LEGL 2700 - Exam 1
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
141 Terms
Why is it important to learn about laws in a business school curriculum?
Keep us out of trouble!
Certainty and predictability
The law is more than just avoiding sanctions. What else can you use it for?
Sometimes law is specifically designed in a way that we can use to our advantage (e.g., intellectual property, tax incentives, start businesses, can get law changed in your favor, professional career, etc.)
What is the Rule of Law?
Laws are generally and equally applied – and requires solid, stable institutions
"No one is above the law"
How important is Rule of Law to business?
Essential! We need to know the how to play the game...again, certainty and predictability...
What can Rule of Law do?
Helps reduce at least one form of "transaction costs" (money spent to enter into and enforce contracts)
Define Property
Property is the term for the right to possess resources and shield from others.
Resources are things.
Right to property is the basis for a private market and basis for modern business.
Do you have the same “Property” as Elon Musk?
Yes. Property is not the same as Resources.
Classifications of Law
Common Law
Civil Law
Criminal Law and Civil Law (different meanings)
Common Law (system level)
Judge-made
Precedent (stare decisis) - let the prior decision stand (courts generally follow the previous court case and apply to these facts to come up with a decision; utilize the same rationale)
Established by the court’s judicial decisions
The role of judges determining the meaning of laws and how they apply
Civil Law (system level)
Relies heavier on legislation
Stricter
Judges don’t do a lot of interpretation of the law
Determine what the law is but doesn’t make law nor are judges obliged to follow prior judicial decisions
Based on legal codes
What “sanctions” apply in Criminal Law?
Death
Imprisonment
Fines
Removal from office
Disqualification from holding office and from voting
What “sanctions” apply in Civil Law?
Compensatory damages
Consequential damages
Punitive damages
Equitable remedies (not actually asking for money; making the court force the other party to do something)
Hierarchy of Laws (congress makes the statutes; agencies make the regulations)
Each higher source of law voids or prevails over every lower source of law in the hierarchy, except that in many instances there will be no conflict between higher and lower sources of law and in other instances, it may not be clear whether or not a higher source of law (such as constitutional right of speech) conflicts with a lower source of law (such as a law regulating advertising expression)
United States Constitution
Federal Statutes
Federal Regulations
State Constitutions
State Statutes
State Regulations
Local Ordinances
Case Law
Specificity
Fill in where the legislative branch can’t provide enough detail
Expertise
Subject matter experts on specific issues
Protection
Assist public when business practices are causing injury
Regulation
Replace competition with regulation in certain areas
Services
Administration of government programs and services
Criticisms of Administrative Process
Hard to hire the best, hard to fire the worst, and political ties
A lot of red tape, favors industry with policies
Adds to cost – directly through funding of agencies
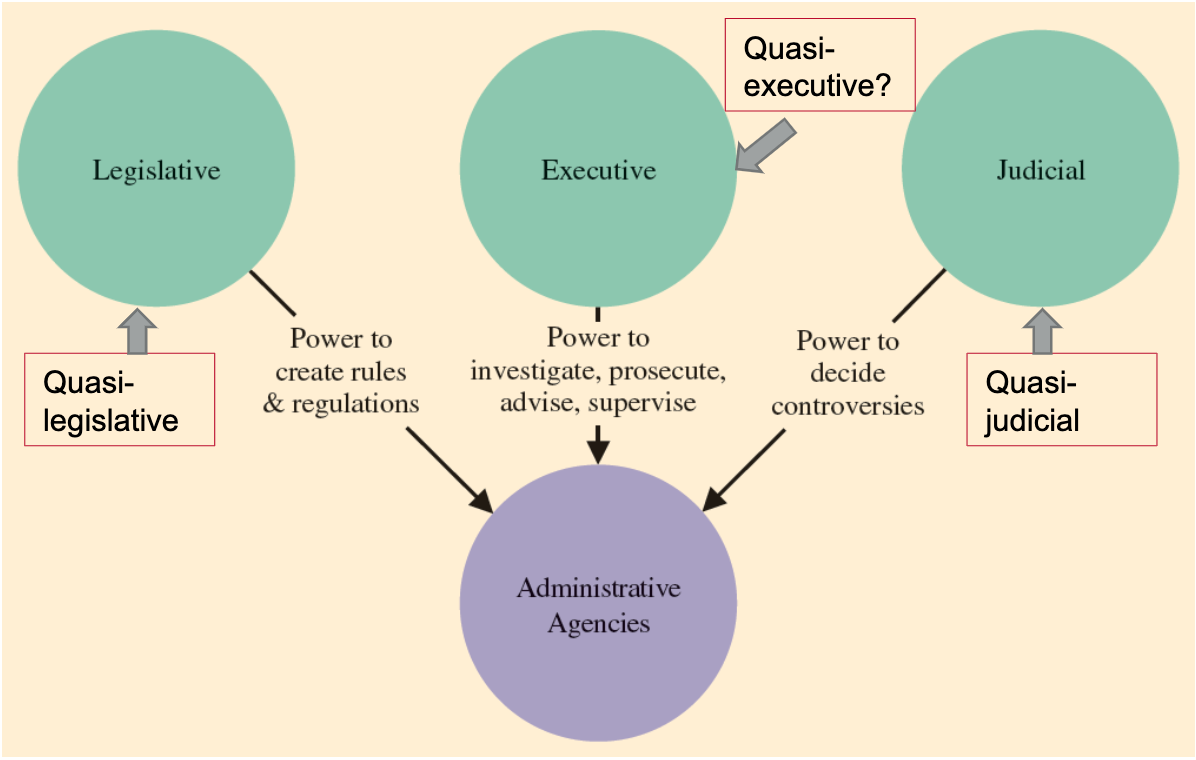
Administrative Agencies
