Mental Health: Major Depressive Disorder
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Major depressive disorder onset
typically in mid-teens to late 20's
Peak prevalence in 30's-40's
Major depressive disorder more commonly affects
women (2-3x more common)
Genetic risk factors for major depressive disorder
2-3 times greater prevalence among first-degree relatives
MTHFR gene shows “meager significant association”
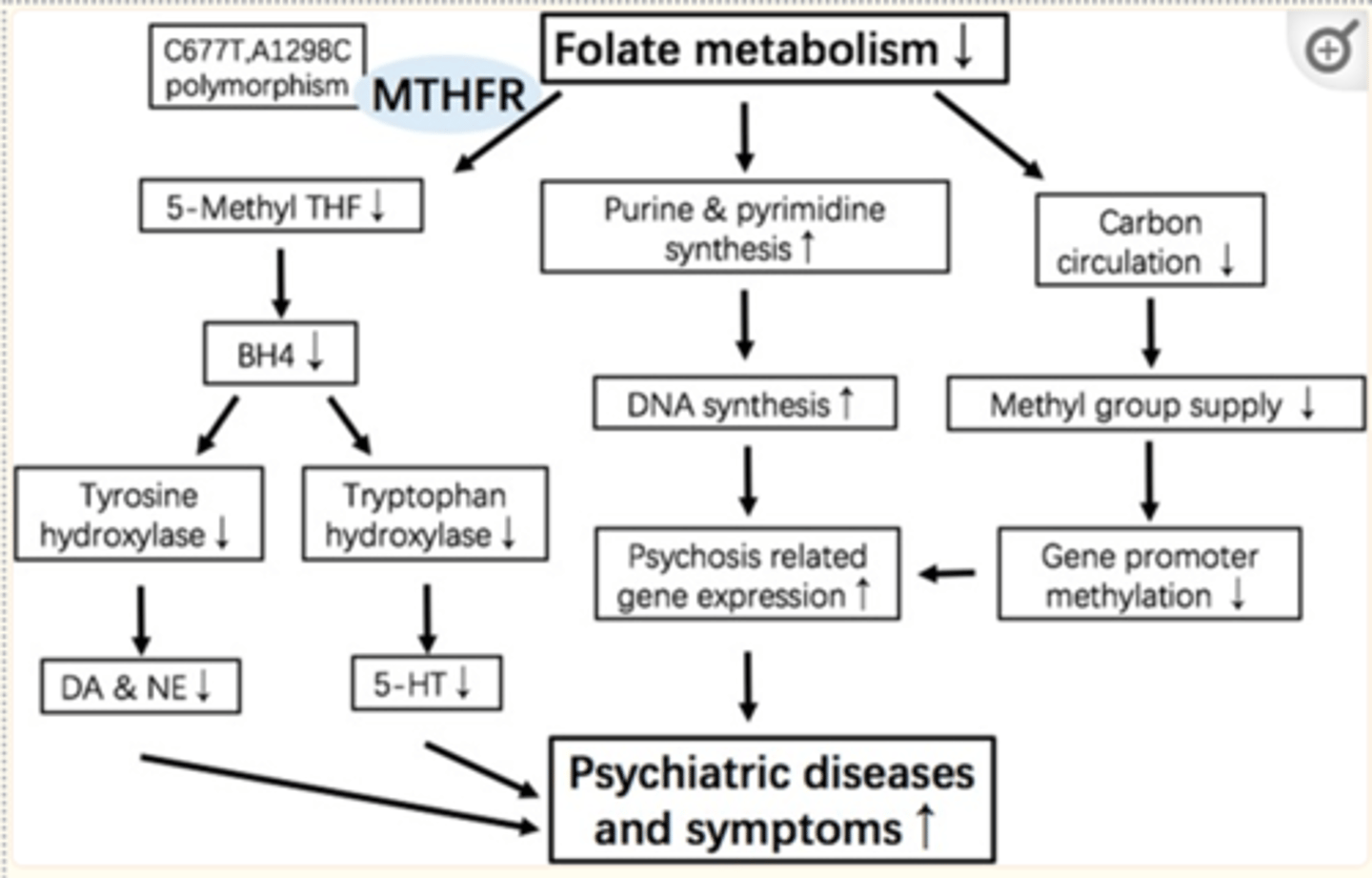
Environmental risk factors for major depressive disorder
High ACE (adverse childhood experience) score
Chronic medical illness/disability
Stressful life events (bereavement, divorce, unemployment, financial loss)
Major depressive disorder pathophysiology: neurotransmitter deficit hypothesis
Low Serotonin- depression and anxiety
Low Norepinephrine- depression
Low Dopamine- depression
Major depressive disorder pathophysiology: other correlations
Elevated cortisol levels
Thyroid hormone imbalance
Decreased hippocampus volume
Cortical thinning (temporal regions)
Major depressive disorder clinical presentation
Depressed mood, Anhedonia (lack of motivation), Sleep disturbance (insomnia or hypersomnia), Appetite changes (increased or decreased), Weight change (increased or decreased), Fatigue, Difficulty concentrating, Indecisiveness, Guilt, Worthlessness, Suicidal ideation

Major depressive disorder diagnosis
Clinical based on DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria:
2 weeks of 5+ symptoms of depression (one of which must be depressed mood or loss of interest or pleasure)
Symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning
Major depressive disorder diagnostic tools
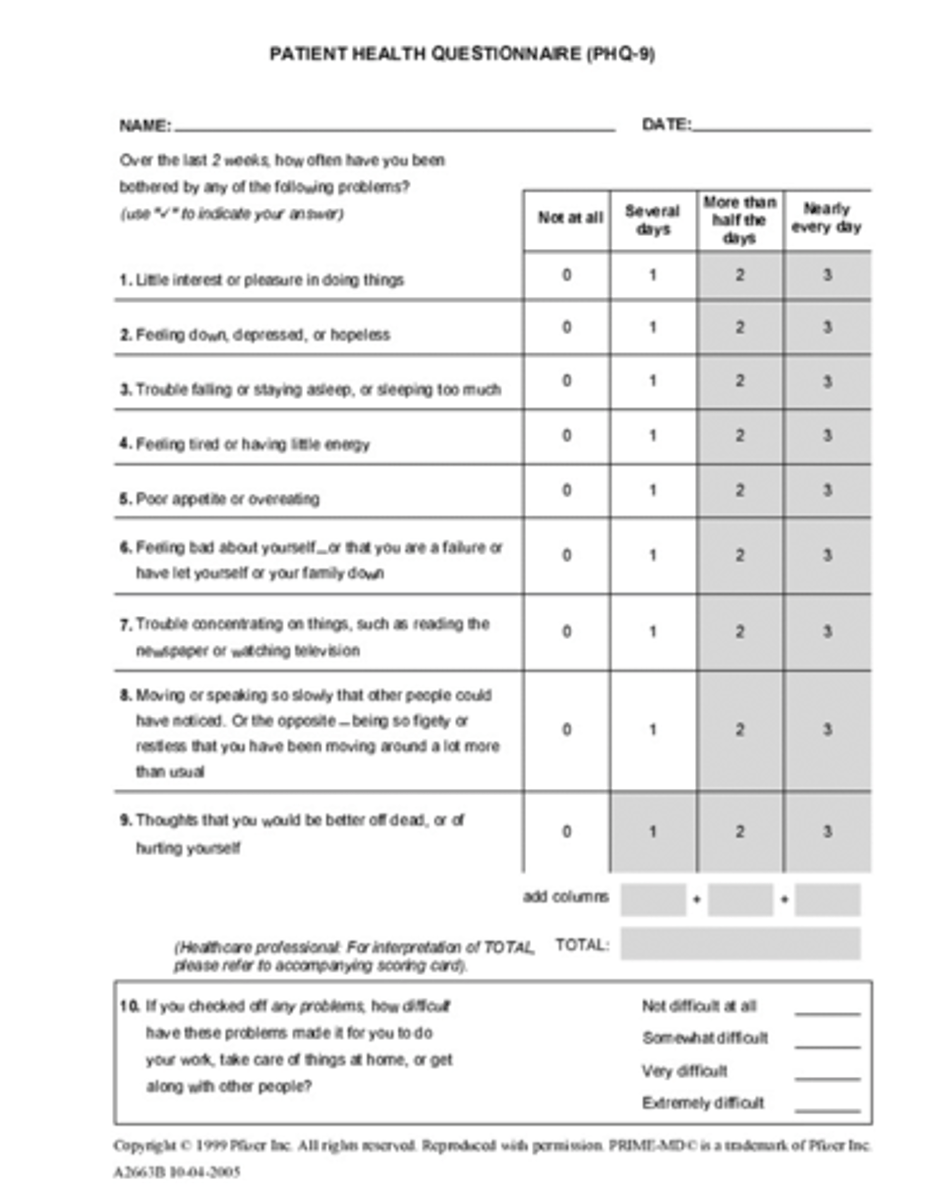
Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9)
Initial screening and tracking progress
Depression score ranges according to the PHQ-9
5 to 9: mild
10 to 14: moderate
15 to 19: moderately severe
≥20: severe
Major depressive disorder specifiers: severity
mild, moderate, severe
Major depressive disorder specifiers: remission
partial, full
Major depressive disorder specifiers: seasonal pattern
AKA Seasonal Affective Disorder
Presence of depressive symptoms at the same season every year (typically winter)
Major depressive disorder specifiers: catatonic depression
Motor immobility, stupor, extreme withdrawal
Major depressive disorder non-pharmacologic management
•Improve diet
•Increase exercise
•Improve sleep routine
•Practice gratitude
•Meditation
•Invest in meaningful relationships
•Serve/volunteer
•Avoid drugs and alcohol
Major depressive disorder additional therapy
Psychotherapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Group Therapy
Major depressive disorder pharmacologic management
SSRI
SSRI MOA
inhibit Serotonin reuptake-> increased levels of Serotonin in the synaptic space
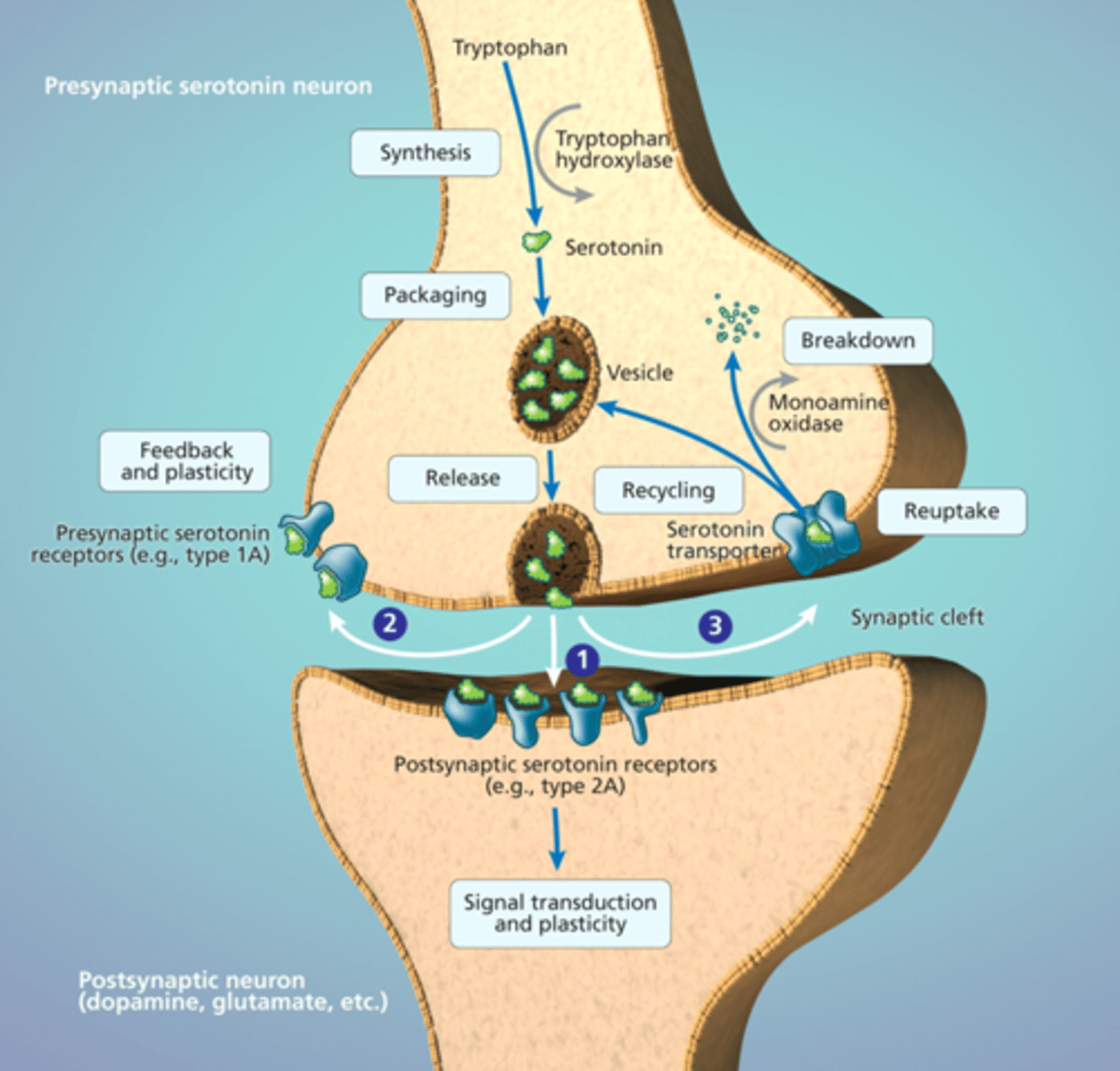
SSRI drugs
Citalopram (Celexa), Escitalopram (Lexapro), Fluoxetine (Prozac), Paroxetine (Paxil), Sertraline (Zoloft)
SSRI that can cause QT prolongation
Citalopram
SSRI that has the longest half life and takes the longest to wash out
