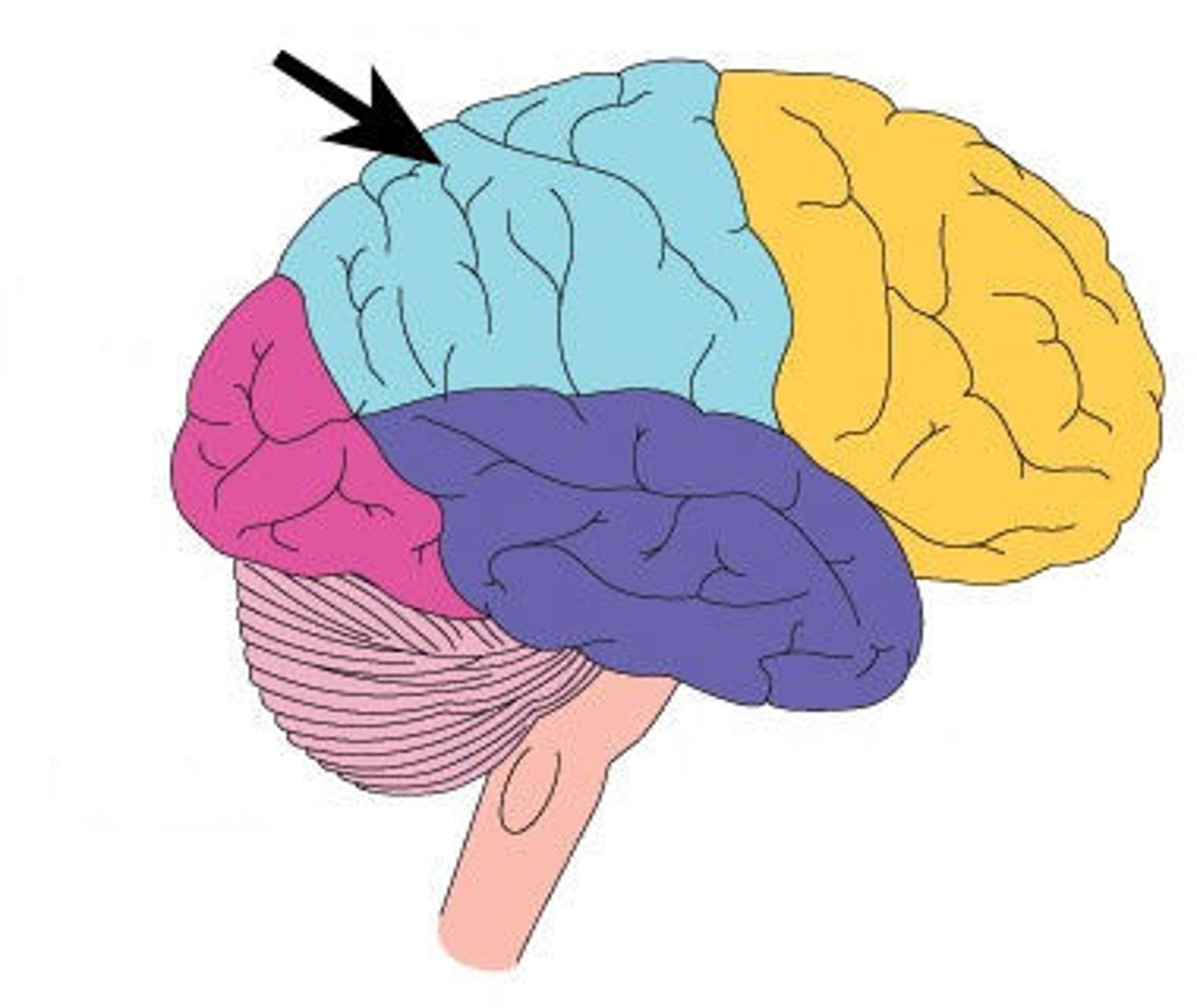
parietal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that receives sensory input