3.2.3 Group 7 halogens
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Describe fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine in terms of colour, state and other properties
fluorine- very pale yellow glass and highly reactive
chlorine- green gas, reactive and poisonous in high concs
bromine- red-brown liquid, gives off dense brown/orange poisonous fumes
iodine- shiny grey solid sublimes to purple gas
What happens to MP and BP down group 7?
increases down the group
as molecules become larger, they have more electrons and have larger VDW forces between molecules
intermolecular forces get larger meaning more energy needed to break forces
What happens to electronegativity down the group?
electronegativity decreases
nuclear charge increases but despite this:
atomic radii increases as number of shells increases
shielding increases- inner electron shells reduce atom’s ability to attract electrons
What happens to reactivity down group 7?
reactivity decreases
atomic radius increases
more electron shells added meaning outer electron experiences more shielding and is further away from nucleus
therefore electrostatic attraction between outer electron and nucleus gets weaker
becomes harder for larger halogens to attract electron
What 4 types of reactions do halogens take part in?
displacement reactions (displacing less reactive halide ions from solution)
reaction with silver nitrate
reaction of halide salts with conc sulfuric acid
disproportionation reactions of chlorine
In a displacement reaction, what is the role of the halogen?
acts as a strong oxidising agent that displaces a halogen with a lower oxidising power from one of its compounds
Why halogens act as oxidising agents?
halogens gain an electron meaning it’s reduced as it’s oxidation number decreases from 0 to -1
causes another substance to be oxidised
How does oxidising strength change down the group and why?
oxidising strength decreases down the group
oxidising agents are electron acceptors
cos reactivity decreases as atoms get larger and outer shell is further from nucleus so electrostatic attraction between outer electron and nucleus gets weaker
When will a halogen displace another halide from solution?
If the halide is below it in the periodic table (less reactive)
What will chlorine displace? Write their ionic equations
bromine (Br-)
Iodide (I-)
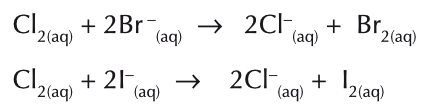
What will bromine displace? Write their ionic equation
Iodide (I-)

What will iodine displace?
It doesn’t displace fluorine chlorine or bromine
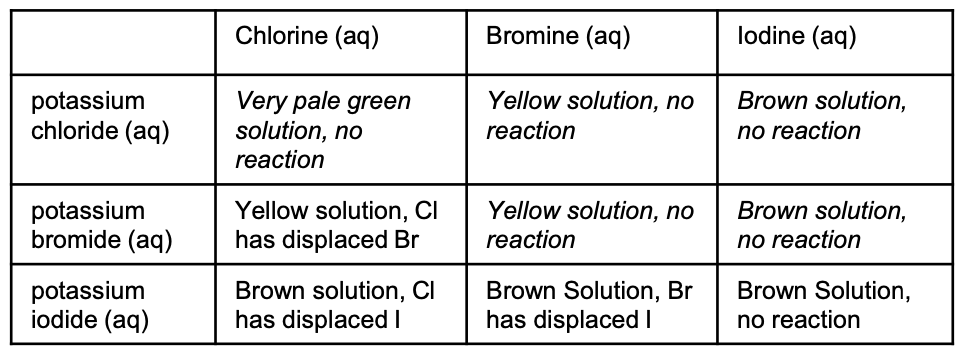
If chlorine was the free halogen present in a solution in a test tube, what colour would show?
very pale green solution (often colourless)
If bromines was the free halogen present in a solution in a test tube, what colour would show?
yellow solution
If iodine was the free halogen present in a solution in a test tube, what colour would show?
brown solution
Fill in this table. In each box, write what colour would show and if a displacement has occurred.