Fluoxetine
good for patients with bulimia or not taking medication out of non-compliance
SSRIs that are the safest to use in pregnancy
Sertraline and Escitalopram
SSRI time taken to induce a response
2-6 weeks of daily use
SSRI BBW
Suicide- Children, adolescents, and young adults (up to age 24) can have increased suicide risk during initial treatment
SSRI ADE
GI dysfunction- 6-18%, sexual dysfunction- 17%, drowsiness- 17%, weight gain- 12%, insomnia- 11%, headache- 10%
SSRIs and serotonin syndrome
Potentially life-threatening syndrome due to increased serotonergic activity in the CNS
Serotonin increasing drugs- SSRIs, SNRIs, TCAs, MAOIs, Triptans, St. Johns Wort, Amphetamines, Ergot derivatives, Tramadol
Serotonin syndrome symptoms
altered mental status, hyperthermia, diarrhea, tremors, clonus, dilated pupils, and/or flushed skin typically within 24 hours of adding a new serotonin increasing drug
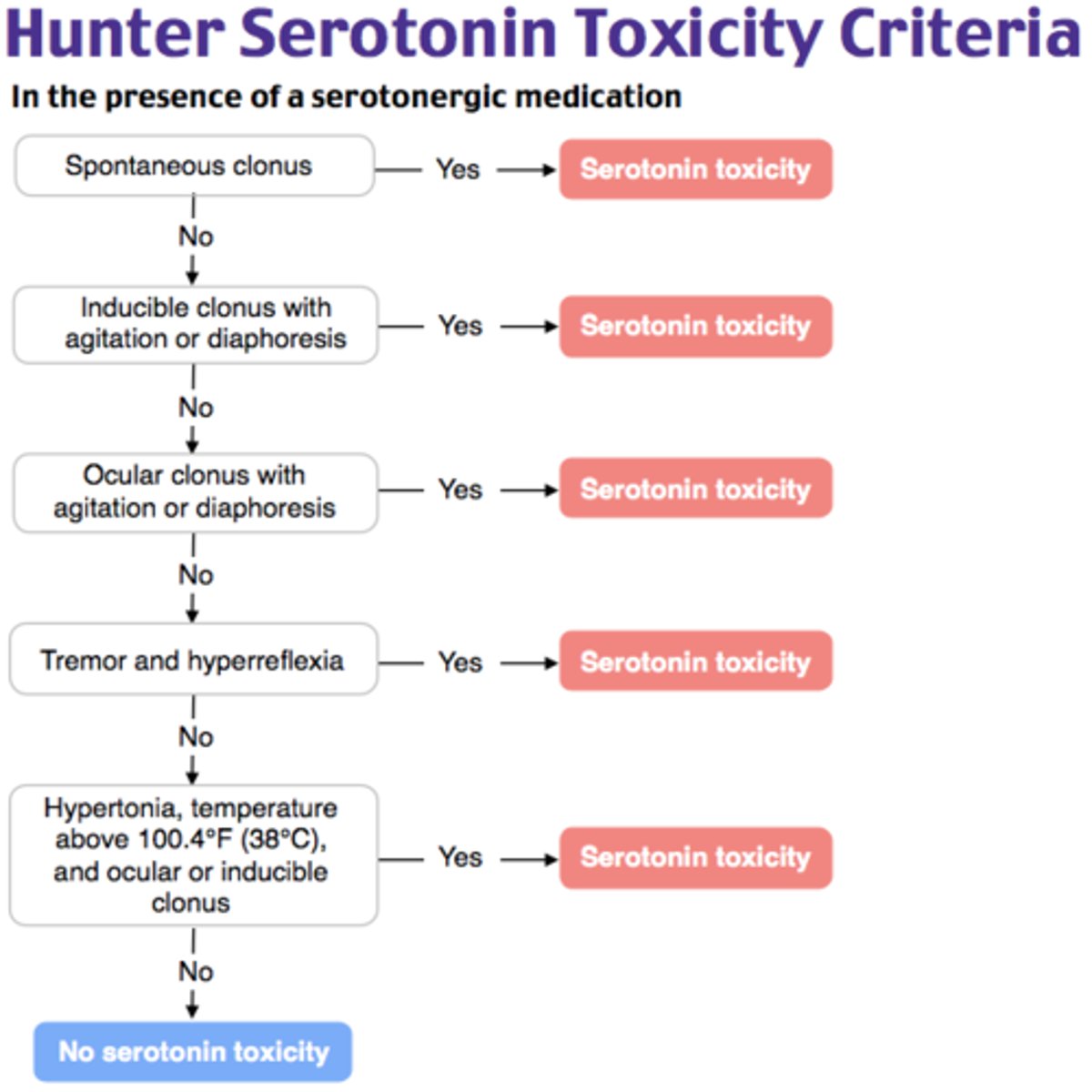
Serotonin syndrome diagnosis
clinical based on Hunter Criteria
Serotonin syndrome management
1) d/c offending drugs
2) supportive care and Benzodiazepines
3) Cyproheptadine (Serotonin Antagonist)
SNRIs MOA
MOA- inhibits Serotonin and Norepinephrine reuptake-> increased levels of Serotonin and Norepinephrine in the synaptic space
SNRI to use first-line in patients with neuropathic pain and/or fibromyalgia
Duloxetine (Cymbalta)
SNRI drugs
Desvenlafaxine (Pristiq), Venlafaxine (Effexor), Duloxetine (Cymbalta)- with weak inhibition of Dopamine
SNRI BBW