for touch and body position
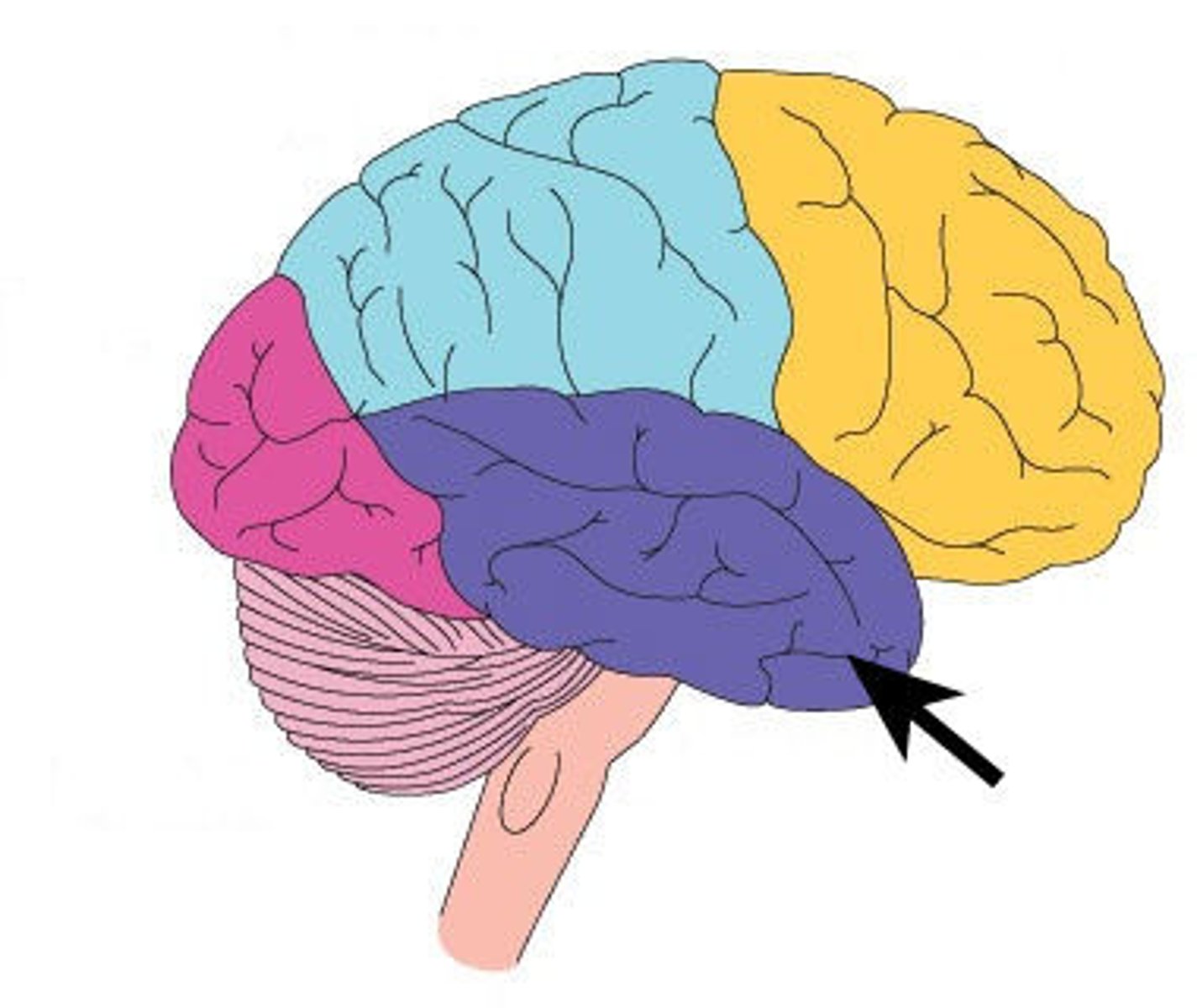
temporal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.
