Ch.3 Dental Anatomy & Periodontium: Key Concepts and Structures
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What is the purpose of the fundamental curvatures of teeth?
They aid in preventing disease, damage, bacterial invasion, calculus buildup, dispersing excessive occlusal trauma, and protecting the gingiva and periodontium.
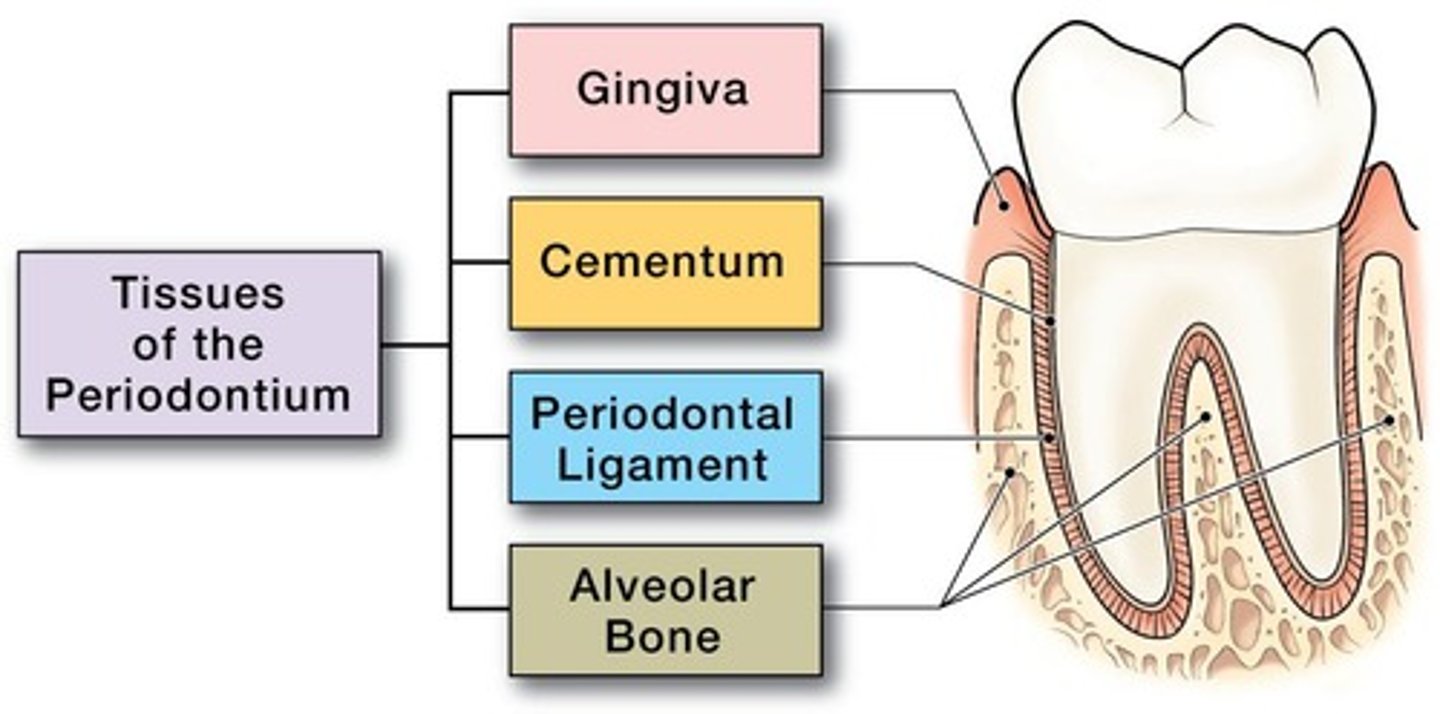
What is the periodontium?
