1.2.3a - price elasticity of demand
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
elasticity of demand is…
…an attempt to measure the responsiveness of demand to changes in other variables
PED definition
a measure of the responsiveness of demand to a change in price of the good
PED formula
%change in demand/%change in price
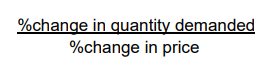
the result of a PED calculation will always be
NEGATIVE because there is an inverse (downwards sloping) relationship between demand and price
factors affecting PED
substitutes availability
necessity vs luxury
addictiveness
percentage of someone’s expenditure
time available to respond to price change
(snapt)
two types of demand
elastic demand
inelastic demand
elastic demand
an increase in price results in a large fall in demand
(demand very responsive to price change)
inelastic demand
an increase in price results in only a small fall in demand
(demand quite unresponsive to price change)
elastic demand qualities:
necessity/luxury
addiction
substitutes?
price
quality
time to change decision
luxury
not addictive
lots of substitutes
expensive
low quality
lots of time
inelastic demand qualities:
necessity/luxury
addiction
substitutes?
price
quality
time to change decision
necessity
addictive
lack of substitutes
cheap
high quality
little time
5 types of PED
unitary elastic
relatively elastic
perfectly elastic
relatively inelastic
perfectly inelastic
when we use a value to find out what PED type we have, how do we approach it
ignore the negative symbol, as it just shows the relationship
focus on the value, as it shows the strength of the relationship
for example, how would you describe a PED of -2
negative = direction of graph (downwards sloping)
2 = 1% price increase leads to 2% demand fall
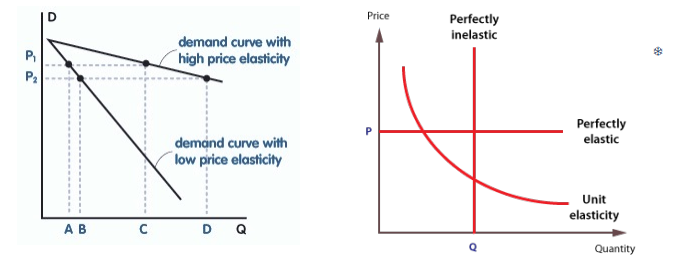
unitary elastic PED
PED = 1
quantity demanded changes by exactly the same percentage as price