Suicide- Children, adolescents, and young adults (up to age 24) can have increased suicide risk during initial treatment
SNRI side effects
nausea- 30%, insomnia- 17-24%, dizziness- 15%, drowsiness- 16%, reduced appetite- 8-22%, weight loss- 7-30%, diaphoresis- 11%, sexual dysfunction- 5-10%
NDRIs MOA
inhibits Norepinephrine and Dopamine reuptake-> increased levels of Norepinephrine and Dopamine in the synaptic space
NDRI indications
First or second choice for depression management
Very useful for MDD with fatigue and anhedonia
Also used to reduce addiction (ex: nicotine cessation)
NDRI drug
Bupropion (Wellbutrin)
NDRI BBW
Suicide- Children, adolescents, and young adults (up to age 24) can have increased suicide risk during initial treatment
NDRI ADE
insomnia- 11-40%, GI disturbance- 30%, headache 30%, dizziness 18%, weight loss 14-28%, tachycardia 11%, sexual dysfunction- 2%
NDRI contraindicated in patients with
Eating Disorder or Seizure Disorder
Bupropion HCl (Auvelity) MOA
CYP2D6 inhibitor to reduce the metabolism of dextromethorphan
Dextromethorphan MOA
antagonizes the NMDA receptor which reduces excitatory neurotransmission by Glutamate (reduces excitotoxicity)
uThird choice for depression management
Dextromethorphan HBr and Bupropion HCl (Auvelity) ADE
dizziness-16%, headache-8%, diarrhea-7%, somnolence-8%, dry mouth-6%, sexual dysfunction-6%, hyperhidrosis-5%
Dextromethorphan HBr and Bupropion HCl (Auvelity) contraindicated in
Eating Disorder or Seizure Disorder
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) MOA