What test is used to identify which halide ion is present?
silver nitrate test- nitric acid is added to the test solution and then silver nitrate is added dropwise
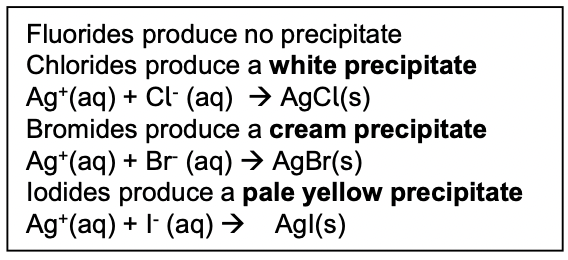
What is observed when F, Cl, Br & I react with the silver nitrate? Write the ionic equations for each
What is the role of nitric acid in the reaction of halide ions with silver nitrate?
to react with any carbonates present to prevent formation of the precipitate Ag2CO3 as this would mask the desired observations
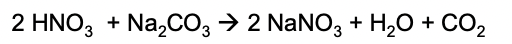
What can you do if the colour of the silver halide precipitates look similar?
treat them with ammonia solution to help differentiate the colours

What is the reducing power of halide ions and what is the trend down group 7?
reducing power refers to the ability of halide ions to donate electrons to other substances
reducing ability of halide ions increase down group 7
increasing ionic radius so electrons are further from nucleus
outer electrons experience more shielding so electrostatic attraction between outer electron and nucleus gets weaker
becomes easier for larger halide ions to lose electrons and become oxidised
Fluoride is the weakest reducing agent and iodide is the strongest
this explains the reactions of halide
What happens when halide ions react with conc H2SO4 ?
hydrogen halide gases are initially produced but subsequent reactions depend on the reducing powers of the hydrogen halide formed
What happens when sodium fluoride and sodium chloride react with conc H2SO4 ? Write the equations
white steamy fumes of HF/HCl gas are evolved
no redox reactions occur only acid-base reactions
fluoride and chloride have low reducing power and are not strong enough reducing agents to reduce the S in H2SO4
oxidation states of halide and sulfur stay the same
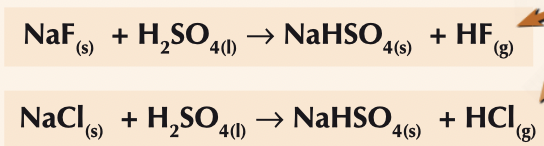
What happens when NaBr reacts with conc H2SO4 ? Write the equations and any half equations involved and also state the role of H2SO4
first acid-base reaction gives white misty fumes of HBr gas
since HBr is a stronger reducing agent it reduces the S in H2SO4 from +6 to +4 - reaction produces toxic fumes of SO2 and orange fumes of Br2 (redox reaction)
overall equation: 2NaBr + 2H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + SO2 + Br2 + 2H2O
H2SO4 acts as acid in first step and then acts as oxidising agent in 2nd step
