PSY 1.11 Social Structures and Demographics
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
Functionalism (structural functionalism)
by Emile Durkhiem
compared society to an organism and proposed that each group in society has a role to play in the overall health and operation of society.
focuses on the function of each component of society and how those components fit together. (work together in an unconscious, automatic way toward the maintenance of equilibrium)
has manifest and latent functions
not suitable to explain social change
manifest functions
intended consequence of the actions of a group within a society
are deliberate actions that serve to help a given system
latent functions
are unexpected, unintended, or unrecognized positive consequences of manifest functions.
dysfunction
negative consequences of the existence of an institution, organisation or interaction
conflict theory
[macro] by Karl Marx
focuses on how power differentials are created and how these differentials contribute to the maintenance of social order.
the disparity between power and resources lead to conflict
it goes beyond social class and power to different generations, religions, regions of a country.
Max Weber's conflict theory argues that social conflict arises from competition over scarce resources, not just economic factors like Karl Marx proposed, but also encompassing power dynamics based on social status and prestige, meaning conflict can occur due to inequalities in areas like gender, race, and education, beyond just class differences between the wealthy and the working class; essentially, Weber believed that power is not solely tied to ownership of the means of production, but also to social standing and legitimacy within a society
symbolic interactionism
by George Herbert Mead
is the study of the ways individuals interact through a shared understanding of words, gestures, and other symbols.
3 assumptions:
human act towards symbols based on the meanings these symbols carry
the meaning symbols carry come from social interaction
human interpret the meaning of symbols and this interpretations influences action
social constructionism
the attempt to understand society through the study of social constructs (an idea that has been accepted by people in society)
explores the ways in which individuals and groups make decisions to agree upon a given social reality.
rational choice theory
states that individuals will make decisions that maximize potential benefit and minimize potential harm
exchange theory applies rational choice theory within social groups.
views all social interactions as transactions and associated with a reward/ punishment
DOES NOT explain charitable, illogical, unselfish and altruistic behaviour
feminist theory
critiques the institutional power structures that disadvantage women in society.
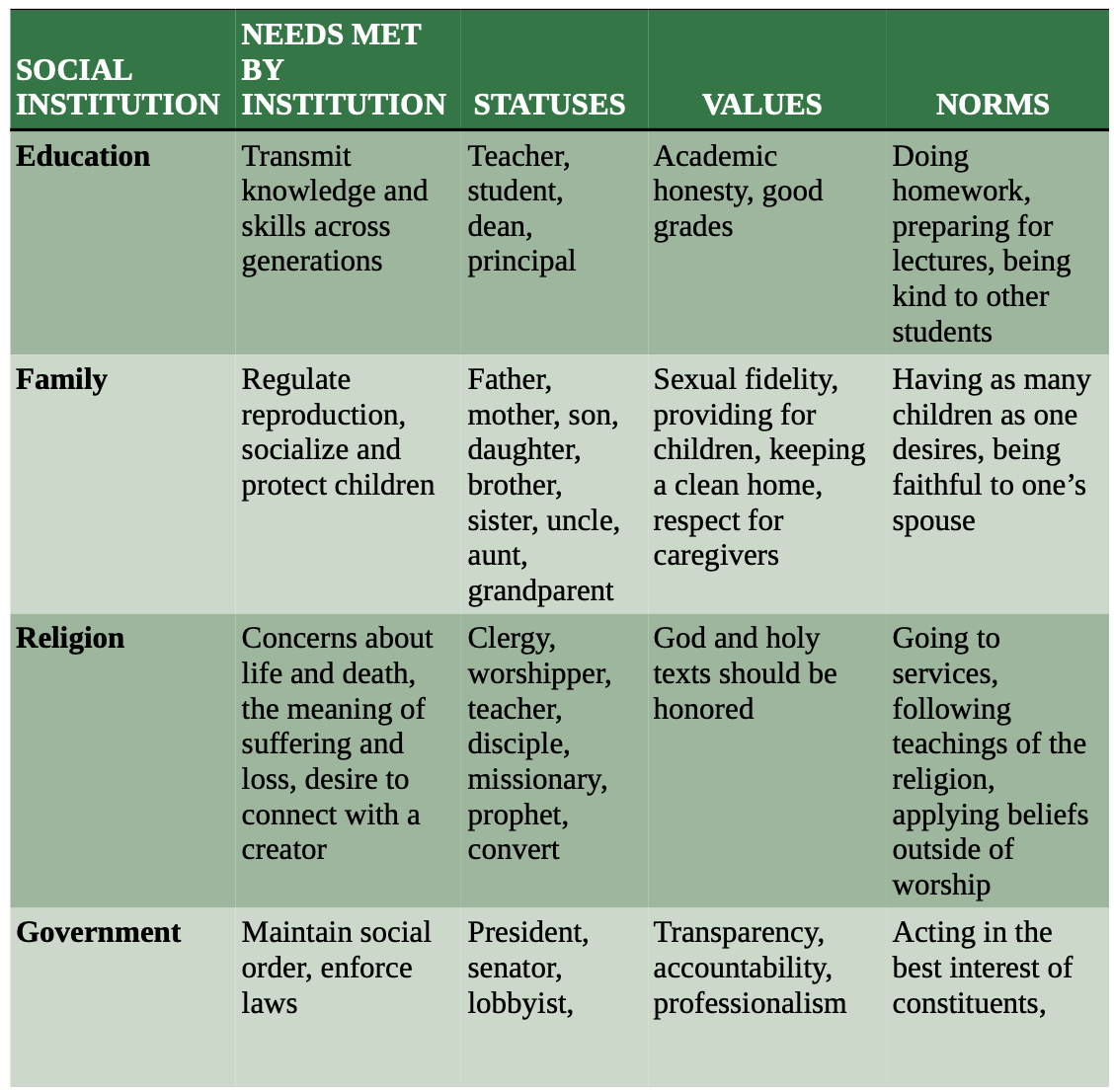
social institutions
[meso level]
are well-established social structures that dictate certain patterns of behavior or relationships and are accepted as a fundamental part of culture. Common social institutions include the family, education, religion, government and the economy, and health and medicine.
There are four key ethical tenets of American medicine.
![<p>[meso level]</p><p>are well-established social structures that dictate certain patterns of behavior or relationships and are accepted as a fundamental part of culture. Common social institutions include the <strong>family, education, religion, government and the economy, and health and medicine.</strong><br>There are four key ethical tenets of American medicine. </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3159bd42-7009-4c3c-aa4d-5608d3d4bcf3.png)
