Chapter 3 Module 9 - Sleep and Dreams
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Sleep
periodic, natural loss of consciousness - as distinct form of unconsciousness resulting from a coma, general anesthesia, or hibernation
importance of sleep
- strengthens mind and body
- affects ability to remember things
- affects ability to manage our feelings
- helps us stay alive
-- brains auditory cortex responds to sound stimuli even during sleep
-- most information is processed outside of conscious awareness
Biological rhythms
the naturally occuring, cyclical patterns of psychological and behavioral changes within living organisms, ofter regulated by an internal "clock" in the brain
Carcadian Rhythm
internal biological clock of 24-hour cycle of day and night
-body temp rises as morning approaches, peaks during the day, dips in the early afternoon, and begins to drop in the evening
-altered by age and experience
90-minute sleep cycle
a sleep cycle is 90-minutes, and during that time we move through 5 stages of sleep
- the first 4 stages make up our non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep, and the fifth stage is our rapid eye movement (REM)
Brain waves and sleep stages
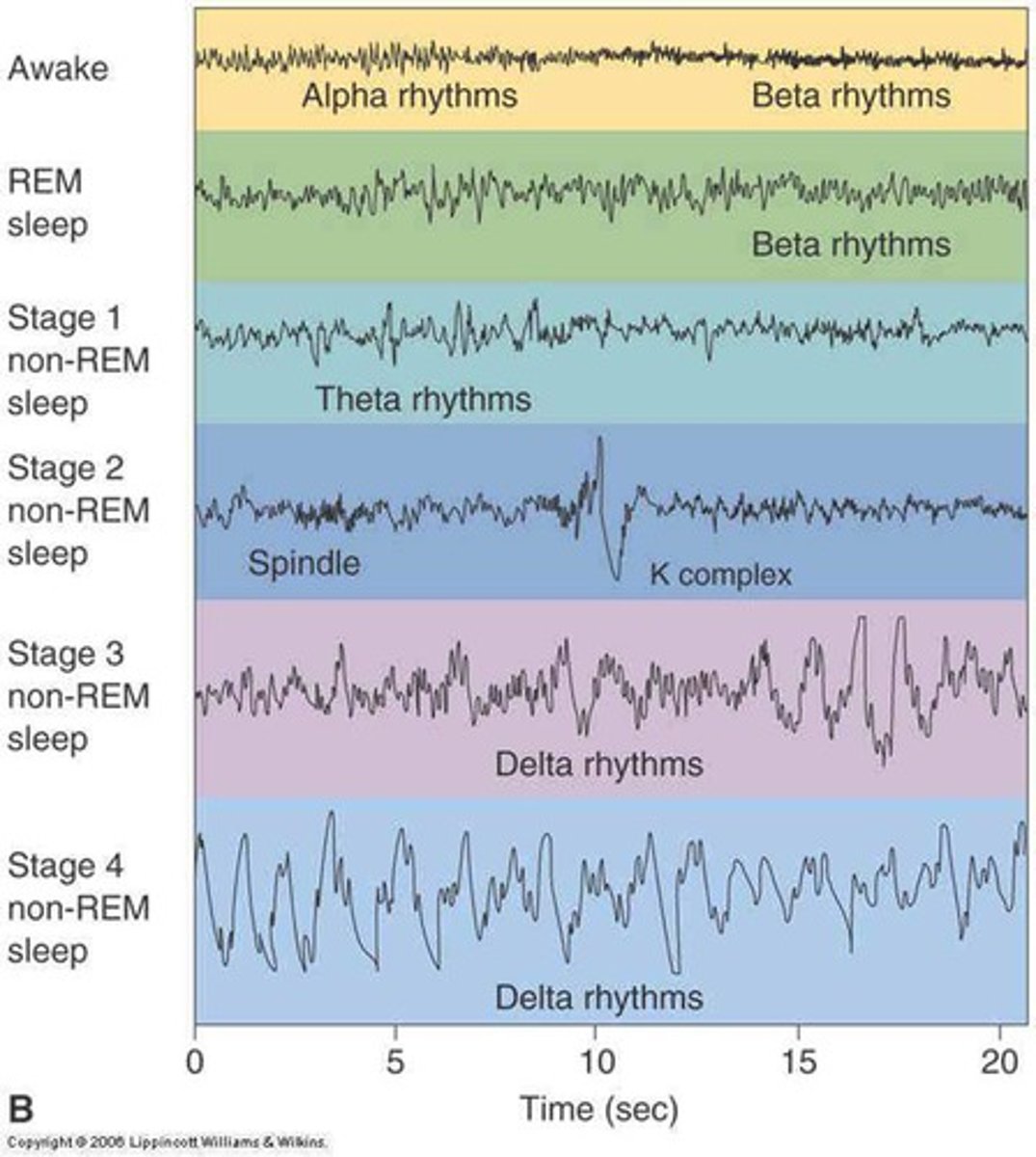
the beta waves of an alert, waking state and the regular alpha waves of an awake, relaxed state differ from the slower, larger delta waves of deep NREM-3 sleep. Although the rapid REM sleep waves resemble the near-waking NREM-1 sleep waves, the body is more aroused during REM sleep than during NREM sleep
rapid eye movement (REM) sleep
a stage of sleep when the eyes move rapidly while closed and is associated with dreaming
Why we sleep?
-helps restore and repair damaged neurons
-helps strengthen neural connections that build memories
-promotes creative thinking and the next day
-during deep sleep the pituitary glad secretes a growth hormone necessary for muscle development
Sleep deprivation
a condition that occurs when someone doesn't get enough sleep, either in quiality or quantity, to maintain their health
ways to improve sleep
-avoid arousing activities, foods, and beverages before bedtime
-go to the dark side of the room
-ride, rest, repeat. cool temps
-have a wind down routine
-manage stress
Insomnia
- ongoing difficulty falling or staying asleep
- REM sleep behavior disorder
Narcolepsy
-sudden attacks of overwhelming sleepiness
-sleepwalking and sleeptalking
Sleep apnea
-stopping breathing repeatedly while sleeping
-night terrors
Dreams and REM
dreams are a sequence of images, emotions, and thoughts passing through a sleeping persons mind
-researchers could catch dreams as they happened, awakening people during or shortly after a REM sleep period to hear a vivid account
Dream Content
made up of two parts: manifest and latent content
manifest content
the literal images and plot of the dream that is remembered when someone wakes up
latent content
unconscious meaning behind the dream
- often symbolic and contains things that are hidden from conscious awareness, such as upsetting or trumatic experiences
Freud wish fulfillment theory
dreams provide "psychic safe value" accepting otherwise unacceptable feelings, dreaming of secret desires
information processing theory
dreams help us sort out the day's events and consolidate our memories
Neurocognitive function theory
REM sleep allows the brain to consolidate memories and process emotional information
Activation synthesis theory
REM sleep triggers neural activity that evokes random visual memories, which our sleeping brain weaves into stories
cognitive development theiry
dream content reflects dreamers level of cognitive development --simulate our lives