Chapter 15: Carbohydrates
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Carbon, oxygen, & hydrogen
Which elements make up carbohydrates?
A molecule with at least one carbon bonded to four different groups
What is a chiral molecule?
monosaccharides
The simplest carbohydrate (think glucose, galactose, & fructose)
disaccharides
consist of two monosaccharides (think lactose, sucrose, & maltose)
polysaccharides
contain more than two monosaccharides
aldehyde & ketone
What kind of groups do monosaccharides contain?
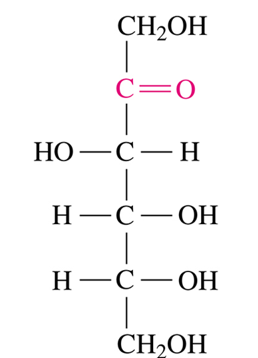
ketohexose
The following monosaccharide is a ______.
aldoses
Aldehyde monosaccharides are called?
ketoses
Ketone monosaccharides are called?
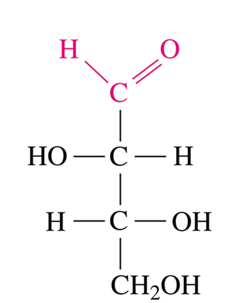
aldotetrose
The following monosaccharide is called?
3-8 carbons
Monosaccharides have how many carbons?
pentose
a monosaccharide with 5 carbons is called a…
triose
a monosaccharide with 3 carbons is called a ….
glucose
Which carbohydrate is known as blood sugar?
achiral
An object whose mirror image is identical to the original and can be superimposed on is …
stereoisomers
When two or more chiral structures have the same molecular formula, but differ in 3D arrangement of atoms
enantiomers
stereoisomers that CANNOT be superimposed on
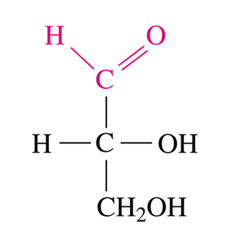
Glyceraldehyde
What is the COMMON name for the following monosaccharide? (Think: aldotriose)
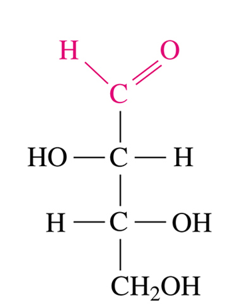
Threose
What is the COMMON name for the following monosaccharide? (Think: aldotetrose)
Ribose
What is the COMMON name for the following monosaccharide?(Think: aldopentose)
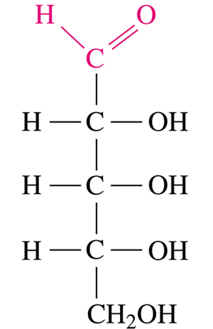
Fructose
What is the COMMON name for the following monosaccharide? (Think: ketohexose)
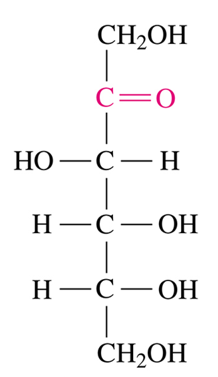
Fischer Projection
A two dimensional representation of a molecule. Places the most oxidized group at the top. Uses vertical lines for bonds that go backward, horizontal likes for bond that go forward. The intersections of vertical & horizontal lines represent a carbon atom that is usually chiral
The hydroxyl (-OH) group on the chiral carbon farthest from the carbonyl group
What determines whether a monosaccharide is classified as D or L
D
Is this Fischer Projection D or L?
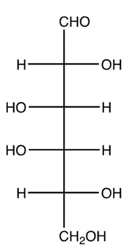
D-Glucose, D-Galactose, D-Fructose because they are all hexoses with the same molecular formula of C6H12O6.
What are the most important monosaccharides and why?
D-glucose
Identify the following D monosaccharide.
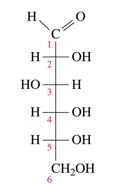
D-galactose
Identify the following D monosaccharide.
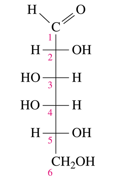
D-fructose
Identify the following D-monosaccharide
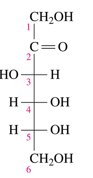
fructose
Which monosaccharide is the sweetest?