the supporting tissue around each tooth: Gingival Unit (Free,Attached, Alveolar Mucosa,) Cementum, Periodontal Ligament, Bone
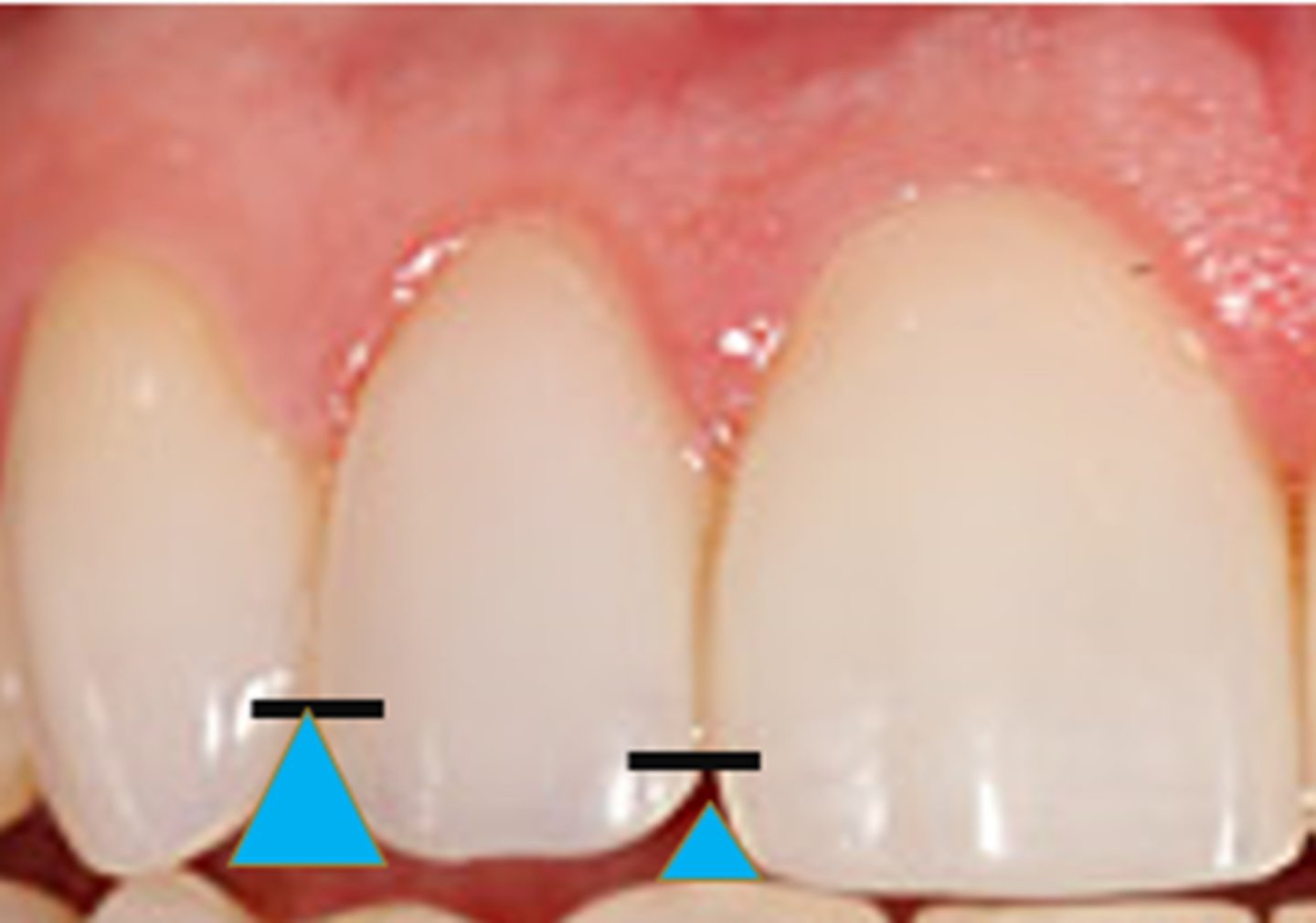
What is a proximal contact area?
A flattened portion of the tooth where it touches the next tooth in the same dental arch.
