Microbial Diversity Exam 2 (copy) for plane
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/122
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
1
New cards
On the electron tower, where are the good electron donors?
At the top
2
New cards
On the electron tower, where are the good electron acceptors?
At the bottom
3
New cards
What does assimilative mean?
Process that requires energy
4
New cards
What does dissimilative mean?
Process that releases energy
5
New cards
What is autotrophy?
When CO2 is used as a carbon source
6
New cards
Even though it is the most studied, what is a downside to the Calvin Cycle?
Not extremely efficient
7
New cards
What is the reducing power for the Calvin Cycle?
NADPH
8
New cards
What type of molecule is Rubisco?
Enzyme
9
New cards
What are the two types of molecules that are trapped in a protein shell bacause of the carboxysome?
* Rubisco
* CO2
* CO2
10
New cards
How do the reverse citric acid cycle and the hydroxypropionate pathways differ from one another?
* Efficiency
* Types of microbes
* Types of microbes
11
New cards
Where was photosynthesis originated?
Bacteria
12
New cards
What theory supports the idea that photosynthesis originated from bacteria?
Endosymbiotic Theory
13
New cards
What are the two types of reactions in photosynthesis?
* Light Independent Reactions
* Light Dependent Reactions
* Light Dependent Reactions
14
New cards
What does photosynthesis require?
* ATP
* Reducing power
* Reducing power
15
New cards
What is the source of electrons is many diffferent reactions?
The reducing power
16
New cards
What is used as the reducing power for oxygenic photosynthesis?
H2O
17
New cards
What is used as the reducing power for anoxygenic photosynthesis?
Anything other than H2O
18
New cards
What are two examples of photosynthetic pigments?
* Chlorophylls
* Bacteriochlorophylls
* Bacteriochlorophylls
19
New cards
Different photosynthetic pigments can absorb different wavelengths of light. What are two results of this?
* Microbes can live at different depths
* Allows for coexistance of microbes
* Allows for coexistance of microbes
20
New cards
What are reaction centers?
Molecules that briefly hold onto light
21
New cards
What are antenna pigments?
Pigments that capture and collect light
* Feeds light into the reaction centers
* Feeds light into the reaction centers
22
New cards
What is the benefit of the reaction center-antenna pigment system?
Allows for the ability to concentrate light
23
New cards
What are the light gathering machinery in Eukaryotes?
Chloroplasts
24
New cards
What are the light gathering machinery in Prokaryotes?
Membrane invaginations
25
New cards
Why are chlorosomes useful?
Great for capturing low density light
26
New cards
Do bacteria have chloroplasts?
No
27
New cards
Where can biomats live?
In the very center of the reaction center
28
New cards
What are carotenoids?
Pigments found in phototrophs that can absorb light
29
New cards
What is the main function of carotenoids?
Photoprotection
30
New cards
What are two benefits of photoprotection?
* Adaptation for high light environments
* Prevents destruction of reaction centers
* Prevents destruction of reaction centers
31
New cards
What is created after the destruction of the reaction centers?
Oxygen singlets
32
New cards
What colors are carotenoids?
* Yellow
* Red
* Brown
* Green
* Red
* Brown
* Green
33
New cards
What pigments are only found in Cyanobacteria?
Phycobilins
34
New cards
Why is anoxygenic photosynthesis different than normal photosynthesis?
Does not produce O2 as a product
35
New cards
What type of reaction is anoxygenic photosynthesis?
Endergonic
36
New cards
What is the source of electrons for anoxygenic photosynthesis?
Inorganic compounds
37
New cards
What are 2 unique characteristics of anoxygenic photosynthesis?
* Cyclic phosphorylation
* Reverse Electron Transport
* Reverse Electron Transport
38
New cards
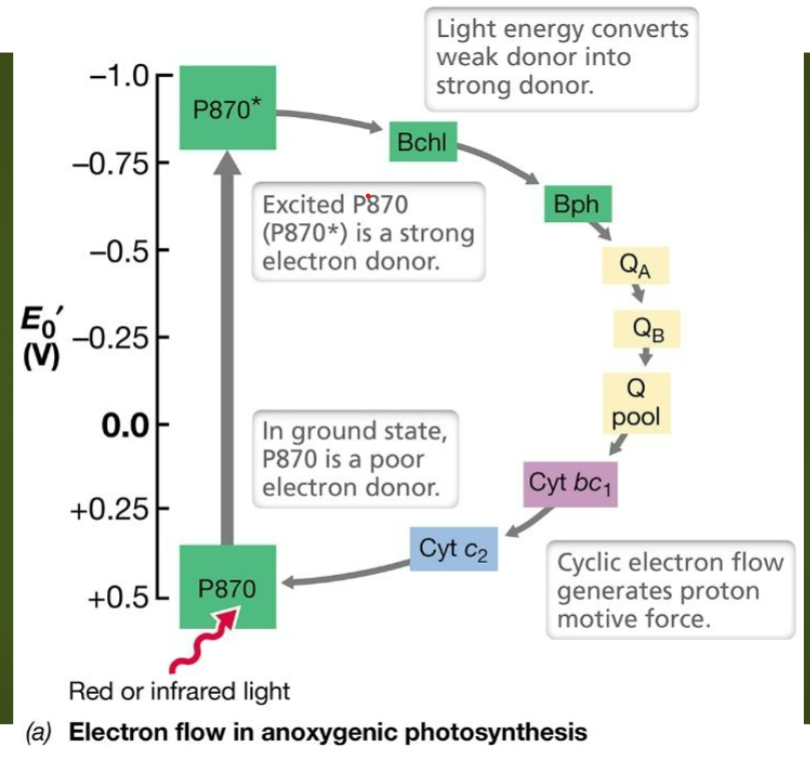
What is the name of this process?