beneficence
refers to acting in the patient’s best interest.
non-maleficence
refers to avoiding treatments for which risk is larger than benefit.
respect for autonomy
refers to respecting patients’ rights to make decisions about their own healthcare.
justice
refers to treating similar patients similarly and distributing healthcare resources fairly.
culture
encompasses the lifestyle of a group of people and includes both material and symbolic elements.
material culture
includes the physical items one associates with a given group, such as artwork, emblems, clothing, jewellery, foods, buildings, and tools.
symbolic culture
[non-material culture] includes the ideas associated with a cultural group.
cultural lag
refers to the idea that material culture changes more quickly than symbolic culture.
cultural barrier
is a social difference that impedes interaction.
language
consists of spoken, signed, or written symbols combined into a system and governed by rules.
values
is what a person deems important in life.
belief
is something a person considers to be true.
ritual
is a formalized ceremonial behavior in which members of a group or community regularly engage. It is governed by specific rules, including appropriate behavior and a predetermined order of events.
norms
are societal rules that define the boundaries of acceptable behavior. [what is appropriate, what we should and should not do]
There is evidence that culture flows from evolutionary principles, and that culture can also influence evolution.
demographics
refer to the statistics of populations and are the mathematical applications of sociology. One can analyze hundreds of demographic variables; some of the most common are age, gender, race and ethnicity, sexual orientation, and immigration status.
ageism
is prejudice or discrimination on the basis of a person’s age.
gender
is the set of behavioral, cultural, or psychological traits typically associated with a biological sex.
gender inequality
is the intentional or unintentional empowerment of one gender to the detriment of the other.
race
is a social construct based on phenotypic differences between groups of people; these may be either real or perceived differences.
ethnicity
is also a social construct that sorts people by cultural factors, including language, nationality, religion, and other factors.
symbolic ethnicity
is recognition of an ethnic identity that is only relevant on special occasions or in specific circumstances and does not specifically impact everyday life.
sexual orientation
can be defined by one’s sexual interest toward members of same or different genders.
immigration
is the movement into a new geographic area. (pull factors)
emigration
is the movement away from a geographic area. (push factors)
fertility rate
Fertility rate = children per woman per lifetime
is the average number of children born to a woman over a lifetime in a population
birth rate
Birth rate = children per 1000 people per year
is relative to a population size over time, usually measured as the number of births per 1000 people per year.
mortality rate
Mortality rate = deaths per 1000 people per year
is the average number of deaths per population size over time, usually measured as the number of deaths per 1000 people per year.
migration
Migration rate = immigration rate minus emigration rate
refers to the movement of people from one geographic location to another.