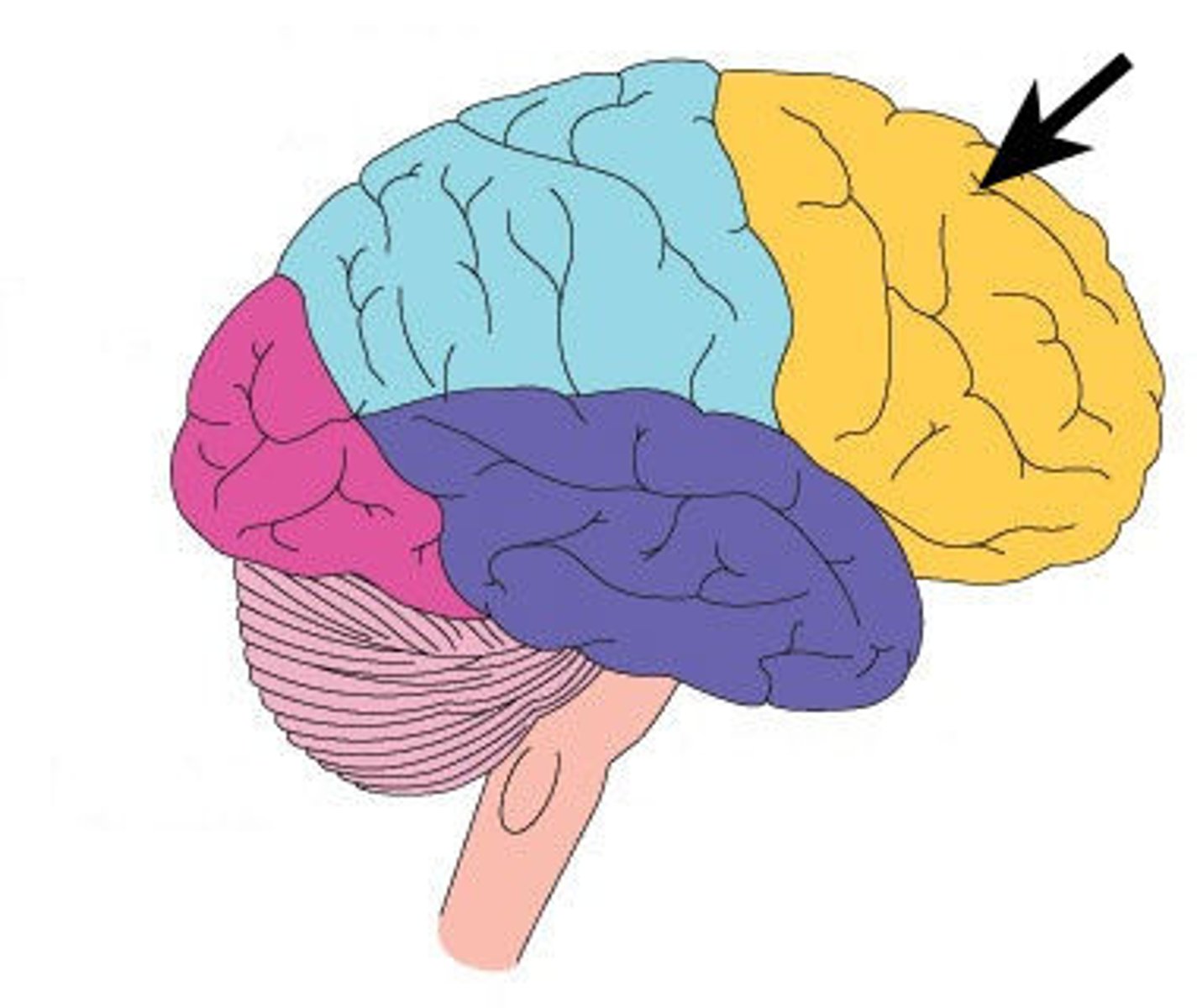
occipital lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
stimulus response model
Stimulus - receptor - sensory neuron - control centre - motor neuron - effector - response
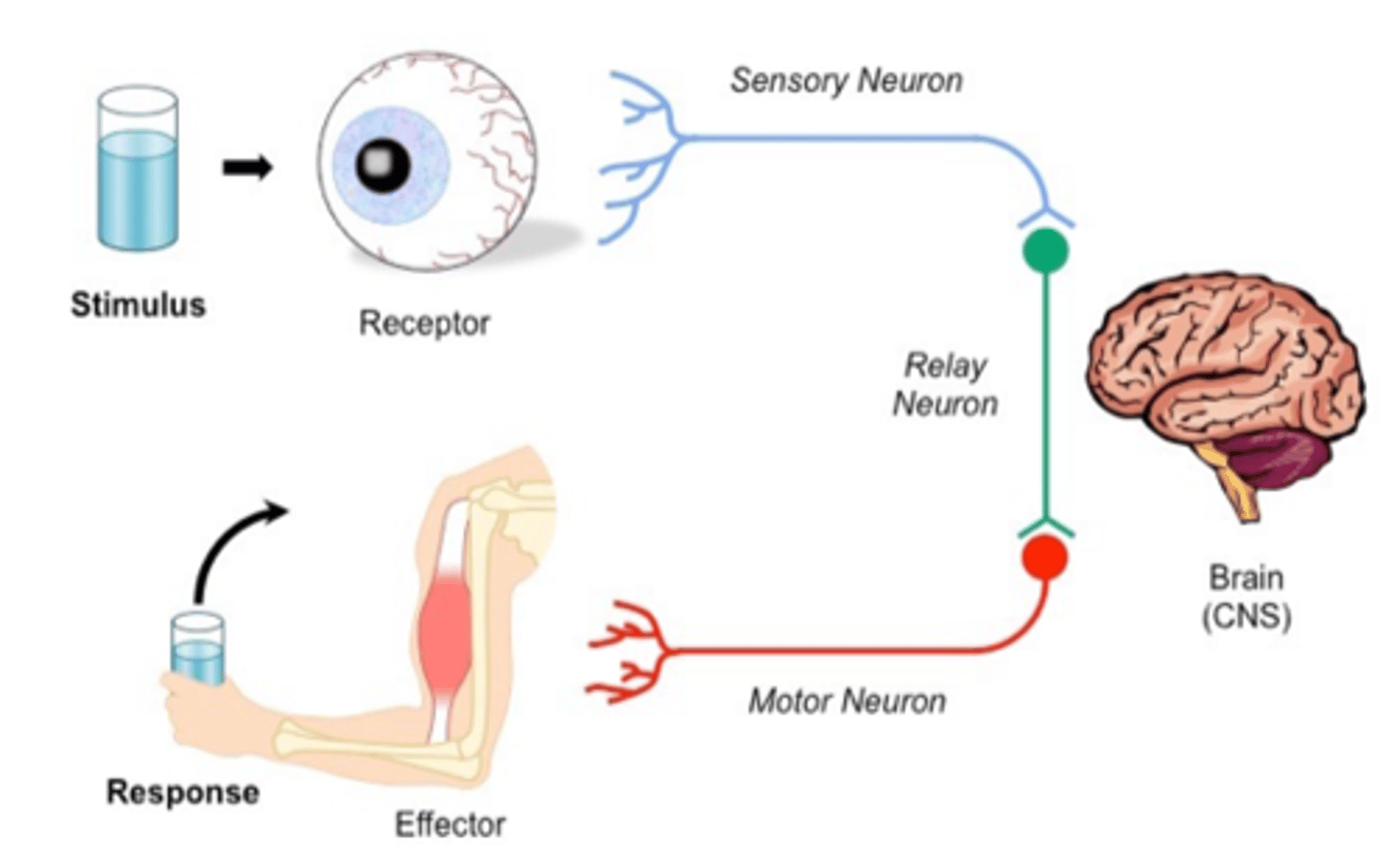
Receptor
special organs or cells that can respond to stimuli and transmit signal to sensory neuron.
photoreceptor - light
chemoreceptor - smell
thermoreceptor - temperature
mechanoreceptor - touch
