Lecture 1: Introduction to Social Psychology
1/3
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Social Psychology II
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
Social Psychology
Social psychology is the scientific study of how thoughts, feelings and behaviours are influenced by the actual, imagined, or implied presence of others
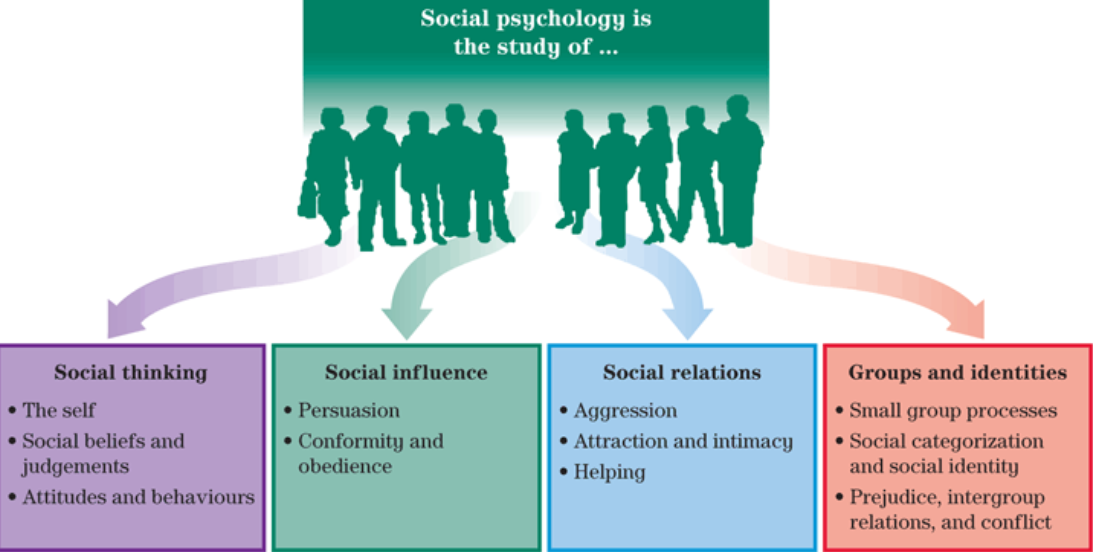
Levels of Social Psychological Study
Macro-level: broader society
social structures
institutions
culture
Meso-level: social context
social groups
specific others
Micro-level: individual psychology
personality
emotions
cognition
History of social psychology
The first social psychology experiments were reported in 1898, but an interest in social psychological issues has a much longer history
in the 18th century, important contributions to social psychological theorising were given by scholars from different disciplines including philosophy, psychology and economics
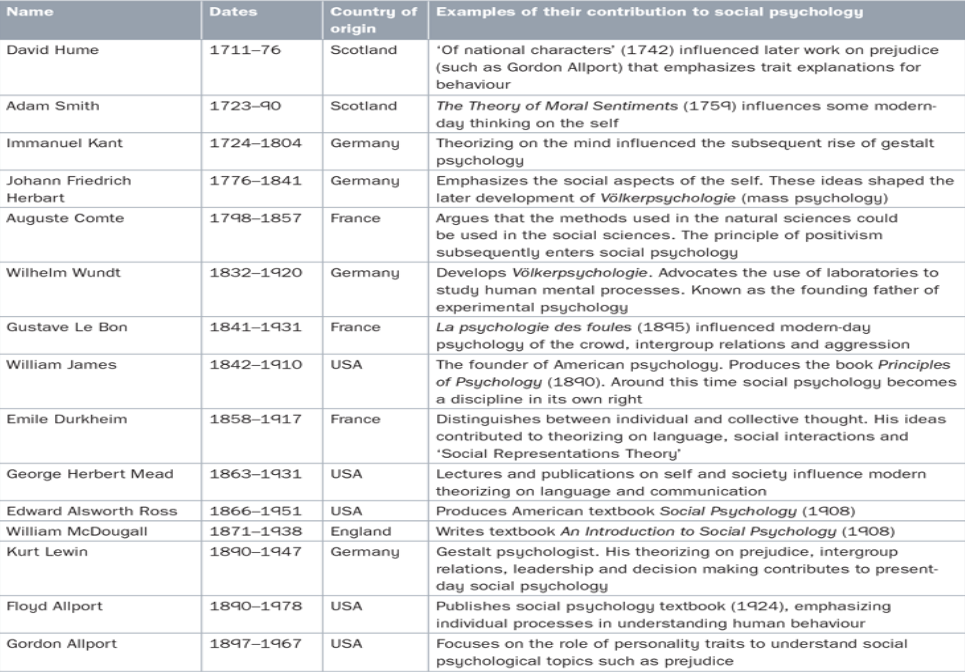
The first crisis in social psychology
In the late 1960s and early 1970s, serious questions were being asked about the direction of the discipline and how well it reflected and acknowledged the social, historical, cultural and political concerns and values of the people it sought to study.
Two main criticisms:
social psychology’s over reliance on experimental methods at the expense of more naturalistic approaches such as observation and interviewing
excessive emphasis on individuals as individuals rather than as parts of more complex social, historical, cultural and political contexts