R&R EXAM 4
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
acute kidney injury (AKI)
OLIGURIA, normal/LARGE kidneys, REVERSIBLE decrease in kidney function that occurs over hours to days.
severe CKD
patient presents with fatigue, confusion, UREMIA, LOSS of APPETITE, and abnormal skin pigmentation what is the most likely diagnosis?
nephritic syndrome
which glomerular disease is LUPUS most commonly associated with?
microalbuminuria
screening for early-stage diabetic nephropathy
proteinuria
major clue that indicates GLOMERULAR (nephritic/nephrotic) disease
pre-renal, renal, post-renal
types of ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY
acute interstitial nephritis
condition where spaces between the kidney tubules become inflamed, type of RENAL AKI
pre-renal AKI
what can hepatorenal syndrome lead to?
pyelonephritis
A bacterial infection of the kidney and renal pelvis, often resulting from a urinary tract infection.
low urine Na and high Urine osm
indicators of pre-renal AKI
chronic kidney disease (CKD)
typically presents with fatigue, ANEMIA, SMALL kidneys
oliguria
DECREASED URINE OUTPUT, <500 ml/day, can indicate ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY
pre-renal
a type of acute kidney injury (AKI) caused by REDUCED BLOOD FLOW to the kidneys
renal
a type of acute kidney injury (AKI) resulting from DIRECT DAMAGE to the KIDNEYS
vascular, glomerular, tubular (ATN), nephritic/interstitial (AIN)
types of RENAL AKI
post-renal AKI
A type of acute kidney injury (AKI) caused by OBSTRUCTION of urine flow AFTER it passes through the kidneys
hydronephrosis
SWELLING of renal pelvis and kidney due to buildup of urine, indication of POST-RENAL AKI
post-renal AKI
what is HYDRONEPHROSIS an indication of?
pre-renal
what does a BUN/Cr ratio larger than 20:1 suggest
pre-renal AKI
what does an INCREASED BUN suggest
fractional excretion of Na (FENa)
percentage of Na secreted in the urine, accounts for abstraction of water by ADH
pre-renal AKI
low urine Na (FENa < 1%) suggests?
pre-renal AKI
what is HIGH URINE OSM an indication of?
acute tubular necrosis
most common cause of hospital acquired AKI
white coat hypertension
a condition where a patient's blood pressure is elevated in a clinical setting but normal in other settings
primary
most common type of hypertension
secondary
type of hypertension more prevalent in younger individuals
weight loss, exercise, low sodium ect.
non-pharmecutical methods of decrease blood pressure
ACEI
best first choice medication for younger pts with hypertension
systolic 130-139 or diastolic 80-89
parameters of stage 1 hypertension
systolic ≥ 140 or diastolic ≥ 90
parameters of stage 2 hypertension
causes glomerular damage that worsens hypertension
how does diabetes affect hypertension?
moderately (1 to 2 carpules)
can local anesthetic be used in patients with hypertension?
delay elective care
a patient presents with BP >180/110 what should be done?
emergency medical attention
a patient presents with BP >180/120 what should be done?
rhabdomyolysis
type of ACUTE TUBULAR NECROSIS (ATN) where muscle tissue breaks down and releases substances into the bloodstream, potentially causing kidney damage
edema, hyperkalemia, acidosis, accumulation of medications and uremic toxins
major complications of AKI
acute tubular necrosis/ATN (renal AKI)
presence of muddy brown casts in urine indicates?
chronic kidney disease (CKD)
urine output >500ml/24hrs ( or normal) is associated with?
chronic kidney disease
IRREVERSIBLE, leads to end stage renal disease (ESRD)
end stage renal disease (ESRD)
GFR <15mL/min indicates?