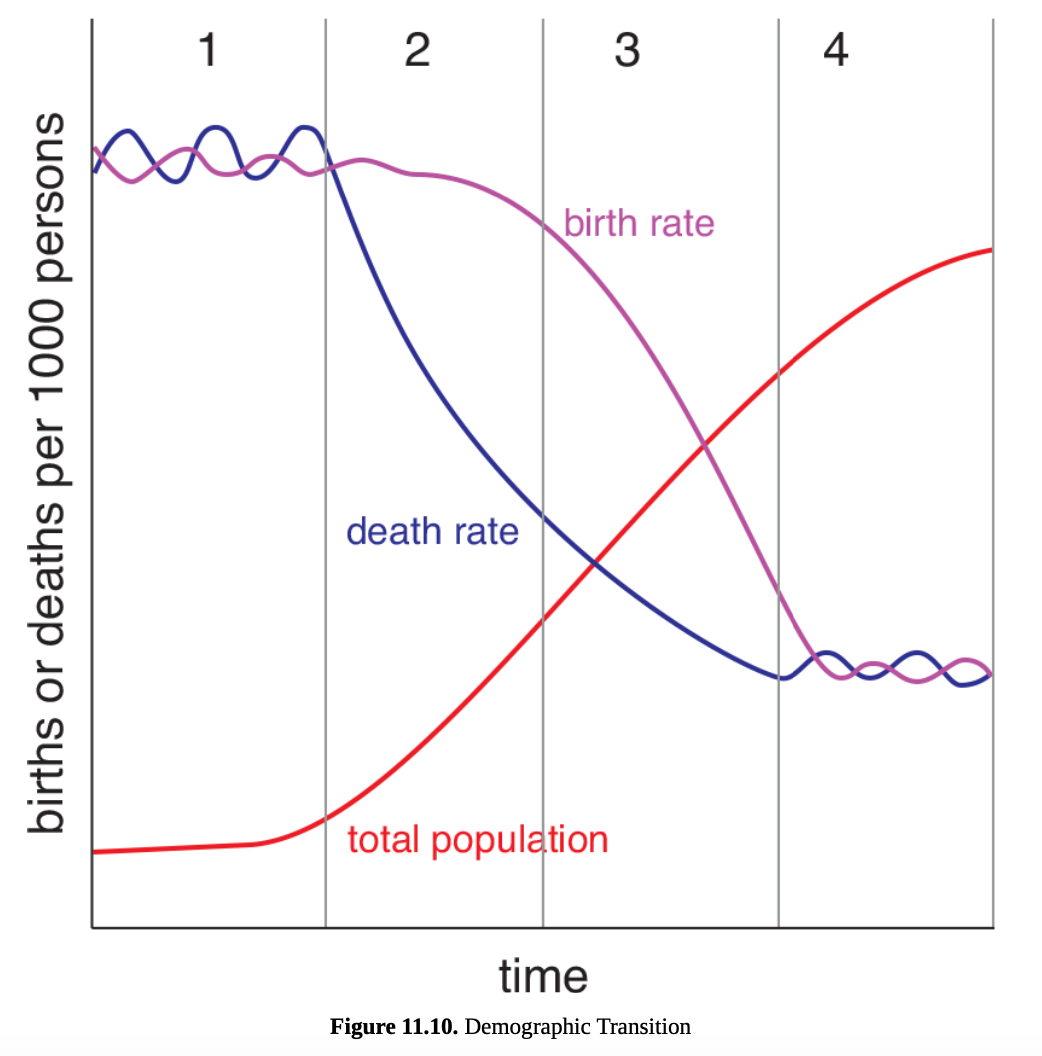
demographic transition theory
is a model used to represent drops in birth and death rates as a result of industrialization.
Stage 1: Preindustrial society; birth and death rates are both high, resulting in a stable population.
Stage 2: Economic progress leads to improvements to healthcare, nutrition, sanitation, and wages, causing a decrease in death rates. Thus, total population increases.
Stage 3: Improvements in contraception, women’s rights, and a shift from an agricultural to an industrial economy cause birth rates to drop. For example, with an industrializing society, children must go to school for many years to be productive in society and may need to be supported by parents for a longer period of time than was formerly the case. Thus families have fewer children, and birth rates drop. As birth and death rates equalize, population growth hits an inflection point and begins to level off.
