AP Macroeconomics Unit 1
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Economizing problem
Unlimited wants, limited resources
Resources
Land, labor, capital, entrepreneurial ability
Four assumptions in PPC
Full employment of resources
No new technology
No new resources
Two goods
Law of Increasing OC
To make one good, increasing amounts of the other will be consumed. They can’t be exchanged 1:1.
OC
The cost to move to the next unit of a good.
OCA in output problems
OCA = (Change in B) / (Change in A)
OC in input problems
OCA = (Change in A) / (Change in B)
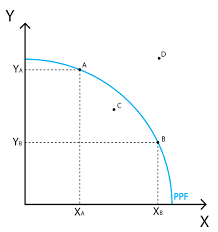
Point C represents…
Point D represents…
Point C = Underutilization of resources
Point D = Unattainable given current resources
Consumer goods
Consumed upon use
More consumer goods results in what for the economy?
Slower growth rate
Capital goods
Can create more consumer goods
More capital goods results in what for the economy?
Allocative Efficiency
Producing what society wants
Productive Efficiency
Producing at the lowest possible opportunity cost
What fifth thing do you consider with international trade?
Constant opportunity cost
Absolute advantage
Whoever produces more of a good
Comparative advantage
Whoever produces the good at the lower opportunity cost
Term of trade
A trade ratio that benefits both sides.
Traditional economy
Generational techniques/methods
Command economy
Government owns resources and decides the economic questions
Market economy
Individuals own resources and decide economic questions