Boards, bureaus, commissions, and organizations that make up the governmental bureaucracy.
Corporations (and to some extent other business entities too)
Owned by shareholders which can mean a lot of different things by depending on type of organization
Corporations organized in a certain way; Board of Directors oversee the business, they hire officers who then hire rest of employees
Officers and Managers are in charge of day-to-day business operations
Corporate Governance (legal rules that structure, power, and regulate the agents of corporations and define their relationship to the owners; relationship with each other, with their customer; and with society)
What issues could the set-up of corporations create?
Principal – Agent Problem (we do not know what they are doing with our money; we are hoping they are making more with it)
Specific Sense of Corporate Governance (Narrow)
Laws, policies, and procedures that protect the property interest that owners have in the business.
Try to prevent people inside the company from abusing their positions for their own advantage to the detriment (hurt) of the owners of the company
Shareholder primacy (increasing shareholder value to increase their power)
Broad Sense of Corporate Governance (General)
Expand corporate governance to include responsibility of company to customers, vendors, society, etc.
Gained a lot of traction
What is controversial with the general sense of corporate governance?
Diversity
Environmental Sustainability
Community involvement
Origins of the Constitution
Articles of Confederation
Series of Compromises
Series of compromises that created the Constitution
Between branches of government
Between state/federal authorities
State versus State
Between the people and government
Separation of Powers
Horizontal: Branches of Government
Vertical: Federal - State/Local
Horizontal: Branches of Government
Legislative – Make
Executive – Enforce
Judiciary – Fair Process, Interpret, and Even Invalidate Laws
Vertical: Federal – State/Local
Federalism
10th Amendment
"The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people."
Supremacy Clause, Article VI (highest power)
Constitution is supreme over all laws
Federal law is supreme over state law
Preemption
Preemption
Express: states not allowed to make rules in certain areas (state and local may not establish their own rules since there are federal rules)
Ex: medical devices
Imply: so pervasive and comprehensive that…
Field: little room exists for states to maneuver (regulation)
Conflict: impossible to comply with both federal and state
Contract Clause, Article I, Section 10
"No State shall...pass any...Law impairing the Obligation of contracts."
States cannot enact laws that impact rights and duties under existing contracts (can’t interfere with existing contracts)
E.g. private (e.g., discharging debt or changing other obligations) and public contracts (e.g., bonds, pension plans, etc.)
Does not apply to federal government!
State laws passed during emergency situations can be approved
Minnesota – mortgages in Great Depression (Home Building & Loan Association v. Blaisdell (1934)
What does the Commerce Clause do?
Federal government has power to regulate business activity:
Foreign Commerce: treaties, embargoes, tariffs
Interstate Commerce: states cannot interfere with interstate commerce
What case applied the Commerce Clause?