pain receptor - pain / damaged cells
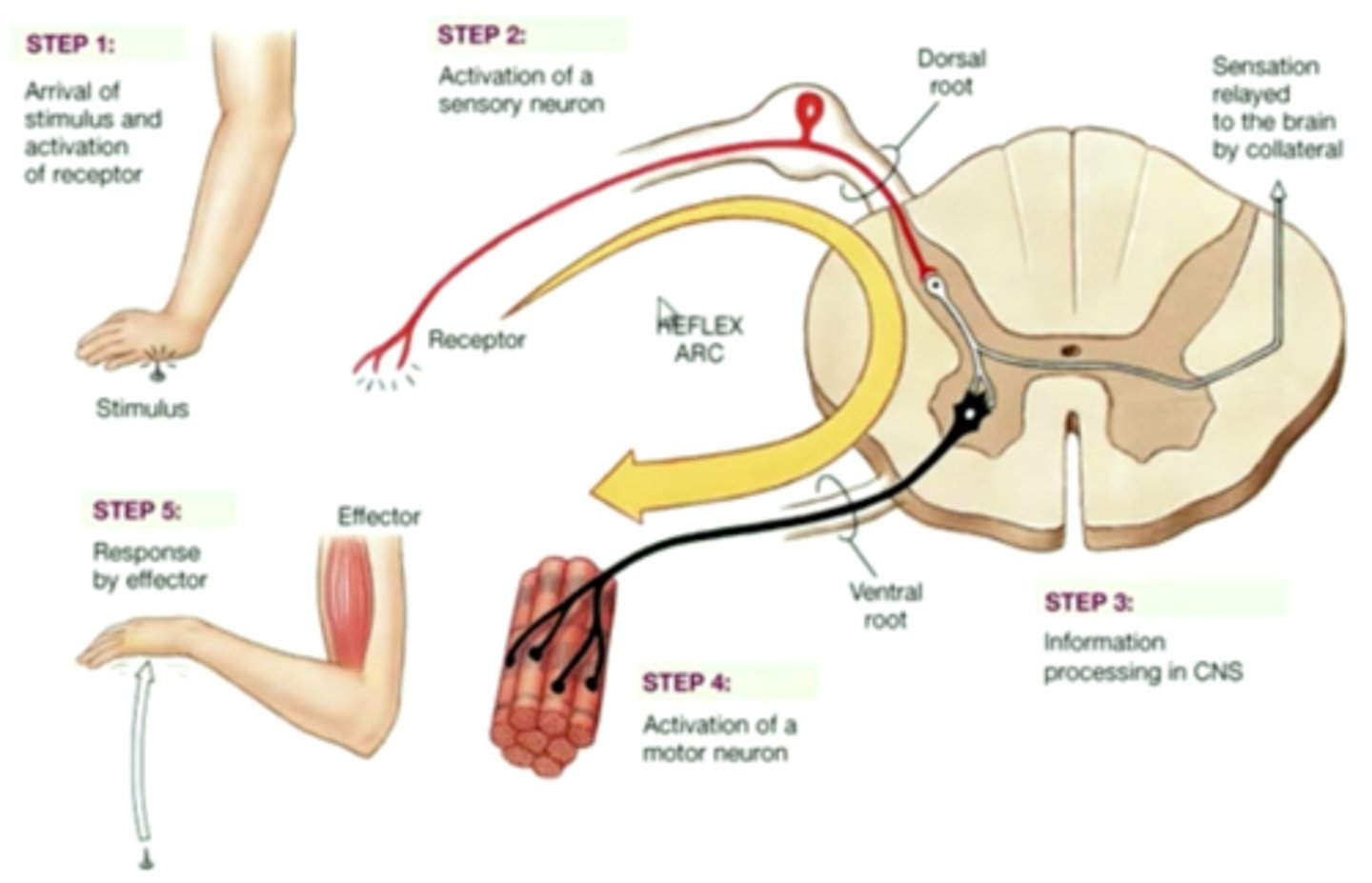
reflex arc
A neural pathway that shortcuts through the spinal cord, resulting in rapid, involuntary action
Metabolism
the chemical processes that occur within a living organism in order to maintain life. catabolic = reactions that break down. anabolic = reactions that build.
cellular respiration
glucose + oxygen --> carbon dioxide + water + energy
Enzymes