Reverse Electron Transport
39
New cards
How many photosystems are in oxygenic photosynthesis?
2
40
New cards
What does oxygenic photosynthesis use as a source of electrons?
H2O
41
New cards
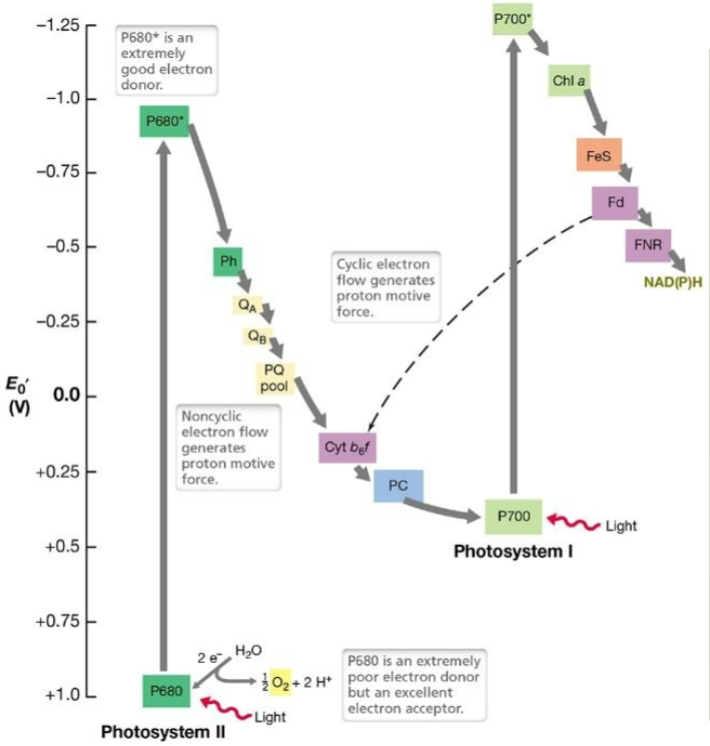
What is the name of this process?
Oxygenic photosynthesis
42
New cards
What is unique about some organisms that can do oxygenic photosynthesis?
They also have the ability to do anoxygenic photosynthesis
43
New cards
What does cyclic flow of electrons generate in anoxygenic photosynthesis?
Proton Motive Force
44
New cards
Why do some microbes perform anoxygenic photosynthesis instead of oxygenic photosynthesis?
Some parts of microbe metabolism are oxygen sensitive
45
New cards
What are 4 processes that are defined by electron donor?
* Oxidation of Sulfur Compounds
* Iron oxidation
* Nitrification
* Anaerobic Ammonia Oxidation
* Iron oxidation
* Nitrification
* Anaerobic Ammonia Oxidation
46
New cards
What is often the end product of the oxidation of sulfur compounds?
Sulfate and H+
47
New cards
What can be a by-product of the large number of sulfur compounds?
Different amounts of electrons can be used
48
New cards
What is a potential side effect of the oxidation of sulfur compounds?
Acidification of the environment
49
New cards
What are two sulfur oxidizers?
* Acid tolerant microbes
* Acidophilic microbes
* Acidophilic microbes
50
New cards
Why is oxidized sulfur held in the cell?
It is not fully oxidized and is a future source of energy
51
New cards
Microbes that can do autotrophy can also oxidize sulfur compounds. What process would result from this?
Reverse electron transport because sulfur comes in low on the electron tower
52
New cards
In the traditional sulfur oxidation pathway, what is generated?
Many H+ and sulfate (by-product)
53
New cards
What is oxidized in iron oxidation?
Fe2+ to Fe3+
54
New cards
What are 2 side effects of iron oxidation?
* Environment acidification
* Color changes
* Color changes
55
New cards
What happens to the iron oxidation process in an acidic environment?
* Large amounts of iron must be oxidized
* Iron oxidation causes little energy to be present in an acidic environment
* Iron oxidation causes little energy to be present in an acidic environment
56
New cards
What happens to the iron oxidation process in a neutral environment?
* O2 is present and oxidation is spontaneous
* Microbes now have to compete with natural iron processes
* Microbes now have to compete with natural iron processes
57
New cards
Under the acidic conditions, what happens with the ETC in iron oxidation?