Stage 4: An industrialized society; birth and death rates are both low, resulting in a relative constant total population.
social movements
motivated the a group’s perceived relative deprivation
are organized to either promote (proactive) or resist (reactive) social change.
globalisation
is the process of integrating a global economy with free trade and tapping of foreign labor markets.
urbanization
refers to the process of dense areas of population creating a pull for migration or, in other words, creating cities.
micro in sociology
individual, family and communities
meso in sociology
organisation, institutions and local communities
macro in sociology
national and international systems
capitalism
an economic system in which individual and corporations rather than governments own and control the means of production
proletariat
working class and performs labour
glass ceiling
refers to the process that limit the progress of women due to invisible social barriers
glass escalator
where invisible forces push men to higher positions
family
the institution most closely tied to the individual and helps meet many of our most basic needs
refers to the patterns of kinship
link to Maslow hierarchy pyramid
domestic violence
#1 cause of injury to women in america
elder abuse
commonly manifests as neglect of an older relative—although physical, psychological, and financial abuse may occur as well.
child abuse
also most commonly manifests as neglect, although physical, sexual, and psychological abuse are also common. During medical school, you will be trained to recognize certain signs suggestive of nonaccidental trauma, such as a broken femur in a child who is too young to have begun walking or burn marks on the buttocks from placing a child in scalding water.
education
an institution
aims to provide a population with a set of skills that will be useful to them or to society
the system also has a social latent function, providing opportunities for peer socialization and reinforcing social stratification, both within individual schools and through comparisons between schools.
hidden curriculum
a set of unspoken lessons, values, and expectations that students learn in school
transmitting social norms, attitudes, and beliefs to students.
teacher expectancy
idea that teachers tend to get what they expect from students.
Thus, a teacher who places high demands on students—but who also believes that students can rise to the challenge—will more often see students succeed than a teacher who places the same demands but doubts that the students can achieve them.
is an example of self-fulfilling prophecy
religion
pattern of social activities organized around a set of beliefs and practices that seek to address the meaning of existence.
religiosity
refers to how religious one considers oneself to be, and includes strength of religious beliefs, engagement in religious practices, and attitudes about religion itself.
denominations
is simply a part of a church, a term which can refer both to a large, universal religious group and to the building in which the congregation of such a group meets.
sect
was historically a pejorative term, it now refers more properly to a religious group that has chosen to break off from the parent religion.
cult
a religious sect may take on extreme or deviant philosophies
secularization
a shift away from religion toward rationality and scientific thinking.
fundamentalism
maintenance of strict adherence to religious code
democracy
allows every citizen a political voice, usually through electing representatives to office (i.e., a representative democracy).
monarchies
include a royal ruler (a king or queen), although the ruler’s powers may be significantly limited by the presence of a constitution
dictatorship
a system where a single person holds power, and usually includes mechanisms to quell threats to this power.
theocracy
system where power is held by religious leaders
charismatic leader
a leader with a compelling personality
socialist economies
treats large industries as collective, shared businesses, and compensation is provided based on the work contribution of each individual into the system. Profit, then, is distributed equally to the workforce.
life course approach to health
maintaining and considering a comprehensive view of the patient’s history beyond the immediate presenting symptoms
sick role
a set of socially constructed behaviors a person is expected to take when sick
medicalisation
now defined and treated as medical conditions
illness experience
is how a person adjusts to interruptions in their health. They understand and cope with their illness which impacts their self identity. They experience the symptom and then assume the sick role.
social epidemiology
the study of the effects of institutions, social structures, and relationships on health.
study the effects of racial and economic inequality or government safety net legislation on health and access to healthcare
ethnography
study of cultures and customs, and ethnographic methods are experimental methods used to study the ethnicity or culture of a group.
age cohorts
generational cohorts
eg. Generation X, silent generation, baby boomers
dependency ratio
ratio of the number of members of a population that are not in the workforce to the number of members that are in the workforce
depends on youth ratio and age dependency ratio
youth ratio
defined by the number of people under the age of 15 divided by the number of people aged 15-65
age dependency ratio
is defined by the number of people over 65 divided by the number of people aged 15-65.
sex
is a biological category
gender identity
an individual can adopt behaviors that project the gender that individual wishes to portray
gender segregation
is the separation of individuals based on perceived gender. Such segregation includes divisions of male, female, and gender-neutral bathrooms, or separating male and female sports teams
gender stratification
is defined as any inequality in access to social resources that is based on gender
generational status
refers to the place of birth of a specific person or that person’s parents.
For instance, first generation refers to someone who is born outside of their place of residence. Second generation refers to a person that has at least one parent that is foreign-born.
intersectionality
interplay between multiple demographic factors—especially when it leads to discrimination or oppression
demographic shifts
changes in the makeup of a population over time
population density
counts the number of people per square kilometer of land area.
Malthusian theory
how the exponential growth of a population can outpace growth of the food supply and lead to social degradation and disorder
The resulting hypothetical mass starvation is called the Malthusian catastrophe