Proteins that speed up chemical reactions. Are not used up during reactions.
Homeostasis
process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment
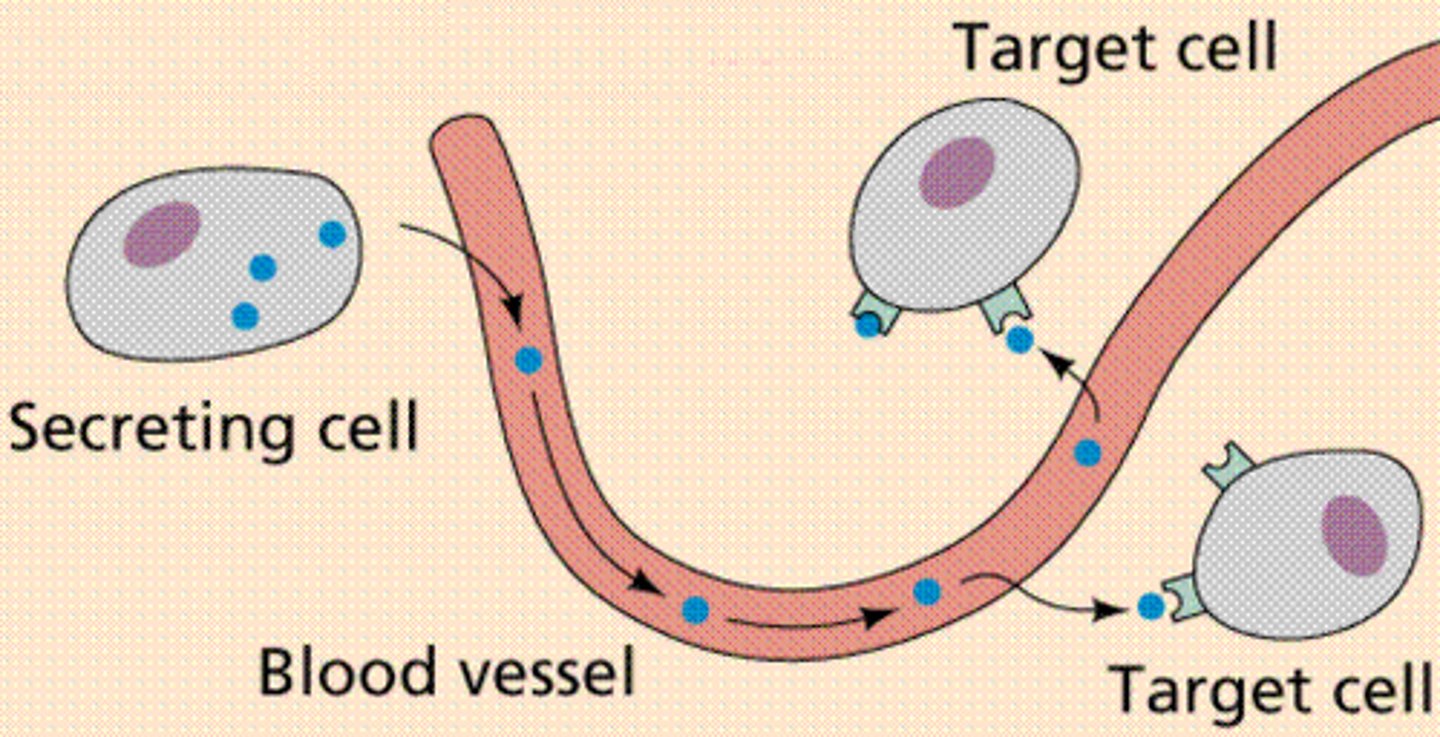
endocrine system
Consists of glands that produce hormones to regulate the body's internal environment
hormones
chemical messengers that travel through the bloodstream, and affect target cells
Hypothalamus
brain region in charge of homeostasis, controls the pituitary gland
pituitary gland