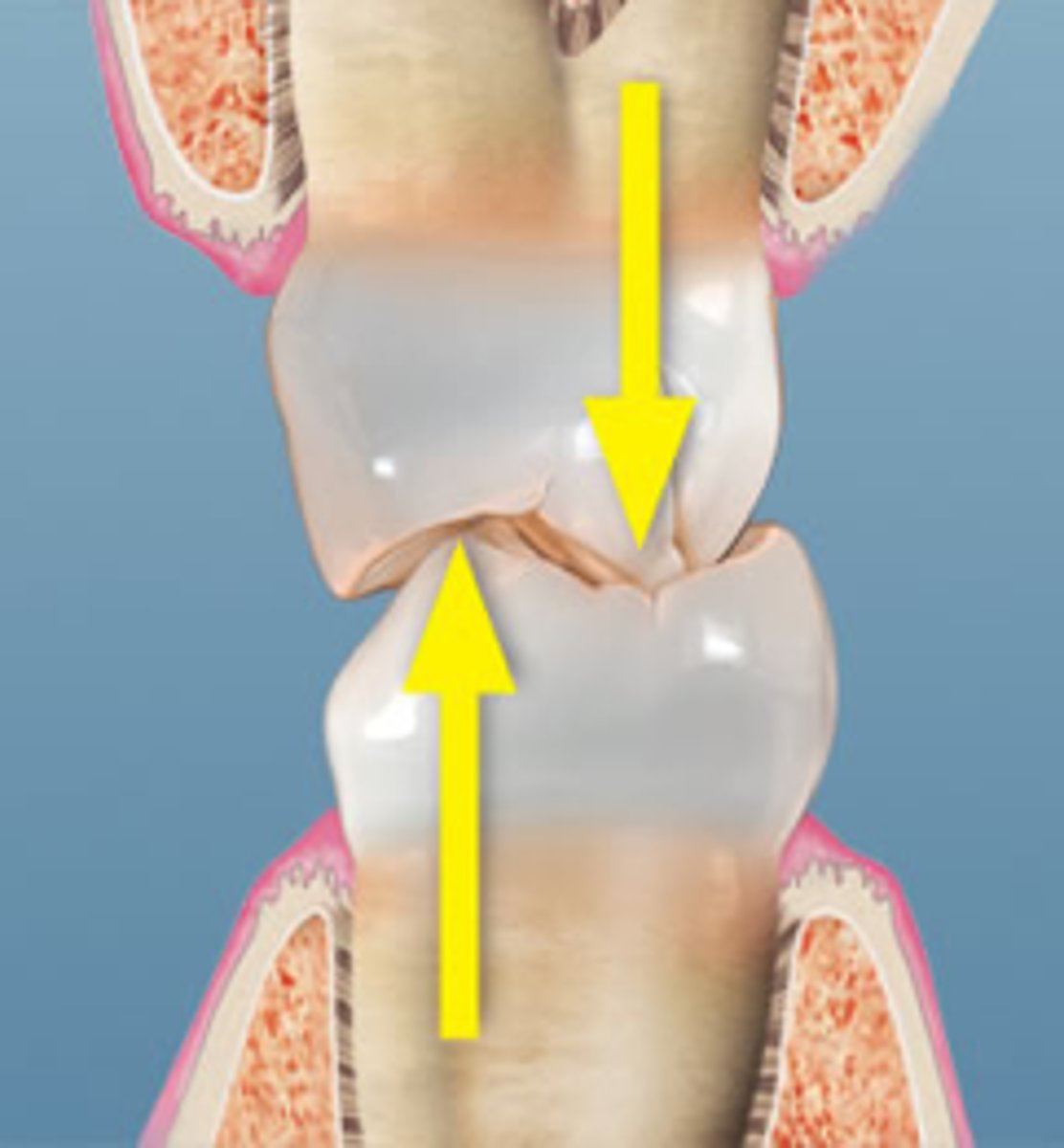
What is a contact point in dental anatomy?
The point where the occlusal cusp of one tooth touches the occlusal portion of another tooth in the opposing arch.
What is a cervical embrasure?
A space that occurs when there is gingival recession between teeth, resulting in missing interdental papilla and bone.