West Lynn Creamery, Inc. V. Healy, (1994)
Massachusetts passes a tax on imported milk
With the proceeds, they will pay the Massachusetts' dairy farmers who are hurt by the cheaper out-of-state milk prices
Bill of Rights
First ten amendments to the Constitution are the Bill of Rights (protect individual freedoms from government interference)
12 voted on and 10 passed
Total amendments now 27
Prohibitions on government power – defining citizens' personal rights ("freedoms")
Not absolute
Limitations based on competing public policy
Exist to remove certain issues from political process and ballot box
Vary from time to time (especially during emergencies)
Part of the 5th Amendment
Protects from government abuse of power
Grand Jury
Double Jeopardy
Right Against Self-Incrimination
Due Process
Eminent Domain
Eminent Domain Test
A Taking
Public Use
Just Compensation
First part of the Eminent Domain Test
"A Taking" is usually clear but not always
Second part of the Eminent Domain Test
"Public Use" doesn't mean the public will use! Public purpose (Berman v. Parker, 1954) - beautification and Kelo v. New London (2005)) - economic redevelopment with private companies (see it as public purpose for economic redevelopment; similar to the expansion of the commerce clause)
Third part of the Eminent Domain Test
"Just Compensation" is generally market price (negotiated price or let a court help settle the issue)
Parts of the 1st Amendment
Freedom of Religion
Establishment of Religion
Free Exercise of Religion
Freedom of Speech
Freedom of Press
Peaceful Assembly
Petition Government
Why do we generally have free speech?
Protects the voice of the minority
What is not considered absolute free speech?
Fighting words
Incitement to riot
Time, place, manner restrictions
Words that violate intellectual property law
Defamation
Obscenity
Commerce Free Speech (the right to advertise or discuss commercial products and services)
Not originally thought to be included in 1st Amendment
Came light in the 1970s
Virginia State Board of Pharmacy v. Virginia Citizens Consumer Council (1976) - drug prices (advertising drug prices are allowed)
Bigelow v. Virginia (1975) - abortion advertising (in other states is allowed)
Central Hudson (1980)
Lawful Activity
Governmental Interest Substantial
Directly Advance Governmental Interest
Not more Extensive than Necessary
Key takeaway – easier to restrict commercial speech than individual speech
Compelled Commercial Speech
Zauderer v. Office of Disciplinary Counsel of Supreme Court of Ohio (1985)
Disclose certain information "as long as disclosure requirements are reasonably related to the State's interest in preventing deception of consumers." (nutritional value, warnings for cigarettes)
Freedom of Press
Press is only organized private business given explicit constitutional protection
Prior Restraint
Defamation
Two forms of Defamation
Libel - printed defamation
Slander - spoken defamation
Freedom of Religion
"Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion, or prohibiting the free exercise thereof..."
What are two “clauses” of Freedom of Religion?
Establishment
Free Exercise
Prior Restraint
Generally must publish work before censorship permitted (may change your mind or content)
Defamation
Falsehood that is injurious to the good name or reputation of another
14th Amendment (it is about the states)
No State shall make or enforce any law which shall:
Abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States
Deprive any person of life, liberty or property, without due process of law
Deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws
Two parts of the 14th Amendment
Due Process
Equal Protection
Due Process
Prevent governmental bodies from acting in a manner that is arbitrary, capricious, or unreasonable - "state action"
Procedural Due Process
Involve cases (for example) regarding whether:
Proper notice was given
Proper hearing was conducted
Substantive Due Process (implied fundamental rights)
involve cases (for example) regarding:
Right to work
Right to marry
What does the 14th Amendment’s Due Process Clause mean for the Dobbs case?
The ruling overturned Roe v. Wade.
Doesn't protect abortion as a fundamental right.
Returned the power to regulate abortion to the states.
Incorporation Doctrine
Due Process clause has been used to incorporate most of the Bill of Rights and make provisions applicable to states
What case utilized the incorporation doctrine of the 14th Amendment Due Process Clause?
Gideon v. Wainwright (1963) - appointment of counsel applied to Florida
Break-in at a pool all
Gideon arrested for petty larceny
Can't afford and attorney and get convicted
Supreme Court says 6th Amendment Applies to the States
Equal Protection
The equal protection clause guarantees that people will not be treated differently under law without adequate justification
Any law creating different classifications is subject to one of three tests.
Who are the players of the court system and litigation
Lawyers
Magistrates/Judges/Justices
Juries
What are the roles of lawyers?