The endocrine system's "master" gland. Controls other endocrine glands.
thyroid gland
produces the hormone thyroxine which increases metabolic heat.
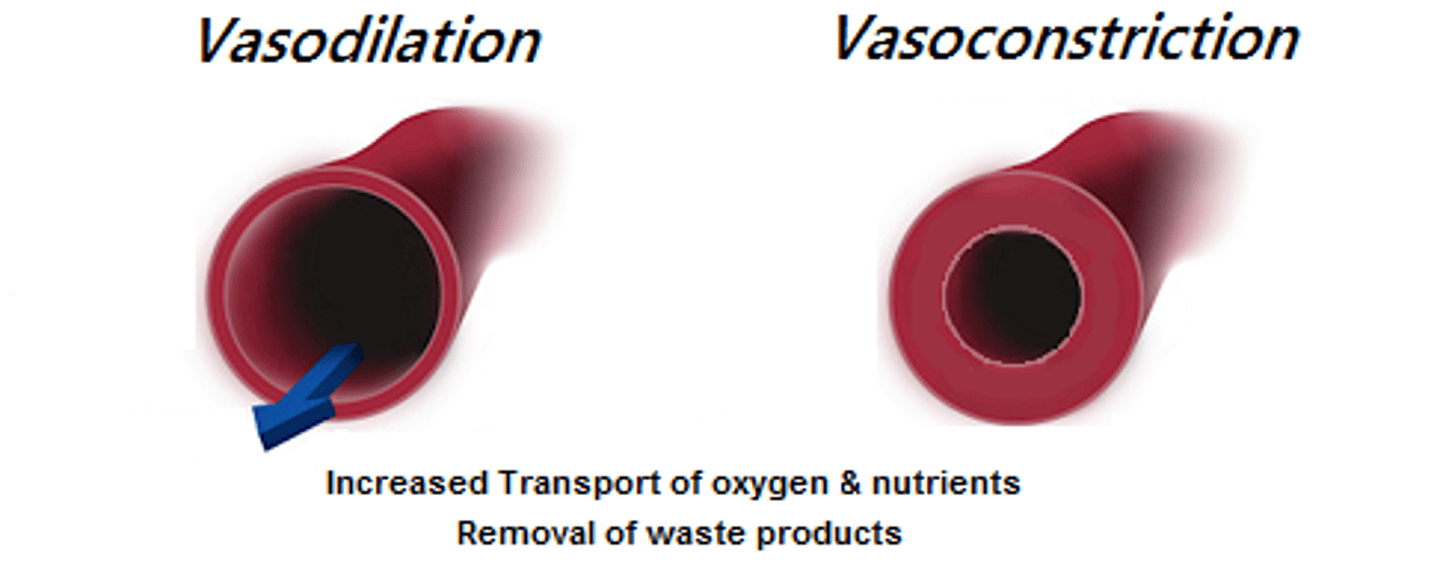
vasoconstriction and vasodilation
narrowing and widening of blood vessels
Sensation vs. Perception
Sensation is arrival of info to brain, perception is interpretation of info in brain
sensory memory
A type of storage that holds sensory information for a few seconds or less.