Haworth structure
The cyclic structure of monosaccharides is called
H on top = alpha (H comes before O) OH on top = beta (think O comes after H
How do you know if a Haworth structure is alpha or beta
alpha D glucose
Identify the following Haworth structure
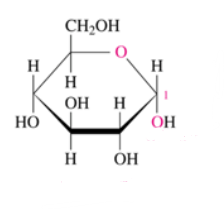
beta D glucose
Identify the following Haworth structure
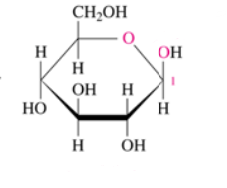
alpha D galactose
Identify the following Haworth structure
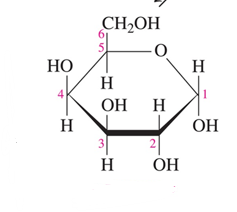
beta D galactose
Identify the following Haworth structure
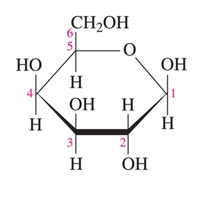
alpha D fructose
Identify the following Haworth structure
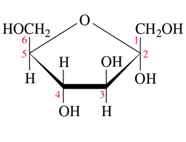
beta D fructose
Identify the following Haworth structure
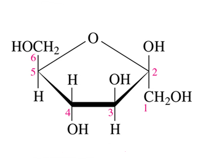
carboxylic acids
Monosaccharides that contain an aldehyde group oxidize to
alcohols
Monosaccharides that contain an aldehyde group reduce to
Fructose cannot further oxidize because it has ketone group. It can rearrange its carbons to oxidize into glucose and is further oxidize to a carboxylic acid.
What does fructose oxidize to and explain why.
D-sorbitol
What sugar is commonly used in sugar free products?
reducing
The following sugars are _____ sugars: glucose, fructose, galactose, maltose, & lactose
non-reducing
Polysaccharides are _______ sugars.
Maltose
Glucose + Glucose
Lactose
Glucose + Galactose
Sucrose
Glucose + Fructose
alpha maltose
Identify the following Haworth Structure
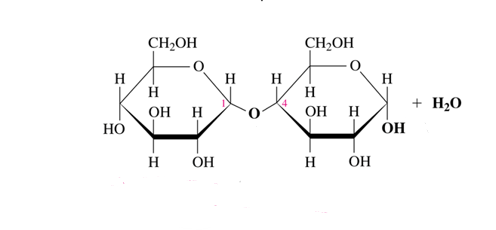
alpha (1-4) glycosidic bond
What glycosidic bond does maltose have?
alpha lactose
Identify the following Haworth structure
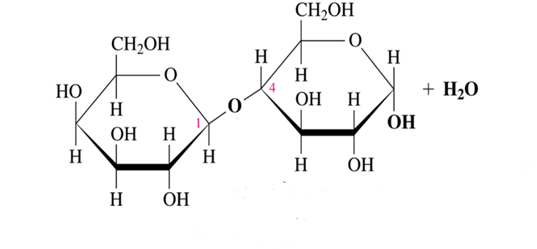
beta (1-4) glycosidic bond
What glycosidic bond does lactose have?
sucrose
Identify the following Haworth structure
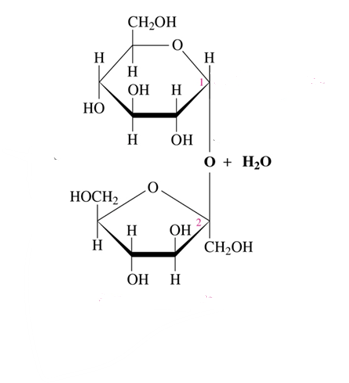
alpha beta (1-2) glycosidic bond
What glycosidic bond does sucrose have?
polysaccharides
What kind of carbohydrates are the following: Amylose, amylopectin, glycogen, cellulose, and starch.
Starch
A storage form of glucose in plants, found as insoluble granules in rice, wheat, potatoes, beans, and cereals.
Composed of 2 kinds of polysaccharides: amylose & amylopectin
unbranched chain of amylose
alpha 1-4 glycosidic bond
what glycosidic bond does amylose have?
amylopectin
makes up 80% of starch
is a branched-chain polysaccharide
alpha (1-4) and alpha (1-6) glycosidic bonds
What glycosidic bond does amylopectin have?
Glycogen
A polymer of glucose that is stored in the liver and muscle of animals
AKA animal starch
hydrolyzed in our cells at a rate that maintains the blood level of glucose and provides energy between meals
alpha (1-4) and alpha (1-6) glycosidic bond
What glycosidic bond does Glycogen have?
Cellulose
The major structural unit of wood and plants, gives a rigid cell walls in wood and fiber, cannot be digested by humans because humans cannot break it down
beta (1-4) glycosidic bond
What glycosidic bond does cellulose have?