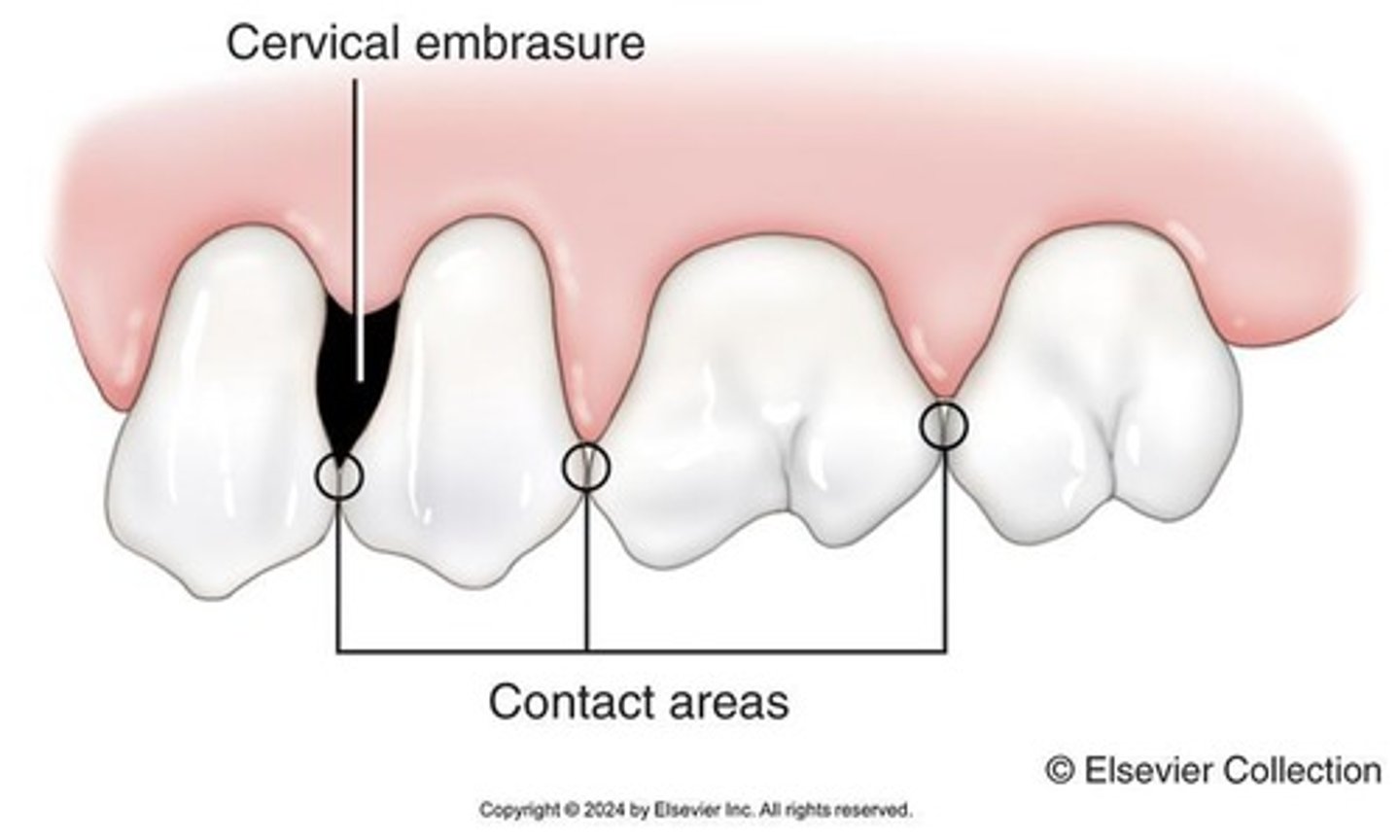
What are the purposes of embrasures?
To allow food to be moved away from contact areas, dissipate occlusal trauma forces, provide self-cleaning, and protect the gingiva.
How do the contact areas of anterior teeth differ from those of posterior teeth?
Anterior teeth contact areas are located closer to the incisal surfaces, while posterior teeth contact areas are closer to the middle third of the teeth.
What is the significance of tooth surface curvature?
It allows for proper deflection of food, ensuring adequate tissue stimulation and protection of gingival crevices.
What is the role of facial and lingual contours of teeth?
They direct food off teeth and against the gingiva at the proper angle to prevent gingival inflammation.
What are the self-cleaning qualities of teeth?
Smooth enamel helps food and sticky substances slip off, keeping the tooth relatively free of bacteria.
What tissues make up the periodontium?
The gingival unit (free gingiva, attached gingiva, alveolar mucosa) and the attachment unit (cementum, periodontal ligament, bone).
What is an open contact in dental anatomy?
A situation where teeth do not touch, creating an environment for food impaction.
What happens if the periodontium tissues are damaged?
It jeopardizes vascularity, interdental papillary tissue, gingiva, and bone, decreasing the life expectancy of the tooth.
What is the impact of too much deflection of food on gingival tissue?
It results in not enough gingival stimulation.
What is the impact of too little deflection of food on gingival tissue?
It allows food to pack into the gingival crevice, potentially causing gingival inflammation or periodontal disease.
What is the relationship between the contact area and interproximal bone?
Two adjacent teeth share the same interproximal bone, which supports the roots of both teeth.
What is the importance of the contact points between opposing teeth?
They ensure proper occlusion and distribute biting forces evenly.
How do the characteristics of tooth shape and alignment protect the periodontium?
They help maintain proper spacing and contact between teeth, reducing trauma and bacterial invasion.
What is the significance of the supporting structures of the periodontium?
They are essential for the support and anchorage of the teeth, protecting them from excessive trauma.