short-term memory
"working" memory that holds a few items briefly, e.g. seven digits of a phone number while dialing
long-term memory
the relatively permanent storage of information
Rehearsal
the conscious repetition of information, either to maintain it in short-term memory (maintenance) or to encode it for long-term storage (elaborate)
Retrieval
the process of getting information out of long-term memory
Chunking
organizing information into familiar, manageable units; helps improve memory
Contextual Clues
improves memory by situating information in familiar contexts
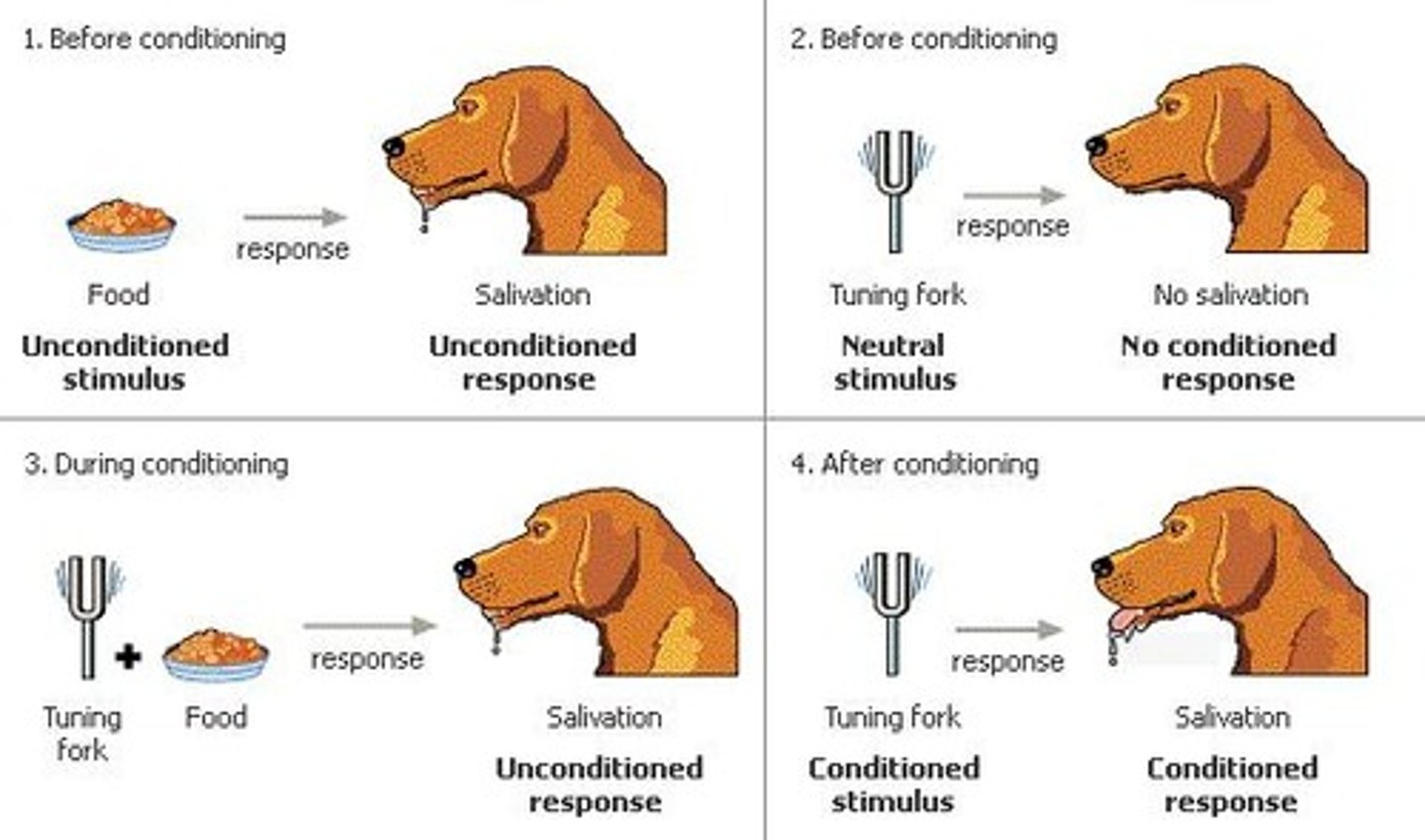
classical conditioning
the learning of involuntary behaviour in which an organism comes to associate stimuli. a response that is at first elicited by the unconditioned stimulus is eventually elicited by the neutral stimulus alone.