Public Servant
Advocate
Counselor
How are lawyers public servants?
Ensure the fair administration of justice
Proceedings are conducted in a dignified and orderly manner
How do lawyers advocate?
Engage in adversarial process with other lawyers
Present evidence, points of law, arguments, etc.
Help to inform and persuade both the judge and jury in making decisions
How are lawyers counselors?
Attorney-Client Privilege
What is the Attorney-Client Privilege?
Lawyer cannot reveal confidential information and cannot be compelled to testify against client
What do Magistrates, Judges, and Justices do?
Essentially operate and control the courtroom and really entire litigation process
Generally consider them "triers of law" (what is the exception? = when there are no juries (bench trials))
Trial Level - "Judges" (some are called "Magistrates" depending on level of court usually)
Appellate Level – often called "Justices" but can also be called "Judges" (they decide these issues of law)
Hear appeals from lower courts alleging problems with the application of the law
Generally provide reasons for their decision in writing ("opinions") (written opinions at the appellate level)
Dual Court System
Federal and State
Why is there a federal and state level?
Federalism
What is Jurisdiction?
A Court's power to enter a judgment against property or person
What types of jurisdictions are both needed?
Subject Matter Jurisdiction
Personal Jurisdiction
Subject Matter Jurisdiction
Can the court settle disputes of this type?
Authority of a court to hear cases involving specific issues of law
Personal Jurisdiction
Does the court have the right to force a person to attend a trial and have power over them to render a decision?
Power of a court over the parties involved in the litigation process
Articles of Confederation
Strong sovereignty of the States
Weak federal government
What was one of the main concerns regarding economic issues in the Articles of Confederation?
States could impose protectionist measures hurting other states
Where is "judicial review" in the Constitution?
It isn't but Supreme Court gave it to themselves: Marbury v. Madison
What is the Dormant Commerce Clause?
RESTRICTS the States from passing certain laws even though there is no contradictory federal law – stop discriminating against other states!
What are the three tests of the equal protection clause?
Miniumum Rationality
Quasi-Strict Scrutiny
Strict Scrutiny
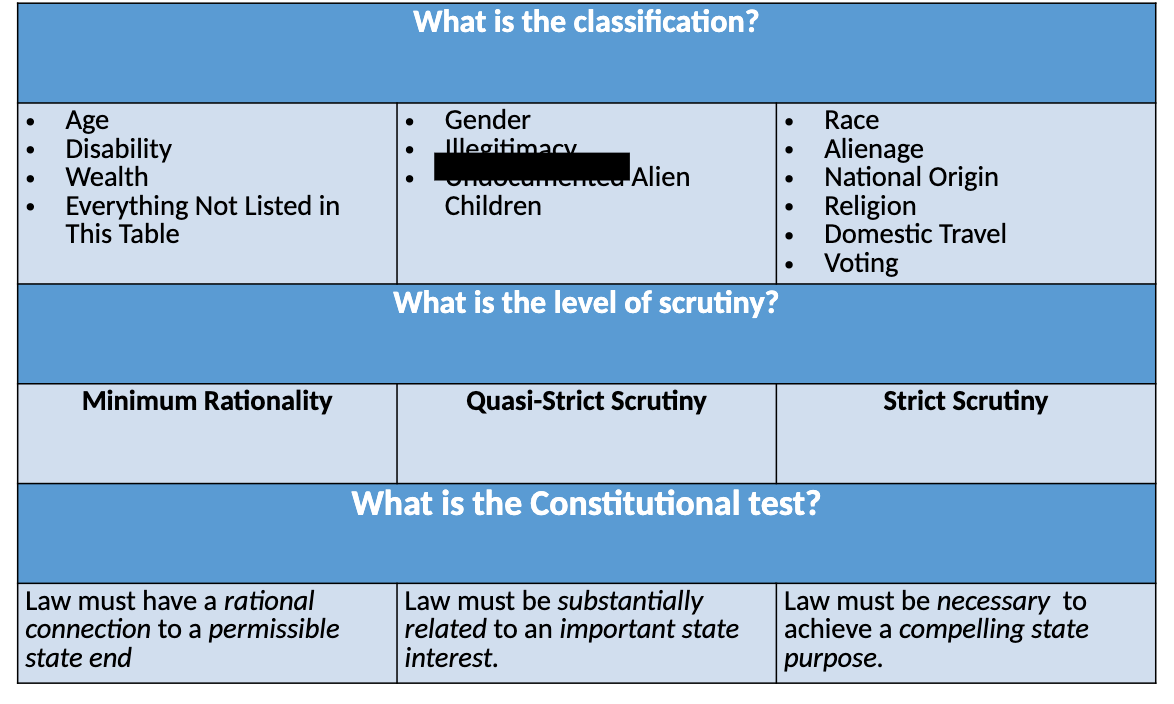
What is the Minimum Rationality test?