shown with a rectangular hyperbola (all the rectangles formed under it are equal in area)
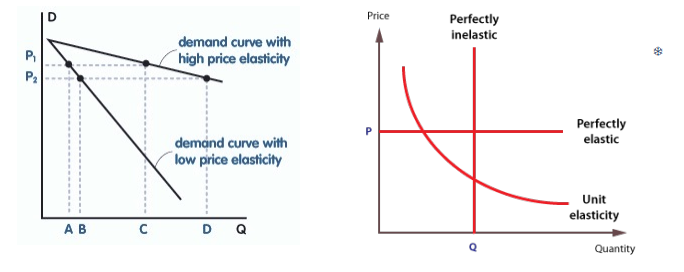
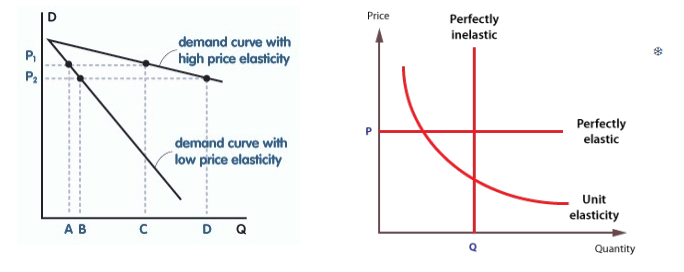
relatively elastic PED
PED>1
demand changes by a larger percentage than price
demand relatively responsive to price changes
shallower line on graph (lots of demand change for small price change)
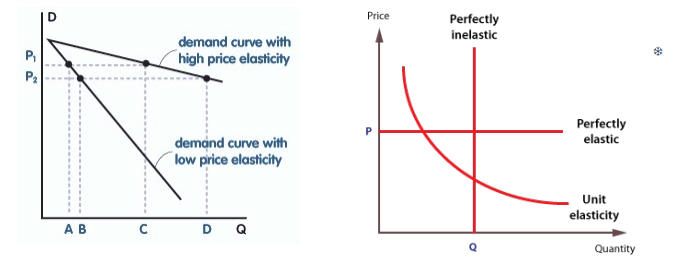
perfectly elastic PED
PED = infinity (demand change/0 = infinity)
change in price would mean quantity falls to 0 (all or nothing) - infinite change in quantity demanded
demand very responsive to price
horizontal line on graph (one price, all the demand)
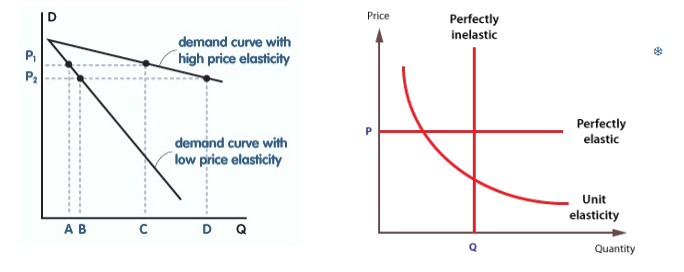
relatively inelastic PED
PED<1
demand changes by a smaller percentage than price
demand relatively unresponsive to price
steep line on graph (little demand change for lots of price change)
perfectly inelastic PED
PED = 0 (0/price change)
change in price has no effect on demand
demand is completely unresponsive to price
vertical line on graph (no demand change for all prices)
what is TR
total revenue = price x quantity sold
the money the firm earns from selling their product
where on a demand curve is TR
the rectangle made when u draw lines from the axes to the curve
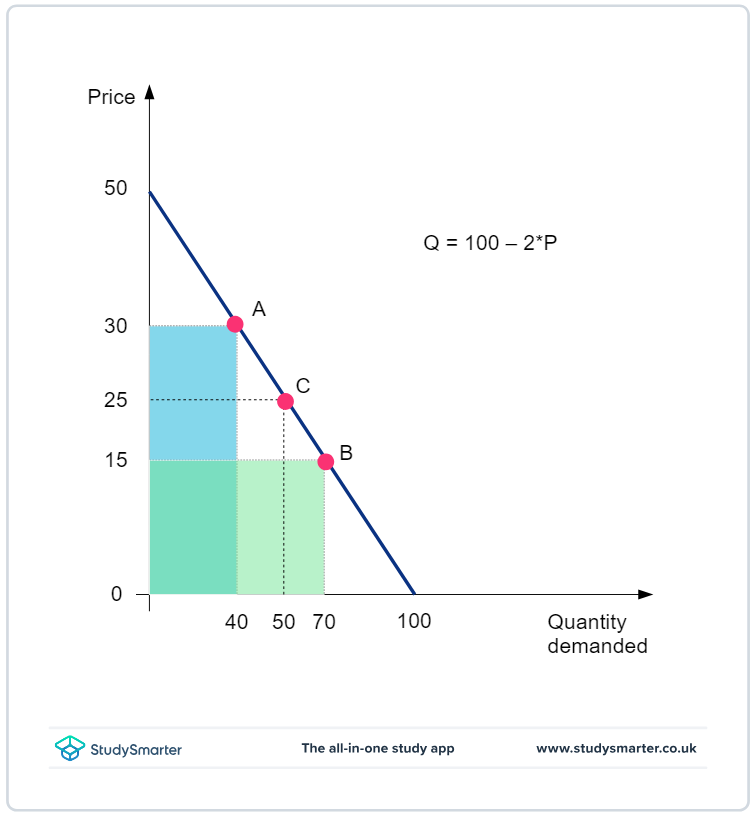
elastic demand total revenue
reduction in price = TR increase
percentage reduction in price = larger percentage increase in the quantity demanded (+ vice versa)
the rectangle increases in area
inelastic demand total revenue
reduction in price = TR decrease
percentage reduction in price = smaller percentage increase in quantity demanded (+ vice versa)
the rectangle decreases in area
unitary elasticity TR
reduction/increase in price = same TR
both increase/reduce by the same percentage
rectangles are all same area (rectangular hyperbola)