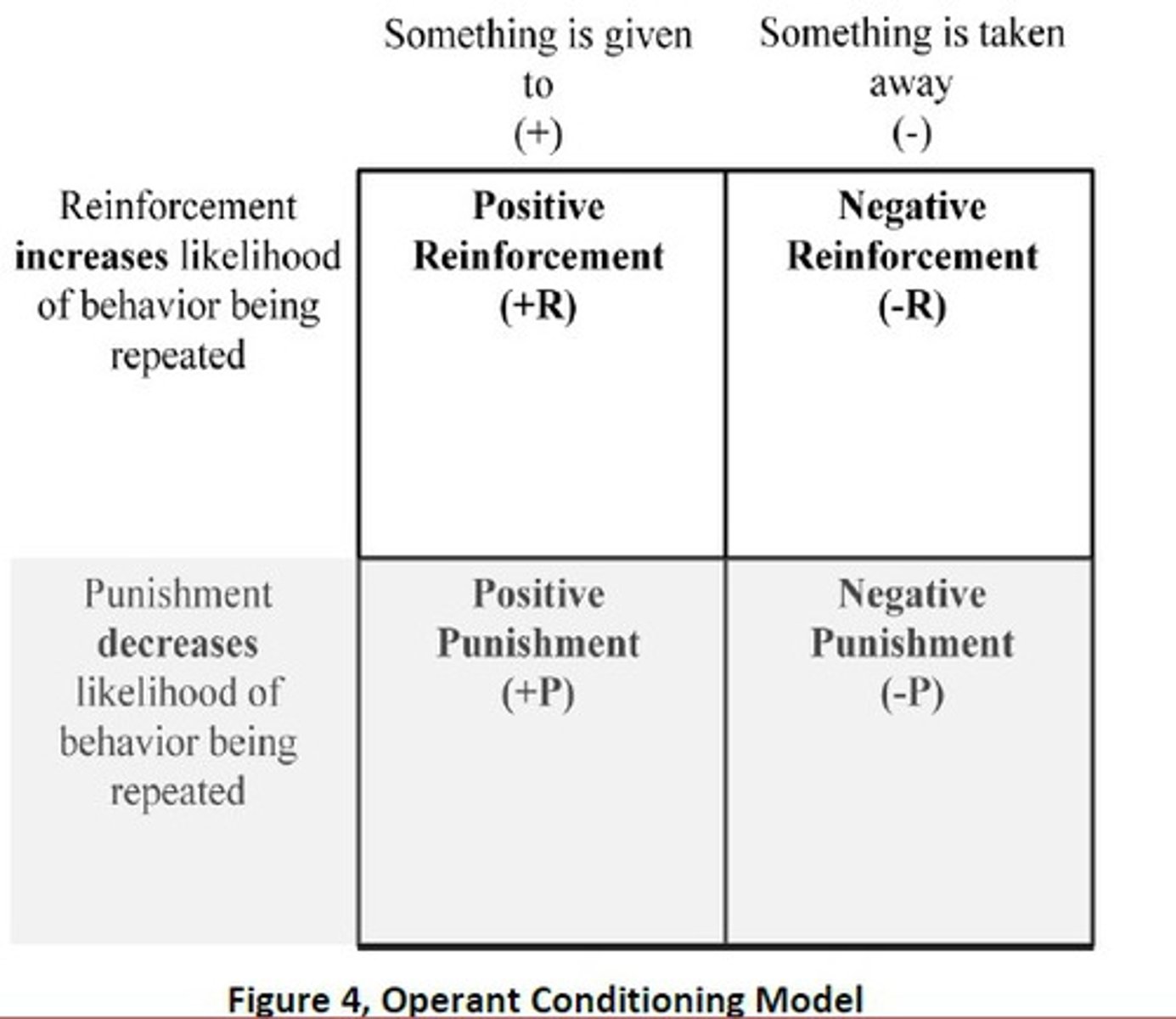
operant conditioning
the learning of voluntary behavior through the effects of reinforcement or punishment
observational learning
learning voluntary behaviour by observing others