Law must have a rational connection to a permissible state end.
What are the Minimum Rationality classifications?
Age
Disability
Wealth
Everything not listed in this table….
What is the Quasi-Strict Scrutiny test?
Law must be substantially related to an important state interest.
What are the Quasi-Strict Scrutiny classifications?
Gender
Illegitmacy
Children
What is the Strict Scrutiny test?
Law must be necessary to achieve a compelling state purpose.
What are the Strict Scrutiny classifications?
Race
Alienage
National Origin
Religion
Domestic Travel
Voting
Juries
“Triers of Fact"
Traditionally has been 12 jurors but sometimes less
Book says: most states require unanimous decisions (trend moving away from requirement)
Note, fairly recent case where Supreme Court said must have unanimous verdicts in criminal cases (Ramos v. Louisiana (2020)
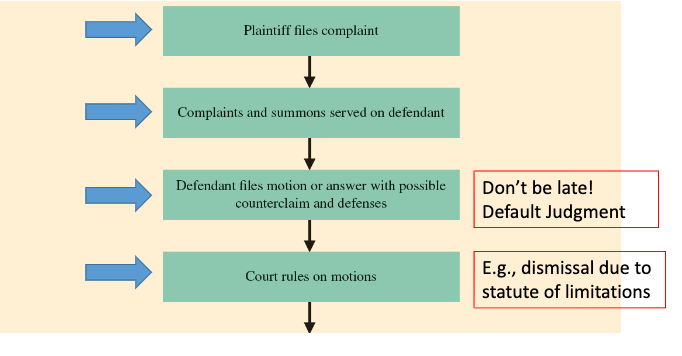
What is the Civil Case Pre-Trial Procedure?
Plaintiff files compliant
Complaints and summons served on defendant
Defendant files motion or answer with possible counterclaims and defenses (don’t be late or default judgment)
Court rules on motions (e.g., dismissal due to statute of limitations)
Attorneys conduct discovery procedures.
Why is the Discovery Procedure needed?
So cases based on merit and surprises
Narrows the issues disputed by the parties
Encourages the settlement of the lawsuit and possibly avoiding actual trial
Discovery Methods
Interrogatories: Series of written questions presented to the opposing parties
Requires for production of documents: Either party asking the other to produce specific documents.
Depositions: Lawyer orally asks questions of the possible witness
Request for an admission
What is the Trial Procedure?
Voir dire—Parties and their attorneys select jury
Court instructs jury on the law
Jury deliberates and makes decisions (verdict)
Judge enters judgment on verdict
Party receiving adverse judgment files notice of appeal
Parties file briefs in reviewing court
Oral argument made in reviewing court
Final decision (successful party may require judicial assistance in enforcing the final decision)
How does the court select the jury?
Priorr to calling of the case, court clerk will have summoned prospective jurors
Voir dire
Speaking the truth
For Cause Challenge
Cause or reason needs to be given to excuse a prospective juror (e.g., related to a party (including attorneys) in the case, bias, etc.)
Peremptory challenge (freebies)
No cause or reason needs to be given to excuse a prospective juror – receive a limited number of these
What is banned in peremptory challenges?
Racial Discrimination (Banson v. Kentucky)
Gender Discrimination (J.E.B v. Alabama Ex Rel. T.B.)
Religion Discrimination
What happens during Voir dire? (= speaking the truth)
Selected jurors are called into jury box to conduct the examination
Criminal Law
Offenses against proper order of the state by a representative of community.
Civil Law
Suing other parties for damages or relief
Shareholder Primacy
Increase its profits to increase power
Prioritizes the interests of shareholders
Stakeholder Theory
Maintaining ethical corporate behavior depends on managers who recognize and take into account the various stakeholders whose interest are the corporation impacts.
Focuses on the legal responsibilities of managers to society and to the investor-owners of the corporation