Inhibits reuptake of Serotonin and Norepinephrine as well as block muscarinic M1, Histamine H1, and alpha-adrenergic receptors-> increased levels of Serotonin and Norepinephrine in the synaptic space as well as anticholinergic, antihistamine, and anti-adrenergic effects
TCAs choice for depression management
3rd line
Easy to overdose (lethal dose is only 8x the average therapeutic dose)
Teratogenic (Pregnancy category C)
TCA drugs
Amitriptyline (Elavil), Nortriptyline (Pamelor), Imipramine (Tofranil)
TCA BBW
Children, adolescents, and young adults (up to age 24) can have increased suicide risk during initial treatment
TCA ADE
sexual dysfunction, orthostatic hypotension, sedation, dry mouth, urinary retention, constipation, weight gain, cardiac toxicity, lower seizure threshold, cardiotoxicity, convulsions, coma
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) MOA
inhibits Monoamine Oxidase from breaking down Serotonin, Norepinephrine, and Dopamine-> increase levels of Serotonin, Norepinephrine, and Dopamine in the synaptic space
MAOIs choice for depression management
3rd line
Teratogenic (Pregnancy category C)
MAOIs drugs
Selegiline (Zelapar), Phenelzine (Nardil)
MAOIs BBW
Suicide- Children, adolescents, and young adults (up to age 24) can have increased suicide risk during initial treatment
MAOIs ADE
sexual dysfunction, weight gain, CNS stimulation (anxiety, insomnia, mania), orthostatic hypotension, hypertensive crises if taken with dietary tyramine
Trazodone (Oleptro) MOA
mildly inhibits Serotonin reuptake and is an alpha-1 adrenergic antagonist