renal insufficiency
MILD renal disease with diminishing GFR
azotemia
WORSENING renal function, BUN build up resulting in LOW GRF and ELEVATED Cr
Uremia
SEVERE renal dysfunction, kidneys UNABLE to filter toxic nitrogenous wastes, kidney failure that REQUIRES intervention
lifestyle, BP, RAAS, glycemic control, lipid control, SGLT2 inhibitor
interventions for CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE (CKD)
diabetes, hypertension, and glomeronephritis
most common causes of chronic kidney disease (CKD)
nephrOtic syndrome
DAMAGE to glomerulus (podocytes) leading to significant proteinuria (>3.5 g)
nephrItic syndrome
INFLAMMATION at glomerulus leading to HEMATURIA (RBC casts) and moderate PROTEINURIA (1-3g)
proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, edema, hyperlipidemia, lipiduria
clinical features of nephrOtic syndrome
blood in urine (hematuria)
characteristic of nephrItic syndrome
edema, protein malnutrition, CVD, thrombosis, and infection
complications of nephrOtic syndrome
minimal change disease, glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), membranous nephropathy
causes of primary nephrOtic syndrome
focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)
most common PRIMARY glomerular disease resulting in ESRD
diabetes, lupus, amyloidosis
SECONDARY causes of nephrOtic syndrome
diabetes
most common SECONDARY glomerular disease resulting in ESRD
hematuria (nephritic syndrome)
what is brown urine an indication of?
post-infectious GN, IgA neuropathy, Progressive GN
primary causes of nephrItic syndrome
post-infectious glomerulonephritis
patient present with dark urine a few weeks after strep throat infection what is likely the cause?
post infectious, IgA, progressive, lupus
immune complex glomeronephritis’s
lupus and ANCA/vasculitis
secondary causes of nephrItis syndrome
lupus
pt presents with fatigue, arthralgia,malar rash, and renal involvement what is the likely diagnosis?
sjogrens
is an autoimmune disorder characterized by dry eyes and dry mouth, can occur alonewith other autoimmune diseases such as lupus
MALT lymphoma
individuals with sjogrens are at increased risk of what?
decrease risk of events (stroke, MI, HF, kidney disease)
What is the main goal of therapy for patients with hypertension?
target patient systolic BP <130
What are evidence-based monitoring parameter goals for patients with hypertension?
ACEI, CCB (calcium channel blocker), a1 blockers, ARBs, hydralazine
Which classes of agents work by decreasing systemic vascular resistance?
thiazide, loop diuretics, K-sparing diuretics
Which classes of agents work by decreasing intravascular volume and thus stroke volume?
ACEI, ARB, CCB (DHP), thiazide
first line therapies for HYPERTENSION
thiazides
inhibit Na-K pump, cause Na and K excretion
ACEIs
block angiotensin II FORMATION, cause VASODILATION and H2O excretion
ARBs
block angiotensin RECEPTOR, cause VASODIALTION and H2O excretion
CCBs(calcium channel blockers)
block calcium channels in smooth muscle, VASODILATION
lisinopril
example of ACEI
losartan
example of ARB
amlodipine
example of CCB
hypokalemia and hyperglycemia
ADRs of THIAZIDES
COUGH, hypotension, hyperkalemia, edema
ADRs of ACEIs
hypotension, hyperkalemia, edema
ADRs of ARBs
edema and constipation
ADRs of CCBs
systolic >180
at what BP should EXt be AVOIDED
epinephrine may worsen hypertension
consideration of epinephrine containing anesthetic with hypertension patients
NSAIDs
increases risk of AKI with antihypertensive agents (diuretics and RAAS)
chronic sustained injury leads to destruction of kidney and replacement with fibrous tissue
HOW does chronic kidney disease progress over time?
compensatory hyperfiltration
what causes the progression of CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
albuminuria
presence of albumin in urine
slowing progression
treatment strategy for CKD
ang II antagonists (ARBs)
first line therapy in HYPERTENSION management in CKD
ang II antagonist and SGLT2 inhibitor
medications to slow progression of CKD
aranesp
treatment for ANEMIA in CKD
low K diet, caution with meds, potassium binders
treatment for HYPERKALEMIA in CKD
calcitriol
treatment for high parathyroid hormone and low vitamin D in CKD
diabetes caused nephrotic syndrome
what is Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules in the kidney and indication of?
rapidly progressive renal failure (RPGN)
subcategory of nephritis with lung involvement (pulmonary renal syndrome), presents with PURPURIC RASH and BLOOD IN URINE
acute interstitial nephritis
often due to DRUG REACTIONS, infections, or autoimmune conditions symptoms such as fever, RASH, and eosinophilia.
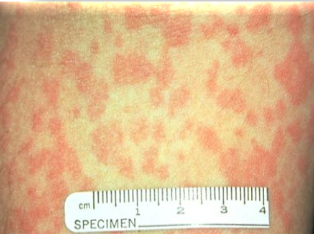
IgA nephropathy
most common glomerulonephritis (nephritic syndrome)