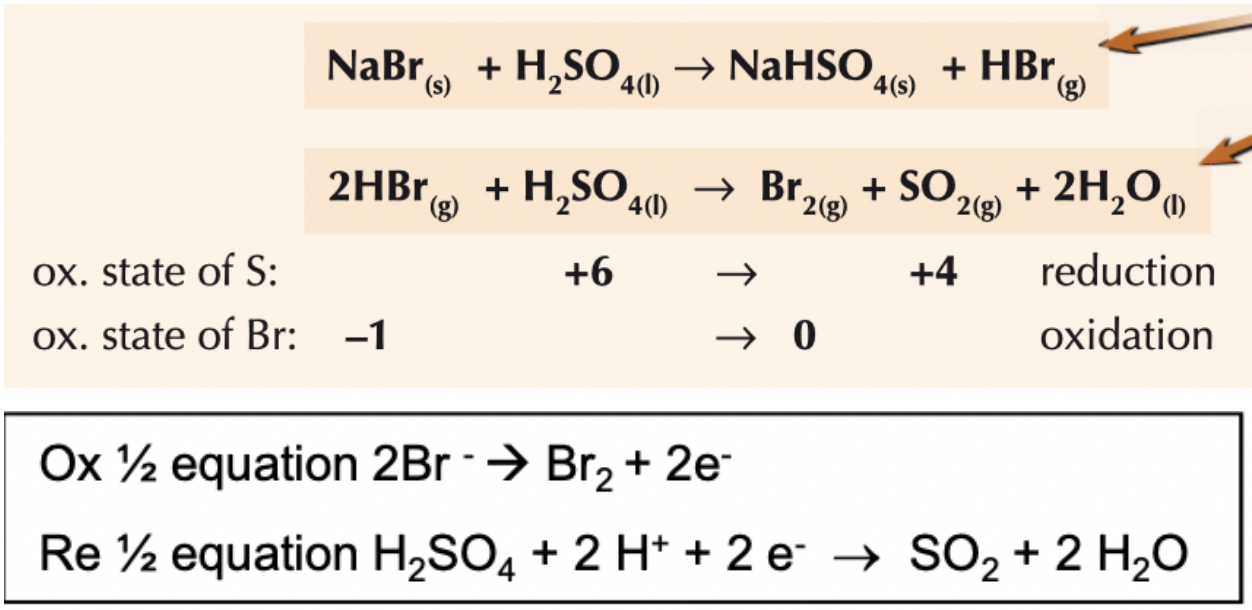
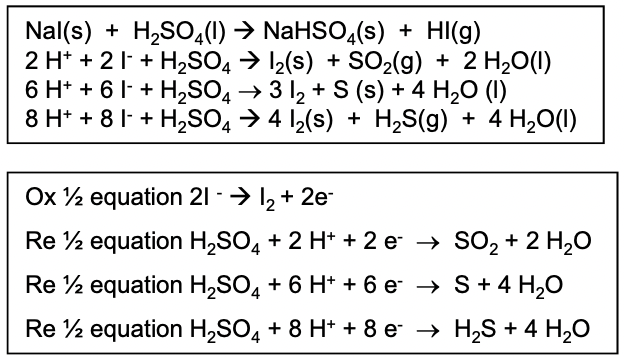
What happens when NaI reacts with conc H2SO4 ? Write the equations and any half equations involved
first acid-base equation gives white steamy fumes of HI gas
I- ions are the strongest halide reducing agents so they can reduce H2SO4 to SO2 , H2S or S
the oxidation state of S goes from +6 to +4 to 0 to -2
black solid and purple fumes of iodine are evolved
yellow solid of sulfur formed
H2S is a toxic gas with a smell of bad eggs
What is a disproportionation reaction?
they occur when a substance is simultaneously oxidised and reduced in the same chemical reaction
Chlorine reacts with water in a disproportionation reaction. Write the equation and explain why this is a disproportionation reaction
Cl2(g) + H2O(l) ⇌ HCl(aq) + HClO(aq)
oxidation of Cl increases from 0 to +1 in HClO and decreases to -1 in HCl
you get a mixture of chloride and chlorate (I) ions
What happens if you add some universal indicator to the solution in Cl2(g) + H2O(l) ⇌ HCl(aq) + HClO(aq)
it will first turn red due to the acidity of both products and then it will turn colourless as the HClO bleaches the colour
What happens when you react chlorine with water in sunlight? Write the equation
2Cl2(g) + 2H2O(l) ⇌ 4H+(aq) + 4Cl-(aq) + O2(g)
chlorine decomposes water to form chloride ions and oxygen
the greenish colour of chlorine water fades as the Cl reacts and a colourless gas O2 is produced
What is chlorine used for?
water treatment to kill bacteria in drinking water and in swimming pools
chlorate ions kill bacteria (ClO-)
What are the downsides of using chlorine for water treatment?
chlorine is toxic
water contains variety of organic compounds and Cl reacts with these compounds to form chlorinated hydrocarbons eg. chloromethane - many are carcinogenic but these risks are small compared to risks from untreated water
How is bleach made from chlorine? Write the equation and state the type of reaction this is
mixing chlorine gas with cold, dilute, aqueous NaOH produces sodium chlorate solution
Cl2(g) + 2NaOH(aq) → NaClO(aq) + NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
oxidation number of Cl increases from 0 to +1 in NaClO and decreases to -1 in NaCl
bleach solution contains chlorate ions that act as oxidising agents to kill bacteria
Name these chlorates/sulfates make sure to add oxidation number
NaClO
NaClO3
K2SO4
K2SO3