Used most often in patients with depression + insomnia
Trazodone (Oleptro)
Trazodone (Oleptro) ADE
somnolence, priapism (rare)
Mirtazapine (Remeron) MOA
increased release of Serotonin and Norepinephrine through blockade of alpha adrenergic receptors (which normally inhibit their release)
Used most often in patients with depression + insomnia + poor appetite
Mirtazapine (Remeron)
used often in elderly patients
Mirtazapine (Remeron) ADE
somnolence, weight gain, increased appetite
Ketamine MOA
antagonizes the NMDA receptor, which reduces excitatory neurotransmission by Glutamate (reduces excitotoxicity)
Used in resistant depression (3rd or 4th line option)
Ketamine
Ketamine PK
IV or Nasal Spray administration
Ketamine patient descriptors
dissociative "out of body" experience where they can process emotions efficiently
Ketamine peak effect
24 hours, but continues to be effective for 1-2 weeks after infusion
Ketamine repeat treatment schedule
Patients return every 2-4 weeks
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) MOA
hypothesized to change pathologic neural pathways
Used in resistant depression (3rd or 4th line option)
TMS
ECT- Electroconvulsive Therapy
Electrical current is passed through the brain while the patient is under general anesthesia
ECT MOA
hypothesized to sensitize neurotransmitter receptors
Used in resistant depression (3rd or 4th line option)
ECT
ECT effectiveness
Remission occurs in 70-90% of patients who receive ECT
60% of patients reach remission within 3 weeks (9 treatments)