* Not many electron carriers between iron and O2
* Produces a short ETC and little energy
* Produces a short ETC and little energy
58
New cards
Under acidic conditions, what happens with the PMF in iron oxidation?
* Acidic environment creates a preformed proton gradient
* The cell cannot utilize the preformed PMF due to pH homeostasis
* Protons still have to be pumped out of the cell to create the PMF
* The cell cannot utilize the preformed PMF due to pH homeostasis
* Protons still have to be pumped out of the cell to create the PMF
59
New cards
What organisms are going to use nitrification for their electrons?
Chemolithotrophs
60
New cards
What is the first of two reactions for nitrification?
Oxidation of ammonia nitrite
61
New cards
What is the second reaction for nitrification?
Oxidation of nitrite to nitrate
62
New cards
What types of microbes oxidize ammonia to nitrite?
Ammonia oxidizers
63
New cards
What types of microbes oxidize nitrite to nitrate?
Nitrite oxidizers
64
New cards
Can any microbes do both of the nitrification processes?
Yes, the genus *Nitrospira*
65
New cards
What is the terminal electron acceptor for nitrification?
O2
66
New cards
What is the reducing power for autotrophs in nitrification?
Reverse electron flow
67
New cards
What is another name for anaerobic ammonia oxidation?
Anammox
68
New cards
When is anammox performed?
NH3 is oxidized under anoxic conditions
69
New cards
What are anammoxosomes?
* Membrane bound
* Produce N2H4
* Intermediate for anammox
* Produce N2H4
* Intermediate for anammox
70
New cards
What is the purpose of anammoxosomes?
Prevent the toxic N2H4 form being released into the cell
71
New cards
What organisms are capable of anammox?
*Planctomycetes*
72
New cards
3 processes that are defined by their electron acceptor?
* Nitrate reduction and denitrification
* Sulfate reduction
* Other electron acceptors
* Sulfate reduction
* Other electron acceptors
73
New cards
What is nitrate reduction?
Inorganic nitrogen compounds are commonly used as electron acceptors
74
New cards
What type of process of denitrification?
Dissimilative
75
New cards
What are 3 possible results of denitrification?
* NO
* N2O
* N2
* N2O
* N2
76
New cards
What is the process of denitrification?
NO3- → N2
77
New cards
What is the proccess of nitrate reduction?
NO3- → NO2-
78
New cards
What are the negative impacts of leaving nitrogen compounds in NO or N2O?
* Increase greenhouse gases
* Formation of acid rain
* Removal of nitrogen from the environment
* Formation of acid rain
* Removal of nitrogen from the environment
79
New cards
How do dead zones and algae blooms form?
Too much nitrogen
80
New cards
Why are waterlogged fields bad for microbes that use nitrogen reduction and denitrification?
Nitrogen reductase enzyme is oxygen sensitive and oxygen will stop the entire process
81
New cards
What types of microbes use sulfate reduction?
Obligate anaerobes
82
New cards
What is the end product of sulfate reduction regardless of the reactants?
H2S
83
New cards
When looking at the electron tower, what is the problem with sulfate reduction?
Sulfate is a good donor, but needs to be used as a terminal electron acceptor for sulfate reduction
84
New cards
What type of process is sulfate reduction?
Endergonic
85
New cards
What is one other example of an electron acceptor?
Arsenic
86
New cards
Is hydrocarbon metabolism an aerobic process or an anaerobic process?
It can be both
87
New cards
What are the two enzymes that can be utilized during aerobic hydrocarbon metabolism?
* Monoxygenase
* Dioxygenase
* Dioxygenase
88
New cards
What must the cell do in hydrocarbon metabolism?
Energize the carbons
89
New cards
What happens once the carbons are energized in hydrocarbon metabolism?
Oxygen is added
90
New cards
What is added in place of oxygen in anaerobic hydrocarbon metabolism?
Fumarate
91
New cards
What are 3 processes that are one-carbon metabolism processes?
* Acetogenesis
* Methanogenesis
* Methanotrophy
* Methanogenesis
* Methanotrophy
92
New cards
What do both accetogenesis and methanogenesis have in common?
* Reduce CO2 (in the form of bicarbonate)
* Strict anaerobes
* Strict anaerobes
93
New cards
What type of gradient is generated in methanogenesis and/or acetogenesis to form ATP?
Ion or proton motive force
94
New cards
What is the electron donor is acetogenesis?
H2
95
New cards
What is the pathway of CO2 reduction called?
Reductive acetyl CoA pathway
96
New cards
What are the two different types of organisms that can do acetogenesis?
* Chemoorganotrophs (heterotrophs)
* Chemolithotrophs (autotrophs)
* Chemolithotrophs (autotrophs)
97
New cards
What makes the Acetyl-CoA pathway unique?
It is linear
98
New cards
What generates the bulk of the ATP in acetogenesis?
Na+ motive force
99
New cards
What is the cluster of proteins called where ferredoxin goes through the redox reaction?
RNF cluster of proteins
100
New cards
If energy is released from the redox of ferredoxin, what does this energy contribute to?
The generation of the ion motive force